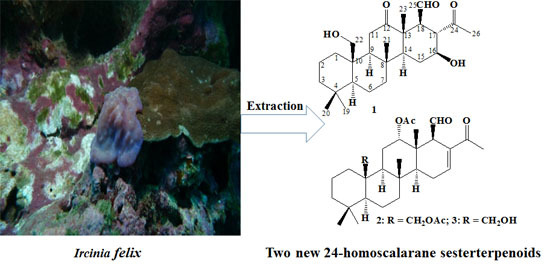
New Cytotoxic 24-Homoscalarane Sesterterpenoids from the Sponge Ircinia felix
Abstract
:1. Introduction

2. Results and Discussion
| Position | δH (J in Hz) | δC, Multiple | 1H–1H COSY | HMBC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2.09 m; 0.55 ddd (12.8, 12.8, 3.2) | 33.9, CH2 | H2-2 | n.o. |
| 2 | 1.54–1.37 m | 17.8, CH2 | H2-1, H2-3 | n.o. |
| 3 | 1.42 m; 1,16 m | 41.5, CH2 | H2-2 | C-4, -20 |
| 4 | 33.0, C | |||
| 5 | 0.94 dd (12.8, 2.4) | 56.8, CH | H2-6 | C-6, -10, -20, -22 |
| 6 | 1.54–1.37 m | 18.2, CH2 | H-5, H2-7 | C-5 |
| 7 | 1.93 m; 1.15 m | 30.0, CH2 | H2-6 | n.o. |
| 8 | 38.2, C | |||
| 9 | 1.28 (14.4, 2.4) | 61.8, CH | H2-11 | C-8, -10, -21, -22 |
| 10 | 42.7, C | |||
| 11 | 3.24 dd (14.4, 14.4); 2.53 dd (14.4, 2.4) | 38.6, CH2 | H-9 | C-8, -9, -12, -13 |
| 12 | 214.6, C | |||
| 13 | 52.4, C | |||
| 14 | 1.29 m | 57.3, CH | H2-15 | C-7, -8, -13, -15, -16, -23 |
| 15 | 1.90 m; 1.02 m | 41.9, CH2 | H-14, H-16 | C-13, -14, -16, -17 |
| 16 | 3.57 ddd (10.8, 10.8, 4.8) | 73.3, CH | H2-15, H-17 | n.o. |
| 17 | 2.91 dd (11.6, 10.8) | 53.0, CH | H-16, H-18 | C-16, -18, -24 |
| 18 | 3.18 d (11.6) | 57.2, CH | H-17, H-25 | C-13, -16, -23, -25 |
| 19 | 0.86 s | 33.5, CH3 | C-3, -4, -5, -20 | |
| 20 | 0.75 s | 21.8, CH3 | C-3, -4, -5, -19 | |
| 21 | 1.26 s | 16.4, CH3 | C-8, -9, -14 | |
| 22 | 4.07 d (11.6); 3.93 d (11.6) | 62.7, CH2 | C-1, -5, -9, -10 | |
| 23 | 1.19 s | 15.6, CH3 | C-12, -13, -14, -18 | |
| 24 | 212.7, C | |||
| 25 | 9.89 s | 204.4, CH | H-18 | C-13, -17, -18 |
| 26 | 2.37 s | 33.8, CH3 | C-17, -24 |

| Position | δH (J in Hz) | δC, Multiple | 1H–1H COSY | HMBC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.98 m; 0.53 ddd (12.5, 12.5, 3.0) | 34.7, CH2 | H2-2 | C-3 |
| 2 | 1.56 m; 1.41 m | 18.1, CH2 | H2-1, H2-3 | C-1, -10 |
| 3 | 1.44 m; 1.18 m | 41.5, CH2 | H2-2 | C-2, -19, -20 |
| 4 | 32.9, C | |||
| 5 | 0.99 dd (17.0, 4.0) | 56.8, CH | H2-6 | C-4, -6, -10, -20, -22 |
| 6 | 1.54 m; 1.44 m | 17.9, CH2 | H-5, H2-7 | C-5, -8 |
| 7 | 1.88 m; 1.18 m | 41.9, CH2 | H2-6 | C-8, -9 |
| 8 | 37.8, C | |||
| 9 | 1.39 m | 51.9, CH | H2-11 | C-1, -8, -10, -11, -12, -14, -21, -22 |
| 10 | 40.1, C | |||
| 11 | 2.15–2.05 m | 24.2, CH2 | H-9, H-12 | n.o. |
| 12 | 4.76 s | 74.8, CH | H2-11 | n.o. |
| 13 | 40.0, C | |||
| 14 | 1.52 m | 49.2, CH | H2-15 | C-9, -15, -23 |
| 15 | 2.26–2.30 m | 23.7, CH2 | H-14, H-16 | C-16, -17 |
| 16 | 7.09 dd (2.5, 2.5) | 142.6, CH | H2-15 | n.o. |
| 17 | 137.2, C | |||
| 18 | 3.53 broad s | 53.0, CH | H-25 | n.o. |
| 19 | 0.89 s | 33.7, CH3 | C-3, -4, -5, -20 | |
| 20 | 0.83 s | 21.9, CH3 | C-3, -4, -5, -19 | |
| 21 | 1.03 s | 16.1, CH3 | C-7, -8, -9, -14 | |
| 22 | 4.58 d (12.0); 4.13 d (12.0) | 64.8, CH2 | C-1, -9, -10, acetate carbonyl | |
| 23 | 0.95 s | 15.2, CH3 | C-12, -13, -14, -18 | |
| 24 | 198.7, C | |||
| 25 | 9.41 d (3.5) | 200.8, CH | H-18 | C-18 |
| 26 | 2.34 s | 25.1, CH3 | C-24 | |
| 12-OAc | 169.9, C | |||
| 2.17 s | 21.2, CH3 | Acetate carbonyl | ||
| 22-OAc | 171.0, C | |||
| 2.04 s | 21.5, CH3 | Acetate carbonyl |

| Compounds | Cell Lines IC50 (μM) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CCRF-CEM | HL-60 | K-562 | MOLT-4 | SUP-T1 | U-937 | DLD-1 | LNCaP | MCF7 | |
| 1 | NT a | NT | 1.27 | 2.59 | 3.56 | 10.65 | 19.26 | 7.22 | NT |
| 2 | 7.90 | 6.50 | 19.9 | NT | NT | 13.08 | 27.08 | 17.14 | NA b |
| Doxorubicin c | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.70 | 0.02 | 0.09 | 0.33 | 0.90 | 3.16 | 0.29 |
3. Experimental Section
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Animal Material
3.3. Extraction and Isolation
3.4. MTT Antiproliferative Assay
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martínez, A.; Duque, C.; Sato, N.; Tanaka, R.; Fujimoto, Y. (18R)-Variabilin from the sponge Ircinia felix. Nat. Prod. Lett. 1995, 6, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, A.; Duque, C.; Hara, N.; Fujimoto, Y. Variabilin 11-methyloctadecanoate, a branched-chain fatty acid ester of furanosesterterpene tetronic acid, from the sponge Ircinia felix. Nat. Prod. Lett. 1995, 6, 281–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, A.; Duque, C.; Sato, N.; Fujimoto, Y. (8Z,13Z,20Z)-Strobilinin and (7Z,13Z,20Z)-felixinin: New furanosesterterpene tetronic acids from marine sponges of the genus Ircinia. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1997, 45, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, A.; Duque, C.; Fujimoto, Y. Novel fatty acid esters of (7E, 12E, 18R, 20Z)-variabilin from the marine sponge Ircinia felix. Lipids 1997, 32, 565–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granato, A.C.; de Oliveira, J.H.H.L.; Seleghim, M.H.R.; Berlinck, R.G.S.; Macedo, M.L.; Ferreira, A.G.; da Rocha, R.M.; Hajdu, E.; Peixinho, S.; Pessoa, C.O.; et al. Produtos naturais da ascídia Botrylloides giganteum, das esponjas Verongula gigantea, Ircinia felix, Cliona delitrix e do nudibrânquio Tambja eliora, da costa do Brasil. Quim. Nova 2005, 28, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waddell, B.; Pawlik, J.R. Defenses of Caribbean sponges against invertebrate predators. II. Assays with sea stars. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2000, 195, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duque, C.; Bonilla, A.; Bautista, E.; Zea, S. Exudation of low molecualr weight compounds (thiobismethane, methyl isocyanide, and methyl isothiocyanate) as a possible chemical defense mechanism in the marine sponge Ircinia felix. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2001, 29, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlik, J.R.; McFall, G.; Zea, S. Does the odor from sponges of the genus Ircinia protect them from fish predators? J. Chem. Ecol. 2002, 28, 1103–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, C.J.; Gleason, D.F. Chemical defenses, nutritional quality, and structural components in three sponges: Ircinia felix, I. campana, and Aplysina fulva. Mar. Biol. 2010, 157, 1083–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, C.J.; Gleason, D.F. Does concentrating chemical defenses within specific regions of marine sponges results in enhanced protection from predators? Anc. Anim. New Chall. 2011, 219, 289–297. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Guiñán, Y.; Hidalgo, J.; Jiménez, M.; Salcedo, J. Obtención de extractos orgánicos con actividad antimicrobiana a partir de Penicillium sp. (Moniliales) aislado de la esponja Ircinia felix (Porifera: Demospongiae). Rev. Biol. Trop. 2003, 51, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sepčić, K.; Kauferstein, S.; Mebs, D.; Turk, T. Biological activities of aqueous and organic extracts from tropical marine sponges. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1550–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, Y.-Y.; Lu, M.-C.; Wang, L.-H.; Chen, J.-J.; Fang, L.-S.; Wu, Y.-C.; Sung, P.-J. New scalarane sesterterpenoids from the Formosan sponge Ircinia felix. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 4296–4309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González, M.A. Scalarane sesterterpenoids. Curr. Bioact. Comp. 2010, 6, 178–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazlauskas, R.; Murphy, P.T.; Wells, R.J. Five new C26 tetracyclic terpenes from a sponge (Lendenfeldia sp.). Aust. J. Chem. 1982, 35, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pronzato, R.; Malva, R.; Manconi, R. The taxonomic status of Ircinia fasciculata, Ircinia felix, and Ircinia variabilis (Dictyoceratida, Irciniidae). Boll. Musei Ist. Biol. Univ. Genova 2004, 68, 553–563. [Google Scholar]
- Alley, M.C.; Scudiero, D.A.; Monks, A.; Hursey, M.L.; Czerwinski, M.J.; Fine, D.L.; Abbott, B.J.; Mayo, J.G.; Shoemaker, R.H.; Boyd, M.R. Feasibility of drug screening with panels of human tumor cell lines using a microculture tetrazolium assay. Cancer Res. 1988, 48, 589–601. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Scudiero, D.A.; Shoemaker, R.H.; Paull, K.D.; Monks, A.; Tierney, S.; Nofziger, T.H.; Currens, M.J.; Seniff, D.; Boyd, M.R. Evaluation of a soluble tetrazolium/formazan assay for cell growth and drug sensitivity in culture using human and other tumor cell lines. Cancer Res. 1988, 48, 4827–4833. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lu, M.-C.; Hwang, S.-L.; Chang, F.-R.; Chen, Y.-H.; Chang, T.-T.; Hung, C.-S.; Wang, C.-L.; Chu, Y.-H.; Pan, S.-H.; Wu, Y.-C. Immunostimulatory effect of Antrodia camphorata extract on functional maturation of dendritic cells. Food Chem. 2009, 113, 1049–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lai, Y.-Y.; Chen, L.-C.; Wu, C.-F.; Lu, M.-C.; Wen, Z.-H.; Wu, T.-Y.; Fang, L.-S.; Wang, L.-H.; Wu, Y.-C.; Sung, P.-J. New Cytotoxic 24-Homoscalarane Sesterterpenoids from the Sponge Ircinia felix. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 21950-21958. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160921950
Lai Y-Y, Chen L-C, Wu C-F, Lu M-C, Wen Z-H, Wu T-Y, Fang L-S, Wang L-H, Wu Y-C, Sung P-J. New Cytotoxic 24-Homoscalarane Sesterterpenoids from the Sponge Ircinia felix. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2015; 16(9):21950-21958. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160921950
Chicago/Turabian StyleLai, Ya-Yuan, Li-Chai Chen, Chug-Fung Wu, Mei-Chin Lu, Zhi-Hong Wen, Tung-Ying Wu, Lee-Shing Fang, Li-Hsueh Wang, Yang-Chang Wu, and Ping-Jyun Sung. 2015. "New Cytotoxic 24-Homoscalarane Sesterterpenoids from the Sponge Ircinia felix" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 16, no. 9: 21950-21958. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160921950
APA StyleLai, Y.-Y., Chen, L.-C., Wu, C.-F., Lu, M.-C., Wen, Z.-H., Wu, T.-Y., Fang, L.-S., Wang, L.-H., Wu, Y.-C., & Sung, P.-J. (2015). New Cytotoxic 24-Homoscalarane Sesterterpenoids from the Sponge Ircinia felix. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 16(9), 21950-21958. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160921950