Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles from Chlorella vulgaris Aqueous Extract and Their Effect on Salmonella enterica and Chicken Embryo Growth
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Green Synthesis Method Allowed Obtaining Spherical, Stable AgNPs with Negative Charge and High Purity
2.2. Silver Nanoparticles Have Antibacterial Activity Against S. enterica
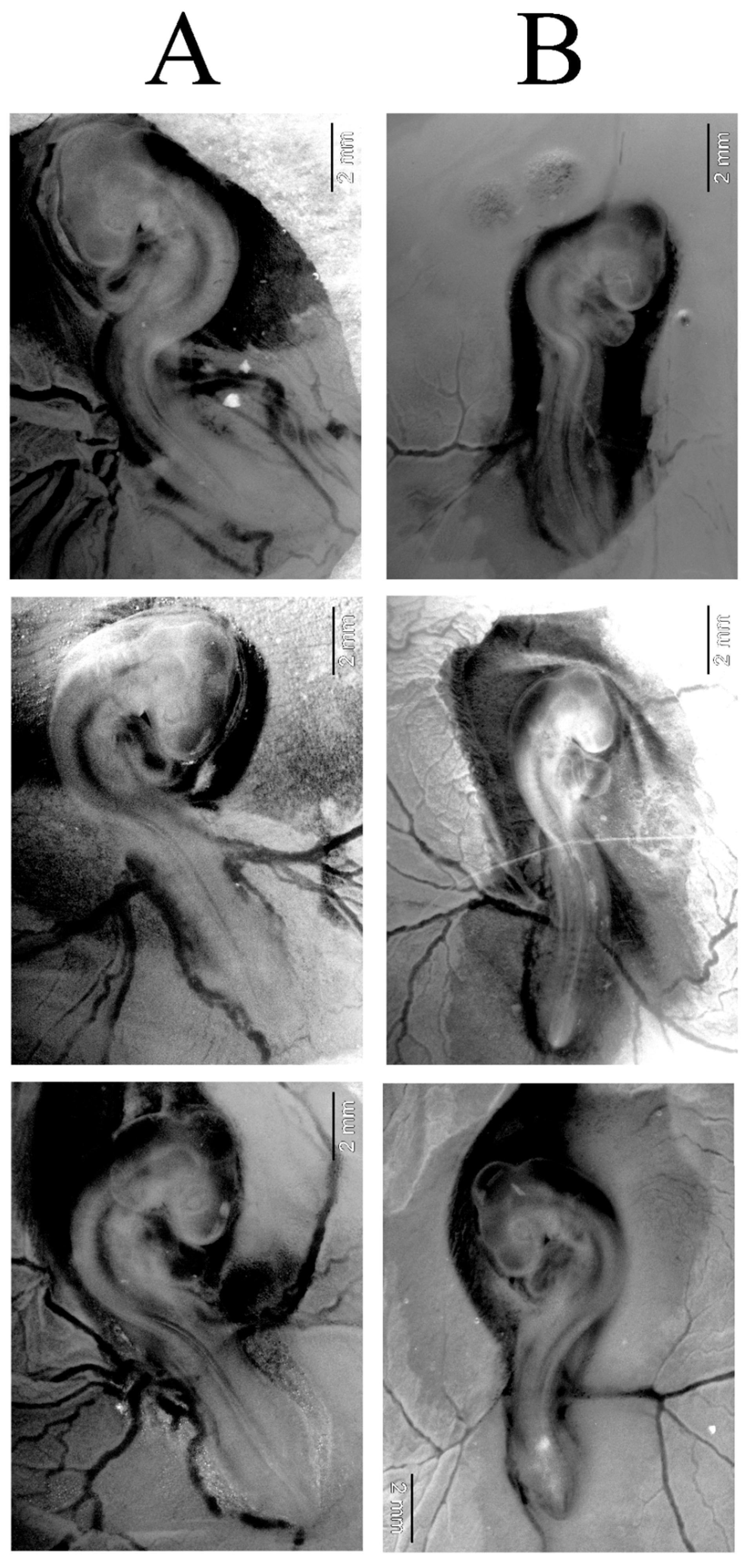
2.3. AgNPs Did Not Change Developmental Stage of Chicken Embryos After 72 H of Incubation
2.4. Long Exposure to AgNPs Caused Mortality of Chicken Embryos and Changed Weight of Key Organs
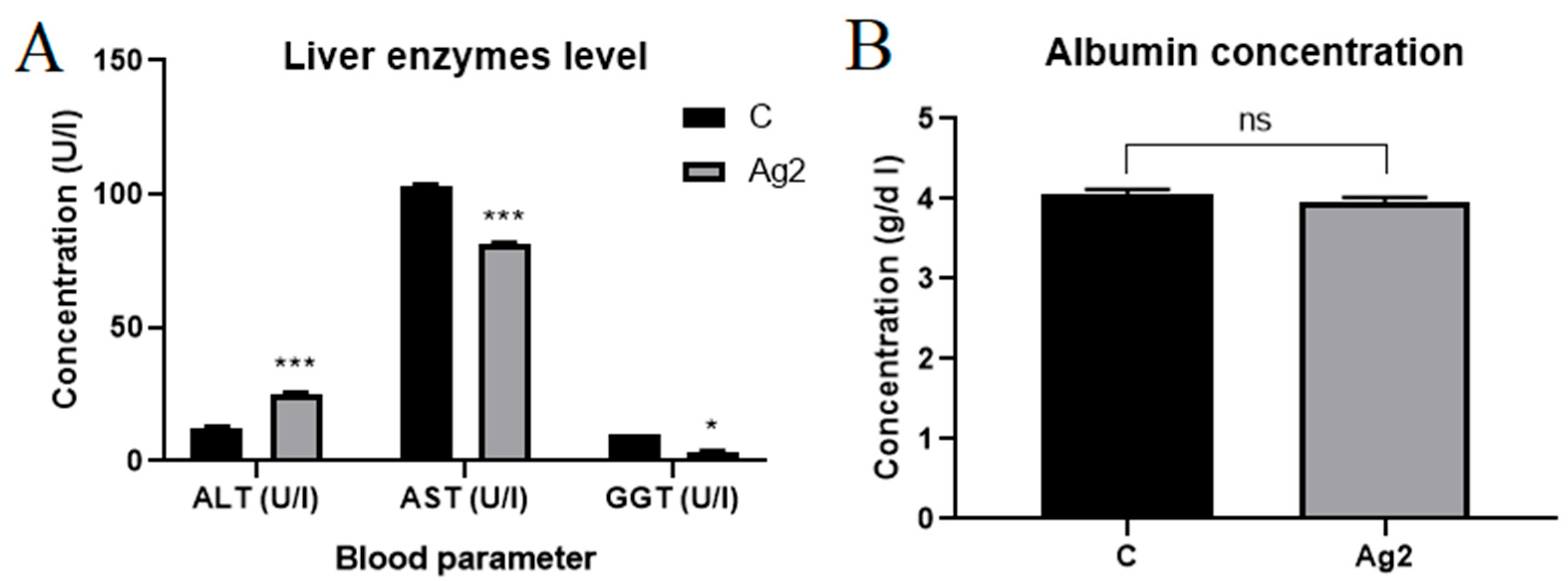
2.5. AgNPs Changed Liver Enzyme Levels
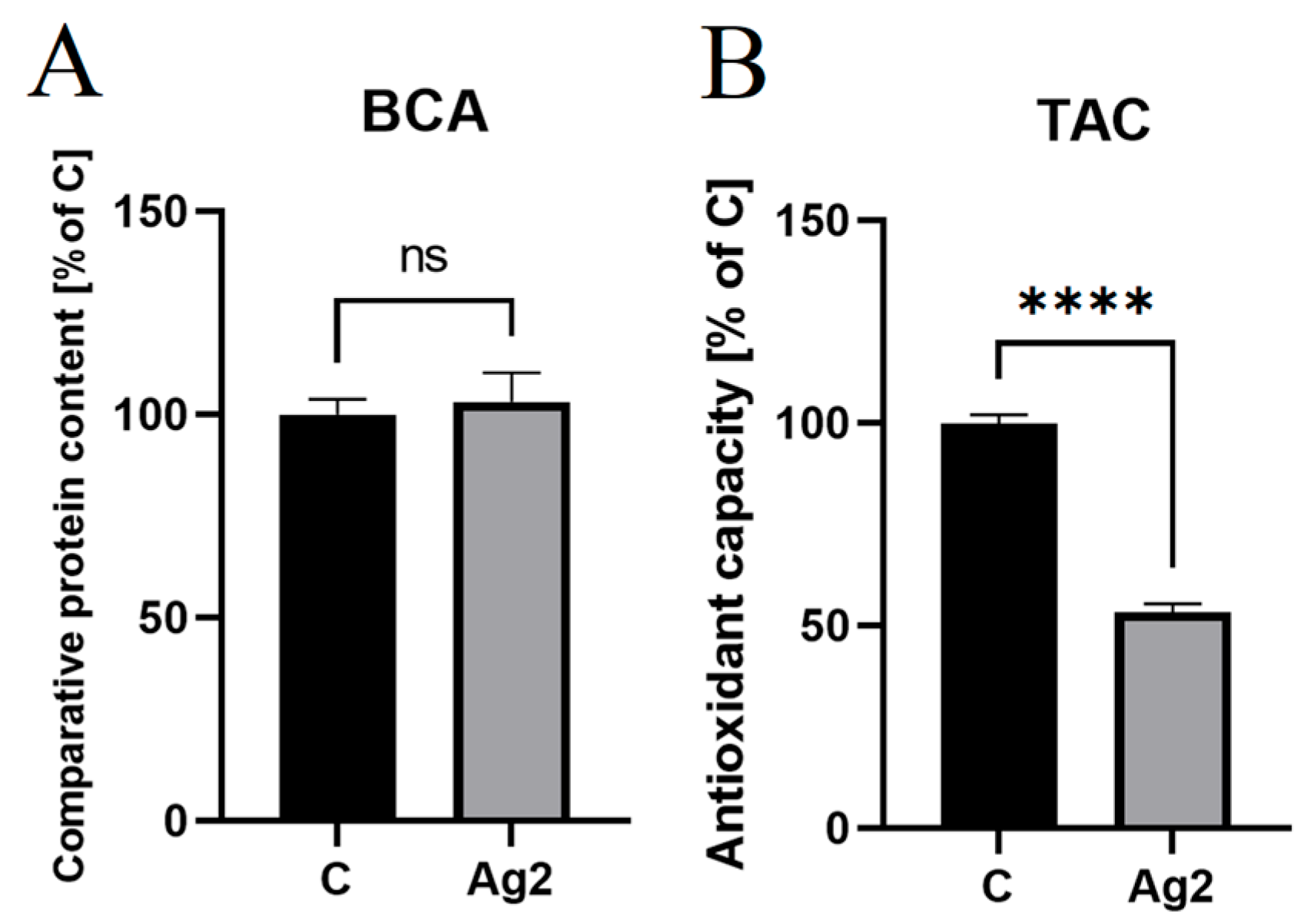
2.6. AgNPs Decreased Antioxidant Levels in Chicken Embryo Plasma
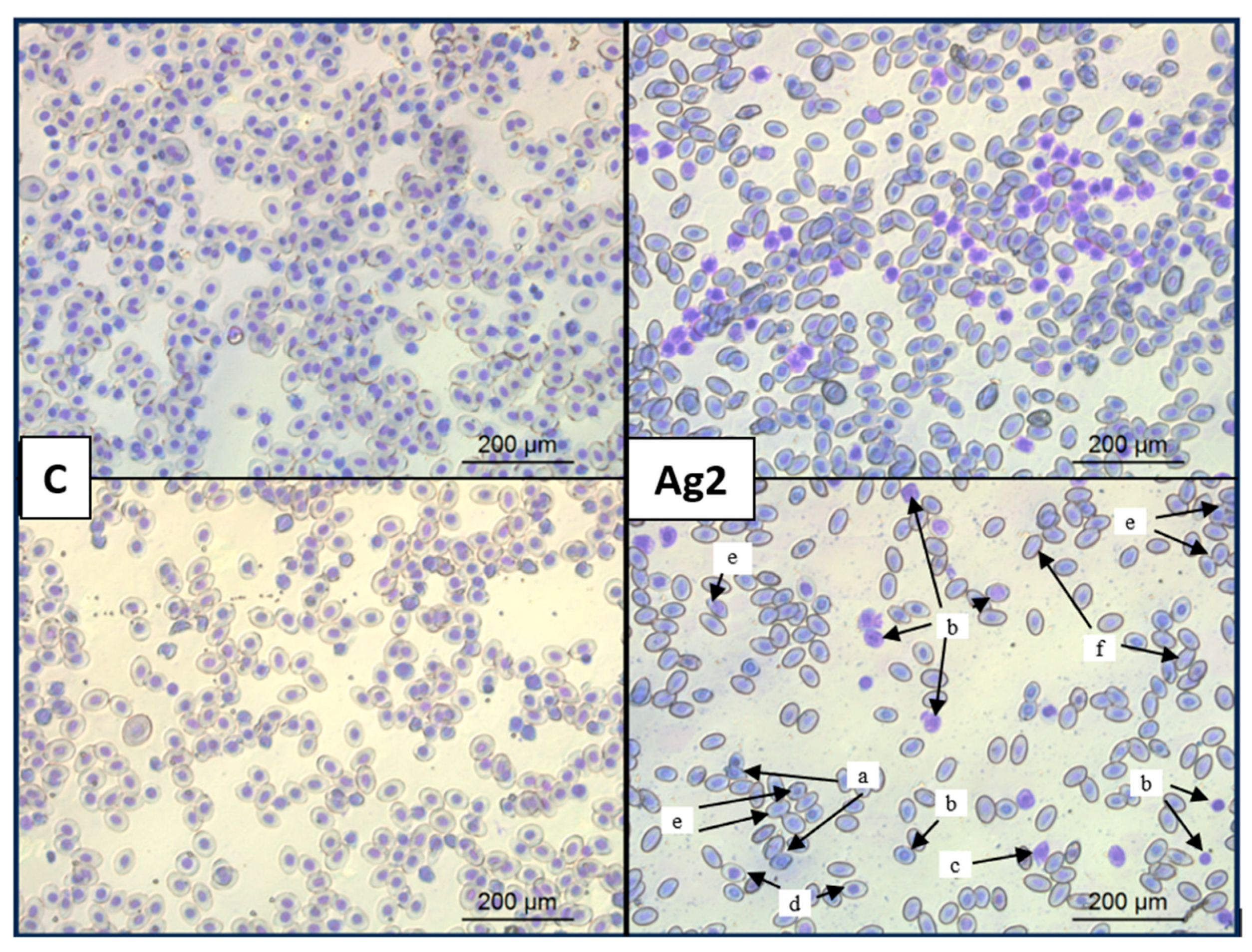
2.7. AgNPs Changed Red Blood Cell Morphology
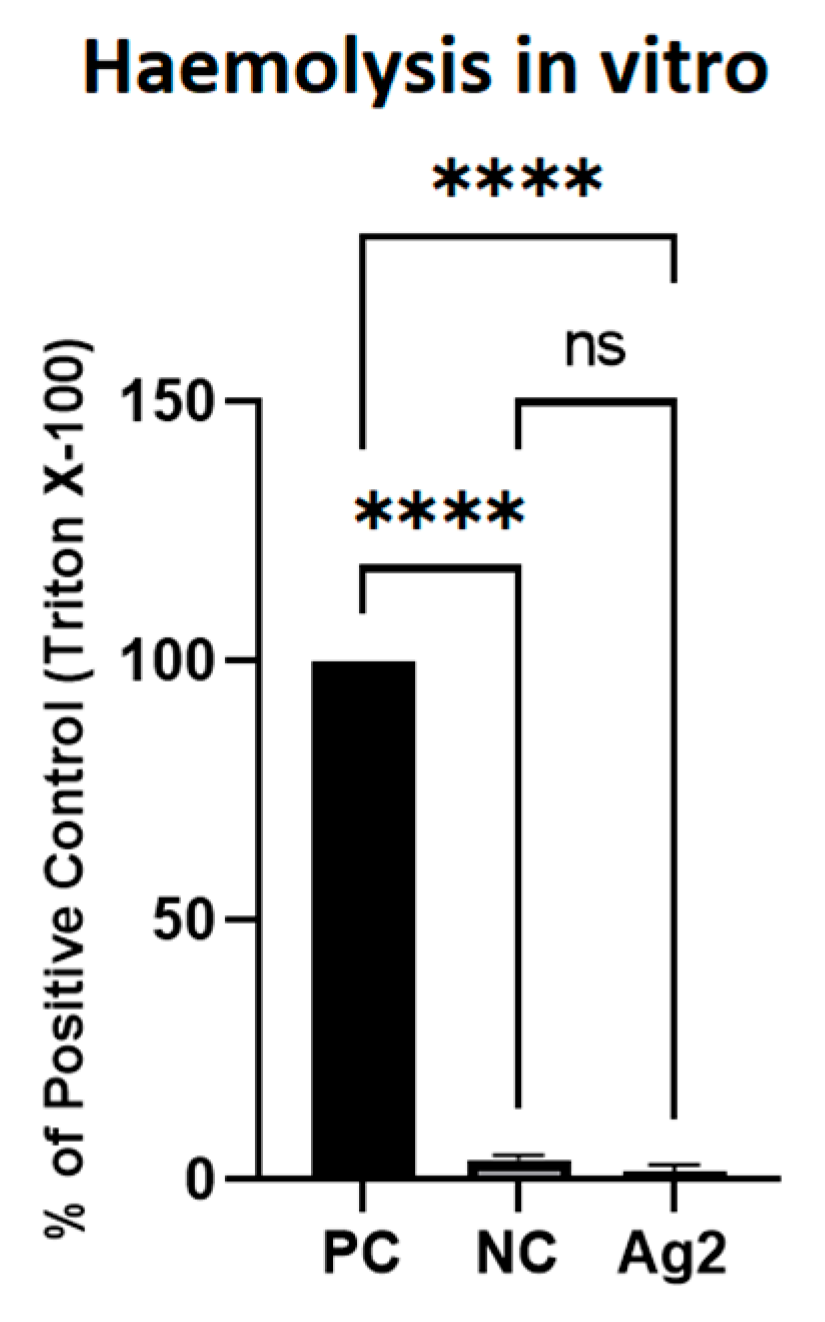
2.8. AgNPs Did Not Cause Lysis of Red Blood Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Green Synthesis of AgNPs from Silver Nitrate and C. vulgaris
Characterisation of AgNPs
4.2. Bacterial Model
4.2.1. Bacterial Culture
4.2.2. MIC and MBC Tests
4.2.3. Viability Assay
4.3. Embryo Model
4.3.1. Embryo Maintenance and AgNP Injection
4.3.2. Experiment 1: 3 D Old Embryos
4.3.3. Experiment 2: 16 D Old Embryos
Biochemical Analysis of Plasma
TAC Assay
Blood Smear Assay
Haemolysis Assay
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Salem, H.M.; Attia, M.M. Accidental intestinal myiasis caused by Musca domestica L. (Diptera: Muscidae) larvae in broiler chickens: A field study. Int. J. Trop. Insect Sci. 2021, 41, 2549–2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Per Capita Consumption of Poultry and Livestock, 1965 to Forecast 2022, in Pounds. Available online: https://www.nationalchickencouncil.org/about-the-industry/statistics/per-capita-consumption-of-poultry-and-livestock-1965-to-estimated-2012-in-pounds (accessed on 28 January 2025).
- Abd El-Hack, M.E.; Abdel-Moneim, A.E.; Shehata, A.M.; Mesalam, N.M.; Salem, H.M.; El-Saadony, M.T.; El-Tarabily, K.A. Microalgae applications in poultry feed. In Handbook of Food and Feed from Microalgae; Jacob-Lopes, E., Queiroz, M.I., Manzoni Maroneze, M., Queiroz Zepka, L., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2023; pp. 435–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, I.A.; Kashyap, S.K.; Maherchandani, S. Isolation, serotype diversity and antibiogram of Salmonella enterica isolated from different species of poultry in India. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2015, 5, 561–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Saadony, M.T.; Salem, H.M.; El-Tahan, A.M.; Abd El-Mageed, T.A.; Soliman, S.M.; Khafaga, A.F.; Swelum, A.A.; Ahmed, A.E.; Alshammari, F.A.; Abd El-Hack, M.E. The control of poultry salmonellosis using organic agents: An updated overview. Poult. Sci. 2022, 101, 101716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farouk, M.M.; El-Molla, A.; Salib, F.A.; Soliman, Y.A.; Shaalan, M. The role of silver nanoparticles in a treatment approach for multidrug-resistant Salmonella species isolates. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 6993–7011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birusanti, A.B.; Espenti, C.S.; Surendra, T.V.; Srinivas, B.; Srinivasulu, M.; Peddulaiah, K.; Rao, K.M.; Han, S.S. Synthesis and characterization of multi-responsive iron oxide nanoparticles: Evaluation of antibacterial properties and photocatalytic activity. J. Mol. Liq. 2025, 417, 126619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Capobianco, J.; Irwin, P.; Reed, S.; Lee, J. Antimicrobial effect of zinc oxide nanoparticles on Campylobacter jejuni and Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis. J. Food Saf. 2022, 42, e12979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalhamed, A.M.; Ghazy, A.A.; Ibrahim, E.S.; Arafa, A.A.; Zeedan, G.S. Therapeutic effect of biosynthetic gold nanoparticles on multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli and Salmonella species isolated from ruminants. Vet. World 2021, 14, 3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Manshian, B.; Jenkins, G.J.S.; Griffiths, S.M.; Williams, P.M.; Maffeis, T.G.G.; Wright, C.J.; Doak, S.H. NanoGenotoxicology: The DNA damaging potential of engineered nanomaterials. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 3891–3914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, P.; Jha, S.; Ramteke, S.; Jain, N.K. Pharmaceutical aspects of silver nanoparticles. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawosz, E.; Grodzik, M.; Lisowski, P.; Zwierzchowski, L.; Niemiec, T.; Zielińska-Górska, M.; Szmidt, M.; Chwalibog, A. Influence of hydrocolloids of Ag, Au, and Ag/Cu alloy nanoparticles on the inflammatory state at transcriptional level. Bull. Vet. Inst. Pulawy 2010, 54, 81–85. [Google Scholar]
- Zienkiewicz-Strzałka, M.; Deryło-Marczewska, A. Small AgNP in the biopolymer nanocomposite system. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruna, T.; Maldonado-Bravo, F.; Jara, P.; Caro, N. Silver nanoparticles and their antibacterial applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.F.; Liu, Z.G.; Shen, W.; Gurunathan, S. Silver nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization, properties, applications, and therapeutic approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, R.R.; Singh, S.K.; Singh, M. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles: Methods, biological applications, delivery and toxicity. Mater. Adv. 2023, 4, 1831–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.P.; Chaudhari, R.Y.; Nemade, M.S. Azadirachta indica leaves mediated green synthesis of metal oxide nanoparticles: A review. Talanta Open 2022, 5, 100083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radulescu, D.M.; Surdu, V.A.; Ficai, A.; Ficai, D.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Andronescu, E. Green synthesis of metal and metal oxide nanoparticles: A review of the principles and biomedical applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, S.S.; Fouda, A. Green synthesis of metallic nanoparticles and their prospective biotechnological applications: An overview. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2021, 199, 344–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Bulut, O.; Some, S.; Mandal, A.K.; Yilmaz, M.D. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles: Biomolecule-nanoparticle organizations targeting antimicrobial activity. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 2673–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldayel, M.F.; Al Kuwayti, M.A.; El Semary, N.A. Investigating the production of antimicrobial nanoparticles by Chlorella vulgaris and the link to its loss of viability. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alprol, A.E.; Mansour, A.T.; Abdelwahab, A.M.; Ashour, M. Advances in green synthesis of metal oxide nanoparticles by marine algae for wastewater treatment by adsorption and photocatalysis techniques. Catalysts 2023, 13, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampath, S.; Madhavan, Y.; Muralidharan, M.; Sunderam, V.; Lawrance, A.V.; Muthupandian, S.A. A review on algal mediated synthesis of metal and metal oxide nanoparticles and their emerging biomedical potential. J. Biotechnol. 2022, 360, 92–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhary, R.; Nawaz, K.; Khan, A.K.; Hano, C.; Abbasi, B.H.; Anjum, S. An overview of the algae-mediated biosynthesis of nanoparticles and their biomedical applications. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zainul Azlan, N.; Mohd Yusof, Y.A.; Makpol, S. Chlorella vulgaris ameliorates oxidative stress and improves the muscle regenerative capacity of young and old Sprague-Dawley rats. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zainul Azlan, N.; Mohd Yusof, Y.A.; Alias, E.; Makpol, S. Chlorella vulgaris modulates genes and muscle-specific microRNAs expression to promote myoblast differentiation in culture. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 2019, 394648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawosz, E.; Binek, M.; Grodzik, M.; Zielińska, M.; Sysa, P.; Szmidt, M.; Niemiec, T.; Chwalibog, A. Influence of hydrocolloidal silver nanoparticles on gastrointestinal microflora and morphology of enterocytes of quails. Arch. Anim. Nutr. 2007, 61, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Q.; Ghimire, S.; Mei, L.; Wu, C. Effects of particle size and surface charge on mutagenicity and chicken embryonic toxicity of new silver nanoclusters. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 17703–17712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akter, M.; Sikder, M.T.; Rahman, M.M.; Ullah, A.A.; Hossain, K.F.B.; Banik, S.; Hosokawa, T.; Saito, T.; Kurasaki, M. A systematic review on silver nanoparticles-induced cytotoxicity: Physicochemical properties and perspectives. J. Adv. Res. 2018, 9, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ognik, K.; Cholewińska, E.; Czech, A.; Kozłowski, K.; Wlazło, Ł.; Nowakowicz-Dębek, B.; Szlązak, R.; Tutaj, K. Effect of silver nanoparticles on the immune, redox, and lipid status of chicken blood. Czech J. Anim. Sci. 2016, 61, 450–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelsalam, M.; Al-Homidan, I.; Ebeid, T.; Abou-Emera, O.; Mostafa, M.; Abd El-Razik, M.; Shehab-El-Deen, M.; Abdel Ghani, S.; Fathi, M. Effect of silver nanoparticle administration on productive performance, blood parameters, antioxidative status, and silver residues in growing rabbits under hot climate. Animals 2019, 9, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansar, S.; Alshehri, S.; Abudawood, M.; Hamed, S.; Ahamad, T. Antioxidant and hepatoprotective role of selenium against silver nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 7789–7797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamburger, V.; Hamilton, H.L. A series of normal stages in the development of the chick embryo. J. Morphol. 1951, 88, 49–92. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hawar, S.N.; Al-Shmgani, H.S.; Al-Kubaisi, Z.A.; Sulaiman, G.M.; Dewir, Y.H.; Rikisahedew, J.J. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from Alhagi graecorum leaf extract and evaluation of their cytotoxicity and antifungal activity. J. Nanomater. 2022, 2022, 1058119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, A.; Sarkar, D.; Sasmal, S. A review of green synthesis of metal nanoparticles using algae. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 693899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero, N.; Visentini, F.F.; Márquez, V.E.; Santiago, L.G.; Castro, G.R.; Gagneten, A.M. Physiological and morphological responses of green microalgae Chlorella vulgaris to silver nanoparticles. Environ. Res. 2020, 189, 109857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodashenas, B.; Ghorbani, H.R. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles with different shapes. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 1823–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iravani, S.; Korbekandi, H.; Mirmohammadi, S.V.; Zolfaghari, B. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles: Chemical, physical and biological methods. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 9, 385–406. [Google Scholar]
- Annamalai, J.; Nallamuthu, T. Characterization of biosynthesized gold nanoparticles from aqueous extract of Chlorella vulgaris and their anti-pathogenic properties. Appl. Nanosci. 2015, 5, 603–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ijaz, I.; Gilani, E.; Nazir, A.; Bukhari, A. Detail review on chemical, physical and green synthesis, classification, characterizations and applications of nanoparticles. Green Chem. Lett. Rev. 2020, 13, 223–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.V.; Neigh, A.M.; Vermeulen, J.P.; de la Fonteyne, L.J.; Verharen, H.W.; Briedé, J.J.; van Loveren, H.; de Jong, W.H. The effect of particle size on the cytotoxicity, inflammation, developmental toxicity and genotoxicity of silver nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 9810–9817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosnowska, M.; Kutwin, M.; Adamiak, A.; Gawin, K.; Bugajska, Z.; Daniluk, K. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles by using aqueous mint (Mentha piperita) and cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitata) extracts and their antibacterial activity. Ann. Wars. Univ. Life Sci.-SGGW Anim. Sci. 2017, 56, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanaja, M.; Rajeshkumar, S.; Paulkumar, K.; Gnanajobitha, G.; Malarkodi, C.; Annadurai, G. Kinetic study on green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Coleus aromaticus leaf extract. Adv. Appl. Sci. Res. 2013, 4, 50–55. [Google Scholar]
- Składanowski, M.; Wypij, M.; Laskowski, D.; Golińska, P.; Dahm, H.; Rai, M. Silver and gold nanoparticles synthesized from Streptomyces sp. isolated from acid forest soil with special reference to its antibacterial activity against pathogens. J. Clust. Sci. 2017, 28, 59–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbeshehy, E.K.; Elazzazy, A.M.; Aggelis, G. Silver nanoparticles synthesis mediated by new isolates of Bacillus spp., nanoparticle characterization and their activity against bean yellow mosaic virus and human pathogens. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torabfam, M.; Yüce, M. Microwave-assisted green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using dried extracts of Chlorella vulgaris and antibacterial activity studies. Green Process. Synth. 2020, 9, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Emery, B.D.; Chitolina, G.Z.; Qadir, M.I.; Furian, T.Q.; Borges, K.A.; de Souza Moraes, H.L.; Pippi Salle, C.T.; do Nascimento, V.P. Antimicrobial and antibiofilm activity of silver nanoparticles against Salmonella Enteritidis. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2022, 54, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omara, S.T.; Zawrah, M.F.; Samy, A.A. Minimum bactericidal concentration of chemically synthesized silver nanoparticles against pathogenic Salmonella and Shigella strains isolated from layer poultry farms. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 7, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estevez, M.B.; Casaux, M.L.; Fraga, M.; Faccio, R.; Alborés, S. Biogenic silver nanoparticles as a strategy in the fight against multi-resistant Salmonella enterica isolated from dairy calves. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 644014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, A.S.; Singh, P.; Mijakovic, I. Interactions of gold and silver nanoparticles with bacterial biofilms: Molecular interactions behind inhibition and resistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateo, E.M.; Jiménez, M. Silver nanoparticle-based therapy: Can it be useful to combat multi-drug resistant bacteria? Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, M.A.; Khan, H.M.; Khan, A.A.; Ahmad, M.K.; Mahdi, A.A.; Pal, R.; Cameotra, S.S. Interaction of silver nanoparticles with Escherichia coli and their cell envelope biomolecules. J. Basic Microbiol. 2014, 54, 905–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saber, H.; Alwaleed, E.A.; Ebnalwaled, K.A.; Sayed, A.; Salem, W. Efficacy of silver nanoparticles mediated by Jania rubens and Sargassum dentifolium macroalgae; Characterization and biomedical applications. Egypt. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2017, 4, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seong, M.; Lee, D.G. Silver nanoparticles against Salmonella enterica serotype typhimurium: Role of inner membrane dysfunction. Curr. Microbiol. 2017, 74, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulak, E.; Ognik, K.; Stępniowska, A.; Drażbo, A. Effect of nanoparticles of silver on redox status and the accumulation of Ag in chicken tissues. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 4085–4096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losasso, C.; Belluco, S.; Cibin, V.; Zavagnin, P.; Mičetić, I.; Gallocchio, F.; Zanella, M.; Bregoli, L.; Biancotto, G.; Ricci, A. Antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles: Sensitivity of different Salmonella serovars. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Topping, V.D.; Keltner, Z.; Sprando, R.L.; Yourick, J.J. Toxicity of nano-and ionic silver to embryonic stem cells: A comparative toxicogenomic study. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2017, 15, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, P.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, H. Synthesis, applications, toxicity and toxicity mechanisms of silver nanoparticles: A review. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2023, 253, 114636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assar, D.H.; Mokhbatly, A.A.A.; Ghazy, E.W.; Elbialy, Z.I.; Gaber, A.A.; Hassan, A.A.; Nabil, A.; Asa, S.A. Silver nanoparticles induced hepatoxicity via the apoptotic/antiapoptotic pathway with activation of TGFβ-1 and α-SMA triggered liver fibrosis in Sprague Dawley rats. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 80448–80465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celá, P.; Veselá, B.; Matalová, E.; Večeřa, Z.; Buchtová, M. Embryonic toxicity of nanoparticles. Cells Tissues Organs 2014, 199, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, A.A.; El-Magd, M.A. Beneficial effects of dietary silver nanoparticles and silver nitrate on broiler nutrition. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 27031–27038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, M.; Sadeghi, R.; Kokini, J. Human exposure to nanoparticles through trophic transfer and the biosafety concerns that nanoparticle-contaminated foods pose to consumers. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 75, 129–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.M.; Ismail, Z.S.; Elwardany, I.; Lohakare, J.; Abdel-Wareth, A.A. In ovo feeding techniques of green nanoparticles of silver and probiotics: Evaluation of performance, physiological, and microbiological responses of hatched one-day-old broiler chicks. Animals 2023, 13, 3725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawosz, E.; Grodzik, M.; Zielińska, M.; Niemiec, T.; Olszańska, B.; Chwalibóg, A. Nanoparticles of silver do not affect growth, development and DNA oxidative damage in chicken embryos. Eur. Poult. Sci. 2009, 73, 208–213. [Google Scholar]
- Pineda, L.; Chwalibog, A.; Sawosz, E.; Lauridsen, C.; Engberg, R.; Elnif, J.; Hotowy, A.; Sawosz, F.; Gao, Y.; Ali, A.; et al. Effect of silver nanoparticles on growth performance, metabolism and microbial profile of broiler chickens. Arch. Anim. Nutr. 2012, 66, 416–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piatkowska, A.M.; Evans, S.E.; Stern, C.D. Cellular aspects of somite formation in vertebrates. Cells Dev. 2021, 168, 203732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.I.; Pak, S.W.; Lee, S.J.; Park, S.H.; Shin, I.S.; Moon, C.; Yu, W.J.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, J.C. In vitro study of silver nanoparticles-induced embryotoxicity using a rat whole embryo culture model. Toxicol. Res. 2025, 41, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, G.; Liu, T.; Wang, Z.; Hou, Y.; Dong, L.; Zhu, J.; Qi, J. The effect of silver nanoparticles on zebrafish embryonic development and toxicology. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2016, 44, 1116–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Rücklin, M.; Poelmann, R.E.; de Mooij, C.L.; Fokkema, M.; Lamers, G.E.M.; de Bakker, M.A.G.; Chin, E.; Bakos, L.J.; Marone, F.; et al. Nanoplastics causes extensive congenital malformations during embryonic development by passively targeting neural crest cells. Environ. Int. 2024, 173, 107865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baharara, J.; Namvar, F.; Mousavi, M.; Ramezani, T.; Mohamad, R. Anti-angiogenesis effect of biogenic silver nanoparticles synthesized using Saliva officinalis on chick chorioalantoic membrane (CAM). Molecules 2014, 19, 13498–13508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawosz, F.; Pineda, L.; Hotowy, A.; Hyttel, P.; Sawosz, E.; Szmidt, M.; Niemiec, T.; Chwalibog, A. Nano-nutrition of chicken embryos. The effect of silver nanoparticles and glutamine on molecular responses, and the morphology of pectoral muscle. Balt. J. Comp. Clin. Syst. Biol. 2012, 2, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa-Cristobal, L.F.; Martinez-Castanon, G.A.; Loyola-Rodriguez, J.P.; Patino-Marin, N.; Reyes-Macias, J.F.; Vargas-Morales, J.M.; Ruiz, F. Toxicity, distribution, and accumulation of silver nanoparticles in Wistar rats. J. Nanopart. Res. 2013, 15, 1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grodzik, M.; Sawosz, E. The influence of silver nanoparticles on chicken embryo development and bursa of Fabricius morphology. J. Anim. Feed Sci. 2006, 15, 111–114. [Google Scholar]
- Recordati, C.; De Maglie, M.; Bianchessi, S.; Argentiere, S.; Cella, C.; Mattiello, S.; Cubadda, F.; Aureli, F.; D’Amato, M.; Raggi, A.; et al. Tissue distribution and acute toxicity of silver after single intravenous administration in mice: Nano-specific and size-dependent effects. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2016, 13, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosoky, W.M.; Fouda, M.M.; Alwan, A.B.; Abdelsalam, N.R.; Taha, A.E.; Ghareeb, R.Y.; El-Aassar, M.R.; Khafaga, A.F. Dietary supplementation of silver-silica nanoparticles promotes histological, immunological, ultrastructural, and performance parameters of broiler chickens. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamohamadi, M.; Pooyanmehr, M.; Maleki, A.; Haghnazari, L. Biochemical modulatory and protective effects of the hydroalcoholic extract of Scrophularia striata on the hepatotoxicity of silver nanoparticles in the rat model. Iran. J. Vet. Med. 2021, 15, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borsa, A.; Kohayagawa, A.; Boretti, L.P.; Saito, M.E.; Kuibida, K. Serum levels of hepatic enzyme function in clinically healthy broiler chickens. Arq. Bras. Med. Vet. Zootec. 2006, 58, 675–677. [Google Scholar]
- Prasek, M.; Sawosz, E.; Jaworski, S.; Grodzik, M.; Ostaszewska, T.; Kamaszewski, M.; Wierzbicki, M.; Chwalibog, A. Influence of nanoparticles of platinum on chicken embryo development and brain morphology. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkloub, K.; El Moustafa, M.; Ghazalah, A.A.; Rehan, A.A.A. Effect of dietary nanosilver on broiler performance. Int. J. Poult. Sci. 2015, 14, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotb, O.A.; Attia, A.I.; Reda, F.M.; Mahgoub, S.A.; Alagawany, M.; El-Kholy, M.S. Impact of silver nanoparticles (Ag-NPs) as a dietary supplement on growth performance, carcass traits, blood metabolites, digestive enzymes, and cecal microbiota of growing rabbits. Ann. Anim. Sci. 2024, 24, 1311–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziyanok-Demirtas, S. Therapeutic potentials of Hibiscus trionum: Antioxidant, anti-lipid peroxidative, hypoglycemic, and hepatoprotective effects in type 1 diabetic rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 175, 116630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malek, R.; Mansuri, S.; Ansari, R.N.; Pathan, S.M. A study of serum ALT, AST and GGT (hepatic markers) in patients with chronic alcoholic liver diseases in tertiary level care hospital. Indian J. Public Health Res. Dev. 2024, 15, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalaby, O.E.; Ahmed, Y.H.; Mekkawy, A.M.; Mahmoud, M.Y.; Elbargeesy, G.A. The ameliorative effect of selenium-loaded chitosan nanoparticles against silver nanoparticles-induced ovarian toxicity in female albino rats. J. Ovarian Res. 2025, 18, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbasz, A.; Oćwieja, M.; Piergies, N.; Duraczyńska, D.; Nowak, A. Antioxidant-modulated cytotoxicity of silver nanoparticles. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2021, 41, 1863–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutwin, M.; Sawosz, E.; Jaworski, S.; Kurantowicz, N.; Strojny, B.; Chwalibog, A. Structural damage of chicken red blood cells exposed to platinum nanoparticles and cisplatin. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, F.B. The dual roles of red blood cells in tissue oxygen delivery: Oxygen carriers and regulators of local blood flow. J. Exp. Biol. 2009, 212, 3387–3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graw, J.A.; Mayeur, C.; Rosales, I.; Liu, Y.; Sabbisetti, V.S.; Riley, F.E.; Rechester, O.; Malhotra, R.; Warren, S.; Colvin, R.B.; et al. Haptoglobin or hemopexin therapy prevents acute adverse effects of resuscitation after prolonged storage of red cells. Circulation 2016, 134, 945–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, E.; Eaton, J.W.; Jeney, V.; Soares, M.P.; Varga, Z.; Galajda, Z.; Szentmiklósi, J.; Méhes, G.; Csonka, T.; Smith, A.; et al. Red cells, hemoglobin, heme, iron, and atherogenesis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2010, 30, 1347–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiagarajan, P.; Parker, C.J.; Prchal, J.T. How do red blood cells die? Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 655393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.Q.; Fang, L.; Ling, J.; Ding, C.Z.; Kang, B.; Huang, C.Z. Nanotoxicity of silver nanoparticles to red blood cells: Size dependent adsorption, uptake, and hemolytic activity. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2015, 28, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, A.; Farzinpour, A.; Vaziry, A.; Jalili, A. Effects of silver nanoparticles on hematological parameters and hepatorenal functions in laying Japanese quails. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2018, 185, 475–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khafaga, A.F.; Fouda, M.M.; Alwan, A.B.; Abdelsalam, N.R.; Taha, A.E.; Atta, M.S.; Dosoky, W.M. Silver-silica nanoparticles induced dose-dependent modulation of histopathological, immunohistochemical, ultrastructural, proinflammatory, and immune status of broiler chickens. BMC Vet. Res. 2022, 18, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Z.; Lin, H.; Li, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Q. In vitro assessment of the toxicity of small silver nanoparticles and silver ions to the red blood cells. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 32373–32380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fareed, N.; Nisa, S.; Bibi, Y.; Fareed, A.; Ahmed, W.; Sabir, M.; Alam, S.; Sajjad, A.; Kumar, S.; Hussain, M.; et al. Green synthesized silver nanoparticles using carrot extract exhibited strong antibacterial activity against multidrug resistant bacteria. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2023, 35, 102477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

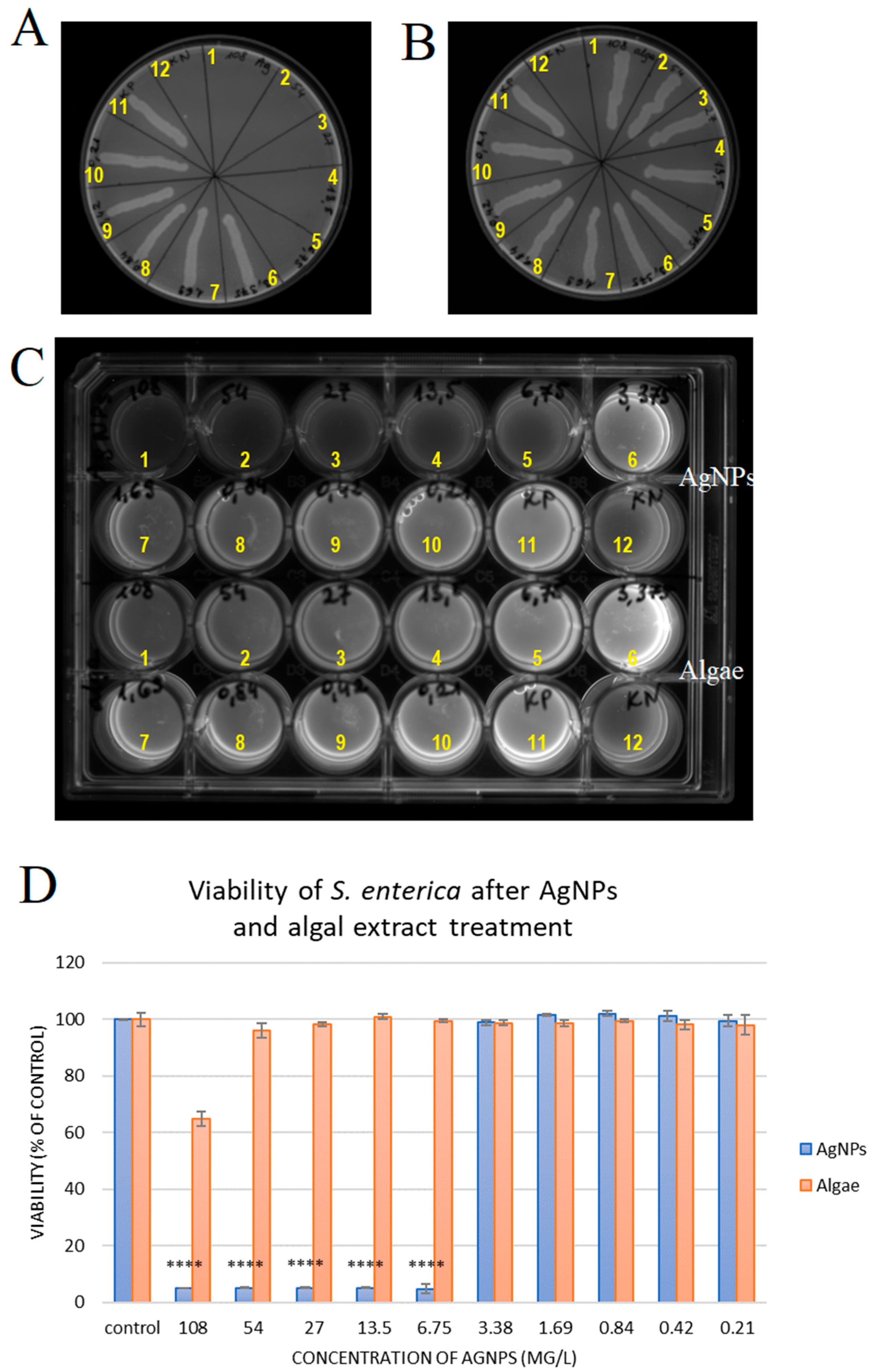
| Concentration [mg/L] | MBC | MIC | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AgNPs | Algae | AgNPs | Algae | |
| 108.00 | − | + | − | +/− |
| 54.00 | − | + | − | + |
| 27.00 | − | + | − | + |
| 13.50 | − | + | − | + |
| 6.75 | − | + | − | + |
| 3.38 | + | + | + | + |
| 1.69 | + | + | + | + |
| 0.84 | + | + | + | + |
| 0.42 | + | + | + | + |
| 0.21 | + | + | + | + |
| positive control | + | + | + | + |
| negative control | − | − | − | − |
| Body Part | Control | AgNPs | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Embryo | 16.92 ± 0.81 | 17.85 ± 1.55 | >0.05 |
| Heart | 0.94 ± 0.04 | 1.33 ± 0.39 | >0.05 |
| Brain | 3.64 ± 0.53 | 2.35 ± 0.56 | ≤0.05 |
| Liver | 2.07 ± 0.09 | 2.60 ± 0.32 | ≤0.05 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Michalec, S.; Nieckarz, W.; Klimek, W.; Lange, A.; Matuszewski, A.; Piotrowska, K.; Hotowy, A.; Kunowska-Slósarz, M.; Sosnowska, M. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles from Chlorella vulgaris Aqueous Extract and Their Effect on Salmonella enterica and Chicken Embryo Growth. Molecules 2025, 30, 1521. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30071521
Michalec S, Nieckarz W, Klimek W, Lange A, Matuszewski A, Piotrowska K, Hotowy A, Kunowska-Slósarz M, Sosnowska M. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles from Chlorella vulgaris Aqueous Extract and Their Effect on Salmonella enterica and Chicken Embryo Growth. Molecules. 2025; 30(7):1521. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30071521
Chicago/Turabian StyleMichalec, Sebastian, Wiktoria Nieckarz, Wiktoria Klimek, Agata Lange, Arkadiusz Matuszewski, Klara Piotrowska, Anna Hotowy, Małgorzata Kunowska-Slósarz, and Malwina Sosnowska. 2025. "Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles from Chlorella vulgaris Aqueous Extract and Their Effect on Salmonella enterica and Chicken Embryo Growth" Molecules 30, no. 7: 1521. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30071521
APA StyleMichalec, S., Nieckarz, W., Klimek, W., Lange, A., Matuszewski, A., Piotrowska, K., Hotowy, A., Kunowska-Slósarz, M., & Sosnowska, M. (2025). Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles from Chlorella vulgaris Aqueous Extract and Their Effect on Salmonella enterica and Chicken Embryo Growth. Molecules, 30(7), 1521. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30071521








