A Novel BODIPY-Zn Complex as Innovative Sonosensitizer for Enhanced Sonodynamic Therapy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
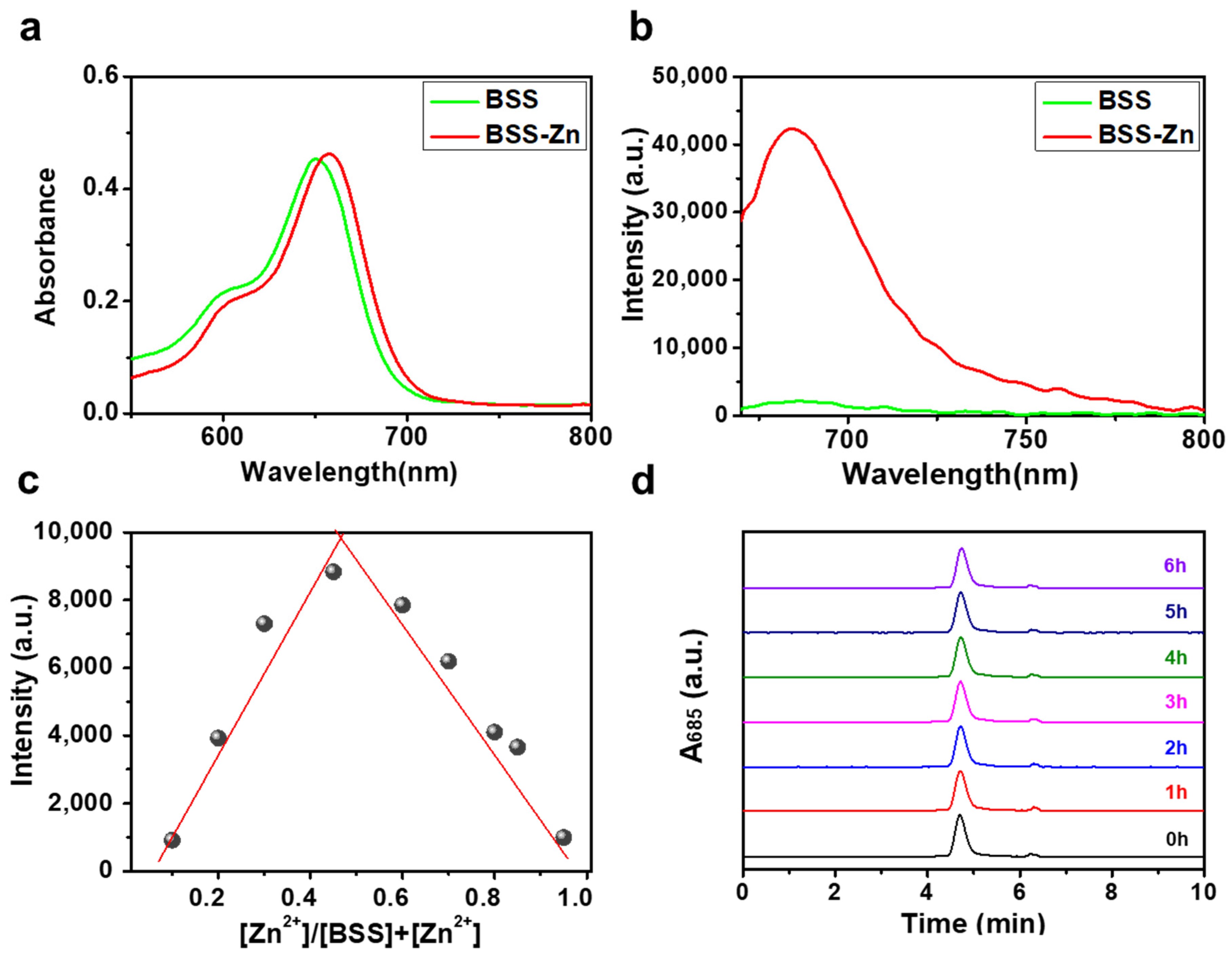
2.1. Design and Characterization of BSS and BSS-Zn
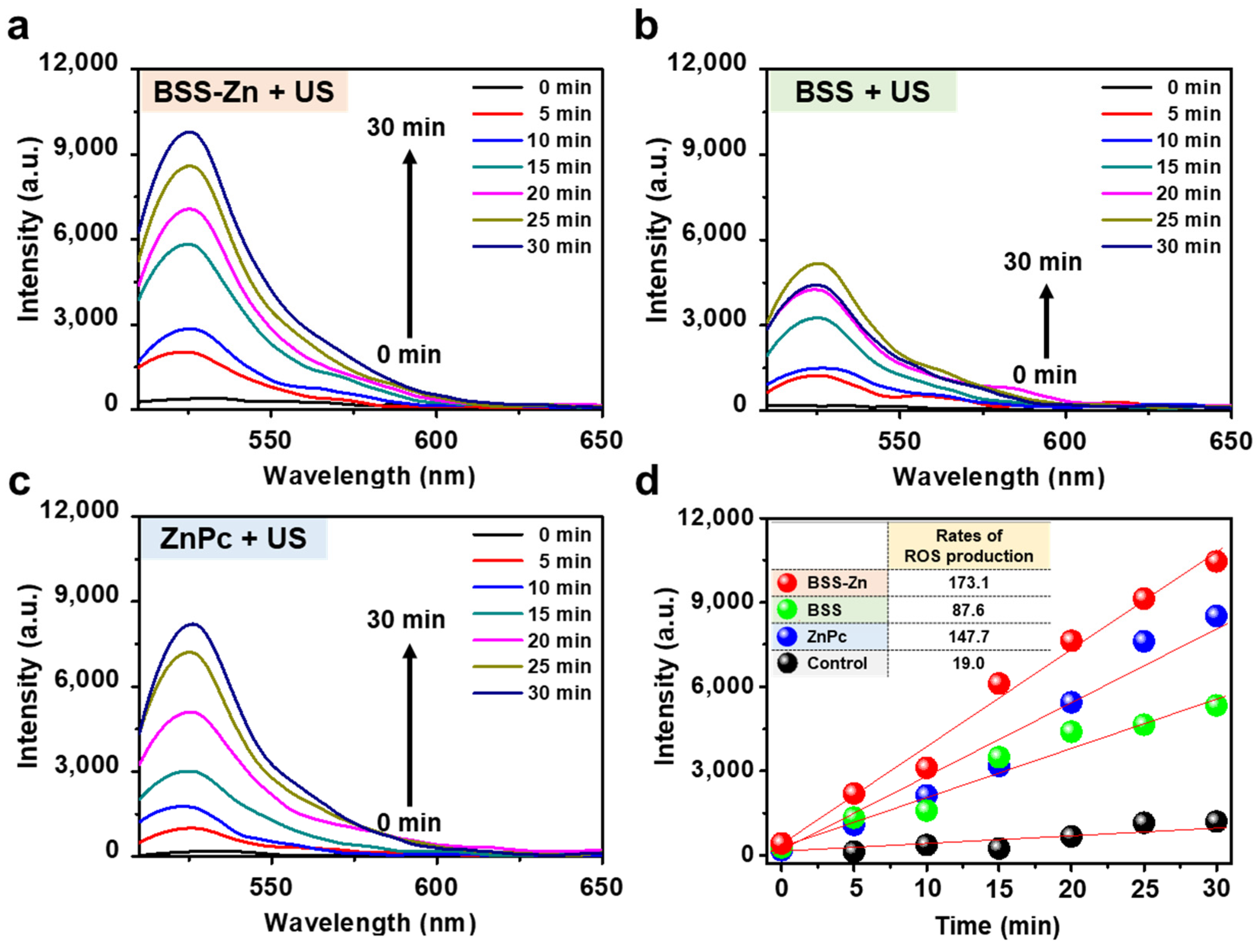
2.2. Photo- and Sonosensitizing Properties of BSS-Zn and BSS
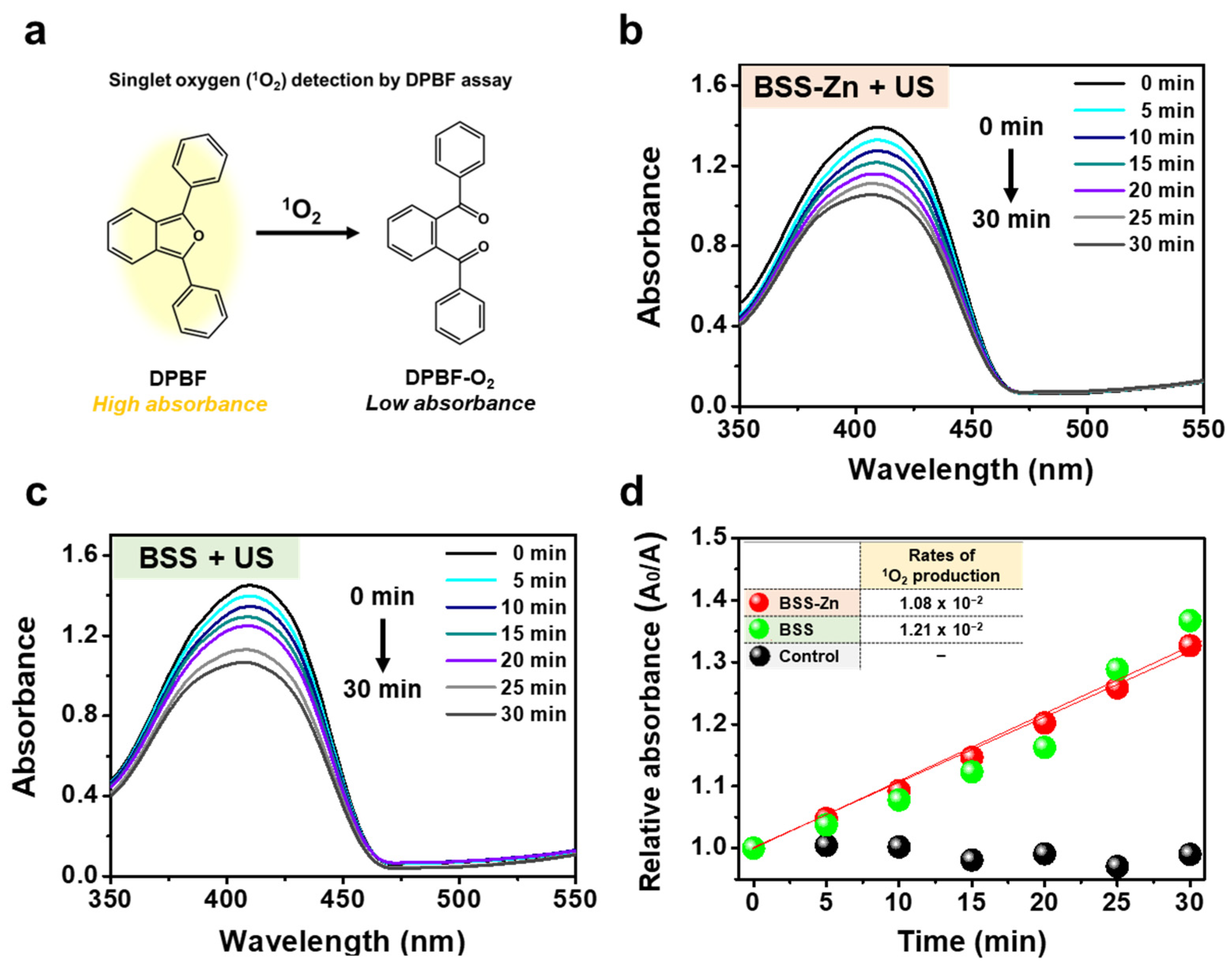
2.3. Three Different Types of ROS Generation Assays Using US-Irradiated BSS-Zn and BSS
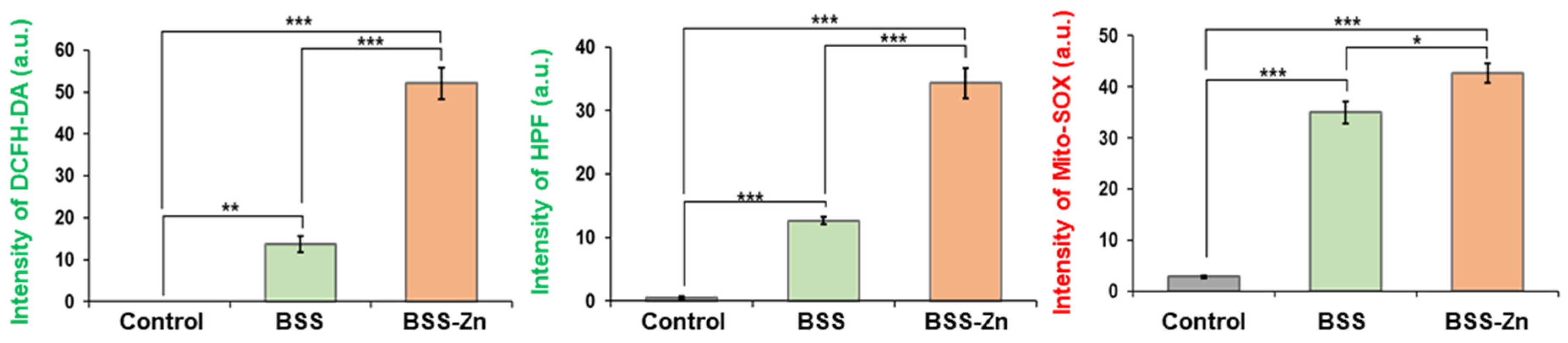
2.4. In Vitro Investigation of BSS-Zn and BSS as Potential Sonosensitizers
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Instrumentation
3.2. Synthesis of BSS-Zn and BSS
3.3. Photophysical Properties
3.4. Assay for Universal ROS
3.5. Assay for Singlet Oxygen (1O2) Generation
3.6. Assay for Hydroxyl Radical (•OH) Generation
3.7. Assay for Superoxide (O2•−) Generation
3.8. Assay for Intracellular ROS Generation
3.9. Assay for In Vitro Cytotoxicity
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yang, H.; Yu, L.; Xu, Y.; Sharma, A.; Yin, P.; Li, X.; Kim, J.S.; Sun, Y. Advanced Biotechnology-Assisted Precise Sonodynamic Therapy. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 11227–11248. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lafond, M.; Yoshizawa, S.; Umemura, S. Sonodynamic Therapy: Advances and Challenges in Clinical Translation. J. Ultrasound Med. 2019, 38, 567–580. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Liu, S.H.; Yin, J.; Yoon, J. Sonodynamic and Chemodynamic Therapy Based on Organic/Organometallic Sensitizers. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 429, 213610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, G.-Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, B.-W.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Wang, Y.-S.; Zhang, N. Recent Advances of Sonodynamic Therapy in Cancer Treatment. Cancer Biol. Med. 2016, 13, 325–338. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cao, T.G.N.; Hoang, Q.T.; Kang, J.H.; Kang, S.J.; Ravichandran, V.; Rhee, W.J.; Lee, M.; Ko, Y.T.; Shim, M.S. Bioreducible Exosomes Encapsulating Glycolysis Inhibitors Potentiate Mitochondria-Targeted Sonodynamic Cancer Therapy via Cancer-Targeted Drug Release and Cellular Energy Depletion. Biomaterials 2023, 301, 122242. [Google Scholar]
- Das, M.; Pandey, V.; Jajoria, K.; Bhatia, D.; Gupta, I.; Shekhar, H. Glycosylated Porphyrin Derivatives for Sonodynamic Therapy: ROS Generation and Cytotoxicity Studies in Breast Cancer Cells. ACS Omega 2023, 9, 1196–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolarova, H.; Tomankova, K.; Bajgar, R.; Kolar, P.; Kubinek, R. Photodynamic and Sonodynamic Treatment by Phthalocyanine on Cancer Cell Lines. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2009, 35, 1397–1404. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Ma, J.; Xue, E.Y.; Wang, S.; Zheng, Y.; Ng, D.K.P.; Wang, A.; Zheng, N. Polymeric Phthalocyanine-Based Nanosensitizers for Enhanced Photodynamic and Sonodynamic Therapies. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2023, 12, 2300481. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Zhou, X.; Gao, Y.; Zheng, B.; Tang, F.; Huang, J. Recent Progress in Development of New Sonosensitizers for Sonodynamic Cancer Therapy. Drug Discov. Today 2014, 19, 502–509. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Luo, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Li, H.; Luo, T.; Zhang, K.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, J. Oxygen-Self-Produced Nanoplatform for Relieving Hypoxia and Breaking Resistance to Sonodynamic Treatment of Pancreatic Cancer. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 12849–12862. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Yi, H.; Song, J.; Huang, J.; Yang, K.; Tan, B.; Wang, D.; Yang, N.; Wang, Z.; Li, X. Mitochondria-Targeted and Ultrasound-Activated Nanodroplets for Enhanced Deep-Penetration Sonodynamic Cancer Therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 9355–9366. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Zhu, F.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, H.; Gao, Y. Ultrasmall Iron-Doped Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles for Ferroptosis Assisted Sono-chemodynamic Cancer Therapy. Colloids Surf. B 2023, 232, 113606. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; Fan, F.; Zhu, X.; Jia, L.; Chen, M.; Du, P.; Yang, L.; Yang, S. Boosting Antitumor Sonodynamic Therapy Efficacy of Black Phosphorus via Covalent Functionalization. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2102422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Ren, Z.; Chen, Z.; Zhu, J.; Liang, J.; Liao, R.; Wen, J. Iron Oxide Nanoparticles as Nanocarriers to Improve Chlorin E6-Based Sonosensitivity in Sonodynamic Therapy. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2018, 12, 4207–4216. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.; Dong, J.; Li, Z.; Wang, Z. Metal–Organic Frameworks (MOF)-Assisted Sonodynamic Therapy in Anticancer Applications. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 4102–4133. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Yang, Y.; Li, D.; Pan, J.; Chu, C.; Liu, G. Organic Sonosensitizers for Sonodynamic Therapy: From Small Molecules and Nanoparticles toward Clinical Development. Small 2021, 17, e2101976. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kaur, P.; Singh, K. Recent Advances in the Application of BODIPY in Bioimaging and Chemosensing. J. Mater. Chem. C 2019, 7, 11361–11405. [Google Scholar]
- Malacarne, M.C.; Gariboldi, M.B.; Caruso, E. BODIPYs in PDT: A Journey through the Most Interesting Molecules Produced in the Last 10 Years. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yogo, T.; Urano, Y.; Ishitsuka, Y.; Maniwa, F.; Nagano, T. Highly Efficient and Photostable Photosensitizer Based on BODIPY Chromophore. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 12162–12163. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.; Li, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, J.; Yang, Y.; Pendharkar, A.I.; Zhang, Y.; Kelmar, S.; Chen, L.; Wu, W.; et al. Enhancing Photodynamic Therapy through Resonance Energy Transfer Constructed Near-Infrared Photosensitized Nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1604789. [Google Scholar]
- Bertrand, B.; Passador, K.; Goze, C.; Denat, F.; Bodio, E.; Salmain, M. Metal-Based BODIPY Derivatives as Multimodal Tools for Life Sciences. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2018, 358, 108–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, A.; Dixit, A.; Banerjee, S.; Roy, B.; Kumar, A.; Karande, A.A.; Chakravarty, A.R. BODIPY Appended Copper(II) Complexes for Cellular Imaging and Singlet Oxygen Mediated Anticancer Activity in Visible Light. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 104474–104482. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, H.S.; Koo, S.; Won, M.; An, S.; Park, H.; Sessler, J.L.; Han, J.; Kim, J.S. Cu(II)-BODIPY Photosensitizer for CAIX Overexpressed Cancer Stem Cell Therapy. Chem. Sci. 2023, 14, 1808–1819. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Wang, L.; Li, Z.; Xie, Z. BODIPY-Containing Nanoscale Metal–Organic Frameworks for Photodynamic Therapy. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 5402–5405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Hou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, K.; Cheng, X.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, X. Two Novel BODIPY–Ru(II) Arene Dyads Enabling Effective Photo-inactivation against Cancer Cells. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 12726–12734. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Qi, F.; Yuan, H.; Chen, Y.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Z.; He, W.; Guo, Z. BODIPY-Based Monofunctional Pt(II) Complexes for Specific Photocytotoxicity against Cancer Cells. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2021, 218, 111394. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, J.J.; Lippard, S.J. Synthetic Methods for the Preparation of Platinum Anticancer Complexes. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 4470–4495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenny, R.G.; Marmion, C.J. Toward Multi-Targeted Platinum and Ruthenium Drugs—A New Paradigm in Cancer Drug Treatment Regimens? Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 1058–1137. [Google Scholar]
- Prieto-Montero, R.; Prieto-Castañeda, A.; Sola-Llano, R.; Agarrabeitia, A.R.; García-Fresnadillo, D.; López-Arbeloa, I.; Villanueva, A.; Ortiz, M.J.; de la Moya, S.; Martínez-Martínez, V. Exploring BODIPY Derivatives as Singlet Oxygen Photosensitizers for PDT. Photochem. Photobiol. 2020, 96, 458–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, G.; Kim, M.; Lee, J.; Lee, C.Y. Zinc-Based Metal Organic Framework Derived from Anthracene and BODIPY Chromophores: Synthesis and Photophysical Properties. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2021, 42, 645–648. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, X.; Zhao, S.; Xu, T.; Huang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Lan, M.; Lin, C.; Zheng, X.; Wang, P. Advances and Perspectives in Organic Sonosensitizers for Sonodynamic Therapy. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 445, 214087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, K.; Nakajima, T.; Miyazaki, K.; Ohuchi, Y.; Ikegami, T.; Choyke, P.L.; Kobayashi, H. Short PEG-Linkers Improve the Performance of Targeted, Activatable Monoclonal Antibody-Indocyanine Green Optical Imaging Probes. Bioconjugate Chem. 2013, 24, 811–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štefane, B.; Perdih, F.; Višnjevac, A.; Požgan, F. Novel Triazole-Based Ligands and Their Zinc(II) and Nickel(II) Complexes with a Nitrogen Donor Environment as Potential Structural Models for Mononuclear Active Sites. New J. Chem. 2015, 39, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diana, R.; Panunzi, B. The Role of Zinc(II) Ion in Fluorescence Tuning of Tridentate Pincers: A Review. Molecules 2020, 25, 4984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thordarson, P. Determining Association Constants from Titration Experiments in Supramolecular Chemistry. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 1305–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morone, M.; Beverina, L.; Abbotto, A.; Silvestri, F.; Collini, E.; Ferrante, C.; Bozio, R.; Pagani, G.A. Enhancement of Two-Photon Absorption Cross-Section and Singlet-Oxygen Generation in Porphyrins upon β-Functionalization with Donor−Acceptor Substituents. Org. Lett. 2006, 8, 2719–2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, A.A.; Kushwaha, R.; Yadav, A.K.; Banerjee, S. Metal Complexes for Cancer Sonodynamic Therapy. ChemBioChem 2023, 24, e202200597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakubowski, W.; Bartosz, G. 2,7-Dichlorofluorescin Oxidation and Reactive Oxygen Species: What Does It Measure? Cell Biol. Int. 2000, 24, 757–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Park, E.-Y.; Kang, Y.; Kwon, N.; Yang, M.; Lee, S.; Kim, W.J.; Kim, C.; Yoon, J. Supramolecular Phthalocyanine Assemblies for Improved Photoacoustic Imaging and Photothermal Therapy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 132, 8708–8712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Wang, M.; Xu, T.; Zhang, M.; Dai, H.; Wang, C.; Ding, D.; Zhong, Z. Reactive Oxygen Species-Powered Cancer Immunotherapy: Current Status and Challenges. J. Control. Release 2023, 356, 623–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, M.; Koo, S.; Li, H.; Sessler, J.L.; Lee, J.Y.; Sharma, A.; Kim, J.S. An Ethacrynic Acid-Brominated BODIPY Photosensitizer (EA-BPS) Construct Enhances the Lethality of Reactive Oxygen Species in Hypoxic Tumor-Targeted Photodynamic Therapy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 3196–3204. [Google Scholar]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, J.; Lee, S.; Jo, G.; Hwang, E.; Lee, J.; Han, J.; Jung, H.S. A Novel BODIPY-Zn Complex as Innovative Sonosensitizer for Enhanced Sonodynamic Therapy. Molecules 2025, 30, 1587. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30071587
Lee J, Lee S, Jo G, Hwang E, Lee J, Han J, Jung HS. A Novel BODIPY-Zn Complex as Innovative Sonosensitizer for Enhanced Sonodynamic Therapy. Molecules. 2025; 30(7):1587. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30071587
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Jungmin, Soeun Lee, Gihoon Jo, Eunbin Hwang, Junhyoung Lee, Jiyou Han, and Hyo Sung Jung. 2025. "A Novel BODIPY-Zn Complex as Innovative Sonosensitizer for Enhanced Sonodynamic Therapy" Molecules 30, no. 7: 1587. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30071587
APA StyleLee, J., Lee, S., Jo, G., Hwang, E., Lee, J., Han, J., & Jung, H. S. (2025). A Novel BODIPY-Zn Complex as Innovative Sonosensitizer for Enhanced Sonodynamic Therapy. Molecules, 30(7), 1587. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30071587






