Mechanisms of Acupuncture Therapy in Ischemic Stroke Rehabilitation: A Literature Review of Basic Studies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Pathophysiology of Ischemic Stroke
1.2. Treatment of Ischemic Stroke in Western Medicine
1.3. Associated Impairments and Rehabilitation
1.4. Acupuncture and Ischemic Stroke
2. Methods
- Acupuncture
- Cerebral ischemia
- Effect
- Specific mechanisms describing how acupuncture exerted its effects
- Ischemic stroke type
- Exclusive use of acupuncture after the ischemic injury
- Related studies cited in these articles
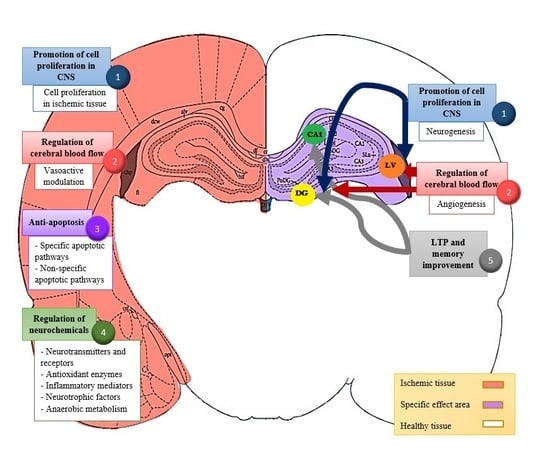
3. Results
3.1. Promotion of Neurogenesis and Cell Proliferation in the Central Nervous System (CNS)
3.1.1. Neurogenesis
3.1.2. Cell Proliferation in Ischemic Tissue
4. Regulation of Cerebral Blood Flow
4.1. Angiogenesis
4.2. Vasoactive Modulation
5. Anti-Apoptosis
5.1. Specific Apoptotic Pathway
5.2. Non-Specific Apoptotic Pathway
6. Regulation of Neurochemicals
6.1. Neurotransmitters and Receptors
6.2. Antioxidant Enzymes
6.3. Inflammatory Mediators
6.4. Neurotrophic Factors
6.5. Anerobic Metabolism
7. Acupuncture Modulates Long-Term Potentiation and Improves Memory
8. Summary of Main Acupoints Selected in the Reviewed Studies
9. Discussion and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sacco, R.L.; Kasner, S.E.; Broderick, J.P.; Caplan, L.R.; Connors, J.J.; Culebras, A.; Elkind, M.S.; George, M.G.; Hamdan, A.D.; Higashida, R.T.; et al. An updated definition of stroke for the 21st century: A statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2013, 44, 2064–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Writing Group Members; Mozaffarian, D.; Benjamin, E.J.; Go, A.S.; Arnett, D.K.; Blaha, M.J.; Cushman, M.; Das, S.R.; de Ferranti, S.; Després, J.P.; et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics–2016 update: A report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2016, 133, e38–e360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurthi, R.V.; Feigin, V.L.; Forouzanfar, M.H.; Mensah, G.A.; Connor, M.; Bennett, D.A.; Moran, A.E.; Sacco, R.L.; Anderson, L.M.; Truelsen, T.; et al. Global and regional burden of first-ever ischaemic and haemorrhagic stroke during 1990–2010: Findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet Glob. Health 2013, 1, e259–e281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouns, R.; de Deyn, P.P. The complexity of neurobiological processes in acute ischemic stroke. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2009, 111, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deb, P.; Sharma, S.; Hassan, K.M. Pathophysiologic mechanisms of acute ischemic stroke: An overview with emphasis on therapeutic significance beyond thrombolysis. Pathophysiology 2010, 17, 197–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kornienko, V.N.; Pronin, I.N. Diagnostic Neuroradiology; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2009; ISBN 978-3-540-75653-8. [Google Scholar]
- Doyle, K.P.; Simon, R.P.; Stenzel-Poore, M.P. Mechanisms of ischemic brain damage. Neuropharmacology 2008, 55, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felling, R.J.; Song, H. Epigenetic mechanisms of neuroplasticity and the implications for stroke recovery. Exp. Neurol. 2015, 268, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, W.S.; Johnston, S.C.; Hemphill, J.C., III. Cerebrovascular diseases. In Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine, 19th ed.; Kasper, D., Fauci, A., Hauser, S., Longo, D., Jameson, J., Loscalzo, J., Eds.; Mc Graw Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2014; Volume 2, ISBN 978-0-07-180215-4. [Google Scholar]
- Intercollegiate Stroke Working Party. National Clinical Guideline for Stroke, 4th ed.; Royal College of Physicians: London, UK, 2012; ISBN 978-1-86016-492-7. [Google Scholar]
- Brainin, M.; Zorowitz, R.D. Advances in stroke: Recovery and rehabilitation. Stroke 2013, 44, 311–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Wang, Q. Acupuncture therapy for stroke patients. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2013, 111, 159–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, A.H.; Zhang, J.M.; Xie, Y.K. Human acupuncture points mapped in rats are associated with excitable muscle/skin-nerve complexes with enriched nerve endings. Brain Res. 2004, 1012, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.Q. Neural mechanism underlying acupuncture analgesia. Prog. Neurobiol. 2008, 85, 355–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manni, L.; Albanesi, M.; Guaragna, M.; Barbaro Paparo, S.; Aloe, L. Neurotrophins and acupuncture. Auton. Neurosci. 2010, 157, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Na, B.J.; Jahng, G.H.; Park, S.U.; Jung, W.S.; Moon, S.K.; Park, J.M.; Bae, H.S. An fMRI study of neuronal specificity of an acupoint: Electroacupuncture stimulation of Yanglingquan (GB34) and its sham point. Neurosci. Lett. 2009, 464, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Hu, J.; Du, F.; Zhou, X.; Xiang, Q.; Miao, F. Long-term changes of diffusion tensor imaging and behavioural status after acupuncture treatment in rats with transient focal cerebral ischaemia. Acup. Med. 2012, 30, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.Y.; Hsieh, C.L.; Wei, T.S.; Liu, P.T.; Chang, Y.J.; Li, T.C. Acupuncture stimulation improves balance function in stroke patients: A single-blinded controlled, randomized study. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2009, 37, 483–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.G.; Cao, C.H.; Liu, C.Z.; Han, B.J.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z.G.; Yu, T.; Wang, X.H.; Zhao, H.; Xu, Z.H. Effect of acupuncture treatment on spastic states of stroke patients. J. Neurol. Sci. 2009, 276, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, T.; Hui-Chan, C.W. Transcutaneous electrical stimulation on acupuncture points improves muscle function in subjects after acute stroke: A randomized controlled trial. J. Rehabil. Med. 2009, 41, 312–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, P.; Mills, E.; Moher, D.; Seely, D. Acupuncture in poststroke rehabilitation: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials. Stroke 2010, 41, e171–e179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.R.; Kim, H.N.; Ahn, S.M.; Choi, Y.H.; Shin, H.K.; Choi, B.T. Electroacupuncture promotes post-stroke functional recovery via enhancing endogenous neurogenesis in mouse focal cerebral ischemia. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, J.; Wu, G.; Zou, Y.; Tao, J.; Chen, L. Electroacupuncture promotes neurological functional recovery via the retinoic acid signaling pathway in rats following cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2013, 31, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Tao, J.; Lin, Y.; Lin, R.; Liu, W.; Chen, L. Electro-acupuncture exerts beneficial effects against cerebral ischemia and promotes the proliferation of neural progenitor cells in the cortical peri-infarct area through the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2015, 36, 1215–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, T.; Luo, Y.; Sun, H.; Qin, W.; Li, Y. Electroacupuncture improves behavioral recovery and increases SCF/c-kit expression in a rat model of focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion. Neurol. Sci. 2013, 34, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Ye, X.; You, Y.; Liu, W.; Gao, Y.; Yang, S.; Peng, J.; Hong, Z.; Tao, J.; Chen, L. Electroacupuncture promotes neural cell proliferation in vivo through activation of the ERK1/2 signaling pathway. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2014, 33, 1547–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, G.; Yang, S.; Chen, A.; Lan, L.; Lin, Z.; Gao, Y.; Huang, J.; Lin, J.; Peng, J.; Tao, J.; Chen, L. Electroacupuncture at Quchi and Zusanli treats cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury through activation of ERK signaling. Exp. Ther. Med. 2013, 5, 1593–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, J.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, W.; Yang, S.; Huang, J.; Xue, X.; Shang, G.; Wang, X.; Lin, R.; Chen, L. Electro-acupuncture at LI11 and ST36 acupoints exerts neuroprotective effects via reactive astrocyte proliferation after ischemia and reperfusion injury in rats. Brain Res. Bull. 2016, 120, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallon, M.; Chang, J.; Zhang, H.; Kuo, C.J. Developmental and pathological angiogenesis in the central nervous system. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2014, 71, 3489–3506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Luo, Y. Effects of electroacupuncture on expressions of angiogenesis factors and anti-angiogenesis factors in brain of experimental cerebral ischemic rats after reperfusion. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2008, 28, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Choi, K.H.; Jang, Y.J.; Bae, S.S.; Shin, B.C.; Choi, B.T.; Shin, H.K. Electroacupuncture acutely improves cerebral blood flow and attenuates moderate ischemic injury via an endothelial mechanism in mice. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; He, J.; Du, Y.; Cui, J.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, X. Electroacupuncture improves cerebral blood flow and attenuates moderate ischemic injury via Angiotensin II its receptors-mediated mechanism in rats. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 14, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broughton, B.R.; Reutens, D.C.; Sobey, C.G. Apoptotic mechanisms after cerebral ischemia. Stroke 2009, 40, e331–e339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, M.H.; Shin, M.C.; Lee, T.H.; Lim, B.V.; Shin, M.S.; Min, B.I.; Kim, H.; Cho, S.; Kim, E.H.; Kim, C.J. Acupuncture suppresses ischemia-induced increase in c-Fos expression and apoptosis in the hippocampal CA1 region in gerbils. Neurosci. Lett. 2003, 347, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Liu, C.Z.; Yu, J.C.; Jiang, W.; Han, J.X. Acupuncture protected cerebral multi-infarction rats from memory impairment by regulating the expression of apoptosis related genes Bcl-2 and Bax in hippocampus. Physiol. Behav. 2009, 96, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.R.; Kim, H.N.; Jang, J.Y.; Park, C.; Lee, J.H.; Shin, H.K.; Choi, Y.H.; Choi, B.T. Effects of electroacupuncture on apoptotic pathways in a rat model of focal cerebral ischemia. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2013, 32, 1303–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.J.; Omori, N.; Li, F.; Jin, G.; Zhang, W.R.; Hamakawa, Y.; Sato, K.; Nagano, I.; Shoji, M.; Abe, K. Potentiation of Akt and suppression of caspase-9 activations by electroacupuncture after transient middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2002, 331, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Lin, Z.; Lan, L.; Xie, G.; Huang, J.; Lin, J.; Peng, J.; Tao, J.; Chen, L. Electroacupuncture at the Quchi and Zusanli acupoints exerts neuroprotective role in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injured rats via activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2012, 30, 791–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, X.; You, Y.; Tao, J.; Ye, X.; Huang, J.; Yang, S.; Lin, Z.; Hong, Z.; Peng, J.; Chen, L. Electro-acupuncture at points of Zusanli and Quchi exerts anti-apoptotic effect through the modulation of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Neurosci. Lett. 2014, 558, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.Y.; Lin, J.G.; Su, S.Y.; Tang, N.Y.; Kao, S.T.; Hsieh, C.L. Electroacupuncture-like stimulation at Baihui and Dazhui acupoints exerts neuroprotective effects through activation of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor-mediated MEK1/2/ERK1/2/p90RSK/bad signaling pathway in mild transient focal cerebral ischemia in rats. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 14, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Wang, J.; Li, C.; Zhou, G.; Xu, X.; Zhang, X.; Lan, X. Effect of electroacupuncture on cell apoptosis and ERK signal pathway in the hippocampus of adult rats with cerebral ischemia-reperfusion. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 2015, 414965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.Y.; Lin, J.G.; Tang, N.Y.; Kao, S.T.; Hsieh, C.L. Electroacupuncture at different frequencies (5 and 25 Hz) ameliorates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats: Possible involvement of p38 MAPK-mediated anti-apoptotic signaling pathways. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 15, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.Y.; Lin, J.G.; Tang, N.Y.; Kao, S.T.; Hsieh, C.L. Electroacupuncture-like stimulation at the Baihui (GV20) and Dazhui (GV14) acupoints protects rats against subacute-phase cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injuries by reducing S100B-mediated neurotoxicity. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.; Yang, S.; Liu, J.; Huang, J.; Peng, J.; Lin, J.; Tao, J.; Chen, L. Electroacupuncture ameliorates cognitive impairment through inhibition of NF-κB-mediated neuronal cell apoptosis in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injured rats. Mol. Med. Rep. 2013, 7, 1516–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Wang, Y.; Sun, N.; Liu, X.; Li, L.; Shi, J. Electroacupuncture regulates TRPM7 expression through the trkA/PI3K pathway after cerebral ischemia-reperfusion in rats. Life Sci. 2007, 81, 1211–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Xu, N.; Yi, W.; Huang, K.; Su, M. Electroacupuncture effect on neurological behavior and tyrosine kinase-JAK 2 in rats with focal cerebral ischemia. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2012, 32, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, C.M.; Hsieh, C.L.; Li, T.C.; Lin, J.G. Acupuncture stimulation at Baihui acupoint reduced cerebral infarct and increased dopamine levels in chronic cerebral hypoperfusion and ischemia-reperfusion injured Sprague-Dawley rats. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2007, 35, 779–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, J.; Itano, T.; Sumitani, K.; Negi, T.; Miyamoto, O. Electroacupuncture attenuates both glutamate release and hyperemia after transient ischemia in gerbils. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2003, 31, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, P.; Cheng, J.S.; Ng, Y.K.; Ling, E.A. Role of GABA in electro-acupuncture therapy on cerebral ischemia induced by occlusion of the middle cerebral artery in rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2005, 383, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.; Yang, J.W.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, L.W.; Zeng, X.H.; Li, F.; Du, S.Q.; Wang, L.P.; Liu, C.Z. Acupuncture improves locomotor function by enhancing GABA receptor expression in transient focal cerebral ischemia rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2015, 588, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauwels, P.J.; Opperdoes, F.R.; Trouet, A. Effects of antimycin, glucose deprivation, and serum on cultures of neurons, astrocytes, and neuroblastoma cells. J. Neurochem. 1985, 44, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.Z.; Yu, J.C.; Zhang, X.Z.; Fu, W.W.; Wang, T.; Han, J.X. Acupuncture prevents cognitive deficits and oxidative stress in cerebral multi-infarction rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2006, 393, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, G.X.; Wang, X.R.; Yan, C.Q.; He, T.; Yang, J.W.; Zeng, X.H.; Xu, Q.; Zhu, W.; Du, S.Q.; Liu, C.Z. Acupuncture elicits neuroprotective effect by inhibiting NAPDH oxidase-mediated reactive oxygen species production in cerebral ischaemia. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siu, F.K.; Lo, S.C.; Leung, M.C. Electroacupuncture reduces the extent of lipid peroxidation by increasing superoxide dismutase and glutathione peroxidase activities in ischemic-reperfused rat brains. Neurosci. Lett. 2004, 354, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, S.; Li, Z.; Huan, L.; Chen, B.Y. Neurochemical mechanism of electroacupuncture: Anti-injury effect on cerebral function after focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2009, 6, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siu, F.K.; Lo, S.C.; Leung, M.C. Electro-acupuncture potentiates the disulphide-reducing activities of thioredoxin system by increasing thioredoxin expression in ischemia-reperfused rat brains. Life Sci. 2005, 77, 386–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Sun, H.; Chen, S.H.; Zhang, Y.M.; Piao, Y.L.; Gao, Y. Effects of acupuncture at Baihui (DU20) and Zusanli (ST36) on the expression of heat shock protein 70 and tumor necrosis factor α in the peripheral serum of cerebral ischemia-reperfusion-injured rats. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 2014, 20, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, L.; Tao, J.; Chen, A.; Xie, G.; Huang, J.; Lin, J.; Peng, J.; Chen, L. Electroacupuncture exerts anti-inflammatory effects in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injured rats via suppression of the TLR4/NF-κB pathway. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2013, 31, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.W.; Chung, Y.C.; Jung, H.C.; Park, M.S.; Han, Y.M.; Chung, Y.A.; Maeng, L.S.; Park, S.I.; Lim, J.; Im, W.S.; et al. Electroacupuncture enhances motor recovery performance with brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression in rats with cerebral infarction. Acupunct. Med. 2012, 30, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Zhao, H.; Wang, Y.; Han, B.; Wang, T.; Zhao, H.; Cui, K.; Wang, S. Electro-acupuncture up-regulates astrocytic MCT1 expression to improve neurological deficit in middle cerebral artery occlusion rats. Life Sci. 2015, 134, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.Q.; Shi, G.X.; Yang, J.W.; Li, Z.X.; Zhang, Z.H.; He, T.; Wang, J.; Liu, L.Y.; Liu, C.Z. Hippocampal cAMP/PKA/CREB is required for neuroprotective effect of acupuncture. Physiol. Behav. 2015, 139, 482–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.W.; Hsieh, C.L. Electroacupuncture at Baihui acupoint (GV20) reverses behavior deficit and long-term potentiation through N-methyl-d-aspartate and transient receptor potential vanilloid subtype 1 receptors in middle cerebral artery occlusion rats. J. Integr. Neurosci. 2010, 9, 269–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, D.; Fan, X.; Ma, C.; Fan, T.; Wang, X.; Chang, N.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, Z.; Wang, S.; Shi, X. A study on the effect of neurogenesis and regulation of GSK3β/PP2A expression in acupuncture treatment of neural functional damage caused by focal ischemia in MCAO rats. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 962343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, N.; Zou, X.; Shi, J.; Liu, X.; Li, L.; Zhao, L. Electroacupuncture regulates NMDA receptor NR1 subunit expression via PI3-K pathway in a rat model of cerebral ischemia-reperfusion. Brain Res. 2005, 1064, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhong, L.L.D.; Chen, Z.; Li, Y.; Zheng, G.; Bian, Z. Acupuncture for neurogenesis in experimental ischemic stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, A.; Wu, H.M.; Tang, J.L.; Xu, L.; Yang, M.; Liu, G.J. Acupuncture for stroke rehabilitation. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2016, 8, CD004131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Lin, H.-P.; Li, Z.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Wang, S. Large-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channel involvement in suppression of cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury after electroacupuncture at Shuigou (GV26) acupoint in rats. Neural Regen. Res. 2016, 11, 957–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, S.; Li, C.-M.; You, Y.-L.; Qian, X.-L.; Zhou, S.; Ling, C.-Q. Electroacupuncture ameliorates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by regulation of autophagy and apoptosis. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2016, 7297425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Lin, R.; Tao, J.; Wu, Y.; Chen, B.; Yu, K.; Chen, J.; Li, X.; Chen, L. Electroacupuncture improves cognitive ability following cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury via CaM-CaMKIV-CREB signaling in the rat hippocampus. Exp. Ther. Med. 2016, 12, 777–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, R.; Wu, Y.; Tao, J.; Chen, B.; Chen, J.; Zhao, C.; Yu, K.; Li, X.; Chen, L.D. Electroacupuncture improves cognitive function through Rho GTPases and enhances dendritic spine plasticity in rats with cerebral ischemia-reperfusion. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 13, 2655–2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Acupoint | Frequency of Appearance |
|---|---|
| Baihui (GV20) | 16 |
| Zusanli (ST36) | 16 |
| Quchi (LI11) | 9 |
| Shuigou (GV26) | 7 |
| Dazhui (GV14) | 5 |
| Hegu (LI4) | 4 |
| Qihai (CV6) | 3 |
| Tanzhong (CV17) | 2 |
| Zhongwan (CV12) | 2 |
| Xuehai (SP10) | 2 |
| Fengfu (GV16) | 2 |
| Chengjiang (CV24) | 2 |
| Fengchi (GB20) | 2 |
| Shenting (GV24) | 1 |
| Chize (LU5) | 1 |
| Sanyinjiao (SP6) | 1 |
| Jiaji (Ex-B2) | 1 |
| Shendao (GV11) | 1 |
| Qubin (GB7) | 1 |
| Neiguan (PC6) | 1 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chavez, L.M.; Huang, S.-S.; MacDonald, I.; Lin, J.-G.; Lee, Y.-C.; Chen, Y.-H. Mechanisms of Acupuncture Therapy in Ischemic Stroke Rehabilitation: A Literature Review of Basic Studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2270. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112270
Chavez LM, Huang S-S, MacDonald I, Lin J-G, Lee Y-C, Chen Y-H. Mechanisms of Acupuncture Therapy in Ischemic Stroke Rehabilitation: A Literature Review of Basic Studies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(11):2270. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112270
Chicago/Turabian StyleChavez, Lina M., Shiang-Suo Huang, Iona MacDonald, Jaung-Geng Lin, Yu-Chen Lee, and Yi-Hung Chen. 2017. "Mechanisms of Acupuncture Therapy in Ischemic Stroke Rehabilitation: A Literature Review of Basic Studies" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 11: 2270. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112270
APA StyleChavez, L. M., Huang, S.-S., MacDonald, I., Lin, J.-G., Lee, Y.-C., & Chen, Y.-H. (2017). Mechanisms of Acupuncture Therapy in Ischemic Stroke Rehabilitation: A Literature Review of Basic Studies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(11), 2270. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112270