Research Progress of the Preparation of Cellulose Ethers and Their Applications: A Short Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Fabrication Process of Different CEs
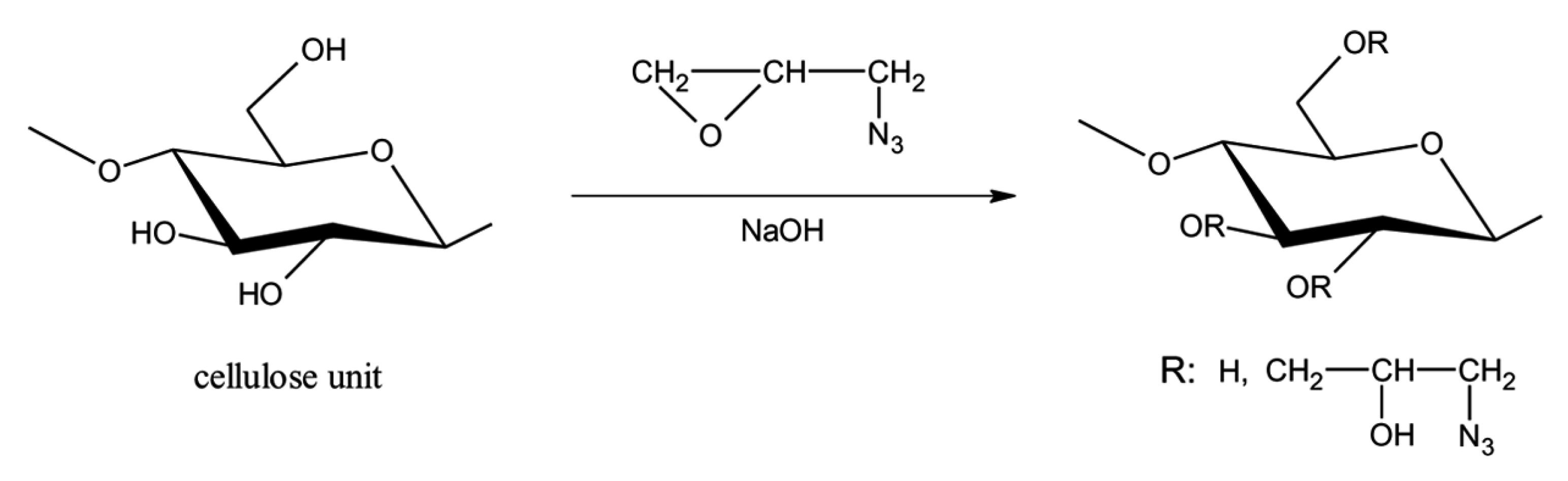
2.1. Heterogeneous Production of CEs
2.2. Homogeneous Preparation Methods of CEs
3. Applications of Different CEs and Their Effects
3.1. Applications and Effects of CEs on Concrete and Mortars
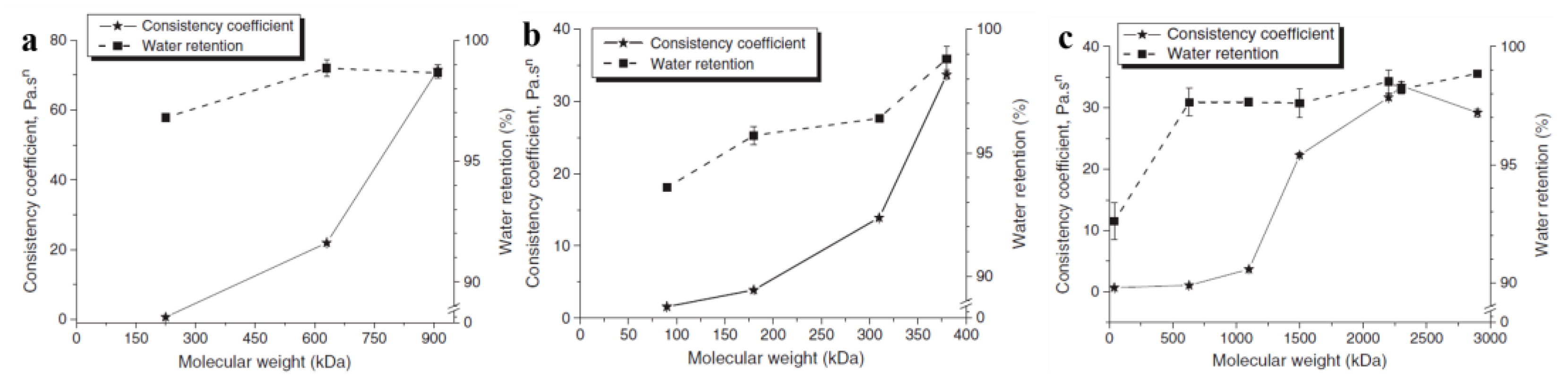
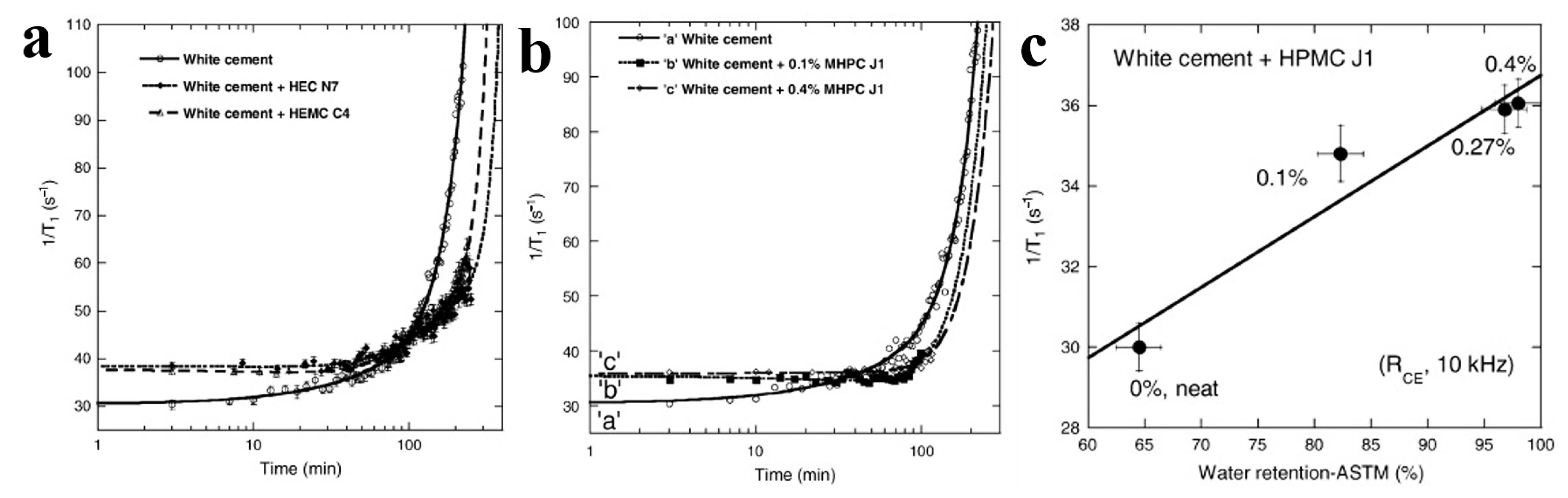
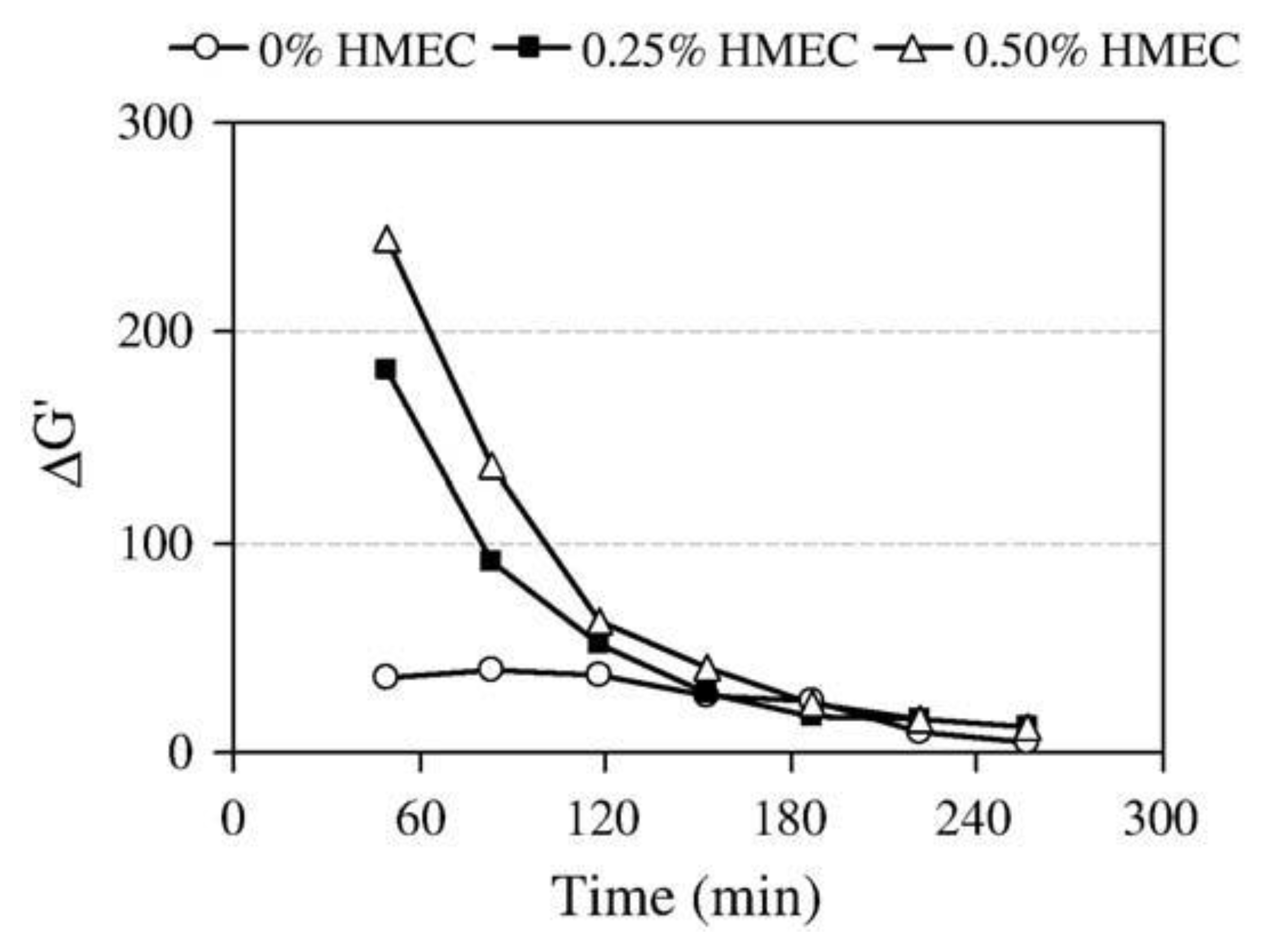
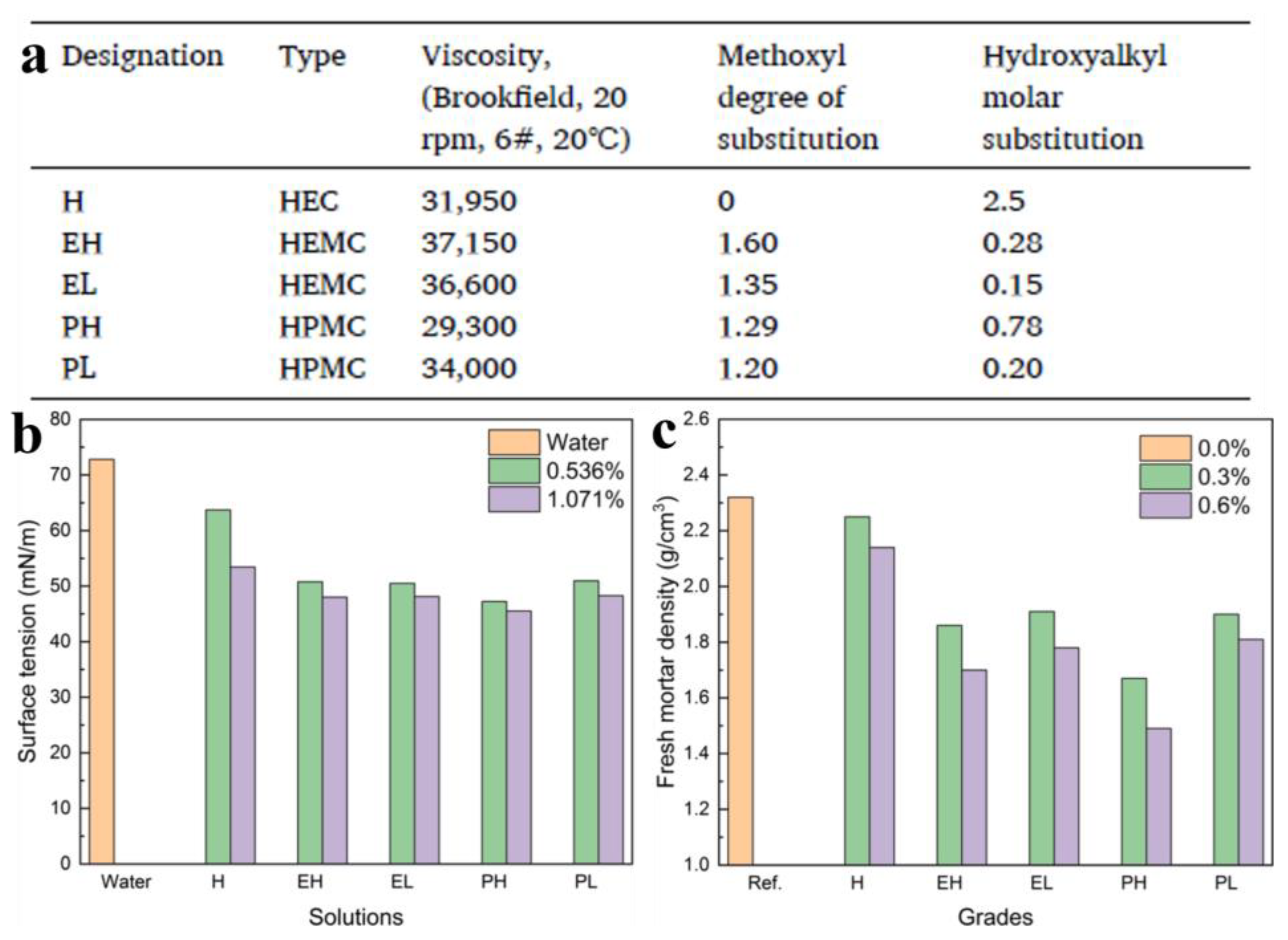
3.1.1. Improvement of Water Retention, Rheological Properties, Workability and Adhesion
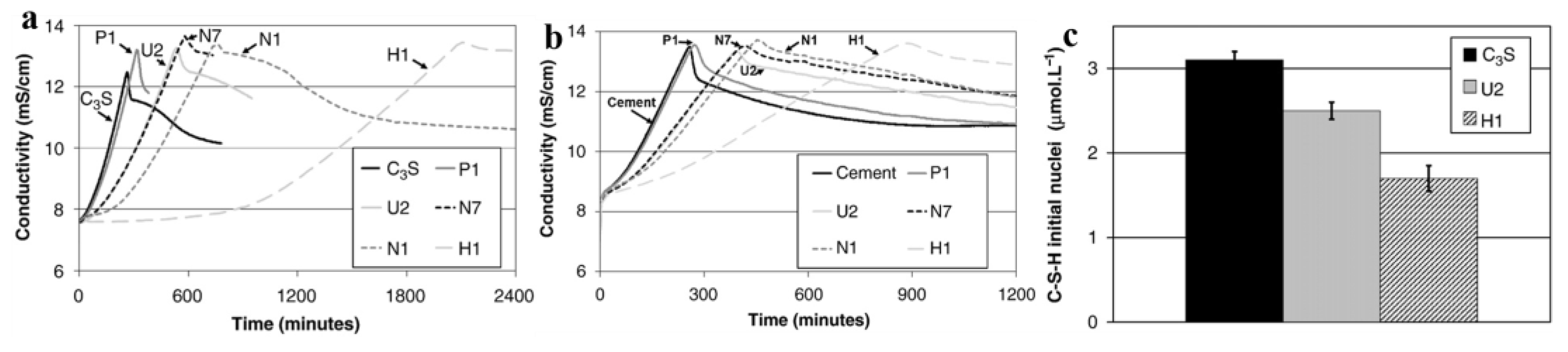
3.1.2. Effects on the Delay of Hydration
3.1.3. Effects on the Pore Structure and Mechanical Properties
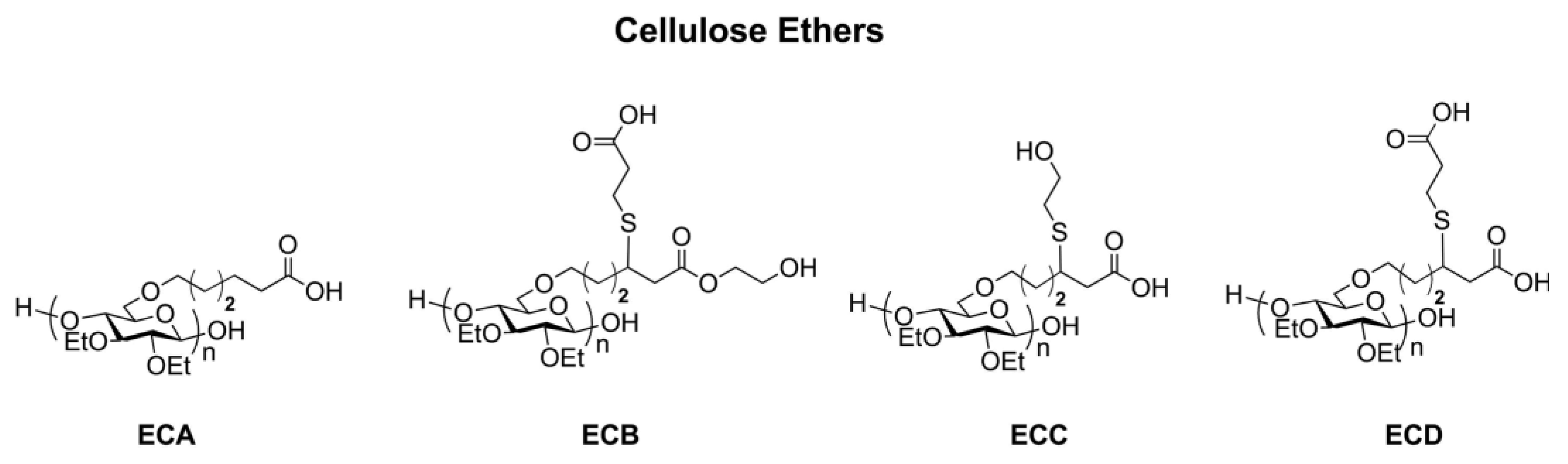
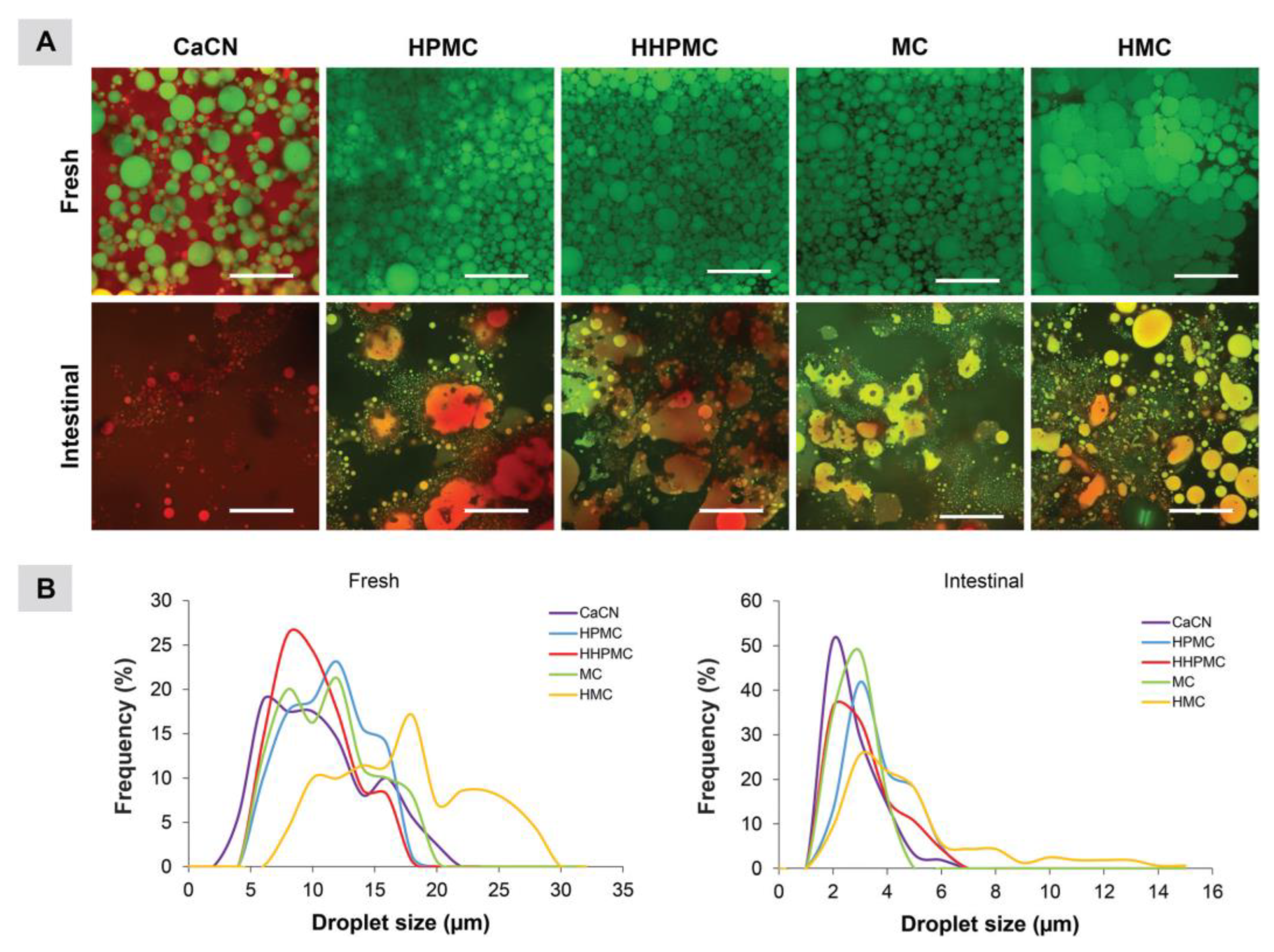
3.2. Other Applications and Effects of CEs
4. Summary and Prospect
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Seilkhan, A. An Overview of Green Applications of Natural Products for Pharmaceutical, Biofuel, and Rubber Industries: Case Study of Kazakh Dandelion (Taraxacum kok-saghyz Rodin). ES Energy Environ. 2024, 25, 1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moktadir, M.A.; Ren, J. Modeling challenges for Industry 4.0 implementation in new energy systems towards carbon neutrality: Implications for impact assessment policy and practice in emerging economies. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 199, 107246. [Google Scholar]
- Habibi, Y. Key advances in the chemical modification of nanocelluloses. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 1519–1542. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, S.; Ul-Islam, M.; Fatima, A.; Manan, S.; Khattak, W.A.; WajidUllah, M.W.; Yang, G. Potential of food and agro-industrial wastes for cost-effective bacterial cellulose production: An updated review of literature. ES Food Agrofor. 2023, 13, 905. [Google Scholar]
- Spiliopoulos, P.; Spirk, S.; Paakkonen, T.; Viljanen, M.; Svedstrom, K.; Pitkanen, L.; Awais, M.; Kontturi, E. Visualizing Degradation of Cellulose Nanofibers by Acid Hydrolysis. Biomacromolecules 2021, 22, 1399–1405. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, K.W.; Ma, K.L.; Yang, H.Z.; Long, G.C.; Xie, Y.J.; Zeng, X.H.; Tang, Z.; Usman, I.U. Influence of cellulose ethers on rheological properties of cementitious materials: A review. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 95, 110347. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.; He, M.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, L. Swelling Behaviors of pH- and Salt-Responsive Cellulose-Based Hydrogels. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 1642–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, E.; Pulham, C.R.; Morrison, C.A. Towards understanding and directing the nitration of cellulose. Cellulose 2024, 32, 1513–1526. [Google Scholar]
- Qosim, N.; Majd, H.; Ahmed, J.; Williams, G.; Edirisinghe, M. Making fibers from cellulose derivatives by pressurized gyration and electrospinning. Cellulose 2024, 31, 2815–2832. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Qi, Y.; Shen, Y.; Li, H. Research Progress on Chemical Modification and Application of Cellulose: A Review. Mater. Sci. 2022, 28, 60–67. [Google Scholar]
- Seddiqi, H.; Oliaei, E.; Honarkar, H.; Jin, J.F.; Geonzon, L.C.; Bacabac, R.G.; Klein-Nulend, J. Cellulose and its derivatives: Towards biomedical applications. Cellulose 2021, 28, 1893–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metalssi, O.O.; Ait-Mokhtar, A.; Ruot, B. Influence of cellulose ether on hydration and carbonation kinetics of mortars. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2014, 49, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keldibekova, R.; Suleimenova, S.; Nurgozhina, G.; Kopishev, E. Interpolymer Complexes Based on Cellulose Ethers: Application. Polymers 2023, 15, 3326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michael, I. Thermochemistry of alkalization and etherification of cellulose. World J. Adv. Res. Rev. 2023, 20, 1166–1174. [Google Scholar]
- You, J.; Zhang, X.; Mi, Q.; Zhang, J.; Wu, J.; Zhang, J. Mild, rapid and efficient etherification of cellulose. Cellulose 2022, 29, 9583–9596. [Google Scholar]
- Kostag, M.; Gericke, M.; Heinze, T.; El Seoud, O.A. Twenty-five years of cellulose chemistry: Innovations in the dissolution of the biopolymer and its transformation into esters and ethers. Cellulose 2019, 26, 139–184. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Rackstraw, N.B.; Weinstein, T.J.; Reiner, B.; Leal, L.; Ogawa, K.; Dauenhauer, P.J.; Reineke, T.M. Cellulose Etherification with Glycidol for Aqueous Rheology Modification. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2024, 6, 6714–6725. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, J.; Yu, M.; Zhang, T.; Huang, N.; Cao, Z.; Wei, L.; Zhu, X. Cellulose-based polypropoxy ether carboxylates as highly compatible, effective, and migration-resistant plasticizers for poly (lactic acid). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 127675. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, D.; Weng, J.; Chen, B.; Liu, H. Synthesis and characterization of photochromic azobenzene cellulose ethers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 99, 748–754. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, W.; Shuai, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, X. Progress on chemical modification of cellulose in “green” solvents. Polym. Chem. 2022, 13, 359–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onwukamike, K.N.; Grelier, S.; Grau, E.; Cramail, H.; Meier, M.A.R. Critical Review on Sustainable Homogeneous Cellulose Modification: Why Renewability Is Not Enough. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 1826–1840. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Qin, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhang, L. Homogenous synthesis of hydroxyethylcellulose in NaOH/urea aqueous solution. Macromol. Biosci. 2006, 6, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rohleder, E.; Heinze, T. Comparison of Benzyl Celluloses Synthesized in Aqueous NaOH and Dimethyl Sulfoxide/Tetrabutylammonium Fluoride. Macromol. Symp. 2010, 294, 107–116. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, L. Homogeneous Quaternization of Cellulose in NaOH/Urea Aqueous Solutions as Gene Carriers. Biomacromolecules 2008, 9, 2259–2264. [Google Scholar]
- Nagel, M.C.V.; Koschella, A.; Voiges, K.; Mischnick, P.; Heinze, T. Homogeneous methylation of wood pulp cellulose dissolved in LiOH/urea/H2O. Eur. Polym. J. 2010, 46, 1726–1735. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, L.; Deng, Q.; Wu, X. Synthesis and characterization of cellulose derivatives prepared in NaOH/urea aqueous solutions. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2004, 42, 5911–5920. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, H.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, L. Structure and physical properties of methylcellulose synthesized in NaOH/urea solution. Polym. Bull. 2006, 56, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Zhang, L.; Li, M.; Wu, X.; Cheng, G. Homogeneous hydroxyethylation of cellulose in NaOH/urea aqueous solution. Polym. Bull. 2005, 53, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.-F.; Sun, S.-N.; Xu, F.; Sun, R.-C. Cold NaOH/urea aqueous dissolved cellulose for benzylation: Synthesis and characterization. Eur. Polym. J. 2011, 47, 1817–1826. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, H.; Liebert, T.; Meister, F.; Heinze, T. Homogenous carboxymethylation of cellulose in the NaOH/urea aqueous solution. React. Funct. Polym. 2009, 69, 779–784. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Y.; Mosquera-Giraldo, L.I.; Taylor, L.S.; Edgar, K.J. Amphiphilic Cellulose Ethers Designed for Amorphous Solid Dispersion via Olefin Cross-Metathesis. Biomacromolecules 2016, 17, 454–465. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Martin, R.; Buchwald, S.L. Palladium-Catalyzed Suzuki−Miyaura Cross-Coupling Reactions Employing Dialkylbiaryl Phosphine Ligands. Acc. Chem. Res. 2008, 41, 1461–1473. [Google Scholar]
- Goncalves, C.; Favre, C.; Feuardant, P.; Klein, S.; Vaca-Garcia, C.; Cecutti, C.; Thiébaud-Roux, S.; Vedrenne, E. Synthesis of new cellulose ethers using Suzuki–Miyaura reactions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 116, 51–59. [Google Scholar]
- Sundman, O.; Gillgren, T.; Brostrom, M. Homogenous benzylation of cellulose—Impact of different methods on product properties. Cellul. Chem. Technol. 2015, 49, 745–755. [Google Scholar]
- Saliu, O.D.; Olatunji, G.A.; Yakubu, A.; Arowona, M.T.; Mohammed, A.A. Catalytic crosslinking of a regenerated hydrophobic benzylated cellulose and nano TiO2 composite for enhanced oil absorbency. E-Polymers 2017, 17, 295–302. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Wu, M.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, C.; Shi, L.; Lv, Y.; Ran, R. Phase-transfer method synthesis hydroxyethyl cellulose lauryl ether. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 562, 383–391. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.-F.; Shao, Z.; Li, N.-K.; Wang, F.-J.; Zhang, Y. A Novel Cellulose-Based Azide Energetic Material: 1-Azido-2-hydroxypropyl Cellulose Ether. J. Energetic Mater. 2011, 29, 241–260. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, W.; Li, Z.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Liu, R.; Liu, H. Synthesis and characterization of azobenzene hydroxypropyl cellulose with photochromic and thermotropic liquid crystal properties. Cellulose 2015, 22, 203–214. [Google Scholar]
- Rohowsky, J.; Heise, K.; Fischer, S.; Hettrich, K. Synthesis and characterization of novel cellulose ether sulfates. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 142, 56–62. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Xu, C.; Liu, L.; Yu, J.; Fan, Y. Facile and sustainable etherification of ethyl cellulose towards excellent UV blocking and fluorescence properties. Green Chem. 2021, 23, 479–489. [Google Scholar]
- Nichols, B.L.B.; Chen, J.; Mischnick, P.; Edgar, K.J. Selective Oxidation of 2-Hydroxypropyl Ethers of Cellulose and Dextran: Simple and Efficient Introduction of Versatile Ketone Groups to Polysaccharides. Biomacromolecules 2020, 21, 4835–4849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, K.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Ma, K.; Shen, J.; Hu, M. Rheological Properties and Early-Age Microstructure of Cement Pastes with Limestone Powder, Redispersible Polymer Powder and Cellulose Ether. Materials 2022, 15, 3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, B.; Peng, Y.; Tan, H.; Jian, S.; Zhi, Z.; Guo, Y.; Qi, H.; Zhang, T.; He, X. Effect of hydroxypropyl-methyl cellulose ether on rheology of cement paste plasticized by polycarboxylate superplasticizer. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 160, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patural, L.; Marchal, P.; Govin, A.; Grosseau, P.; Ruot, B.; Devès, O. Cellulose ethers influence on water retention and consistency in cement-based mortars. Cem. Concr. Res. 2011, 41, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marliere, C.; Mabrouk, E.; Lamblet, M.; Coussot, P. How water retention in porous media with cellulose ethers works. Cem. Concr. Res. 2012, 42, 1501–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patural, L.; Porion, P.; Van Damme, H.; Govin, A.; Grosseau, P.; Ruot, B.; Devès, O. A pulsed field gradient and NMR imaging investigations of the water retention mechanism by cellulose ethers in mortars. Cem. Concr. Res. 2010, 40, 1378–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patural, L.; Korb, J.-P.; Govin, A.; Grosseau, P.; Ruot, B.; Devès, O. Nuclear magnetic relaxation dispersion investigations of water retention mechanism by cellulose ethers in mortars. Cem. Concr. Res. 2012, 42, 1371–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Huang, J.; Wang, T.; Yang, R.; Hu, H.; Manuka, M.; Zhou, F.; Min, J.; Wan, H.; Yuan, D.; et al. Effect of Hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose (HPMC) on rheology and printability of the first printed layer of cement activated slag-based 3D printing concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 405, 133347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, A.; Du, H.; Yang, C.; Ma, S.; Feng, Q.; Song, K.; Li, H. Modification of grouting materials and mechanical properties of coal slurry couplings. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 38, 108350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Wang, S.; Liu, J.; Wang, H.; Xu, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, Z. Effect of hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose (HPMC) as foam stabilizer on the workability and pore structure of iron tailings sand autoclaved aerated concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 376, 130979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Q.; Wang, Z.; Huang, T.; Wang, R. Water retention mechanism of cellulose ethers in calcium sulfoaluminate cement-based materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 301, 124118. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.; Ou, Y.; Hecker, A.; Rößler, C.; Ludwig, H.M.; Yang, Z.; Wu, K. State of water in calcium sulfoaluminate cement paste modified by hydroxyethyl methyl cellulose ether. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 43, 102894. [Google Scholar]
- Poinot, T.; Bartholin, M.-C.; Govin, A.; Grosseau, P. Influence of the polysaccharide addition method on the properties of fresh mortars. Cem. Concr. Res. 2015, 70, 50–59. [Google Scholar]
- Spychał, E. The rheology of cement pastes with the addition of hydrated lime and cellulose ether in comparison with selected properties of plastering mortars. Cem. Wapno Beton 2020, 25, 21–30. [Google Scholar]
- Pourchez, J.; Ruot, B.; Debayle, J.; Pourchez, E.; Grosseau, P. Some aspects of cellulose ethers influence on water transport and porous structure of cement-based materials. Cem. Concr. Res. 2010, 40, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciobanu, C.; Lazǎu, I.; Pǎcurariu, C. Investigation of the cellulose ethers effect on the Portland cement hydration by thermal analysis. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2013, 112, 325–330. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, C.; Zhou, M. Properties comparison of mortars with welan gum or cellulose ether. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 102, 648–653. [Google Scholar]
- Pourchez, J.; Grosseau, P.; Guyonnet, R.; Ruot, B. HEC influence on cement hydration measured by conductometry. Cem. Concr. Res. 2006, 36, 1777–1780. [Google Scholar]
- Ou, Z.H.; Ma, B.G.; Jian, S.W. Influence of cellulose ethers molecular parameters on hydration kinetics of Portland cement at early ages. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 33, 78–83. [Google Scholar]
- Betioli, A.M.; Gleize, P.J.P.; Silva, D.A.; John, V.M.; Pileggi, R.G. Effect of HMEC on the consolidation of cement pastes: Isothermal calorimetry versus oscillatory rheometry. Cem. Concr. Res. 2009, 39, 440–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; He, R.; Lu, X.; Wang, P. Early hydration of calcium sulfoaluminate cement in the presence of hydroxyethyl methyl cellulose. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2018, 134, 1429–1438. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Wang, R.; Xu, Y. Influence of cellulose ethers chemistry and substitution degree on the setting and early-stage hydration of calcium sulphoaluminate cement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 344, 128266. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, L.; Hu, Y.; Chen, H.; Cui, Y.; Liu, P.; Xu, D. Ultrasonic propagation characteristics and microstructure analysis of cement paste doped with cellulose ether. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 420, 135653. [Google Scholar]
- Pourchez, J.; Grosseau, P.; Ruot, B. Current understanding of cellulose ethers impact on the hydration of C3A and C3A-sulphate systems. Cem. Concr. Res. 2009, 39, 664–669. [Google Scholar]
- Pourchez, J.; Grosseau, P.; Ruot, B. Changes in C3S hydration in the presence of cellulose ethers. Cem. Concr. Res. 2010, 40, 179–188. [Google Scholar]
- Wyrzykowski, M.; Kiesewetter, R.; Münch, B.; Baumann, R.; Lura, P. Pore structure of mortars with cellulose ether additions—Study of the air-void structure. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2015, 62, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumate, E.; Moldovan, D.; Manea, D.L.; Demco, D.E.; Fechete, R. The Effects of Cellulose Ethers and Limestone Fillers in Portland Cement-Based Mortars by 1H NMR relaxometry. Appl. Magn. Reson. 2016, 47, 1353–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetzel, A.; Herwegh, M.; Zurbriggen, R.; Winnefeld, F. Influence of shrinkage and water transport mechanisms on microstructure and crack formation of tile adhesive mortars. Cem. Concr. Res. 2012, 42, 39–50. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, R.; Xu, L.; Hecker, A.; Ludwig, H.-M.; Wang, P. Properties of Calcium Sulfoaluminate Cement Mortar Modified by Hydroxyethyl Methyl Celluloses with Different Degrees of Substitution. Molecules 2021, 26, 2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, R.; Li, L. Influence of cellulose ethers structure on mechanical strength of calcium sulphoaluminate cement mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 303, 124514. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, L.; Xu, L.; Diao, G.; Liu, G. Effects of hydroxyethyl methyl cellulose ether on the hydration and compressive strength of calcium aluminate cement. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2020, 140, 545–553. [Google Scholar]
- Wyrzykowski, M.; Kiesewetter, R.; Kaufmann, J.; Baumann, R.; Lura, P. Pore structure of mortars with cellulose ether additions—Mercury intrusion porosimetry study. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2014, 53, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brumaud, C.; Bessaies-Bey, H.; Mohler, C.; Baumann, R.; Schmitz, M.; Radler, M.; Roussel, N. Cellulose ethers and water retention. Cem. Concr. Res. 2013, 53, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Zhang, D.; Li, H.; Yin, L.; Song, H.; Wang, W.; Zhang, S. Effects of additives on the mechanical properties, rheology, and printing properties of Pcc-based 3DPMs. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 28354–28368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Wang, S.; Qiu, D.; Wang, B.; Wu, X.; Wu, M. Investigation on the performance of hydroxyethyl methyl cellulose modified cement mortars with Portland cement-calcium sulfoaluminate cement binders. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 283, 122721. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; Huang, T.; Wang, P.; Zhang, G. Mechanical strengths, drying shrinkage and pore structure of cement mortars with hydroxyethyl methyl cellulose. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 314, 125683. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Z.; Huang, T.; Wang, P. Evolutions in the properties and microstructure of cement mortars containing hydroxyethyl methyl cellulose after controlling the air content. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2022, 129, 104487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, A.N.; Tufan, M.Z.; Özel, C. Investigation of some cellulose derivatives effects on concrete properties using response surface methodology. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 416, 135115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, L.; Wei, J.; Khayat, K.H.; Assaad, J.J. Effect of competitive adsorption between specialty admixtures and superplasticizer on structural build-up and hardened property of mortar phase of ultra-high-performance concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2023, 141, 105130. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, B.; Chen, Y.; Liu, F.; Xie, X.; Guo, W.; Wang, H. Development of a high strength cementitious grout for filling the joints of UHPC permanent formwork. Dev. Built Environ. 2023, 13, 100120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, W.; Gao, Y.; Kong, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, X. Effects of HPMC on Workability and Mechanical Properties of Concrete Using Iron Tailings as Aggregates. Materials 2021, 14, 6451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arca, H.C.; Mosquera-Giraldo, L.I.; Bi, V.; Xu, D.; Taylor, L.S.; Edgar, K.J. Pharmaceutical Applications of Cellulose Ethers and Cellulose Ether Esters. Biomacromolecules 2018, 19, 2351–2376. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.; Modi, S.; Bansal, A. Co-processing as a tool to improve aqueous dispersibility of cellulose ethers. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2015, 41, 1745–1758. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mosquera-Giraldo, L.I.; Borca, C.H.; Parker, A.S.; Dong, Y.; Edgar, K.J.; Beaudoin, S.P.; Slipchenko, L.V.; Taylor, L.S. Crystallization Inhibition Properties of Cellulose Esters and Ethers for a Group of Chemically Diverse Drugs: Experimental and Computational Insight. Biomacromolecules 2018, 19, 4593–4606. [Google Scholar]
- Wali, A.; Zhang, Y.; Sengupta, P.; Higaki, Y.; Takahara, A.; Badiger, M.V. Electrospinning of non-ionic cellulose ethers/polyvinyl alcohol nanofibers: Characterization and applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 181, 175–182. [Google Scholar]
- Tundisi, L.L.; Mostaco, G.B.; Carricondo, P.C.; Petri, D.F.S. Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose: Physicochemical properties and ocular drug delivery formulations. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 159, 105736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Jiang, S.; Yang, J.; Qiu, J.; Jiao, X.; Yue, X.; Ke, X.; Yang, G.; Zhang, L. Application of 3D-bioprinted nanocellulose and cellulose derivative-based bio-inks in bone and cartilage tissue engineering. Int. J. Bioprint. 2023, 9, 637. [Google Scholar]
- Ahlfeld, T.; Kohler, T.; Czichy, C.; Lode, A.; Gelinsky, M. A Methylcellulose Hydrogel as Support for 3D Plotting of Complex Shaped Calcium Phosphate Scaffolds. Gels 2018, 4, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Deng, Q.; Wang, S.; Li, Q.; Zhao, W.; Lin, B.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, X. Hydroxyethyl Cellulose As a Rheological Additive for Tuning the Extrusion Printability and Scaffold Properties. 3D Print. Addit. Manuf. 2021, 8, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, T.; Štiglic, A.D.; Beaumont, M.; Konnerth, J.; Gürer, F.; Makuc, D.; Maver, U.; Gradišnik, L.; Plavec, J.; Kargl, R.; et al. Generic Method for Designing Self-Standing and Dual Porous 3D Bioscaffolds from Cellulosic Nanomaterials for Tissue Engineering Applications. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 3, 1197–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotz, L.-M.; Holeczek, K.; Groll, J.; Jungst, T.; Gbureck, U. Extrusion-Based 3D Printing of Calcium Magnesium Phosphate Cement Pastes for Degradable Bone Implants. Materials 2021, 14, 5197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torcello-Gómez, A.; Foster, T.J. Influence of interfacial and bulk properties of cellulose ethers on lipolysis of oil-in-water emulsions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 144, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Espert, M.; Wiking, L.; Salvador, A.; Sanz, T. Reduced-fat spreads based on anhydrous milk fat and cellulose ethers. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 99, 105330. [Google Scholar]
- Borreani, J.; Espert, M.; Salvador, A.; Sanz, T.; Quiles, A.; Hernando, I. Oil-in-water emulsions stabilised by cellulose ethers: Stability, structure and in vitro digestion. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 1547–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, G.; Tunio, A.H.; Memon, K.R.; Mahesar, A.A.; Memon, F.H.; Abbasi, G.R. Modification of Cellulose Ether with Organic Carbonate for Enhanced Thermal and Rheological Properties: Characterization and Analysis. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 25453–25466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliu, A.O.; Guo, J.; Wang, S.; Zhao, X. Hydraulic fracture fluid for gas reservoirs in petroleum engineering applications using sodium carboxy methyl cellulose as gelling agent. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2016, 32, 491–500. [Google Scholar]
- Abbas, G.; Irawan, S.; Memon, K.R.; Khan, J. Application of cellulose-based polymers in oil well cementing. J. Pet. Explor. Prod. Technol. 2019, 10, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaggero, G.; Delucchi, M.; Allegretta, G.; Vicini, S.; Botter, R. Interaction of sodium alginate thickener with components of architectural water-based coatings. Prog. Org. Coat. 2021, 151, 106016. [Google Scholar]
- Hynninen, V.; Patrakka, J.; Nonappa. Methylcellulose-Cellulose Nanocrystal Composites for Optomechanically Tunable Hydrogels and Fibers. Materials 2021, 14, 5137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coughlin, M.L.; Liberman, L.; Ertem, S.P.; Edmund, J.; Bates, F.S.; Lodge, T.P. Methyl cellulose solutions and gels: Fibril formation and gelation properties. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2021, 112, 101324. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Y.; Zhu, T.; Cheng, Y.; Zhao, K.; Meng, Z.; Huang, J.; Cai, W.; Lai, Y. Recent Advances in Functional Cellulose-Based Materials: Classification, Properties, and Applications. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2024, 6, 1343–1368. [Google Scholar]

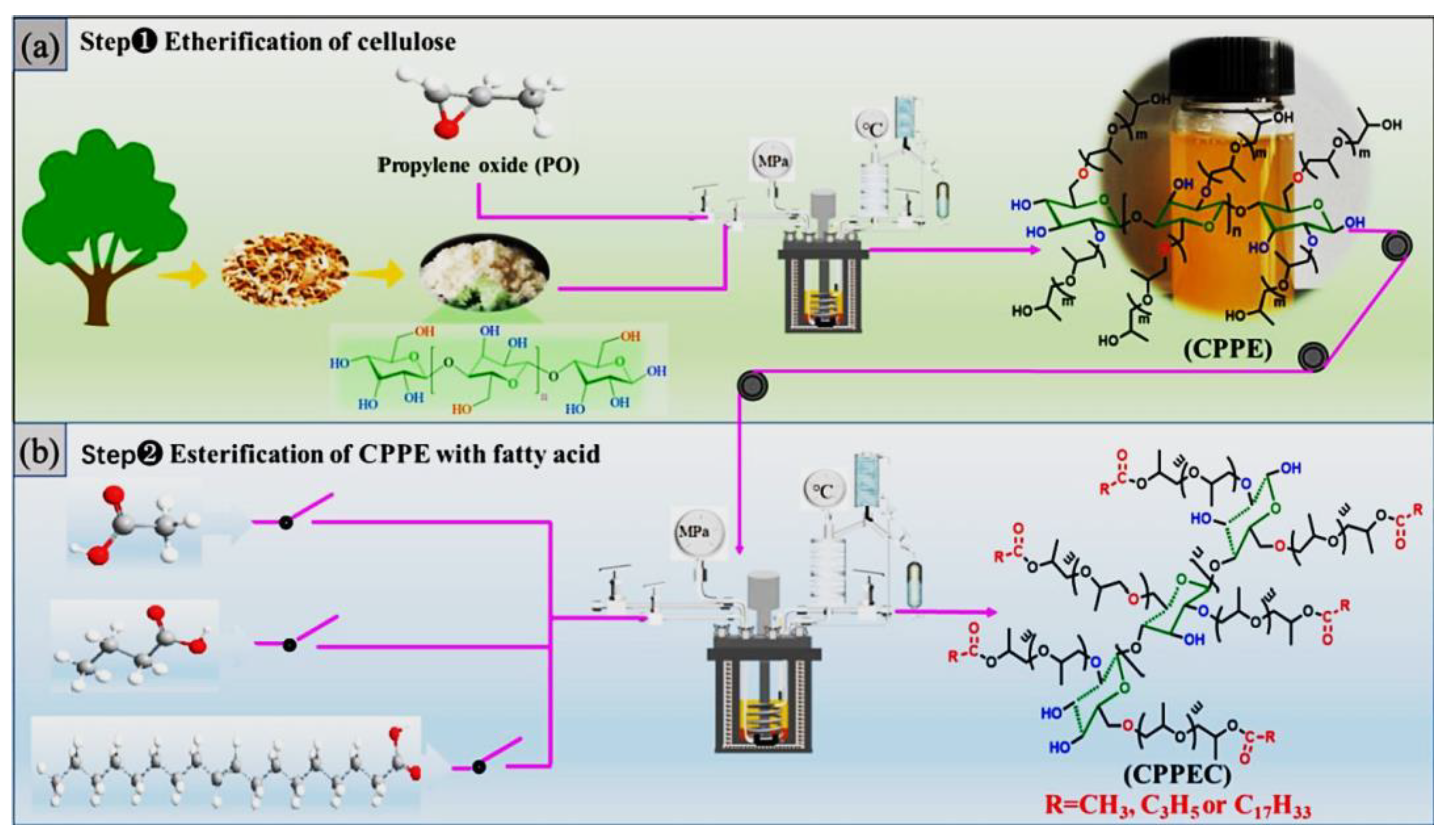

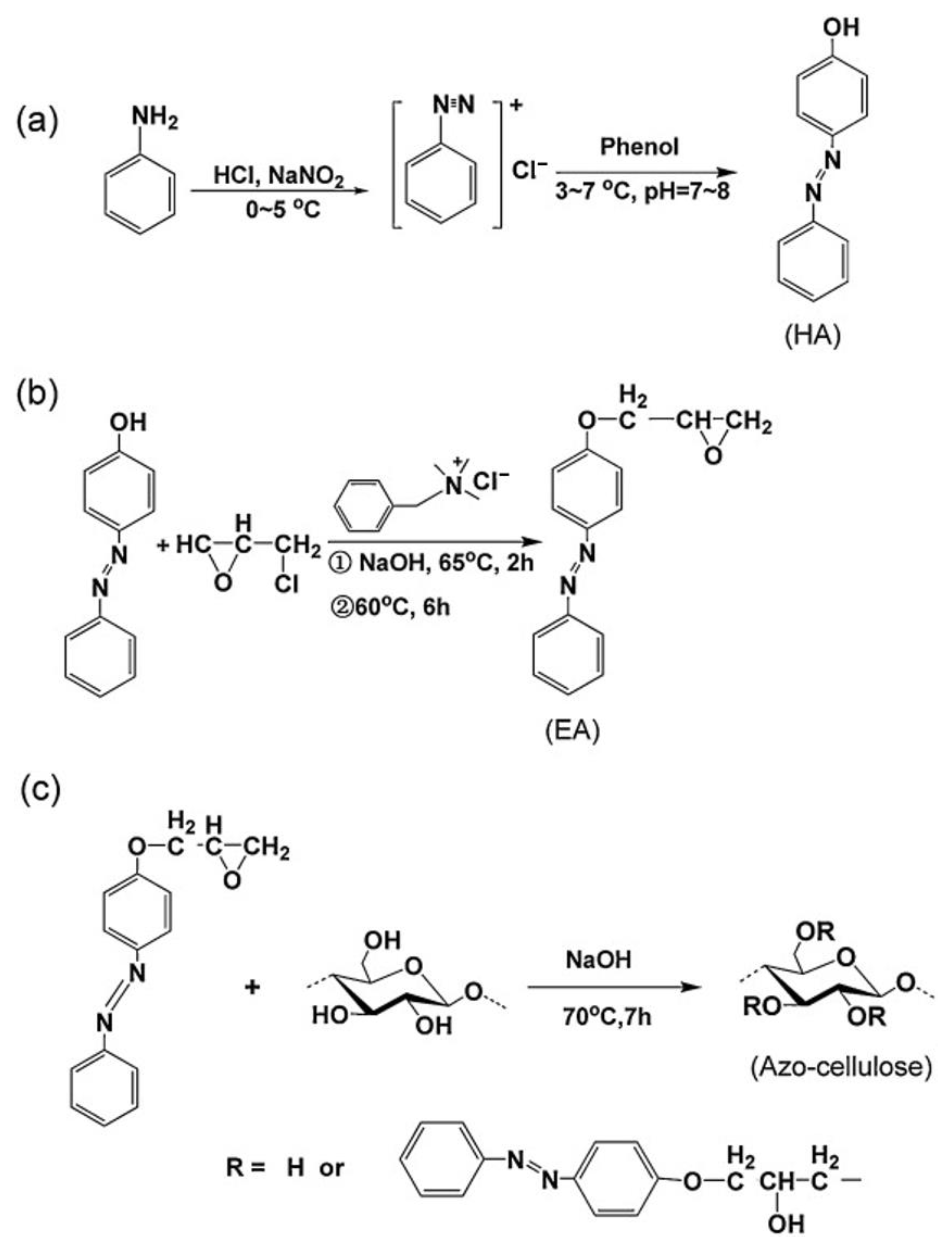
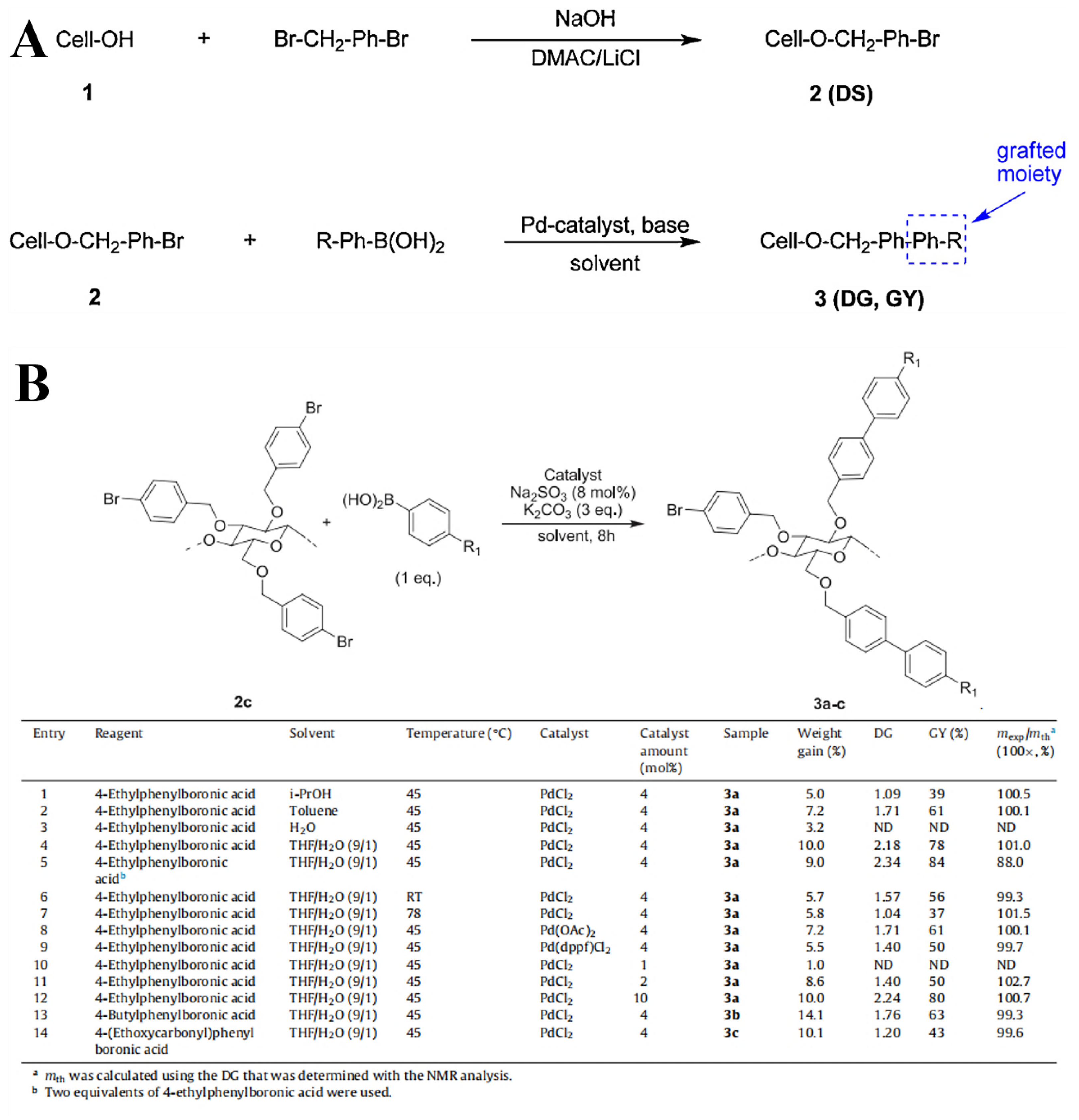
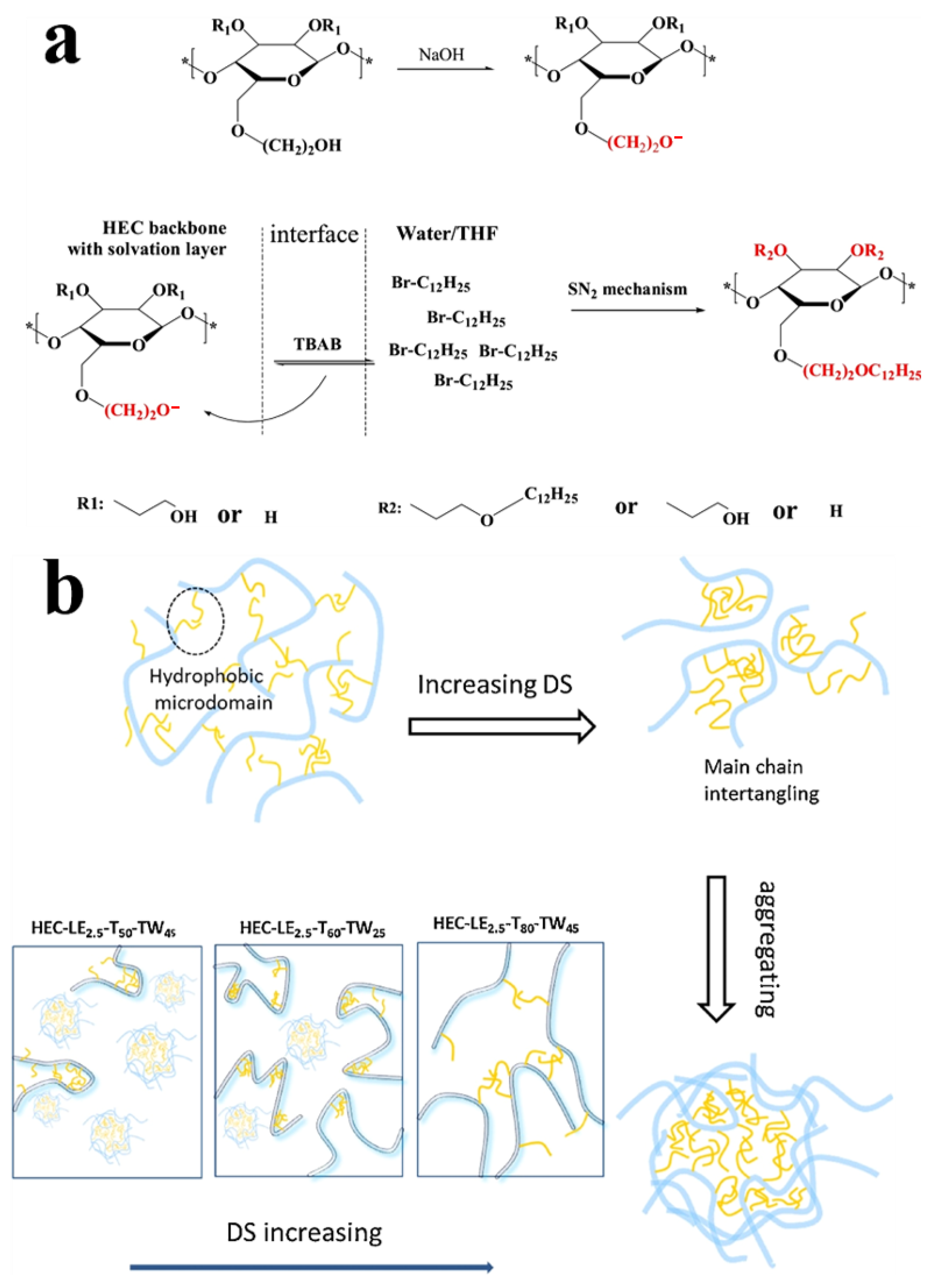




| Types | Specific Functional Groups | Major Application Fields | Abbreviations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Methyl cellulose | –OH or –OCH3 | Food industry, biomedical, cosmetics | MC |
| Carboxymethyl cellulose | –OH or –OCH2COOH | Building, food or paper industry, biomedical, water treatment, textile | CMC |
| Ethyl cellulose | –OH or –OCH2CH3 | Food industry, paper industry, biomedical, textile | EC |
| Hydroxy-ethyl cellulose | –OH or –OCH2CH2OH | Building, cosmetic, cleaning solutions, textile | HEC |
| Hydroxy-propyl cellulose | –OH or –OCH2CH(OH)CH3 | Building, food or paper industry, biomedical, water treatment, textile | HPC |
| Cyanoethyl cellulose | –OH or –CH2-CH2-CN | Coatings, biomedical, paper industry | CEC |
| Ethyl hydroxyethyl cellulose | –OH or –CH2-CH3 or –CH2-CH2-OH | Biomedical, coatings | EHEC |
| Hydroxyethyl methyl cellulose | –OH or –CH2-CH2-OH or –CH3 | Building, cosmetics, food or paper industry | HEMC |
| Hydroxypropyl carboxymethyl cellulose | –OH or –CH2-CHOH-CH3 or –CH2-COOH | Building, food industry, biomedical, cosmetics | HPCMC |
| Hydroxyethyl carboxymethyl cellulose | –OH or –CH2-CH2-OH or –CH2-COOH | Building, biomedical, food industry, cosmetics | ECMC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, M.; Lin, Y.; Huang, Y.; Fang, Y.; Xiong, X. Research Progress of the Preparation of Cellulose Ethers and Their Applications: A Short Review. Molecules 2025, 30, 1610. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30071610
He M, Lin Y, Huang Y, Fang Y, Xiong X. Research Progress of the Preparation of Cellulose Ethers and Their Applications: A Short Review. Molecules. 2025; 30(7):1610. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30071610
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Meng, Yanmei Lin, Yujia Huang, Yunhui Fang, and Xiaopeng Xiong. 2025. "Research Progress of the Preparation of Cellulose Ethers and Their Applications: A Short Review" Molecules 30, no. 7: 1610. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30071610
APA StyleHe, M., Lin, Y., Huang, Y., Fang, Y., & Xiong, X. (2025). Research Progress of the Preparation of Cellulose Ethers and Their Applications: A Short Review. Molecules, 30(7), 1610. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30071610







