Cleansing Mechanisms and Efficacy on Artificial Skin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
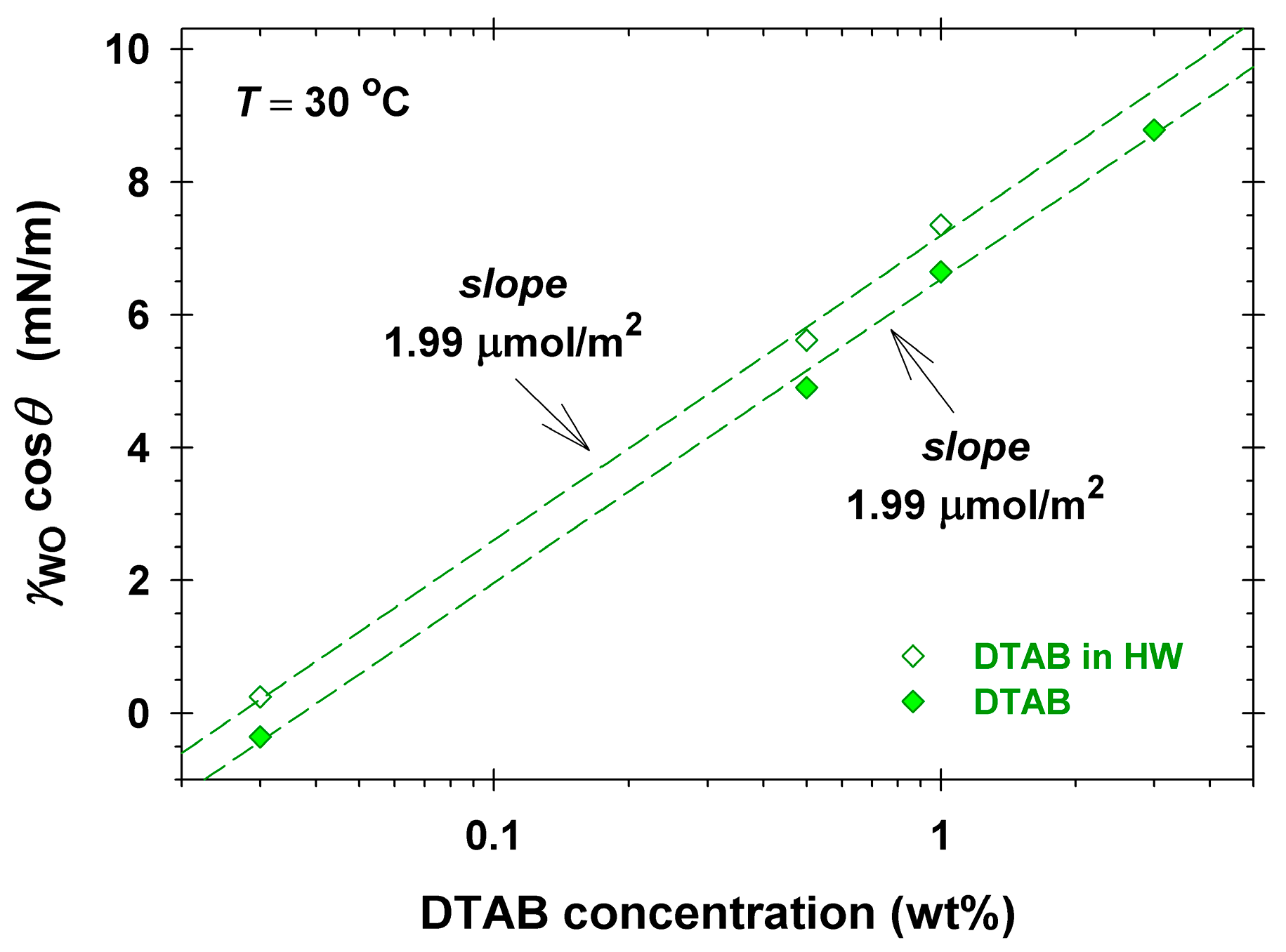
2.1. Surface and Interfacial Tension Isotherms of the Used Surfactants
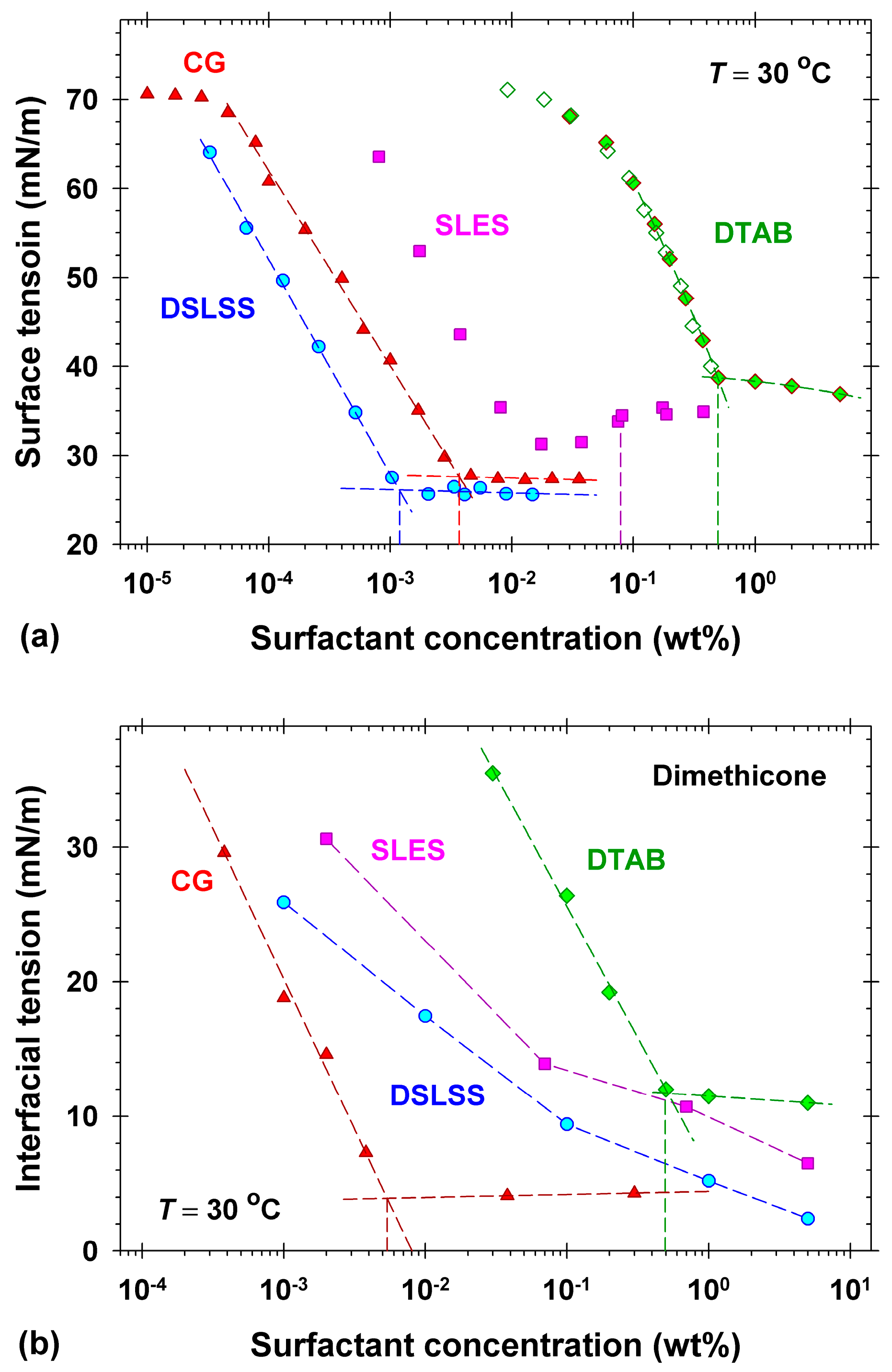
2.2. Oily Soils Removal from Vitroskin® in Single Surfactant Solutions
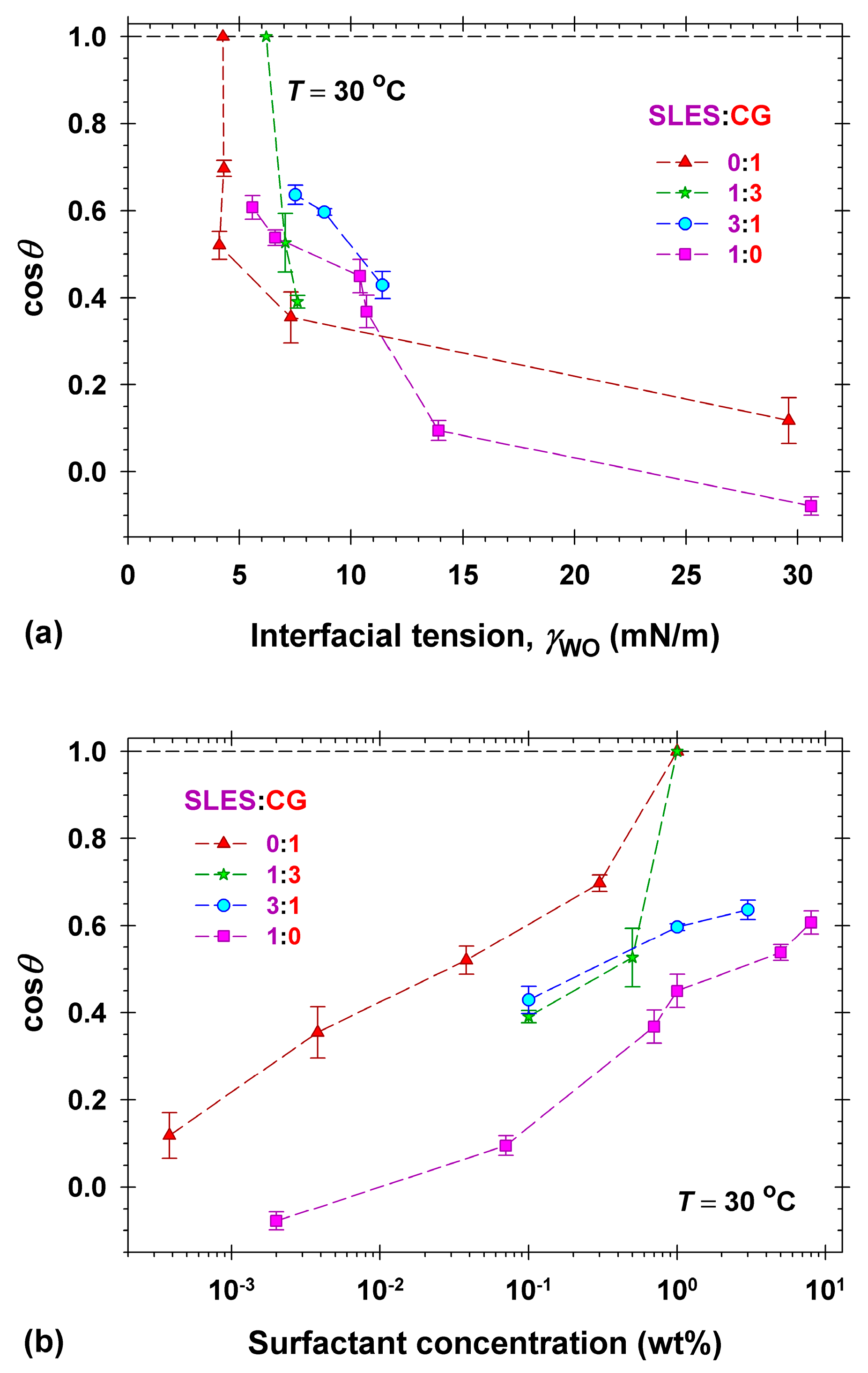
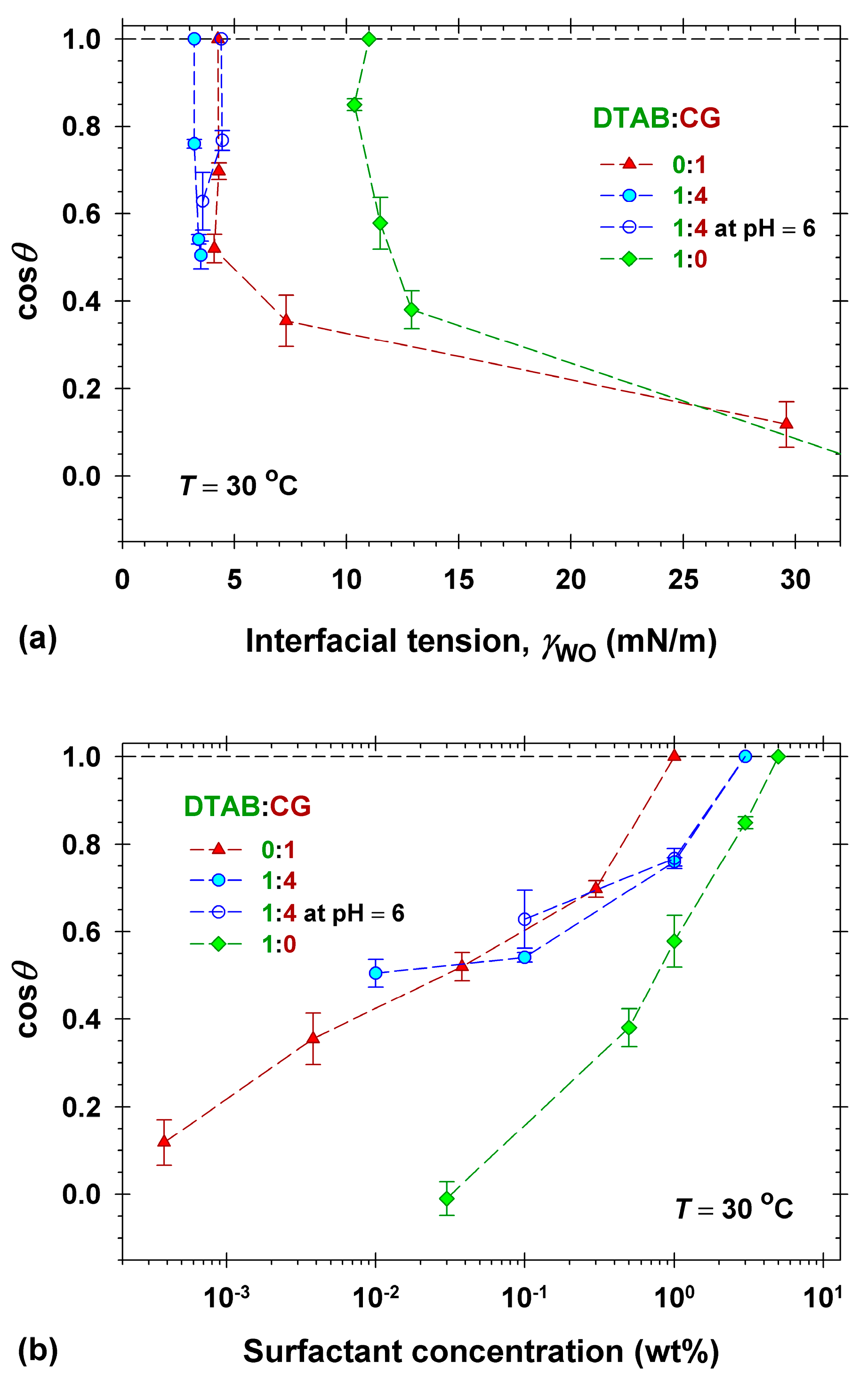
2.3. Dimethicone Soils Removal in Mixed Surfactant Solutions
2.4. Dimethicone Soils Removal in Model Cleansing Formulations
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Methods
4.2.1. Surface and Interfacial Tension Measurements, pH, and Conductivity Determination
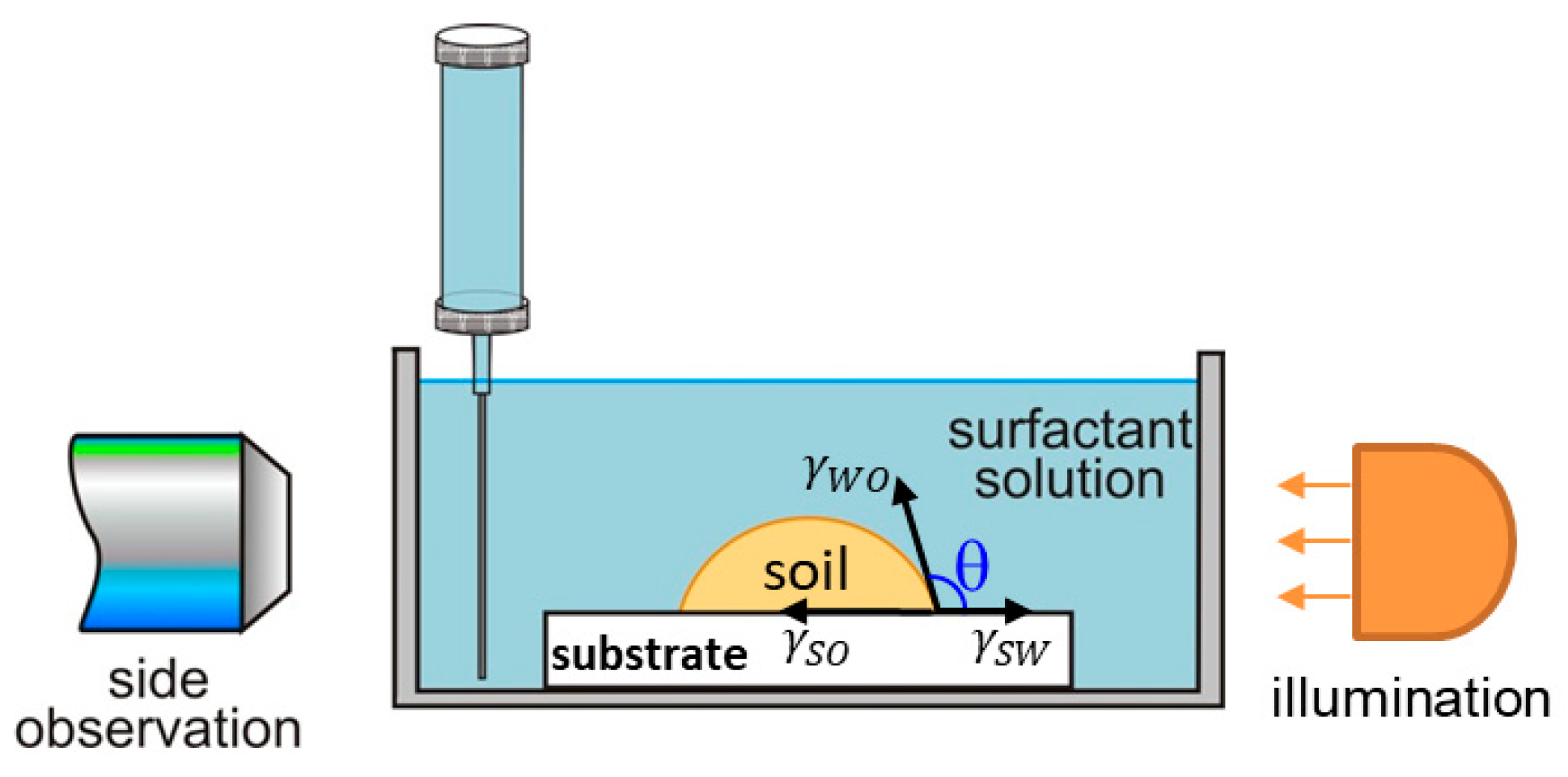
4.2.2. Direct Observations of the Soil Removal from Vitroskin®
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baki, G.; Alexander, K.S. Introduction to Cosmetic Formulation and Technology; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Abe, T. Psychology of Cosmetic Behavior. In Cosmetic Science and Technology: Theoretical Principles and Applications; Sakamoto, K., Lochhead, R.Y., Maibach, H.I., Yamashita, Y., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsui, T. New Cosmetic Science; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Ananthapadmanabhan, K.P. Amino-Acid Surfactants in Personal Cleansing (Review). Tenside Surf. Det. 2019, 56, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahan, R.; Bodratti, A.M.; Tsianou, M.; Alexandridis, P. Biosurfactants, Natural Alternatives to Synthetic Surfactants: Physicochemical Properties and Applications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 275, 102061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Union. Regulation (EC) No 1223/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 30 November 2009 on Cosmetic Products; European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ginn, M.E.; Noyes, C.M.; Jungermann, E. The Contact Angle of Water on Viable Human Skin. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1968, 26, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eudier, F.; Savary, G.; Grisel, M.; Picard, C. Skin Surface Physico-chemistry: Characteristics, Methods of Measurement, Influencing Factors and Future Developments. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 264, 11–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aßmus, U.; Banowski, B.; Brock, M.; Erasmy, J.; Fitzner, A.; Kortemeier, U.; Langer, S.; Munke, S.; Schmidt-Lewerkühne, H.; Segger, D.; et al. Impact of Cleansing Products on the Skin Surface pH. IFSCC Mag. 2013, 16, 17–24. [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins, S.; Dasgupta, B.R.; Ananthapadmanabhan, K.P. Role of pH in Skin Cleansing. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2021, 43, 474–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavon, A.; Zahouani, H.; Redoules, D.; Agache, P.; Gall, Y.; Humbert, P. Sebum and Stratum Corneum Lipids Increase Human Skin Surface Free Energy as Determined from Contact Angle Measurement: A Study on Two Anatomical Sites. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 1997, 8, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavon, A.; Redoules, D.; Humbert, P.; Agache, P.; Gall, Y. Changes in Sebum Levels and Skin Surface Free Energy Components Following Skin Surface Washing. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 1998, 10, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- German, G.K.; Pashkovski, E.; Dufresne, E.R. Surfactant Treatments Influence Drying Mechanics in Human Stratum Corneum. J. Biomech. 2013, 46, 2145–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkhyat, A.; Agache, P.; Zahouani, H.; Humbert, P. A New Method to Measure In Vivo Human Skin Hydrophobia. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2001, 23, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkhyat, A.; Mavon, A.; Leduc, M.; Agache, P.; Humbert, P. Skin Critical Surface Tension: A Way to Assess the Skin Wettability Quantitatively. Skin Res Technol. 1996, 2, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krawczyk, J. Surface Free Energy of the Human Skin and its Critical Surface Tension of Wetting in the Skin/Surfactant Aqueous Solution/Air System. Skin Res. Technol. 2015, 21, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujii, K. Wetting and Surface Characterization. In Cosmetic Science and Technology: Theoretical Principles and Applications; Sakamoto, K., Lochhead, R.Y., Maibach, H.I., Yamashita, Y., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 373–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsner, P.; Seyfarth, F.; Sonsmann, F.; John, S.-M.; Diepgen, T.; Schliemann, S. Development of a Standardized Procedure for Testing the Efficacy of Workplace Cleansers. Contact Dermat. 2014, 70, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonsmann, F.K.; Strunk, M.; Gediga, K.; Schliemann, S.; Seyfarth, F.; Elsner, P.; Diepgen, T.L.; Kutz, G.; John, S.M. Standardization of Skin Cleansing In Vivo: Part II. Validation of a Newly Developed Automated Cleansing Device (ACiD). Skin Res. Technol. 2014, 20, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, K.-Y. (Ed.) Liquid Detergents; Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Ringstad, L.; Skedung, L.; Falkman, P.; Wahlgren, M.; Engblom, J. Tactile Friction of Topical Creams and Emulsions: Friction Measurements on Excised Skin and VitroSkin® using ForceBoard™. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 615, 121502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lir, I.; Haber, M.; Dodiuk, H. Skin Surface Model Material as a Substrate for Adhesion-to-Skin Testing. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2007, 21, 1497–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhein, L. Surfactant Action on Skin and Hair: Cleansing and Skin Reactivity Mechanisms. In Handbook for Cleaning/Decontamination of Surfaces; Johansson, I., Somasundaran, P., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 305–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornwell, P.A. A Review of Shampoo Surfactant Technology: Consumer Benefits, Raw Materials and Recent Developments. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2018, 40, 16–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lochhead, R.Y. Basic Physical Sciences for the Formulation of Cosmetic Products. In Cosmetic Science and Technology: Theoretical Principles and Applications; Sakamoto, K., Lochhead, R.Y., Maibach, H.I., Yamashita, Y., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 39–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flaten, G.E.; Palac, Z.; Engesland, A.; Filipović-Grĉić, J.; Vanić, Z.; Škalko-Basnet, N. In Vitro Skin Models as a Tool in Optimization of Drug Formulation. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 75, 10–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, F.F.; Nowakowski, S.; Kluger, P.J. Improvement of a Three-Layered In Vitro Skin Model for Topical Application of Irritating Substances. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jermann, R.; Toumiat, M.; Imfeld, D. Development of an in Vitro Efficacy Test for Self-Tanning Formulations. Int. J. Cosm. Sci. 2002, 24, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhushan, B. Nanotribological and Nanomechanical Properties of Skin with and without Cream Treatment using Atomic Force Microscopy and Nanoindentation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 367, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.; Zhang, J.; Chen, S.; Chen, N.; Zhu, H.; Ge, S.; Zhang, S. Tactile Perception of Skin and Skin Cream. Tribol. Lett. 2015, 59, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douguet, M.; Picard, C.; Savary, G.; Merlaud, F.; Loubat-bouleuc, N.; Grisel, M. Spreading Properties of Cosmetic Emollients: Use of Synthetic Skin Surface to Elucidate Structural Effect. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 154, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, R.B.; Biedermann, K.A.; Morgan, J.M.; Keswick, B.; Ertel, K.D.; Barker, M.F. Efficacy of Organic Acids in Hand Cleansers for Prevention of Rhinovirus Infections. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 2595–2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeMarco, G.M.; Ekman-Gunn, E.; Poccia, J.F., III. Gel Wipe Composition Comprising a Superabsorbent Gel Fiber. U.S. Patent US20160367102A1, 22 December 2016. [Google Scholar]
- VITRO-SKIN® The Global Standard for Rapid, Predictive In Vitro Testing. Available online: https://ims-usa.com/vitro-skin-substrates/vitro-skin/ (accessed on 12 April 2025).
- Marinova, K.; Slavova, T.; Stanimirova, R.; Danov, K. Artificial Skin Characterization for Cleansing Observation and Quantification. In Proceedings of the 33rd IFSCC Congress, Barcelona, Spain, 4–7 September 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S. Calculation of Interfacial Tensions in Polymer Systems. J. Polym. Sci. 1971, 34, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulik, S.P.; Haque, M.d.E.; Jana, P.K.; Das, A.R. Micellar Properties of Cationic Surfactants in Pure and Mixed State. J. Phys. Chem. 1996, 100, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christov, N.C.; Danov, K.D.; Kralchevsky, P.A.; Ananthapadmanabhan, K.P.; Lips, A. Maximum Bubble Pressure Method: Universal Surface Age and Transport Mechanisms in Surfactant Solutions. Langmuir 2006, 22, 7528–7542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battal, T.; Shearman, G.C.; Valkovska, D.; Bain, C.D. Determination of the Dynamic Surface Excess of a Homologous Series of Cationic Surfactants by Ellipsometry. Langmuir 2003, 19, 1244–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranieri, D.; Preisig, N.; Stubenrauch, C. On the Influence of Intersurfactant H-Bonds on Foam Stability: A Study with Technical Grade Surfactants. Tenside Surfact. Det. 2018, 55, 6–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunkenheimer, K.; Czichocki, G. On the Stability of Aqueous Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate Solutions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1993, 160, 509–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Lenick, A.J. Surfactants: Strategic Personal Care Ingredients; Allured Publishing Corporation: Carol Stream, IL, USA, 2014; pp. 43–91. [Google Scholar]
- Vollhardt, D.; Czichocki, G.; Rubert, R. Effect of the Molecular Structure on the Adsorption of Alkyl Ether Sulphates and Alkane Ether Sulphonates at the Air–Water Interface. Colloids Surf. A 1998, 142, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danov, K.D.; Kralchevsky, P.A.; Ananthapadmanabhan, K.P. Micelle–Monomer Equilibria in Solutions of Ionic Surfactants and in Ionic–Nonionic Mixtures: A Generalized Phase Separation model. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 207, 17–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catanoiu, G.; Carey, E.; Patil, S.R.; Engelskirchen, S.; Stubenrauch, C. Partition Coefficients of Nonionic Surfactants in Water/n-Alkane Systems. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 355, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varvil, J.; McCurry, P.; Pickens, C. Production of Alkyl Glucosides. In Handbook of detergents. Part F: Production; Zoller, U., Sosis, C., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009; pp. 69–82. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, W.; Heldreth, B.; Bergfeld, W.F.; Belsito, D.V.; Hill, R.A.; Klaassen, C.D.; Liebler, D.C.; Marks, J.G.; Shank, R.C. Safety Assessment of Alkyl PEG Sulfosuccinates as Used in Cosmetics. Int. J. Toxicol. 2015, 34, 70S–83S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuoka, K.; Noshiro, N.; Kuroki, H.; Tsuyuzaki, K.; Hashimoto, G. Vesicle Formation of Disodium Lauryl Sulfosuccinate. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 348, 118422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillan, K.W.; Goddard, E.D.; McKenzie, D.A. Oily Soil Removal from a Polyester Substrate by Aqueous Nonionic Surfactant Systems. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1979, 56, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolev, V.L.; Kochijashky, I.I.; Danov, K.D.; Kralchevsky, P.A.; Broze, G.; Mehreteab, A. Spontaneous Detachment of Oil Drops from Solid Substrates: Governing Factors. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 257, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yavrukova, V.I.; Shandurkov, D.N.; Marinova, K.G.; Kralchevsky, P.A.; Ung, Y.W.; Petkov, J.T. Cleaning Ability of Mixed Solutions of Sulfonated Fatty Acid Methyl Esters. J. Surfact. Deterg. 2020, 23, 617–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, C.A.; Raney, K.H. Solubilization-Emulsification Mechanisms of Detergency. Colloids Surf. A 1993, 74, 169–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raney, K.H.; Benton, W.J.; Miller, C.A. Optimum Detergency Conditions with Nonionic Surfactants. I. Ternary Water-Surfactant-Hydrocarbon Systems. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1987, 117, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.S.; Stanimirova, R.D.; Xu, H.; Petkov, J. Sulphonated Methyl Ester a Promising Surfactant for Detergency in Hard Water Conditions. HPC Today 2016, 11, 47–51. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Peña, L.; Guzmán, E. Physicochemical Aspects of the Performance of Hair-Conditioning Formulations. Cosmetics 2020, 7, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Somasundaran, P. Advances in Adsorption of Surfactants and their Mixtures at Solid/Solution Interfaces. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 123–126, 213–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halla, N.; Fernandes, I.P.; Heleno, S.A.; Costa, P.; Boucherit-Otmani, Z.; Boucherit, K.; Rodrigues, A.E.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R.; Barreiro, M.F. Cosmetics Preservation: A Review on Present Strategies. Molecules 2018, 23, 1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavrukova, V.I.; Radulova, G.M.; Danov, K.D.; Kralchevsky, P.A.; Xu, H.; Ung, Y.W.; Petkov, J.T. Rheology of Mixed Solutions of Sulfonated Methyl Esters and Betaine in Relation to the Growth of Giant Micelles and Shampoo Applications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 275, 102062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitrinova, Z.; Alexandrov, H.; Denkov, N.; Tcholakova, S. Effect of Counter-Ion on Rheological Properties of Mixed Surfactant Solutions. Colloids Surf. A 2022, 643, 128746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavrukova, V.; Cooban, E.; Blanco, I.; Pambou, E.; Marinova, K.; Petkov, J. Investigation of the detergency properties of mixtures of biocides and nonionic surfactants using a new simplified hard surface cleaning method. J. Surf. Det. 2025, 28, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brycki, B.E.; Kowalczyk, I.H.; Szulc, A.M.; Brycka, J.A. Quaternary alkylammonium salts as cleaning and disinfectant agents. Tenside Surfactant Deterg. 2018, 55, 55–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standard Operating Procedure for Preparation of Hard Water and Other Diluents for Antimicrobial Products; Environmental Science Center: Ft. Meade, MD, USA, 2019; SOP Number: MB-30-02, 08-21-19.
- Lu, G.W.; Valiveti, S.; Spence, J.; Zhuang, C.; Robosky, L.; Wade, K.; Love, A.; Hu, L.-Y.; Pole, D.; Mollan, M. Comparison of Artificial Sebum with Human and Hamster Sebum Samples. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 367, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walters, K.A.; Roberts, M.S. The Structure and Function of Skin. In Dermatological and Transdermal Formulations; Walters, K.A., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA; Taylor and Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002; pp. 1–40. [Google Scholar]





| Surfactant | CMC, wt% | pH Range | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Air/Water | Dimethicone/Water | ||
| CG | 0.0037 | 0.0054 | 6.7–10.8 |
| DSLSS | 0.0012 | >0.1 | 7.0–5.0 |
| SLES | 0.079 | >0.1 | 7.0–6.0 |
| DTAB | 0.49 | 0.49 | 6.5–5.7 |
| Composition, wt% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Substances | F-G | F-ES | F-SS | F-G+ES | F-G+SS |
| water | qs to 100 | qs to 100 | qs to 100 | qs to 100 | qs to 100 |
| CG | 12 | – | – | 6 | 6 |
| SLES | – | 12 | – | 6 | – |
| DSLSS | – | - | 12 | - | 6 |
| Glycerin | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| NaCl | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Na Benzoate | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Citric acid | qs | qs | qs | qs | qs |
| PC | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 |
| Surfactants, 1 wt% | Contact Angle, θ, deg | cosθ | , mN/m | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CG | 0 | 1 | 4.5 | 6.0 |
| F-G | 0 | 1 | 4.5 | 5.6 |
| SLES | 63.3 | 0.45 | 10.4 | 6.8 |
| F-ES | 63.5 | 0.44 | 9.3 | 5.5 |
| DSLSS | 56.5 | 0.55 | 5.4 | 4.8 |
| F-SS | 61.2 | 0.48 | 5.2 | 4.7 |
| 1:1 CG+SLES | 66.5 | 0.40 | 7.7 | 10.4 |
| F-G+ES | 61.3 | 0.48 | 7.3 | 5.5 |
| 1:1 CG+DSLSS | 0 | 1 | 5.2 | 6.8 |
| F-G+SS | 47.1 | 0.68 | 4.3 | 4.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Slavova, T.; Stanimirova, R.; Marinova, K.; Danov, K. Cleansing Mechanisms and Efficacy on Artificial Skin. Molecules 2025, 30, 1813. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30081813
Slavova T, Stanimirova R, Marinova K, Danov K. Cleansing Mechanisms and Efficacy on Artificial Skin. Molecules. 2025; 30(8):1813. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30081813
Chicago/Turabian StyleSlavova, Tatiana, Rumyana Stanimirova, Krastanka Marinova, and Krassimir Danov. 2025. "Cleansing Mechanisms and Efficacy on Artificial Skin" Molecules 30, no. 8: 1813. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30081813
APA StyleSlavova, T., Stanimirova, R., Marinova, K., & Danov, K. (2025). Cleansing Mechanisms and Efficacy on Artificial Skin. Molecules, 30(8), 1813. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30081813










