Recent Advances in Targeting the EGFR Signaling Pathway for the Treatment of Metastatic Colorectal Cancer
Abstract
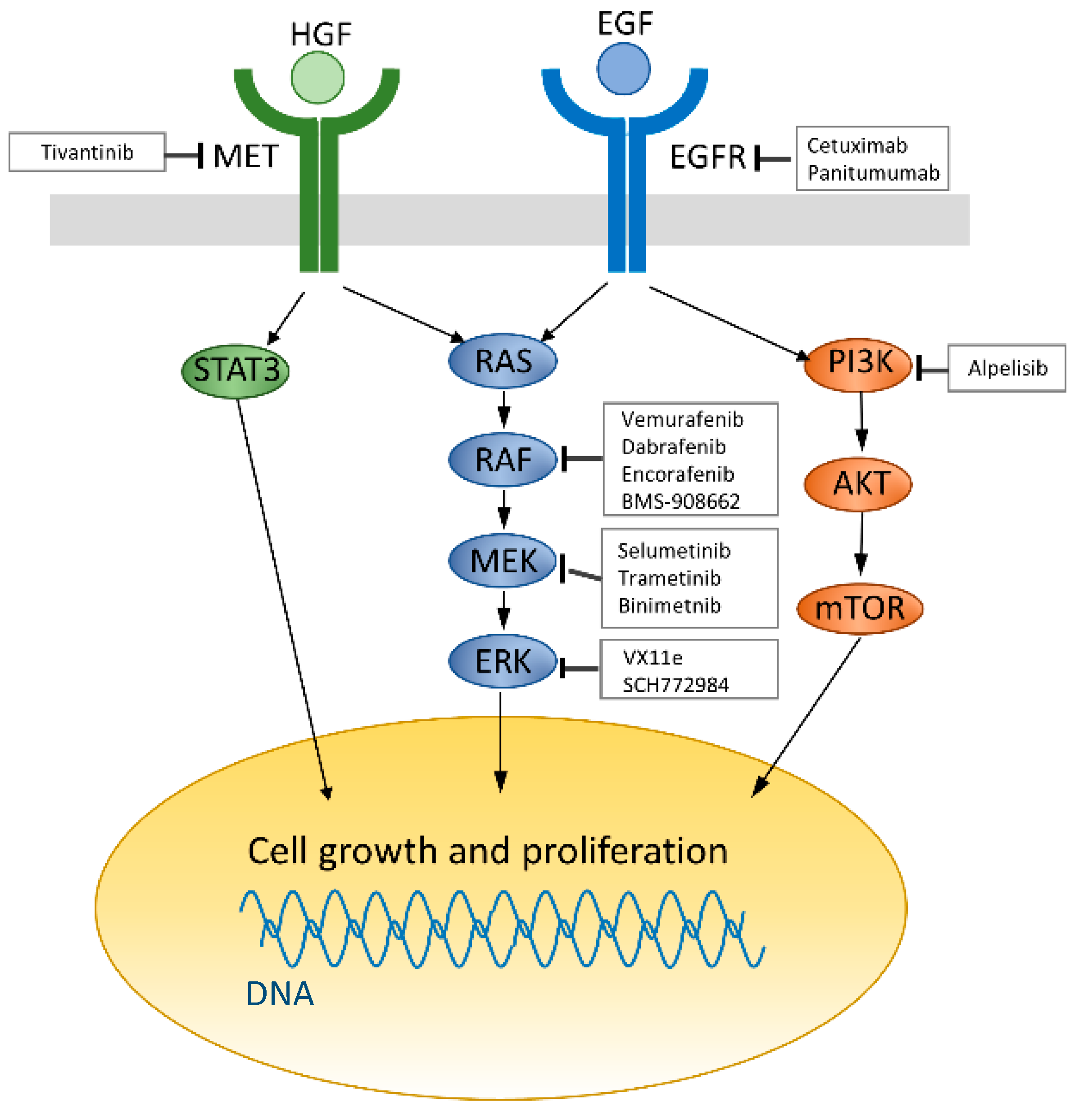
:1. Introduction
2. Clinical Advances in Anti-EGFR Antibodies
3. The Effect of RAS Status on Anti-EGFR Therapies
4. KRASG13D Mutation
5. Anti-EGFR Therapies versus Bevacizumab in First Line Chemotherapy
6. Primary Tumor Location as a Prognostic and Predictive Biomarker in mCRC
7. Resistance Mechanism to Anti-EGFR Therapies
8. BRAF Mutation in Colorectal Cancer
9. Combination Therapies with BRAF Inhibitors
10. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saltz, L.B.; Cox, J.V.; Blanke, C.; Rosen, L.S.; Fehrenbacher, L.; Moore, M.J.; Maroun, J.A.; Ackland, S.P.; Locker, P.K.; Pirotta, N.; et al. Irinotecan plus fluorouracil and leucovorin for metastatic colorectal cancer. Irinotecan Study Group. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 343, 905–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Gramont, A.; Figer, A.; Seymour, M.; Homerin, M.; Hmissi, A.; Cassidy, J.; Boni, C.; Cortes-Funes, H.; Cervantes, A.; Freyer, G.; et al. Leucovorin and fluorouracil with or without oxaliplatin as first-line treatment in advanced colorectal cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2000, 18, 2938–2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassidy, J.; Clarke, S.; Diaz-Rubio, E.; Scheithauer, W.; Figer, A.; Wong, R.; Koski, S.; Lichinitser, M.; Yang, T.-S.; Rivera, F.; et al. Randomized phase III study of capecitabine plus oxaliplatin compared with fluorouracil/folinic acid plus oxaliplatin as first-line therapy for metastatic colorectal cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 2006–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurwitz, H.; Fehrenbacher, L.; Novotny, W.; Cartwright, T.; Hainsworth, J.; Heim, W.; Berlin, J.; Baron, A.; Griffing, S.; Holmgren, E.; et al. Bevacizumab plus irinotecan, fluorouracil, and leucovorin for metastatic colorectal cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 2335–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saltz, L.B.; Clarke, S.; Díaz-Rubio, E.; Scheithauer, W.; Figer, A.; Wong, R.; Koski, S.; Lichinitser, M.; Yang, T.-S.S.; Rivera, F.; et al. Bevacizumab in combination with oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy as first-line therapy in metastatic colorectal cancer: A randomized phase III study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 2013–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Cutsem, E.; Tabernero, J.; Lakomy, R.; Prenen, H.; Prausova, J.; Macarulla, T.; Ruff, P.; van Hazel, G.A.; Moiseyenko, V.; Ferry, D.; et al. Addition of aflibercept to fluorouracil, leucovorin, and irinotecan improves survival in a phase III randomized trial in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer previously treated with an oxaliplatin-based regimen. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 3499–3506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabernero, J.; Yoshino, T.; Cohn, A.L.; Obermannova, R.; Bodoky, G.; Garcia-Carbonero, R.; Ciuleanu, T.-E.E.; Portnoy, D.C.; van Cutsem, E.; Grothey, A.; et al. Ramucirumab versus placebo in combination with second-line FOLFIRI in patients with metastatic colorectal carcinoma that progressed during or after first-line therapy with bevacizumab, oxaliplatin, and a fluoropyrimidine (RAISE): A randomised, double-blin. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Cutsem, E.; Kohne, C.H.; Hitre, E.; Zaluski, J.; Chang Chien, C.-R.; Makhson, A.; D’Haens, G.; Pinter, T.; Lim, R.; Bodoky, G.; et al. Cetuximab and chemotherapy as initial treatment for metastatic colorectal cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 1408–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Cutsem, E.; Lenz, H.J.; Kohne, C.H.; Heinemann, V.; Tejpar, S.; Melezinek, I.; Beier, F.; Stroh, C.; Rougier, P.; van Krieken, J.H.; et al. Fluorouracil, leucovorin, and irinotecan plus cetuximab treatment and RAS mutations in colorectal cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 692–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douillard, J.Y.; Siena, S.; Cassidy, J.; Tabernero, J.; Burkes, R.; Barugel, M.; Humblet, Y.; Bodoky, G.; Cunningham, D.; Jassem, J.; et al. Randomized, phase III trial of panitumumab with infusional fluorouracil, leucovorin, and oxaliplatin (FOLFOX4) versus FOLFOX4 alone as first-line treatment in patients with previously untreated metastatic colorectal cancer: The PRIME study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 4697–4705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douillard, J.Y.; Oliner, K.S.; Siena, S.; Tabernero, J.; Burkes, R.; Barugel, M.; Humblet, Y.; Bodoky, G.; Cunningham, D.; Jassem, J.; et al. Panitumumab-FOLFOX4 treatment and RAS mutations in colorectal cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 1023–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grothey, A.; van Cutsem, E.; Sobrero, A.; Siena, S.; Falcone, A.; Ychou, M.; Humblet, Y.; Bouché, O.; Mineur, L.; Barone, C.; et al. Regorafenib monotherapy for previously treated metastatic colorectal cancer (CORRECT): An international, multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2013, 381, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, R.J.; van Cutsem, E.; Falcone, A.; Yoshino, T.; Garcia-Carbonero, R.; Mizunuma, N.; Yamazaki, K.; Shimada, Y.; Tabernero, J.; Komatsu, Y.; et al. Randomized trial of TAS-102 for refractory metastatic colorectal cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 1909–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinemann, V.; von Weikersthal, L.F.; Decker, T.; Kiani, A.; Vehling-kaiser, U.; Scholz, M.; Müller, S.; Link, H.; Niederle, N.; Rost, A.; et al. FOLFIRI plus cetuximab versus FOLFIRI plus bevacizumab as first-line treatment for patients with metastatic colorectal cancer (FIRE-3): A randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 1065–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, Y.; Takahari, D.; Matsumoto, H.; Baba, H.; Nakamura, M.; Yoshida, K.; Yoshida, M.; Iwamoto, S.; Shimada, K.; Komatsu, Y.; et al. Leucovorin, fluorouracil, and oxaliplatin plus bevacizumab versus S-1 and oxaliplatin plus bevacizumab in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer (SOFT): An open-label, non-inferiority, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, 1278–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loupakis, F.; Cremolini, C.; Masi, G.; Lonardi, S.; Zagonel, V.; Salvatore, L.; Cortesi, E.; Tomasello, G.; Ronzoni, M.; Spadi, R.; et al. Initial therapy with FOLFOXIRI and bevacizumab for metastatic colorectal cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 1609–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waring, P.; Tie, J.; Maru, D.; Karapetis, C.S. RAS mutations as predictive biomarkers in clinical management of metastatic colorectal cancer. Clin. Colorectal Cancer 2016, 15, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN). Guidelines Version 1. 2016 Colon Cancer; National Comprehensive Cancer Network: Washington, PA, USA, 2016.
- Van Cutsem, E.; Cervantes, A.; Adam, R.; Sobrero, A.; van Krieken, J.H.; Aderka, D.; Aranda Aguilar, E.; Bardelli, A.; Benson, A.; Bodoky, G.; et al. ESMO consensus guidelines for the management of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 1386–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peeters, M.; Price, T.J.; Cervantes, A.; Sobrero, A.F.; Ducreux, M.; Hotko, Y.; Andre, T.; Chan, E.; Lordick, F.; Punt, C.J.A.; et al. Randomized phase III study of panitumumab with fluorouracil, leucovorin, and irinotecan (FOLFIRI) compared with FOLFIRI alone as second-line treatment in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 4706–4713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bokemeyer, C.; Bondarenko, I.; Makhson, A.; Hartmann, J.T.; Aparicio, J.; De Braud, F.; Donea, S.; Ludwig, H.; Schuch, G.; Stroh, C.; et al. Fluorouracil, leucovorin, and oxaliplatin with and without cetuximab in the first-line treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 663–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snyder, L.C.; Astsaturov, I.; Weiner, L.M. Overview of monoclonal antibodies and small molecules targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor pathway in colorectal cancer. Clin. Colorectal Cancer 2005, 5, S71–S80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, Y.; Ishii, Y.; Ochiai, H.; Fukuda, K.; Akimoto, S.; Hayashida, T.; Okabayashi, K.; Tsuruta, M.; Hasegawa, H.; Kitagawa, Y. Cetuximab-mediated ADCC activity is correlated with the cell surface expression level of EGFR but not with the KRAS/BRAF mutational status in colorectal cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 31, 2115–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, T.J.; Peeters, M.; Kim, T.W.; Li, J.; Cascinu, S.; Ruff, P.; Suresh, A.S.; Thomas, A.; Tjulandin, S.; Zhang, K.; et al. Panitumumab versus cetuximab in patients with chemotherapy-refractory wild-type KRAS exon 2 metastatic colorectal cancer (ASPECCT): A randomised, multicentre, open-label, non-inferiority phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonacopoulou, A.G.; Tsamandas, A.C.; Petsas, T.; Liava, A.; Scopa, C.D.; Papavassiliou, A.G.; Kalofonos, H.P. EGFR, HER-2 and COX-2 levels in colorectal cancer. Histopathology 2008, 53, 698–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKay, J.A.; Murray, L.J.; Curran, S.; Ross, V.G.; Clark, C.; Murray, G.I.; Cassidy, J.; McLeod, H.L. Evaluation of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) in colorectal tumours and lymph node metastases. Eur. J. Cancer 2002, 38, 2258–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saltz, L.B.; Meropol, N.J.; Loehrer, P.J.S.; Needle, M.N.; Kopit, J.; Mayer, R.J. Phase II trial of cetuximab in patients with refractory colorectal cancer that expresses the epidermal growth factor receptor. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 22, 1201–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hecht, J.R.; Mitchell, E.; Neubauer, M.A.; Burris, H.A., 3rd; Swanson, P.; Lopez, T.; Buchanan, G.; Reiner, M.; Gansert, J.; Berlin, J. Lack of correlation between epidermal growth factor receptor status and response to Panitumumab monotherapy in metastatic colorectal cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 2205–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunningham, D.; Humblet, Y.; Siena, S.; Khayat, D.; Bleiberg, H.; Santoro, A.; Bets, D.; Mueser, M.; Harstrick, A.; Verslype, C.; et al. Cetuximab monotherapy and cetuximab plus irinotecan in irinotecan-refractory metastatic colorectal cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, D.M.; Coyle, V.M.; Kennedy, R.D.; Wilson, R.H. Molecular subtypes and personalized therapy in metastatic colorectal cancer. Curr. Colorectal Cancer Rep. 2016, 12, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amado, R.G.; Wolf, M.; Peeters, M.; Van Cutsem, E.; Siena, S.; Freeman, D.J.; Juan, T.; Sikorski, R.; Suggs, S.; Radinsky, R.; et al. Wild-type KRAS is required for panitumumab efficacy in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 1626–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peeters, M.; Kafatos, G.; Taylor, A.; Gastanaga, V.M.; Oliner, K.S.; Hechmati, G.; Terwey, J.-H.; van Krieken, J.H. Prevalence of RAS mutations and individual variation patterns among patients with metastatic colorectal cancer: A pooled analysis of randomised controlled trials. Eur. J. Cancer 2015, 51, 1704–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, C.-B.; Li, F.; Ma, J.-T.; Zou, H.-W. Concordant KRAS mutations in primary and metastatic colorectal cancer tissue specimens: A meta-analysis and systematic review. Cancer Investig. 2012, 30, 741–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loupakis, F.; Ruzzo, A.; Cremolini, C.; Vincenzi, B.; Salvatore, L.; Santini, D.; Masi, G.; Stasi, I.; Canestrari, E.; Rulli, E.; et al. KRAS codon 61, 146 and BRAF mutations predict resistance to cetuximab plus irinotecan in KRAS codon 12 and 13 wild-type metastatic colorectal cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2009, 101, 715–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorich, M.J.; Wiese, M.D.; Rowland, A.; Kichenadasse, G.; McKinnon, R.A.; Karapetis, C.S. Extended RAS mutations and anti-EGFR monoclonal antibody survival benefit in metastatic colorectal cancer: A meta-analysis of randomized, controlled trials. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Cutsem, E.; Kohne, C.H.; Lang, I.; Folprecht, G.; Nowacki, M.P.; Cascinu, S.; Shchepotin, I.; Maurel, J.; Cunningham, D.; Tejpar, S.; et al. Cetuximab plus irinotecan, fluorouracil, and leucovorin as first-line treatment for metastatic colorectal cancer: Updated analysis of overall survival according to tumor KRAS and BRAF mutation status. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 2011–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bokemeyer, C.; Bondarenko, I.; Hartmann, J.T.; de Braud, F.; Schuch, G.; Zubel, A.; Celik, I.; Schlichting, M.; Koralewski, P. Efficacy according to biomarker status of cetuximab plus FOLFOX-4 as first-line treatment for metastatic colorectal cancer: The OPUS study. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2011, 22, 1535–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bokemeyer, C.; van Cutsem, E.; Rougier, P.; Ciardiello, F.; Heeger, S.; Schlichting, M.; Celik, I.; Köhne, C.H. Addition of cetuximab to chemotherapy as first-line treatment for KRAS wild-type metastatic colorectal cancer: Pooled analysis of the CRYSTAL and OPUS randomised clinical trials. Eur. J. Cancer 2012, 48, 1466–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Roock, W.; Jonker, D.J.; di Nicolantonio, F.; Sartore-Bianchi, A.; Tu, D.; Siena, S.; Lamba, S.; Arena, S.; Frattini, M.; Piessevaux, H.; et al. Association of KRAS p.G13D mutation with outcome in patients with chemotherapy-refractory metastatic colorectal cancer treated with cetuximab. JAMA 2010, 304, 1812–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tejpar, S.; Celik, I.; Schlichting, M.; Sartorius, U.; Bokemeyer, C.; van Cutsem, E. Association of KRAS G13D tumor mutations with outcome in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer treated with first-line chemotherapy with or without cetuximab. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 3570–3577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segelov, E.; Thavaneswaran, S.; Waring, P.M.; Desai, J.; Robledo, K.P.; Gebski, V.J.; Elez, E.; Nott, L.M.; Karapetis, C.S.; Lunke, S.; et al. Response to cetuximab with or without irinotecan in patients with refractory metastatic colorectal cancer harboring the KRAS G13D mutation: Australasian gastro-intestinal trials group ICECREAM study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 2258–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenz, H.J.; Niedzwiecki, D.; Innocenti, F.; Blanke, C.; Mahony, M.R.; O’Neil, B.H.; Shaw, J.E.; Polite, B.; Hochster, H.; Atkins, J.; et al. CALGB/SWOG 80405: Phase III trial of FOLFIRI or mFOLFOX6 with bevacizumab or cetuximab for patients with expanded RAS analyses in untreated metastatic adenocarcinoma of the colon or rectum. Ann. Oncol. 2014, 32, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Schwartzberg, L.S.; Rivera, F.; Karthaus, M.; Fasola, G.; Canon, J.L.; Hecht, J.R.; Yu, H.; Oliner, K.S.; Go, W.Y. PEAK: A randomized, multicenter phase II study of panitumumab plus modified fluorouracil, leucovorin, and oxaliplatin (mFOLFOX6) or bevacizumab plus mFOLFOX6 in patients with previously untreated, unresectable, wild-type KRAS exon 2 metastatic colorectal. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 2240–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinemann, V.; Rivera, F.; O’Neil, B.H.; Stintzing, S.; Koukakis, R.; Terwey, J.H.H.; Douillard, J.Y.Y. A study-level meta-analysis of efficacy data from head-to-head first-line trials of epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors versus bevacizumab in patients with RAS wild-type metastatic colorectal cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2016, 67, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshino, T.; Uetake, H.; Tsuchihara, K.; Shitara, K.; Yamazaki, K.; Oki, E.; Sato, T.; Naitoh, T.; Komatsu, Y.; Takeshi, K.; et al. PARADIGM study: A multicenter, randomized, phase III study of 5-fluorouracil, leucovorin, and oxaliplatin (mFOLFOX6) plus panitumumab or bevacizumab as first-line treatment in patients with RAS (KRAS/NRAS) wild-type metastatic colorectal cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, TPS776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papagiorgis, P.C. Segmental distribution of some common molecular markers for colorectal cancer (CRC): Influencing factors and potential implications. Tumor Biol. 2016, 37, 5727–5734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, H. Different treatment strategies and molecular features between right-sided and left-sided colon cancers. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 6470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciombor, K.K.; Goldberg, R.M. Primary tumor sidedness as prognostic and predictive biomarker in metastatic colorectal cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamada, H.; Meno, C.; Watanabe, D.; Saijoh, Y. Establishment of vertebrate left-right asymmetry. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2002, 3, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tejpar, S.; Stintzing, S.; Ciardiello, F.; Tabernero, J.; Van Cutsem, E.; Beier, F.; Esser, R.; Lenz, H.-J.; Heinemann, V. Prognostic and predictive relevance of primary tumor location in patients with ras wild-type metastatic colorectal cancer retrospective analyses of the CRYSTAL and FIRE-3 Trials. JAMA Oncol. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrelli, F.; Tomasello, G.; Borgonovo, K.; Ghidini, M.; Turati, L.; Dallera, P.; Passalacqua, R.; Sgroi, G.; Barni, S. Prognostic survival associated with left-sided vs. right-sided colon cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.; Advani, S.; Morris, J.; Jiang, Z.; Manyam, G.; Menter, D.; Broom, B.; Eng, C.; Overman, M.; Maru, D.; et al. Association of primary (1°) site and molecular features with progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) of metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) after anti-epidermal growth factor receptor (αEGFR) therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 3506. [Google Scholar]
- Ciardiello, F.; Tortora, G.; Magrassi, S.F.; Lanzara, A. EGFR antagonists in cancer treatment. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 1160–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morelli, M.P.; Overman, M.J.; Dasari, A.; Kazmi, S.M.A.; Mazard, T.; Vilar, E.; Morris, V.K.; Lee, M.S.; Herron, D.; Eng, C.; et al. Characterizing the patterns of clonal selection in circulating tumor DNA from patients with colorectal cancer refractory to anti-EGFR treatment. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 731–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz, L.A., Jr.; Williams, R.T.; Wu, J.; Kinde, I.; Hecht, J.R.; Berlin, J.; Allen, B.; Bozic, I.; Reiter, J.G.; Nowak, M.A.; et al. The molecular evolution of acquired resistance to targeted EGFR blockade in colorectal cancers. Nature 2012, 486, 4–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taly, V.; Pekin, D.; Benhaim, L.; Kotsopoulos, S.K.; Le Corre, D.; Li, X.; Atochin, I.; Link, D.R.; Griffiths, A.D.; Pallier, K.; et al. Multiplex picodroplet digital PCR to detect KRAS mutations in circulating DNA from the plasma of colorectal cancer patients. Clin. Chem. 2013, 59, 1722–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bettegowda, C.; Sausen, M.; Leary, R.J.; Kinde, I.; Wang, Y.; Agrawal, N.; Bartlett, B.R.; Wang, H.; Luber, B.; Alani, R.M.; et al. Detection of circulating tumor DNA in early- and late-stage human malignancies. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 224ra24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montagut, C.; Dalmases, A.; Bellosillo, B.; Crespo, M.; Pairet, S.; Iglesias, M.; Salido, M.; Gallen, M.; Marsters, S.; Tsai, S.P.; et al. Identification of a mutation in the extracellular domain of the epidermal growth factor receptor conferring cetuximab resistance in colorectal cancer. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 221–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dienstmann, R.; Patnaik, A.; Garcia-Carbonero, R.; Cervantes, A.; Benavent, M.; Rosello, S.; Tops, B.B.J.; van der Post, R.S.; Argiles, G.; Skartved, N.J.; et al. Safety and activity of the first-in-class Sym004 anti-EGFR antibody mixture in patients with refractory colorectal cancer. Cancer Discov. 2015, 5, 598–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, M.W.; Jacobsen, H.J.; Koefoed, K.; Hey, A.; Pyke, C.; Haurum, J.S.; Kragh, M. Sym004: A novel synergistic anti-epidermal growth factor receptor antibody mixture with superior anticancer efficacy. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 588–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koefoed, K.; Steinaa, L.; Soderberg, J.N.; Kjaer, I.; Jacobsen, H.J.; Meijer, P.-J.; Haurum, J.S.; Jensen, A.; Kragh, M.; Andersen, P.S.; et al. Rational identification of an optimal antibody mixture for targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor. MAbs 2011, 3, 584–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iida, M.; Brand, T.M.; Starr, M.M.; Li, C.; Huppert, E.J.; Luthar, N.; Pedersen, M.W.; Horak, I.D.; Kragh, M.; Wheeler, D.L. Sym004, a novel EGFR antibody mixture, can overcome acquired resistance to cetuximab. Neoplasia 2013, 15, 1196–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanna, D.L.; Lenz, H.-J. Novel therapeutics in metastatic colorectal cancer: Molecular insights and pharmacogenomic implications. Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2016, 2433, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kearns, J.D.; Bukhalid, R.; Sevecka, M.; Tan, G.; Gerami-Moayed, N.; Werner, S.L.; Kohli, N.; Burenkova, O.; Sloss, C.M.; King, A.M.; et al. Enhanced targeting of the EGFR network with MM-151, an oligoclonal anti-EGFR antibody therapeutic. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2015, 14, 1625–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arena, S.; Siravegna, G.; Mussolin, B.; Kearns, J.D.; Wolf, B.B.; Misale, S.; Lazzari, L.; Bertotti, A.; Trusolino, L.; Adjei, A.A.; et al. MM-151 overcomes acquired resistance to cetuximab and panitumumab in colorectal cancers harboring EGFR extracellular domain mutations. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 324ra14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lieu, C.; Harb, W.; Beeram, M.; Power, P.; Kearns, J.; Nering, R.; Moyo, V.; Wolf, B.; Adjei, A. Phase 1 trial of MM-151, a novel oligoclonal anti-EGFR antibody combination in patients with refractory solid tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 2518. [Google Scholar]
- Martincorena, I.; Campbell, P.J. Somatic mutation in cancer and normal cells. Science 2015, 349, 1483–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Therkildsen, C.; Bergmann, T.K.; Henrichsen-Schnack, T.; Ladelund, S.; Nilbert, M. The predictive value of KRAS, NRAS, BRAF, PIK3CA and PTEN for anti-EGFR treatment in metastatic colorectal cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Oncol. 2014, 53, 852–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misale, S.; di Nicolantonio, F.; Sartore-Bianchi, A.; Siena, S.; Bardelli, A. Resistance to anti-EGFR therapy in colorectal cancer: From heterogeneity to convergent evolution. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 1269–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, N.; Yamada, Y.; Furuta, K.; Honma, Y.; Iwasa, S.; Takashima, A.; Kato, K.; Hamaguchi, T.; Shimada, Y. Serum levels of hepatocyte growth factor and epiregulin are associated with the prognosis on anti-EGFR antibody treatment in KRAS wild-type metastatic colorectal cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 110, 2716–2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inno, A.; di Salvatore, M.; Cenci, T.; Martini, M.; Orlandi, A.; Strippoli, A.; Ferrara, A.M.; Bagal, C.; Cassano, A.; Larocca, L.M.; et al. Is there a role for IGF1R and c-MET pathways in resistance to cetuximab in metastatic colorectal cancer? Clin. Colorectal Cancer 2011, 10, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardelli, A.; Corso, S.; Bertotti, A.; Hobor, S.; Valtorta, E.; Siravegna, G.; Sartore-Bianchi, A.; Scala, E.; Cassingena, A.; Zecchin, D.; et al. Amplification of the MET receptor drives resistance to anti-EGFR therapies in colorectal cancer. Cancer Discov. 2013, 3, 658–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yonesaka, K.; Zejnullahu, K.; Okamoto, I.; Satoh, T.; Cappuzzo, F.; Souglakos, J.; Ercan, D.; Rogers, A.; Roncalli, M.; Takeda, M.; et al. Activation of ERBB2 signaling causes resistance to the EGFR-directed therapeutic antibody cetuximab. Sci. Transl. Med. 2011, 3, 99ra86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertotti, A.; Migliardi, G.; Galimi, F.; Sassi, F.; Torti, D.; Isella, C.; Corà, D.; di Nicolantonio, F.; Buscarino, M.; Petti, C.; et al. A molecularly annotated platform of patient- derived xenografts (“xenopatients”) identifies HER2 as an effective therapeutic target in cetuximab-resistant colorectal cancer. Cancer Discov. 2011, 1, 508–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takegawa, N.; Yonesaka, K.; Sakai, K.; Ueda, H.; Watanabe, S.; Nonagase, Y.; Okuno, T.; Takeda, M.; Maenishi, O.; Tsurutani, J.; et al. HER2 genomic amplification in circulating tumor DNA from patients with cetuximab-resistant colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 3453–3460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siravegna, G.; Mussolin, B.; Buscarino, M.; Corti, G.; Cassingena, A.; Crisafulli, G.; Ponzetti, A.; Cremolini, C.; Amatu, A.; Lauricella, C.; et al. Clonal evolution and resistance to EGFR blockade in the blood of colorectal cancer patients. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 795–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, H.; Bignell, G.R.; Cox, C.; Stephens, P.; Edkins, S.; Clegg, S.; Teague, J.; Woffendin, H.; Garnett, M.J.; Bottomley, W.; et al. Mutations of the BRAF gene in human cancer. Nature 2002, 417, 949–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokota, T.; Ura, T.; Shibata, N.; Takahari, D.; Shitara, K.; Nomura, M.; Kondo, C.; Mizota, A.; Utsunomiya, S.; Muro, K.; et al. BRAF mutation is a powerful prognostic factor in advanced and recurrent colorectal cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 104, 856–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Nicolantonio, F.; Martini, M.; Molinari, F.; Sartore-Bianchi, A.; Arena, S.; Saletti, P.; de Dosso, S.; Mazzucchelli, L.; Frattini, M.; Siena, S.; et al. Wild-type BRAF is required for response to panitumumab or cetuximab in metastatic colorectal cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 5705–5712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samatar, A.A.; Poulikakos, P.I. Targeting RAS–ERK signalling in cancer: Promises and challenges. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2014, 13, 928–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajagopalan, H.; Bardelli, A.; Lengauer, C.; Kinzler, K.W.; Vogelstein, B.; Velculescu, V.E. Tumorigenesis: RAF/RAS oncogenes and mismatch-repair status. Nature 2002, 418, 934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, P.B.; Hauschild, A.; Robert, C.; Haanen, J.B.; Ascierto, P.; Larkin, J.; Dummer, R.; Garbe, C.; Testori, A.; Maio, M.; et al. Improved survival with vemurafenib in melanoma with BRAFV600E mutation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 2507–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauschild, A.; Grob, J.-J.; Demidov, L.V.; Jouary, T.; Gutzmer, R.; Millward, M.; Rutkowski, P.; Blank, C.U.; Miller, W.H.J.; Kaempgen, E.; et al. Dabrafenib in BRAF-mutated metastatic melanoma: A multicentre, open-label, phase 3 randomised controlled trial. Lancet (London, England) 2012, 380, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lito, P.; Pratilas, C.A.; Joseph, E.W.; Tadi, M.; Halilovic, E.; Zubrowski, M.; Huang, A.; Wong, W.L.; Callahan, M.K.; Merghoub, T.; et al. Relief of profound feedback inhibition of mitogenic signaling by RAF inhibitors attenuates their activity in BRAFV600E melanomas. Cancer Cell 2012, 22, 668–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corcoran, R.; André, T.; Yoshino, T.; Bendell, J.; Atreya, C.; Schellens, J.; Ducreux, M.; McRee, A.; Siena, S.; Middleton, G.; et al. Efficacy and circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) analysis of the BRAF inhibitor dabrafenib (D), MEK inhibitor trametinib (T), and anti-EGFR antibody panitumumab (P) in patients (pts) with BRAF V600E–mutated (BRAFm) metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC). Ann Oncol. 2016, 27, 4550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcoran, R.B.; Ebi, H.; Turke, A.B.; Coffee, E.M.; Nishino, M.; Cogdill, A.P.; Brown, R.D.; Della Pelle, P.; Dias-Santagata, D.; Hung, K.E.; et al. EGFR-mediated re-activation of MAPK signaling contributes to insensitivity of BRAF mutant colorectal cancers to RAF inhibition with vemurafenib. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Higgins, B.; Kolinsky, K.; Packman, K.; Bradley, W.D.; Lee, R.J.; Schostack, K.; Simcox, M.E.; Kopetz, S.; Heimbrook, D.; et al. Antitumor activity of BRAF inhibitor vemurafenib in preclinical models of BRAF-mutant colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 779–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corcoran, R.B.; Atreya, C.E.; Falchook, G.S.; Kwak, E.L.; Ryan, D.P.; Bendell, J.C.; Hamid, O.; Messersmith, W.A.; Daud, A.; Kurzrock, R.; et al. Combined BRAF and MEK inhibition with dabrafenib and trametinib in BRAF V600-mutant colorectal cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 4023–4031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaeger, R.; Cercek, A.; O’Reilly, E.; Reidy, D.; Kemeny, N.; Wolinsky, T.; Gollub, M.; Lacouture, M.; Rosen, N.; Vakiani, E.; et al. Pilot study of vemurafenib and panitumumab combination therapy in patients with BRAFV600E mutated metastatic colorectal cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabernero, J.; Geel, R.; Guren, T.; Yaeger, R.; Spreafico, A.; Faris, J.; Yoshino, T.; Yamada, Y.; Kim, T.; Bendell, J.; et al. Phase 2 results: Encorafenib (ENCO) and cetuximab (CETUX) with or without alpelisib (ALP) in patients with advanced BRAF-mutant colorectal cancer (BRAFm CRC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 3544. [Google Scholar]
- Kopetz, S.; McDonough, S.; Morris, V.; Lenz, H.; Magliocco, A.; Atreya, C.; Diaz, L.; Allegra, C.; Wang, S.; Lieu, C.; et al. Randomized trial of irinotecan and cetuximab with or without vemurafenib in BRAF-mutant metastatic colorectal cancer (SWOG 1406). J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35 (Suppl. S4), 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahronian, L.G.; Sennott, E.M.; van Allen, E.M.; Wagle, N.; Kwak, E.L.; Faris, J.E.; Godfrey, J.T.; Nishimura, K.; Lynch, K.D.; Mermel, C.H.; et al. Clinical acquired resistance to RAF inhibitor combinations in BRAF-mutant colorectal cancer through MAPK pathway alterations. Cancer Discov. 2015, 5, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopetz, S.; Desai, J.; Chan, E.; Hecht, J.R.; O’Dwyer, P.J.; Maru, D.; Morris, V.; Janku, F.; Dasari, A.; Chung, W.; et al. Phase II pilot study of vemurafenib in patients with metastatic braf-mutated colorectal cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 4032–4038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyman, D.M.; Puzanov, I.; Subbiah, V.; Faris, J.E.; Chau, I.; Blay, J.-Y.; Wolf, J.; Raje, N.S.; Diamond, E.L.; Hollebecque, A.; et al. Vemurafenib in multiple nonmelanoma cancers with BRAFV600 mutations. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 726–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hochster, H.; Messersmith, W.; O’Neil, B.; Groshen, S.; Cohen, D.; Denlinger, C.; Gold, P.; Eckhardt, S.; Locker, G.; Ames, P.; et al. Second-line therapy of KRAS-mutated (KRASm) metastatic colorectal cancer (CRC) with the MEK inihibitor selumetinib ([SEL], AZ6244, ARRY-142886) in combination with irinotecan (IRI): An AGICC study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eng, C.; Hart, L.; Severtsev, A.; Gladkov, O.; Mueller, L.; Kopp, M.; Vladimirov, V.; Langdon, R.; Kotiv, B.; Barni, S.; et al. A randomized, placebo-controlled, phase I/II study of tivantinib (ARQ 197) in combination with cetuximab and irinotecan in patients (pts) with KRAS wild-type (WT) metastatic colorectal cancer (CRC) who had received previous front-line systemic therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 3508. [Google Scholar]
| Strategy | Treatment | Genomic Profile | Phase | N | ORR (%) | PFS (M) | OS (M) | Clinical Development | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BRAF monotherapy | Vemurafenib | BRAFmut | I/II | 21 | 5 | 2.1 | 7.7 | Complete | NCT00405587 [93] |
| BRAF monotherapy | Vemurafenib | BRAFmut | II | 10 | 0 | 4.5 | 9.3 | Complete | NCT01524978 [94] |
| BRAF + MEK | Dabrafenib + Trametinib | BRAFmut | I/II | 43 | 12 | 3.5 | (−) | Complete | NCT01726738 [88] |
| BRAF + EGFR | Vemurafenib + Cetuximab | BRAFmut | II | 27 | 4 | 3.7 | 7.1 | Complete | NCT01524978 [94] |
| BRAF + EGFR | Vemurafenib + Panitumumab | BRAFmut | Pilot | 15 | 13 | 3.2 | 7.6 | Complete | NCT01791309 [89] |
| BRAF + EGFR | Encorafenib + Cetuximab | BRAFmut | II | 50 | 22 | 4.2 | 12.4 | Ongoing | NCT01719380 [90] |
| BRAF + EGFR | Dabrafenib + Panitumumab | BRAFmut | I/II | 20 | 10 | 3.4 | (−) | Ongoing | NCT01750918 [85] |
| BRAF + EGFR | BMS-908662 + Cetuximab | Kras mut or BRAF mut | I/II | 17 * | (−) | (−) | (−) | Ongoing | NCT01086267 |
| BRAF + EGFR + CT | Vemurafenib + Cetuximab + irinotecan | BRAFmut | I | 12 | 50 | (−) | (−) | Ongoing | NCT01787500 |
| BRAF + EGFR + CT | Cetuximab + irinotecan ± Vemurafenib | BRAFmut | II (RCT) | 78 * | (−) | (−) | (−) | Ongoing | NCT02164916 |
| BRAF + EGFR + MEK | Dabrafenib + Panitumumab + Trametinib | BRAFmut | I/II | 83 | 18 | (−) | (−) | Ongoing | NCT01750918 [85] |
| BRAF + EGFR ± MEK | Encorafenib + Cetuximab ± Binimetinib | None | III | 645 * | (−) | (−) | (−) | Ongoing | NCT02928224 |
| BRAF + EGFR + PI3K | Encorafenib + Cetuximab + Alpelisib | BRAFmut | II | 52 | 27 | 5.4 | 13.1 | Ongoing | NCT01719380 [90] |
| MEK + CT | Selumetinib + irinotecan | Kras mut or BRAF mut | II | 32 | 9 | (−) | (−) | Complete | NCT01116271 [95] |
| MEK + EGFR | Binimetinib + Panitumumab | RAS wt or RAS mut | I/II | 90 * | (−) | (−) | (−) | Ongoing | NCT01927341 |
| MEK + EGFR | Panitumumab + Trametinib | BRAFmut | I/II | 31 | 0 | 2.8 | Ongoing | NCT01750918 [85] | |
| MEK + EGFR | Trametinib + Panitumumab | KRAS BRAF wt | II | 26 * | (−) | (−) | (−) | Ongoing | NCT02399943 |
| MET + EGFR + CT | Cetuximab + irinotecan ± Tivantinib | KRAS wt | I/II (RCT) | 60 | 45 | 8.3 | 19.8 | Complete | NCT01075048 [96] |
| MEK + AKT | Selumetinib + MK-2206 | KRAS wt or KRAS mut | II | 21 * | (−) | (−) | (−) | Ongoing | NCT01333475 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miyamoto, Y.; Suyama, K.; Baba, H. Recent Advances in Targeting the EGFR Signaling Pathway for the Treatment of Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 752. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18040752
Miyamoto Y, Suyama K, Baba H. Recent Advances in Targeting the EGFR Signaling Pathway for the Treatment of Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(4):752. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18040752
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiyamoto, Yuji, Koichi Suyama, and Hideo Baba. 2017. "Recent Advances in Targeting the EGFR Signaling Pathway for the Treatment of Metastatic Colorectal Cancer" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 4: 752. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18040752
APA StyleMiyamoto, Y., Suyama, K., & Baba, H. (2017). Recent Advances in Targeting the EGFR Signaling Pathway for the Treatment of Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(4), 752. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18040752





