A Genomic Survey of SCPP Family Genes in Fishes Provides Novel Insights into the Evolution of Fish Scales
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Collection of SPARCL1 and SCPP Genes and Transcriptome Confirmation
2.2. Phylogenetic Topologies of SPARCL1 and SCPP Genes
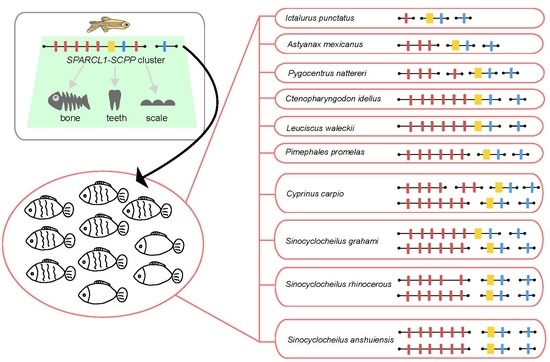
2.3. The Putative SPARCL1-SCPP Cluster and Pseudogenes
2.4. SCPP1 and SCPP5: Gene Structure Comparison between Cavefishes and Other Fishes
3. Discussion
3.1. Comparison of the SPARCL1-SCPP Cluster in Teleosts
3.2. Evolution of SPARCL1 and SCPP Genes during Whole Genome Duplication
3.3. Comparison of SCPP1 and SCPP5 in Scaled, Sparsely Scaled and Scaleless Fishes
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Gene Collection and Transcriptome Confirmation
4.2. Sequence Alignment and Phylogenetic Reconstruction
4.3. Genomic Location and Pseudogene Identification
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AM | Astyanax mexicanus |
| CC | Cyprinus carpio |
| CI | Ctenopharyngodon idellus |
| IP | Ictalurus punctatus |
| LW | Leuciscus waleckii |
| Oca2 | Gene encoding oculocutaneous albinism II (melanocyte-specific transporter protein) |
| ODAM | Gene encoding odontogenic ameloblast-associated protein (Ameloblast-associated odontogenic protein) |
| PP | Pimephales promelas |
| PN | Pygocentrus nattereri |
| SA | Sinocyclocheilus anshuiensis |
| SG | Sinocyclocheilus grahamin |
| SR | Sinocyclocheilus rhinocerous |
| SCPP1 | secretory calcium-binding phosphoprotein 1 |
| SCPP5 | secretory calcium-binding phosphoprotein 5 |
| SCPP6 | secretory calcium-binding phosphoprotein 6 |
| SCPP7 | secretory calcium-binding phosphoprotein 7 |
| SCPP9 | secretory calcium-binding phosphoprotein 9 |
| SPARC | secreted protein acidic and rich in cysteine |
| SPARCL1 | Gene encoding SPARC-like protein 1 |
| SPP1 | Gene encoding secreted phosphoprotein 1 |
| TSGD | teleosts-specific genome duplication |
| WGD | whole genome duplication |
References
- Kaessmann, H. Origins, evolution, and phenotypic impact of new genes. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 1313–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawasaki, K.; Buchanan, A.V.; Weiss, K.M. Gene Duplication and the evolution of vertebrate skeletal mineralization. Cells Tissues Organs 2007, 186, 7–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawasaki, K.; Weiss, K.M. Mineralized tissue and vertebrate evolution: The secretory calcium-binding phosphoprotein gene cluster. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 4060–4065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawasaki, K.; Weiss, K.M. Evolutionary genetics of vertebrate tissue mineralization: The origin and evolution of the secretory calcium-binding phosphoprotein family. J. Exp. Zool. B Mol. Dev. Evol. 2006, 306, 295–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawasaki, K.; Weiss, K.M. SCPP gene evolution and the dental mineralization continuum. J. Dent. Res. 2008, 87, 520–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatesh, B.; Lee, A.P.; Ravi, V.; Maurya, A.K.; Lian, M.M.; Swann, J.B.; Ohta, Y.; Flajnik, M.F.; Sutoh, Y.; Kasahara, M. Elephant shark genome provides unique insights into gnathostome evolution. Nature 2014, 505, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Q.; Fan, S.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, M.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Y.; Lee, A.P.; Woltering, J.M.; Ravi, V.; Gunter, H.M.; et al. The seahorse genome and the evolution of its specialized morphology. Nature 2016, 540, 395–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braasch, I.; Gehrke, A.R.; Smith, J.J.; Kawasaki, K.; Manousaki, T.; Pasquier, J.; Amores, A.; Desvignes, T.; Batzel, P.; Catchen, J.; et al. The spotted gar genome illuminates vertebrate evolution and facilitates human-teleost comparisons. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawasaki, K.; Amemiya, C.T. SCPP genes in the coelacanth: tissue mineralization genes shared by sarcopterygians. J. Exp. Zool. B Mol. Dev. Evol. 2014, 322, 390–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawasaki, K.; Suzuki, T.; Weiss, K.M. Phenogenetic drift in evolution: The changing genetic basis of vertebrate teeth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 18063–18068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawasaki, K. The SCPP gene repertoire in bony vertebrates and graded differences in mineralized tissues. Dev. Genes Evol. 2009, 219, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, H.; Yu, H.; Ravi, V.; Li, C.; Lee, A.P.; Lian, M.M.; Tay, B.H.; Brenner, S.; Wang, J.; Yang, H.; et al. The genome of the largest bony fish, ocean sunfish (Mola mola), provides insights into its fast growth rate. GigaScience 2016, 5, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, S.; Yao, J.; Bao, L.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Jiang, C.; Sun, L.; Wang, R.; Zhang, Y.; et al. The channel catfish genome sequence provides insights into the evolution of scale formation in teleosts. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGaugh, S.E.; Gross, J.B.; Aken, B.; Blin, M.; Borowsky, R.; Chalopin, D.; Hinaux, H.; Jeffery, W.R.; Keene, A.; Ma, L.; et al. The cavefish genome reveals candidate genes for eye loss. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Chen, X.; Bai, J.; Fang, D.; Qiu, Y.; Jiang, W.; Yuan, H.; Bian, C.; Lu, J.; He, S.; et al. The sinocyclocheilus cavefish genome provides insights into cave adaptation. BMC Biol. 2016, 14, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guyomard, R.; Boussaha, M.; Krieg, F.; Hervet, C.; Quillet, E. A synthetic rainbow trout linkage map provides new insights into the salmonid whole genome duplication and the conservation of synteny among teleosts. BMC Genet. 2012, 13, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glasauer, S.M.; Neuhauss, S.C. Whole-genome duplication in teleost fishes and its evolutionary consequences. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2014, 289, 1045–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kasahara, M.; Naruse, K.; Sasaki, S.; Nakatani, Y.; Qu, W.; Ahsan, B.; Yamada, T.; Nagayasu, Y.; Doi, K.; Kasai, Y.; et al. The medaka draft genome and insights into vertebrate genome evolution. Nature 2007, 447, 714–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, A.; Van de Peer, Y. From 2R to 3R: evidence for a fish-specific genome duplication (FSGD). Bioessays 2005, 27, 937–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaillon, O.; Aury, J.M.; Brunet, F.; Petit, J.L.; Stange-Thomann, N.; Mauceli, E.; Bouneau, L.; Fischer, C.; Ozouf-Costaz, C.; Bernot, A.; et al. Genome duplication in the teleost fish Tetraodon nigroviridis reveals the early vertebrate proto-karyotype. Nature 2004, 431, 946–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, J.; Sato, Y.; Sinclair, R.; Tsukamoto, K.; Nishida, M. Rapid genome reshaping by multiple-gene loss after whole-genome duplication in teleost fish suggested by mathematical modeling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 14918–14923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lien, S.; Koop, B.F.; Sandve, S.R.; Miller, J.R.; Kent, M.P.; Nome, T.; Hvidsten, T.R.; Leong, J.S.; Minkley, D.R.; et al. The Atlantic salmon genome provides insights into rediploidization. Nature 2016, 533, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Protas, M.E.; Hersey, C.; Kochanek, D.; Zhou, Y.; Wilkens, H.; Jeffery, W.R.; Zon, L.I.; Borowsky, R.; Tabin, C.J. Genetic analysis of cavefish reveals molecular convergence in the evolution of albinism. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mount, D.W. Using the Basic Local Alignment Search Tool (Blast). Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slater, G.S.C.; Birney, E. Automated generation of heuristics for biological sequence comparison. BMC Bioinform. 2005, 6, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posada, D.; Buckley, T.R. Model selection and model averaging in phylogenetics: Advantages of akaike information criterion and bayesian approaches over likelihood ratio tests. Syst. Biol. 2004, 53, 793–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darriba, D.; Taboada, G.L.; Doallo, R.; Posada, D. JModelTest 2: More models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guindon, S.; Dufayard, J.F.; Lefort, V.; Anisimova, M.; Hordijk, W.; Gascuel, O. New algorithms and methods to estimate maximum-likelihood phylogenies: Assessing the performance of PhyML 3.0. Syst. Biol. 2010, 59, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guindon, S.; Delsuc, F.; Dufayard, J.F.; Gascuel, O. Estimating Maximum Likelihood Phylogenies with PhyML. In Bioinformatics for DNA Sequence Analysis; Posada, D., Ed.; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 113–137. [Google Scholar]



© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lv, Y.; Kawasaki, K.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Bian, C.; Huang, Y.; You, X.; Shi, Q. A Genomic Survey of SCPP Family Genes in Fishes Provides Novel Insights into the Evolution of Fish Scales. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2432. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112432
Lv Y, Kawasaki K, Li J, Li Y, Bian C, Huang Y, You X, Shi Q. A Genomic Survey of SCPP Family Genes in Fishes Provides Novel Insights into the Evolution of Fish Scales. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(11):2432. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112432
Chicago/Turabian StyleLv, Yunyun, Kazuhiko Kawasaki, Jia Li, Yanping Li, Chao Bian, Yu Huang, Xinxin You, and Qiong Shi. 2017. "A Genomic Survey of SCPP Family Genes in Fishes Provides Novel Insights into the Evolution of Fish Scales" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 11: 2432. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112432
APA StyleLv, Y., Kawasaki, K., Li, J., Li, Y., Bian, C., Huang, Y., You, X., & Shi, Q. (2017). A Genomic Survey of SCPP Family Genes in Fishes Provides Novel Insights into the Evolution of Fish Scales. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(11), 2432. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112432