Antibacterial Activity and Chemical Composition of Popular Plant Essential Oils and Their Positive Interactions in Combination
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
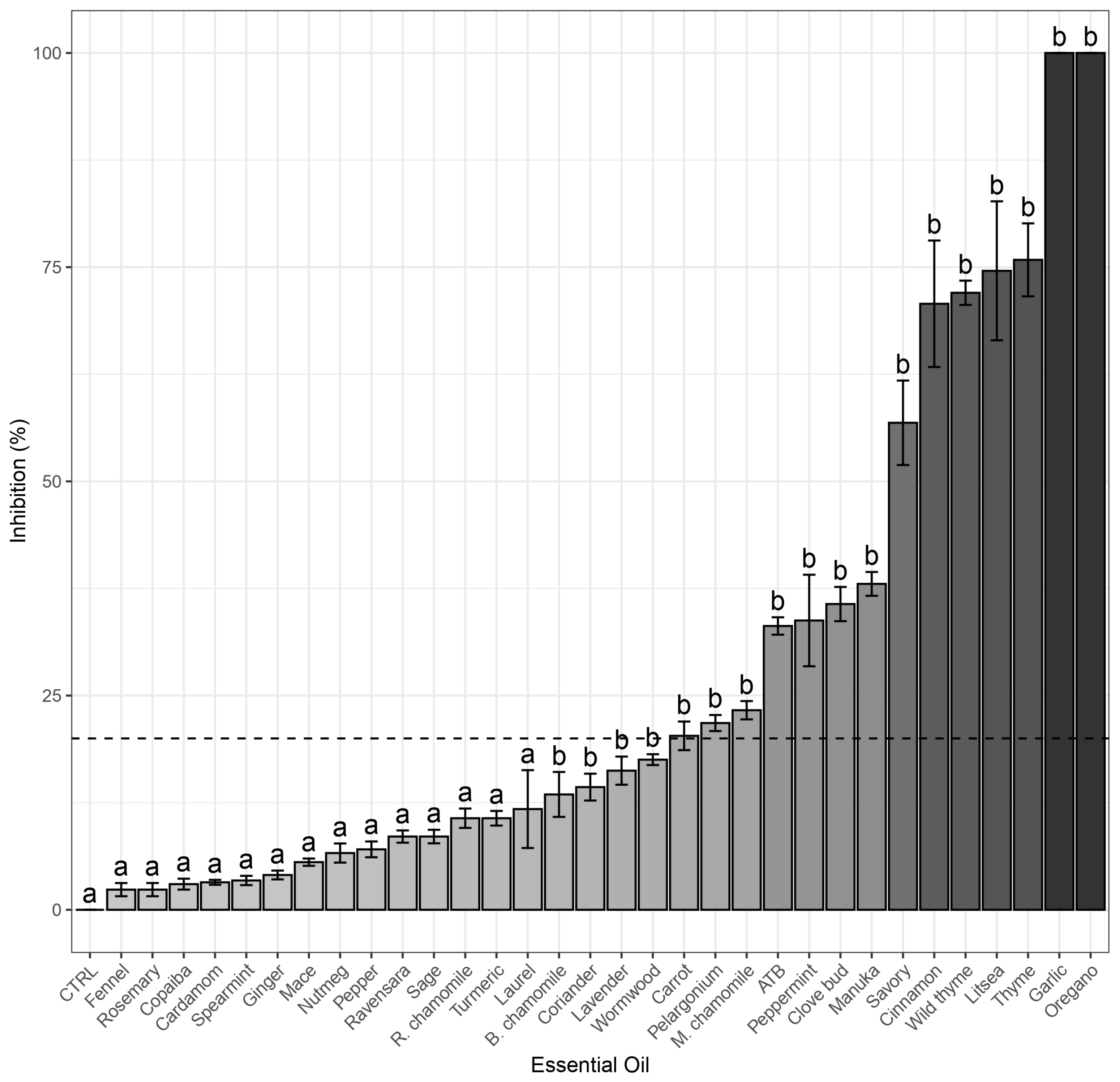
2.1. Screening of EOs for Their Antimicrobial Activity (Agar Disc Diffusion Method)
2.2. Determination of MIC of Selected EOs by Broth Microdilution Assay
2.3. Interactions of EOs in Mixtures
2.4. The Composition of Selected EOs
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strains Used in the Study
4.2. EOs Used in the Study
4.3. Agar Disc Diffusion Method
4.4. Broth Microdilution Assay
4.5. Positive Interactions of the Most Efficient EOs in Combinations
4.6. Determination of MCs of the Selected EOs
4.7. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rees, G.; Barrett, D.C.; Sánchez-Vizcaíno, F.; Reyher, K. Measuring Antimicrobial Use on Dairy Farms: A Method Comparison Cohort Study. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 4715–4726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caniça, M.; Manageiro, V.; Abriouel, H.; Moran-Gilad, J.; Franz, C.M. Antibiotic Resistance in Foodborne Bacteria. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 84, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghernaout, D.; Elboughdiri, N. Antibiotics Resistance in Water Mediums: Background, Facts, and Trends. Appl. Eng. 2020, 4, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Hiltunen, T.; Virta, M.; Laine, A.-L. Antibiotic Resistance in the Wild: An Eco-Evolutionary Perspective. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2017, 372, 20160039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Salinas, S.; Elizondo-Castillo, H.; Arruebo, M.; Mendoza, G.; Irusta, S. Evaluation of the Antimicrobial Activity and Cytotoxicity of Different Components of Natural Origin Present in Essential Oils. Molecules 2018, 23, 1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dadgostar, P. Antimicrobial Resistance: Implications and Costs. Infect. Drug Resist. 2019, 12, 3903–3910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burt, S. Essential Oils: Their Antibacterial Properties and Potential Applications in Foods—A Review. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2004, 94, 223–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavela, R.; Benelli, G. Essential Oils as Ecofriendly Biopesticides? Challenges and Constraints. Trends Plant Sci. 2016, 21, 1000–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perricone, M.; Arace, E.; Corbo, M.R.; Sinigaglia, M.; Bevilacqua, A. Bioactivity of Essential Oils: A Review on Their Interaction with Food Components. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakkali, F.; Averbeck, S.; Averbeck, D.; Idaomar, M. Biological Effects of Essential Oils–a Review. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 446–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrar, N.; Oukil, N.; Bedjou, F. Antioxidant and Antibacterial Activities of Thymus Numidicus and Salvia Officinalis Essential Oils Alone or in Combination. Ind. Crops Prod. 2016, 88, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chantawannakul, P.; Puchanichanthranon, T.; Wongsiri, S. Inhibitory Effects of Some Medicinal Plant Extracts on the Growth of Ascosphaera Apis. In Proceedings of the III WOCMAP Congress on Medicinal and Aromatic Plants-Volume 4: Targeted Screening of Medicinal and Aromatic Plants Economics and Law, Chiang Mai, Thailand, 3–7 February 2003; Volume 678, pp. 183–189. [Google Scholar]
- Lambert, R.; Skandamis, P.N.; Coote, P.J.; Nychas, G. A Study of the Minimum Inhibitory Concentration and Mode of Action of Oregano Essential Oil, Thymol and Carvacrol. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2001, 91, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdallah, F.B.; Lagha, R.; Gaber, A. Biofilm Inhibition and Eradication Properties of Medicinal Plant Essential Oils against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Clinical Isolates. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oussalah, M.; Caillet, S.; Saucier, L.; Lacroix, M. Inhibitory Effects of Selected Plant Essential Oils on the Growth of Four Pathogenic Bacteria: E. Coli O157: H7, Salmonella Typhimurium, Staphylococcus Aureus and Listeria Monocytogenes. Food Control. 2007, 18, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thielmann, J.; Muranyi, P.; Kazman, P. Screening Essential Oils for Their Antimicrobial Activities against the Foodborne Pathogenic Bacteria Escherichia Coli and Staphylococcus Aureus. Heliyon 2019, 5, e01860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyldgaard, M.; Mygind, T.; Meyer, R.L. Essential Oils in Food Preservation: Mode of Action, Synergies, and Interactions with Food Matrix Components. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikulášová, M.; Chovanová, R.; Vaverková, Š. Synergism between Antibiotics and Plant Extracts or Essential Oils with Efflux Pump Inhibitory Activity in Coping with Multidrug-Resistant Staphylococci. Phytochem. Rev. 2016, 15, 651–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apolónio, J.; Faleiro, M.L.; Miguel, M.G.; Neto, L. No Induction of Antimicrobial Resistance in Staphylococcus Aureus and Listeria Monocytogenes during Continuous Exposure to Eugenol and Citral. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2014, 354, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; He, T.; Wang, X.; Shen, M.; Yan, X.; Fan, S.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Xu, X.; Sui, H.; et al. Traditional Uses, Chemical Constituents and Biological Activities of Plants from the Genus Thymus. Chem. Biodivers. 2019, 19, e1900254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khwaza, V.; Aderibigbe, B.A. Antibacterial Activity of Selected Essential Oil Components and Their Derivatives: A Review. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, J.; Barry-Ryan, C.; Bourke, P. The Antimicrobial Efficacy of Plant Essential Oil Combinations and Interactions with Food Ingredients. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2008, 124, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutlu-Ingok, A.; Tasir, S.; Seven, A.; Akgun, N.; Karbancioglu-Guler, F. Evaluation of the Single and Combined Antibacterial Efficiency of Essential Oils for Controlling Campylobacter Coli, Campylobacter Jejuni, Escherichia Coli, Staphylococcus Aureus, and Mixed Cultures. Flavour Fragr. J. 2019, 34, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brazel, M.; Desai, A.; Are, A.; Motaparthi, K. Staphylococcal Scalded Skin Syndrome and Bullous Impetigo. Medicina 2021, 57, 1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenwood, D.; Slack, R.C.; Barer, M.R.; Irving, W.L. Medical Microbiology E-Book: A Guide to Microbial Infections: Pathogenesis, Immunity, Laboratory Diagnosis and Control; with STUDENT CONSULT Online Access; Elsevier Health Sciences: London, UK, 2012; ISBN 0-7020-5119-5. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, J.R.; Russo, T.A. Extraintestinal Pathogenic Escherichia Coli:“The Other Bad E Coli”. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 2002, 139, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penha, C.B.; Bonin, E.; da Silva, A.F.; Hioka, N.; Zanqueta, É.B.; Nakamura, T.U.; de Abreu Filho, B.A.; Campanerut-Sá, P.A.Z.; Mikcha, J.M.G. Photodynamic Inactivation of Foodborne and Food Spoilage Bacteria by Curcumin. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 76, 198–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darbre, P.D.; Harvey, P.W. Parabens Can Enable Hallmarks and Characteristics of Cancer in Human Breast Epithelial Cells: A Review of the Literature with Reference to New Exposure Data and Regulatory Status. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2014, 34, 925–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, J.; Ma, X.; Xie, J. Review on Natural Preservatives for Extending Fish Shelf Life. Foods 2019, 8, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.; Wu, L.; Guan, W. Dietary Nitrates, Nitrites, and Nitrosamines Intake and the Risk of Gastric Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2015, 7, 9872–9895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Atki, Y.; Aouam, I.; El Kamari, F.; Taroq, A.; Nayme, K.; Timinouni, M.; Lyoussi, B.; Abdellaoui, A. Antibacterial Activity of Cinnamon Essential Oils and Their Synergistic Potential with Antibiotics. J. Adv. Pharm. Technol. Res. 2019, 10, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, P.S.X.; Lim, S.H.E.; Hu, C.P.; Yiap, B.C. Combination of Essential Oils and Antibiotics Reduce Antibiotic Resistance in Plasmid-Conferred Multidrug Resistant Bacteria. Phytomedicine 2013, 20, 710–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sales, J.A.; Pashazadeh, M. Study of Chemical Composition and Antimicrobial Properties of Rosemary (Rosmarinus Officinalis) Essential Oil on Staphylococcus Aureus and Escherichia Coli in Vitro. Int. J. Life Sci. Biotechnol. 2020, 3, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazzaro, F.; Fratianni, F.; De Martino, L.; Coppola, R.; De Feo, V. Effect of Essential Oils on Pathogenic Bacteria. Pharmaceuticals 2013, 6, 1451–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langeveld, W.T.; Veldhuizen, E.J.; Burt, S.A. Synergy between Essential Oil Components and Antibiotics: A Review. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 40, 76–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raikwar, G.; Kumar, D.; Mohan, S.; Dahiya, P. Synergistic Potential of Essential Oils with Antibiotics for Antimicrobial Resistance with Emphasis on Mechanism of Action: A Review. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2024, 61, 103384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Virgous, C.; Si, H. Synergistic Anti-Inflammatory Effects and Mechanisms of Combined Phytochemicals. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2019, 69, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayari, S.; Shankar, S.; Follett, P.; Hossain, F.; Lacroix, M. Potential Synergistic Antimicrobial Efficiency of Binary Combinations of Essential Oils against Bacillus Cereus and Paenibacillus Amylolyticus-Part A. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 141, 104008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakkas, H.; Papadopoulou, C. Antimicrobial Activity of Basil, Oregano, and Thyme Essential Oils. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 27, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cáceres, M.; Hidalgo, W.; Stashenko, E.; Torres, R.; Ortiz, C. Essential Oils of Aromatic Plants with Antibacterial, Anti-Biofilm and Anti-Quorum Sensing Activities against Pathogenic Bacteria. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharopov, F.S.; Zhang, H.; Setzer, W.N. Composition of Geranium (Pelargonium Graveolens) Essential Oil from Tajikistan. Am. J. Essent. Oils Nat. Prod. 2014, 2, 13–16. [Google Scholar]
- Rosato, A.; Vitali, C.; De Laurentis, N.; Armenise, D.; Milillo, M.A. Antibacterial Effect of Some Essential Oils Administered Alone or in Combination with Norfloxacin. Phytomedicine 2007, 14, 727–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigos, M.; Wasiela, M.; Kalemba, D.; Sienkiewicz, M. Antimicrobial Activity of Geranium Oil against Clinical Strains of Staphylococcus Aureus. Molecules 2012, 17, 10276–10291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Essid, R.; Hammami, M.; Gharbi, D.; Karkouch, I.; Hamouda, T.B.; Elkahoui, S.; Limam, F.; Tabbene, O. Antifungal Mechanism of the Combination of Cinnamomum Verum and Pelargonium Graveolens Essential Oils with Fluconazole against Pathogenic Candida Strains. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 6993–7006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, J.; Lee, C.; Lee, H. Food Protective Effect of Geraniol and Its Congeners against Stored Food Mites. J. Food Prot. 2009, 72, 1468–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabuseenivasan, S.; Jayakumar, M.; Ignacimuthu, S. In Vitro Antibacterial Activity of Some Plant Essential Oils. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2006, 6, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloucek, P.; Smid, J.; Flesar, J.; Havlik, J.; Titera, D.; Rada, V.; Drabek, O.; Kokoska, L. In Vitro Inhibitory Activity of Essential Oil Vapors against Ascosphaera Apis. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2012, 7, 1934578X1200700237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hýbl, M.; Bohatá, A.; Rádsetoulalová, I.; Kopecký, M.; Hoštičková, I.; Vaníčková, A.; Mráz, P. Evaluating the Efficacy of 30 Different Essential Oils against Varroa Destructor and Honey Bee Workers (Apis mellifera). Insects 2021, 12, 1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radünz, M.; da Trindade, M.L.M.; Camargo, T.M.; Radünz, A.L.; Borges, C.D.; Gandra, E.A.; Helbig, E. Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Activity of Unencapsulated and Encapsulated Clove (Syzygium aromaticum, L.) Essential Oil. Food Chem. 2019, 276, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchese, A.; Barbieri, R.; Coppo, E.; Orhan, I.E.; Daglia, M.; Nabavi, S.F.; Izadi, M.; Abdollahi, M.; Nabavi, S.M.; Ajami, M. Antimicrobial Activity of Eugenol and Essential Oils Containing Eugenol: A Mechanistic Viewpoint. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 43, 668–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mraz, P.; Bohata, A.; Hostickova, I.; Kopecky, M.; Zabka, M.; Hybl, M.; Curn, V. Inhibitory Effect of Selected Botanical Compounds on the Honey Bee Fungal Pathogen Ascosphaera Apis. In Proceedings of the MendelNet, Brno, Czech Republic, 6–7 November 2019; pp. 6–7. [Google Scholar]
- Mráz, P.; Žabka, M.; Hoštičková, I.; Kopecký, M.; Bohatá, A.; Tomčala, A.; Hýbl, M. Effect of Selected Botanical Compounds on Ascosphaera Apis and Apis Mellifera. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 197, 116649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Woo, S.; Hong, I.; Han, S.; Byoun, G.; Thapa, R.; Lee, M. Effects of Limonene Composition for Controlling of the Varroa Destructor and Tropilaelaps Clareae in Apis Mellifera Hives. Korean J. Apic. 2012, 27, 137–142. [Google Scholar]
- Leite, A.M.; Lima, E.d.O.; Souza, E.L.d.; Diniz, M.d.F.F.M.; Trajano, V.N.; Medeiros, I.A.d. Inhibitory Effect of Beta-Pinene, Alpha-Pinene and Eugenol on the Growth of Potential Infectious Endocarditis Causing Gram-Positive Bacteria. Rev. Bras. Ciências Farm. 2007, 43, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Li, C.; Dai, J.; Cui, H.; Lin, L. Antibacterial Activity and Mechanism of Litsea Cubeba Essential Oil against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA). Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 130, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.-T.; Yang, T.-S. Antimicrobial Impact of the Components of Essential Oil of Litsea Cubeba from Taiwan and Antimicrobial Activity of the Oil in Food Systems. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2012, 156, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, M.; Chaves, F.; Almeida, C.A.; Bizzo, H.R.; Duarte, R.S.; Campos-Takaki, G.M.; Alviano, C.S.; Alviano, D.S. Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Activities of 7-Hydroxy-Calamenene-Rich Essential Oils from Croton Cajucara Benth. Molecules 2013, 18, 1128–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, B.; Marques, A.; Ramos, C.; Neng, N.R.; Nogueira, J.M.; Saraiva, J.A.; Nunes, M.L. Chemical Composition and Antibacterial and Antioxidant Properties of Commercial Essential Oils. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 43, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanner, J.; Schmidt, E.; Bail, S.; Jirovetz, L.; Buchbauer, G.; Gochev, V.; Girova, T.; Atanasova, T.; Stoyanova, A. Chemical Composition, Olfactory Evaluation and Antimicrobial Activity of Selected Essential Oils and Absolutes from Morocco. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2010, 5, 1934578X1000500903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatwalkar, S.B.; Mondal, R.; Krishna, S.B.N.; Adam, J.K.; Govender, P.; Anupam, R. Antibacterial Properties of Organosulfur Compounds of Garlic (Allium Sativum). Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 613077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seydim, A.; Sarikus, G. Antimicrobial Activity of Whey Protein Based Edible Films Incorporated with Oregano, Rosemary and Garlic Essential Oils. Food Res. Int. 2006, 39, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Díez, J.; Alheiro, J.; Pinto, A.L.; Soares, L.; Falco, V.; Fraqueza, M.J.; Patarata, L. Influence of Food Characteristics and Food Additives on the Antimicrobial Effect of Garlic and Oregano Essential Oils. Foods 2017, 6, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubec, R.; Svobodová, M.; Velíšek, J. Gas Chromatographic Determination of S-Alk (En) Ylcysteine Sulfoxides. J. Chromatogr. A 1999, 862, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, T.; Singh, P.; Pant, S.; Chauhan, N.; Lohani, H. Potentiation of Antimicrobial Activity of Ciprofloxacin by Pelargonium Graveolens Essential Oil against Selected Uropathogens. Phytother. Res. 2011, 25, 1225–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, J. Constituents of the Essential Oils of Garlic and Citronella and Their Vapor-Phase Inhibition Mechanism against S. Aureus. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2019, 25, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Kim, H.; Beuchat, L.R.; Ryu, J.-H. Synergistic Antimicrobial Activities of Essential Oil Vapours against Penicillium Corylophilum on a Laboratory Medium and Beef Jerky. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2019, 291, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Akacha, B.; Michalak, M.; Generalić Mekinić, I.; Kačániová, M.; Chaari, M.; Brini, F.; Ben Saad, R.; Mnif, W.; Garzoli, S.; Ben Hsouna, A. Mixture Design of A-pinene, A-terpineol, and 1, 8-cineole: A Multiobjective Response Followed by Chemometric Approaches to Optimize the Antibacterial Effect against Various Bacteria and Antioxidant Activity. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 12, 574–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorman, H.; Deans, S.G. Antimicrobial Agents from Plants: Antibacterial Activity of Plant Volatile Oils. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2000, 88, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Li, F.; Gu, D.; Wang, W.; Huang, J.; Jiao, X. Antimicrobial Effect and the Mechanism of Diallyl Trisulfide against Campylobacter Jejuni. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Niu, H.; Zhang, W.; Mu, H.; Sun, C.; Duan, J. Synergy among Thymol, Eugenol, Berberine, Cinnamaldehyde and Streptomycin against Planktonic and Biofilm-associated Food-borne Pathogens. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 60, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Ji, B.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, H.; Yang, Z.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Yan, W. The Antibacterial Effect of Cinnamaldehyde, Thymol, Carvacrol and Their Combinations against the Foodborne Pathogen Salmonella Typhimurium. J. Food Saf. 2007, 27, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Khan, M.A.; Xie, Z.; Tao, S.; Li, Y.; Liang, L. A Peppermint Oil Emulsion Stabilized by Resveratrol-Zein-Pectin Complex Particles: Enhancing the Chemical Stability and Antimicrobial Activity in Combination with the Synergistic Effect. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 103, 105675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.-K.; Yap, P.S.-X.; Krishnan, T.; Yusoff, K.; Kok-Gan, C.; Yap, W.-S.; Kok-Song, L.; Swee-Hua, E.L. Mode of Action: Synergistic Interaction of Peppermint (Mentha × Piperita L. Carl) Essential Oil and Meropenem Against Plasmid-Mediated Resistant E. Col Shun-Kai Yang, Polly Soo-Xi Yap, Thiba Krishnan, Khatijah Yusoff, Kok-Gan Chan, Wai-Sum Yap, Kok-Song Lai and Swee-Hua Erin Lim. Rec. Nat. Prod. 2018, 12, 582. [Google Scholar]
- Basavegowda, N.; Baek, K.-H. Combination Strategies of Different Antimicrobials: An Efficient and Alternative Tool for Pathogen Inactivation. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosakowska, O.; Węglarz, Z.; Styczyńska, S.; Synowiec, A.; Gniewosz, M.; Bączek, K. Activity of Common Thyme (Thymus vulgaris L.), Greek Oregano (Origanum vulgare L. ssp. Hirtum), and Common Oregano (Origanum vulgare L. ssp. Vulgare) Essential Oils against Selected Phytopathogens. Molecules 2024, 29, 4617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| S. aureus | E. coli | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| EO | MIC (µg/mL) | EO | MIC (µg/mL) |
| Oregano | 128 | Oregano | 128 |
| Garlic | 128 | Thyme | 256 |
| Pelargonium | 256 | Wild thyme | 512 |
| Cinnamon | 256 | Clove bud | 512 |
| Thyme | 256 | Peppermint | 512 |
| Wild thyme | 256 | Cinnamon | 1024 |
| Clove bud | 512 | Savory | 1024 |
| Savory | 512 | ||
| Manuka | 512 | ||
| Peppermint | 1024 | ||
| Litsea cubeba | 1024 | ||
| Carrot | 4096 | ||
| Moroccan chamomile | 4096 | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus | Escherichia coli | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EO Mixtures | MIC (µg/mL) | FIC (µg/mL) | EO Mixtures | MIC (µg/mL) | FIC (µg/mL) |
| Pelargonium/Garlic | 32 | 0.375 syn. | Thyme/Oregano | 64 | 0.75 add. |
| Garlic/Moroccan chamomile | 64 | 0.516 add. | Peppermint/Wild thyme | 256 | 1 add. |
| Moroccan chamomile/Oregano | 64 | 0.516 add. | |||
| Carrot/Clove bud | 256 | 0.562 add. | |||
| Essential Oil | Main Components (%) |
|---|---|
| Carrot | Carotol (30.29), α-Pinene (15.46), Sabinene (10.22), β-Caryophyllene (8.31), β-Bisabolene (5.63), β-Pinene (3.08), and Caryophyllene Oxide (2.07). |
| Cinnamon | Trans-cinnamaldehyde (77.69), Eugenol (7.50), Limonene (2.51), and β-Caryophyllene (2.02) |
| Clove Bud | Eugenol (86.63), β-Caryophyllene (10.21), and α-Humulene (2.41). |
| Garlic | Diallyl disulfide (34.27), Diallyl trisulfide (34.20), and Diallyl sulfide (18.89). |
| Litsea | Citral A (Geranial) (39.04), Citral B (Neral) (29.36), and Limonene (13.74). |
| Manuka | Calamenene (17.92), Leptospermone (16.02), Flaveson (5.92), α-Selinene (4.62), Cadina-1,4-diene (4.50), β-Selinene (4.42), α-Copaene (4.40), Cadina-3,5-diene (3.77), α-Cubebene (2.67), Cadina-1(6),4-diene (2.60), and β-Caryophyllene (2.03). |
| Moroccan chamomile | α-Pinene (20.14), Germacrene (10.23), Santolina Alcohol (7.41), (E)-β-Farnesene (6.42), 1,8-Cineol (6.22), Fenchone (5.46), Limonene (5.27), and Myrcene (4.08). |
| Oregano | Carvacrol (73.56), p-Cymene (6.97), γ-Terpinene (6.03), Myrcene (2.16), and β-Caryophyllene (2.14). |
| Pelargonium | Citronellol (33.53), Geraniol (15.36), Citronellyl formate (7.81), 10-epi-gamma-Eudesmol (5.37), Linalool (5.22), Isomenthone (5.16), Geranyl formate (3.29), and Menthone (2.35). |
| Peppermint | Limonene (38.02), Menthol (16.42), α-Pinene (15.93), β-Pinene (11.47), Menthone (5.65), and Isomenthone (2.52). |
| Savory | Carvacrol (41.67), γ-Terpinene (35.82), p-Cymene (11.73), α-Terpinene (2.41), and Myrcen (2.26). |
| Thyme | Thymol (46.30), p-Cymene (17.02), β-Caryophyllene (7.41), γ-Terpinene (5.83), Linalool (4.93), and Carvacrol (2.38). |
| Wild thyme | Thymol (16.33), Carvacrol (15.38), p-Cymene (15.01), Geraniol (10.62), γ-Terpinene (10.30), Linalool (4.94), Geranyl acetate (4.20), β-Caryophyllene (2.35), Borneol (2.33), and Terpinen-4-ol (2.13). |
| Common Name | Latin Name | Origin | Part of Plant | Voucher |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Black pepper | Piper nigrum | India | berry | 2017115374 |
| Blue chamomile | Matricaria chamomilla | Egypt | flower | 2018108255 |
| Carrot | Daucus carota | France | seeds | 2019100662 |
| Cinnamon | Cinnamomum zeylanicum | Sri Lanka | bark | 2018112546 |
| Clove Bud | Eugenia caryophyllata | Indonesia | leaves, buds, twigs | 2018113001 |
| Copaiba | Copaifera reticulata | Brazil | resin | 2018112037 |
| Coriander | Coriandrum sativum | Russia | seeds | 2019109145 |
| Fennel | Foeniculum vulgare | Moldova | seeds | 2017107690 |
| Garlic | Allium sativum | China | bulb | 2017107690 |
| Ginger | Zingiber officinale | Sri Lanka | rhizome | 2019114043 |
| Green cardamom | Elettaria cardamomum | India | seeds | 2017103290 |
| Laurel | Laurus nobilis | Turkey | leaves | 2018113872 |
| Lavender | Lavandula angustifolia | France | flowering herb | 2018113954 |
| Litsea | Litsea cubeba | China | fruits | 2018104405 |
| Mace | Myristica fragrans | Indonesia | flower | 2019102915 |
| Manuka | Leptospermum scoparium | New Zealand | leaves and twigs | 2019113318 |
| Moroccan chamomile | Ormenis multicaulis | Morocco | herb | 2017114089 |
| Nutmeg | Myristica fragrans | Indonesia | seeds | 2017110236 |
| Oregano | Origanum vulgare | Moldova | herb | 2017108440 |
| Pelargonium | Pelargonium graveolens | Egypt | leaves, flowers | 2017108440 |
| Peppermint | Mentha piperita | India | herb | 2016109735 |
| Ravensara | Ravensara aromatica | Madagascar | leaves and twigs | 2018108724 |
| Roman chamomile | Anthemis nobilis | Italy | flower | 2016110437 |
| Rosemary | Rosmarinus officinalis | Tunisia | herb | 2017101984 |
| Sage | Salvia officinalis | Romania | leaves | 2018110420 |
| Savory | Satureja montana | Germany | herb | 2016113787 |
| Spearmint | Mentha spicata crispa | USA | flowering herb | 2018111114 |
| Thyme | Thymus vulgaris | EU | herb | 2018111114 |
| Turmeric | Curcuma longa | India | root | 2019111945 |
| Wild thyme | Thymus serpyllum | Albania | herb | 2018109107 |
| Wormwood | Artemisia absinthium | USA | herb | 2020101503 |
| Obtained Effect | FIC Index |
|---|---|
| Synergy | ≤0.5 |
| Addition | 0.5–1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mráz, P.; Kopecký, M.; Hasoňová, L.; Hoštičková, I.; Vaníčková, A.; Perná, K.; Žabka, M.; Hýbl, M. Antibacterial Activity and Chemical Composition of Popular Plant Essential Oils and Their Positive Interactions in Combination. Molecules 2025, 30, 1864. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30091864
Mráz P, Kopecký M, Hasoňová L, Hoštičková I, Vaníčková A, Perná K, Žabka M, Hýbl M. Antibacterial Activity and Chemical Composition of Popular Plant Essential Oils and Their Positive Interactions in Combination. Molecules. 2025; 30(9):1864. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30091864
Chicago/Turabian StyleMráz, Petr, Marek Kopecký, Lucie Hasoňová, Irena Hoštičková, Alena Vaníčková, Kristýna Perná, Martin Žabka, and Marian Hýbl. 2025. "Antibacterial Activity and Chemical Composition of Popular Plant Essential Oils and Their Positive Interactions in Combination" Molecules 30, no. 9: 1864. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30091864
APA StyleMráz, P., Kopecký, M., Hasoňová, L., Hoštičková, I., Vaníčková, A., Perná, K., Žabka, M., & Hýbl, M. (2025). Antibacterial Activity and Chemical Composition of Popular Plant Essential Oils and Their Positive Interactions in Combination. Molecules, 30(9), 1864. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30091864







