The Inhibitory Effect of Quercetin on Asymmetric Dimethylarginine-Induced Apoptosis Is Mediated by the Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Pathway in Glomerular Endothelial Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
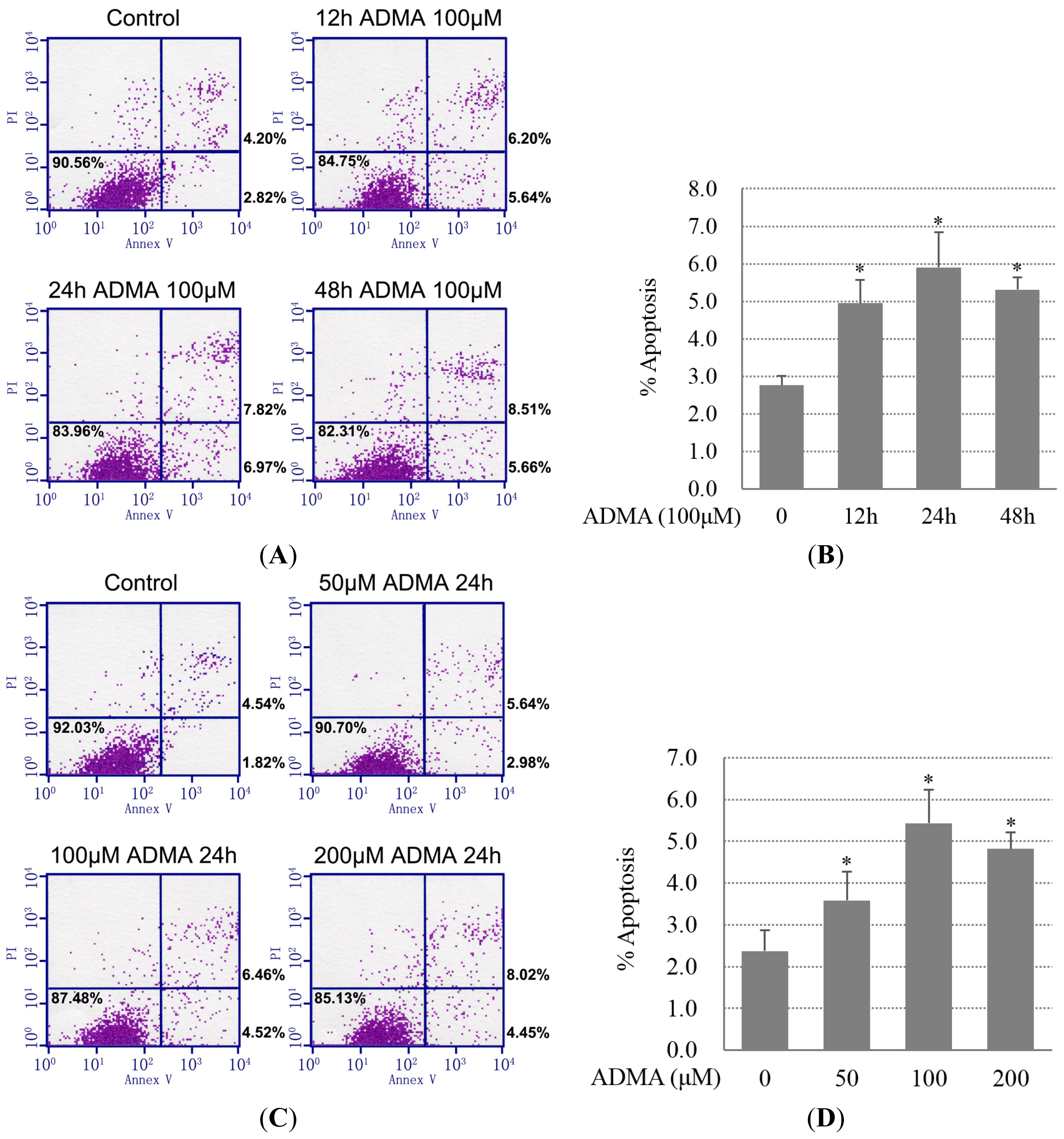
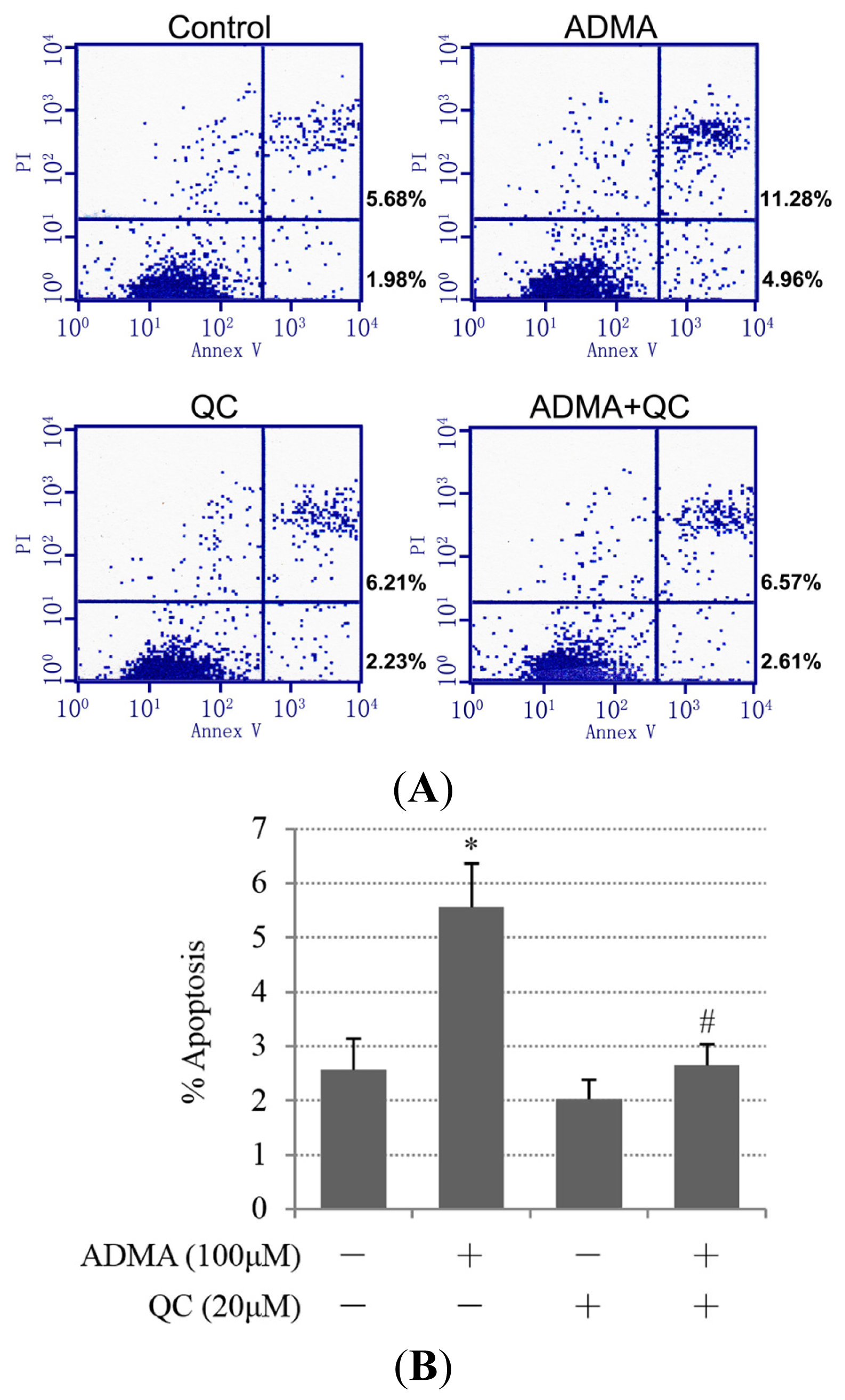
2.1. QC Inhibited ADMA-Induced Apoptosis in GEnCs
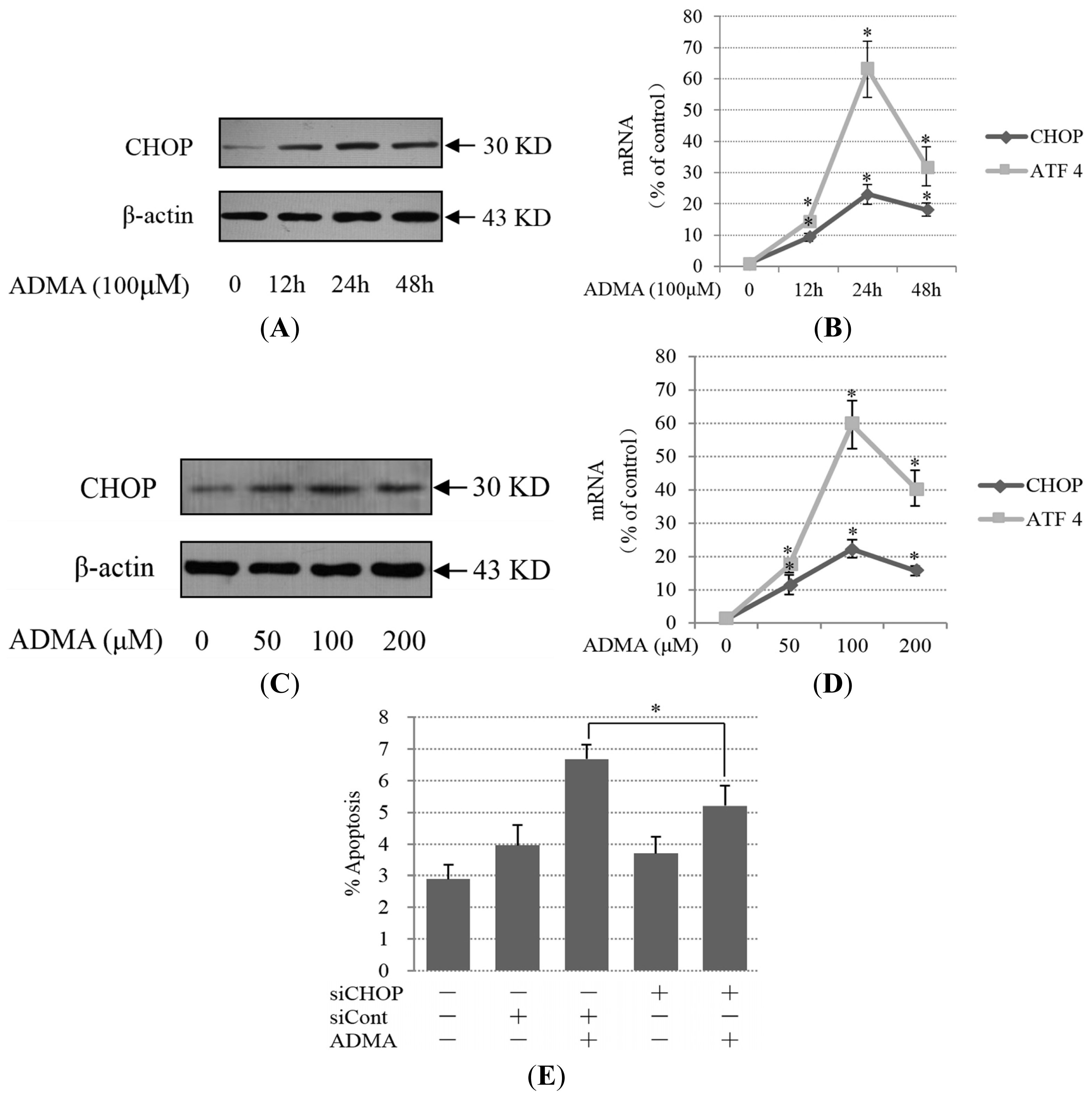
2.2. Role of ER Stress in ADMA-Mediated GEnC Apoptosis
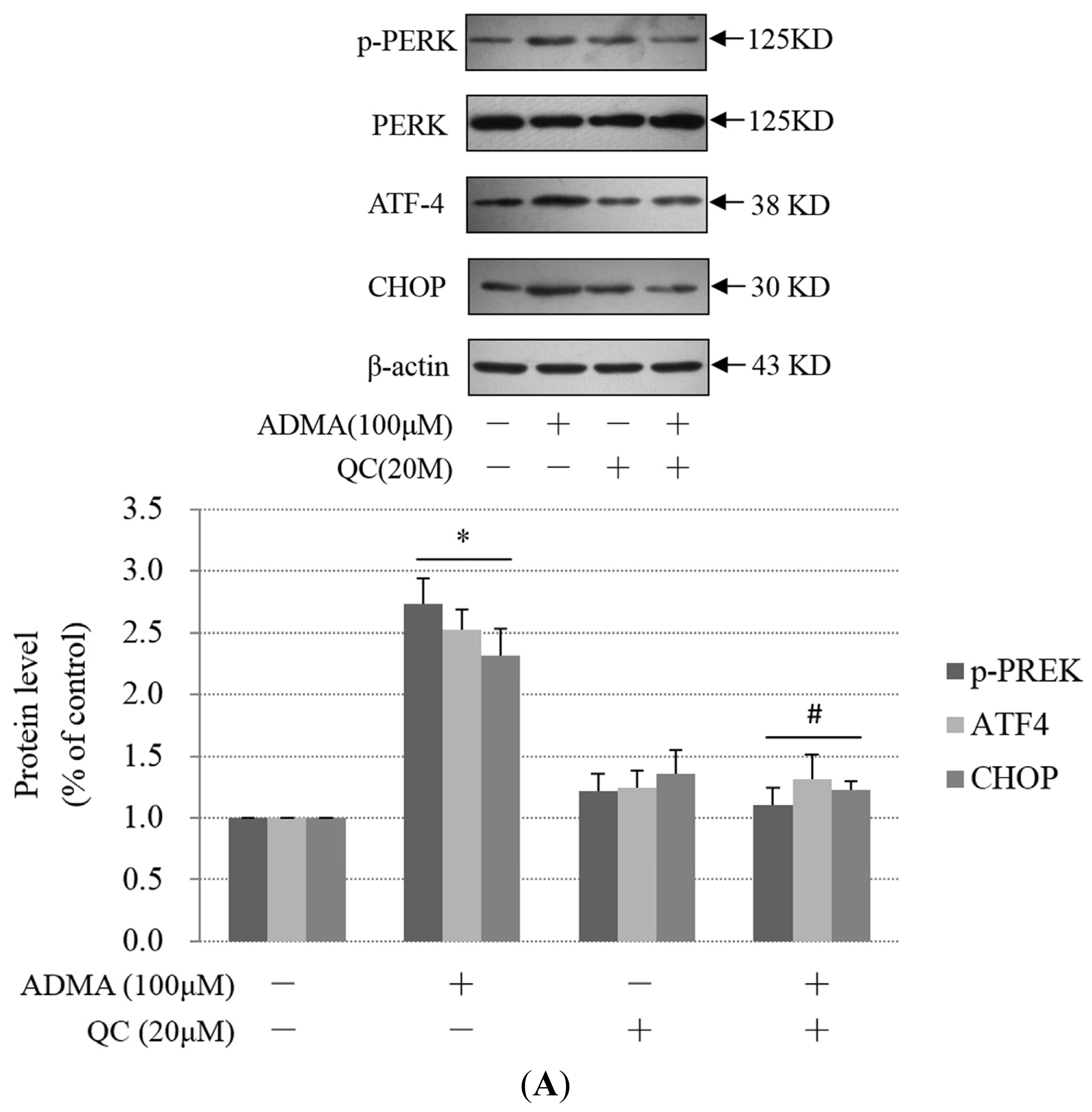
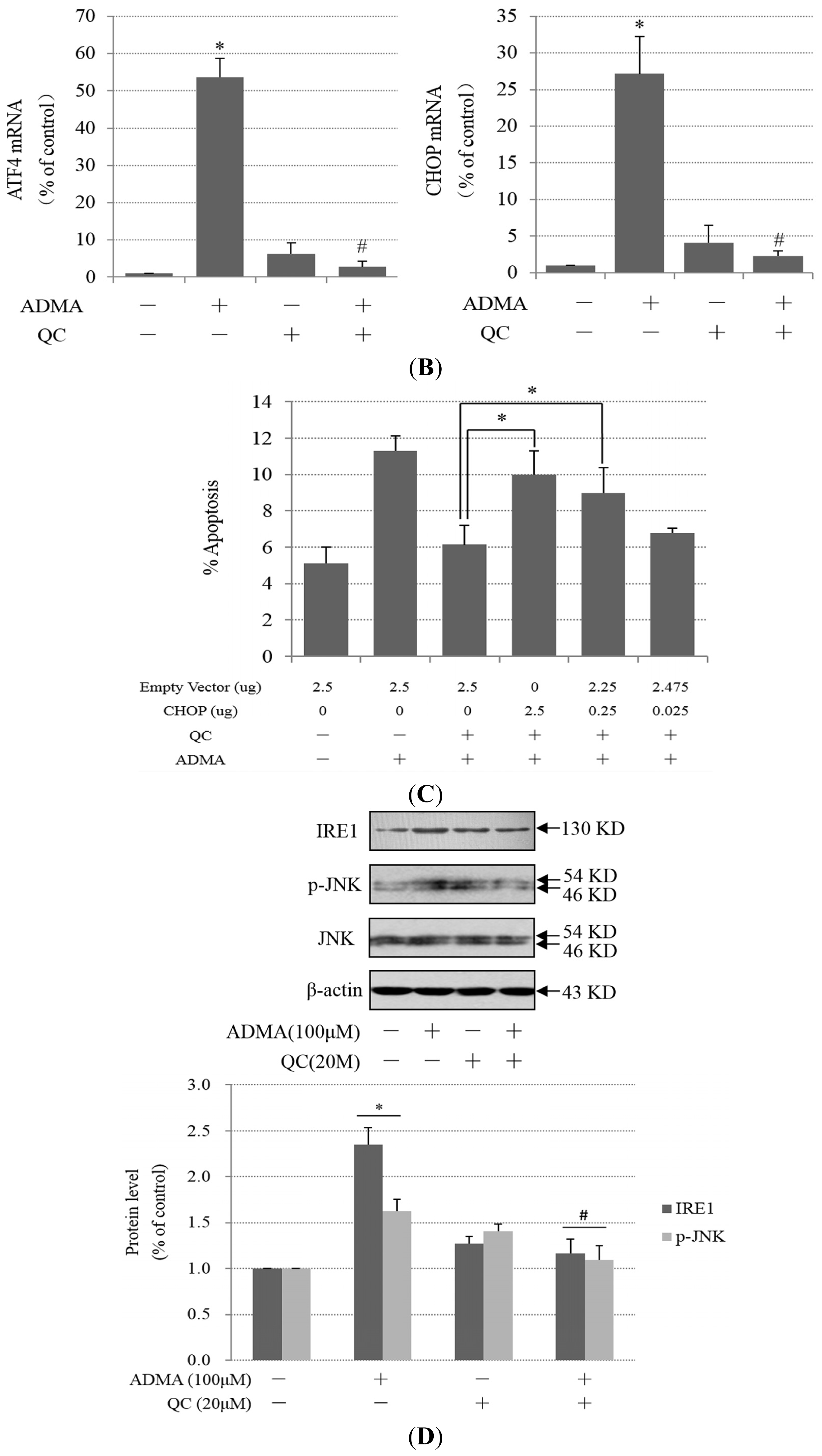
2.3. QC Suppressed ADMA-Induced ER Stress in GEnCs
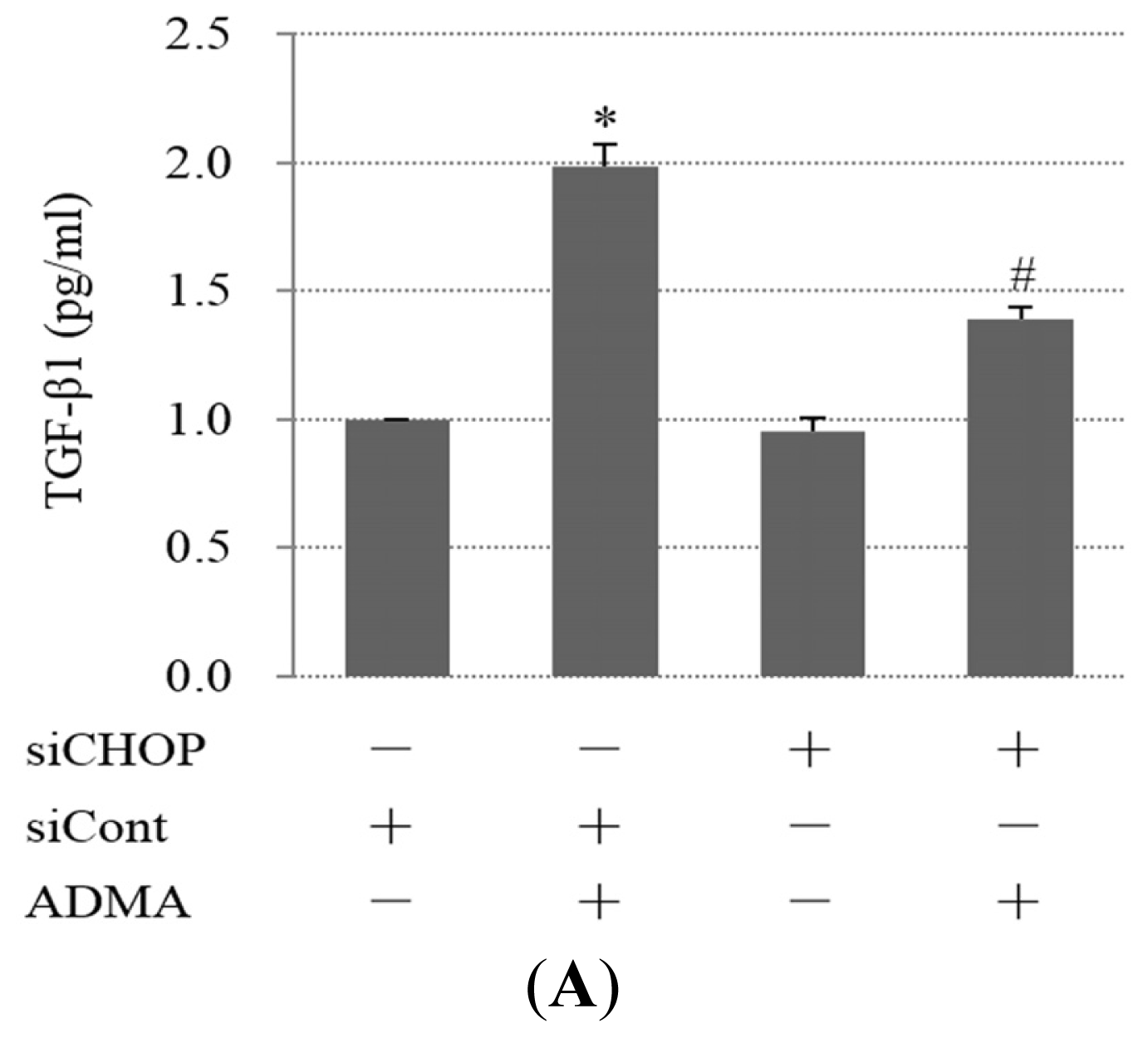
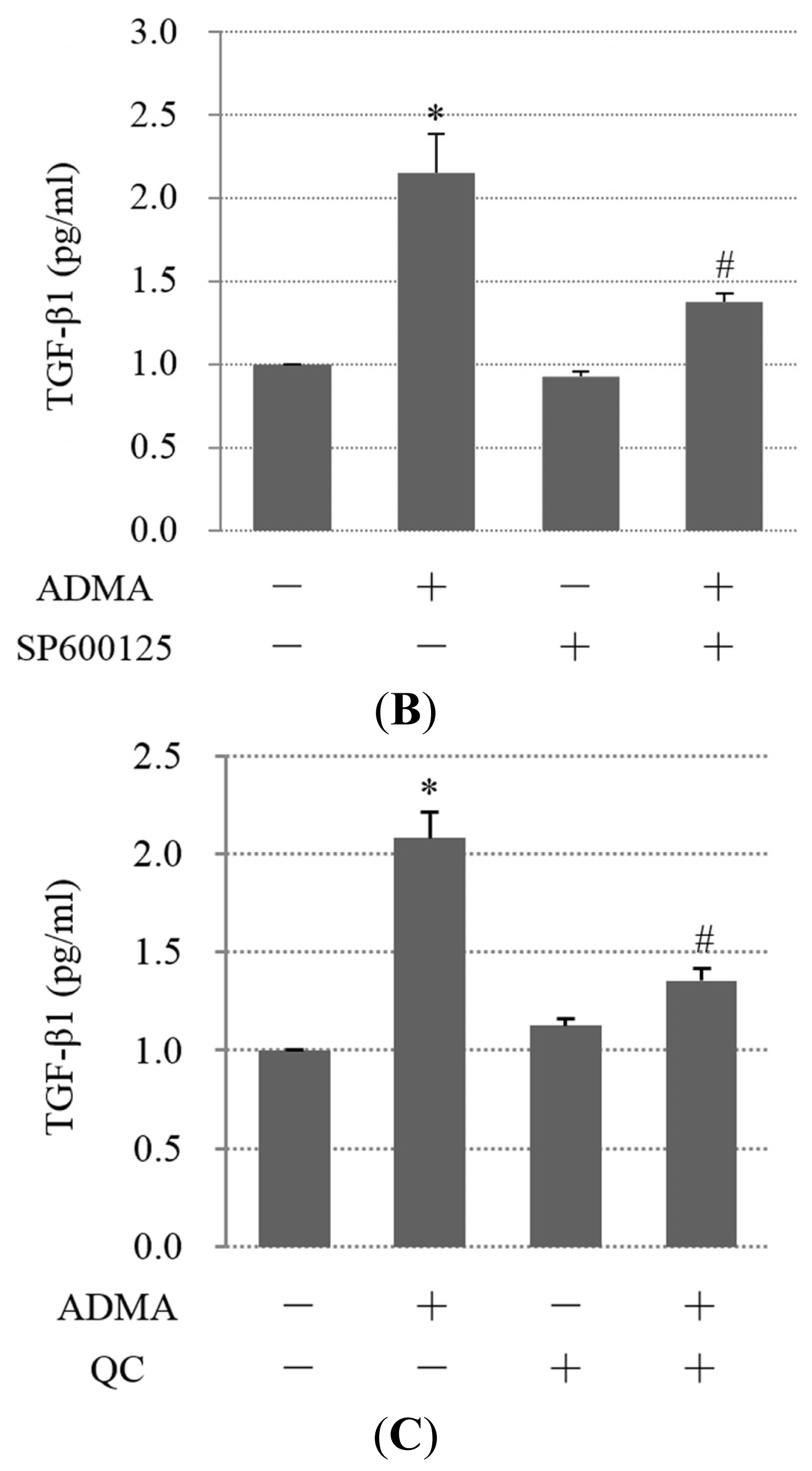
2.4. QC Inhibits ADMA-Induced TGF-β Expression in GEnCs
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemical Reagents
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Apoptosis Assays
4.4. Western Blot Analysis
4.5. Estimation of mRNA Levels
4.6. Transfection of Silencing RNA (siRNA)
4.7. Plasmid Preparation
4.8. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Information
ijms-15-00484-s002.pdfAcknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vallance, P.; Leone, A.; Calver, A.; Collier, J.; Moncada, S. Accumulation of an endogenous inhibitor of nitric oxide synthesis in chronic renal failure. Lancet 1992, 339, 572–575. [Google Scholar]
- Kielstein, J.T.; Böger, R.H.; Bode-Böger, S.M.; Frölich, J.C.; Haller, H.; Ritz, E.; Fliser, D. Marked increase of asymmetric dimethylarginine in patients with incipient primary chronic renal disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol 2002, 13, 170–176. [Google Scholar]
- Mihout, F.; Shweke, N.; Bigé, N.; Jouanneau, C.; Dussaule, J.C.; Ronco, P.; Chatziantoniou, C.; Boffa, J.J. Asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) induces chronic kidney disease through a mechanism involving collagen and TGF-β1 synthesis. J. Pathol 2011, 223, 37–45. [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto, Y.; Ueda, S.; Yamagishi, S.; Matsuguma, K.; Shibata, R.; Fukami, K.; Matsuoka, H.; Imaizumi, T.; Okuda, S. Dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase prevents progression of renal dysfunction by inhibiting loss of peritubular capillaries and tubulointerstitial fibrosis in a rat model of chronic kidney disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol 2007, 18, 1525–1533. [Google Scholar]
- Shibata, R.; Ueda, S.; Yamagishi, S.; Kaida, Y.; Matsumoto, Y.; Fukami, K.; Hayashida, A.; Matsuoka, H.; Kato, S.; Kimoto, M.; et al. Involvement of asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) in tubulointerstitial ischaemia in the early phase of diabetic nephropathy. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl 2009, 24, 1162–1169. [Google Scholar]
- Ravani, P.; Tripepi, G.; Malberti, F.; Testa, S.; Mallamaci, F.; Zoccali, C. Asymmetrical dimethylarginine predicts progression to dialysis and death in patients with chronic kidney disease: A competing risks modeling approach. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol 2005, 16, 2449–2455. [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu, A.; Kitamura, H.; Masuda, Y.; Ishizaki, M.; Sugisaki, Y.; Yamanaka, N. Rare glomerular capillary regeneration and subsequent capillary regression with endothelial cell apoptosis in progressive glomerulonephritis. Am. J. Pathol 1997, 151, 1231–1239. [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura, H.; Shimizu, A.; Masuda, Y.; Ishizaki, M.; Sugisaki, Y.; Yamanaka, N. Apoptosis in glomerular endothelial cells during the development of glomerulosclerosis in the remnant-kidney model. Exp. Nephrol 1998, 6, 328–336. [Google Scholar]
- Woehlbier, U.; Hetz, C. Modulating stress responses by the UPRosome: A matter of life and death. Trends Biochem. Sci 2011, 36, 329–337. [Google Scholar]
- Walter, P.; Ron, D. The unfolded protein response: From stress pathway to homeostatic regulation. Science 2011, 334, 1081–1086. [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Vizcaino, F.; Duarte, J. Flavonols and cardiovascular disease. Mol. Aspects Med 2010, 31, 478–494. [Google Scholar]
- Shoskes, D.A. Effect of bioflavonoids quercetin and curcumin on ischemic renal injury: A new class of renoprotective agents. Transplantation 1998, 66, 147–152. [Google Scholar]
- Anjaneyulu, M.; Chopra, K. Quercetin, an anti-oxidant bioflavonoid, attenuates diabetic nephropathy in rats. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol 2004, 31, 244–248. [Google Scholar]
- Satyanarayana, P.S.; Singh, D.; Chopra, K. Quercetin, a bioflavonoid, protects against oxidative stress-related renal dysfunction by cyclosporine in rats. Methods Find Exp. Clin. Pharmacol 2001, 23, 175–181. [Google Scholar]
- Morales, A.I.; Vicente-Sánchez, C.; Jerkic, M.; Santiago, J.M.; Sánchez-González, P.D.; Pérez-Barriocanal, F.; López-Novoa, J.M. Effect of quercetin on metallothionein, nitric oxide synthases and cyclooxygenase-2 expression on experimental chronic cadmium nephrotoxicity in rats. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol 2006, 210, 128–135. [Google Scholar]
- Kahraman, A.; Erkasap, N.; Serteser, M.; Köken, T. Protective effect of quercetin on renal ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. J. Nephrol 2003, 16, 219–224. [Google Scholar]
- Cybulsky, A.V.; Takano, T.; Papillon, J.; Bijian, K. Role of the endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response in glomerular epithelial cell injury. J. Biol. Chem 2005, 280, 24396–24403. [Google Scholar]
- Nakajo, A.; Khoshnoodi, J.; Takenaka, H.; Hagiwara, E.; Watanabe, T.; Kawakami, H.; Kurayama, R.; Sekine, Y.; Bessho, F.; Takahashi, S.; et al. Mizoribine corrects defective nephrin biogenesis by restoring intracellular energy balance. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol 2007, 18, 2554–2564. [Google Scholar]
- Cybulsky, A.V.; Takano, T.; Papillon, J.; Bijian, K.; Guillemette, J.; Kennedy, C.R. Glomerular epithelial cell injury associated with mutant alpha-actinin-4. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol 2009, 297, 987–995. [Google Scholar]
- Ueda, S.; Yamagishi, S.; Matsumoto, Y.; Kaida, Y.; Fujimi-Hayashida, A.; Koike, K.; Tanaka, H.; Fukami, K.; Okuda, S. Involvement of asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) in glomerular capillary loss and sclerosis in a rat model of chronic kidney disease (CKD). Life Sci 2009, 84, 853–856. [Google Scholar]
- Portt, L.; Norman, G.; Clapp, C.; Greenwood, M.; Greenwood, M.T. Anti-apoptosis and cell survival: A review. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1813, 238–259. [Google Scholar]
- Hetz, C. The unfolded protein response: Controlling cell fate decisions under ER stress and beyond. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol 2012, 13, 89–102. [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura, M. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and unfolded protein response in renal pathophysiology: Janus faces. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol 2008, 295, 323–334. [Google Scholar]
- Lundman, P.; Eriksson, M.J.; Stühlinger, M.; Cooke, J.P.; Hamsten, A.; Tornvall, P. Mild-to-moderate hypertriglyceridemia in young men is associated with endothelial dysfunction and increased plasma concentrations of asymmetric dimethylarginine. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol 2001, 38, 111–116. [Google Scholar]
- Surdacki, A.; Nowicki, M.; Sandmann, J.; Tsikas, D.; Boeger, R.H.; Bode-Boeger, S.M.; Kruszelnicka-Kwiatkowska, O.; Kokot, F.; Dubiel, J.S.; Froelich, J.C. Reduced urinary excretion of nitric oxide metabolites and increased plasma levels of asymmetric dimethylarginine in men with essential hypertension. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol 1999, 33, 652–658. [Google Scholar]
- Kielstein, J.T.; Böger, R.H.; Bode-Böger, S.M.; Schäffer, J.; Barbey, M.; Koch, K.M.; Frölich, J.C. Asymmetric dimethylarginine plasma concentrations differ in patients with end-stage renal disease: Relationship to treatment method and atherosclerotic disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol 1999, 10, 594–600. [Google Scholar]
- Wojciak-Stothard, B.; Torondel, B.; Zhao, L.; Renné, T.; Leiper, J.M. Modulation of Rac1 activity by ADMA/DDAH regulates pulmonary endothelial barrier function. Mol. Biol. Cell 2009, 20, 33–42. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, C.L.; Anthony, S.; Hubank, M.; Leiper, J.M.; Vallance, P. Effects of ADMA upon gene expression: An insight into the pathophysiological significance of raised plasma ADMA. PLoS Med 2005, 2, e264. [Google Scholar]
- MacAllister, R.J.; Fickling, S.A.; Whitley, G.S.; Vallance, P. Metabolism of methylarginines by human vasculature; implications for the regulation of nitric oxide synthesis. Br. J. Pharmacol 1994, 112, 43–48. [Google Scholar]
- Sud, N.; Wells, S.M.; Sharma, S.; Wiseman, D.A.; Wilham, J.; Black, S.M. Asymmetric dimethylarginine inhibits HSP90 activity in pulmonary arterial endothelial cells: Role of mitochondrial dysfunction. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol 2008, 294, 1407–1418. [Google Scholar]
- Terao, J.; Piskula, M.; Yao, Q. Protective effect of epicatechin, epicatechin gallate, and quercetin on lipid peroxidation in phospholipid bilayers. Arch. Biochem. Biophys 1994, 308, 278–284. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, J.E.; Khodr, H.; Hider, R.C.; Rice-Evans, C.A. Structural dependence of flavonoid interactions with Cu2+ ions: Implications for their antioxidant properties. Biochem. J 1998, 330, 1173–1178. [Google Scholar]
- Nagao, A.; Seki, M.; Kobayashi, H. Inhibition of xanthine oxidase by flavonoids. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem 1999, 63, 1787–1790. [Google Scholar]
- Middleton, E., Jr.; Anne, S. Quercetin inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced expression of endothelial cell intracellular adhesion molecule-1. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol 1995, 107, 435–436. [Google Scholar]
- Kobuchi, H.; Roy, S.; Sen, C.K.; Nguyen, H.G.; Packer, L. Quercetin inhibits inducible ICAM-1 expression in human endothelial cells through the JNK pathway. Am. J. Physiol 1999, 277, 403–411. [Google Scholar]
- Richter, M.; Ebermann, R.; Marian, B. Quercetin-induced apoptosis in colorectal tumor cells: Possible role of EGF receptor signaling. Nutr. Cancer 1999, 34, 88–99. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Tran, E.; Nguyen, T.H.; Do, P.T.; Huynh, T.H.; Huynh, H. The role of activated MEK-ERK pathway in quercetin-induced growth inhibition and apoptosis in A549 lung cancer cells. Carcinogenesis 2004, 25, 647–659. [Google Scholar]
- Mertens-Talcott, S.U.; Percival, S.S. Ellagic acid and quercetin interact synergistically with resveratrol in the induction of apoptosis and cause transient cell cycle arrest in human leukemia cells. Cancer Lett 2005, 218, 141–151. [Google Scholar]
- Aalinkeel, R.; Bindukumar, B.; Reynolds, J.L.; Sykes, D.E.; Mahajan, S.D.; Chadha, K.C.; Schwartz, S.A. The dietary bioflavonoid, quercetin, selectively induces apoptosis of prostate cancer cells by down-regulating the expression of heat shock protein 90. Prostate 2009, 68, 1773–1789. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, J.H.; An, J.Y.; Kwon, Y.T.; Rhee, J.G.; Lee, Y.J. Effects of low dose quercetin: Cancer cell-specific inhibition of cell cycle progression. J. Cell Biochem 2009, 106, 73–82. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, S.; Sang, H.; Song, G.; Yang, N.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Jiao, P.; Zong, C.; Qin, S. Quercetin protects macrophages from oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced apoptosis by inhibiting the endoplasmic reticulum stress-C/EBP homologous protein pathway. Exp. Biol. Med 2012, 237, 822–831. [Google Scholar]
- Park, C.; So, H.S.; Shin, C.H.; Baek, S.H.; Moon, B.S.; Shin, S.H.; Lee, H.S.; Lee, D.W.; Park, R. Quercetin protects the hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis via inhibition of mitochondrial dysfunction in H9c2 cardiomyoblast cells. Biochem. Pharmacol 2003, 66, 1287–1295. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.C.; Kim, J.; Park, J.K.; Chung, G.H.; Jang, Y.S. The antioxidant, rather than prooxidant, activities of quercetin on normal cells: Quercetin protects mouse thymocytes from glucose oxidase-mediated apoptosis. Exp. Cell Res. 2003, 291, 386–397. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, K.C.; Yen, C.Y.; Wu, R.S.; Yang, J.S.; Lu, H.F.; Lu, K.W.; Lo, C.; Chen, H.Y.; Tang, N.Y.; Wu, C.C.; et al. The roles of endoplasmic reticulum stress and mitochondrial apoptotic signaling pathway in quercetin-mediated cell death of human prostate cancer PC-3 cells. Environ. Toxicol 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.S.; Kwon, D.Y.; Kim, M.S.; Kim, H.K.; Lee, Y.C.; Park, S.J.; Yoo, W.H.; Chae, S.W.; Chung, M.J.; Kim, H.R.; et al. The involvement of endoplasmic reticulum stress in flavonoid-induced protection on cardiac cell death caused by ischaemia/reperfusion. J. Pharm. Pharmacol 2010, 62, 197–204. [Google Scholar]
- Wiseman, R.L.; Zhang, Y.; Lee, K.P.; Harding, H.P.; Haynes, C.M.; Price, J.; Sicheri, F.; Ron, D. Flavonol activation defines an unanticipated ligand-binding site in the kinase-RNase domain of IRE1. Mol. Cell 2010, 38, 291–304. [Google Scholar]
- Crespo, I.; García-Mediavilla, M.V.; Gutiérrez, B.; Sánchez-Campos, S.; Tuñón, M.J.; González-Gallego, J. A comparison of the effects of kaempferol and quercetin on cytokine-induced pro-inflammatory status of cultured human endothelial cells. Br. J. Nutr 2008, 100, 968–976. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, Y.J.; Kang, J.S.; Park, J.H.; Lee, Y.J.; Choi, J.S.; Kang, Y.H. Polyphenolic flavonoids differ in their antiapoptotic efficacy in hydrogen peroxide-treated human vascular endothelial cells. J. Nutr 2003, 133, 985–991. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, Y.J.; Choi, Y.J.; Kwon, H.M.; Kang, S.W.; Park, H.S.; Lee, M.; Kang, Y.H. Differential inhibition of oxidized LDL-induced apoptosis in human endothelial cells treated with different flavonoids. Br. J. Nutr 2005, 93, 581–591. [Google Scholar]
- Huynh, M.L.; Fadok, V.A.; Henson, P.M. Phosphatidylserine-dependent ingestion of apoptotic cells promotes TGF-β1 secretion and the resolution of inflammation. J. Clin. Invest 2002, 109, 41–50. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, K.; Ziyadeh, F.N. Biochemical events and cytokine inter-actions linking glucose metabolism to the development of dia-betic nephropathy. Semin. Nephrol 1997, 17, 80–92. [Google Scholar]




© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, W.; Ding, J.; Zhang, A.; Dai, W.; Liu, S.; Diao, Z.; Wang, L.; Han, X.; Liu, W. The Inhibitory Effect of Quercetin on Asymmetric Dimethylarginine-Induced Apoptosis Is Mediated by the Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Pathway in Glomerular Endothelial Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 484-503. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms15010484
Guo W, Ding J, Zhang A, Dai W, Liu S, Diao Z, Wang L, Han X, Liu W. The Inhibitory Effect of Quercetin on Asymmetric Dimethylarginine-Induced Apoptosis Is Mediated by the Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Pathway in Glomerular Endothelial Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2014; 15(1):484-503. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms15010484
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Weikang, Jiaxiang Ding, Aihua Zhang, Wendi Dai, Sha Liu, Zongli Diao, Liyan Wang, Xue Han, and Wenhu Liu. 2014. "The Inhibitory Effect of Quercetin on Asymmetric Dimethylarginine-Induced Apoptosis Is Mediated by the Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Pathway in Glomerular Endothelial Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 15, no. 1: 484-503. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms15010484
APA StyleGuo, W., Ding, J., Zhang, A., Dai, W., Liu, S., Diao, Z., Wang, L., Han, X., & Liu, W. (2014). The Inhibitory Effect of Quercetin on Asymmetric Dimethylarginine-Induced Apoptosis Is Mediated by the Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Pathway in Glomerular Endothelial Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 15(1), 484-503. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms15010484



