Proteomic Challenges: Sample Preparation Techniques for Microgram-Quantity Protein Analysis from Biological Samples
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Macroscale versus Microscale Techniques
2.1. Obtaining a Sample for Proteomic Analysis
| Detergent Name | Type | Molecular Weight | CMC, mM | Mol. Weight (Micelle) | Suggested Removal |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Triton X-100 | Nonionic | 647 | 0.24 | 90,000 | TCA/Acetone |
| NP-40 | Nonionic | 617 | 0.29 | 90,000 | Acetone |
| Tween 20 | Nonionic | 1228 | 0.06 | Acetone | |
| Tween 80 | Nonionic | 1310 | 0.01 | 76,000 | Acetone |
| Octyl Glucoside | Nonionic | 292 | 23–24 | 8000 | Ethyl acetate |
| Octyl thioglucoside | Nonionic | 308 | 9 | Ethyl Acetate | |
| Big CHAP | Nonionic | 878 | 3–4 | 8781 | Filtration |
| Deoxycholate | Anionic | 415 | 2–6 | 2000 | Acetone, TCA |
| Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate | Anionic | 288 | 6–8 | 17,887 | Filtration/FASP |
| CHAPS | Zwitterionic | 615 | 8–10 | 6149 | Filtration |
| CHAPSO | Zwitterionic | 631 | 8–10 | 7000 | Filtration |
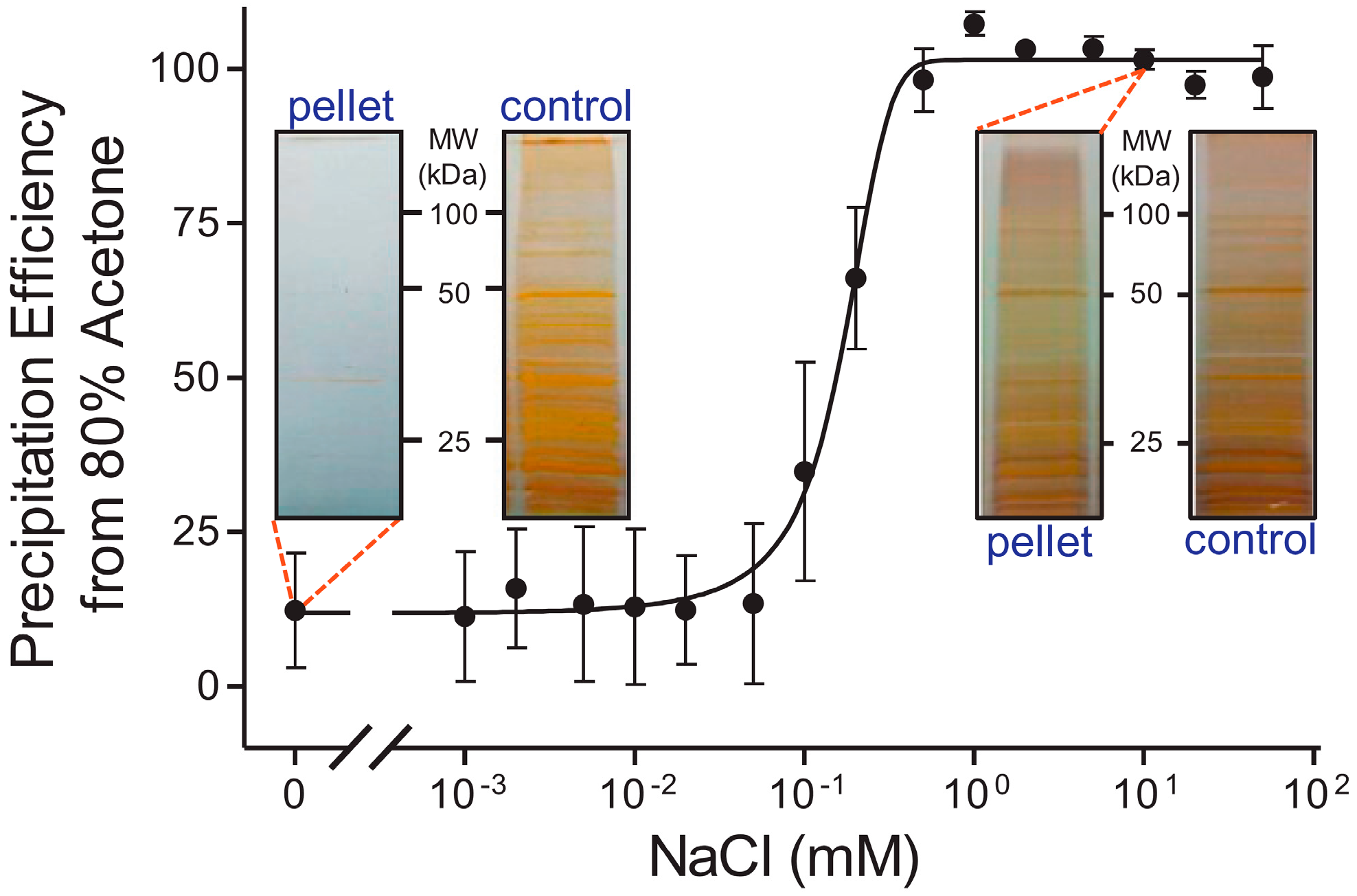
2.2. Contaminant Removal
| Approach | Description | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| “Salting out” | Precipitation uses saturation of salt to precipitate protein from solution. Most commonly an ammonium sulfate precipitation, but also uses sodium sulfate. | [57,58,59] |
| Ultrafiltration | Centrifugation at high speed using molecular weight cutoff filter to remove contaminants; prominent in Filter-Aided Sample Preparation (FASP). | [57,60] |
| Polyethyleneimine (PEI) | Cationic polymer precipitates nucleic acids in 1 M NaCl, leaving proteins in the supernatant. PEI must be removed before further analysis. | [57,58,61,62] |
| Isoelectric Point (PI) | The pH of solution is adjusted with mineral acid to the isoelectric point of most proteins (pH 4–6). Neutral proteins will aggregate and precipitate. | [57,63,64] |
| Thermal | Cell extracts are denatured using heat; denatured proteins aggregate and precipitate, but stability is enhanced. | [57,65,66] |
| Nonionic polymer Polyethylene glycol (PEG) | Concentration of PEG unique to the protein mixture is added. Proteins precipitate based on an excluded volume principle. Centrifugation pellets the precipitated protein. PEG must be removed before mass spectrometry analysis. | [57,67,68,69] |
2.3. Digestion Strategies

2.4. Fractionation and Separation of Proteomic Mixtures
3. Microproteomics
3.1. Sensitivity and Microscale Analysis
3.2. Clean Sample Preparation

3.3. Microproteomic Fractionation and Separation
3.4. One Application of Microproteomics: Exploring Cancer Samples
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wilson, R. Sensitivity and specificity: Twin goals of proteomics assays. Can they be combined? Expert Rev. Proteomics 2013, 10, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonge, R.; Shaw, J.; Middleton, B.; Rowlinson, R.; Rayner, S.; Young, J.; Pognan, F.; Hawkins, E.; Currie, I.; Davison, M. Validation and development of fluorescence two-dimensional differential gel electrophoresis proteomics technology. Proteomics 2001, 1, 377–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lilley, K.S.; Friedman, D.B. All about DIGE: Quantification technology for differential-display 2D-gel proteomics. Expert Rev. Proteomics 2004, 1, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karas, M.; Hillenkamp, F. Laser desorption ionization of proteins with molecular masses exceeding 10,000 daltons. Anal. Chem. 1988, 60, 2299–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, K.; Waki, H.; Ido, Y.; Akita, S.; Yoshida, Y.; Yoshida, T.; Matsuo, T. Protein and polymer analyses up to m/z 100,000 by laser ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 1988, 2, 151–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenn, J.B.; Mann, M.; Meng, C.K.; Wong, S.F.; Whitehouse, C.M. Electrospray ionization for mass spectrometry of large biomolecules. Science 1989, 246, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weaver, E.M.; Hummon, A.B. Imaging mass spectrometry: From tissue sections to cell cultures. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 1039–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutstein, H.B.; Morris, J.S.; Annangudi, S.P.; Sweedler, J.V. Microproteomics: Analysis of protein diversity in small samples. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2008, 27, 316–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aebersold, R.; Mann, M. Mass spectrometry-based proteomics. Nature 2003, 422, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scigelova, M.; Makarov, A. Orbitrap mass analyzer—Overview and applications in proteomics. Proteomics 2006, 6, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahlf, D.R.; Compton, P.D.; Tran, J.C.; Early, B.P.; Thomas, P.M.; Kelleher, N.L. Evaluation of the compact high-field orbitrap for top-down proteomics of human cells. J. Proteome Res. 2012, 11, 4308–4314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebert, A.S.; Richards, A.L.; Bailey, D.J.; Ulbrich, A.; Coughlin, E.E.; Westphall, M.S.; Coon, J.J. The one hour yeast proteome. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2014, 13, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, M.; Kelleher, N.L. Precision proteomics: The case for high resolution and high mass accuracy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 18132–18138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stahl-Zeng, J.; Lange, V.; Ossola, R.; Eckhardt, K.; Krek, W.; Aebersold, R.; Domon, B. High sensitivity detection of plasma proteins by multiple reaction monitoring of N-glycosites. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2007, 6, 1809–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Shaler, T.A.; Becker, C.H. Quantification of intermediate-abundance proteins in serum by multiple reaction monitoring mass spectrometry in a single-quadrupole ion trap. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 5762–5767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- March, R.E.; Todd, J.F.J. Practical Aspects of Trapped Ion Mass Spectrometry, Volume IV: Theory and Instrumentation; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010; pp. 61–64. [Google Scholar]
- Dancík, V.; Addona, T.A.; Clauser, K.R.; Vath, J.E.; Pevzner, P.A. De novo peptide sequencing via tandem mass spectrometry. J. Comput. Biol. 1999, 6, 327–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medzihradszky, K.F.; Chalkley, R.J. Lessons in de novo peptide sequencing by tandem mass spectrometry. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2015, 34, 43–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiede, B.; Höhenwarter, W.; Krah, A.; Mattow, J.; Schmid, M.; Schmidt, F.; Jungblut, P.R. Peptide mass fingerprinting. Methods (San Diego Calif.) 2005, 35, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, J.; Oxley, D. Peptide mass fingerprinting: Protein identification using MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. Methods Mol. Biol. (Clifton N.J.) 2005, 310, 227–240. [Google Scholar]
- Pappin, D.J.; Hojrup, P.; Bleasby, A.J. Rapid identification of proteins by peptide-mass fingerprinting. Curr. Biol. 1993, 3, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sommerer, N.; Centeno, D.; Rossignol, M. Peptide mass fingerprinting. In Plant Proteomics; Thiellement, H., Zivy, M., Damerval, C., Méchin, V., Eds.; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 219–234. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, Y.; Valeja, S.G.; Rouse, J.C.; Hendrickson, C.L.; Marshall, A.G. Top-down structural analysis of an intact monoclonal antibody by electron capture dissociation-Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance-mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 4239–4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syka, J.E.P.; Coon, J.J.; Schroeder, M.J.; Shabanowitz, J.; Hunt, D.F. Peptide and protein sequence analysis by electron transfer dissociation mass spectrometry. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 9528–9533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhurov, K.O.; Fornelli, L.; Wodrich, M.D.; Laskay, Ü.A.; Tsybin, Y.O. Principles of electron capture and transfer dissociation mass spectrometry applied to peptide and protein structure analysis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 5014–5030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jedrychowski, M.P.; Huttlin, E.L.; Haas, W.; Sowa, M.E.; Rad, R.; Gygi, S.P. Evaluation of HCD- and CID-type fragmentation within their respective detection platforms for murine phosphoproteomics. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2011, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michalski, A.; Neuhauser, N.; Cox, J.; Mann, M. A systematic investigation into the nature of tryptic HCD spectra. J. Proteome Res. 2012, 11, 5479–5491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papayannopoulos, I.A. The interpretation of collision-induced dissociation tandem mass spectra of peptides. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 1995, 14, 49–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medzihradszky, K.F.; Campbell, J.M.; Baldwin, M.A.; Falick, A.M.; Juhasz, P.; Vestal, M.L.; Burlingame, A.L. The characteristics of peptide collision-induced dissociation using a high-performance MALDI-TOF/TOF tandem mass spectrometer. Anal. Chem. 2000, 72, 552–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, J.P.; Brodbelt, J.S. Structural characterization of gangliosides and glycolipids via ultraviolet photodissociation mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 10399–10407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brodbelt, J.S. Photodissociation mass spectrometry: New tools for characterization of biological molecules. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 2757–2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keough, T.; Youngquist, R.S.; Lacey, M.P. A method for high-sensitivity peptide sequencing using postsource decay matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization mass spectrometry. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 7131–7136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Tolić, N.; Xie, F.; Zhao, R.; Purvine, S.O.; Schepmoes, A.A.; Moore, R.J.; Anderson, G.A.; Smith, R.D. Effectiveness of CID, HCD, and ETD with FT MS/MS for degradomic-peptidomic analysis: Comparison of peptide identification methods. J. Proteome Res. 2011, 10, 3929–3943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, C.T.; Caulfield, T.; Borgelt, E.; Illes, J. Personal medicine—The new banking crisis. Nat. Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guidelines for the Use of Human Tissue for Future Unspecified Research Purposes. Available online: http://www.health.govt.nz/publication/guidelines-use-human-tissue-future-unspecified-research-purposes-0 (accessed on 31 October 2014).
- Salvaterra, E.; Lecchi, L.; Giovanelli, S.; Butti, B.; Bardella, M.T.; Bertazzi, P.A.; Bosari, S.; Coggi, G.; Coviello, D.A.; Lalatta, F.; et al. Banking together. A unified model of informed consent for biobanking. EMBO Rep. 2008, 9, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raynie, D.E. Modern extraction techniques. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 4911–4916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cañas, B.; Piñeiro, C.; Calvo, E.; López-Ferrer, D.; Gallardo, J.M. Trends in sample preparation for classical and second generation proteomics. J. Chromatogr. 2007, 1153, 235–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traditional Methods of Cell Lysis. Available online: http://www.piercenet.com/method/traditional-methods-cell-lysis (accessed on 31 October 2014).
- Detergents for Cell Lysis and Protein Extraction. Available online: http://www.piercenet.com/method/detergents-cell-lysis-protein-extraction (accessed on 31 October 2014).
- Swiderek, K.M.; Alpert, A.J.; Heckendorf, A.; Nugent, K.; Patterson, S.D. Structural analysis of proteins and peptides in the presence of detergents: Tricks of the trade. ABRF News Artic. Methodol. 1997, 8, 17–25. [Google Scholar]
- Bodzon-Kulakowska, A.; Bierczynska-Krzysik, A.; Dylag, T.; Drabik, A.; Suder, P.; Noga, M.; Jarzebinska, J.; Silberring, J. Methods for samples preparation in proteomic research. J. Chromatogr. 2007, 849, 1–31. [Google Scholar]
- Visser, N.F.C.; Lingeman, H.; Irth, H. Sample preparation for peptides and proteins in biological matrices prior to liquid chromatography and capillary zone electrophoresis. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2005, 382, 535–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilbrig, F.; Freitag, R. Protein purification by affinity precipitation. J. Chromatogr. 2003, 790, 79–90. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.-Y.; Dann, G.P.; Shi, T.; Wang, L.; Gao, X.; Su, D.; Nicora, C.D.; Shukla, A.K.; Moore, R.J.; Liu, T.; et al. Simple sodium dodecyl sulfate-assisted sample preparation method for LC–MS-based proteomics applications. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 2862–2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buxton, T.B.; Crockett, J.K.; Moore, W.L.; Moore, W.L.; Rissing, J.P. Protein precipitation by acetone for the analysis of polyethylene glycol in intestinal perfusion fluid. Gastroenterology 1979, 76, 820–824. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Peterson, G.L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal. Biochem. 1977, 83, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bensadoun, A.; Weinstein, D. Assay of proteins in the presence of interfering materials. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 70, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, U.; Ulbrich-Hofmann, R. Quantitative protein precipitation from guanidine hydrochloride-containing solutions by sodium deoxycholate/trichloroacetic acid. Anal. Biochem. 1999, 271, 197–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wessel, D.; Flügge, U.-I. A method for the quantitative recovery of protein in dilute solution in the presence of detergents and lipids. Anal. Biochem. 1984, 138, 141–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeung, Y.-G.; Stanley, E.R. Rapid detergent removal from peptide samples with ethyl acetate for mass spectrometry analysis. Curr. Protoc. Protein Sci. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, Y.-G.; Nieves, E.; Angeletti, R.H.; Stanley, E.R. Removal of detergents from protein digests for mass spectrometry analysis. Anal. Biochem. 2008, 382, 135–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, B.; Oberholzer, V.G.; Whitehead, T.P. Serum protein fractions: A comparison of precipitation methods with electrophoresis. J. Clin. Pathol. 1950, 3, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fic, E.; Kedracka-Krok, S.; Jankowska, U.; Pirog, A.; Dziedzicka-Wasylewska, M. Comparison of protein precipitation methods for various rat brain structures prior to proteomic analysis. Electrophoresis 2010, 31, 3573–3579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabilloud, T. Detergents and chaotropes for protein solubilization before two-dimensional electrophoresis. Methods Mol. Biol. (Clifton N.J.) 2009, 528, 259–267. [Google Scholar]
- Chapel, A.; Salvi, D.; Garin, J.; Joyard, J.; de Biologie, D.; et Structurale, M.; VØgØtale, C.; Fourier, U.J. Organic solvent extraction as a versatile procedure to identify hydrophobic chloroplast membrane proteins. Electrophoresis 2000, 21, 3517–3526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Englard, S.; Seifter, S. Precipitation techniques. Methods Enzymol. 1990, 182, 285–300. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Burgess, R.R. Protein precipitation techniques. Methods Enzymol. 2009, 463, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; He, L.; Fountoulakis, M. Comparison of protein precipitation methods for sample preparation prior to proteomic analysis. J. Chromatogr. 2004, 1023, 317–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiśniewski, J.R.; Zielinska, D.F.; Mann, M. Comparison of ultrafiltration units for proteomic and N-glycoproteomic analysis by the filter-aided sample preparation method. Anal. Biochem. 2011, 410, 307–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, M.N.; Kaul, R.; Guoqiang, D.; Dissing, U.; Mattiasson, B. Affinity precipitation of proteins. J. Mol. Recognit. 1996, 9, 356–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holler, C.; Vaughan, D.; Zhang, C. Polyethyleneimine precipitation versus anion exchange chromatography in fractionating recombinant β-glucuronidase from transgenic tobacco extract. J. Chromatogr. 2007, 1142, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegg, P.O. Precipitation of egg white proteins below their isoelectric points by sodium dodecyl sulphate and temperature. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1979, 579, 73–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaffé, W.G. A simple method for the approximate estimation of the isoelectric point of soluble proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 1943, 148, 185–186. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.; Huang, B.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.C. Thermal precipitation fluorescence assay for protein stability screening. J. Struct. Biol. 2011, 175, 465–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, A.R.; Irvine, D.M. Effects of pH on the thermal precipitation of proteins in acid and sweet cheese wheys. Can. Inst. Food Sci. Technol. J. 1988, 21, 386–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingham, K.C. Precipitation of proteins with polyethylene glycol. Methods Enzymol. 1990, 182, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ingham, K.C. Protein precipitation with polyethylene glycol. Methods Enzymol. 1984, 104, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sim, S.-L.; He, T.; Tscheliessnig, A.; Mueller, M.; Tan, R.B.H.; Jungbauer, A. Protein precipitation by polyethylene glycol: A generalized model based on hydrodynamic radius. J. Biotechnol. 2012, 157, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowell, A.M.J.; Wall, M.J.; Doucette, A.A. Maximizing recovery of water-soluble proteins through acetone precipitation. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 796, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barritault, D.; Expert-Bezançon, A.; Guérin, M.-F.; Hayes, D. The use of acetone precipitation in the isolation of ribosomal proteins. Eur. J. Biochem. 1976, 63, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puchades, M.; Westman, A.; Blennow, K.; Davidsson, P. Analysis of intact proteins from cerebrospinal fluid by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry after two-dimensional liquid-phase electrophoresis. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 1999, 13, 2450–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thongboonkerd, V.; Mcleish, K.R.; Arthur, J.M.; Klein, J.B. Proteomic analysis of normal human urinary proteins isolated by acetone precipitation or ultracentrifugation. Kidney Int. 2002, 62, 1461–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, O.P.; Srivastava, K. Purification of gamma-crystallin from human lenses by acetone precipitation method. Curr. Eye Res. 1998, 17, 1074–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Hagen, J. Proteomics Sample Preparation; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Xiong, E.; Wang, W.; Scali, M.; Cresti, M. Universal sample preparation method integrating trichloroacetic acid/acetone precipitation with phenol extraction for crop proteomic analysis. Nat. Protoc. 2014, 9, 362–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chevallet, M.; Diemer, H.; van Dorssealer, A.; Villiers, C.; Rabilloud, T. Toward a better analysis of secreted proteins: The example of the myeloid cells secretome. Proteomics 2007, 7, 1757–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Robinson, P.J.; Liu, J.P.; Chen, W.; Wenzel, T. Activation of protein kinase C in vitro and in intact cells or synaptosomes determined by acetic acid extraction of MARCKS. Anal. Biochem. 1993, 210, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isaacson, T.; Damasceno, C.M.B.; Saravanan, R.S.; He, Y.; Catalá, C.; Saladié, M.; Rose, J.K.C. Sample extraction techniques for enhanced proteomic analysis of plant tissues. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 769–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, X.; Young, R.; Straubinger, R.M.; Page, B.; Cao, J.; Wang, H.; Yu, H.; Canty, J.M.; Qu, J. A straightforward and highly efficient precipitation/on-pellet digestion procedure coupled with a long gradient nano-LC separation and orbitrap mass spectrometry for label-free expression profiling of the swine heart mitochondrial proteome. J. Proteome Res. 2009, 8, 2838–2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Godoy, L.M.F.; Olsen, J.V.; Cox, J.; Nielsen, M.L.; Hubner, N.C.; Fröhlich, F.; Walther, T.C.; Mann, M. Comprehensive mass-spectrometry-based proteome quantification of haploid versus diploid yeast. Nature 2008, 455, 1251–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Shaw, A.R.E.; Zhang, N.; Mak, A.; Li, L. Lipid raft proteomics: Analysis of in-solution digest of sodium dodecyl sulfate-solubilized lipid raft proteins by liquid chromatography-matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Proteomics 2004, 4, 3156–3166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Souza, G.A.; Godoy, L.M.F.; Mann, M. Identification of 491 proteins in the tear fluid proteome reveals a large number of proteases and protease inhibitors. Genome Biol. 2006, 7, R72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Go, E.P.; Rebecchi, K.R.; Desaire, H. In-solution digestion of glycoproteins for glycopeptide-based mass analysis. Methods Mol. Biol. (Clifton N.J.) 2013, 951, 103–111. [Google Scholar]
- Lasonder, E.; Ishihama, Y.; Andersen, J.S.; Vermunt, A.M.W.; Pain, A.; Sauerwein, R.W.; Eling, W.M.C.; Hall, N.; Waters, A.P.; Stunnenberg, H.G.; et al. Analysis of the Plasmodium falciparum proteome by high-accuracy mass spectrometry. Nature 2002, 419, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pomastowski, P.; Buszewski, B. Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis in the light of new developments. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2014, 53, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shevchenko, A.; Wilm, M.; Vorm, O.; Mann, M. Mass spectrometric sequencing of proteins from silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. Anal. Chem. 1996, 68, 850–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbert, B. Advances in protein solubilisation for two-dimensional electrophoresis. Electrophoresis 1999, 20, 660–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Görg, A.; Weiss, W.; Dunn, M.J. Current two-dimensional electrophoresis technology for proteomics. Proteomics 2004, 4, 3665–3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabilloud, T. Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis in proteomics: Old, old fashioned, but it still climbs up the mountains. Proteomics 2002, 2, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabilloud, T.; Chevallet, M.; Luche, S.; Lelong, C. Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis in proteomics: Past, present and future. J. Proteomics 2010, 73, 2064–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Granvogl, B.; Plöscher, M.; Eichacker, L.A. Sample preparation by in-gel digestion for mass spectrometry-based proteomics. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 389, 991–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shevchenko, A.; Tomas, H.; Havlis, J.; Olsen, J.V.; Mann, M. In-gel digestion for mass spectrometric characterization of proteins and proteomes. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 2856–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, D.; Rejtar, T.; Wang, D.; Bones, J.; Cha, S.; Clodfelder-Miller, B.; Richardson, E.; Binns, S.; Dahiya, S.; Sgroi, D.; et al. Microproteomic analysis of 10,000 laser captured microdissected breast tumor cells using short-range sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and porous layer open tubular liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. 2011, 1218, 8168–8174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabilloud, T.; Lelong, C. Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis in proteomics: A tutorial. J. Proteomics 2011, 74, 1829–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Craven, R.A.; Totty, N.; Harnden, P.; Selby, P.J.; Banks, R.E. Laser capture microdissection and two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Am. J. Pathol. 2002, 160, 815–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiner, A.M.; Platt, T.; Weber, K. Amino-terminal sequence analysis of proteins purified on a nanomole scale by gel electrophoresis. J. Biol. Chem. 1972, 247, 3242–3251. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Speicher, K.; Kolbas, O.; Harper, S.; Speicher, D. Systematic analysis of peptide recoveries from in-gel digestions for protein identifications in proteome studies. J. Biomol. Tech. 2000, 11, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gundry, R.L.; White, M.Y.; Murray, C.I.; Kane, L.A.; Fu, Q.; Stanley, B.A.; van Eyk, J.E. Preparation of proteins and peptides for mass spectrometry analysis in a bottom-up proteomics workflow. Curr. Protoc. Mol. Biol. 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Bailey, M.J.; Dunn, M.J.; Preedy, V.R.; Emery, P.W. A quantitative investigation into the losses of proteins at different stages of a two-dimensional gel electrophoresis procedure. Proteomics 2005, 5, 2739–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manza, L.L.; Stamer, S.L.; Ham, A.-J.L.; Codreanu, S.G.; Liebler, D.C. Sample preparation and digestion for proteomic analyses using spin filters. Proteomics 2005, 5, 1742–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X. Bioinformatics of Human Proteomics; Springer Science + Business Media B.V.: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wiśniewski, J.R.; Zougman, A.; Nagaraj, N.; Mann, M. Universal sample preparation method for proteome analysis. Nat. Methods 2009, 6, 359–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erde, J.; Loo, R.R.O.; Loo, J.A. Enhanced FASP (eFASP) to increase proteome coverage and sample recovery for quantitative proteomic experiments. J. Proteome Res. 2014, 13, 1885–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zielinska, D.F.; Gnad, F.; Wiśniewski, J.R.; Mann, M. Precision mapping of an in vivo N-glycoproteome reveals rigid topological and sequence constraints. Cell 2010, 141, 897–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanshin, E.; Michnick, S.; Thibault, P. Sample preparation and analytical strategies for large-scale phosphoproteomics experiments. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2012, 23, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiśniewski, J.R.; Mann, M. Reply to “Spin filter-based sample preparation for shotgun proteomics”. Nat. Methods 2009, 6, 785–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eggler, A.L.; Luo, Y.; van Breemen, R.B.; Mesecar, A.D. Identification of the highly reactive cysteine 151 in the chemopreventive agent-sensor Keap1 protein is method-dependent. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2007, 20, 1878–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liebler, D.C.; Ham, A.-J.L. Spin filter-based sample preparation for shotgun proteomics. Nat. Methods 2009, 6, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiśniewski, J.R.; Ostasiewicz, P.; Mann, M. High recovery FASP applied to the proteomic analysis of microdissected formalin fixed paraffin embedded cancer tissues retrieves known colon cancer markers. J. Proteome Res. 2011, 10, 3040–3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weston, L.A.; Bauer, K.M.; Hummon, A.B. Comparison of bottom-up proteomic approaches for LC–MS analysis of complex proteomes. Anal. Methods 2013, 5, 4615–4621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Washburn, M.P.; Wolters, D.; Yates, J.R. Large-scale analysis of the yeast proteome by multidimensional protein identification technology. Nat. Biotechnol. 2001, 19, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipton, M.S.; Pasa-Tolic, L.; Anderson, G.A.; Anderson, D.J.; Auberry, D.L.; Battista, J.R.; Daly, M.J.; Fredrickson, J.; Hixson, K.K.; Kostandarithes, H.; et al. Global analysis of the Deinococcus radiodurans proteome by using accurate mass tags. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 11049–11054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, F.; Liu, T.; Qian, W.-J.; Petyuk, V.A.; Smith, R.D. Liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry-based quantitative proteomics. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 25443–25449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.; Elias, J.E.; Thoreen, C.C.; Licklider, L.J.; Gygi, S.P. Evaluation of multidimensional chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry (LC/LC–MS/MS) for large-scale protein analysis: The yeast proteome. J. Proteome Res. 2003, 2, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jungblut, P.R. Protein and Peptide Mass Spectrometry in Drug Discovery; Gross, M.L., Chen, G., Pramanik, B., Eds.; ChemMedChem: Weinheim, Germany, 2012; Volume 7, pp. 2241–2242. [Google Scholar]
- You, J.; Wang, L.; Saji, M.; Olesik, S.V.; Ringel, M.D.; Lucas, D.M.; Byrd, J.C.; Freitas, M.A. High-sensitivity TFA-free LC–MS for profiling histones. Proteomics 2011, 11, 3326–3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; James, C.A. LC–MS bioanalysis of peptides and polypeptides. In Handbook of LC–MS Bioanalysis; Li, W., Zhang, J., Tse, F.L.S., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 535–549. [Google Scholar]
- De Jong, E.P.; Griffin, T.J. Online nanoscale ERLIC–MS outperforms RPLC–MS for shotgun proteomics in complex mixtures. J. Proteome Res. 2012, 11, 5059–5064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, P.; Qian, J.; Dutta, B.; Cheow, E.S.H.; Sim, K.H.; Meng, W.; Adav, S.S.; Alpert, A.; Sze, S.K. Enhanced separation and characterization of deamidated peptides with RP-ERLIC-based multidimensional chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry. J. Proteome Res. 2012, 11, 1804–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarei, M.; Sprenger, A.; Metzger, F.; Gretzmeier, C.; Dengjel, J. Comparison of ERLIC-TiO2, HILIC-TiO2, and SCX-TiO2 for global phosphoproteomics approaches. J. Proteome Res. 2011, 10, 3474–3483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, P.; Guo, T.; Li, X.; Adav, S.S.; Yang, J.; Wei, M.; Sze, S.K. Novel application of electrostatic repulsion-hydrophilic interaction chromatography (ERLIC) in shotgun proteomics: Comprehensive profiling of rat kidney proteome. J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 3520–3526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Qian, W.-J.; Mottaz, H.M.; Clauss, T.R.W.; Anderson, D.J.; Moore, R.J.; Camp, D.G.; Khan, A.H.; Sforza, D.M.; Pallavicini, M.; et al. Development and evaluation of a micro- and nanoscale proteomic sample preparation method. J. Proteome Res. 2005, 4, 2397–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emmert-Buck, M.R.; Gillespie, J.W.; Paweletz, C.P.; Ornstein, D.K.; Basrur, V.; Appella, E.; Wang, Q.H.; Huang, J.; Hu, N.; Taylor, P.; et al. An approach to proteomic analysis of human tumors. Mol. Carcinog. 2000, 27, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gozal, Y.M.; Cheng, D.; Duong, D.M.; Lah, J.J.; Levey, A.I.; Peng, J. Merger of laser capture microdissection and mass spectrometry: A window into the amyloid plaque proteome. Methods Enzymol. 2006, 412, 77–93. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Picotti, P.; Bodenmiller, B.; Mueller, L.N.; Domon, B.; Aebersold, R. Full dynamic range proteome analysis of S. cerevisiae by targeted proteomics. Cell 2009, 138, 795–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, N.L.; Anderson, N.G. The human plasma proteome: History, character, and diagnostic prospects. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2002, 1, 845–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, P. Proteomics retrenches. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 665–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Xu, M.; Wang, P.; Li, L. Development of mass spectrometry-based shotgun method for proteome analysis of 500 to 5000 cancer cells. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 2262–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Bertke, M.M.; Champion, M.M.; Zhu, G.; Huber, P.W.; Dovichi, N.J. Quantitative proteomics of Xenopus laevis embryos: Expression kinetics of nearly 4000 proteins during early development. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4365. [Google Scholar]
- Sleno, L. The use of mass defect in modern mass spectrometry. JMS 2012, 47, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Zhu, G.; Dovichi, N.J. Comparison of the LTQ-Orbitrap Velos and the Q-Exactive for proteomic analysis of 1–1000 ng RAW 264.7 cell lysate digests. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2013, 27, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, J.G.; Komives, E.A. Charge state coalescence during electrospray ionization improves peptide identification by tandem mass spectrometry. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2012, 23, 1390–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahne, H.; Pachl, F.; Ruprecht, B.; Maier, S.K.; Klaeger, S.; Helm, D.; Médard, G.; Wilm, M.; Lemeer, S.; Kuster, B. DMSO enhances electrospray response, boosting sensitivity of proteomic experiments. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 989–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tjernberg, A.; Markova, N.; Griffiths, W.J.; Hallén, D. DMSO-related effects in protein characterization. J. Biomol. Screen. 2006, 11, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korfmacher, W.A. Using Mass Spectrometry for Drug Metabolism Studies, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Brash, J.L.; ten Hove, P. Effect of plasma dilution on adsorption of fibrinogen to solid surfaces. Thromb. Haemost. 1984, 51, 326–330. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Horbett, T.A. Chapter 13 Principles underlying the role of adsorbed plasma proteins in blood interactions with foreign materials. Cardiovasc. Pathol. 1993, 2, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hervey, W.J.; Strader, M.B.; Hurst, G.B. Comparison of digestion protocols for microgram quantities of enriched protein samples. J. Proteome Res. 2007, 6, 3054–3061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strader, M.B.; Tabb, D.L.; Hervey, W.J.; Pan, C.; Hurst, G.B. Efficient and specific trypsin digestion of microgram to nanogram quantities of proteins in organic-aqueous solvent systems. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.C.; Chen, Y.; Mirza, S.; Xu, Y.; Lee, J.; Liu, P.; Zhao, Y. A clean, more efficient method for in-solution digestion of protein mixtures without detergent or urea. J. Proteome Res. 2006, 5, 3446–3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, G. Proteins: Biochemistry and Biotechnology; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Puchades, M.; Westman, A.; Blennow, K.; Davidsson, P. Removal of sodium dodecyl sulfate from protein samples prior to matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 1999, 13, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, K.L.; Williams, K.R. 2-Enzymatic digestion of proteins and HPLC peptide isolation. In A Practical Guide to Protein and Peptide Purification for Microsequencing,, 2nd ed.; Matsudaira, P., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1993; pp. 43–69. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, J.M. The Proteomics Protocols Handbook; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Zhou, T.; Cao, R.; Liu, Z.; Shen, J.; Chen, P.; Wang, X.; Liang, S. Evaluation of the application of sodium deoxycholate to proteomic analysis of rat hippocampal plasma membrane. J. Proteome Res. 2006, 5, 2547–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDowell, G.S.; Gaun, A.; Steen, H. iFASP: Combining isobaric mass tagging with filter-aided sample preparation. J. Proteome Res. 2013, 12, 3809–3812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber, M.L.; Sacco, R.; Parapatics, K.; Skucha, A.; Khamina, K.; Muller, A.C.; Rudashevskaya, E.L.; Bennett, K.L. abFASP-MS: Affinity-based filter-aided sample preparation mass spectrometry for quantitative analysis of chemically labeled protein complexes. J. Proteome Res. 2014, 13, 1147–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cha, S.; Imielinski, M.B.; Rejtar, T.; Richardson, E.A.; Thakur, D.; Sgroi, D.C.; Karger, B.L. In Situ proteomic analysis of human breast cancer epithelial cells using laser capture microdissection: Annotation by protein set enrichment analysis and gene ontology. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2010, 9, 2529–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorgenson, J.W.; Lukacs, K.D. Zone electrophoresis in open-tubular glass capillaries. Anal. Chem. 1981, 53, 1298–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karger, B.L.; Guttman, A. DNA sequencing by capillary electrophoresis. Electrophoresis 2009, 30, S196–S202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heemskerk, A.A.M.; Deelder, A.M.; Mayboroda, O.A. CE–ESI-MS for bottom-up proteomics: Advances in separation, interfacing and applications. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Champion, M.M.; Sun, L.; Champion, P.A.D.; Wojcik, R.; Dovichi, N.J. Capillary zone electrophoresis-electrospray ionization-tandem mass spectrometry as an alternative proteomics platform to ultraperformance liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-tandem mass spectrometry for samples of intermediate complexity. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 1617–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Zhu, G.; Yan, X.; Champion, M.M.; Dovichi, N.J. Capillary zone electrophoresis for analysis of complex proteomes using an electrokinetically pumped sheath flow nanospray interface. Proteomics 2014, 14, 622–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Zhu, G.; Mou, S.; Zhao, Y.; Champion, M.M.; Dovichi, N.J. Capillary zone electrophoresis-electrospray ionization-tandem mass spectrometry for quantitative parallel reaction monitoring of peptide abundance and single-shot proteomic analysis of a human cell line. J. Chromatogr. 2014, 1359, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Sun, L.; Yan, X.; Dovichi, N.J. Stable, reproducible, and automated capillary zone electrophoresis–tandem mass spectrometry system with an electrokinetically pumped sheath–flow nanospray interface. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 810, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, G.; Sun, L.; Yan, X.; Dovichi, N.J. Single-shot proteomics using capillary zone electrophoresis–electrospray ionization-tandem mass spectrometry with production of more than 1250 Escherichia coli peptide identifications in a 50 min separation. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 2569–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Compton, P.D.; Tran, J.C.; Ntai, I.; Kelleher, N.L. Optimizing capillary electrophoresis for top-down proteomics of 30–80 kDa proteins. Proteomics 2014, 14, 1158–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Sun, L.; Champion, M.M.; Knierman, M.D.; Dovichi, N.J. Capillary zone electrophoresis-electrospray ionization-tandem mass spectrometry for top-down characterization of the Mycobacterium marinum secretome. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 4873–4878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diamond, D.L.; Jacobs, J.M.; Paeper, B.; Proll, S.C.; Gritsenko, M.A.; Carithers, R.L.; Larson, A.M.; Yeh, M.M.; Camp, D.G.; Smith, R.D.; et al. Proteomic profiling of human liver biopsies: Hepatitis C virus-induced fibrosis and mitochondrial dysfunction. Hepatol. (Baltim. Md.) 2007, 46, 649–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlinger, M.; Rowan, A.J.; Horswell, S.; Larkin, J.; Endesfelder, D.; Gronroos, E.; Martinez, P.; Matthews, N.; Stewart, A.; Tarpey, P.; et al. Intratumor heterogeneity and branched evolution revealed by multiregion sequencing. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 883–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cancer Symptoms, Causes, Treatment—How is cancer diagnosed? Available online: http://www.medicinenet.com/cancer/article.htm (accessed on 3 November 2014).
- Bruening, W.; Schoelles, K.; Treadwell, J.; Launders, J.; Fontanarosa, J.; Tipton, K. Comparative Effectiveness of Core-Needle and Open Surgical Biopsy for the Diagnosis of Breast Lesions; AHRQ Comparative Effectiveness Reviews; Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US): Rockville, MD, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Breast Biopsy—Cancer & Biopsies Susan G. Komen®. Available online: http://ww5.komen.org/BreastCancer/Biopsies.html (accessed on 3 November 2014).
- Rodenburg, W.; Pennings, J.L.A.; van Oostrom, C.T.M.; Roodbergen, M.; Kuiper, R.V.; Luijten, M.; de Vries, A. Identification of breast cancer biomarkers in transgenic mouse models: A proteomics approach. Proteomics Clin. Appl. 2010, 4, 603–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taguchi, A.; Politi, K.; Pitteri, S.J.; Lockwood, W.W.; Faça, V.M.; Kelly-Spratt, K.; Wong, C.-H.; Zhang, Q.; Chin, A.; Park, K.-S.; et al. Lung cancer signatures in plasma based on proteome profiling of mouse tumor models. Cancer Cell 2011, 20, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feist, P; Sun, L; Liu, X; Dovichi, N.J.; Hummon, A.B. Bottom-up proteomic analysis of single HCT 116 colon carcinoma multicellular spheroids. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2015, in press. [Google Scholar]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feist, P.; Hummon, A.B. Proteomic Challenges: Sample Preparation Techniques for Microgram-Quantity Protein Analysis from Biological Samples. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 3537-3563. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms16023537
Feist P, Hummon AB. Proteomic Challenges: Sample Preparation Techniques for Microgram-Quantity Protein Analysis from Biological Samples. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2015; 16(2):3537-3563. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms16023537
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeist, Peter, and Amanda B. Hummon. 2015. "Proteomic Challenges: Sample Preparation Techniques for Microgram-Quantity Protein Analysis from Biological Samples" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 16, no. 2: 3537-3563. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms16023537
APA StyleFeist, P., & Hummon, A. B. (2015). Proteomic Challenges: Sample Preparation Techniques for Microgram-Quantity Protein Analysis from Biological Samples. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 16(2), 3537-3563. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms16023537