Duloxetine Protects against Oxaliplatin-Induced Neuropathic Pain and Spinal Neuron Hyperexcitability in Rodents
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effects of Different Doses of Duloxetine and Its Time Course on Oxaliplatin-Induced Cold and Mechanical Allodynia in Mice
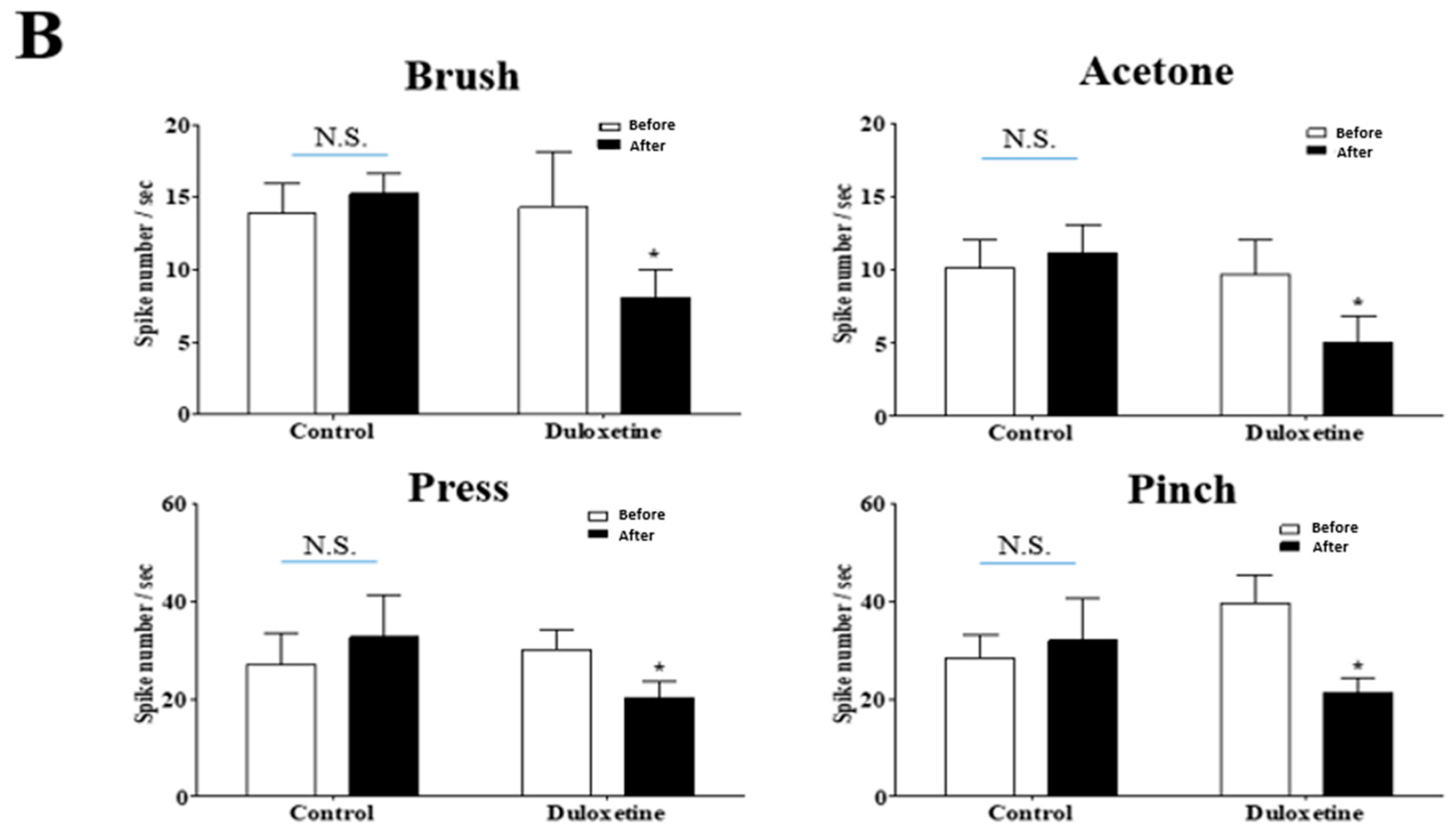
2.2. Effects of Duloxetine on Increased Neuronal Response to Mechanical and Cold Stimulations Induced by Oxaliplatin Injection in the Spinal Dorsal Horn
2.3. Effect of α-Adrenergic Receptor Antagonists on the Analgesic Effect of Duloxetine on Cold and Mechanical Allodynia in Mice
3. Discussion
4. Materials & Methods
4.1. Experimental Animals
4.2. Behavioral Tests Experimental Protocol
4.3. Allodynic Behavior Measurements
4.4. Oxaliplatin Administration
4.5. Duloxetine and α-Adrenergic Receptor Antagonists Administration
4.6. In Vivo Extracellular Recording
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Andre, T.; Boni, C.; Mounedji-Boudiaf, L.; Navarro, M.; Tabernero, J.; Hickish, T.; Topham, C.; Zaninelli, M.; Clingan, P.; Bridgewater, J.; et al. Oxaliplatin, fluorouracil, and leucovorin as adjuvant treatment for colon cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 2343–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Gramont, A.; Figer, A.; Seymour, M.; Homerin, M.; Hmissi, A.; Cassidy, J.; Boni, C.; Cortes-Funes, H.; Cervantes, A.; Freyer, G.; et al. Leucovorin and fluorouracil with or without oxaliplatin as first-line treatment in advanced colorectal cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2000, 18, 2938–2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belani, C.P. Recent updates in the clinical use of platinum compounds for the treatment of lung, breast, and genitourinary tumors and myeloma. Semin. Oncol. 2004, 31, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balayssac, D.; Ferrier, J.; Pereira, B.; Gillet, B.; Petorin, C.; Vein, J.; Libert, F.; Eschalier, A.; Pezet, D. Prevention of oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy by a polyamine-reduced diet-neuroxapol: Protocol of a prospective, randomised, controlled, single-blind and monocentric trial. BMJ Open 2015, 5, e007479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beijers, A.J.; Mols, F.; Vreugdenhil, G. A systematic review on chronic oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy and the relation with oxaliplatin administration. Support. Care Cancer 2014, 22, 1999–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, B.; Coudore, F.; Decalonne, L.; Eschalier, A.; Authier, N. Comparative antiallodynic activity of morphine, pregabalin and lidocaine in a rat model of neuropathic pain produced by one oxaliplatin injection. Neuropharmacology 2008, 55, 724–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, B.; Coudore-Civiale, M.A.; Balayssac, D.; Eschalier, A.; Coudore, F.; Authier, N. Behavioral and immunohistological assessment of painful neuropathy induced by a single oxaliplatin injection in the rat. Toxicology 2007, 234, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, S.; Barton, D.; Kottschade, L.; Grothey, A.; Loprinzi, C. Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: Prevention and treatment strategies. Eur. J. Cancer 2008, 44, 1507–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argyriou, A.A.; Polychronopoulos, P.; Iconomou, G.; Chroni, E.; Kalofonos, H.P. A review on oxaliplatin-induced peripheral nerve damage. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2008, 34, 368–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sultan, A.; Gaskell, H.; Derry, S.; Moore, R.A. Duloxetine for painful diabetic neuropathy and fibromyalgia pain: Systematic review of randomised trials. BMC Neurol. 2008, 8, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chappell, A.S.; Ossanna, M.J.; Liu-Seifert, H.; Iyengar, S.; Skljarevski, V.; Li, L.C.; Bennett, R.M.; Collins, H. Duloxetine, a centrally acting analgesic, in the treatment of patients with osteoarthritis knee pain: A 13-week, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Pain 2009, 146, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skljarevski, V.; Desaiah, D.; Liu-Seifert, H.; Zhang, Q.; Chappell, A.S.; Detke, M.J.; Iyengar, S.; Atkinson, J.H.; Backonja, M. Efficacy and safety of duloxetine in patients with chronic low back pain. Spine 2010, 35, E578–E585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McIntyre, R.S.; Panjwani, Z.D.; Nguyen, H.T.; Woldeyohannes, H.O.; Alsuwaidan, M.; Soczynska, J.K.; Lourenco, M.T.; Konarski, J.Z.; Kennedy, S.H. The hepatic safety profile of duloxetine: A review. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2008, 4, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, E.M.; Pang, H.; Cirrincione, C.; Fleishman, S.; Paskett, E.D.; Ahles, T.; Bressler, L.R.; Fadul, C.E.; Knox, C.; Le-Lindqwister, N.; et al. Effect of duloxetine on pain, function, and quality of life among patients with chemotherapy-induced painful peripheral neuropathy: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2013, 309, 1359–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hershman, D.L.; Lacchetti, C.; Dworkin, R.H.; Lavoie Smith, E.M.; Bleeker, J.; Cavaletti, G.; Chauhan, C.; Gavin, P.; Lavino, A.; Lustberg, M.B.; et al. Prevention and management of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in survivors of adult cancers: American society of clinical oncology clinical practice guideline. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 1941–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pertovaara, A. Noradrenergic pain modulation. Prog. Neurobiol. 2006, 80, 53–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.; Yamada, A.; Kim, W.; Kim, S.K.; Furue, H. Noradrenergic inhibition of spinal hyperexcitation elicited by cutaneous cold stimuli in rats with oxaliplatin-induced allodynia: Electrophysiological and behavioral assessments. J. Physiol. Sci. 2017, 67, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, W.; Kim, M.J.; Go, D.; Min, B.-I.; Na, H.S.; Kim, S.K. Combined effects of bee venom acupuncture and morphine on oxaliplatin-induced neuropathic pain in mice. Toxins 2016, 8, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, D.E. Oxaliplatin: A new drug for the treatment of metastatic carcinoma of the colon or rectum. Rev. Gastroenterol. Disord. 2003, 3, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Farquhar-Smith, P. Chemotherapy-induced neuropathic pain. Curr. Opin. Support. Palliat. Care 2011, 5, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kannarkat, G.; Lasher, E.E.; Schiff, D. Neurologic complications of chemotherapy agents. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2007, 20, 719–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrato, A.; Gallego, J.; Dı́az-Rubio, E. Oxaliplatin: Results in colorectal carcinoma. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2002, 44, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnerup, N.B.; Sindrup, S.H.; Jensen, T.S. The evidence for pharmacological treatment of neuropathic pain. Pain 2010, 150, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyengar, S.; Webster, A.A.; Hemrick-Luecke, S.K.; Xu, J.Y.; Simmons, R.M.A. Efficacy of duloxetine, a potent and balanced serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor in persistent pain models in rats. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2004, 311, 576–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munro, G.; Storm, A.; Hansen, M.K.; Dyhr, H.; Marcher, L.; Erichsen, H.K.; Sheykhzade, M. The combined predictive capacity of rat models of algogen-induced and neuropathic hypersensitivity to clinically used analgesics varies with nociceptive endpoint and consideration of locomotor function. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2012, 101, 465–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giordano, J. The neurobiology of nociceptive and anti-nociceptive systems. Pain Phys. 2005, 8, 277–290. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, T.S.; Gottrup, H.; Sindrup, S.H.; Bach, F.W. The clinical picture of neuropathic pain. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 429, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alba-Delgado, C.; Borges, G.; Sanchez-Blazquez, P.; Ortega, J.E.; Horrillo, I.; Mico, J.A.; Meana, J.J.; Neto, F.; Berrocoso, E. The function of α2-adrenoceptors in the rat locus coeruleus is preserved in the chronic constriction injury model of neuropathic pain. Psychopharmacology 2012, 221, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alba-Delgado, C.; Mico, J.A.; Sanchez-Blazquez, P.; Berrocoso, E. Analgesic antidepressants promote the responsiveness of locus coeruleus neurons to noxious stimulation: Implications for neuropathic pain. Pain 2012, 153, 1438–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, S.; Hemrick-Luecke, S.K.; Thompson, L.K.; Evans, D.C.; Threlkeld, P.G.; Nelson, D.L.; Perry, K.W.; Bymaster, F.P. Comparison of effects of dual transporter inhibitors on monoamine transporters and extracellular levels in rats. Neuropharmacology 2003, 45, 935–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baba, H.; Goldstein, P.A.; Okamoto, M.; Kohno, T.; Ataka, T.; Yoshimura, M.; Shimoji, K. Norepinephrine facilitates inhibitory transmission in substantia gelatinosa of adult rat spinal cord (part 2) effects on somatodendritic sites of gabaergic neurons. Anesthesiology 2000, 92, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thor, K.B.; Katofiasc, M.A. Effects of duloxetine, a combined serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor, on central neural control of lower urinary tract function in the chloralose-anesthetized female cat. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1995, 274, 1014–1024. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Flatters, S.J.; Bennett, G.J. Ethosuximide reverses paclitaxel- and vincristine-induced painful peripheral neuropathy. Pain 2004, 109, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, E.K.; Levine, J.D. Comparison of oxaliplatin- and cisplatin-induced painful peripheral neuropathy in the rat. J. Pain 2009, 10, 534–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibata, K.; Sugawara, T.; Fujishita, K.; Shinozaki, Y.; Matsukawa, T.; Suzuki, T.; Koizumi, S. The astrocyte-targeted therapy by bushi for the neuropathic pain in mice. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, J.D.; Campisi, J.; Sharkey, C.M.; Kennedy, S.L.; Nickerson, M.; Greenwood, B.N.; Fleshner, M. Catecholamines mediate stress-induced increases in peripheral and central inflammatory cytokines. Neuroscience 2005, 135, 1295–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, L.E.; Lu, J.; Guo, T.; Saper, C.B.; Franks, N.P.; Maze, M. The α2-adrenoceptor agonist dexmedetomidine converges on an endogenous sleep-promoting pathway to exert its sedative effects. Anesthesiology 2003, 98, 428–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarrindast, M.R.; Homayoun, H.; Khavandgar, S.; Fayaz-Dastgerdi, M.; Fayaz-Dastgerdi, M. The effects of simultaneous administration of α2-adrenergic agents with l-name or l-arginine on the development and expression of morphine dependence in mice. Behav. Pharmacol. 2002, 13, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, W.; Chung, Y.; Choi, S.; Min, B.-I.; Kim, S.K. Duloxetine Protects against Oxaliplatin-Induced Neuropathic Pain and Spinal Neuron Hyperexcitability in Rodents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2626. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18122626
Kim W, Chung Y, Choi S, Min B-I, Kim SK. Duloxetine Protects against Oxaliplatin-Induced Neuropathic Pain and Spinal Neuron Hyperexcitability in Rodents. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(12):2626. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18122626
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Woojin, Yeongu Chung, Seunghwan Choi, Byung-Il Min, and Sun Kwang Kim. 2017. "Duloxetine Protects against Oxaliplatin-Induced Neuropathic Pain and Spinal Neuron Hyperexcitability in Rodents" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 12: 2626. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18122626
APA StyleKim, W., Chung, Y., Choi, S., Min, B.-I., & Kim, S. K. (2017). Duloxetine Protects against Oxaliplatin-Induced Neuropathic Pain and Spinal Neuron Hyperexcitability in Rodents. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(12), 2626. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18122626




