Transducer of ERBB2.1 (TOB1) as a Tumor Suppressor: A Mechanistic Perspective
Abstract
:1. Introduction

2. Status of TOB1 Expression in Human Cancers
3. Underlying Mechanisms of TOB1 Inactivation

4. Mechanisms of TOB1 Tumor Suppressor Functions
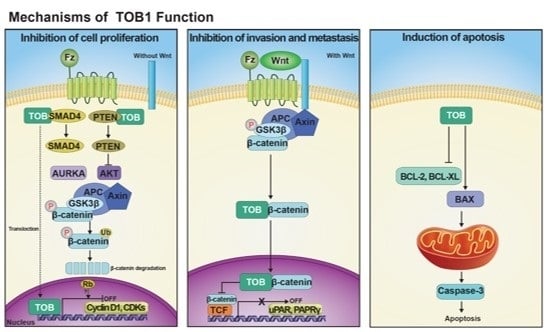
4.1. Role of TOB1 in Cell Cycle Regulation



4.2. Role of TOB1 in the Induction of Apoptosis
4.3. Anti-Invasive and Anti-Migratory Roles of TOB1
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mauxion, F.; Chen, C.Y.; Seraphin, B.; Shyu, A.B. BTG/TOB factors impact deadenylases. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2009, 34, 640–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guehenneux, F.; Duret, L.; Callanan, M.B.; Bouhas, R.; Hayette, S.; Berthet, C.; Samarut, C.; Rimokh, R.; Birot, A.M.; Wang, Q.; et al. Cloning of the mouse BTG3 gene and definition of a new gene family (the BTG family) involved in the negative control of the cell cycle. Leukemia 1997, 11, 370–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winkler, G.S. The mammalian anti-proliferative BTG/TOB protein family. J. Cell. Physiol. 2010, 222, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzachanis, D.; Boussiotis, V.A. TOB, a member of the APRO family, regulates immunological quiescence and tumor suppression. Cell Cycle 2009, 8, 1019–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradbury, A.; Possenti, R.; Shooter, E.M.; Tirone, F. Molecular cloning of PC3, a putatively secreted protein whose mRNA is induced by nerve growth factor and depolarization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 3353–3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fletcher, B.S.; Lim, R.W.; Varnum, B.C.; Kujubu, D.A.; Koski, R.A.; Herschman, H.R. Structure and expression of TIS21, a primary response gene induced by growth factors and tumor promoters. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 14511–14518. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rouault, J.P.; Rimokh, R.; Tessa, C.; Paranhos, G.; Ffrench, M.; Duret, L.; Garoccio, M.; Germain, D.; Samarut, J.; Magaud, J.P. BTG1, a member of a new family of antiproliferative genes. EMBO J. 1992, 11, 1663–1670. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rouault, J.P.; Falette, N.; Guehenneux, F.; Guillot, C.; Rimokh, R.; Wang, Q.; Berthet, C.; Moyret-Lalle, C.; Savatier, P.; Pain, B.; et al. Identification of BTG2, an antiproliferative p53-dependent component of the DNA damage cellular response pathway. Nat. Genet. 1996, 14, 482–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuda, S.; Kawamura-Tsuzuku, J.; Ohsugi, M.; Yoshida, M.; Emi, M.; Nakamura, Y.; Onda, M.; Yoshida, Y.; Nishiyama, A.; Yamamoto, T. TOB, a novel protein that interacts with p185erbB2, is associated with anti-proliferative activity. Oncogene 1996, 12, 705–713. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Matsuda, S.; Rouault, J.; Magaud, J.; Berthet, C. In search of a function for the TIS21/PC3/BTG1/TOB family. FEBS Lett. 2001, 497, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Wang, X.M.; Tu, Y.; Zhang, X.H.; Gao, X.; Guo, N.; Xie, Z.; Zhao, G.; Jing, N.; Li, B.M.; et al. The negative cell cycle regulator, TOB (transducer of ErbB-2), is a multifunctional protein involved in hippocampus-dependent learning and memory. Neuroscience 2005, 131, 647–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamaid, A.; Giraldez, F. BTG1 and BTG2 gene expression during early chick development. Dev. Dyn. 2008, 237, 2158–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farioli-Vecchioli, S.; Tanori, M.; Micheli, L.; Mancuso, M.; Leonardi, L.; Saran, A.; Ciotti, M.T.; Ferretti, E.; Gulino, A.; Pazzaglia, S.; et al. Inhibition of medulloblastoma tumorigenesis by the antiproliferative and pro-differentiative gene PC3. FASEB J. 2007, 21, 2215–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwanaga, K.; Sueoka, N.; Sato, A.; Sakuragi, T.; Sakao, Y.; Tominaga, M.; Suzuki, T.; Yoshida, Y.; Yamamoto, T.; Hayashi, S.; et al. Alteration of expression or phosphorylation status of tob, a novel tumor suppressor gene product, is an early event in lung cancer. Cancer Lett. 2003, 202, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanagie, H.; Sumimoto, H.; Nonaka, Y.; Matsuda, S.; Hirose, I.; Hanada, S.; Sugiyama, H.; Mikamo, S.; Takeda, Y.; Yoshizaki, I.; et al. Inhibition of human pancreatic cancer growth by the adenovirus-mediated introduction of a novel growth suppressing gene, TOB, in vitro. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1998, 451, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- O’Malley, S.; Su, H.; Zhang, T.; Ng, C.; Ge, H.; Tang, C.K. TOB suppresses breast cancer tumorigenesis. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 125, 1805–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanagie, H.; Tanabe, T.; Sumimoto, H.; Sugiyama, H.; Matsuda, S.; Nonaka, Y.; Ogiwara, N.; Sasaki, K.; Tani, K.; Takamoto, S.; et al. Tumor growth suppression by adenovirus-mediated introduction of a cell-growth-suppressing gene TOB in a pancreatic cancer model. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2009, 63, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Yoshida, H.; Tomoda, C.; Uruno, T.; Takamura, Y.; Miya, A.; Kobayashi, K.; Matsuzuka, F.; Kuma, K.; et al. Phosphorylation and inactivation of TOB contributes to the progression of papillary carcinoma of the thyroid. Cancer Lett. 2005, 220, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Liu, P.; Cui, X.; Sui, Y.; Ji, G.; Guan, R.; Sun, D.; Ji, W.; Liu, F.; Liu, A.; et al. Identification of novel subregions of LOH in gastric cancer and analysis of the HIC1 and TOB1 tumor suppressor genes in these subregions. Mol. Cells 2011, 32, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stack, M.; Jones, D.; White, G.; Liscia, D.S.; Venesio, T.; Casey, G.; Crichton, D.; Varley, J.; Mitchell, E.; Heighway, J.; et al. Detailed mapping and loss of heterozygosity analysis suggests a suppressor locus involved in sporadic breast cancer within a distal region of chromosome band 17p13.3. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1995, 4, 2047–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klebig, C.; Seitz, S.; Korsching, E.; Kristiansen, G.; Gustavus, D.; Scherneck, S.; Petersen, I. Profile of differentially expressed genes after transfer of chromosome 17 into the breast cancer cell line CAL51. Genes Chromosom. Cancer 2005, 44, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, T.; Matsuda, S.; Tsuzuku, J.K.; Yoshida, Y.; Yamamoto, T. A serine/threonine kinase p90rsk1 phosphorylates the anti-proliferative protein TOB. Genes Cells 2001, 6, 13113–13118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Ajima, R.; Nakamura, T.; Yoshida, Y.; Yamamoto, T. Phosphorylation of three regulatory serines of TOB by Erk1 and Erk2 is required for Ras-mediated cell proliferation and transformation. Genes Dev. 2002, 16, 1356–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maekawa, M.; Nishida, E.; Tanoue, T. Identification of the anti-proliferative protein TOB as a MAPK substrate. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 37783–37787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiramatsu, Y.; Kitagawa, K.; Suzuki, T.; Uchida, C.; Hattori, T.; Kikuchi, H.; Oda, T.; Hatakeyama, S.; Nakayama, K.I.; Yamamoto, T.; et al. Degradation of TOB1 mediated by SCFSkp2-dependent ubiquitination. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 8477–8483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, T.; Kim, M.; Kozuka-Hata, H.; Watanabe, M.; Oyama, M.; Tsumoto, K.; Yamamoto, T. Monoubiquitination of TOB/BTG family proteins competes with degradation-targeting polyubiquitination. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 409, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.S.; Zuo, Q.F.; Zhao, Y.L.; Xiao, B.; Zhuang, Y.; Mao, X.H.; Wu, C.; Yang, S.M.; Zeng, H.; Zou, Q.M.; et al. MicroRNA-25 promotes gastric cancer migration, invasion and proliferation by directly targeting transducer of ERBB2, 1 and correlates with poor survival. Oncogene 2015, 10, 2256–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, L.; Lee, H.S.; Wu, C.F.; Kundu, J.; Park, S.G.; Kim, R.N.; Wang, L.H.; Erkin, O.C.; Choi, J.S.; Chae, S.W.; et al. SMAD4 suppresses AURKA-induced metastatic phenotypes via degradation of AURKA in a TGFβ-independent manner. Mol. Cancer Res. 2014, 12, 1779–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kundu, J.; Wahab, S.M.; Kundu, J.K.; Choi, Y.L.; Erkin, O.C.; Lee, H.S.; Park, S.G.; Shin, Y.K. TOB1 induces apoptosis and inhibits proliferation, migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells by activating SMAD4 and inhibiting betacatenin signaling. Int. J. Oncol. 2012, 41, 839–848. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tzachanis, D.; Freeman, G.J.; Hirano, N.; van Puijenbroek, A.A.; Delfs, M.W.; Berezovskaya, A.; Nadler, L.M.; Boussiotis, V.A. TOB is a negative regulator of activation that is expressed in anergic and quiescent T cells. Nat. Immunol. 2001, 2, 1174–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, Y.; Nakamura, T.; Komoda, M.; Satoh, H.; Suzuki, T.; Tsuzuku, J.K.; Miyasaka, T.; Yoshida, E.H.; Umemori, H.; Kunisaki, R.K.; et al. Mice lacking a transcriptional corepressor TOB are predisposed to cancer. Genes Dev. 2003, 17, 1201–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helms, M.W.; Kemming, D.; Contag, C.H.; Pospisil, H.; Bartkowiak, K.; Wang, A.; Chang, S.Y.; Buerger, H.; Brandt, B.H. TOB1 is regulated by EGF-dependent HER2 and EGFR signaling, is highly phosphorylated, and indicates poor prognosis in node-negative breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 5049–5056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guardavaccaro, D.; Corrente, G.; Covone, F.; Micheli, L.; D’Agnano, I.; Starace, G.; Caruso, M.; Tirone, F. Arrest of G(1)-S progression by the p53-inducible gene PC3 is Rb dependent and relies on the inhibition of cyclin D1 transcription. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000, 20, 1797–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, B.; Rui, Y.; Zhang, M.; Shi, K.; Jia, S.; Tian, T.; Yin, K.; Huang, H.; Lin, S.; Zhao, X.; et al. TOB1 controls dorsal development of zebrafish embryos by antagonizing maternal β-catenin transcriptional activity. Dev. Cell 2006, 11, 225–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, K.J.; Do, N.L.; Otu, H.H.; Dib, M.J.; Ren, X.; Enjyoji, K.; Robson, S.C.; Terwilliger, E.F.; Karp, S.J. TOB1 is a constitutively expressed repressor of liver regeneration. J. Exp. Med. 2010, 207, 1197–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobson, A.; Peltz, S.W. Interrelationships of the pathways of mRNA decay and translation in eukaryotic cells. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1996, 65, 693–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shyu, A.B.; Wilkinson, M.F.; van Hoof, A. Messenger RNA regulation: To translate or to degrade. EMBO J. 2008, 27, 471–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horiuchi, M.; Takeuchi, K.; Noda, N.; Muroya, N.; Suzuki, T.; Nakamura, T.; Kawamura-Tsuzuku, J.; Takahasi, K.; Yamamoto, T.; Inagaki, F. Structural basis for the antiproliferative activity of the TOB-hCaf1 complex. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 13244–13255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogami, K.; Hosoda, N.; Funakoshi, Y.; Hoshino, S. Antiproliferative protein TOB directly regulates c-MYC proto-oncogene expression through cytoplasmic polyadenylation element-binding protein CPEB. Oncogene 2014, 33, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fussbroich, B.; Wagener, N.; Macher-Goeppinger, S.; Benner, A.; Falth, M.; Sultmann, H.; Holzer, A.; Hoppe-Seyler, K.; Hoppe-Seyler, F. EZH2 depletion blocks the proliferation of colon cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.C.; Choi, J.H.; Park, C.Y.; Ahn, C.M.; Hong, S.J.; Lim, D.S. Nanog regulates molecules involved in stemness and cell cycle-signaling pathway for maintenance of pluripotency of P19 embryonal carcinoma stem cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2012, 227, 3678–3692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maekawa, M.; Yamamoto, T.; Nishida, E. Regulation of subcellular localization of the antiproliferative protein TOB by its nuclear export signal and bipartite nuclear localization signal sequences. Exp. Cell Res. 2004, 295, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawamura-Tsuzuku, J.; Suzuki, T.; Yoshida, Y.; Yamamoto, T. Nuclear localization of TOB is important for regulation of its antiproliferative activity. Oncogene 2004, 23, 6630–6638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donato, L.J.; Suh, J.H.; Noy, N. Suppression of mammary carcinoma cell growth by retinoic acid: The cell cycle control gene BTG2 is a direct target for retinoic acid receptor signaling. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, Y.; Ge, C.M.; Meng, Q.H.; Cao, J.P.; Tong, J.; Fan, S.J. Adenovirus-mediated expression of TOB1 sensitizes breast cancer cells to ionizing radiation. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2007, 28, 1628–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, T.; Tsuzuku, J.; Kawakami, K.; Miyasaka, T.; Yamamoto, T. Proteasome-mediated degradation of TOB is pivotal for triggering UV-induced apoptosis. Oncogene 2009, 28, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tenca, P.; Brotherton, D.; Montagnoli, A.; Rainoldi, S.; Albanese, C.; Santocanale, C. CDC7 is an active kinase in human cancer cells undergoing replication stress. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuji, T.; Lau, E.; Chiang, G.G.; Jiang, W. The role of Dbf4/Drf1-dependent kinase CDC7 in DNA-damage checkpoint control. Mol. Cell 2008, 32, 862–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, T.; Tsuzuku, J.; Hayashi, A.; Shiomi, Y.; Iwanari, H.; Mochizuki, Y.; Hamakubo, T.; Kodama, T.; Nishitani, H.; Masai, H.; et al. Inhibition of DNA damage-induced apoptosis through CDC7-mediated stabilization of TOB. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 40256–40265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Che, J.; Lu, Y.W.; Sun, K.K.; Feng, C.; Dong, A.J.; Jiao, Y. Overexpression of TOB1 confers radioprotection to bronchial epithelial cells through the MAPK/ERK pathway. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 30, 637–642. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jiao, Y.; Sun, K.K.; Zhao, L.; Xu, J.Y.; Wang, L.L.; Fan, S.J. Suppression of human lung cancer cell proliferation and metastasis in vitro by the transducer of ErbB-2.1 (TOB1). Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2012, 33, 250–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, B.T.; Kimble, J. A new look at TCF and β-catenin through the lens of a divergent C. elegans Wnt pathway. Dev. Cell 2009, 17, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, S.; Hao, C.; Li, X.; Zhao, H.; Chen, J.; Zhou, Q. Effects of BTG2 on proliferation inhibition and anti-invasion in human lung cancer cells. Tumour Biol. 2012, 33, 1223–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Micheli, L.; Ceccarelli, M.; Farioli-Vecchioli, S.; Tirone, F. Control of the normal and pathological development of neural stem and progenitor cells by the PC3/Tis21/Btg2 and Btg1 Genes. J. Cell. Physiol. 2015, 230, 2881–2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherr, C.J. Principles of tumor suppression. Cell 2004, 116, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athar, M.; Elmets, C.A.; Kopelovich, L. Pharmacological activation of p53 in cancer cells. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2011, 17, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.W.; Nasto, R.E.; Varghese, R.; Jablonski, S.A.; Serebriiskii, I.G.; Surana, R.; Calvert, V.S.; Bebu, I.; Murray, J.; Jin, L.; et al. Acquisition of estrogen independence induces TOB1-related mechanisms supporting breast cancer cell proliferation. Oncogene 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, H.S.; Kundu, J.; Kim, R.N.; Shin, Y.K. Transducer of ERBB2.1 (TOB1) as a Tumor Suppressor: A Mechanistic Perspective. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 29815-29828. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161226203
Lee HS, Kundu J, Kim RN, Shin YK. Transducer of ERBB2.1 (TOB1) as a Tumor Suppressor: A Mechanistic Perspective. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2015; 16(12):29815-29828. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161226203
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Hun Seok, Juthika Kundu, Ryong Nam Kim, and Young Kee Shin. 2015. "Transducer of ERBB2.1 (TOB1) as a Tumor Suppressor: A Mechanistic Perspective" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 16, no. 12: 29815-29828. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161226203
APA StyleLee, H. S., Kundu, J., Kim, R. N., & Shin, Y. K. (2015). Transducer of ERBB2.1 (TOB1) as a Tumor Suppressor: A Mechanistic Perspective. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 16(12), 29815-29828. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161226203