Magnetic Ionic Liquid: A Multifunctional Platform for the Design of Hybrid Graphene/Carbon Nanotube Networks as Electromagnetic Wave-Absorbing Materials
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
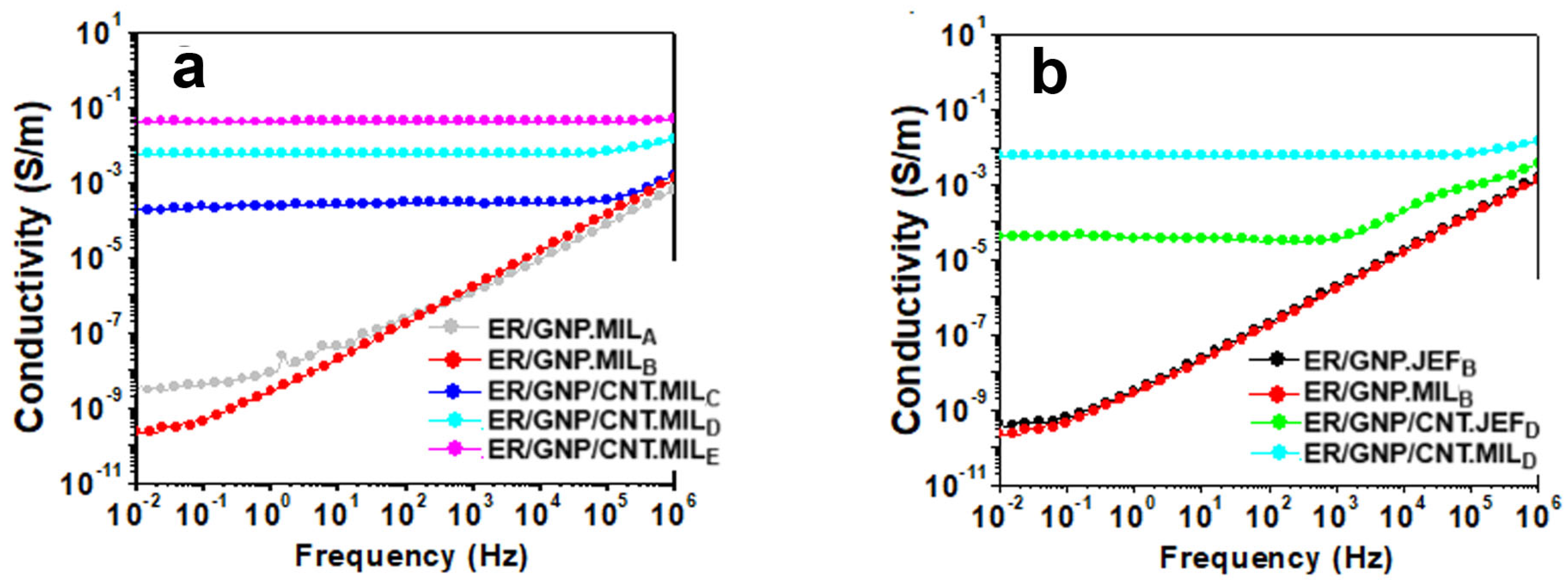
2.1. AC Conductivity of the Epoxy Composites
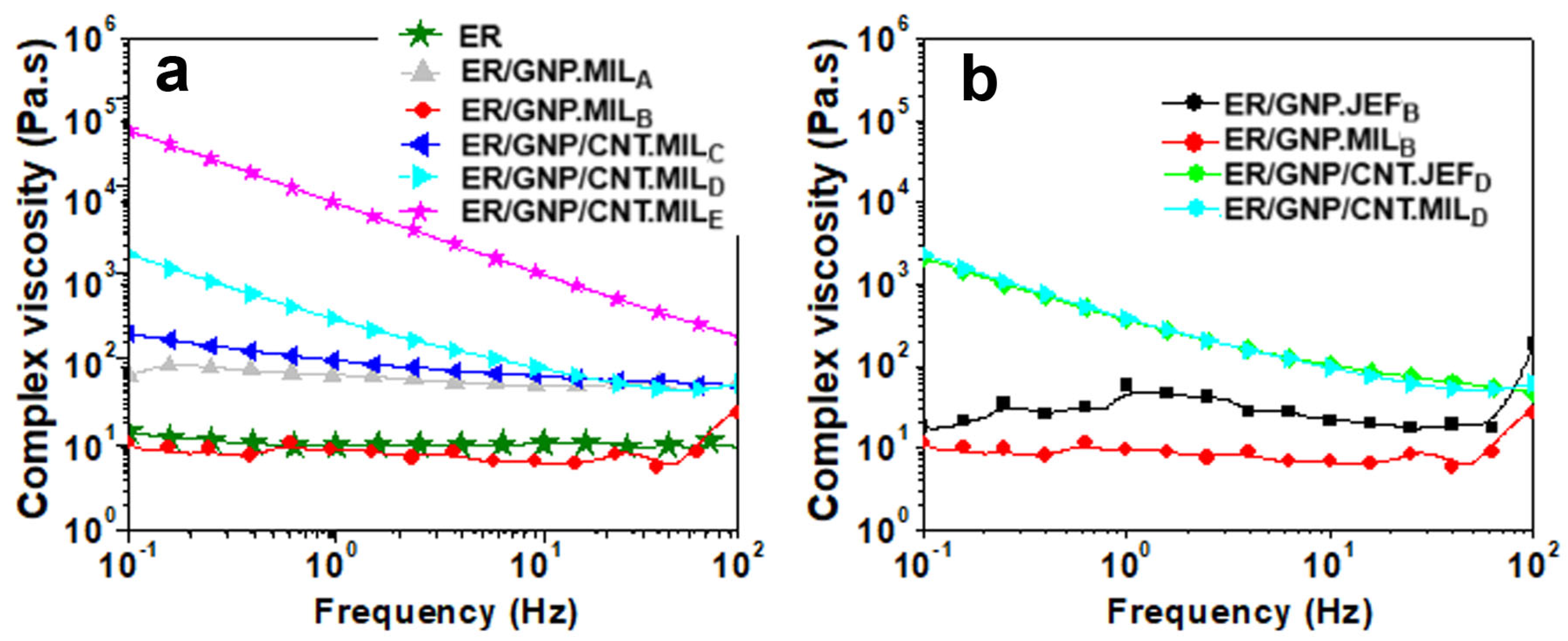
2.2. Rheology of Uncured Epoxy Dispersions
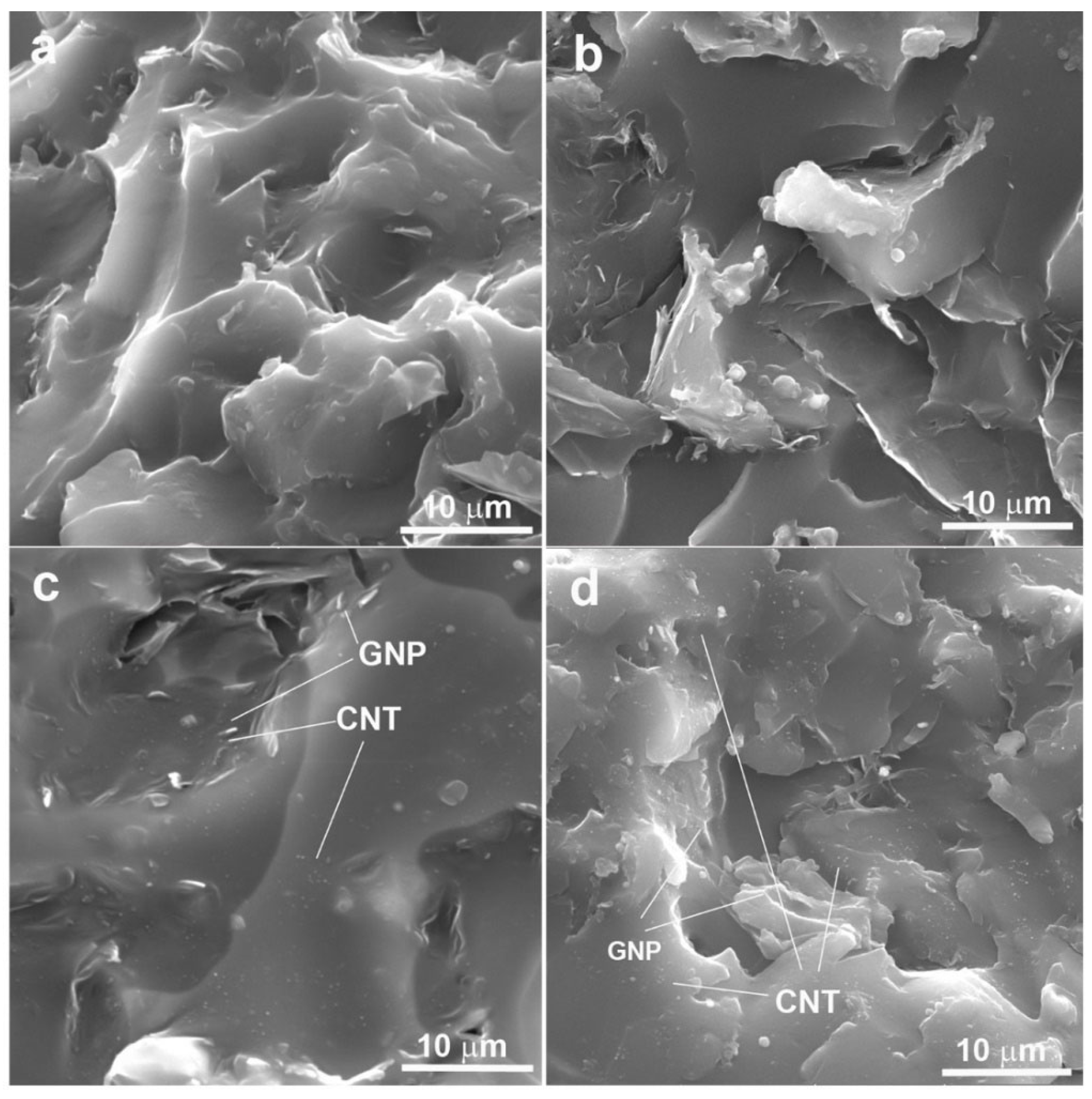
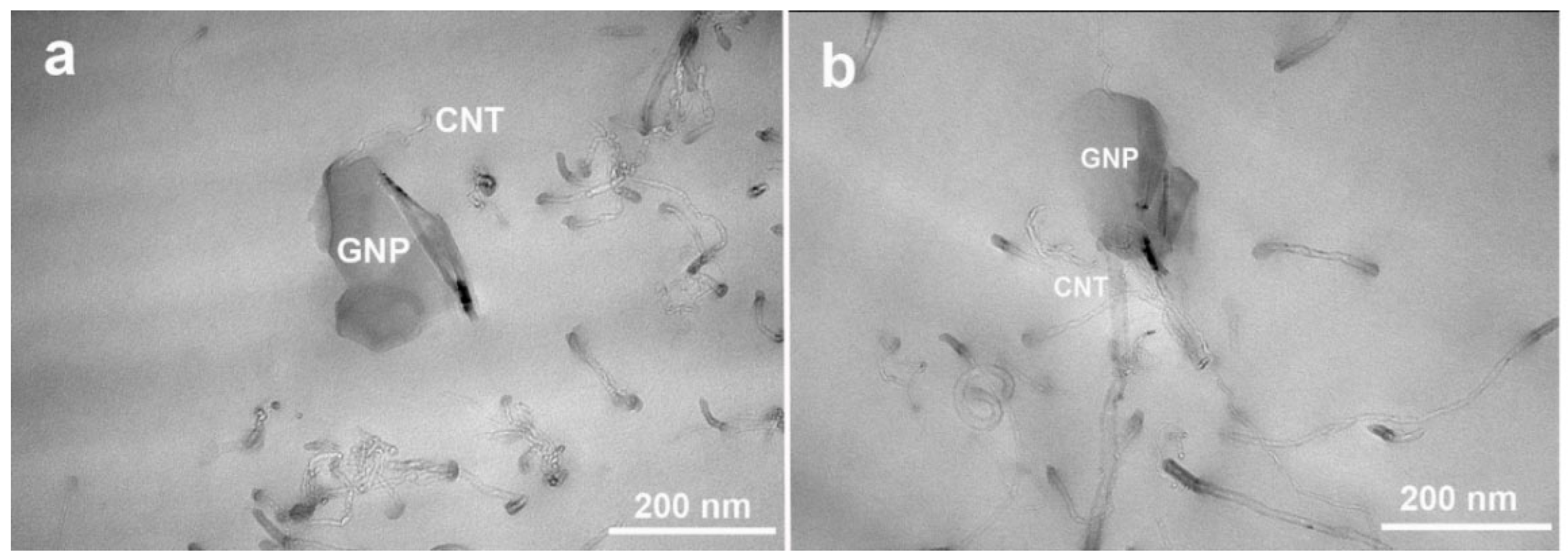
2.3. XRD and Morphology of Hybrid System
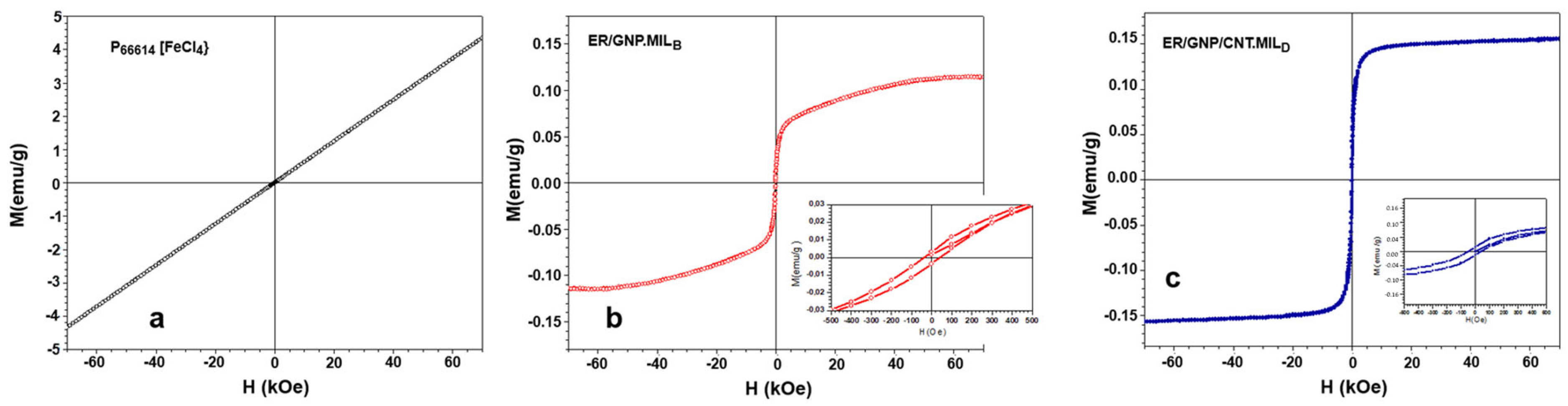
2.4. Magnetic Properties of Composites Cured with MIL
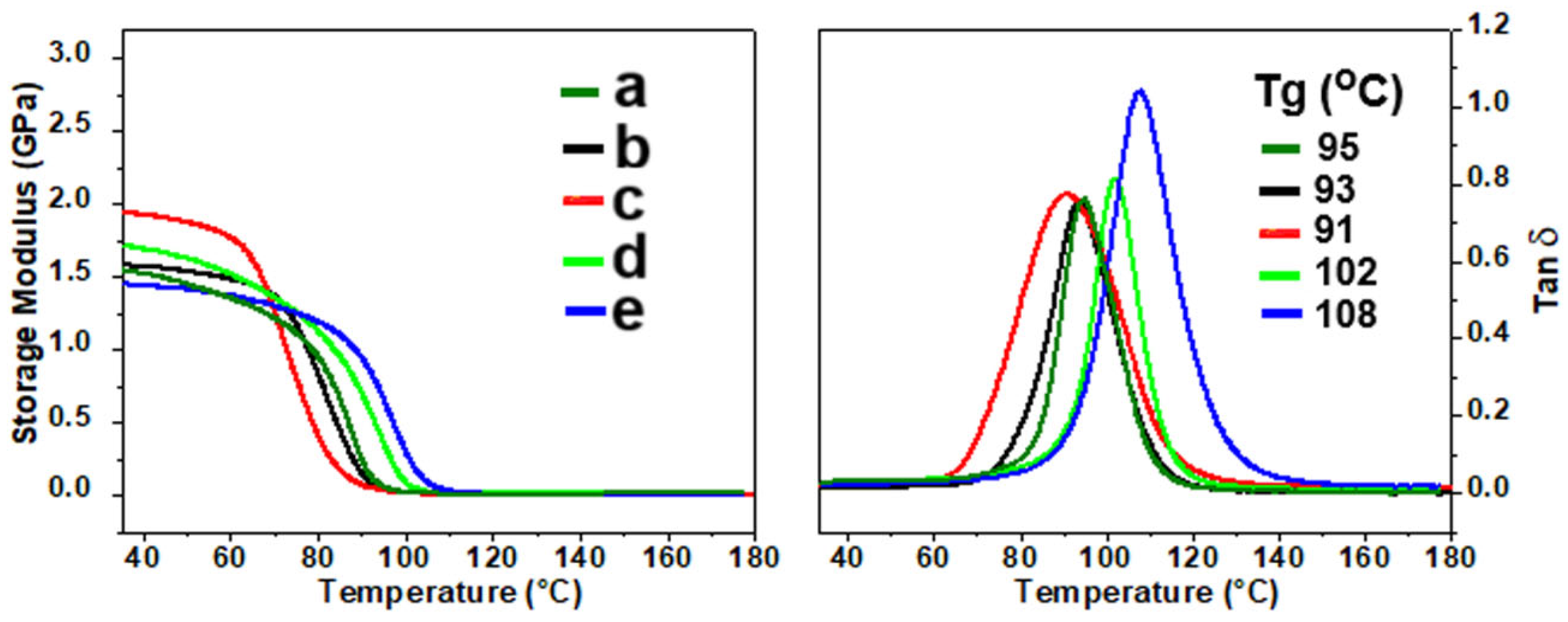
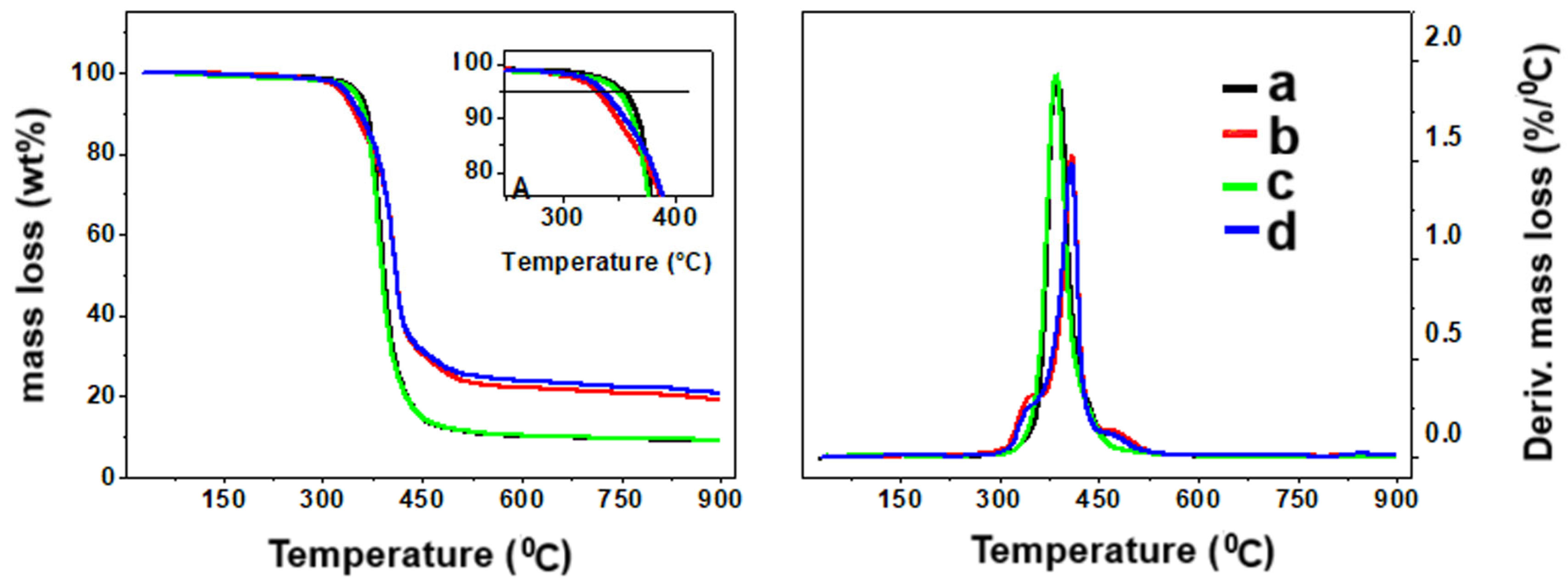
2.5. Dynamic Mechanical Analysis and Thermal Stability
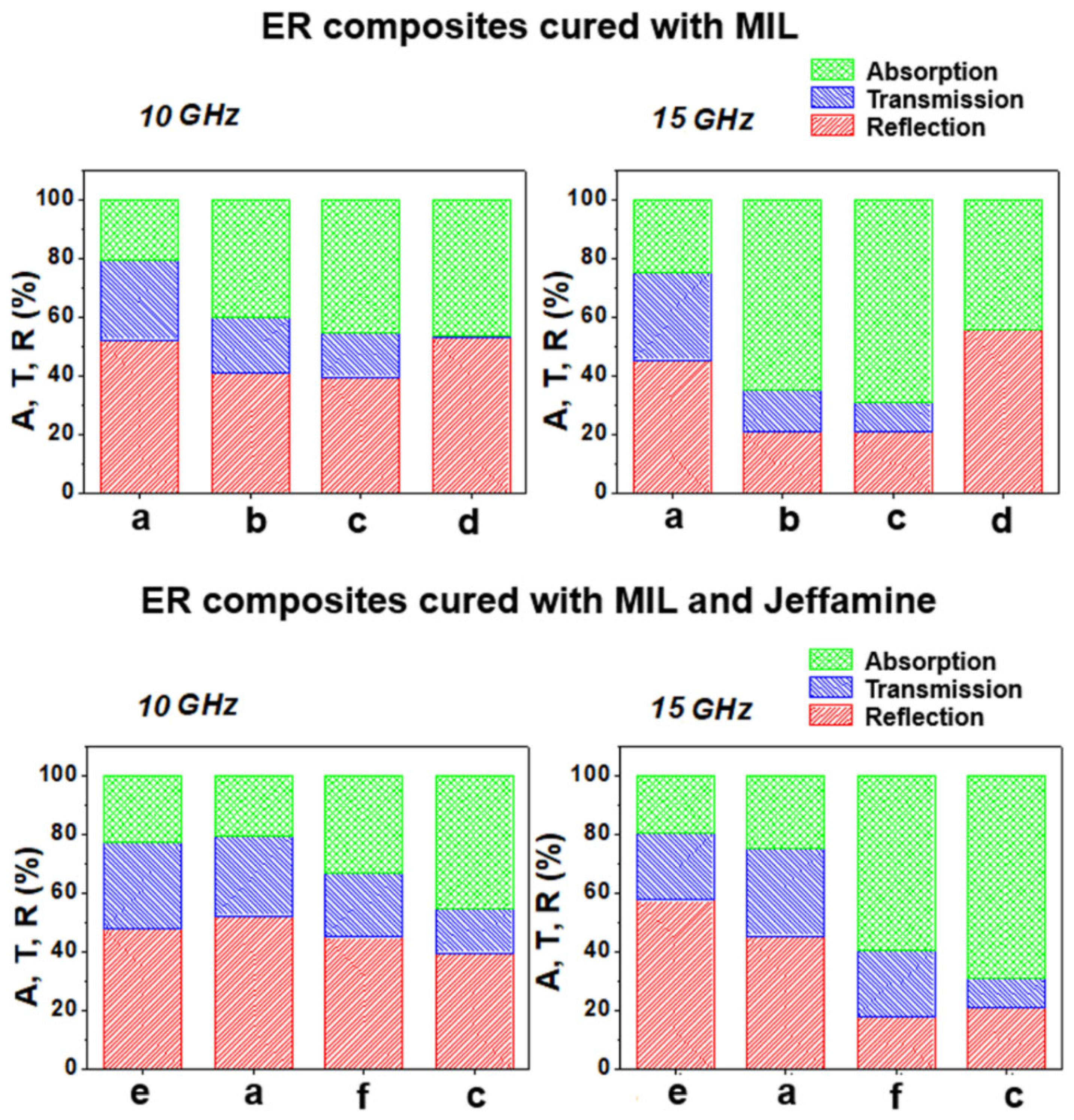
2.6. Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Effectiveness and Absorbing Properties
3. Experimental
3.1. Materials
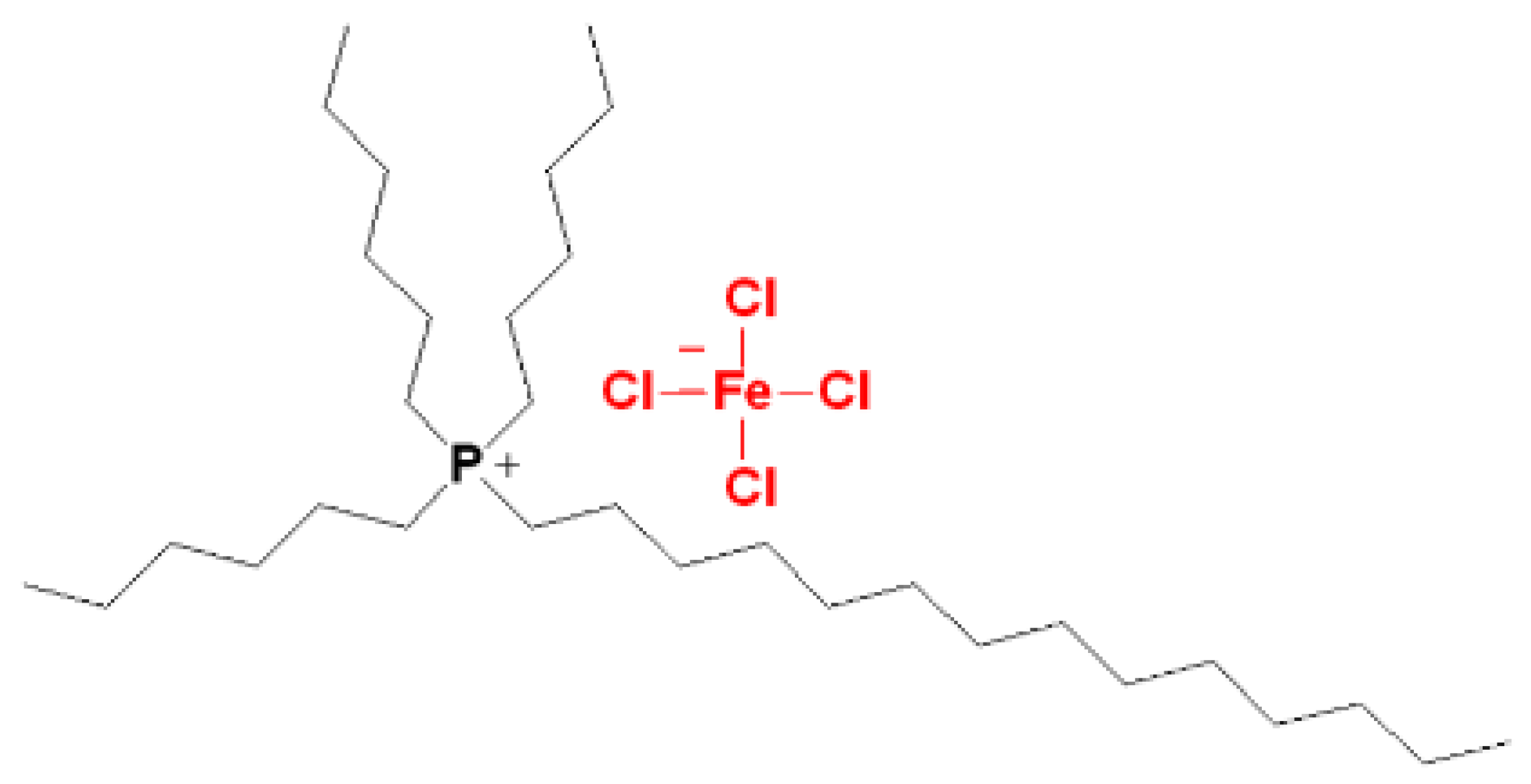
3.2. Synthesis of Magnetic Ionic Liquid (MIL)
3.3. Preparation of Epoxy Resin (ER) with Hybrid Fillers
3.4. Characterization
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thomassin, J.M.; Jerôme, C.; Pardoen, T.; Bailly, C.; Huynen, I.; Detrembleur, C. Polymer/carbon based composites as electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding materials. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2013, 74, 211–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.S.; Huang, H.; Zhou, Y.J.; Zhang, C.Y.; Li, Z.T. Research progress of graphene-based microwave absorbing materials in the last decade. Mater. Res. 2017, 32, 1213–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Murugadoss, V.; Kong, J.; He, Z.; Mai, X.; Shao, Q.; Chen, Y.; Guo, L.; Liu, C.; Angaiah, S. Overview of carbon nanostructures and nanocomposites for electromagnetic wave shielding. Carbon 2018, 140, 696–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayalakshmi, C.G.; Inamdar, A.; Anand, A.; Kandasubramanian, B. Polymer matrix composites as broadband radar absorbing structures for stealth aircrafts. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 47241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, S.; Bhawal, P.; Ravindren, R.; Das, N.C. Polymer nanocomposites for electromagnetic interference shielding: A review. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2018, 18, 7641–7669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, J.; Liang, R.; Wang, J.; Jia, L.; Yang, X.; Yu, W.; Zhang, Z. A review of the establishment of effective conductive pathways of conductive polymer composites and advances in electromagnetic shielding. Polymers 2024, 16, 2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, F.-L.; Li, X.; Park, S.-J. Synthesis and application of epoxy resins: A review. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 29, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liu, H.; Hu, D.; Liu, H.; Ma, W. Recent advances in carbon nanotubes-based microwave absorbing composites. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 23749–23761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankaran, S.; Deshmukh, K.; Ahamed, M.B.; Pasha, S.K. Recent advances in electromagnetic interference shielding properties of metal and carbon filler reinforced flexible polymer composites: A review. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2018, 114, 49–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kausar, A. Influence of interfacial aspects on electromagnetic interference shielding performance of graphene reinforced nanocomposites: An overview. Compos. Interfaces 2022, 29, 1373–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Liu, W.; Cheng, Y.; Lv, J.; Dai, S.; Tang, D.; Zhang, B.; Ji, G. Recent process in the design of carbon-based nanostructures with optimized electromagnetic properties. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 749, 887–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kausar, A.; Ahmad, I.; Zhao, T.; Aldaghri, O.; Ibnaouf, K.H.; Eisa, M.H.; Lam, T.D. Graphene nanocomposites for electromagnetic interference shielding—Trends and advancements. J. Compos. Sci. 2023, 7, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.; Han, C.; Wang, X.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Shu, J.; Yang, H.; Fang, X.; Yuan, J. Graphene nanohybrids: Excellent electromagnetic properties for the absorbing and shielding of electromagnetic waves. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 4586–4602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, W.R.; Pezzin, S.H.; Lafratta, F.H. Airbrushing of carbon nanotubes on glass fibers for electromagnetic shielding epoxy composites. Polímeros 2023, 33, e20230001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wei, X.; Bai, Y.A.; Zhou, H.; Wang, X.; Wen, B.; Wang, Y. Designing improved electromagnetic shielding efficacy of poly (3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3hydroxyvalerate) nanocomposites foam using carbon nanotubes and graphene nanoplatelets. J. Vinyl Addit. Technol. 2024, 30, 72–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Anjos, E.G.R.; Brazil, T.R.; de Melo Morgado, G.F.; Antonelli, E.; Medeiros, N.C.D.F.L.; Santos, A.P.; Indrusiak, T.; Baldan, M.R.; Rezende, M.C.; Pessan, L.A.; et al. Graphene related materials as effective additives for electrical and electromagnetic performance of epoxy nanocomposites. FlatChem 2023, 41, 100542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelal, N.; Dib, N.; Young, D.; Slanker, A. Electromagnetic interference shielding and dielectric properties of graphene nanoplatelets/epoxy composites in the x-band frequency range. J. Mater. Sci. 2022, 57, 13928–13944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kargar, F.; Barani, Z.; Balinskiy, M.; Magana, A.S.; Lewis, J.S.; Balandin, A.A. Dual-functional graphene composites for electromagnetic shielding and thermal management. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2019, 5, 1800558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Liu, Z.; Cai, J.; Zhang, C.; Gao, H.; Chen, Y. Electromagnetic interference shielding of graphene/epoxy composites. Carbon 2009, 47, 922–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.F.; Ab Aziz, S.; Abbas, Z.; Obaiys, S.J.; Khamis, A.M.; Hussain, I.R.; Zaid, M.H.M. Preparation of a chemically reduced graphene oxide reinforced epoxy resin polymer as a composite for electromagnetic interference shielding and microwave-absorbing applications. Polymers 2018, 10, 1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, D.; Zhou, W.; Qing, Y.; Luo, F.; Zhu, D. Single-layer and double-layer microwave absorbers based on graphene nanosheets/epoxy resin composite. Nano 2017, 12, 1750089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Luo, J.; Zhao, G.L. Dielectric and microwave attenuation properties of graphene nanoplatelet–epoxy composites. AIP Adv. 2014, 4, 017139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.A.; Stein, R.; Campos, D.; Indrusiak, T.; Soares, B.G.; Barra, G.M. Conducting materials based on epoxy/graphene nanoplatelet composites with microwave absorbing properties: Effect of the processing conditions and ionic liquid. Front. Mater. 2019, 6, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collado, I.; Jiménez-Suárez, A.; Vázquez-López, A.; del Rosario, G.; Prolongo, S.G. Ultrasonication Influence on the Morphological Characteristics of Graphene Nanoplatelet Nanocomposites and Their Electrical and Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Behavior. Polymers 2024, 16, 1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira, M.M.; Forsberg, S.; Selegård, L.; Carastan, D.J. The influence of sonication processing conditions on electrical and mechanical properties of single and hybrid epoxy nanocomposites filled with carbon nanoparticles. Polymers 2021, 13, 4128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jen, Y.M.; Chang, H.H.; Lu, C.M.; Liang, S.Y. Temperature-dependent synergistic effect of multi-walled carbon nanotubes and graphene nanoplatelets on the tensile quasi-static and fatigue properties of epoxy nanocomposites. Polymers 2021, 13, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Nafezarefi, F.; Tai, N.H.; Schlagenhauf, L.; Nüesch, F.A.; Chu, B.T.T. Size and synergy effects of nanofiller hybrids including graphene nanoplatelets and carbon nanotubes in mechanical properties of epoxy composites. Carbon 2012, 50, 5380–5386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safdari, M.; Al-Haik, M.S. Synergistic electrical and thermal transport properties of hybrid polymeric nanocomposites based on carbon nanotubes and graphite nanoplatelets. Carbon 2013, 64, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, L.; Pircheraghi, G.; Monemian, S.A.; Manas-Zloczower, I. Epoxy composites with carbon nanotubes and graphene nanoplatelets–Dispersion and synergy effects. Carbon 2014, 78, 268–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Dichiara, A.; Bai, J. Carbon nanotube–graphene nanoplatelet hybrids as high-performance multifunctional reinforcements in epoxy composites. Comp. Sci. Technol. 2013, 74, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prolongo, S.G.; Moriche, R.; Ureña, A.; Flórez, S.; Gaztelumendi, I.; Arribas, C.; Prolongo, M.G. Carbon nanotubes and graphene into thermosetting composites: Synergy and combined effect. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 46475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Galicia, L.; Pérez-Ramírez, E.E.; Velasco-Santos, C.; Licea-Jiménez, L.; Martínez-Hernández, A.L.; Pérez-García, S.A.; López-Ortiz, A. Hybrid based on graphene nanoplatelets and carbon nanotubes obtained in a single-step approach and its reinforcement effect in an epoxy matrix. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2022, 139, e53227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopsidas, S.; Olowojoba, G.B. Multifunctional epoxy composites modified with a graphene nanoplatelet/carbon nanotube hybrid. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, 50890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raimondo, M.; Naddeo, C.; Catauro, M.; Guadagno, L. Viscoelastic Behavior of Structural Epoxy Resins Loaded with Different Carbon Nanostructured Forms. Macromol. Symp. 2022, 405, 2100209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parasuram, S.; Banerjee, P.; Raj, R.; Kumar, S.; Bose, S. Electrophoretically Deposited Multiscale Graphene Oxide/Carbon Nanotube Construct Mediated Interfacial Engineering in Carbon Fiber Epoxy Composites. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 28581–28593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, A.; Ramesh, P.; Sun, X.; Bekyarova, E.; Itkis, M.E.; Haddon, R.C. Enhanced thermal conductivity in a hybrid graphite nanoplatelet–carbon nanotube filler for epoxy composites. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 4740–4744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.S.; Zhang, H.X.; Yoon, K.B. Hybrid rGO–CNT/Epoxy Nanocomposites as Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Materials. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2014, 7, 10770–10778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Li, K.; Xiao, C.; Yin, X.; Gui, X.; Song, Q.; Ye, F. Carbon nanotube-vertical edge rich graphene hybrid sponge as multifunctional reinforcements for high performance epoxy composites. Carbon 2023, 201, 871–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.S.; Park, Y.H.; Yoon, K.H. Flexural, electrical, thermal and electromagnetic interference shielding properties of xGnP and carbon nanotube filled epoxy hybrid nanocomposites. Carbon Lett. 2017, 24, 41–46. [Google Scholar]
- Huangfu, Y.; Ruan, K.; Qiu, H.; Lu, Y.; Liang, C.; Kong, J.; Gu, J. Fabrication and investigation on the PANI/MWCNT/thermally annealed graphene aerogel/epoxy electromagnetic interference shielding nanocomposites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2019, 121, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Sha, P.; Wang, B.; Ding, Y.; Du, S. High-efficiency electromagnetic wave absorption of epoxy composites filled with ultralow content of reduced graphene/carbon nanotube oxides. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2020, 189, 108020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; He, D.; Dubrunfaut, O.; Zhang, A.; Zhang, H.; Pichon, L.; Bai, J. GO-CNTs hybrids reinforced epoxy composites with porous structure as microwave absorbers. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2020, 200, 108450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdi, M.K.; Noorbakhsh, B.; Nazari, B.; Ranjbar, Z. Preparation and EMI shielding performance of epoxy/non-metallic conductive fillers nano-composites. Prog. Org. Coat. 2020, 145, 105674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chu, H.; Li, Y. Why single-walled carbon nanotubes can be dispersed in imidazolium-based ionic liquids. ACS Nano 2008, 2, 2540–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tunckol, M.; Durand, J.; Serp, P. Carbon nanomaterial–ionic liquid hybrids. Carbon 2012, 50, 4303–4334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Throckmorton, J.A.; Watters, A.L.; Geng, X.; Palmese, G.R. Room temperature ionic liquids for epoxy nanocomposite synthesis: Direct dispersion and cure. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2013, 86, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes Pereira, E.C.; Soares, B.G. Conducting epoxy networks modified with noncovalently functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotube with imidazolium-based ionic liquid. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133, 43976–43977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanes, J.; Saurín, N.; Carrión, F.J.; Ojados, G.; Bermúdez, M.D. Synergy between singlewalled carbon nanotubes and ionic liquids in epoxy resin nanocomposites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2016, 105, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, B.G.; Riany, N.; Silva, A.A.; Barra, G.M.O.; Livi, S. Dual-role of phosphonium –based ionic liquid in epoxy/MWCNT systems: Electric, rheological behavior and electromagnetic interference shielding effectiveness. Eur. Polym. J. 2016, 84, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Park, S.J. Imidazolium-optimized conductive interfaces in multilayer graphene nanoplatelet/epoxy composites for thermal management applications and electroactive devices. Polymer 2019, 168, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dermani, A.K.; Kowsari, E.; Ramezanzadeh, B.; Amini, R. Screening the effect of graphene oxide nanosheets functionalization with ionic liquid on the mechanical properties of an epoxy coating. Prog. Org. Coat. 2018, 122, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Chevali, V.S.; Xu, Z.; Hui, D.; Wang, H. A review of extending performance of epoxy resins using carbon nanomaterials. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 136, 197–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriques, R.R.; de Oliveira, C.P.; Stein, R.; Pontes, K.; Silva, A.A.; Soares, B.G. Dual Role of Magnetic Ionic Liquids as Curing Agents of Epoxy Resin and Microwave-Absorbing Additives. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2022, 4, 1207–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Cheng, H.W.; Jin, C.; Yang, B.; Xu, C.; Pei, K.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Z.; Che, R. Dimensional design and core-shell engineering of nanomaterials for electromagnetic wave absorption. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2107538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamatha, G.M.; Dixit, P.; Krishna, R.H.; Girish Kumar, S. Polymer based composites for electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding: The role of magnetic fillers in effective attenuation of microwave, a review. Hybrid Adv. 2024, 6, 100200. [Google Scholar]
- Shukla, V. Review of electromagnetic interference shielding materials fabricated by iron ingredients. Nanoscale 2019, 1, 1640–17671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Cao, Q.; Bi, H.; Liang, C.; Yuan, K.; She, W.; Yang, Y.; Che, R. CoNi@SiO2@TiO2 and CoNi@Air@TiO2 microsphere with strong wideband microwave absorption. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 486–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Che, R.; Peng, L.M.; Duan, X.; Chen, Q.; Liang, X. Microwave absorption enhancement and complex permittivity and permeability of Fe encapsulated within carbon nanotubes. Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabino, A.A.P.; Soares, B.G. Flexible microwave absorbing composites based on polydimethylsiloxane filled with hybrid carbonaceous materials: Statistical analysis of the synergistic effect. Polym. Comp. 2023, 44, 4623–4640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Zhao, C.; Li, R.; Hamidinejad, M.; Park, C.B. Flexible, ultrathin, and high-efficiency electromagnetic shielding properties of poly(vinylidene fluoride)/carbon composite films. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 20873–20884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genovese, D.B. Shear rheology of hard-sphere, dispersed, and aggregated suspensions, and filler-matrix composites. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 171, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, F.A.M.M.; Santos, M.; Cernadas, T.; Alves, P.; Ferreira, P. Influence of fillers on epoxy resins properties: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 57, 15183–15212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, M.; Yousefi, A.A.; Ehsani, M. Thermorheological analysis of blend of high- and low-density polyethylenes. J. Polym. Res. 2012, 19, 9798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, X.; Yan, Y.H.; Yan, L.; Yang, P.; Wang, J.; Xu, R.; Chan-Park, M.B. A magnetically responsive material of single-walled carbon nanotubes functionalized with magnetic ionic liquid. Carbon 2010, 48, 2501–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coey, J.M.D. Magnetism and Magnetic Materials; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Del Sesto, R.E.; McCleskey, T.M.; Burrell, A.K.; Baker, G.A.; Thompson, J.D.; Scott, B.L.; Wilkes, J.S.; Williams, P. Structure and magnetic behavior of transition metal based ionic liquids. Chem. Commun. 2008, 447–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Liang, C.; Chen, J.; Huang, Y.; Cheng, F.; Wen, F.; Xu, B.; Wang, B. Novel 3D network porous graphene nanoplatelets/Fe3O4/epoxy nanocomposites with enhanced electromagnetic interference shielding efficiency. Comp. Sci. Technol. 2019, 169, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, R.; Agarwal, K.; Kumar, R.; Kumar, R.; Mukhopadhyay, K.; Prasad, N.E. EMI and microwave absorbing efficiency of polyaniline-functionalized reduced graphene oxide/γ-Fe2O3/epoxy nanocomposites. Soft Mater 2020, 16, 6643–6653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zecchi, S.; Cristoforo, G.; Bartoli, M.; Tagliaferro, A.; Torsello, D.; Rosso, C.; Boccaccio, M.; Acerra, F. A Comprehensive Review of Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Composite Materials. Micromachines 2024, 15, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menon, A.V.; Choudhury, B.; Madras, G.; Bose, S. “Trigger-free” self-healable electromagnetic shielding material assisted by co-doped graphene nanostructures. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 382, 122816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manna, R.; Srivastava, S.K. Reduced graphene oxide/Fe3O4/polyaniline ternary composites as a superior microwave absorber in the shielding of electromagnetic pollution. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 9164–9175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.J.; Wang, B.; Wang, J.N. Magnetic and microwave absorbing properties of electrospun Ba(1−x)LaxFe12O19 nanofibers. J. Magn. Magn. Mater 2012, 324, 1305–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayrakdar, H. Complex permittivity, complex permeability and microwave absorption properties of ferrite–paraffin polymer composites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2011, 323, 1882–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, D.P.; Soares, B.G.; Barra, G.M.O.; Santana, L. Sandwich structures based on fused filament fabrication 3D-printed polylactic acid honeycomb and poly(vinylidene fluoride) nanocomposites for microwave absorbing applications. Polym. Compos. 2023, 44, 2250–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Meng, F.; Chen, J.; Du, S. Broadband and strong electromagnetic wave absorption of epoxy composites filled with ultralow content of non-covalently modified reduced graphene oxides. Carbon 2019, 154, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowsari, E.; Mohammadi, M. Synthesis of reduced and functional graphene oxide with magnetic ionic liquid and its application as an electromagnetic-absorbing coating. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2016, 126, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratap, V.; Soni, A.K.; Siddiqui, A.M.; Abbas, S.M.; Katiyar, R.; Prasad, N.E. Dielectric and radar-absorbing properties of exfoliated graphite dispersed epoxy composites. J. Electron. Mater. 2020, 49, 3972–3981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, E.; Albo, J.; Rosatella, A.; Afonso, C.A.M.; Irabien, A. Synthesis and characterization of magnetic ionic liquids (MILs) for CO2 separation. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2014, 89, 866–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


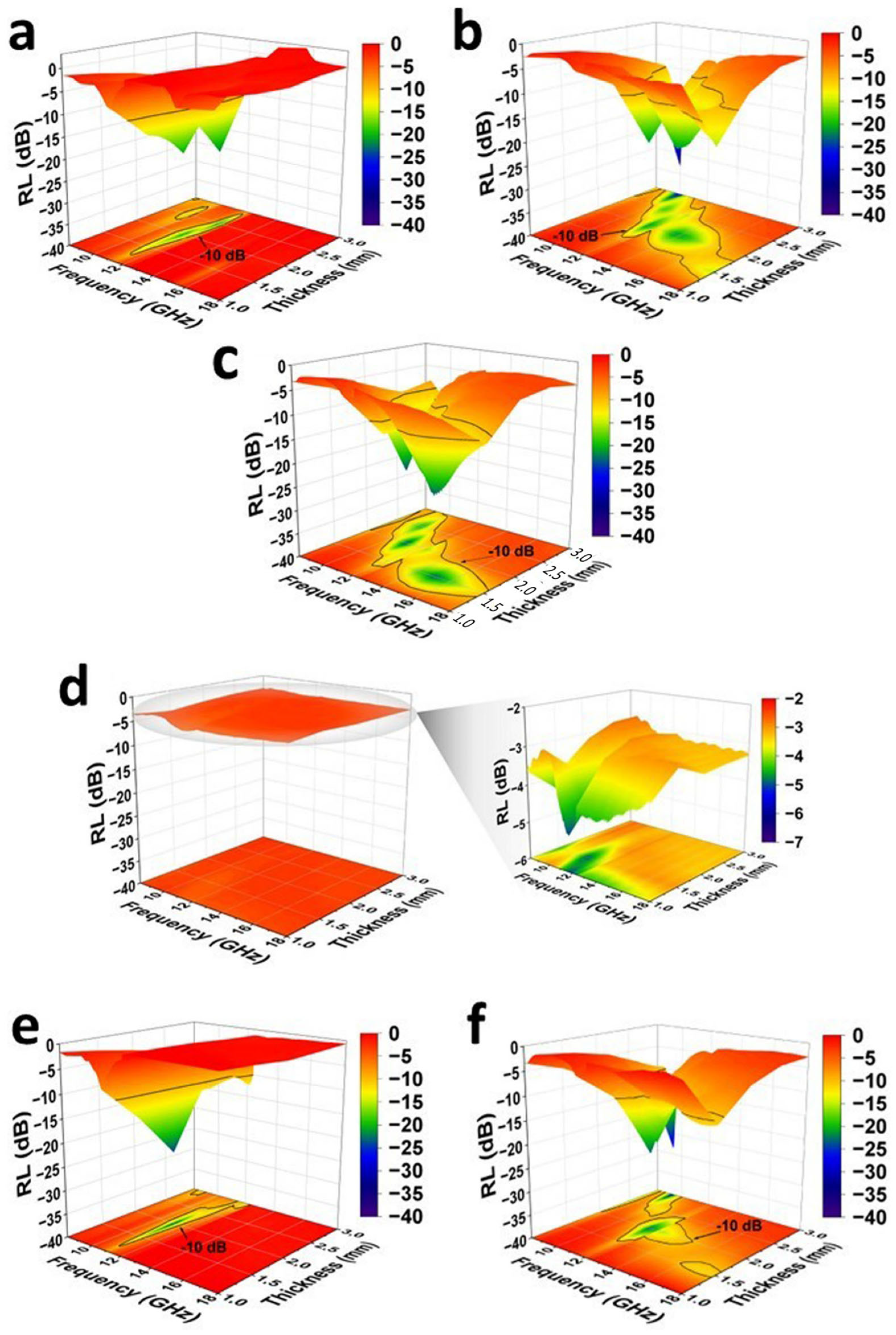
| Composites | Thickness (mm) | RL (dB) | Frequency (GHz) | EAB (GHz) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Effect of the CNT content (samples cured with MIL) | ||||
| ER/GNP.MILB | 1.0 | −8.93 | 12.97 | - |
| 1.5 | −30.41 | 12.94 | 1.24 | |
| 2.0 | −22.71 | 12.61 | 1.46 | |
| 2.5 | −22.26 | 11.99 | 1.69 | |
| 3.0 | −10.68 | 8.27 | 0.32 | |
| ER/GNP/CNT.MILC | 1.0 | −3.58 | 11.88 | - |
| 1.5 | −15.52 | 18.00 | 1.96 | |
| 2.0 | −21.56 | 11.92 | 1.16 | |
| 2.5 | −18.35 | 10.97 | 2.33 | |
| 3.0 | −33.07 | 9.99 | 2.14 | |
| ER/GNP/CNT.MILD | 1.0 | −5.86 | 18.00 | - |
| 1.5 | −23.41 | 15.03 | 5.18 | |
| 2.0 | −23.69 | 11.10 | 2.31 | |
| 2.5 | −20.55 | 10.01 | 2.10 | |
| 3.0 | −10.80 | 9.21 | 0.48 | |
| ER/GNP/CNT.MILE | 1.0 | −5.03 | 11.75 | - |
| 1.5 | −4.91 | 10.83 | - | |
| 2.0 | −3.76 | 10.62 | - | |
| 2.5 | −3.39 | 16.99 | - | |
| 3.0 | −3.35 | 16.99 | - | |
| Effect of the CNT content (samples cured with Jeffamine) | ||||
| ER/GNP.JEFB | 1.0 | −11.49 | 13.24 | 0.17 |
| 1.5 | −30.74 | 13.19 | 1.36 | |
| 2.0 | −24.17 | 11.04 | 1.63 | |
| 2.5 | −12.09 | 14.77 | 1.40 | |
| 3.0 | −13.51 | 14.23 | 1.81 | |
| ER/GNP/CNT.JEFD | 1.0 | −4.06 | 11.81 | - |
| 1.5 | −11.64 | 17.10 | 2.07 | |
| 2.0 | −23.28 | 11.94 | 3.65 | |
| 2.5 | −15.75 | 8.20 | 1.64 | |
| 3.0 | −28.59 | 9.40 | 1.53 | |
| Filler | Amount | Thickness (mm) | EMI SE (dB)/ Freq (GHz) | RL (dB)/ Freq (GHz) | EAB | Method | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GNP | 30 (wt%) | 2.5 | 20 (11) | −3.5 (10.5) | - | Mechanical mixing | [16] |
| nanographite | 15 (wt%) | 7.5 | 12 (11.6) | −10.5 (12) | 1.3 | Mechanical mixing | [16] |
| GNP | 17 (wt%) | 2 | 8 (8.4) | - | - | Sonication without solvent | [17] |
| GNP | 30 (wt%) | 1 | 23 (8.2) | - | - | high-shear speed mixer | [18] |
| RGO | 15 (wt%) | 3 | 21 (8–12) | Sonication with solvent | [19] | ||
| RGO | 5 (wt%) | 6 | 25 (12) | - | - | Mini-mechanical vortex mixer | [20] |
| GNP | 15 (wt%) | 3 | - | −14 (18.9) | 2.0 | Sonication with solvent | [22] |
| GNP | 15 (wt%) | 2.5 | 5.85 (2) | - | - | Sonication without solvent | [24] |
| RGO/CNT | 15 (wt%) | 1.2 | 70 (12) | - | - | Chemical grafting of CNT onto GO/reduction | [37] |
| RGTO | 1 (wt%) | 1.9 | - | −61.8 (13.5) | 5.38 | Expanded graphite/CNT oxidized together—sonication with solvent | [41] |
| TRGO/CNT (2.5:2.5) | 5 (wt%) | 2 | 12 (10) | - | - | Sonication with solvent | [43] |
| RGO-imid | 1 (wt%) | 3 | - | −47.2 (12) | 6.04 | Sonication with solvent—modif. of RGO with imidazole | [75] |
| MFRGO | 40 (wt%) | 4 | - | −25 (8.6) | 1.2 | Covalent functionalization of GO by imidazolium IL/reduction | [76] |
| Exfoliated graphite | 44.7 (vol%) | 4 | −23.8 (11) | 5.6 | chemical treatment with maceration and microwave-assisted thermal exfoliation | [77] | |
| GNP/CNT | 2.6 (wt%) | 3 | 10 (15–18) | - | - | Mixing in a ball-milling and cured with MIL | This work |
| GNP/CNT | 2.6 (wt%) | 1.5 | −23.4 | 5.18 | Mixing in a ball-milling and cured with MIL | This work | |
| GNP/CNT | 4.4 (wt%) | 3 | 33.2 (17) | Mixing in a ball-milling and cured with MIL | This work |
| Sample Code | ER | MIL | GNP | CNT | Jef | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (phr) | (wt%) | (phr) | (wt%) | (phr) | (wt%) | (phr) | (wt%) | (phr) | (wt%) | |
| ER/GNP.MILA | 100 | 83.4 | 10.0 | 8.3 | 10.0 | 8.3 | ||||
| ER/GNP.MILB | 100 | 88.9 | 10.0 | 8.9 | 2.5 | 2.2 | - | |||
| ER/GNP/CNT.MILC | 100 | 88.7 | 10.0 | 8.9 | 2.5 | 2.2 | 0.25 | 0.2 | ||
| ER/GNP/CNT.MILD | 100 | 88.5 | 10.0 | 8.9 | 2.5 | 2.2 | 0.5 | 0.4 | ||
| ER/GNP/CNT.MILE | 100 | 87.0 | 10.0 | 8.6 | 2.5 | 2.2 | 2.5 | 2.2 | ||
| ER/GNP.JEFB | 100 | 74.3 | - | 2.5 | 1.9 | - | 32 | 23.8 | ||
| ER/GNP/CNT.JEFD | 100 | 74.1 | - | 2.5 | 1.8 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 32 | 23.7 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carelo, J.C.; Soares, B.G.; Schmitz, D.P.; Henriques, R.R.; Silva, A.A.; Barra, G.M.O.; Barthem, V.M.T.S.; Livi, S. Magnetic Ionic Liquid: A Multifunctional Platform for the Design of Hybrid Graphene/Carbon Nanotube Networks as Electromagnetic Wave-Absorbing Materials. Molecules 2025, 30, 985. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30050985
Carelo JC, Soares BG, Schmitz DP, Henriques RR, Silva AA, Barra GMO, Barthem VMTS, Livi S. Magnetic Ionic Liquid: A Multifunctional Platform for the Design of Hybrid Graphene/Carbon Nanotube Networks as Electromagnetic Wave-Absorbing Materials. Molecules. 2025; 30(5):985. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30050985
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarelo, Jean C., Bluma G. Soares, Debora P. Schmitz, Ruan R. Henriques, Adriana A. Silva, Guilherme M. O. Barra, Vitoria M. T. S. Barthem, and Sebastien Livi. 2025. "Magnetic Ionic Liquid: A Multifunctional Platform for the Design of Hybrid Graphene/Carbon Nanotube Networks as Electromagnetic Wave-Absorbing Materials" Molecules 30, no. 5: 985. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30050985
APA StyleCarelo, J. C., Soares, B. G., Schmitz, D. P., Henriques, R. R., Silva, A. A., Barra, G. M. O., Barthem, V. M. T. S., & Livi, S. (2025). Magnetic Ionic Liquid: A Multifunctional Platform for the Design of Hybrid Graphene/Carbon Nanotube Networks as Electromagnetic Wave-Absorbing Materials. Molecules, 30(5), 985. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30050985






