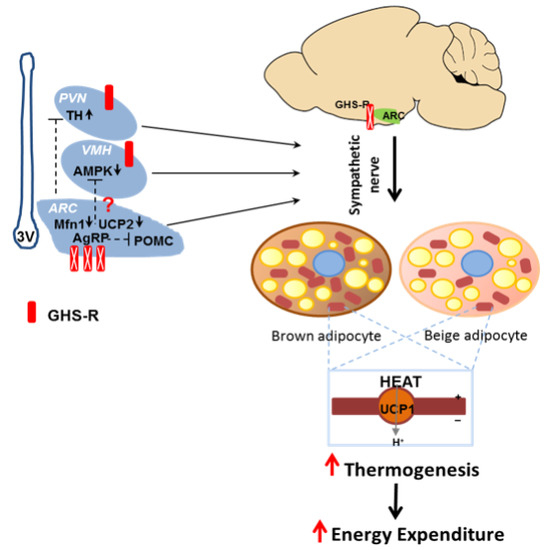
Suppression of GHS-R in AgRP Neurons Mitigates Diet-Induced Obesity by Activating Thermogenesis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Generation of AgRP-Cre;Ghsrf/f Mice
2.2. GHS-R Deletion in AgRP Neurons Abolishes Ghrelin-Induced GH Secretion and Food Intake
2.3. GHS-R Deletion in AgRP Neurons Attenuates Ghrelin-Induced Obesity
2.4. GHS-R Deletion in AgRP Neurons Does Not Affect Energy Homeostasis under Regular Diet Feeding
2.5. AgRP Neuron-Specific GHS-R Deletion Attenuates Diet-Induced Obesity
2.6. AgRP Neuron-Specific GHS-R Deletion Enhances Thermogenesis
2.7. Putative Regulators Invloved in GHS-R Associated Thermogenic Regulation
2.8. Putative Downstream Regulators That May Mediate GHS-R Suppression-Induced Thermogenesis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Body Composition and Indirect Calorimetry Studies
4.3. Glucose Tolerance Tests (GTT) and Insulin Tolerance Tests (ITT)
4.4. Brain Processing for Immunofluorescence Imaging
4.5. Brain Regions for Expression Analysis
4.6. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
4.7. Growth Hormone Assay
4.8. Ghrelin-Induced Spontaneous and Chronic Food Intake
4.9. Cold Challenge Study
4.10. Western Blot Analyses
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AgRP | Agouti-related peptide |
| ARC | Arcuate nucleus |
| BAT | Brown adipose tissue |
| DIO | Diet-induced obesity |
| GH | Growth hormone |
| GHS-R | Growth Hormone Secretagogue Receptor |
| HFD | High fat diet |
| NPY | Neuropeptide Y |
| PVN | Paraventricular nucleus of hypothalamus |
| SNS | Sympathetic nervous system |
| TH | Tyrosine hydroxylase |
| UCP1 | Uncoupling protein-1 |
| VMH | Ventromedial hypothalamus |
| WAT | White adipose tissue |
References
- Muller, T.D.; Nogueiras, R.; Andermann, M.L.; Andrews, Z.B.; Anker, S.D.; Argente, J.; Batterham, R.L.; Benoit, S.C.; Bowers, C.Y.; Broglio, F.; et al. Ghrelin. Mol. Metab. 2015, 4, 437–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kojima, M.; Hosoda, H.; Date, Y.; Nakazato, M.; Matsuo, H.; Kangawa, K. Ghrelin is a growth-hormone-releasing acylated peptide from stomach. Nature 1999, 402, 656–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, P.; Zheng, H.; Smith, R.G. Ghrelin stimulation of growth hormone release and appetite is mediated through the growth hormone secretagogue receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 4679–4684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kojima, M.; Kangawa, K. Ghrelin: Structure and function. Physiol. Rev. 2005, 85, 495–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowley, M.A.; Smith, R.G.; Diano, S.; Tschop, M.; Pronchuk, N.; Grove, K.L.; Strasburger, C.J.; Bidlingmaier, M.; Esterman, M.; Heiman, M.L.; et al. The distribution and mechanism of action of ghrelin in the cns demonstrates a novel hypothalamic circuit regulating energy homeostasis. Neuron 2003, 37, 649–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.G.; Jiang, H.; Sun, Y. Developments in ghrelin biology and potential clinical relevance. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 16, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tschop, M.; Smiley, D.L.; Heiman, M.L. Ghrelin induces adiposity in rodents. Nature 2000, 407, 908–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zigman, J.M.; Nakano, Y.; Coppari, R.; Balthasar, N.; Marcus, J.N.; Lee, C.E.; Jones, J.E.; Deysher, A.E.; Waxman, A.R.; White, R.D.; et al. Mice lacking ghrelin receptors resist the development of diet-induced obesity. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 3564–3572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Lee, J.H.; Bongmba, O.Y.; Ma, X.; Zhu, X.; Sheikh-Hamad, D.; Sun, Y. The suppression of ghrelin signaling mitigates age-associated thermogenic impairment. Aging 2014, 6, 1019–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Lee, J.H.; Buras, E.D.; Yu, K.; Wang, R.; Smith, C.W.; Wu, H.; Sheikh-Hamad, D.; Sun, Y. Ghrelin receptor regulates adipose tissue inflammation in aging. Aging 2016, 8, 178–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Saha, P.K.; Ma, X.; Henshaw, I.O.; Shao, L.; Chang, B.H.; Buras, E.D.; Tong, Q.; Chan, L.; McGuinness, O.P.; et al. Ablation of ghrelin receptor reduces adiposity and improves insulin sensitivity during aging by regulating fat metabolism in white and brown adipose tissues. Aging Cell 2011, 10, 996–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Lin, L.; Xu, P.; Saito, K.; Wei, Q.; Meadows, A.G.; Bongmba, O.Y.N.; Pradhan, G.; Zheng, H.; Xu, Y.; et al. Neuronal deletion of ghrelin receptor almost completely prevents diet-induced obesity. Diabetes 2016, 65, 2169–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Garcia, J.M.; Smith, R.G. Ghrelin and growth hormone secretagogue receptor expression in mice during aging. Endocrinology 2007, 148, 1323–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKee, K.K.; Palyha, O.C.; Feighner, S.D.; Hreniuk, D.L.; Tan, C.P.; Phillips, M.S.; Smith, R.G.; van der Ploeg, L.H.; Howard, A.D. Molecular analysis of rat pituitary and hypothalamic growth hormone secretagogue receptors. Mol. Endocrinol. 1997, 11, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gnanapavan, S.; Kola, B.; Bustin, S.A.; Morris, D.G.; McGee, P.; Fairclough, P.; Bhattacharya, S.; Carpenter, R.; Grossman, A.B.; Korbonits, M. The tissue distribution of the mrna of ghrelin and subtypes of its receptor, ghs-r, in humans. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 87, 2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zigman, J.M.; Jones, J.E.; Lee, C.E.; Saper, C.B.; Elmquist, J.K. Expression of ghrelin receptor mrna in the rat and the mouse brain. J. Comp. Neurol. 2006, 494, 528–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mani, B.K.; Walker, A.K.; Lopez Soto, E.J.; Raingo, J.; Lee, C.E.; Perello, M.; Andrews, Z.B.; Zigman, J.M. Neuroanatomical characterization of a growth hormone secretagogue receptor-green fluorescent protein reporter mouse. J. Comp. Neurol. 2014, 522, 3644–3666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, H.B.; Dietrich, M.O.; Liu, Z.W.; Zimmer, M.R.; Li, M.D.; Singh, J.P.; Zhang, K.; Yin, R.; Wu, J.; Horvath, T.L.; et al. O-glcnac transferase enables AgRP neurons to suppress browning of white fat. Cell 2014, 159, 306–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varela, L.; Horvath, T.L. Leptin and insulin pathways in POMC and AgRP neurons that modulate energy balance and glucose homeostasis. EMBO Rep. 2012, 13, 1079–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coll, A.P.; Farooqi, I.S.; O’Rahilly, S. The hormonal control of food intake. Cell 2007, 129, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, T.M.; Breininger, J.F.; Baskin, D.G.; Schwartz, M.W. Coexpression of AgRP and NPY in fasting-activated hypothalamic neurons. Nat. Neurosci. 1998, 1, 271–272. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Kong, D.; Shah, B.P.; Ye, C.; Koda, S.; Saunders, A.; Ding, J.B.; Yang, Z.; Sabatini, B.L.; Lowell, B.B. Fasting activation of AgRP neurons requires NMDA receptors and involves spinogenesis and increased excitatory tone. Neuron 2012, 73, 511–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, K.A.; Cone, R.D. Fasting induces a large, leptin-dependent increase in the intrinsic action potential frequency of orexigenic arcuate nucleus neuropeptide Y/Agouti-related protein neurons. Endocrinology 2005, 146, 1043–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, B.L.; Wang, Q.; Zigman, J.M. The central nervous system sites mediating the orexigenic actions of ghrelin. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2014, 76, 519–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, Z.B.; Liu, Z.W.; Walllingford, N.; Erion, D.M.; Borok, E.; Friedman, J.M.; Tschop, M.H.; Shanabrough, M.; Cline, G.; Shulman, G.I.; et al. UCP2 mediates ghrelin’s action on NPY/AgRP neurons by lowering free radicals. Nature 2008, 454, 846–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horvath, T.L.; Andrews, Z.B.; Diano, S. Fuel utilization by hypothalamic neurons: Roles for ROS. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 20, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, C.; Uchida, A.; Chuang, J.C.; Walker, A.; Liu, T.; Osborne-Lawrence, S.; Mason, B.L.; Mosher, C.; Berglund, E.D.; et al. Arcuate AgRP neurons mediate orexigenic and glucoregulatory actions of ghrelin. Mol. Metab. 2014, 3, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.Y.; Trumbauer, M.E.; Chen, A.S.; Weingarth, D.T.; Adams, J.R.; Frazier, E.G.; Shen, Z.; Marsh, D.J.; Feighner, S.D.; Guan, X.M.; et al. Orexigenic action of peripheral ghrelin is mediated by neuropeptide Y and agouti-related protein. Endocrinology 2004, 145, 2607–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Atasoy, D.; Su, H.H.; Sternson, S.M. Hunger states switch a flip-flop memory circuit via a synaptic AMPK-dependent positive feedback loop. Cell 2011, 146, 992–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitamura, T.; Feng, Y.; Kitamura, Y.I.; Chua, S.C., Jr.; Xu, A.W.; Barsh, G.S.; Rossetti, L.; Accili, D. Forkhead protein FoxO1 mediates AgRP-dependent effects of leptin on food intake. Nat. Med. 2006, 12, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, A.W.; Kaelin, C.B.; Takeda, K.; Akira, S.; Schwartz, M.W.; Barsh, G.S. PI3K integrates the action of insulin and leptin on hypothalamic neurons. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 951–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooke, A.M.; Drake, W.M. Serum IGF-I levels in the diagnosis and monitoring of acromegaly. Pituitary 2007, 10, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckway, C.K.; Guevara-Aguirre, J.; Pratt, K.L.; Burren, C.P.; Rosenfeld, R.G. The IGF-I generation test revisited: A marker of GH sensitivity. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 5176–5183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Tilve, D.; Heppner, K.; Kirchner, H.; Lockie, S.H.; Woods, S.C.; Smiley, D.L.; Tschop, M.; Pfluger, P. Ghrelin-induced adiposity is independent of orexigenic effects. FASEB J. 2011, 25, 2814–2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wren, A.M.; Small, C.J.; Abbott, C.R.; Dhillo, W.S.; Seal, L.J.; Cohen, M.A.; Batterham, R.L.; Taheri, S.; Stanley, S.A.; Ghatei, M.A.; et al. Ghrelin causes hyperphagia and obesity in rats. Diabetes 2001, 50, 2540–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Asnicar, M.; Saha, P.K.; Chan, L.; Smith, R.G. Ablation of ghrelin improves the diabetic but not obese phenotype of ob/ob mice. Cell. Metab. 2006, 3, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannon, B.; Nedergaard, J. Brown adipose tissue: Function and physiological significance. Physiol. Rev. 2004, 84, 277–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harms, M.; Seale, P. Brown and beige fat: Development, function and therapeutic potential. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1252–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velasquez, D.A.; Martinez, G.; Romero, A.; Vazquez, M.J.; Boit, K.D.; Dopeso-Reyes, I.G.; Lopez, M.; Vidal, A.; Nogueiras, R.; Dieguez, C. The central sirtuin 1/p53 pathway is essential for the orexigenic action of ghrelin. Diabetes 2011, 60, 1177–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietrich, M.O.; Antunes, C.; Geliang, G.; Liu, Z.W.; Borok, E.; Nie, Y.; Xu, A.W.; Souza, D.O.; Gao, Q.; Diano, S.; et al. AgRP neurons mediate sirt1’s action on the melanocortin system and energy balance: Roles for Sirt1 in neuronal firing and synaptic plasticity. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 11815–11825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, M.; Lage, R.; Saha, A.K.; Perez-Tilve, D.; Vazquez, M.J.; Varela, L.; Sangiao-Alvarellos, S.; Tovar, S.; Raghay, K.; Rodriguez-Cuenca, S.; et al. Hypothalamic fatty acid metabolism mediates the orexigenic action of ghrelin. Cell Metab. 2008, 7, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liesa, M.; Shirihai, O.S. Mitochondrial dynamics in the regulation of nutrient utilization and energy expenditure. Cell Metab. 2013, 17, 491–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietrich, M.O.; Liu, Z.W.; Horvath, T.L. Mitochondrial dynamics controlled by mitofusins regulate AgRP neuronal activity and diet-induced obesity. Cell 2013, 155, 188–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, Q.; Ye, C.P.; Jones, J.E.; Elmquist, J.K.; Lowell, B.B. Synaptic release of GABA by AgRP neurons is required for normal regulation of energy balance. Nat. Neurosci. 2008, 11, 998–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monge-Roffarello, B.; Labbe, S.M.; Roy, M.C.; Lemay, M.L.; Coneggo, E.; Samson, P.; Lanfray, D.; Richard, D. The PVH as a site of CB1-mediated stimulation of thermogenesis by MC4R agonism in male rats. Endocrinology 2014, 155, 3448–3458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Bi, S. Hypothalamic regulation of brown adipose tissue thermogenesis and energy homeostasis. Front. Endocrinol. 2015, 6, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.C.; Lau, J.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhai, L.; Sperk, G.; Heilbronn, R.; Mietzsch, M.; Weger, S.; Huang, X.F.; et al. Arcuate NPY controls sympathetic output and bat function via a relay of tyrosine hydroxylase neurons in the PVN. Cell Metab. 2013, 17, 236–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beiroa, D.; Imbernon, M.; Gallego, R.; Senra, A.; Herranz, D.; Villarroya, F.; Serrano, M.; Ferno, J.; Salvador, J.; Escalada, J.; et al. GLP-1 agonism stimulates brown adipose tissue thermogenesis and browning through hypothalamic AMPK. Diabetes 2014, 63, 3346–3358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardinal, P.; Andre, C.; Quarta, C.; Bellocchio, L.; Clark, S.; Elie, M.; Leste-Lasserre, T.; Maitre, M.; Gonzales, D.; Cannich, A.; et al. CB1 cannabinoid receptor in SF1-expressing neurons of the ventromedial hypothalamus determines metabolic responses to diet and leptin. Mol. Metab. 2014, 3, 705–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez de Morentin, P.B.; Gonzalez-Garcia, I.; Martins, L.; Lage, R.; Fernandez-Mallo, D.; Martinez-Sanchez, N.; Ruiz-Pino, F.; Liu, J.; Morgan, D.A.; Pinilla, L.; et al. Estradiol regulates brown adipose tissue thermogenesis via hypothalamic AMPK. Cell Metab. 2014, 20, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; He, X.; Zhao, Z.; Feng, Q.; Lin, R.; Sun, Y.; Ding, T.; Xu, F.; Luo, M.; Zhan, C. Whole-brain mapping of the direct inputs and axonal projections of pomc and AgRP neurons. Front. Neuroanat. 2015, 9, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhillon, H.; Zigman, J.M.; Ye, C.; Lee, C.E.; McGovern, R.A.; Tang, V.; Kenny, C.D.; Christiansen, L.M.; White, R.D.; Edelstein, E.A.; et al. Leptin directly activates SF1 neurons in the VMH, and this action by leptin is required for normal body-weight homeostasis. Neuron 2006, 49, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luquet, S.; Perez, F.A.; Hnasko, T.S.; Palmiter, R.D. NPY/AgRP neurons are essential for feeding in adult mice but can be ablated in neonates. Science 2005, 310, 683–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aponte, Y.; Atasoy, D.; Sternson, S.M. AgRP neurons are sufficient to orchestrate feeding behavior rapidly and without training. Nat. Neurosci. 2011, 14, 351–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakazato, M.; Murakami, N.; Date, Y.; Kojima, M.; Matsuo, H.; Kangawa, K.; Matsukura, S. A role for ghrelin in the central regulation of feeding. Nature 2001, 409, 194–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wren, A.M.; Seal, L.J.; Cohen, M.A.; Brynes, A.E.; Frost, G.S.; Murphy, K.G.; Dhillo, W.S.; Ghatei, M.A.; Bloom, S.R. Ghrelin enhances appetite and increases food intake in humans. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 5992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McFarlane, M.R.; Brown, M.S.; Goldstein, J.L.; Zhao, T.J. Induced ablation of ghrelin cells in adult mice does not decrease food intake, body weight, or response to high-fat diet. Cell Metab. 2014, 20, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howard, A.D.; Feighner, S.D.; Cully, D.F.; Arena, J.P.; Liberator, P.A.; Rosenblum, C.I.; Hamelin, M.; Hreniuk, D.L.; Palyha, O.C.; Anderson, J.; et al. A receptor in pituitary and hypothalamus that functions in growth hormone release. Science 1996, 273, 974–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pong, S.S.; Chaung, L.Y.; Dean, D.C.; Nargund, R.P.; Patchett, A.A.; Smith, R.G. Identification of a new G-protein-linked receptor for growth hormone secretagogues. Mol. Endocrinol. 1996, 10, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Patchett, A.A.; Nargund, R.P.; Tata, J.R.; Chen, M.H.; Barakat, K.J.; Johnston, D.B.; Cheng, K.; Chan, W.W.; Butler, B.; Hickey, G.; et al. Design and biological activities of L-163,191 (MK-0677): A potent, orally active growth hormone secretagogue. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 7001–7005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popovic, V.; Miljic, D.; Micic, D.; Damjanovic, S.; Arvat, E.; Ghigo, E.; Dieguez, C.; Casanueva, F.F. Ghrelin main action on the regulation of growth hormone release is exerted at hypothalamic level. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 88, 3450–3453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osterstock, G.; Escobar, P.; Mitutsova, V.; Gouty-Colomer, L.A.; Fontanaud, P.; Molino, F.; Fehrentz, J.A.; Carmignac, D.; Martinez, J.; Guerineau, N.C.; et al. Ghrelin stimulation of growth hormone-releasing hormone neurons is direct in the arcuate nucleus. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Forlano, P.M.; Cone, R.D. AgRP and pomc neurons are hypophysiotropic and coordinately regulate multiple endocrine axes in a larval teleost. Cell Metab. 2012, 15, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steyn, F.J.; Huang, L.; Ngo, S.T.; Leong, J.W.; Tan, H.Y.; Xie, T.Y.; Parlow, A.F.; Veldhuis, J.D.; Waters, M.J.; Chen, C. Development of a method for the determination of pulsatile growth hormone secretion in mice. Endocrinology 2011, 152, 3165–3171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Butte, N.F.; Garcia, J.M.; Smith, R.G. Characterization of adult ghrelin and ghrelin receptor knockout mice under positive and negative energy balance. Endocrinology 2008, 149, 843–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Cohen, P.; Spiegelman, B.M. Adaptive thermogenesis in adipocytes: Is beige the new brown? Genes Dev. 2013, 27, 234–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Major, G.C.; Doucet, E.; Trayhurn, P.; Astrup, A.; Tremblay, A. Clinical significance of adaptive thermogenesis. Int. J. Obes. 2007, 31, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briggs, D.I.; Enriori, P.J.; Lemus, M.B.; Cowley, M.A.; Andrews, Z.B. Diet-induced obesity causes ghrelin resistance in arcuate NPY/AgRP neurons. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 4745–4755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lockie, S.H.; Dinan, T.; Lawrence, A.J.; Spencer, S.J.; Andrews, Z.B. Diet-induced obesity causes ghrelin resistance in reward processing tasks. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2015, 62, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zigman, J.M.; Bouret, S.G.; Andrews, Z.B. Obesity impairs the action of the neuroendocrine ghrelin system. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 27, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Lin, L.; Qin, G.; Lu, X.; Fiorotto, M.; Dixit, V.D.; Sun, Y. Ablations of ghrelin and ghrelin receptor exhibit differential metabolic phenotypes and thermogenic capacity during aging. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, C.-S.; Bongmba, O.Y.N.; Yue, J.; Lee, J.H.; Lin, L.; Saito, K.; Pradhan, G.; Li, D.-P.; Pan, H.-L.; Xu, A.; et al. Suppression of GHS-R in AgRP Neurons Mitigates Diet-Induced Obesity by Activating Thermogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 832. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18040832
Wu C-S, Bongmba OYN, Yue J, Lee JH, Lin L, Saito K, Pradhan G, Li D-P, Pan H-L, Xu A, et al. Suppression of GHS-R in AgRP Neurons Mitigates Diet-Induced Obesity by Activating Thermogenesis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(4):832. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18040832
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Chia-Shan, Odelia Y. N. Bongmba, Jing Yue, Jong Han Lee, Ligen Lin, Kenji Saito, Geetali Pradhan, De-Pei Li, Hui-Lin Pan, Allison Xu, and et al. 2017. "Suppression of GHS-R in AgRP Neurons Mitigates Diet-Induced Obesity by Activating Thermogenesis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 4: 832. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18040832
APA StyleWu, C.-S., Bongmba, O. Y. N., Yue, J., Lee, J. H., Lin, L., Saito, K., Pradhan, G., Li, D.-P., Pan, H.-L., Xu, A., Guo, S., Xu, Y., & Sun, Y. (2017). Suppression of GHS-R in AgRP Neurons Mitigates Diet-Induced Obesity by Activating Thermogenesis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(4), 832. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18040832