Role of Antioxidants in Neonatal Hypoxic–Ischemic Brain Injury: New Therapeutic Approaches
Abstract
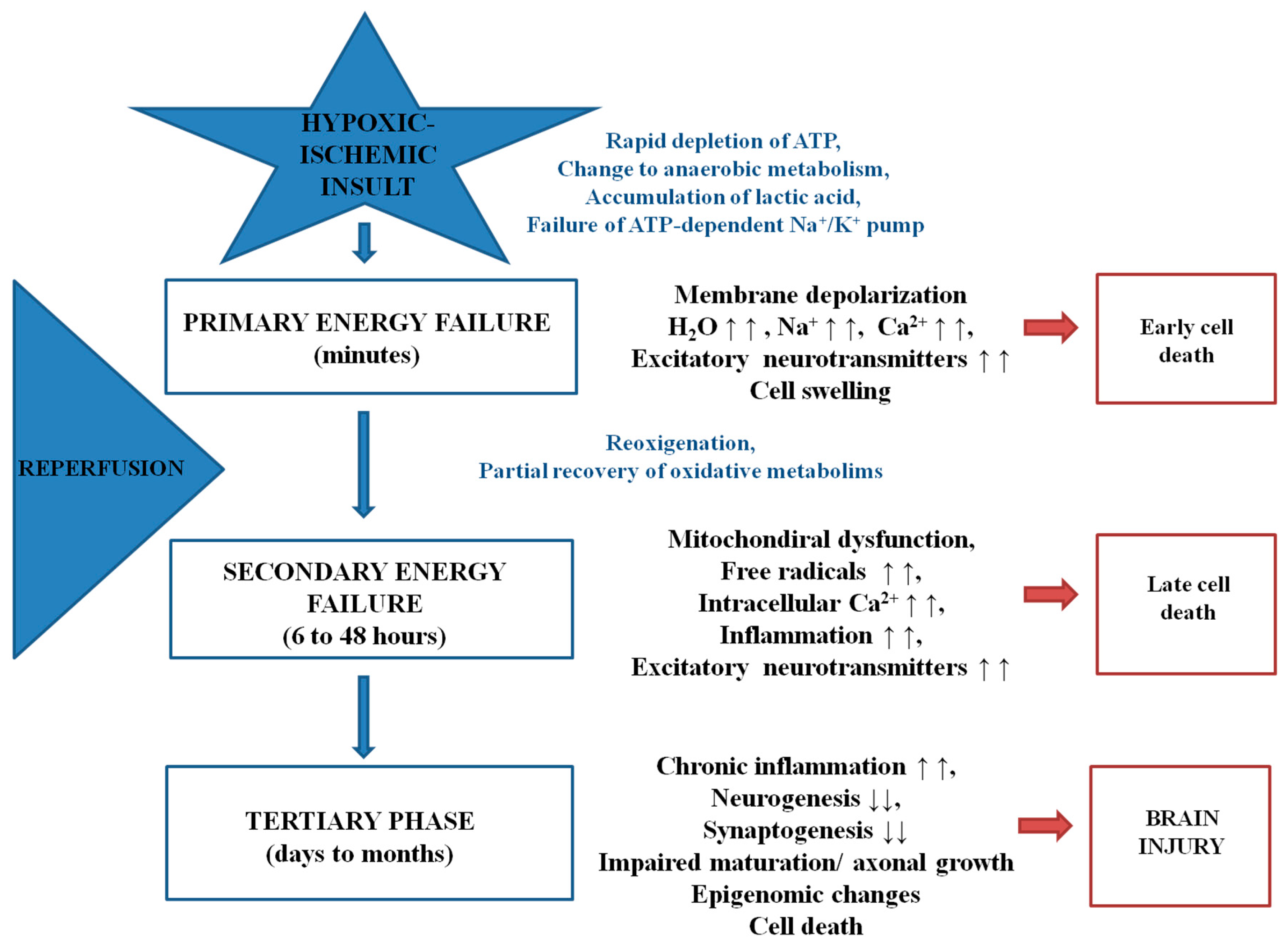
:1. Introduction
2. Oxidative Stress and Endogenous Antioxidants
3. New Approaches to Antioxidant Therapy
3.1. Allopurinol
3.2. Erythropoietin
3.3. Resveratrol
3.4. Omega-3 Fatty Acids
3.5. N-Acetyl-l-cysteine
3.6. Deferoxamine
3.7. Melatonin
3.8. Other Antioxidants
4. Conclusions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tagin, M.; Abdel-Hady, H.; Rahman, S.; Azzopardi, D.V.; Gunn, A.J. Neuroprotection for perinatal hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy in low- and middle-income countries. J. Pediatr. 2015, 167, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Oza, S.; Hogan, D.; Perin, J.; Rudan, I.; Lawn, J.E.; Cousens, S.; Mathers, C.; Black, R.E. Global, regional, and national causes of child mortality in 2000–2013, with projections to inform post-2015 priorities: An updated systematic analysis. Lancet 2015, 385, 430–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurinczuk, J.J.; White-Koning, M.; Badawi, N. Epidemiology of neonatal encephalopathy and hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy. Early Hum. Dev. 2010, 86, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.C.C.; Kozuki, N.; Blencowe, H.; Vos, T.; Bahalim, A.; Darmstadt, G.L.; Niermeyer, S.; Ellis, M.; Robertson, N.J.; Cousens, S.; et al. Intrapartum-related neonatal encephalopathy incidence and impairment at regional and global levels for 2010 with trends from 1990. Pediatr. Res. 2013, 74, 50–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, B.J.; Reis, C.; Ho, W.M.; Tang, J.; Zhang, J.H. Neuroprotective Strategies after Neonatal Hypoxic Ischemic Encephalopathy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 22368–22401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azra Haider, B.; Bhutta, Z.A. Birth Asphyxia in Developing Countries: Current Status and Public Health Implications. Curr. Probl. Pediatr. Adolesc. Health Care 2006, 36, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, D.J. Induced hypothermia for neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy: Pathophysiology, current treatment, and nursing considerations. Neonatal Netw. 2011, 30, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryce, J.; Boschi-Pinto, C.; Shibuya, K.; Black, R.E.; WHO Child Health Epidemiology Reference Group. WHO estimates of the causes of death in children. Lancet 2005, 365, 1147–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpe, J.J. Perinatal brain injury: From pathogenesis to neuroprotection. Ment. Retard. Dev. Disabil. Res. Rev. 2001, 7, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, J.A. Determining the contribution of asphyxia to brain damage in the neonate. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 2004, 30, 276–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vannucci, S.J.; Hagberg, H. Hypoxia-ischemia in the immature brain. J. Exp. Biol. 2004, 207, 3149–3154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aridas, J.D.S.; Yawno, T.; Sutherland, A.E.; Nitsos, I.; Ditchfield, M.; Wong, F.Y.; Fahey, M.C.; Malhotra, A.; Wallace, E.M.; Jenkin, G.; et al. Detecting brain injury in neonatal hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy: Closing the gap between experimental and clinical research. Exp. Neurol. 2014, 261, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arteaga, O.; Revuelta, M.; Montalvo, H.; Cañavate, M.L.; Alonso-Alconada, D.; Martinez-Ibargüen, A.; Hilario, E.; Alvarez, A. Neuroprotective effect of antioxidants in neontal rat brain after hypoxia-ischemia. In Microscopy: Advances in Scientific Research and Education; Méndez-Vilas, A., Ed.; 2014; pp. 335–343. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Q.; Chen, W.; Sinha, B.; Tu, Y.; Manning, S.; Thomas, N.; Zhou, S.; Jiang, H.; Ma, H.; Kroessler, D.A.; et al. Neuroprotective agents for neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury. Drug Discov. Today 2015, 20, 1372–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, J.O.; Wassink, G.; van den Heuij, L.G.; Bennet, L.; Gunn, A.J. Therapeutic Hypothermia for Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy-Where to from Here? Front. Neurol. 2015, 6, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buonocore, G.; Groenendaal, F. Anti-oxidant strategies. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2007, 12, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrone, S.; Negro, S.; Tataranno, M.L.; Buonocore, G. Oxidative stress and antioxidant strategies in newborns. J. Matern. Fetal. Neonatal Med. 2010, 23, 63–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Towfighi, J.; Zec, N.; Yager, J.; Housman, C.; Vannucci, R.C. Temporal evolution of neuropathologic changes in an immature rat model of cerebral hypoxia: A light microscopic study. Acta Neuropathol. 1995, 90, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez-Díaz, A.; Hilario, E.; Goñi de Cerio, F.; Valls-i-Soler, A.; Alvarez-Díaz, F.J. Hypoxic-Ischemic Injury in the Immature Brain—Key Vascular and Cellular Players. Neonatology 2007, 92, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saugstad, O.D. Oxidative stress in the newborn—A 30-year perspective. Biol. Neonate 2005, 88, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferriero, D.M. Neonatal brain injury. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 1985–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLean, C.; Ferriero, D. Mechanisms of hypoxic-ischemic injury in the term infant. Semin. Perinatol. 2004, 28, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheldon, R.A.; Jiang, X.; Francisco, C.; Christen, S.; Vexler, Z.S.; Täuber, M.G.; Ferriero, D.M. Manipulation of antioxidant pathways in neonatal murine brain. Pediatr. Res. 2004, 56, 656–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halliwell, B. Reactive oxygen species and the central nervous system. J. Neurochem. 1992, 59, 1609–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Mittal, R.; Khanna, H.D.; Basu, S. Free radical injury and blood-brain barrier permeability in hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Pediatrics 2008, 122, e722–e727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilario, E.; Alvarez, A.; Alvarez, F.J.; Gastiasoro, E.; Valls-i-Soler, A. Cellular mechanisms in perinatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury. Curr. Pediatr. Rev. 2006, 2, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, N.J.; Faulkner, S.; Fleiss, B.; Bainbridge, A.; Andorka, C.; Price, D.; Powell, E.; Lecky-Thompson, L.; Thei, L.; Chandrasekaran, M.; et al. Melatonin augments hypothermic neuroprotection in a perinatal asphyxia model. Brain 2013, 136, 90–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giesinger, R.E.; Bailey, L.J.; Deshpande, P.; McNamara, P.J. Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy and therapeutic hypothermia: The hemodynamic perspective. J. Pediatr. 2017, 180, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.L.; Rosenkrantz, T.S.; Fitch, R.H. Effects of sex and mild intrainsult hypothermia on neuropathology and neural reorganization following neonatal hypoxic ischemic brain injury in rats. Neural Plast. 2016, 2016, 2585230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso-Alconada, D.; Broad, K.D.; Bainbridge, A.; Chandrasekaran, M.; Faulkner, S.D.; Kerenyi, Á.; Hassell, J.; Rocha-Ferreira, E.; Hristova, M.; Fleiss, B.; et al. Brain cell death is reduced with cooling by 3.5 °C to 5 °C but increased with cooling by 8.5 °C in a piglet asphyxia model. Stroke 2015, 46, 275–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, S.E.; Berg, M.; Hunt, R.; Tarnow-Mordi, W.O.; Inder, T.E.; Davis, P.G. Cooling for newborns with hypoxic ischaemic encephalopathy. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 1, CD003311. [Google Scholar]
- Edwards, A.D.; Brocklehurst, P.; Gunn, A.J.; Halliday, H.; Juszczak, E.; Levene, M.; Strohm, B.; Thoresen, M.; Whitelaw, A.; Azzopardi, D. Neurological outcomes at 18 months of age after moderate hypothermia for perinatal hypoxic ischaemic encephalopathy: Synthesis and meta-analysis of trial data. BMJ 2010, 340, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha-Ferreira, E.; Rudge, B.; Hughes, M.P.; Rahim, A.A.; Hristova, M.; Robertson, N.J. Immediate remote ischemic postconditioning reduces brain nitrotyrosine formation in a piglet asphyxia model. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 5763743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, W.S.; Sung, S.I.; Ahn, S.Y.; Yoo, H.S.; Sung, D.K.; Im, G.H.; Choi, S.J.; Chang, Y.S. Hypothermia augments neuroprotective activity of mesenchymal stem cells for neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lafuente, H.; Pazos, M.R.; Alvarez, A.; Mohammed, N.; Santos, M.; Arizti, M.; Alvarez, F.J.; Martinez-Orgado, J.A. Effects of cannabidiol and hypothermia on short-term brain damage in new-born piglets after acute hypoxia-ischemia. Front. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-López, D.; Lizasoain, I.; Moro, M.A.; Martínez-Orgado, J. Cannabinoids: Well-suited candidates for the treatment of perinatal brain injury. Brain Sci. 2013, 3, 1043–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juul, S.E.; Ferriero, D.M. Pharmacologic neuroprotective strategies in neonatal brain injury. Clin. Perinatol. 2014, 41, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, M.V.; Fatemi, A.; Wilson, M.A.; Northington, F. Treatment advances in neonatal neuroprotection and neurointensive care. Lancet. Neurol. 2011, 10, 372–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cilio, M.R.; Ferriero, D.M. Synergistic neuroprotective therapies with hypothermia. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2010, 15, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tataranno, M.L.; Perrone, S.; Longini, M.; Buonocore, G. New antioxidant drugs for neonatal brain injury. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2015, 2015, 108251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, G.A.; Cooke, R.W. Randomised controlled trial of allopurinol prophylaxis in very preterm infants. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 1995, 73, F27–F31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, C.; Vannucci, R.C.; Towfighi, J. Reduction of perinatal hypoxic-ischemic brain damage with allopurinol. Pediatr. Res. 1990, 27, 332–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, C.; Towfighi, J.; Roberts, R.L.; Heitjan, D.F. Allopurinol administered after inducing hypoxia-ischemia reduces brain injury in 7-day-old rats. Pediatr. Res. 1993, 33, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Marro, P.J.; Mishra, O.P.; Delivoria-Papadopoulos, M. Effect of allopurinol on brain adenosine levels during hypoxia in newborn piglets. Brain Res. 2006, 1073–1074, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benders, M.J.N.L.; Bos, A.F.; Rademaker, C.M.A.; Rijken, M.; Torrance, H.L.; Groenendaal, F.; van Bel, F. Early postnatal allopurinol does not improve short term outcome after severe birth asphyxia. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2006, 91, F163–F165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhari, T.; McGuire, W. Allopurinol for preventing mortality and morbidity in newborn infants with hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2008, 63, 845–848. [Google Scholar]
- Van Bel, F.; Shadid, M.; Moison, R.M.; Dorrepaal, C.A.; Fontijn, J.; Monteiro, L.; van de Bor, M.; Berger, H.M. Effect of allopurinol on postasphyxial free radical formation, cerebral hemodynamics, and electrical brain activity. Pediatrics 1998, 101, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torrance, H.L.; Benders, M.J.; Derks, J.B.; Rademaker, C.M.A.; Bos, A.F.; van den Berg, P.; Longini, M.; Buonocore, G.; Venegas, M.; Baquero, H.; et al. Maternal allopurinol during fetal hypoxia lowers cord blood levels of the brain injury marker S-100B. Pediatrics 2009, 124, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunes, T.; Ozturk, M.A.; Koklu, E.; Kose, K.; Gunes, I. Effect of allopurinol supplementation on nitric oxide levels in asphyxiated newborns. Pediatr. Neurol. 2007, 36, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaandorp, J.J.; van Bel, F.; Veen, S.; Derks, J.B.; Groenendaal, F.; Rijken, M.; Roze, E.; Venema, M.M.A.U.; Rademaker, C.M.A.; Bos, A.F.; et al. Long-term neuroprotective effects of allopurinol after moderate perinatal asphyxia: Follow-up of two randomised controlled trials. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2012, 97, F162–F166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.W.; Gonzalez, F.F. Erythropoietin: A novel therapy for hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy? Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2015, 57, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Shacka, J.J.; Eells, J.B.; Suarez-Quian, C.; Przygodzki, R.M.; Beleslin-Cokic, B.; Lin, C.-S.; Nikodem, V.M.; Hempstead, B.; Flanders, K.C.; et al. Erythropoietin receptor signalling is required for normal brain development. Development 2002, 129, 505–516. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bernaudin, M.; Tang, Y.; Reilly, M.; Petit, E.; Sharp, F.R. Brain genomic response following hypoxia and re-oxygenation in the neonatal rat. Identification of genes that might contribute to hypoxia-induced ischemic tolerance. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 39728–39738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, D.; Chang, Y.S.; Vexler, Z.S.; Ferriero, D.M. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1α and erythropoietin upregulation with deferoxamine salvage after neonatal stroke. Exp. Neurol. 2005, 195, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernaudin, M.; Marti, H.H.; Roussel, S.; Divoux, D.; Nouvelot, A.; MacKenzie, E.T.; Petit, E. A potential role for erythropoietin in focal permanent cerebral ischemia in mice. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 1999, 19, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brines, M.L.; Ghezzi, P.; Keenan, S.; Agnello, D.; de Lanerolle, N.C.; Cerami, C.; Itri, L.M.; Cerami, A. Erythropoietin crosses the blood-brain barrier to protect against experimental brain injury. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 10526–10531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Chopp, M. Treatment of stroke with erythropoietin enhances neurogenesis and angiogenesis and improves neurological function in rats. Stroke 2004, 35, 1732–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Zhou, C.; Polk, P.; Nanda, A.; Zhang, J.H. Mechanisms of erythropoietin-induced brain protection in neonatal hypoxia-ischemia rat model. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2004, 24, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Solaroglu, I.; Solaroglu, A.; Kaptanoglu, E.; Dede, S.; Haberal, A.; Beskonakli, E.; Kilinc, K. Erythropoietin prevents ischemia-reperfusion from inducing oxidative damage in fetal rat brain. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2003, 19, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kumral, A.; Ozer, E.; Yilmaz, O.; Akhisaroglu, M.; Gokmen, N.; Duman, N.; Ulukus, C.; Genc, S.; Ozkan, H. Neuroprotective effect of erythropoietin on hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in neonatal rats. Biol. Neonate 2003, 83, 224–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumral, A.; Uysal, N.; Tugyan, K.; Sonmez, A.; Yilmaz, O.; Gokmen, N.; Kiray, M.; Genc, S.; Duman, N.; Koroglu, T.F.; et al. Erythropoietin improves long-term spatial memory deficits and brain injury following neonatal hypoxia-ischemia in rats. Behav. Brain Res. 2004, 153, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.; Heijnen, C.J.; van der Kooij, M.A.; Groenendaal, F.; van Bel, F. Beneficial effect of erythropoietin on sensorimotor function and white matter after hypoxia-ischemia in neonatal mice. Pediatr. Res. 2011, 69, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kellert, B.A.; McPherson, R.J.; Juul, S.E. A comparison of high-dose recombinant erythropoietin treatment regimens in brain-injured neonatal rats. Pediatr. Res. 2007, 61, 451–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, M.L.; Hill, C.A.; Rosenkrantz, T.S.; Fitch, R.H. Evaluation of the therapeutic benefit of delayed administration of erythropoietin following early hypoxic-ischemic injury in rodents. Dev. Neurosci. 2012, 34, 515–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larpthaveesarp, A.; Georgevits, M.; Ferriero, D.M.; Gonzalez, F.F. Delayed erythropoietin therapy improves histological and behavioral outcomes after transient neonatal stroke. Neurobiol. Dis. 2016, 93, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, F.F.; Larpthaveesarp, A.; McQuillen, P.; Derugin, N.; Wendland, M.; Spadafora, R.; Ferriero, D.M. Erythropoietin increases neurogenesis and oligodendrogliosis of subventricular zone precursor cells after neonatal stroke. Stroke 2013, 44, 753–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, F.F.; Abel, R.; Almli, C.R.; Mu, D.; Wendland, M.; Ferriero, D.M. Erythropoietin sustains cognitive function and brain volume after neonatal stroke. Dev. Neurosci. 2009, 31, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, K.-M.; Tien, L.-T.; Cai, Z.; Lin, S.; Pang, Y.; Tanaka, S.; Rhodes, P.G.; Bhatt, A.J.; Savich, R.D.; Fan, L.W. Erythropoietin ameliorates neonatal hypoxia-ischemia-induced neurobehavioral deficits, neuroinflammation, and hippocampal injury in the juvenile rat. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Q.; Zhang, X.-F.; Yang, J.-Y. Erythropoietin reduces white matter damage in two-day-old rats exposed to hypoxic/ischemia injury. Neurol. Res. 2016, 38, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jantzie, L.L.; Corbett, C.J.; Firl, D.J.; Robinson, S. Postnatal erythropoietin mitigates impaired cerebral cortical development following subplate loss from prenatal hypoxia-ischemia. Cereb. Cortex 2015, 25, 2683–2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jantzie, L.L.; Miller, R.H.; Robinson, S. Erythropoietin signaling promotes oligodendrocyte development following prenatal systemic hypoxic-ischemic brain injury. Pediatr. Res. 2013, 74, 658–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traudt, C.M.; McPherson, R.J.; Bauer, L.A.; Richards, T.L.; Burbacher, T.M.; McAdams, R.M.; Juul, S.E. Concurrent erythropoietin and hypothermia treatment improve outcomes in a term nonhuman primate model of perinatal asphyxia. Dev. Neurosci. 2013, 35, 491–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Wang, H.; Yu, X.; Jin, W.; Qiao, L.; Lu, T.; Hu, Z.; Zhou, J. Erythropoietin prevents zinc accumulation and neuronal death after traumatic brain injury in rat hippocampus: In vitro and in vivo studies. Brain Res. 2009, 1289, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmahdy, H.; El-Mashad, A.-R.; El-Bahrawy, H.; El-Gohary, T.; El-Barbary, A.; Aly, H. Human recombinant erythropoietin in asphyxia neonatorum: Pilot trial. Pediatrics 2010, 125, e1135–e1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.W.; Bauer, L.A.; Ballard, R.A.; Ferriero, D.M.; Glidden, D.V.; Mayock, D.E.; Chang, T.; Durand, D.J.; Song, D.; Bonifacio, S.L.; et al. Erythropoietin for neuroprotection in neonatal encephalopathy: Safety and pharmacokinetics. Pediatrics 2012, 130, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, E.E.; Bonifacio, S.L.; Glass, H.C.; Juul, S.E.; Chang, T.; Mayock, D.E.; Durand, D.J.; Song, D.; Barkovich, A.J.; Ballard, R.A.; Wu, Y.W. Erythropoietin and hypothermia for hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Pediatr. Neurol. 2014, 51, 657–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.W.; Mathur, A.M.; Chang, T.; McKinstry, R.C.; Mulkey, S.B.; Mayock, D.E.; van Meurs, K.P.; Rogers, E.E.; Gonzalez, F.F.; Comstock, B.A.; et al. High-Dose Erythropoietin and Hypothermia for hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy: A Phase II trial. Pediatrics 2016, 137, e20160191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastianetto, S.; Ménard, C.; Quirion, R. Neuroprotective action of resveratrol. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1852, 1195–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venturini, C.D.; Merlo, S.; Souto, A.A.; Fernandes, M.; Gomez, R.; Rhoden, C.R. Resveratrol and red wine function as antioxidants in the nervous system without cellular proliferative effects during experimental diabetes. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2010, 3, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gülçin, İ. Antioxidant properties of resveratrol: A structure-activity insight. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2010, 11, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermann, D.M.; Zechariah, A.; Kaltwasser, B.; Bosche, B.; Caglayan, A.B.; Kilic, E.; Doeppner, T.R. Sustained neurological recovery induced by resveratrol is associated with angioneurogenesis rather than neuroprotection after focal cerebral ischemia. Neurobiol. Dis. 2015, 83, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, L.; Gao, H.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y. Resveratrol alleviates nerve injury after cerebral ischemia and reperfusion in mice by inhibiting inflammation and apoptosis. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 3219–3226. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Yan, Z.; Zhu, J.; Yang, J.; He, J. Neuroprotective effects of resveratrol on ischemic injury mediated by improving brain energy metabolism and alleviating oxidative stress in rats. Neuropharmacology 2011, 60, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousuf, S.; Atif, F.; Ahmad, M.; Hoda, N.; Ishrat, T.; Khan, B.; Islam, F. Resveratrol exerts its neuroprotective effect by modulating mitochondrial dysfunctions and associated cell death during cerebral ischemia. Brain Res. 2009, 1250, 242–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, K.; Chaudhary, G.; Gupta, Y.K. Protective effect of resveratrol against oxidative stress in middle cerebral artery occlusion model of stroke in rats. Life Sci. 2002, 71, 655–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arteaga, O.; Revuelta, M.; Urigüen, L.; Álvarez, A.; Montalvo, H.; Hilario, E. Pretreatment with resveratrol prevents neuronal injury and cognitive deficits induced by perinatal hypoxia-ischemia in rats. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karalis, F.; Soubasi, V.; Georgiou, T.; Nakas, C.T.; Simeonidou, C.; Guiba-Tziampiri, O.; Spandou, E. Resveratrol ameliorates hypoxia/ischemia-induced behavioral deficits and brain injury in the neonatal rat brain. Brain Res. 2011, 1425, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, T.; Atzeva, M.; Holtzman, D.M. Pomegranate polyphenols and resveratrol protect the neonatal brain against hypoxic-ischemic injury. Dev. Neurosci. 2007, 29, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Revuelta, M.; Arteaga, O.; Montalvo, H.; Alvarez, A.; Hilario, E.; Martinez-Ibargüen, A. Antioxidant treatments recover the alteration of auditory-evoked potentials and reduce morphological damage in the inferior colliculus after perinatal asphyxia in rat. Brain Pathol. 2016, 26, 186–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arteaga, O.; Revuelta, M.; Urigüen, L.; Martínez-Millán, L.; Hilario, E.; Álvarez, A. Docosahexaenoic acid reduces cerebral damage and ameliorates long-term cognitive impairments caused by neonatal hypoxia-ischemia in rats. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girbovan, C.; Plamondon, H. Resveratrol downregulates type-1 glutamate transporter expression and microglia activation in the hippocampus following cerebral ischemia reperfusion in rats. Brain Res. 2015, 1608, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morin, C.; Zini, R.; Albengres, E.; Bertelli, A.A.E.; Bertelli, A.; Tillement, J.P. Evidence for resveratrol-induced preservation of brain mitochondria functions after hypoxia-reoxygenation. Drugs Exp. Clin. Res. 2003, 29, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Toader, A.-M.; Filip, A.; Decea, N.; Muresan, A. Neuroprotective strategy in an experimental newborn rat model of brain ischemia and hypoxia: Effects of Resveratrol and hypothermia. Clujul Med. 2013, 86, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Heurteaux, C.; Laigle, C.; Blondeau, N.; Jarretou, G.; Lazdunski, M. α-Linolenic acid and riluzole treatment confer cerebral protection and improve survival after focal brain ischemia. Neuroscience 2006, 137, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blondeau, N.; Nguemeni, C.; Debruyne, D.N.; Piens, M.; Wu, X.; Pan, H.; Hu, X.; Gandin, C.; Lipsky, R.H.; Plumier, J.-C.; et al. Subchronic α-linolenic acid treatment enhances brain plasticity and exerts an antidepressant effect: A versatile potential therapy for stroke. Neuropsychopharmacology 2009, 34, 2548–2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguemeni, C.; Delplanque, B.; Rovère, C.; Simon-Rousseau, N.; Gandin, C.; Agnani, G.; Nahon, J.L.; Heurteaux, C.; Blondeau, N. Dietary supplementation of α-linolenic acid in an enriched rapeseed oil diet protects from stroke. Pharmacol. Res. 2010, 61, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourourou, M.; Heurteaux, C.; Blondeau, N. α-Linolenic acid given as enteral or parenteral nutritional intervention against sensorimotor and cognitive deficits in a mouse model of ischemic stroke. Neuropharmacology 2016, 108, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueda, M.; Inaba, T.; Nito, C.; Kamiya, N.; Katayama, Y. Therapeutic impact of eicosapentaenoic acid on ischemic brain damage following transient focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Brain Res. 2013, 1519, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okabe, N.; Nakamura, T.; Toyoshima, T.; Miyamoto, O.; Lu, F.; Itano, T. Eicosapentaenoic acid prevents memory impairment after ischemia by inhibiting inflammatory response and oxidative damage. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2011, 20, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, H.-C.; Kao, T.-K.; Ou, Y.-C.; Yang, D.-Y.; Yen, Y.-J.; Wang, C.-C.; Chuang, Y.-H.; Liao, S.-L.; Raung, S.-L.; Wu, C.-W.; et al. Protective effect of docosahexaenoic acid against brain injury in ischemic rats. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2009, 20, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belayev, L.; Khoutorova, L.; Atkins, K.D.; Bazan, N.G. Robust docosahexaenoic acid-mediated neuroprotection in a rat model of transient, focal cerebral ischemia. Stroke 2009, 40, 3121–3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belayev, L.; Khoutorova, L.; Atkins, K.D.; Eady, T.N.; Hong, S.; Lu, Y.; Obenaus, A.; Bazan, N.G. Docosahexaenoic Acid therapy of experimental ischemic stroke. Transl. Stroke Res. 2011, 2, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eady, T.N.; Khoutorova, L.; Atkins, K.D.; Bazan, N.G.; Belayev, L. Docosahexaenoic acid complexed to human albumin in experimental stroke: Neuroprotective efficacy with a wide therapeutic window. Exp. Transl. Stroke Med. 2012, 4, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.-H.; Khoutorova, L.; Bazan, N.G.; Belayev, L. Docosahexaenoic acid improves behavior and attenuates blood-brain barrier injury induced by focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Exp. Transl. Stroke Med. 2015, 7, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eady, T.N.; Belayev, L.; Khoutorova, L.; Atkins, K.D.; Zhang, C.; Bazan, N.G. Docosahexaenoic acid signaling modulates cell survival in experimental ischemic stroke penumbra and initiates long-term repair in young and aged rats. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, C.; Zhang, J.; Chen, F.; Lin, Y. Neuroprotectin D1 attenuates brain damage induced by transient middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats through TRPC6/CREB pathways. Mol. Med. Rep. 2013, 8, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Belayev, L.; Marcheselli, V.L.; Khoutorova, L.; Rodriguez de Turco, E.B.; Busto, R.; Ginsberg, M.D.; Bazan, N.G. Docosahexaenoic acid complexed to albumin elicits high-grade ischemic neuroprotection. Stroke 2005, 36, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eady, T.N.; Khoutorova, L.; Anzola, D.V.; Hong, S.-H.; Obenaus, A.; Mohd-Yusof, A.; Bazan, N.G.; Belayev, L. Acute treatment with docosahexaenoic acid complexed to albumin reduces injury after a permanent focal cerebral ischemia in rats. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e77237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eady, T.N.; Khoutorova, L.; Obenaus, A.; Mohd-Yusof, A.; Bazan, N.G.; Belayev, L. Docosahexaenoic acid complexed to albumin provides neuroprotection after experimental stroke in aged rats. Neurobiol. Dis. 2014, 62, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mucci, D.; Fernandes, F.S.; Souza, A.D.S.; Sardinha, F.L.; Soares-Mota, M.; Tavares do Carmo, M. Flaxseed mitigates brain mass loss, improving motor hyperactivity and spatial memory, in a rodent model of neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Prostaglandins. Leukot. Essent. Fatty Acids 2015, 97, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Hu, X.; Yang, W.; Gao, Y.; Chen, J. Ω-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid supplementation confers long-term neuroprotection against neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury through anti-inflammatory actions. Stroke 2010, 41, 2341–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, J.; Hu, X.; Li, P.; Leak, R.K.; Gao, Y.; Chen, J. n-3 Polyunsaturated fatty acids reduce neonatal hypoxic/ischemic brain injury by promoting phosphatidylserine formation and akt signaling. Stroke 2015, 46, 2943–2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, J.J.; Mayurasakorn, K.; Vannucci, S.J.; Mastropietro, C.; Bazan, N.G.; Ten, V.S.; Deckelbaum, R.J. N-3 fatty acid rich triglyceride emulsions are neuroprotective after cerebral hypoxic-ischemic injury in neonatal mice. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayurasakorn, K.; Niatsetskaya, Z.V.; Sosunov, S.A.; Williams, J.J.; Zirpoli, H.; Vlasakov, I.; Deckelbaum, R.J.; Ten, V.S. DHA but Not EPA Emulsions Preserve Neurological and Mitochondrial Function after Brain Hypoxia-Ischemia in Neonatal Mice. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0160870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berman, D.R.; Mozurkewich, E.; Liu, Y.; Barks, J. Docosahexaenoic acid pretreatment confers neuroprotection in a rat model of perinatal cerebral hypoxia-ischemia. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2009, 200, 305.e1–305.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berman, D.R.; Liu, Y.; Barks, J.; Mozurkewich, E. Treatment with docosahexaenoic acid after hypoxia-ischemia improves forepaw placing in a rat model of perinatal hypoxia-ischemia. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2010, 203, 385.e1–385.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.-Q.; Zhang, L.; Liu, H.-A.; Yuan, N.; Hou, P.-Q.; Zhang, R.-Q.; Wu, T. Expansion of CD14(+)CD16(+) monocytes is related to acute leukemia. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 12297–12306. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Berman, D.R.; Mozurkewich, E.; Liu, Y.; Shangguan, Y.; Barks, J.D.; Silverstein, F.S. Docosahexaenoic acid augments hypothermic neuroprotection in a neonatal rat asphyxia model. Neonatology 2013, 104, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.; Sekhon, B.; Jatana, M.; Giri, S.; Gilg, A.G.; Sekhon, C.; Singh, I.; Singh, A.K. Administration of N-acetylcysteine after focal cerebral ischemia protects brain and reduces inflammation in a rat model of experimental stroke. J. Neurosci. Res. 2004, 76, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekhon, B.; Sekhon, C.; Khan, M.; Patel, S.J.; Singh, I.; Singh, A.K. N-Acetyl cysteine protects against injury in a rat model of focal cerebral ischemia. Brain Res. 2003, 971, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yan, J.; Taheri, S.; Liu, K.J.; Shi, H. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 contributes to N-acetylcysteine’s protection in stroke. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2014, 68, 8–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, D.; Shin, K.; Choi, E.-K.; Choi, Y.; Jang, J.-Y.; Kim, J.; Jeong, H.-S.; Lee, W.; Lee, Y.-B.; Kim, S.U.; et al. Protective effects of N-acetyl-l-cysteine in human oligodendrocyte progenitor cells and restoration of motor function in neonatal rats with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Evid. Based. Complement. Alternat. Med. 2015, 2015, 764251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, X.; Lowe, D.W.; Rollins, L.G.; Bentzley, J.; Fraser, J.L.; Martin, R.; Singh, I.; Jenkins, D. Sex-specific effects of N-acetylcysteine in neonatal rats treated with hypothermia after severe hypoxia-ischemia. Neurosci. Res. 2016, 108, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jatana, M.; Singh, I.; Singh, A.K.; Jenkins, D. Combination of systemic hypothermia and N-acetylcysteine attenuates hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in neonatal rats. Pediatr. Res. 2006, 59, 684–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Svedin, P.; Nie, C.; Lapatto, R.; Zhu, C.; Gustavsson, M.; Sandberg, M.; Karlsson, J.-O.; Romero, R.; Hagberg, H.; et al. N-acetylcysteine reduces lipopolysaccharide-sensitized hypoxic-ischemic brain injury. Ann. Neurol. 2007, 61, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, T.-F.; Jantzie, L.L.; Todd, K.G.; Cheung, P.-Y. Postresuscitation N-acetylcysteine treatment reduces cerebral hydrogen peroxide in the hypoxic piglet brain. Intensive Care Med. 2008, 34, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, T.-F.; Tymafichuk, C.N.; Bigam, D.L.; Cheung, P.-Y. Effects of postresuscitation N-acetylcysteine on cerebral free radical production and perfusion during reoxygenation of hypoxic newborn piglets. Pediatr. Res. 2008, 64, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mobarra, N.; Shanaki, M.; Ehteram, H.; Nasiri, H.; Sahmani, M.; Saeidi, M.; Goudarzi, M.; Pourkarim, H.; Azad, M. A review on iron chelators in treatment of iron overload syndromes. Int. J. Hematol. Stem Cell Res. 2016, 10, 239–247. [Google Scholar]
- Hamrick, S.E.G.; McQuillen, P.S.; Jiang, X.; Mu, D.; Madan, A.; Ferriero, D.M. A role for hypoxia-inducible factor-1α in desferoxamine neuroprotection. Neurosci. Lett. 2005, 379, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papazisis, G.; Pourzitaki, C.; Sardeli, C.; Lallas, A.; Amaniti, E.; Kouvelas, D. Deferoxamine decreases the excitatory amino acid levels and improves the histological outcome in the hippocampus of neonatal rats after hypoxia-ischemia. Pharmacol. Res. 2008, 57, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarco, D.P.; Becker, J.; Palmer, C.; Sheldon, R.A.; Ferriero, D.M. The neuroprotective effect of deferoxamine in the hypoxic-ischemic immature mouse brain. Neurosci. Lett. 2000, 282, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shadid, M.; Buonocore, G.; Groenendaal, F.; Moison, R.; Ferrali, M.; Berger, H.M.; van Bel, F. Effect of deferoxamine and allopurinol on non-protein-bound iron concentrations in plasma and cortical brain tissue of newborn lambs following hypoxia-ischemia. Neurosci. Lett. 1998, 248, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shadid, M.; Moison, R.; Steendijk, P.; Hiltermann, L.; Berger, H.M.; van Bel, F. The effect of antioxidative combination therapy on post hypoxic-ischemic perfusion, metabolism, and electrical activity of the newborn brain. Pediatr. Res. 1998, 44, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groenendaal, F.; Shadid, M.; McGowan, J.E.; Mishra, O.P.; van Bel, F. Effects of deferoxamine, a chelator of free iron, on NA(+), K(+)-ATPase activity of cortical brain cell membrane during early reperfusion after hypoxia-ischemia in newborn lambs. Pediatr. Res. 2000, 48, 560–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peeters-Scholte, C.; Braun, K.; Koster, J.; Kops, N.; Blomgren, K.; Buonocore, G.; van Buul-Offers, S.; Hagberg, H.; Nicolay, K.; van Bel, F.; et al. Effects of allopurinol and deferoxamine on reperfusion injury of the brain in newborn piglets after neonatal hypoxia-ischemia. Pediatr. Res. 2003, 54, 516–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welin, A.-K.; Svedin, P.; Lapatto, R.; Sultan, B.; Hagberg, H.; Gressens, P.; Kjellmer, I.; Mallard, C. Melatonin reduces inflammation and cell death in white matter in the mid-gestation fetal sheep following umbilical cord occlusion. Pediatr. Res. 2007, 61, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tutunculer, F.; Eskiocak, S.; BaSaran, U.N.; Ekuklu, G.; Ayvaz, S.; Vatansever, U. The protective role of melatonin in experimental hypoxic brain damage. Pediatr. Int. 2005, 47, 434–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, O.P.; Delivoria-Papadopoulos, M. Lipid peroxidation in developing fetal guinea pig brain during normoxia and hypoxia. Brain Res. Dev. Brain Res. 1989, 45, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, D.-X.; Manchester, L.C.; Terron, M.P.; Flores, L.J.; Reiter, R.J. One molecule, many derivatives: A never-ending interaction of melatonin with reactive oxygen and nitrogen species? J. Pineal Res. 2007, 42, 28–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosen, J.; Than, N.N.; Koch, D.; Poeggeler, B.; Laatsch, H.; Hardeland, R. Interactions of melatonin and its metabolites with the ABTS cation radical: Extension of the radical scavenger cascade and formation of a novel class of oxidation products, C2-substituted 3-indolinones. J. Pineal Res. 2006, 41, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomás-Zapico, C.; Coto-Montes, A. A proposed mechanism to explain the stimulatory effect of melatonin on antioxidative enzymes. J. Pineal Res. 2005, 39, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acuña-Castroviejo, D.; Martín, M.; Macías, M.; Escames, G.; León, J.; Khaldy, H.; Reiter, R.J. Melatonin, mitochondria, and cellular bioenergetics. J. Pineal Res. 2001, 30, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiter, R.J.; Tan, D.X.; Osuna, C.; Gitto, E. Actions of melatonin in the reduction of oxidative stress. A review. J. Biomed. Sci. 2000, 7, 444–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso-Alconada, D.; Alvarez, A.; Lacalle, J.; Hilario, E. Histological study of the protective effect of melatonin on neural cells after neonatal hypoxia-ischemia. Histol. Histopathol. 2012, 27, 771–783. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ozyener, F.; Çetinkaya, M.; Alkan, T.; Gören, B.; Kafa, I.M.; Kurt, M.A.; Koksal, N. Neuroprotective effects of melatonin administered alone or in combination with topiramate in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic rat model. Restor. Neurol. Neurosci. 2012, 30, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cetinkaya, M.; Alkan, T.; Ozyener, F.; Kafa, I.M.; Kurt, M.A.; Koksal, N. Possible neuroprotective effects of magnesium sulfate and melatonin as both pre- and post-treatment in a neonatal hypoxic-ischemic rat model. Neonatology 2011, 99, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carloni, S.; Perrone, S.; Buonocore, G.; Longini, M.; Proietti, F.; Balduini, W. Melatonin protects from the long-term consequences of a neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in rats. J. Pineal Res. 2008, 44, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, K.; Hamada, F.; Wakatsuki, A.; Nagai, R.; Shinohara, K.; Hayashi, Y.; Imamura, R.; Fukaya, T. Prophylactic administration of melatonin to the mother throughout pregnancy can protect against oxidative cerebral damage in neonatal rats. J. Matern. Fetal. Neonatal Med. 2012, 25, 1254–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamada, F.; Watanabe, K.; Wakatsuki, A.; Nagai, R.; Shinohara, K.; Hayashi, Y.; Imamura, R.; Fukaya, T. Therapeutic effects of maternal melatonin administration on ischemia/reperfusion-induced oxidative cerebral damage in neonatal rats. Neonatology 2010, 98, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Revuelta, M.; Arteaga, O.; Alvarez, A.; Martinez-Ibargüen, A.; Hilario, E. Characterization of gene expression in the rat brainstem after neonatal hypoxic-ischemic injury and antioxidant treatment. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balduini, W.; Carloni, S.; Perrone, S.; Bertrando, S.; Tataranno, M.L.; Negro, S.; Proietti, F.; Longini, M.; Buonocore, G. The use of melatonin in hypoxic-ischemic brain damage: An experimental study. J. Matern. Fetal. Neonatal Med. 2012, 25, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Signorini, C.; Ciccoli, L.; Leoncini, S.; Carloni, S.; Perrone, S.; Comporti, M.; Balduini, W.; Buonocore, G. Free iron, total F-isoprostanes and total F-neuroprostanes in a model of neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy: Neuroprotective effect of melatonin. J. Pineal Res. 2009, 46, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, S.L.; Chai, M.; Loose, J.; Castillo-Meléndez, M.; Walker, D.W.; Jenkin, G.; Wallace, E.M. The effects of maternal betamethasone administration on the intrauterine growth-restricted fetus. Endocrinology 2007, 148, 1288–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carloni, S.; Albertini, M.C.; Galluzzi, L.; Buonocore, G.; Proietti, F.; Balduini, W. Melatonin reduces endoplasmic reticulum stress and preserves sirtuin 1 expression in neuronal cells of newborn rats after hypoxia-ischemia. J. Pineal Res. 2014, 57, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, K.; Wakatsuki, A.; Shinohara, K.; Ikenoue, N.; Yokota, K.; Fukaya, T. Maternally administered melatonin protects against ischemia and reperfusion-induced oxidative mitochondrial damage in premature fetal rat brain. J. Pineal Res. 2004, 37, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okatani, Y.; Wakatsuki, A.; Shinohara, K.; Taniguchi, K.; Fukaya, T. Melatonin protects against oxidative mitochondrial damage induced in rat placenta by ischemia and reperfusion. J. Pineal Res. 2001, 31, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, H.R.; Morken, T.S.; Vettukattil, R.; Brubakk, A.-M.; Sonnewald, U.; Widerøe, M. No improvement of neuronal metabolism in the reperfusion phase with melatonin treatment after hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in the neonatal rat. J. Neurochem. 2016, 136, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buendia, I.; Gómez-Rangel, V.; González-Lafuente, L.; Parada, E.; León, R.; Gameiro, I.; Michalska, P.; Laudon, M.; Egea, J.; López, M.G. Neuroprotective mechanism of the novel melatonin derivative Neu-P11 in brain ischemia related models. Neuropharmacology 2015, 99, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aly, H.; Elmahdy, H.; El-Dib, M.; Rowisha, M.; Awny, M.; El-Gohary, T.; Elbatch, M.; Hamisa, M.; El-Mashad, A.-R. Melatonin use for neuroprotection in perinatal asphyxia: A randomized controlled pilot study. J. Perinatol. 2015, 35, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galinsky, R.; Bennet, L.; Groenendaal, F.; Lear, C.A.; Tan, S.; van Bel, F.; Juul, S.E.; Robertson, N.J.; Mallard, C.; Gunn, A.J. Magnesium is not consistently neuroprotective for perinatal hypoxia-ischemia in term-equivalent models in preclinical studies: A systematic review. Dev. Neurosci. 2014, 36, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goñi-de-Cerio, F.; Alvarez, A.; Alvarez, F.J.; Rey-Santano, M.C.; Alonso-Alconada, D.; Mielgo, V.E.; Gastiasoro, E.; Hilario, E. MgSO4 treatment preserves the ischemia-induced reduction in S-100 protein without modification of the expression of endothelial tight junction molecules. Histol. Histopathol. 2009, 24, 1129–1138. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pazaiti, A.; Soubasi, V.; Spandou, E.; Karkavelas, G.; Georgiou, T.; Karalis, P.; Guiba-Tziampiri, O. Evaluation of long-lasting sensorimotor consequences following neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in rats: The neuroprotective role of MgSO4. Neonatology 2009, 95, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arteaga, O.; Álvarez, A.; Revuelta, M.; Santaolalla, F.; Urtasun, A.; Hilario, E. Role of Antioxidants in Neonatal Hypoxic–Ischemic Brain Injury: New Therapeutic Approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 265. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18020265
Arteaga O, Álvarez A, Revuelta M, Santaolalla F, Urtasun A, Hilario E. Role of Antioxidants in Neonatal Hypoxic–Ischemic Brain Injury: New Therapeutic Approaches. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(2):265. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18020265
Chicago/Turabian StyleArteaga, Olatz, Antonia Álvarez, Miren Revuelta, Francisco Santaolalla, Andoni Urtasun, and Enrique Hilario. 2017. "Role of Antioxidants in Neonatal Hypoxic–Ischemic Brain Injury: New Therapeutic Approaches" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 2: 265. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18020265
APA StyleArteaga, O., Álvarez, A., Revuelta, M., Santaolalla, F., Urtasun, A., & Hilario, E. (2017). Role of Antioxidants in Neonatal Hypoxic–Ischemic Brain Injury: New Therapeutic Approaches. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(2), 265. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18020265





