Chitosan in Molecularly-Imprinted Polymers: Current and Future Prospects
Abstract
:1. Introduction
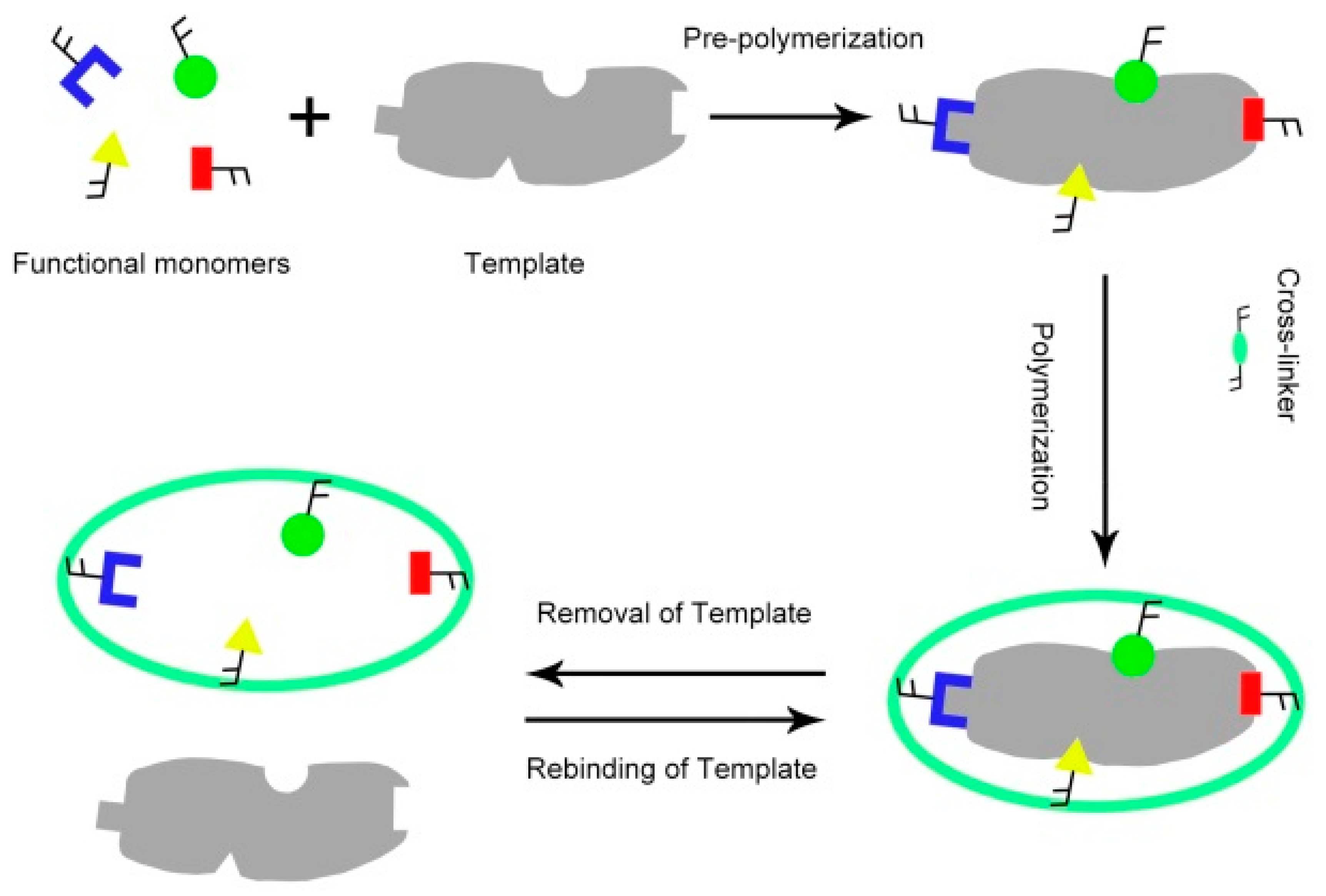

2. Performance of Cross-Linkers in MIPs
3. Crosslinking Effect of Different Categories of Compounds
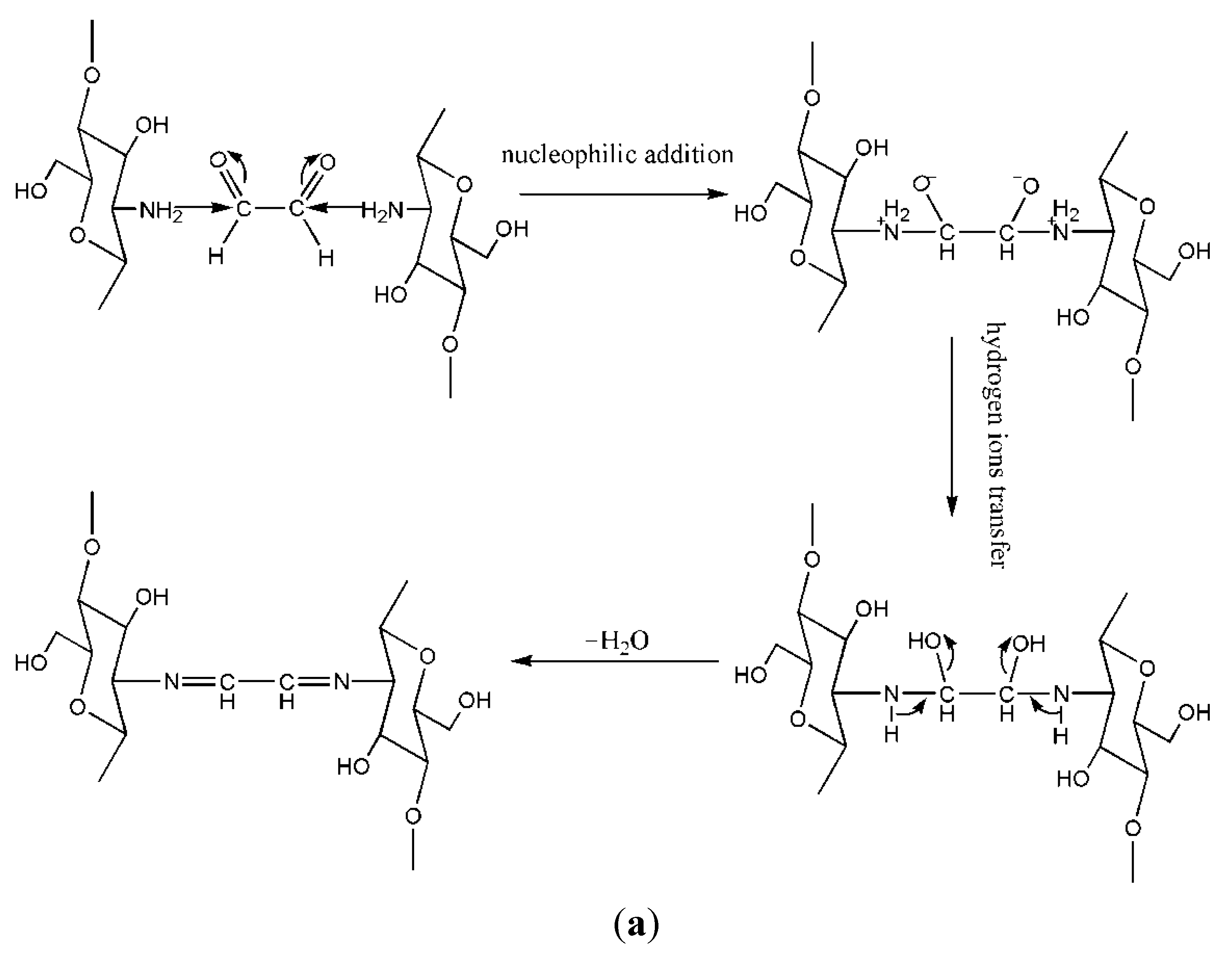
3.1. Aldehydes

3.2. Heterocyclic Compounds
3.2.1. Epichlorohydrin (ECH)

3.2.2. Genipin


3.3. Ethers

3.4. Amides

3.5. Acids

| Classification | Cross-Linker | Template | Adsorption Capacity | Polymerization Method | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| aldehyde | glyoxal | l-aspartic acid | 48 ± 0.70 mg/g | sol-gel method | [30] |
| glutaraldehyde | As3+ | 6.18 mg/g | emulsion polymerization | [31] | |
| glutaraldehyde | Cd2+ | 20.70 mg/g | ultraviolet-initiated polymerization | [61] | |
| glutaraldehyde | bilirubin | 8.70 mg/g | inverse phase suspension | [62] | |
| glutaraldehyde | l-Glutamic acid | 42 ± 0.80 mg/g | sol-gel method | [63] | |
| heterocyclic | ECH | Cr6+ | 51 mg/g | precipitation polymerization | [18] |
| ECH | Ag+ | 199.20 mg/g | surface imprinting | [39] | |
| ECH | Co2+ | 92.20 μmol/g | precipitation polymerization | [64] | |
| ECH | Ag+ | 4.93 mmol/g | surface imprinting | [65] | |
| ECH | Pb2+ | 139.60 mg/g | surface imprinting | [66] | |
| ECH | Cu2+ | 21.80 mg/g | precipitation polymerization | [67] | |
| ECH | Ni2+ | 26 mg/g | precipitation polymerization | [67] | |
| ECH | Zn2+ | 20.30 mg/g | precipitation polymerization | [67] | |
| ECH | Ni2+ | 27.39 mg/g | sol-gel method | [68] | |
| ECH | Ni2+ | 2.75 mmol/g | precipitation polymerization | [69] | |
| ECH | Hg2+ | 9.02 mg/g | suspension polymerization | [70] | |
| ECH | perfluorooctane sulfonate | 560 μmol/g | precipitation polymerization | [40] | |
| ECH | alizarin red | 40.12 mg/g | surface imprinting | [71] | |
| ECH | urea | 9.61 mg/g | surface imprinting | [72] | |
| genipin | O-xylene | 103.30 mg/g | sol-gel method | [46] | |
| ester | EGD | Cu2+ | 35.20 mg/g | surface imprinting | [73] |
| EGD | carbamazepine | 450 μmol/g | precipitation polymerization | [74] | |
| ether | EGDE | uranyl ion | 132 mg/g | sol-gel method | [52] |
| amide | MBA | bovine serum albumin | 39.49 mg/g | bulk polymerization | [53] |
| MBA | hemoglobin | 35.70 mg/g | bulk polymerization | [54] | |
| MBA | hemoglobin | 36.53 mg/g | sol-gel method | [55] | |
| MBA | lysozyme | 129.80 ± 1.20 mg/g | surface imprinting | [75] | |
| MBA | ovalbumin | 22.94 mg/g | sol-gel method | [76] | |
| Acid | sulfuric acid | l-tryptophane | - | phase inversion | [59] |
| sulfuric acid | l-phenylalanine | - | phase inversion | [60] |
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wuff, G.; Sarhan, A. The use of polymers with enzyme-analogous structures for the resolution of racemate. J. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1972, 11, 341–345. [Google Scholar]
- Arshady, R.; Mosbach, K. Synthesis of substrate-selective polymers by host-guest polymerization. Makromol. Chem. 1981, 182, 687–692. [Google Scholar]
- Vlatakis, G.; Andersson, L.I.; Müller, R.; Mosbach, K. Drug assay using antibody mimics made by molecular imprinting. Nature 1993, 361, 645–647. [Google Scholar]
- Alexander, C.; Andersson, H.S.; Andersson, L.I.; Ansell, R.J.; Kirsch, N.; Nicholls, I.A.; O’Mahony, J.; Whitcombe, M.J. Molecular imprinting science and technology: A survey of the literature for the years up to and including 2003. J. Mol. Recognit. 2006, 19, 106–180. [Google Scholar]
- He, C.; Long, Y.; Pan, J.; Li, K.; Liu, F. Application of molecularly imprinted polymers to solid-phase extraction of analytes from real samples. J Biochem Bioph Meth 2007, 70, 133–150. [Google Scholar]
- Turiel, E.; Martín-Esteban, A. Molecularly imprinted polymers for sample preparation: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 668, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- López, M.M.C.; Pérez, M.C.; García, M.S.D.; Vilarino, J.M.L.; Rodríguez, M.V.G.; Losada, L.F.B. Preparation, evaluation and characterization of quercetin-molecularly imprinted polymer for preconcentration and clean-up of catechins. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 721, 68–78. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, M.G.; Vitor, R.V.; Andrade, F.L.; Martins, I.; Figueiredo, E.C. Molecularly imprinted solid phase extraction of urinary diethyl thiophosphate and diethyl dithiophosphate and their analysis by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2012, 909, 70–76. [Google Scholar]
- Haupt, K.; Mosbach, K. Molecularly imprinted polymers and their use in biomimetic sensors. Chem. Rev. 2000, 100, 2495–2504. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Volkmann, A.; Brüggemann, O. Catalysis of an ester hydrolysis applying molecularly imprinted polymer shells based on an immobilised chiral template. React. Funct. Polym. 2006, 66, 1725–1733. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, X.; Wu, A.; Qu, G.; Li, R.; Zhang, D. Development and characterisation of molecularly imprinted polymers based on methacrylic acid for selective recognition of drugs. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 3741–3749. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Chen, L. Quercetin molecularly imprinted polymers: Preparation, recognition characteristics and properties as sorbent for solid-phase extraction. Talanta 2009, 80, 694–702. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shuguo, H.; Li, L.; Xiwen, H. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers: A New Kind of Sorbent with High Selectivity in Solid Phase Extraction. Prog. Chem. 2005, 17, 531–543. [Google Scholar]
- Benito-Peña, E.; Martins, S.; Orellana, G.; Moreno-Bondi, M.C. Water-compatible molecularly imprinted polymer for the selective recognition of fluoroquinolone antibiotics in biological samples. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 393, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ngah, W.W.; Teong, L.; Hanafiah, M. Adsorption of dyes and heavy metal ions by chitosan composites: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 1446–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Q. Pervaporation and characterization of chitosan membranes cross-linked by 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 292, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jameela, S.; Jayakrishnan, A. Glutaraldehyde cross-linked chitosan microspheres as a long acting biodegradable drug delivery vehicle: Studies on the in vitro release of mitoxantrone and in vivo degradation of microspheres in rat muscle. Biomaterials 1995, 16, 769–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, T.; He, X.; Du, W. Adsorption behaviour of metal ions on imprinted chitosan resin. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2001, 76, 191–195. [Google Scholar]
- Mukoma, P.; Jooste, B.; Vosloo, H. Synthesis and characterization of cross-linked chitosan membranes for application as alternative proton exchange membrane materials in fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2004, 136, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinesi, L.S.; Cavalheiro, E.T.G. Influence of some reactional parameters on the substitution degree of biopolymeric Schiff bases prepared from chitosan and salicylaldehyde. Carbohydr. Polym. 2006, 65, 557–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiou, M.-S.; Ho, P.-Y.; Li, H.-Y. Adsorption of anionic dyes in acid solutions using chemically cross-linked chitosan beads. Dyes Pigment. 2004, 60, 69–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Xu, S.; Li, J. Recent advances in molecular imprinting technology: Current status, challenges and highlighted applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 2922–2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cormack, P.A.; Elorza, A.Z. Molecularly imprinted polymers: Synthesis and characterisation. J. Chromatogr. B 2004, 804, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Bai, s. The design synthesis of molecularly imprinted polymers. Ion Exch. Adsorpt. 2001, 17, 360–368. [Google Scholar]
- Muhammad, T.; Nur, Z.; Piletska, E.V.; Yimit, O.; Piletsky, S.A. Rational design of molecularly imprinted polymer: The choice of cross-linker. Analyst 2012, 137, 2623–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beppu, M.; Vieira, R.; Aimoli, C.; Santana, C. Crosslinking of chitosan membranes using glutaraldehyde: Effect on ion permeability and water absorption. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 301, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monier, M.; Ayad, D.; Wei, Y.; Sarhan, A. Adsorption of Cu (II), Co (II), and Ni (II) ions by modified magnetic chitosan chelating resin. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 177, 962–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Dou, F.; Liang, B.; Shen, Q. Studies of cross-linking reaction on chitosan fiber with glyoxal. Carbohydr. Polym. 2005, 59, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, K.; Jabrail, F.H. Glutaraldehyde and glyoxal cross-linked chitosan microspheres for controlled delivery of centchroman. Carbohydr. Res. 2006, 341, 744–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monier, M.; Ayad, D.; Wei, Y.; Sarhan, A. Preparation of cross-linked chitosan/glyoxal molecularly imprinted resin for efficient chiral resolution of aspartic acid isomers. Biochem. Eng. J. 2010, 51, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Wang, D.; Li, H.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, L. As(III) removal from aqueous solution using α-Fe2O3 impregnated chitosan beads with As(III) as imprinted ions. Desalination 2011, 272, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Wang, D.; Xu, Y.; Huang, G. Adsorption properties of Cd(II)-imprinted chitosan resin. J. Mater. Sci. 2010, 46, 1535–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, H.-W.; Huang, R.-N.; Huang, L.L.; Tsai, C.-C. In vitro evaluation of cytotoxicity of a naturally occurring cross-linking reagent for biological tissue fixation. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 1999, 10, 63–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, F.-L.; Li, X.-Q.; Xiao, Y.; Zhou, Y.-T.; Zhang, H. Crosslinking Reaction of Chitosan and Gelatin with Genipin (In Chinese). J. Tianjin Univ. 2008, 40, 1485–1489. [Google Scholar]
- Congli, Q.; Xiping, M. Preparation of a New Water-soluble Derivatives of Chitosan. Chem. Ind. Times 2004, 18, 42–43. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Z.-J.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Hu, X.-Q. The Effects of Reaction Conditions on the Properties of N-Maleyl Chitosan (In Chinese). J. Southwest Petrol. Inst. 2006, 28, 73–76. [Google Scholar]
- Crini, G.; Morcellet, M. Synthesis and applications of adsorbents containing cyclodextrins. J. Sep. Sci. 2002, 25, 789–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Zeng, G.; Chen, G.; Hu, X.; Yan, M.; Guan, S.; Shang, C.; Lu, L.; Zou, Z.; Xie, G. Novel thiourea-modified magnetic ion-imprinted chitosan/TiO2 composite for simultaneous removal of cadmium and 2,4-dichlorophenol. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 191, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, H.; Su, H.; Tan, T. Adsorption of Ag+ by a surface molecular-imprinted biosorbent. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 150, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Deng, S.; Yu, G. Selective removal of perfluorooctane sulfonate from aqueous solution using chitosan-based molecularly imprinted polymer adsorbents. Water Res. 2008, 42, 3089–3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.-N.; Pan, X.-Y.; Huang, Y.; Shen, H.-B. Adaptive compressive learning for prediction of protein–protein interactions from primary sequence. J. Theor. Biol. 2011, 283, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trevor, S.L.; Butler, M.F.; Adams, S.; Laity, P.R.; Burley, J.C.; Cameron, R.E. Structure and phase transitions of genipin, an herbal medicine and naturally occurring cross-linker. Cryst. Growth Des. 2008, 8, 1748–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsm, T.-H.; Westly, J.; Lee, T.-F.; Chen, C.-F. Identification and determination of geniposide, genipin, gardenoside, and geniposidic acid from herbs by HPLC/photodiode-array detection. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 1994, 17, 2199–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujikawa, S.; Yokota, T.; Koga, K.; Kumada, J.-I. The continuous hydrolysis of geniposide to genipin using immobilized β-glucosidase on calcium alginate gel. Biotechnol. Lett. 1987, 9, 697–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryousuke, T.; Yoshio, T.; Kenichiro, I.; IKuo, K.; Masahiko, Y.; Takeshi, I.; Tetsuro, S.; Toshio, Y.; Hiroyuki, I. Studies on the blue pigments produced from genipin and methylamine. I. Structures of the brownish-red pigments, intermediates leading to the blue pigments. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1994, 42, 668–673. [Google Scholar]
- Espinosa-Garcı´a, B.M.; Argu¨elles-Monal, W.M.; ndez, J.H.; lix-Valenzuela, L.F.; Acosta, N.; Goycoolea, F.M. Molecularly Imprinted Chitosan -Genipin Hydrogels with Recognition Capacity toward O-Xylene. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 3355–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H. Preparation of new crosslinked chitosan with crown ether and their adsorption for silver ion for antibacterial activities. Carbohydr. Polym. 2003, 53, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.; Wang, Y.; Qian, S. Study on the adsorption properties of novel crown ether crosslinked chitosan for metal ions. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2002, 84, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuting, W.; Songqi, G.; Yurong, T. Synthesis of a Novel Chitoson-Crown Ether Crosslinked Compound and Its Adsorption Properties (In Chinese). Environ. Pollut. Control 2000, 22, 8–10. [Google Scholar]
- Sung, H.W.; Hsu, C.S.; Lee, Y.S.; Lin, D.S. Crosslinking characteristics of an epoxy-fixed porcine tendon: Effects of pH, temperature, and fixative concentration. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1996, 31, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, R.; Shen, S.H.; Lin, D.; Hata, C.; Thyagarajan, K.; Noishiki, Y.; Quijano, R.C. Fixation of bioprosthetic tissues with monofunctional and multifunctional polyepoxy compounds. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1994, 28, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Cao, X.; Hua, R.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Pang, C.; Wang, Y. Selective adsorption of uranyl ion on ion-imprinted chitosan/PVA cross-linked hydrogel. Hydrometallurgy 2010, 104, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, G.; Zhao, J.; Yu, H.; Liu, L.; He, B. Bovine serum albumin-imprinted polymer gels prepared by graft copolymerization of acrylamide on chitosan. React. Funct. Polym. 2007, 67, 442–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.-Y.; Xia, Y.-Q.; Hao, G.-J.; Zhang, B.-H.; Fu, G.-Q.; Yuan, Z.; He, B.-L.; Kennedy, J.F. Chemically modified chitosan beads as matrices for adsorptive separation of proteins by molecularly imprinted polymer. Carbohydr. Polym. 2005, 62, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.-Q.; Guo, T.-Y.; Song, M.-D.; Zhang, B.-H.; Zhang, B.-L. Hemoglobin recognition by imprinting in semi-interpenetrating polymer network hydrogel based on polyacrylamide and chitosan. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 2601–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Z.; Xiang, Y.; Si, J.; Yang, M.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, T. Ionic interactions between sulfuric acid and chitosan membranes. Carbohydr. Polym. 2008, 73, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, D.A.; Smitha, B.; Sridhar, S.; Aminabhavi, T. Pervaporation separation of isopropanol/water mixtures through crosslinked chitosan membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 262, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Cui, Y.; Yan, Y.; Jiang, W. The effect of structure on pervaporation of chitosan membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2000, 165, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan-Ping, N.; Min, H.; Yu-Ping, Z. Preparationand Selective Permeation Characterization of l-Tryptophane Molecular Imprinting Chitosan Film. Chem. Res. 2009, 20, 15–18. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Zhao, Y.-Y.; Yu, Y.-X.; Jiang, Z.-Y. Molecularly Imprinted Chitosan Membrane for Chiral Resolution of Phenylalanine Isomers. J. Funct. Polym. 2007, 20, 262–266. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.-Q.; Liu, Y.-G.; Hu, X.-J.; Guo, Y.-M. Adsorption of Cr (VI) by modified chitosan from heavy-metal polluted water of Xiangjiang River, China. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2013, 23, 3095–3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liping, W.; Weihua, W.; Qian, L.; Qian, Z.; Yong, W.; Wei, L.; Zhengpu, Z. The preparation of functionalized crosslinked macroporous chitosan microspheres and their adsorption properties for bilirubin. Macromol. Symp. 2010, 297, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monier, M.; El-Sokkary, A. Preparation of molecularly imprinted cross-linked chitosan/glutaraldehyde resin for enantioselective separation of l-glutamic acid. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2010, 47, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishad, P.A.; Bhaskarapillai, A.; Velmurugan, S.; Narasimhan, S.V. Cobalt (II) imprinted chitosan for selective removal of cobalt during nuclear reactor decontamination. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 87, 2690–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Luo, C.; Lv, Z.; Lu, F.; Qiu, H. Removal of Ag+ from water environment using a novel magnetic thiourea-chitosan imprinted Ag+. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 194, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.; Su, H.; Huo, H.; Tan, T. Synthesis and properties of surface molecular imprinting adsorbent for removal of Pb2+. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2010, 160, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.-Y.; Yang, C.-Y.; Chen, A.-H. Biosorption of Cu (II), Zn (II), Ni (II) and Pb (II) ions by cross-linked metal-imprinted chitosans with epichlorohydrin. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 796–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qaddafi, M.; Wahab, W.; La Nafie, N.; Taba, P. Imprinted Nickel-Cobalt Chitosan As A Specific Adsorbent Of Nickel (Ni2+) And Cobalt (Co2+). Int. J. Sci. Technol. Res. 2014, 3, 37–42. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, X.; Wang, C. Adsorption of Ni (II) from Aqueous Solution by Polyaminated Crosslinked Ni (II)-Imprinted Chitosan Derivative Beads. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2013, 30, 646–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Niu, D.; Bi, C.; Shen, B. Hg2+ Adsorption from a Low-Concentration Aqueous Solution on Chitosan Beads Modified by Combining Polyamination with Hg2+-Imprinted Technologies. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 13120–13127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Luo, C.; Lu, F.; Qiu, H. Removal of alizarin red from water environment using magnetic chitosan with Alizarin Red as imprinted molecules. Coll. Surf. B. Biointerfaces 2012, 91, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Xu, K.; Li, H.; Li, Y.; Liang, B. Preparation of Urea-Imprinted Cross-Linked Chitosan and Its Adsorption Behavior. Anal. Lett. 2014, 47, 1063–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Feng, L.; Xiong, Q.; Chen, J. Preparation and adsorption characters of Cu (II)-imprinted chitosan/attapulgite polymer. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2014, 31, 821–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Zhang, J.; Dai, C.M.; Zhou, X.F.; Liu, S.G. Sorption of carbamazepine from water by magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers based on chitosan-Fe3O4. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 97, 809–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Yuan, D.; Fu, G. Enhanced surface imprinting of lysozyme over a new kind of magnetic chitosan submicrospheres. J. Coll. Interface Sci. 2015, 440, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dan, R.; Wang, Y.; Du, L.; Du, S.; Huang, M.; Yang, S.; Zhang, M. The synthesis of molecular imprinted chitosan-gels copolymerized with multiform functional monomers at three different temperatures and the recognition for the template ovalbumin. Analyst 2013, 138, 3433–3443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, L.; Huang, Y.-A.; Zhu, Q.-J.; Ye, C. Chitosan in Molecularly-Imprinted Polymers: Current and Future Prospects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 18328-18347. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160818328
Xu L, Huang Y-A, Zhu Q-J, Ye C. Chitosan in Molecularly-Imprinted Polymers: Current and Future Prospects. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2015; 16(8):18328-18347. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160818328
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Long, Yun-An Huang, Qiu-Jin Zhu, and Chun Ye. 2015. "Chitosan in Molecularly-Imprinted Polymers: Current and Future Prospects" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 16, no. 8: 18328-18347. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160818328
APA StyleXu, L., Huang, Y.-A., Zhu, Q.-J., & Ye, C. (2015). Chitosan in Molecularly-Imprinted Polymers: Current and Future Prospects. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 16(8), 18328-18347. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160818328