Binding of Natural and Synthetic Polyphenols to Human Dihydrofolate Reductase
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Structural Requirements for the Binding of Tea Polyphenols to Human DHFR
2.2. Binding of Synthetic Catechins to Human DHFR
2.3. Binding of Natural Flavonoids to Human DHFR
2.4. Physiological and Therapeuthical Relevance
3. Experimental Section
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Mukhtar, H; Ahmad, N. Tea polyphenols: Prevention of cancer and optimizing health. Am. J. Clin. Nutr 2000, 71, 1698S–1702S. [Google Scholar]
- Fujiki, H; Sugunuma, M; Imai, K; Nakachi, K. Green tea: Cancer preventive beverage and/or drug. Cancer Lett 2002, 188, 9–13. [Google Scholar]
- Mabe, K; Yamada, M; Oguni, I; Takahashi, T. In vitro and in vivo activities of tea catechins against Helicobacter Pylori. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother 1999, 43, 1788–1791. [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton-Miller, JMT. Anti-cariogenic properties of tea (Camellia Sinensis). J. Med. Microbiol 2001, 50, 299–302. [Google Scholar]
- Yam, TS; Hamilton-Miller, JMT; Shah, S. The effect of a component of tea (Camellia Sinensis) on methicillin resistance, PBP2′ synthesis, and beta-lactamase production in Staphylococcus Aureus. J. Antimicrob. Chemother 1998, 42, 211–216. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, YD; Ellis, LM. Inhibition of tumour invasion and angiogenesis by epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), a major component of green tea. Int. J. Exp. Path 2001, 82, 309–316. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, S; Hussain, T; Makhtar, H. Molecular pathway for (-)epigallocatechin-3-gallate-induced cell arrest and apoptosis of human prostate carcinoma cells. Arch. Biochem. Biophys 2003, 410, 177–185. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, GY; Liao, J; Kim, K; Yurkow, EJ; Yang, CS. Inhibition of growth and induction of apoptosis in human cancer cell lines by tea polyphenols. Carcinogenesis 1998, 19, 611–616. [Google Scholar]
- Lockshin, A; Moran, RG; Danenberg, PV. Thymidylate synthetase purified to homogeneity from human leukemic cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1979, 76, 750–754. [Google Scholar]
- Blakley, RL. The Biochemistry of Folic Acid and Related Pteridines; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Schnell, JR; Dyson, HJ; Wright, PE. Structure, dynamics, and catalytic function of dihydrofolate reductase. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct 2004, 33, 119–140. [Google Scholar]
- Navarro-Perán, E; Cabezas-Herrera, J; García-Cánovas, F; Durrant, MC; Thorneley, RNF; Rodríguez-López, JN. The antifolate activity of tea catechins. Cancer Res 2005, 65, 2059–2064. [Google Scholar]
- Navarro-Perán, E; Cabezas-Herrera, J; Hiner, ANP; Sadunishvili, T; García-Cánovas, F; Rodríguez-López, JN. Kinetics of the inhibition of bovine liver dihydrofolate reductase by tea catechins: Origin of slow-binding inhibition and pH studies. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 7512–7525. [Google Scholar]
- Berman, HM; Westbrook, J; Feng, Z; Gilliland, G; Bhat, TN; Weissig, H; Shindyalov, IN; Bourne, PE. The protein data bank. Nucleic Acids Res 2000, 28, 235–242. [Google Scholar]
- Cody, V; Luft, JR; Pangborn, W; Gangjee, A; Queener, SF. Structure determination of tetrahydroquinazoline antifolates in complex with human and Pneumocystis Carinii dihydrofolate reductase: Correlations between enzyme selectivity and stereochemistry. Acta Cryst. Sect. D 2004, 60, 646–655. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, WS; Cody, V; Galitsky, N; Luft, JR; Pangborn, W; Chunduru, SK; Spencer, HT; Appleman, JR; Blakley, RL. Methotrexate-resistant variants of human dihydrofolate reductase with substitutions of leucine 22. J. Biol. Chem 1995, 270, 5057–5064. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, J; Lu, H; Meng, X; Ryu, JH; Hara, Y; Yang, CS. Stability, cellular uptake, biotransformation, and efflux of tea polyphenol (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate in HT-29 human colon adenocarcinoma cells. Cancer Res 2002, 62, 7241–7246. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-del-Campo, L; Otón, F; Tárraga, A; Cabezas-Herrera, J; Chazarra, S; Rodríguez-López, JN. Synthesis and biological activity of a 3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoyl ester analogue of epicatechin-3-gallate. J. Med. Chem 2008, 51, 2018–2026. [Google Scholar]
- Timbola, AK; de Souza, CD; Giacomelli, C; Spinelli, A. Electrochemical oxidation of quercetin in hydro-alcoholic solution. J. Braz. Chem. Soc 2006, 17, 139–148. [Google Scholar]
- Middleton, E, Jr; Kandaswami, C; Theoharides, TC. The effects of plant flavonoids on mammalian cells: Implications for inflammation, heart disease, and cancer. Pharmacol. Rev 2000, 52, 673–751. [Google Scholar]
- Ramos, S. Effects of dietary flavonoids on apoptotic pathways related to cancer chemoprevention. J. Nutr. Biochem 2007, 18, 427–442. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, JA; Kim, JY; Lee, JY; Kang, CM; Kwon, HJ; Yoo, YD; Kim, TW; Lee, YS; Lee, SJ. Induction of cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human breast cancer cells by quercetin. Int. J. Oncol 2001, 19, 837–844. [Google Scholar]
- Ong, CS; Tran, E; Nguyen, TT; Ong, CK; Lee, SK; Lee, JJ; Ng, CP; Leong, C; Huynh, H. Quercetin-induced growth inhibition and cell death in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells are associated with increase in bad and hypophosphorylated retinoblastoma expressions. Oncol. Rep 2004, 11, 727–733. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, TT; Tran, E; Nguyen, TH; Do, PT; Huynh, TH; Huynh, H. The role of activated MEK-ERK pathway in quercetin-induced growth inhibition and apoptosis in A549 lung cancer cells. Carcinogenesis 2004, 25, 647–659. [Google Scholar]
- Hertog, MG; Hollman, PC; Katan, MB; Kromhout, D. Intake of potentially anticarcinogenic flavonoids and their determinants in adults in The Netherlands. Nutr. Cancer 1993, 20, 21–29. [Google Scholar]
- Manach, C; Scalbert, A; Morand, C; Remesy, C; Jimenez, L. Polyphenols: Food sources and bioavailability. Am. J. Clin. Nutr 2004, 79, 727–747. [Google Scholar]
- Sueoka, N; Suganuma, M; Sueoka, E; Okabe, S; Matsuyama, S; Imai, K; Nakachi, K; Fujiki, H. A new function of green tea: Prevention of lifestyle-related diseases. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci 2001, 928, 274–280. [Google Scholar]
- Pikarsky, E; Porat, RM; Stein, I; Abramovitch, R; Amit, S; Kasem, S; Gutkovich-Pyest, E; Urieli-Shoval, S; Galun, E; Ben-Neriah, Y. NF-κB functions as a tumour promoter in inflammation-associated cancer. Nature 2004, 431, 461–466. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, N; Gupta, S; Mukhtar, H. Green tea polyphenol epigallocatechin-3-gallate differentially modulates nuclear factor κB in cancer cells versus normal cells. Arch. Biochem. Biophys 2000, 376, 338–346. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-del-Campo, L; Rodríguez-López, JN. Targeting the methionine cycle for melanoma therapy with 3-O-(3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoyl)-(-)-epicatechin. Int. J. Cancer 2008, 123, 2446–2455. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, SL; Patrick, P; Stone, D; Phillips, AW; Burchall, JJ. Porcine liver dihydrofolate reductase: Purification, properties, and amino acids sequence. J. Biol. Chem 1979, 254, 11475–11484. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, JW; Morrison, JF; Duggleby, RG. Methotrexate, a high-affinity pseudosubstrate of dihydrofolate reductase. Biochemistry 1979, 18, 2567–2573. [Google Scholar]
- Birdsall, B; Burgen, ASV; Rodrigues de Miranda, J; Roberts, GCK. Cooperativity in ligand binding to dihydrofolate reductase. Biochemistry 1978, 17, 2102–2110. [Google Scholar]


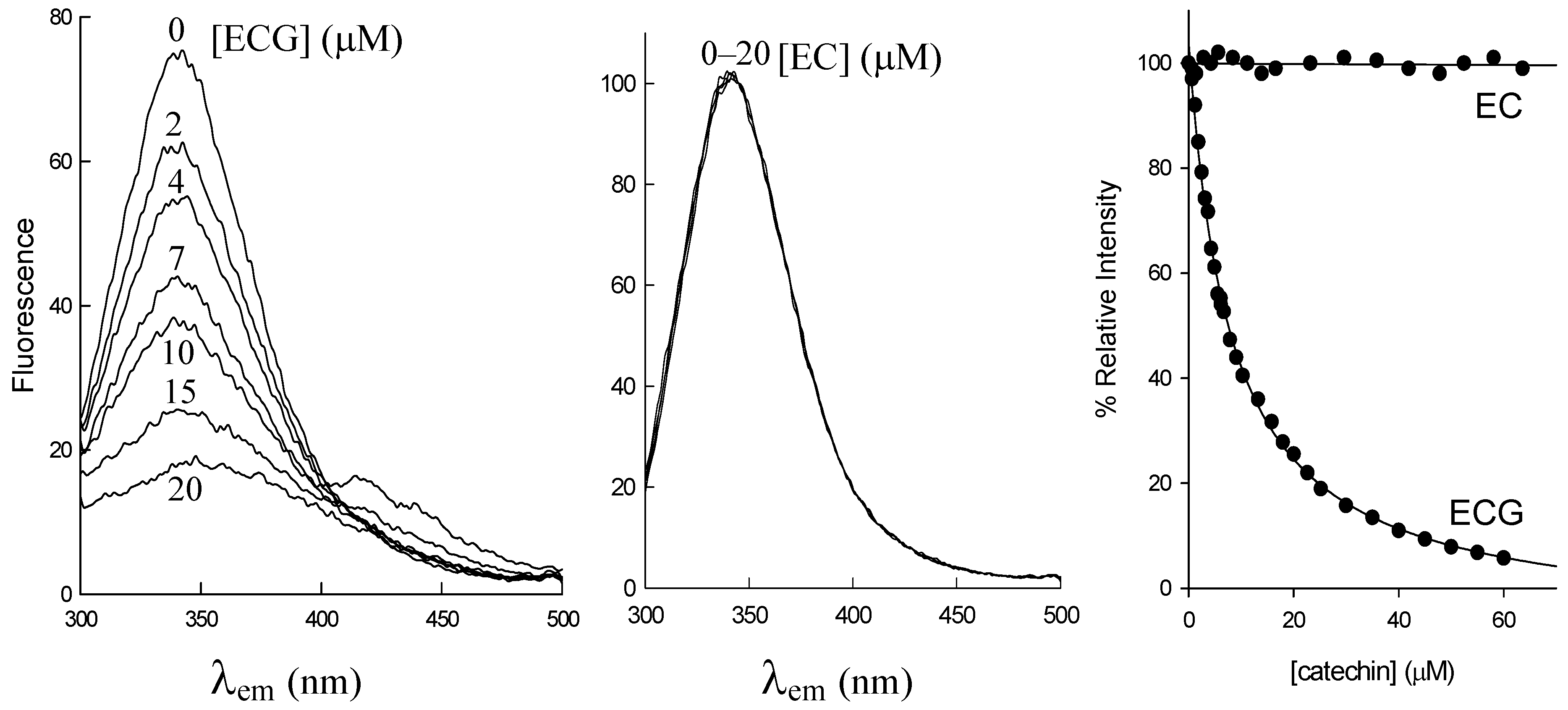

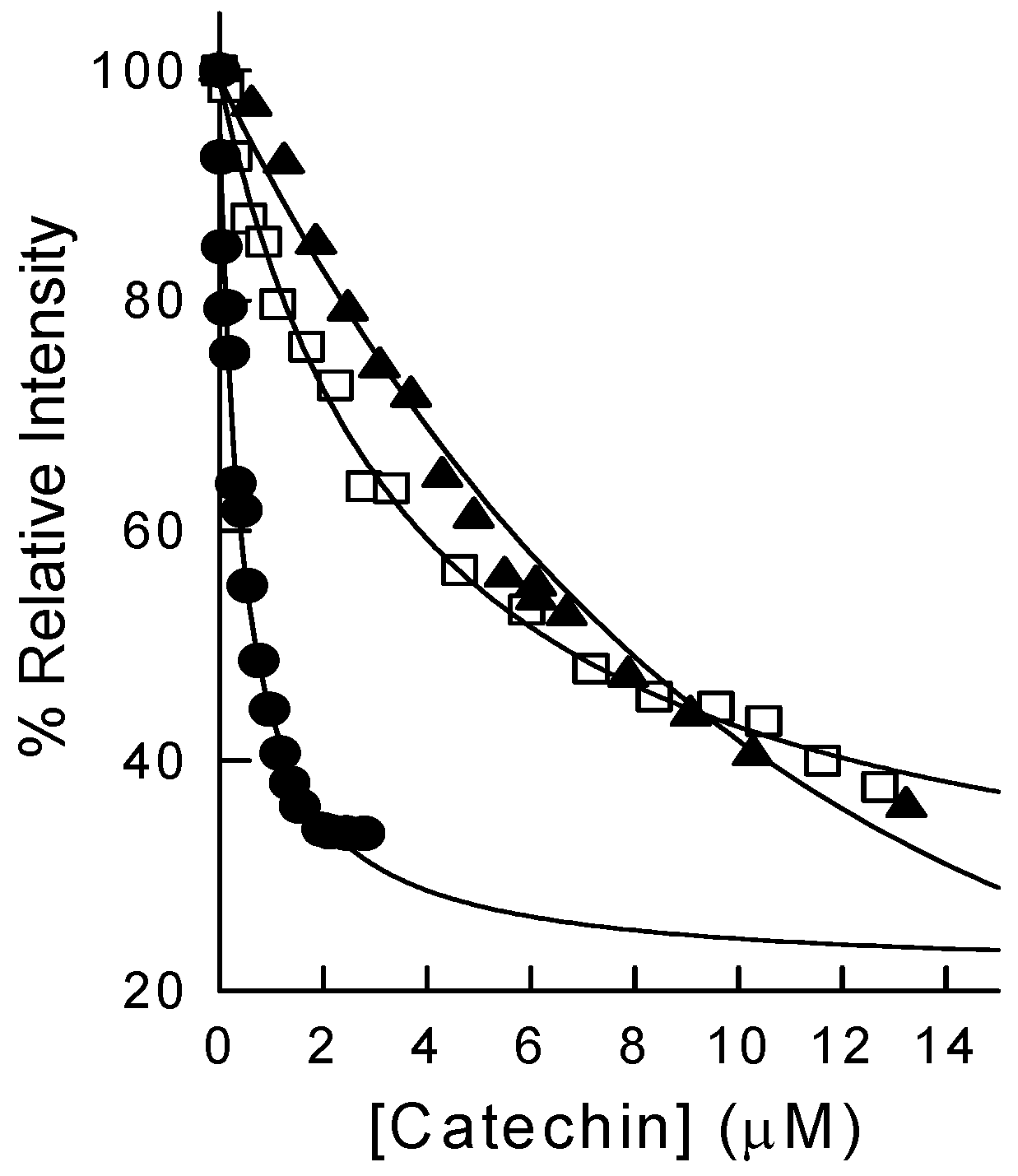



| Polyphenol | KD (μM) |
|---|---|
| Tea Catechins | |
| EC | n.d.A |
| EGC | n.d. |
| ECG | 1.78 ± 0.10 |
| EGCG | 0.92 ± 0.12 |
| Synthetic Catechins | |
| TMECG | 2.1 ± 0.20 |
| TMECG-QM | (8.2 ± 0.21) × 10−3 |
| Flavonoids | |
| Qglc | 102 ± 9 |
| Qxyl | 0.59 ± 0.08 |
| Qrha | 17.2 ± 2.4 |
| Qgal | 22.8 ± 3.2 |
© 2009 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Sánchez-del-Campo, L.; Sáez-Ayala, M.; Chazarra, S.; Cabezas-Herrera, J.; Rodríguez-López, J.N. Binding of Natural and Synthetic Polyphenols to Human Dihydrofolate Reductase. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009, 10, 5398-5410. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms10125398
Sánchez-del-Campo L, Sáez-Ayala M, Chazarra S, Cabezas-Herrera J, Rodríguez-López JN. Binding of Natural and Synthetic Polyphenols to Human Dihydrofolate Reductase. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2009; 10(12):5398-5410. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms10125398
Chicago/Turabian StyleSánchez-del-Campo, Luís, Magalí Sáez-Ayala, Soledad Chazarra, Juan Cabezas-Herrera, and José Neptuno Rodríguez-López. 2009. "Binding of Natural and Synthetic Polyphenols to Human Dihydrofolate Reductase" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 10, no. 12: 5398-5410. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms10125398




