Development of Layer-by-Layer Magnetic Nanoparticles for Application to Radiotherapy of Pancreatic Cancer
Abstract
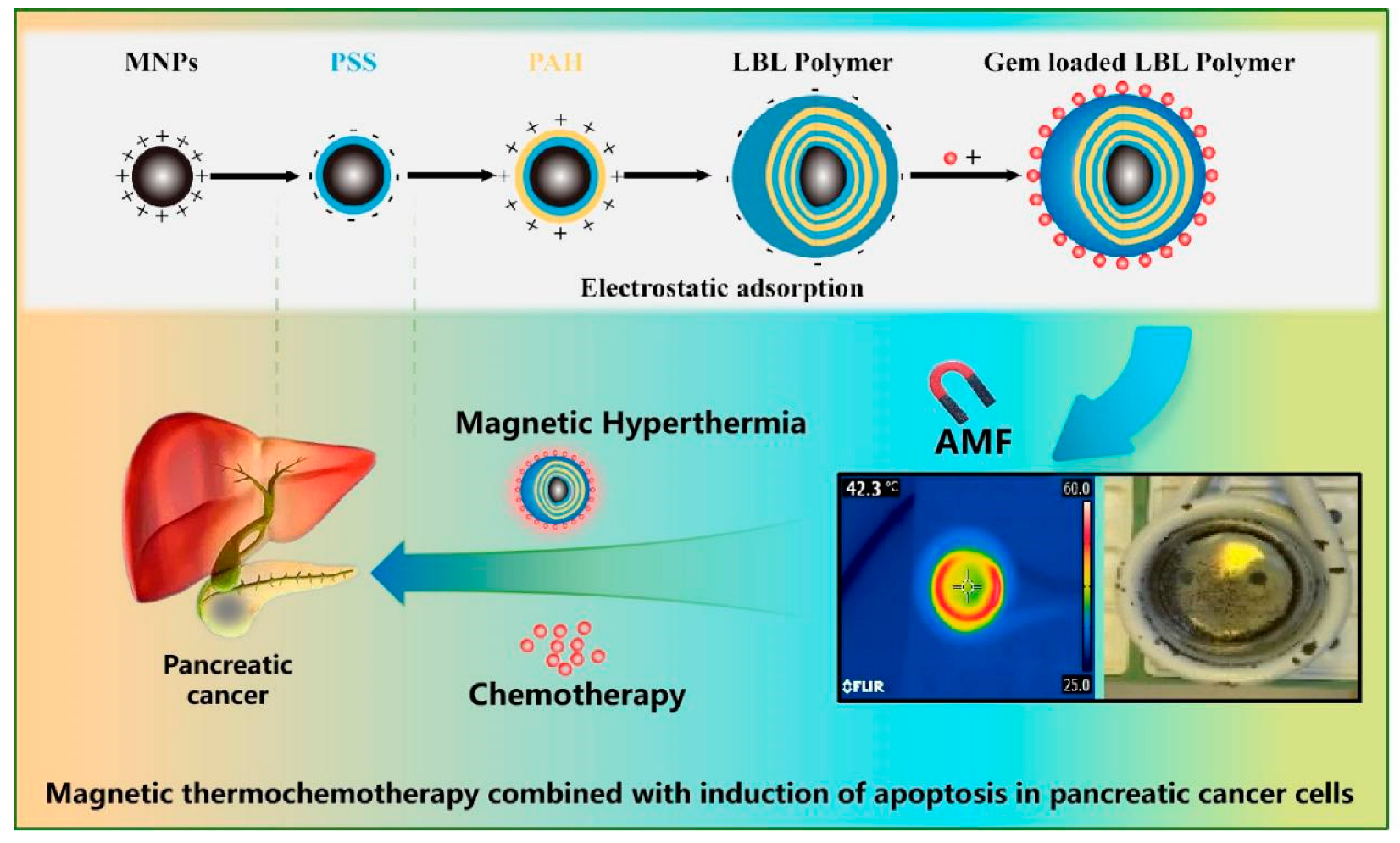
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
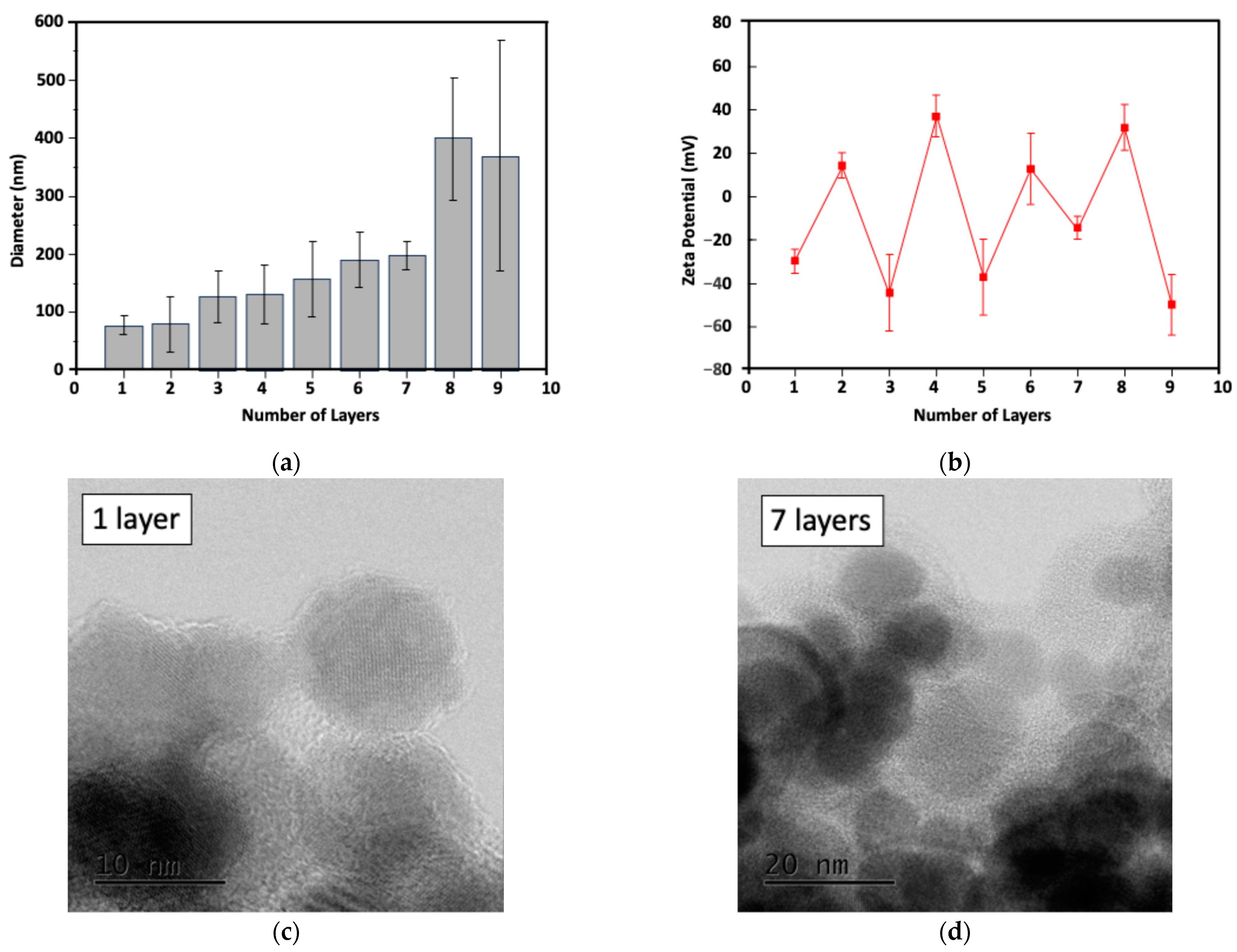
2.1. Characterization of the Particle Size and Potential of LBL MNPs
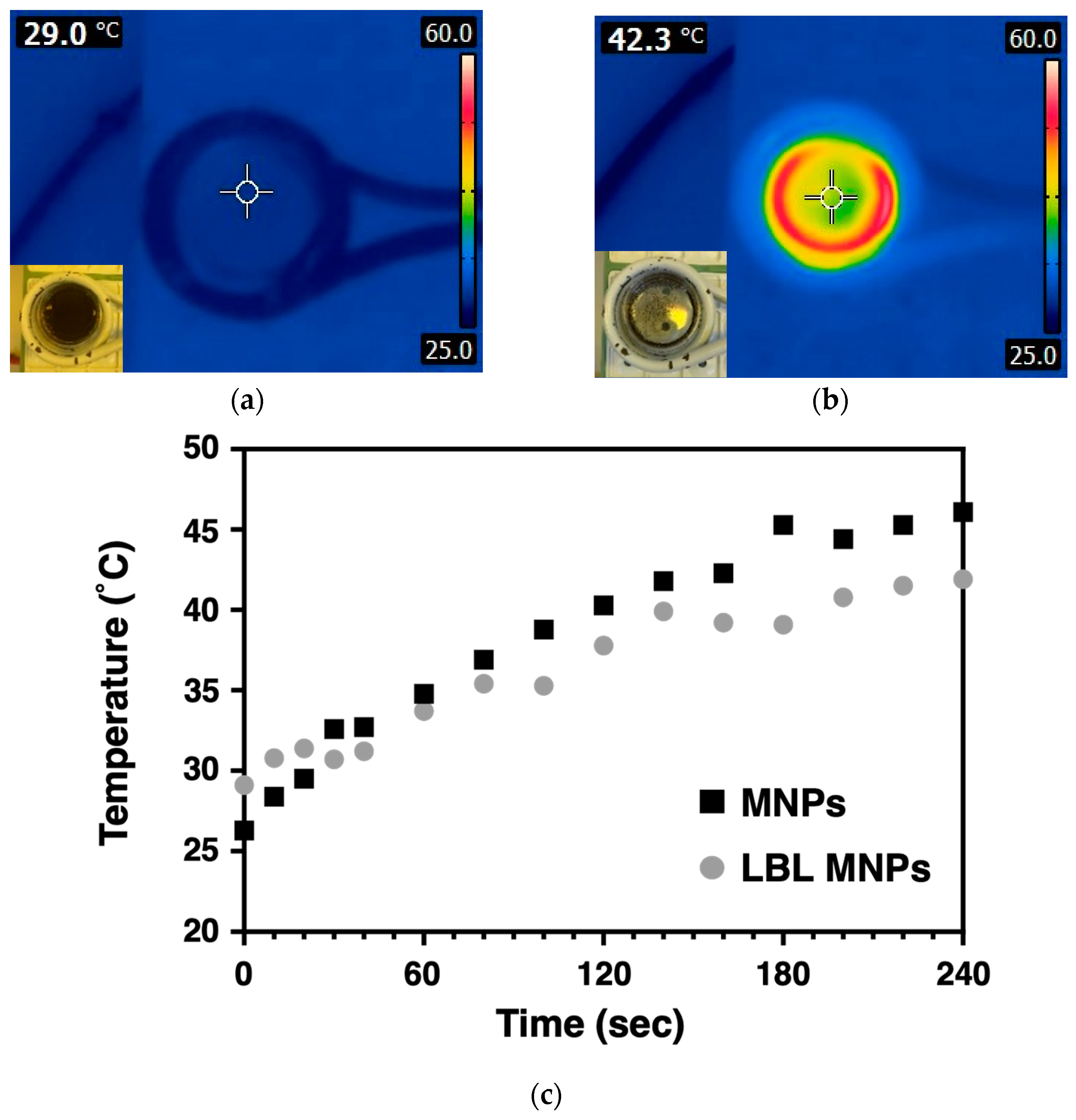
2.2. Heat Generation Behavior of LBL MNPs
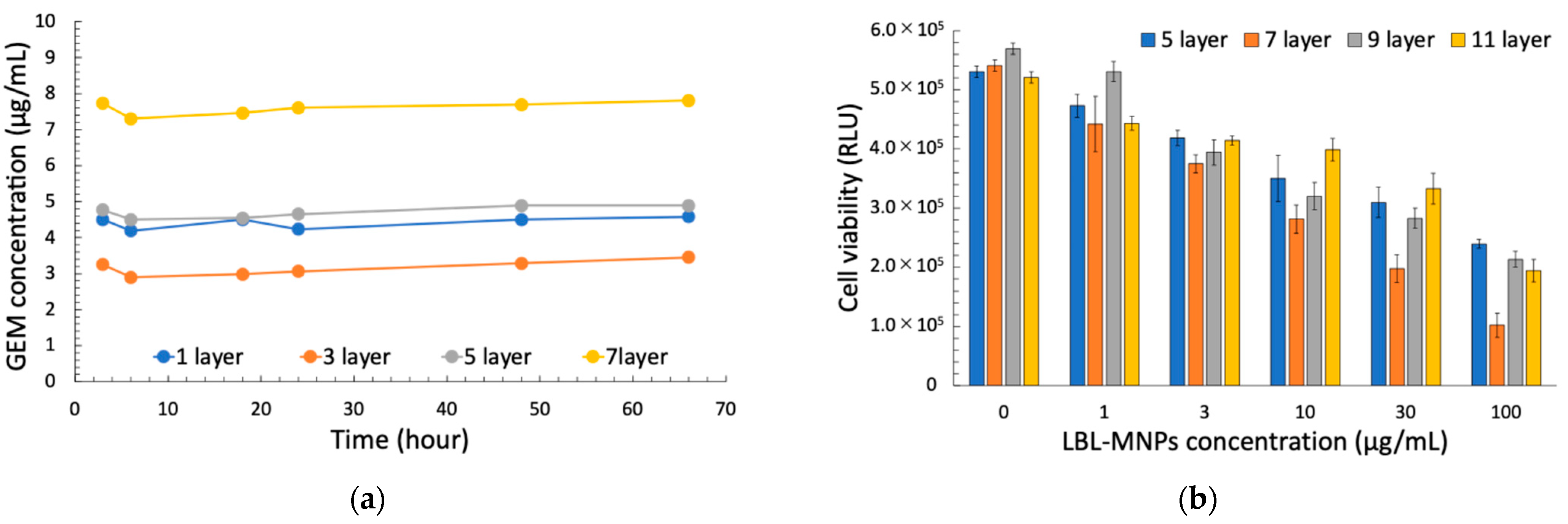
2.3. Relationship Between Cell Killing Effect of LBL MNPs, Concentration, and Layer Number
2.4. Enhancement of the Synergistic Cell-Killing Effect by LBL MNPs and AMF Application
2.5. Enhancement of the Synergistic Cell-Killing Effect by LBL MNPs, AMF, and X-Ray Irradiation
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Preparation of LBL Nanoparticles and LBL Nanoparticles Loaded with GEM
3.2. Characterization of LBL Nanoparticle and Size Distribution and Zeta Potential Measurements
3.3. Heat Generation Behavior of LBL MNPs upon AMF
3.4. Cell Culture
3.5. Cytotoxic Effects of LBL MNPs Alone
3.6. Cytotoxic Effects Using LBL Nanoparticles Combined with AMF and/or X-Rays
3.7. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LBL | Layer-by Layer |
| GEM | Gemcitabine |
| MNP | Magnetic Nanoparticle |
| EPR | Enhanced Permeability and Retention |
| DLS | Dynamic Light Scattering |
| PDI | Polydispersity Index |
| PSS | Poly (sodium 4-styrenesulfonate) |
| PAH | Poly (Allylamine hydrochloride) |
| TEM | Transmission Electron Microscopy |
| AMF | Alternated Magnetic Field |
| ROS | Reactive Light Scattering |
| RT | Radiotherapy |
| DDS | Drug Delivery System |
| FBS | Fetal Bovine Serum |
| PBS | Phosphate-Buffered Saline |
| RLU | Relative Light Units |
References
- Cancer Information Service; Institute for Cancer Control; National Cancer Center. Available online: https://ganjoho.jp/public/qa_links/report/statistics/2023_jp.html (accessed on 26 December 2024).
- Okusaka, T.; Nakamura, M.; Yoshida, M.; Kitano, M.; Ito, Y.; Mizuno, N.; Hanada, K.; Ozaka, M.; Morizane, C.; Takeyama, Y.; et al. Clinical Practice Guidelines for Pancreatic Cancer 2022 from the Japan Pancreas Society: A Synopsis. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 28, 493–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohal, D.P.S.; Mangu, P.B.; Khorana, A.A.; Shah, M.A.; Philip, P.A.; O’Reilly, E.M.; Uronis, H.E.; Ramanathan, R.K.; Crane, C.H.; Engebretson, A.; et al. Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 2784–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tschoep-Lechner, K.E.; Milani, V.; Berger, F.; Dieterle, N.; Abdel-Rahman, S.; Salat, C.; Issels, R.-D. Gemcitabine and Cisplatin Combined with Regional Hyperthermia as Second-Line Treatment in Patients with Gemcitabine-Refractory Advanced Pancreatic Cancer. Int. J. Hyperth. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Hyperthermic Oncol. N. Am. Hyperth. Group 2013, 29, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, F.; Meng, Y.; Wang, H.; Le, T.; Wei, B.; Lee, D.; Willis, P.; Shen, B.; Yang, X. Diffusion-Weighted MRI Monitoring of Pancreatic Cancer Response to Radiofrequency Heat-Enhanced Intratumor Chemotherapy. NMR Biomed. 2013, 26, 1762–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Le, T.; Wu, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, T.; Meng, Y.; Wei, B.; Soriano, S.S.; Willis, P.; Kolokythas, O.; et al. Intrabiliary RF Heat-Enhanced Local Chemotherapy of a Cholangiocarcinoma Cell Line: Monitoring with Dual-Modality Imaging—Preclinical Study. Radiology 2014, 270, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Huang, H.; Sun, L.; Ma, L.; Du, Y.; Pei, C.; Zhang, Q.; Li, H.; et al. Activating Layered Metal Oxide Nanomaterials via Structural Engineering as Biodegradable Nanoagents for Photothermal Cancer Therapy. Small 2021, 17, 2007486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Li, B.; Shen, C.; Wu, D.; Fan, H.; Zhao, J.; Li, H.; Zeng, Z.; Luo, Z.; Ma, L.; et al. Metallic 1T Phase Enabling MoS2 Nanodots as an Efficient Agent for Photoacoustic Imaging Guided Photothermal Therapy in the Near-Infrared-II Window. Small 2020, 16, 2004173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Xue, B.; Meng, F.; Ma, L.; Du, Y.; Yu, S.; Ye, R.; Li, H.; Zhang, Q.; Gu, L.; et al. Preparation of 2D Polyaniline/MoO3− Superlattice Nanosheets via Intercalation-Induced Morphological Transformation for Efficient Chemodynamic Therapy. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2023, 12, 2202911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niiyama, E.; Uto, K.; Lee, C.M.; Sakura, K.; Ebara, M. Alternating Magnetic Field-Triggered Switchable Nanofiber Mesh for Cancer Thermo-Chemotherapy. Polymers 2018, 10, 1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niiyama, E.; Uto, K.; Lee, C.M.; Sakura, K.; Ebara, M. Hyperthermia Nanofiber Platform Synergized by Sustained Release of Paclitaxel to Improve Antitumor Efficiency. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2019, 8, e1900102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Fujisawa, N.; Takanohashi, M.; Najmina, M.; Uto, K.; Ebara, M. A Smart Hyperthermia Nanofiber-Platform-Enabled Sustained Release of Doxorubicin and 17AAG for Synergistic Cancer Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Fujisawa, N.; Takanohashi, M.; Ebara, M. An Injectable Hyperthermic Nanofiber Mesh with Switchable Drug Release to Stimulate Chemotherapy Potency. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 1046147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouchi, S.; Niiyama, E.; Sugo, K.; Uto, K.; Takenaka, S.; Kikuchi, A.; Ebara, M. Shape-Memory Balloon Offering Simultaneous Thermo/Chemotherapies to Improve Anti-Osteosarcoma Efficacy. Biomater. Sci. 2021, 9, 6957–6965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Matsumoto, Y.; Chen, L.; Sugawara, Y.; Oe, E.; Fujisawa, N.; Ebara, M.; Sakurai, H. Smart Nanofiber Mesh with Locally Sustained Drug Release Enabled Synergistic Combination Therapy for Glioblastoma. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oe, E.; Fujisawa, N.; Chen, L.; Uto, K.; Matsumoto, Y.; Ebara, M. Locally Implantable Nanofibre Meshes by Sustained Release of Temozolomide for Combined Thermo-Chemotherapy to Treat Glioblastoma. New J. Chem. 2023, 47, 5816–5824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujisawa, N.; Chen, L.; Ebara, M. Design of Remote-Controllable Diels-Alder Platform on Magnetic Nanoparticles via Layer-by-Layer Assembly for AC Magnetic Field-Triggered Drug Release. Langmuir ACS J. Surf. Colloids 2024, 40, 23895–23901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decher, G. Fuzzy Nanoassemblies: Toward Layered Polymeric Multicomposites. Science 1997, 277, 1232–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariga, K.; Lvov, Y.; Decher, G. There Is Still Plenty of Room for Layer-by-Layer Assembly for Constructing Nanoarchitectonics-Based Materials and Devices. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. PCCP 2022, 24, 4097–4115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.-Y.; Wu, P.-C.; Fang, C.-L.; Chen, C.-H. Intravesical Delivery of 5-Aminolevulinic Acid from Water-in-Oil Nano/Submicron-Emulsion Systems. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 99, 2375–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamiya, H.; Takeda, Y.; Naka, T.; Kawazoe, N.; Chen, G.; Jeyadevan, B. Practical Solution for Effective Whole-Body Magnetic Fluid Hyperthermia Treatment. J. Nanomater. 2017, 2017, 1047697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Zhou, X.; He, C.; Qiu, K.; Nie, W.; Chen, L.; Wang, H.; Mo, X.; Zhang, Y. Polyelectrolyte Multilayer Functionalized Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for pH-Responsive Drug Delivery: Layer Thickness-Dependent Release Profiles and Biocompatibility. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 5886–5898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Men, W.; Zhu, P.; Dong, S.; Liu, W.; Zhou, K.; Bai, Y.; Liu, X.; Gong, S.; Zhang, S. Layer-by-Layer pH-Sensitive Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery and Controlled Release with Improved Therapeutic Efficacy in Vivo. Drug Deliv. 2020, 27, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T. Cancer Hyperthermia Using Magnetic Nanoparticles. Biotechnol. J. 2011, 6, 1342–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, L.; Supuran, C.T.; Alfarouk, K.O. The Warburg Effect and the Hallmarks of Cancer. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2017, 17, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozissnik, B.; Bohorquez, A.C.; Dobson, J.; Rinaldi, C. Magnetic Fluid Hyperthermia: Advances, Challenges, and Opportunity. Int. J. Hyperth. 2013, 29, 706–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannsen, M.; Thiesen, B.; Wust, P.; Jordan, A. Magnetic Nanoparticle Hyperthermia for Prostate Cancer. Int. J. Hyperth. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Hyperthermic Oncol. N. Am. Hyperth. Group 2010, 26, 790–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivanna, A.T.; Dash, B.S.; Chen, J.-P. Functionalized Magnetic Nanoparticles for Alternating Magnetic Field- or Near Infrared Light-Induced Cancer Therapies. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chen, S.; Pei, W.; Huang, B.; Niu, C. Magnetically Targeted Erythrocyte Membrane Coated Nanosystem for Synergistic Photothermal/Chemotherapy of Cancer. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 4132–4142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Bu, W.; Ren, J.; Li, J.; Deng, L.; Gao, M.; Gao, X.; Wang, P. Enhanced Synergism of Thermo-Chemotherapy For Liver Cancer with Magnetothermally Responsive Nanocarriers. Theranostics 2018, 8, 693–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauwels, B.; Korst, A.E.C.; Lardon, F.; Vermorken, J.B. Combined Modality Therapy of Gemcitabine and Radiation. Oncologist 2005, 10, 34–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toulany, M. Targeting DNA Double-Strand Break Repair Pathways to Improve Radiotherapy Response. Genes 2019, 10, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, C.S.S.R.; Mohammad, F. Magnetic Nanomaterials for Hyperthermia-Based Therapy and Controlled Drug Delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2011, 63, 789–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picchi, D.F.; Biglione, C.; Horcajada, P. Nanocomposites Based on Magnetic Nanoparticles and Metal–Organic Frameworks for Therapy, Diagnosis, and Theragnostics. ACS Nanosci. Au J. 2023, 4, 85–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minaei, S.E.; Khoei, S.; Khoee, S.; Mahdavi, S.R. Sensitization of Glioblastoma Cancer Cells to Radiotherapy and Magnetic Hyperthermia by Targeted Temozolomide-Loaded Magnetite Tri-Block Copolymer Nanoparticles as a Nanotheranostic Agent. Life Sci. 2022, 306, 120729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spirou, S.V.; Basini, M.; Lascialfari, A.; Sangregorio, C.; Innocenti, C. Magnetic Hyperthermia and Radiation Therapy: Radiobiological Principles and Current Practice. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arruebo, M.; Vilaboa, N.; Sáez-Gutierrez, B.; Lambea, J.; Tres, A.; Valladares, M.; González-Fernández, A. Assessment of the Evolution of Cancer Treatment Therapies. Cancers 2011, 3, 3279–3330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayat Mokhtari, R.; Homayouni, T.S.; Baluch, N.; Morgatskaya, E.; Kumar, S.; Das, B.; Yeger, H. Combination Therapy in Combating Cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 38022–38043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, R.; Bhardwaj, A.; Gupta, S. Cancer Treatment Therapies: Traditional to Modern Approaches to Combat Cancers. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2023, 50, 9663–9676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Hoff, D.D.; Ervin, T.; Arena, F.P.; Chiorean, E.G.; Infante, J.; Moore, M.; Seay, T.; Tjulandin, S.A.; Ma, W.W.; Saleh, M.N.; et al. Increased Survival in Pancreatic Cancer with Nab-Paclitaxel plus Gemcitabine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 1691–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorani, E.; Wong, H.H.; Hewitt, C.; Calder, J.; Corrie, P.; Basu, B. Safety and Efficacy of Modified FOLFIRINOX for Advanced Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma: A UK Single-Centre Experience. Oncology 2015, 89, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral, H.; Matsumoto, Y.; Mizuno, K.; Chen, Q.; Murakami, M.; Kimura, M.; Terada, Y.; Kano, M.R.; Miyazono, K.; Uesaka, M.; et al. Accumulation of Sub-100 Nm Polymeric Micelles in Poorly Permeable Tumours Depends on Size. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2011, 6, 815–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fukumitsu, N.; Matsumoto, Y.; Chen, L.; Sugawara, Y.; Fujisawa, N.; Niiyama, E.; Ouchi, S.; Oe, E.; Saito, T.; Ebara, M. Development of Layer-by-Layer Magnetic Nanoparticles for Application to Radiotherapy of Pancreatic Cancer. Molecules 2025, 30, 1382. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30061382
Fukumitsu N, Matsumoto Y, Chen L, Sugawara Y, Fujisawa N, Niiyama E, Ouchi S, Oe E, Saito T, Ebara M. Development of Layer-by-Layer Magnetic Nanoparticles for Application to Radiotherapy of Pancreatic Cancer. Molecules. 2025; 30(6):1382. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30061382
Chicago/Turabian StyleFukumitsu, Nobuyoshi, Yoshitaka Matsumoto, Lili Chen, Yu Sugawara, Nanami Fujisawa, Eri Niiyama, Sosuke Ouchi, Emiho Oe, Takashi Saito, and Mitsuhiro Ebara. 2025. "Development of Layer-by-Layer Magnetic Nanoparticles for Application to Radiotherapy of Pancreatic Cancer" Molecules 30, no. 6: 1382. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30061382
APA StyleFukumitsu, N., Matsumoto, Y., Chen, L., Sugawara, Y., Fujisawa, N., Niiyama, E., Ouchi, S., Oe, E., Saito, T., & Ebara, M. (2025). Development of Layer-by-Layer Magnetic Nanoparticles for Application to Radiotherapy of Pancreatic Cancer. Molecules, 30(6), 1382. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30061382







