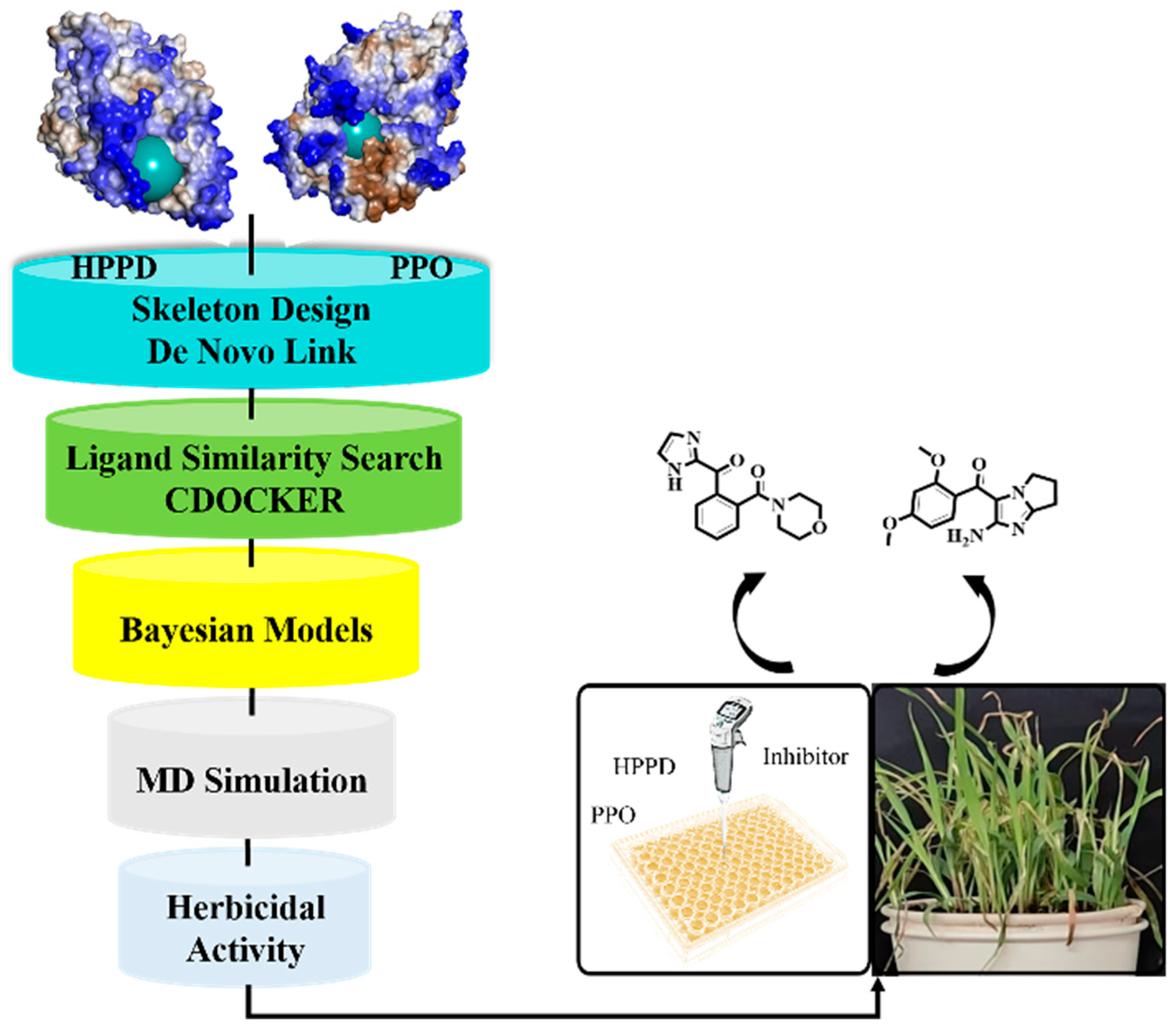
Virtual Screening and Bioassay of Novel Protoporphyrinogen Oxidase and p-Hydroxyphenylpyruvate Dioxygenase Dual-Target Inhibitors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Screening Based on Fragment Library and Molecular Docking
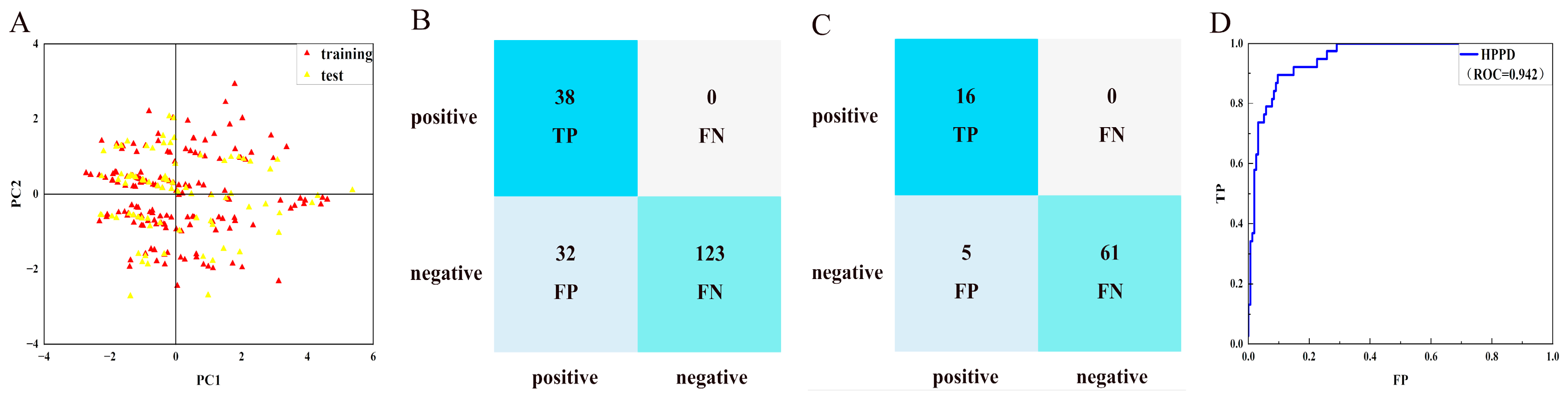
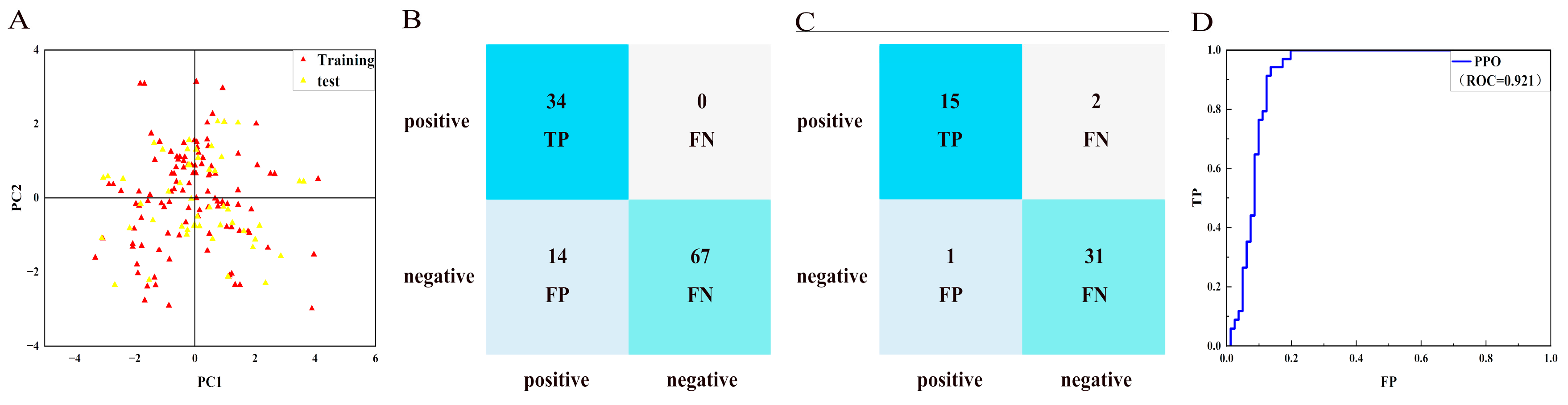
2.2. Generation and Verification of NBC Model
2.3. Virtual Screening via Ligand Similarity Search
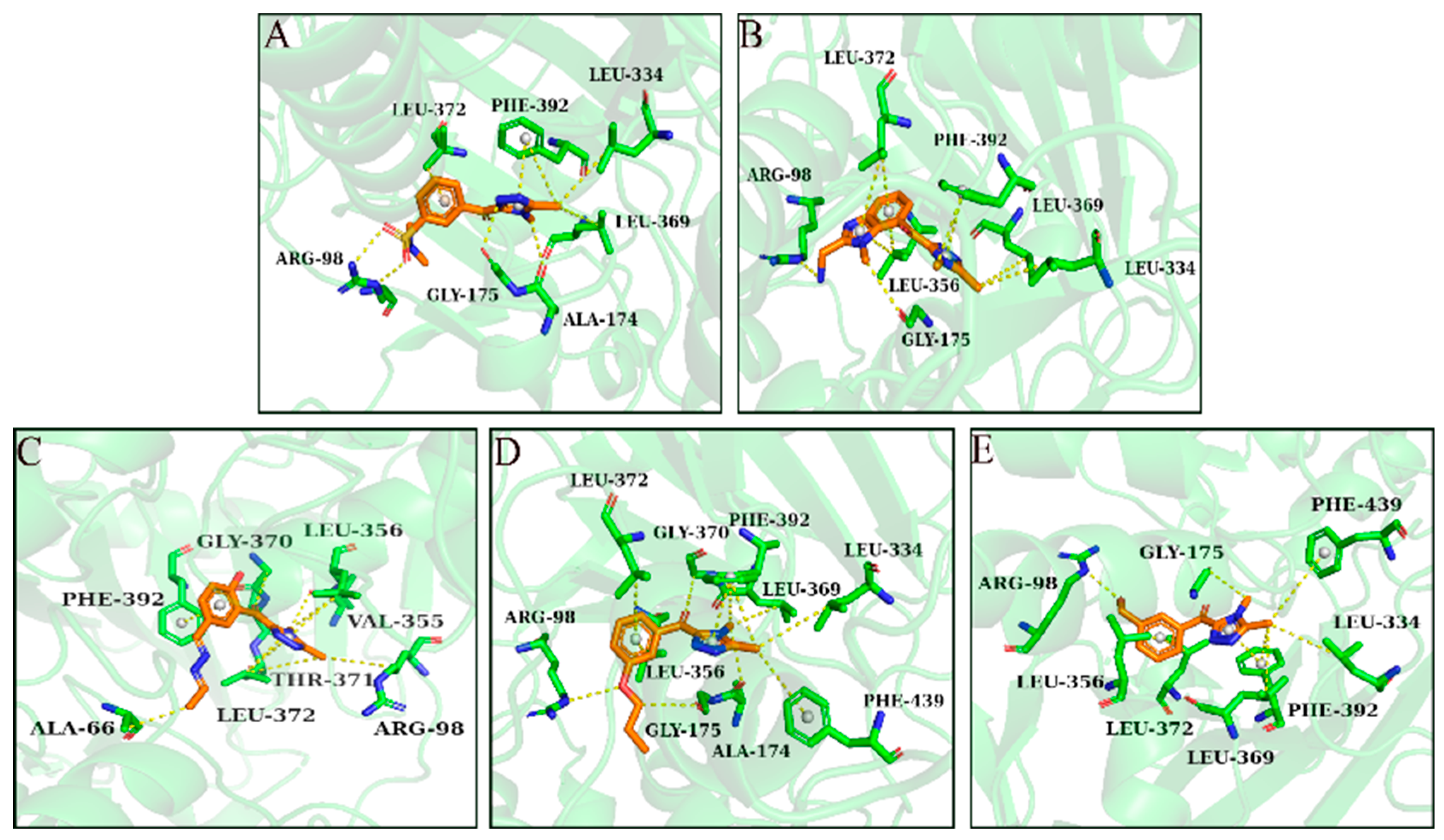
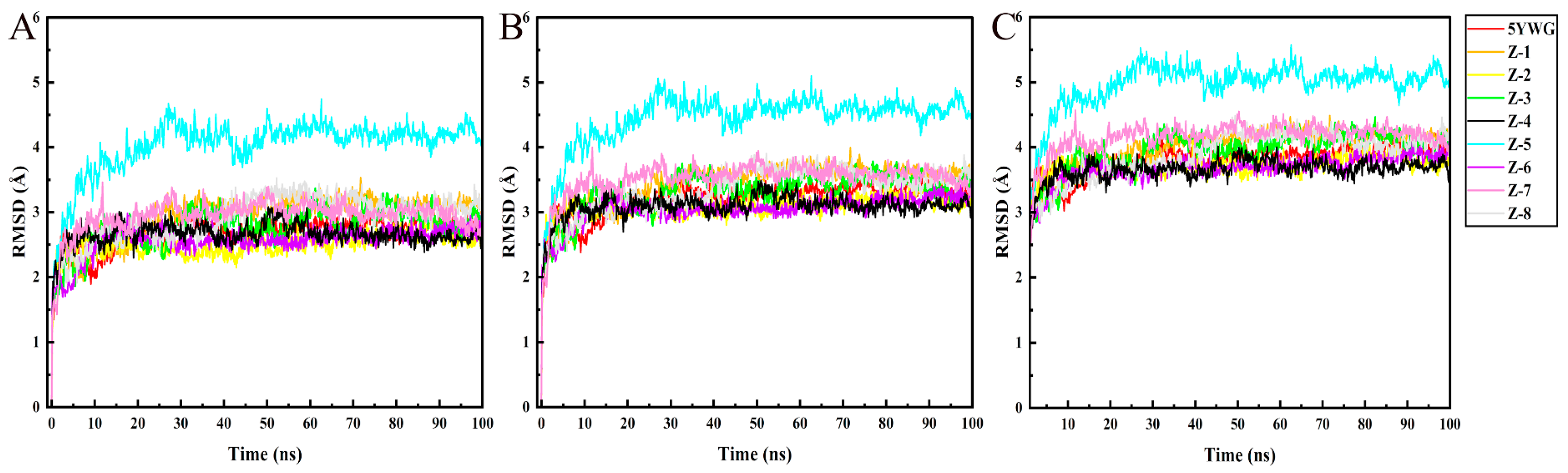
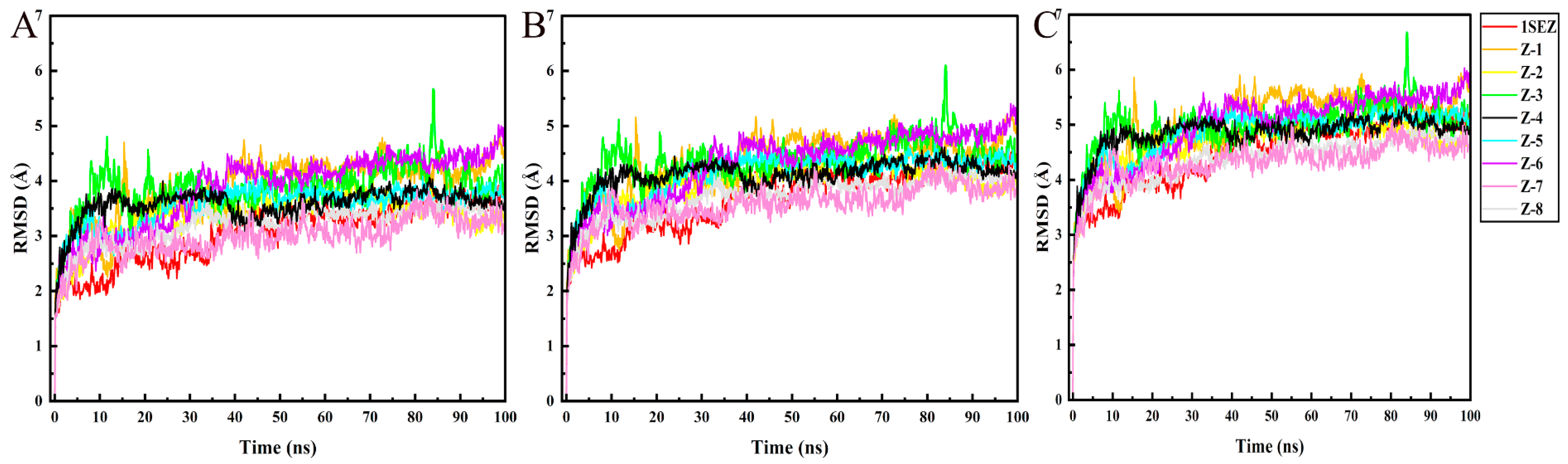
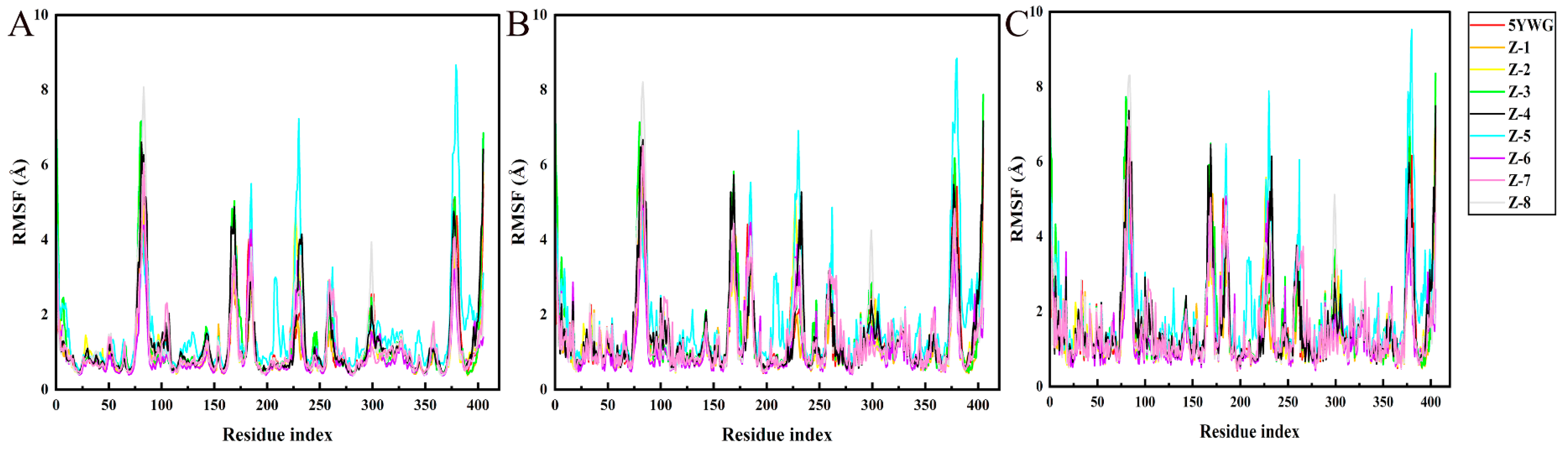
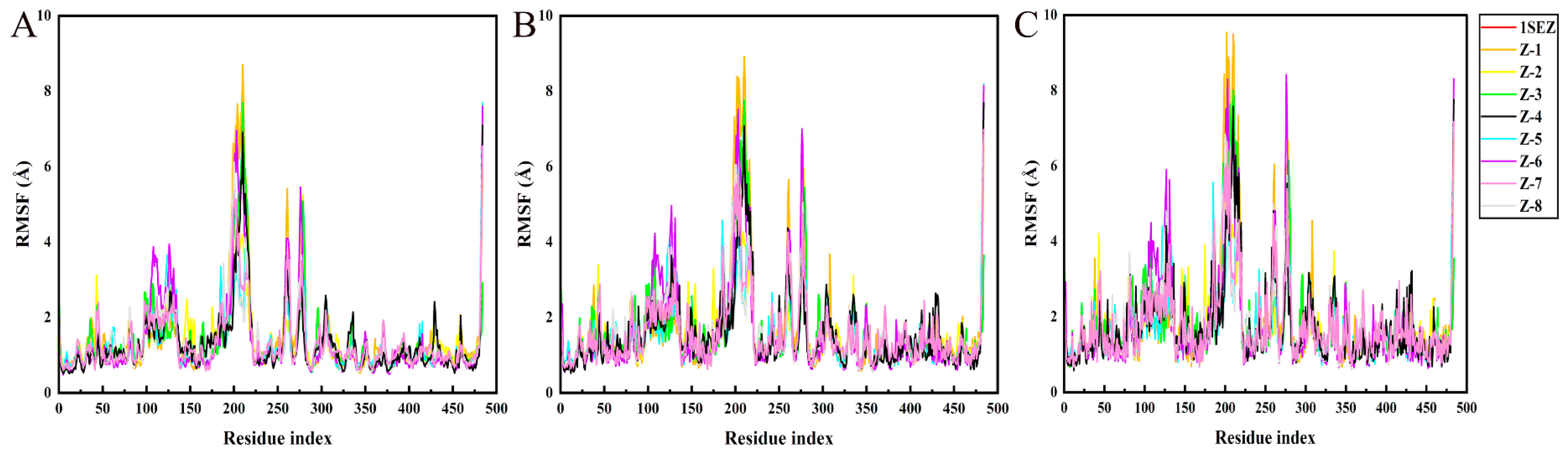
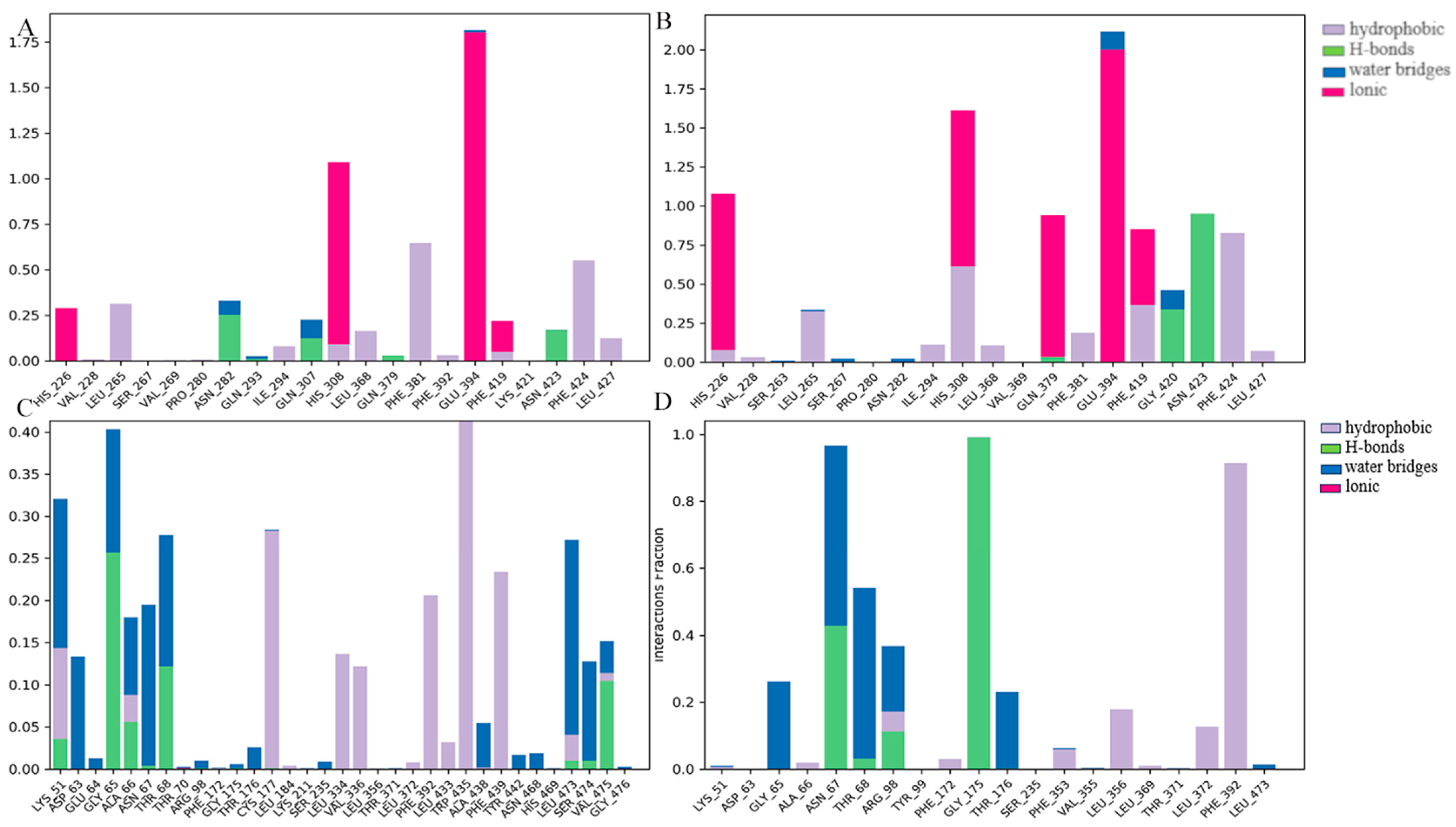
2.4. MD Simulation
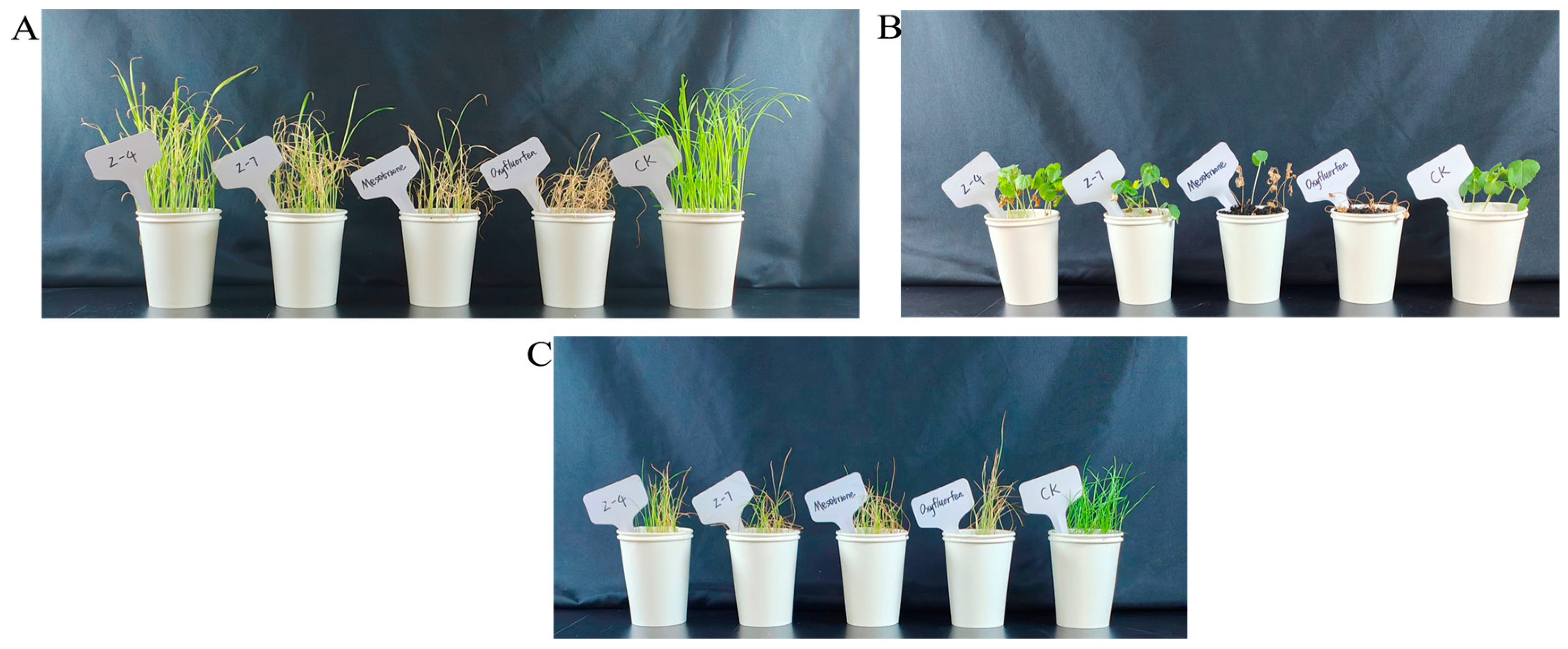
2.5. HPPD and PPO Enzyme Activities In Vitro and Herbicidal Activity
2.6. Results of Reverse Synthesis Analysis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Fragment-Based Drug Design (FBDD) and Molecular Docking
3.2. Construct and Evaluate Naïve Bayesian Classification (NBC) Models
3.3. Virtual Screening for Ligand Similarity Search
3.4. MD Simulation and Binding Free Energy Calculation
3.5. AtHPPD and PPO Inhibition Experiment and Herbicidal Activity In Vitro
3.6. Reverse Synthesis Method
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zeng, X.; Huang, Y.; Dong, J.; Ma, X.; Nan, J.X.; Chen, W.; Lin, H.Y.; Yang, W.C.; Liu, X.; Yin, J.; et al. Design of an HPPD fluorescent probe and visualization of plant responses to abiotic stress. Adv. Agrochem. 2022, 1, 73–84. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Gao, S.; Yang, L.; Liu, Y.L.; Li, P.; Ye, F.; Fu, Y. Cobalt (II) complex as a fluorescent sensing platform for the selective and sensitive detection of triketone HPPD inhibitors. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 404, 124015. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Ye, T.; Liu, Y.X.; Wang, J.; Ye, F. Based on the Virtual Screening of Multiple Pharmacophores, Docking and Molecular Dynamics Simulation Approaches toward the Discovery of Novel HPPD Inhibitors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simkin, A.J.; Kapoor, L.; Doss, C.G.P.; Hofmann, T.A.; Lawson, T.; Ramamoorthy, S. The role of photosynthesis related pigments in light harvesting, photoprotection and enhancement of photosynthetic yield in planta. Photosynth. Res. 2022, 152, 23–42. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, T.; Tan, Q.; Chen, L.; Wang, J.; Qiu, Z.; Ling, X.; Chen, T.; Yang, X.; et al. Multisite Mutagenesis of 4-Hydroxyphenylpyruvate Dioxygenase (HPPD) Enhances Rice Resistance to HPPD Inhibitors and Its Carotenoid Contents. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 40, 22063–22072. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, S.T.; Han, L.; Li, W.R.; Dai, G.Y.; Liu, Y.; Lu, A.M.; Yang, C.L.; Chen, M. Design, synthesis and herbicidal activity of novel cyclohexanedione derivations containing pyrazole and pyridine groups as potential HPPD inhibitors. Mol. Divers. 2024, 29, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Dong, J.; Yu, X.H.; Yan, Y.C.; Nan, J.X.; Ye, B.Q.; Yang, W.C.; Lin, H.Y.; Yang, G.F. Discovery of Subnanomolar Inhibitors of 4-Hydroxyphenylpyruvate Dioxygenase via Structure-Based Rational Design. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 1170–1177. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Wang, H.; Zhang, K.; Zhu, J.; He, Q.; He, J. Improved Herbicide Resistance of 4-Hydroxyphenylpyruvate Dioxygenase from Sphingobium sp. TPM-19 through Directed Evolution. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 12365–12374. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, H.; Cui, D.; Li, B. Tetrahydrophthalimidobenzoates as protoporphyrinogen IX oxidase inhibiting herbicides. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2017, 139, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.Y.; Yu, L.K.; Qin, S.N.; Yang, H.Z.; Wang, D.W.; Xi, Z. Design, Synthesis, and Metabolism Studies of N-1,4-Diketophenyltriazinones as Protoporphyrinogen IX Oxidase Inhibitors. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 3225–3238. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Song, C.; Shen, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Lou, M.; Wu, Z.; Song, R.; Song, B. Design, Synthesis and Proteomics-Based Analysis of Novel Triazinone Derivatives Containing Amide Structures as Safer Protoporphyrinogen IX Oxidase Inhibitors. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 18378–18390. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Xu, J.; Yan, S.; Liang, B.; Xing, D. Epidermal growth factor receptor dual-target inhibitors as a novel therapy for cancer: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 127440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Cao, H.F.; Wang, C.F.; Gao, S.; Wang, J.Y.; Zhao, L.X.; Ye, F.; Fu, Y. In silico approach of novel HPPD/PDS dual target inhibitors by pharmacophore, AILDE and molecular docking. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2023, 143, 104711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, D.; Yang, B.; Shen, Y.Q. Computer especially AI-assisted drug virtual screening and design in traditional Chinese medicine. Phytomedicine 2022, 107, 154481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolluri, S.; Lin, J.; Liu, R.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W. Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence in Pharmaceutical Research and Development: A Review. AAPS J. 2022, 24, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, K.A.; Cohen, D.S.; Jarrell, J.T.; Huang, X. Deep learning and virtual drug screening. Future Med. Chem. 2018, 10, 2557–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabe, V.T.; Ntombela, T.; Jhamba, L.A.; Maguire, G.E.M.; Govender, T.; Naicker, T.; Kruger, H.G. Current trends in computer aided drug design and a highlight of drugs discovered via computational techniques: A review. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 224, 113705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Zhu, K.; Ruan, J.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, M.; He, C.; Zuo, Z. Screening of potential oestrogen receptor α agonists in pesticides via in silico, in vitro and in vivo methods. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 270, 116015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Wu, F.X.; Yu, L.K.; Wu, L.; Chen, Q.; Hao, G.F.; Yang, W.C.; Lin, H.Y.; Yang, G.F. Discovery of Novel Pyrazole–Quinazoline-2,4-dione Hybrids as 4-Hydroxyphenylpyruvate Dioxygenase Inhibitors. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 5059–5067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, M.; Breithaupt, C.; Kiefersauer, R.; Freigang, J.; Huber, R.; Messerschmidt, A. Crystal structure of protoporphyrinogen IX oxidase: A key enzyme in haem and chlorophyll biosynthesis. EMBO J. 2024, 23, 1720–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, C.; Hu, L. Fragment-Based Dynamic Combinatorial Chemistry for Identification of Selective α-Glucosidase Inhibitors. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2022, 13, 1791–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.Z.; Shi, X.X.; Huang, G.Y.; Hao, G.F.; Yang, G.F. Fragment-based drug design facilitates selective kinase inhibitor discovery. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2021, 42, 551–565. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.F.; Wang, F.; Jiang, W.; Zhou, G.Y.; Li, C.Z.; Zhu, X.L.; Hao, G.F.; Yang, G.F. PADFrag: A Database Built for the Exploration of Bioactive Fragment Space for Drug Discovery. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2018, 58, 1725–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Hassab, M.A.; Shoun, A.A.; Al-Rashood, S.T.; Al-Warhi, T.; Eldehna, W.M. Identification of a New Potential SARS-CoV-2 RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase Inhibitor via Combining Fragment-Based drug Design, Docking, Molecular Dynamics, and MM-PBSA Calculations. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 584894. [Google Scholar]
- Hoarau, M.; Sermmai, P.; Varatthan, T.; Thiabma, R.; Jantra, T.; Rattanajak, R.; Vitsupakorn, D.; Vanichtanankul, J.; Saepua, S.; Yuthavong, Y.; et al. Discovery of rigid biphenyl Plasmodium falciparum DHFR inhibitors using a fragment linking strategy. RSC Med. Chem. 2023, 14, 1755–1766. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.Y.; Zhao, L.X.; Shi, J.; Gao, S.; Ye, F.; Fu, Y. Discovery of novel HPPD inhibitors based on a combination strategy of pharmacophore, consensus docking and molecular dynamics. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 362, 119683. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, J.; Yang, R.; Gao, L.; Zhou, D.; Yang, S.; Liu, A.L.; Du, G.H. Predictions of BuChE Inhibitors Using Support Vector Machine and Naive Bayesian Classification Techniques in Drug Discovery. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2013, 53, 3009–3020. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, D.; Pang, X.; Lian, W.; Xu, L.; Wang, J.; Jia, H.; Zhang, B.; Liu, A.L.; Du, G.H. Discovery of VEGFR2 inhibitors by integrating naïve Bayesian classification, molecular docking and drug screening approaches. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 5286–5297. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Xiong, W.; Jia, L.; Xu, L.; Cai, Y.; Chen, Y.; Jin, J.; Gao, M.; Zhu, J. Developing a Naïve Bayesian Classification Model with PI3Kγ structural features for virtual screening against PI3Kγ: Combining molecular docking and pharmacophore based on multiple PI3Kγ conformations. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 244, 4824. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Lei, Y.; Guo, S.; Zuo, Z. Ensemble-based virtual screening in discovering potent inhibitors targeting Von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) E3 ubiquitin ligase. Life Sci. 2020, 262, 118495. [Google Scholar]
- Poongavanam, V.; Kongsted, J. Virtual Screening Models for Prediction of HIV-1 RT Associated RNase H Inhibition. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73478. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, C.Y.; Li, J.Y.; Hao, G.F.; Yang, G.F. A drug-likeness toolbox facilitates ADMET study in drug discovery. Drug Discov. Today 2020, 25, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Y.; Cai, T.; Peng, C.; Wu, L.; Zhou, L.; Han, J.; Ma, M.; Zhu, W.; et al. D3CARP: A comprehensive platform with multiple-conformation based docking, ligand similarity search and deep learning approaches for target prediction and virtual screening. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 164, 107283. [Google Scholar]
- Lanka, G.; Begum, D.; Banerjee, S.; Adhikari, Y.P.; Ghosh, B. Pharmacophore-based virtual screening, 3D QSAR, Docking, ADMET, and MD simulation studies: An in silico perspective for the identification of new potential HDAC3 inhibitors. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 166, 107481. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, J.; Zhao, L.X.; Wang, J.Y.; Ye, T.; Wang, M.; Gao, S.; Ye, F.; Fu, Y. The novel 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase inhibitors in vivo and in silico approach: 3D-QSAR analysis, molecular docking, bioassay and molecular dynamics. Arab. J. Chem. 2022, 15, 103919. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, N.; Wuhanqimuge; Shuang, Q. Screening, Characterization, and Mechanistic Evaluation of Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Peptides Derived from Milk Fermented with Lactobacillus delbrueckii QS306 with and without Ultrahigh-Pressure Treatment. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 17420–17431. [Google Scholar]

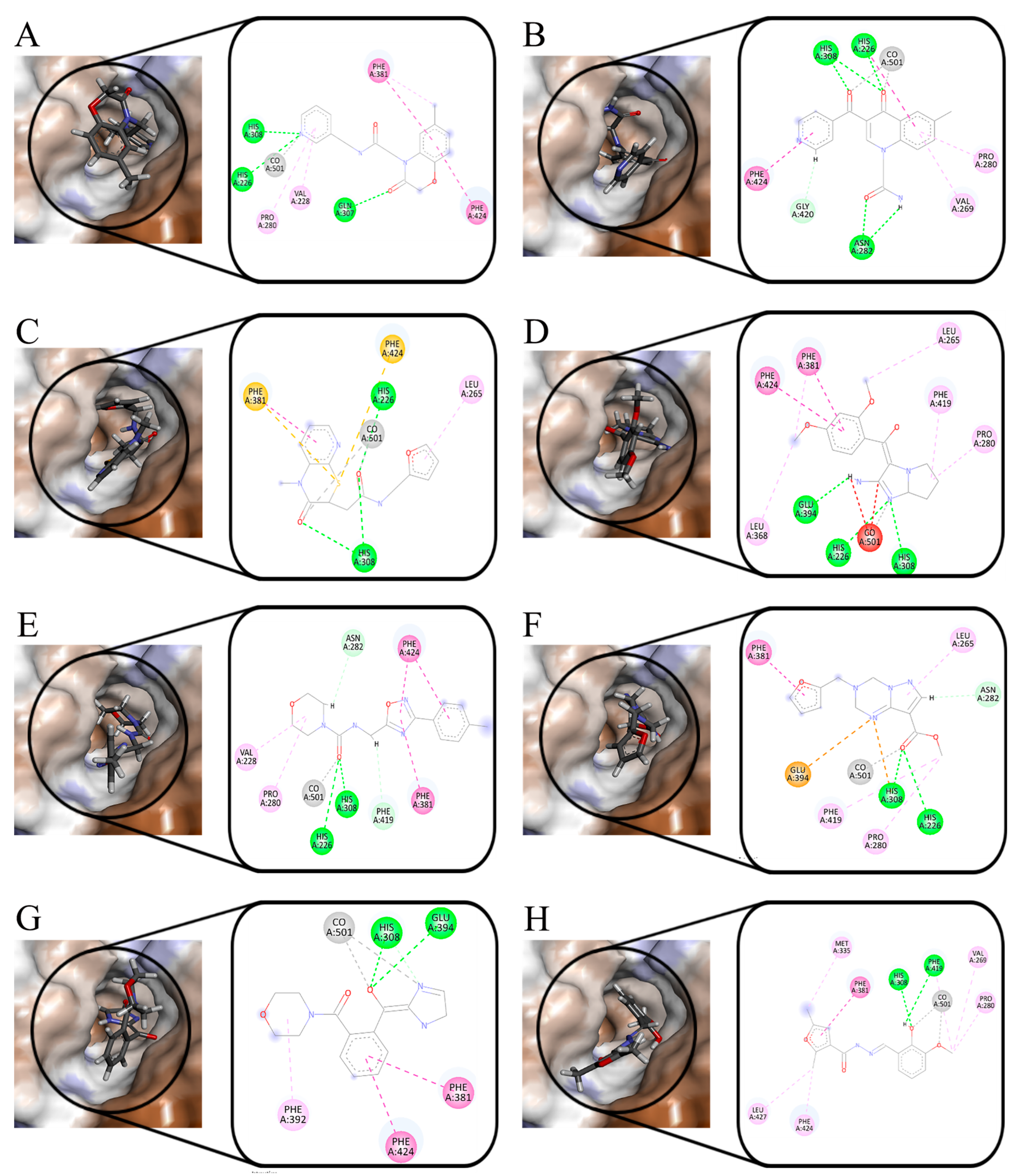



| Sequence | Structure | -CDOCKER ENERGY-HPPD (kcal/mol) | -CDOCKER ENERGY-PPO (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|
| natural ligand | / | 25.65 | 4.722 |
| Compound 5 |  | 25.98 | 18.24 |
| Compound 8 | 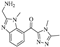 | 21.20 | 12.34 |
| Compound 10 | 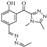 | 24.35 | 15.65 |
| Compound 11 |  | 31.93 | 11.29 |
| Compound 25 | 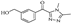 | 30.01 | 14.28 |
| Models | ROC Score | ROC Rating | SE | SP | MCC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HPPD (training set) | 0.94 | Excellent | 1.00 | 0.79 | 0.66 |
| HPPD (test set) | 0.98 | Excellent | 1.00 | 0.92 | 0.84 |
| PPO (training set) | 0.92 | Excellent | 1.00 | 0.83 | 0.77 |
| PPO (test set) | 0.96 | Excellent | 0.88 | 0.97 | 0.86 |
| Name | Structure | -CDOCKER ENERGY-HPPD (kcal/mol) | -CDOCKER ENERGY-PPO (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|
| natural ligand | / | 42.04 | 4.72 |
| Z-1 |  | 59.64 | 34.63 |
| Z-2 | 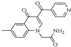 | 69.41 | 34.90 |
| Z-3 | 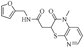 | 45.86 | 35.57 |
| Z-4 | 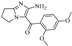 | 25.40 | 10.20 |
| Z-5 | 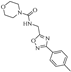 | 58.32 | 37.40 |
| Z-6 | 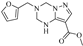 | 48.79 | 31.39 |
| Z-7 |  | 26.26 | 16.48 |
| Z-8 | 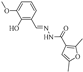 | 44.54 | 31.43 |
| Compound | ΔGbind | ΔGbind Coulomb | ΔGbind Covalent | ΔGbind Hbond | ΔGbind Lipo | ΔGbind vdW |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Z-1 | −36.91 | −12.53 | 4.55 | −0.75 | −18.92 | −44.86 |
| Z-2 | −34.73 | −34.40 | 9.92 | −1.65 | −19.61 | −42.88 |
| Z-3 | −24.94 | −22.71 | 5.191 | −0.68 | −16.33 | −40.32 |
| Z-4 | −20.50 | −23.72 | 12.58 | −1.15 | −15.55 | −38.51 |
| Z-5 | −33.13 | −14.67 | 8.83 | −0.03 | −17.47 | −35.81 |
| Z-6 | −28.49 | −24.05 | 4.94 | −0.44 | −13.78 | −35.43 |
| Z-7 | −39.40 | −31.50 | 3.16 | −0.99 | −14.86 | −35.36 |
| Z-8 | −39.66 | −36.73 | 6.02 | −0.57 | −18.71 | −37.43 |
| Compound | ΔGbind | ΔGbind Coulomb | ΔGbind Covalent | ΔGbind Hbond | ΔGbind Lipo | ΔGbind vdW |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Z-1 | −49.84 | −20.31 | 2.76 | −1.54 | −17.89 | −40.42 |
| Z-2 | −58.94 | −15.02 | 5.23 | −1.28 | −18.88 | −51.46 |
| Z-3 | −55.10 | −27.19 | 3.87 | −2.05 | −20.16 | −45.03 |
| Z-4 | −44.89 | 8.97 | 5.78 | −0.15 | −18.61 | −49.66 |
| Z-5 | −57.61 | −7.89 | 6.61 | −0.55 | −21.20 | −53.81 |
| Z-6 | −40.96 | 5.09 | 4.33 | −0.06 | −20.02 | −41.90 |
| Z-7 | −41.93 | −26.29 | 9.25 | −1.59 | −18.06 | −37.22 |
| Z-8 | −55.53 | 0.15 | 4.41 | −0.81 | −21.33 | −45.27 |
| Compound | IC50 (μM) | |
|---|---|---|
| AtHPPD | PPO | |
| Mesotrione | 0.904 | - |
| Oxyfluofen | - | 0.726 |
| Z-4 | 1.607 | 2.932 |
| Z-7 | 1.494 | 4.232 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, P.; Cao, H.; Li, T.; Fu, Y. Virtual Screening and Bioassay of Novel Protoporphyrinogen Oxidase and p-Hydroxyphenylpyruvate Dioxygenase Dual-Target Inhibitors. Molecules 2025, 30, 1491. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30071491
Zhang P, Cao H, Li T, Fu Y. Virtual Screening and Bioassay of Novel Protoporphyrinogen Oxidase and p-Hydroxyphenylpyruvate Dioxygenase Dual-Target Inhibitors. Molecules. 2025; 30(7):1491. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30071491
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Panxiu, Haifeng Cao, Tiansong Li, and Ying Fu. 2025. "Virtual Screening and Bioassay of Novel Protoporphyrinogen Oxidase and p-Hydroxyphenylpyruvate Dioxygenase Dual-Target Inhibitors" Molecules 30, no. 7: 1491. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30071491
APA StyleZhang, P., Cao, H., Li, T., & Fu, Y. (2025). Virtual Screening and Bioassay of Novel Protoporphyrinogen Oxidase and p-Hydroxyphenylpyruvate Dioxygenase Dual-Target Inhibitors. Molecules, 30(7), 1491. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30071491





