MicroRNAs Associated with Von Hippel–Lindau Pathway in Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
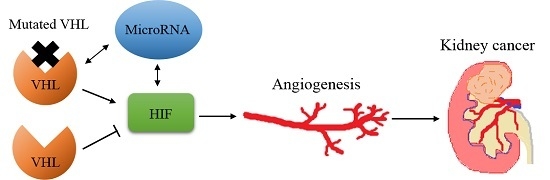
:1. Introduction
2. Von Hippel–Lindau/Hypoxia Inducible Factor (HIF)
3. Angiogenesis in Renal Cell Carcinoma (RCC)
4. Current Anti-Angiogenic Therapy
5. MiRNA Biogenesis and Function
6. MiRNAs Associated with VHL in Clear Cell RCC
6.1. MiR-30c
6.2. MiR-182-5p
6.3. MiR-92a/ MiR-210
6.4. MiR-17-5p/MiR-224
6.5. MiR-28-5p
6.6. MiR-204
6.7. MiR-155
7. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RCC | renal cell carcinoma |
| VHL | Von Hippel Lindau |
| HIF | hypoxia inducible factor |
| miRNAs | microRNAs |
| VEGF | vascular endothelial growth factor |
| FGF | fibroblast growth factor |
| PDGF-B | platelet-derived growth factor B chain |
| TGF-β | transforming growth factor β |
| GLUT1 | glucose transporter isoform 1 |
| EMT | epithelial-mesenchymal transition |
| PI3K | phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase |
| CREB3L1 | cyclic AMP-responsive element-binding protein 3-like 1 |
| PHDs | prolyl hydroxylase proteins |
| FGFBP1 | fibroblast growth factor binding protein 1 |
| mTOR | mammalian target of rapamycin |
| HIF1AN | Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha inhibitor |
| EGLN3 | Egl nine homolog 3 |
| MAP3K1 | activated protein kinase kinase kinase 1 |
References
- Cairns, R.A.; Harris, I.S.; Mak, T.W. Regulation of cancer cell metabolism. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lunt, S.Y.; Vander Heiden, M.G. Aerobic glycolysis: Metabolic. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2011, 27, 441–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koppenol, W.H.; Bounds, P.L.; Dang, C.V. Otto Warburg’s contributions to current concepts of cancer metabolism. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirschhaeuser, F.; Sattler, U.G.A.; Mueller-Klieser, W.; Warburg, O.; Altenberg, B.; Greulich, K.; DeBerardinis, R.; Levine, A.; Puzio-Kuter, A.; Lu, H.; et al. Lactate: A metabolic key player in cancer. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 6921–6925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ljungberg, B.; Bensalah, K.; Canfield, S.; Dabestani, S.; Hofmann, F.; Hora, M.; Kuczyk, M.A.; Lam, T.; Marconi, L.; Merseburger, A.S.; et al. EAU guidelines on renal cell carcinoma: 2014 update. Eur. Urol. 2015, 67, 913–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zbar, B.; Klausner, R.; Linehan, W.M. Studying Cancer Families to Identify Kidney Cancer Genes. Annu. Rev. Med. 2003, 54, 217–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bukowski, R.M. Natural history and therapy of metastatic renal cell carcinoma: The role of interleukin-2. Cancer 1997, 80, 1198–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, E.A.; Gopta, N.G.; Srinivasan, R. Update on targeted therapies for clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2011, 23, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motzer, R.J.; Escudier, B.; McDermott, D.F.; George, S.; Hammers, H.J.; Srinivas, S.; Tykodi, S.S.; Sosman, J.A.; Procopio, G.; Plimack, E.R.; et al. Nivolumab versus Everolimus in Advanced Renal-Cell Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1803–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buonerba, C.; Di Lorenzo, G.; Sonpavde, G. Combination therapy for metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Ann. Transl. Med. 2016, 4, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pichler, M.; Calin, G.A. MicroRNAs in cancer: From developmental genes in worms to their clinical application in patients. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 113, 569–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calin, G.A.; Croce, C.M. MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 857–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, Biogenesis, Mechanism, and Function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigoutsos, I.; Lee, S.K.; Nam, S.Y.; Anfossi, S.; Pasculli, B.; Pichler, M.; Jing, Y.; Rodriguez-Aguayo, C.; Telonis, A.G.; Rossi, S.; et al. N-BLR, a primate-specific non-coding transcript leads to colorectal cancer invasion and migration. Genome Biol. 2017, 18, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smolle, M.A.; Calin, H.N.; Pichler, M.; Calin, G.A. Noncoding RNAs and immune checkpoints—Clinical implications as cancer therapeutics. FEBS J. 2017, 284, 1952–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goblirsch, M.; Richtig, G.; Slaby, O.; Berindan-Neagoe, I.; Gerger A, P.M. MicroRNAs as a tool to aid stratification of colorectal cancer patients and to guide therapy. Pharmacogenomics 2017, 18, 1027–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seles, M.; Hutterer, G.C.; Kiesslich, T.; Pummer, K.; Berindan-Neagoe, I.; Perakis, S.; Schwarzenbacher, D.; Stotz, M.; Gerger, A.; Pichler, M. Current insights into long non-coding RNAs in renal cell carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latif, F.; Tory, K.; Gnarra, J.; Yao, M.; Duh, F.; Orcutt, M.; Stackhouse, T.; Kuzmin, I.; Modi, W.; Geil, L.; et al. Identification of the von Hippel—Lindau disease tumor suppressor gene. Science 1993, 260, 1317–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaelin, W.G. The von Hippel—Lindau tumor suppressor protein and clear cell renal carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 680–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mena, A.C.; Pulido, E.G.; Guillén-Ponce, C. Understanding the molecular-based mechanism of action of the tyrosine kinase inhibitor: Sunitinib. Anticancer Drugs 2010, 21, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shenoy, N.; Pagliaro, L. Sequential pathogenesis of metastatic VHL mutant clear cell renal cell carcinoma: Putting it together with a translational perspective. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 1685–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gudas, L.J.; Fu, L.; Minton, D.R.; Mongan, N.P.; Nanus, D.M. The role of HIF1α in renal cell carcinoma tumorigenesis. J. Mol. Med. 2014, 92, 825–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forristal, C.E.; Wright, K.L.; Hanley, N.A.; Oreffo, R.O.; Houghton, F.D. Hypoxia inducible factors regulate pluripotency and proliferation in human embryonic stem cells cultured at reduced oxygen tensions. Reproduction 2010, 139, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaelin, W.G.; Ratcliffe, P.J. Oxygen Sensing by Metazoans: The Central Role of the HIF Hydroxylase Pathway. Mol. Cell 2008, 30, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimoda, L.A. 55th Bowditch Lecture: Effects of chronic hypoxia on the pulmonary circulation: Role of HIF-1. J. Appl. Physiol. 2012, 113, 1343–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brahimi-Horn, M.C.; Chiche, J.; Pouysségur, J. Hypoxia signalling controls metabolic demand. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2007, 19, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arjumand, W.; Sultana, S. Role of VHL gene mutation in human renal cell carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 2012, 33, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshino, S.; Kato, M.; Okada, K. Clinical significance of angiogenesis, proliferation and apoptosis in renal cell carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2000, 20, 591–594. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.D.; Wei, S.Q.; Wang, Q.Y. Targeting oncogenic KRAS in non-small cell lung cancer cells by phenformin inhibits growth and angiogenesis. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2015, 5, 3339–3349. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Howe, G.A.; Kazda, K.; Addison, C.L. MicroRNA-30b controls endothelial cell capillary morphogenesis through regulation of transforming growth factor beta 2. PLoS ONE 2017, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cross, M.J.; Claesson-Welsh, L. FGF and VEGF function in angiogenesis: Signalling pathways, biological responses and therapeutic inhibition. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2001, 22, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, F.; Goto, K.; Weindel, K.; Folkman, J. Synergistic effects of vascular endothelial growth factor and basic fibroblast growth factor on the proliferation and cord formation of bovine capillary endothelial cells within collagen gels. Lab. Investig. 1993, 69, 508–517. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhu, H.; Wei, X.; Li, H.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, H.M.; Liu, W.C. LPS induces HUVEC angiogenesis in vitro through miR-146a-mediated TGF-β 1 inhibition. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2017, 9, 591–600. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Takano, S.; Yoshii, Y.; Kondo, S.; Suzuki, H.; Maruno, T.; Shirai, S.; Nose, T. Concentration of vascular endothelial growth factor in the serum and tumor tissue of brain tumor patients. Cancer Res. 1996, 56, 2185–2190. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Bai, W.; Liu, J.; Zheng, Z.; Guan, H.; Zhou, Q.; Su, L.; Xie, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Li, N.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Hu, D. Up-regulation of FGFBP1 signaling contributes to miR-146a-induced angiogenesis in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrara, N.; Kerbel, R.S. Angiogenesis as a therapeutic target. Nature 2005, 438, 967–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simons, M.; Bonow, R.O.; Chronos, N.A.; Cohen, D.J.; Giordano, F.J.; Hammond, H.K.; Laham, R.J.; Li, W.; Pike, M.; Sellke, F.W.; Stegmann, T.J.; Udelson, J.E.; Rosengart, T.K. Clinical trials in coronary angiogenesis: Issues, problems, consensus: An expert panel summary. Circulation 2000, 102, E73–E86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battelli, C.; Cho, D.C. mTOR inhibitors in renal cell carcinoma. Therapy 2011, 8, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roskoski, R. Classification of small molecule protein kinase inhibitors based upon the structures of their drug-enzyme complexes. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 103, 26–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McTigue, M.; Murray, B.W.; Chen, J.H.; Deng, Y.L.; Solowiej, J.; Kania, R.S. Molecular conformations, interactions, and properties associated with drug efficiency and clinical performance among VEGFR TK inhibitors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 18281–18289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wullschleger, S.; Loewith, R.; Hall, M.N. TOR signaling in growth and metabolism. Cell 2006, 124, 471–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meric-Bernstam, F.; Gonzalez-Angulo, A.M. Targeting the mTOR signaling network for cancer therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 2278–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panwalkar, A.; Verstovsek, S.; Giles, F.J. Mammalian target of rapamycin inhibition as therapy for hematologic malignancies. Cancer 2004, 100, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guertin, D.A.; Sabatini, D.M. Defining the Role of mTOR in Cancer. Cancer Cell 2007, 12, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, R.T.; Gibbons, J.J. The mammalian target of rapamycin signaling pathway: Twists and turns in the road to cancer therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 3109–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voss, M.H.; Molina, A.M.; Motzer, R.J. MTOR inhibitors in advanced renal cell carcinoma. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2011, 25, 835–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motzer, R.J.; Hutson, T.E.; Glen, H.; Michaelson, M.D.; Molina, A.; Eisen, T.; Jassem, J.; Zolnierek, J.; Maroto, J.P.; Mellado, B.; et al. Lenvatinib, everolimus, and the combination in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: A randomised, phase 2, open-label, multicentre trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 1473–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloosterman, W.P.; Plasterk, R.H.A. The Diverse Functions of MicroRNAs in Animal Development and Disease. Dev. Cell 2006, 11, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefani, G.; Slack, F.J. Small non-coding RNAs in animal development. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2008, 9, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, H.; Vincent, K.; Pichler, M.; Fodde, R.; Berindan-Neagoe, I.; Slack, F.J.; Calin, G.A. Junk DNA and the long non-coding RNA twist in cancer genetics. Oncogene 2015, 34, 5003–5011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero-Cordoba, S.L.; Salido-Guadarrama, I.; Rodriguez-Dorantes, M.; Hidalgo-Miranda, A. miRNA biogenesis: Biological impact in the development of cancer. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2014, 15, 1444–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, R.; Qin, Y.; Macara, I.G.; Cullen, B.R. Exportin-5 mediates the nuclear export of pre-microRNAs and short hairpin RNAs. Genes Dev. 2003, 17, 3011–3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Kelly, F.; Marignol, L.; Meunier, A.; Lynch, T.H.; Perry, A.S.; Hollywood, D. MicroRNAs as putative mediators of treatment response in prostate cancer. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2012, 9, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benson, E.A.; Skaar, T.C. Incubation of whole blood at room temperature does not alter the plasma concentrations of microRNA-16 and -223. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2013, 41, 1778–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, P.S.; Parkin, R.K.; Kroh, E.M.; Fritz, B.R.; Wyman, S.K.; Pogosova-Agadjanyan, E.L.; Peterson, A.; Noteboom, J.; O’Briant, K.C.; Allen, A.; et al. Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based markers for cancer detection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 10513–10518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croce, C.M. Causes and consequences of microRNA dysregulation in cancer. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 10, 704–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pichler, M.; Stiegelbauer, V.; Vychytilova-Faltejskova, P.; Ivan, C.; Ling, H.; Winter, E.; Zhang, X.; Goblirsch, M.; Wulf-Goldenberg, A.; Ohtsuka, M.; et al. Genome-Wide miRNA Analysis Identifies miR-188-3p as a Novel Prognostic Marker and Molecular Factor Involved in Colorectal Carcinogenesis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 23, 1323–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stiegelbauer, V.; Vychytilova-Faltejskova, P.; Karbiener, M.; Pehserl, A.M.; Reicher, A.; Resel, M.; Heitzer, E.; Ivan, C.; Bullock, M.; Ling, H.; et al. MicroRNA-196b-5p regulates colorectal cancer cell migration and metastases through interaction of HOXB7 and GALNT5. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 5255–5266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karbiener, M.; Neuhold, C.; Opriessnig, P.; Prokesch, A.; Bogner-Strauss, J.G.; Scheideler, M. MicroRNA-30c promotes human adipocyte differentiation and co-represses PAI-1 and ALK2. RNA Biol. 2011, 8, 850–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Yao, X.; Zhang, J.; Dong, B.; Chen, Q.; Xue, W.; Liu, D.; Huang, Y. Hypoxia-induced downregulation of miR-30c promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2013, 104, 1609–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Li, H.; Ma, X.; Gao, Y.; Bao, X.; Du, Q.; Ma, M.; Liu, K.; Yao, Y.; Huang, Q.; et al. Dicer suppresses the malignant phenotype in VHL-deficient clear cell renal cell carcinoma by inhibiting HIF-2α. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 18280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, V.N. MicroRNA biogenesis: Coordinated cropping and dicing. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 6, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valera, V.A.; Walter, B.A.; Linehan, W.M.; Merino, M.J. Regulatory effects of microRNA-92 (miR-92) on VHL Gene expression and the hypoxic activation of miR-210 in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. J. Cancer 2011, 2, 515–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, K.; Xu, H. Prognostic value of meta-signature miRNAs in renal cell carcinoma: An integrated miRNA expression profiling analysis. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lichner, Z.; Mejia-Guerrero, S.; Ignacak, M.; Krizova, A.; Bao, T.T.; Girgis, A.H.F.; Youssef, Y.M.; Yousef, G.M. Pleiotropic action of renal cell carcinoma-dysregulated miRNAs on hypoxia-related signaling pathways. Am. J. Pathol. 2012, 180, 1675–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, H.; Pickard, K.; Ivan, C.; Isella, C.; Ikuo, M.; Mitter, R.; Spizzo, R.; Bullock, M.D.; Braicu, C.; Pileczki, V.; et al. The clinical and biological significance of MIR-224 expression in colorectal cancer metastasis. Gut 2016, 65, 977–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, G.; Yin, M.; Lian, J.; Tian, H.; Liu, L.; Li, X.; Sun, F. MicroRNA-224 Is Involved in Transforming Growth Factor-β-Mediated Mouse Granulosa Cell Proliferation and Granulosa Cell Function by Targeting Smad4. Mol. Endocrinol. 2010, 24, 540–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, D.J.; Resio, B.; Pellman, D. Causes and consequences of aneuploidy in cancer. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2012, 13, 189–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michel, L.S.; Liberal, V.; Chatterjee, A.; Kirchwegger, R.; Pasche, B.; Gerald, W.; Dobles, M.; Sorger, P.K.; Murty, V.V.; Benezra, R. MAD2 haplo-insufficiency causes premature anaphase and chromosome instability in mammalian cells. Nature 2001, 409, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sotillo, R.; Hernando, E.; Díaz-Rodríguez, E.; Teruya-Feldstein, J.; Cordón-Cardo, C.; Lowe, S.W.; Benezra, R. Mad2 Overexpression Promotes Aneuploidy and Tumorigenesis in Mice. Cancer Cell 2007, 11, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hell, M.P.; Thoma, C.R.; Fankhauser, N.; Christinat, Y.; Weber, T.C.; Krek, W. Mir-28-5p promotes chromosomal instability in VHL-Associated cancers by inhibiting mad2 translation. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 2432–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, E. The role for autophagy in cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathew, R.; Karantza-Wadsworth, V.; White, E. Role of autophagy in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 961–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikhaylova, O.; Stratton, Y.; Hall, D.; Kellner, E.; Ehmer, B.; Drew, A.F.; Gallo, C.A.; Plas, D.R.; Biesiada, J.; Meller, J.; Czyzyk-Krzeska, M.F. VHL-Regulated MiR-204 Suppresses Tumor Growth through Inhibition of LC3B-Mediated Autophagy in Renal Clear Cell Carcinoma. Cancer Cell 2012, 21, 532–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, K.; Tsuchihara, K.; Fujii, S.; Sugiyama, M.; Goya, T.; Atomi, Y.; Ueno, T.; Ochiai, A.; Esumi, H. Autophagy is activated in colorectal cancer cells and contributes to the tolerance to nutrient deprivation. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 9677–9684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neal, C.S.; Michael, M.Z.; Rawlings, L.H.; Van der Hoek, M.B.; Gleadle, J.M. The VHL-dependent regulation of microRNAs in renal cancer. BMC Med. 2010, 8, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


| MicroRNA | Chromosomal Location | Tumor Suppressor/OncomiR | Proven Target Genes | Pathway Involved |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MiR-30c | Unknown | Tumor suppressor | Unknown | Hypoxia, Epithelial-mesenchymal transition |
| MiR-182-5p | 7q32.2 | Tumor suppressor | HIF2α | Hypoxia |
| MiR-92a | Unknown | OncomiR | Unknown | Unknown |
| MiR-210 | 11p15.5 | OncomiR | HIF1α | Hypoxia |
| MiR-17-5p | 13q31.3 | Unknown | HIF1, VHL, HIF1AN, VEGFA, EGLN3, PI3K, MAP3K1 | Hypoxia |
| MiR-224 | Xq28 | OncomiR | VHL, SMAD4/5 | Hypoxia |
| MiR-28-5p | 3q28 | OncomiR | Mad2 | Mitotic checkpoint |
| MiR-204 | 9q21.12 | Tumor suppressor | MAP1LC3B | Macroautophagy |
| MiR-155 | 21q21.3 | OncomiR | CAIX | Hypoxia |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schanza, L.-M.; Seles, M.; Stotz, M.; Fosselteder, J.; Hutterer, G.C.; Pichler, M.; Stiegelbauer, V. MicroRNAs Associated with Von Hippel–Lindau Pathway in Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Comprehensive Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2495. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112495
Schanza L-M, Seles M, Stotz M, Fosselteder J, Hutterer GC, Pichler M, Stiegelbauer V. MicroRNAs Associated with Von Hippel–Lindau Pathway in Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Comprehensive Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(11):2495. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112495
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchanza, Lisa-Maria, Maximilian Seles, Michael Stotz, Johannes Fosselteder, Georg C. Hutterer, Martin Pichler, and Verena Stiegelbauer. 2017. "MicroRNAs Associated with Von Hippel–Lindau Pathway in Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Comprehensive Review" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 11: 2495. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112495