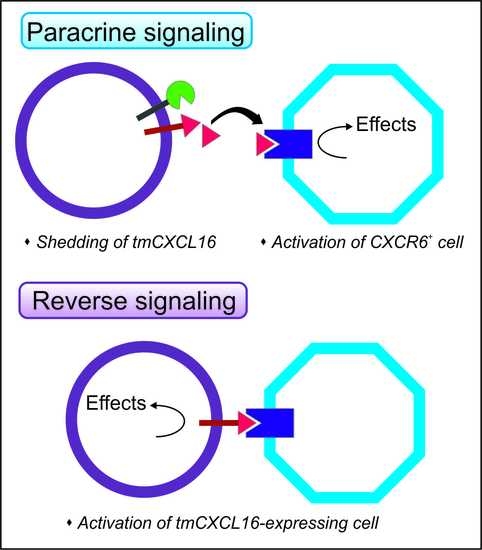
The Chemokine Receptor CXCR6 Evokes Reverse Signaling via the Transmembrane Chemokine CXCL16
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Expression of CXCL16 and CXCR6 in Native and Stably-Transfected Human Tumor Cell Lines
2.2. Recombinant CXCR6 Induces ERK1/2 Phosphorylation via CXCL16 in Glioblastoma Cells
2.3. Signaling of Recombinant and Membrane-Expressed CXCR6 Depends on the Expression of Intact Transmembrane CXCL16
2.4. Biological Effects of Reverse Signaling via CXCL16
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Cultures and Freshly-Isolated Glioma Cells
4.2. Stable Transfected Cell Lines
4.3. Immunocytochemistry
4.4. Reverse Transcription and Quantitative Real-Time PCR
4.5. RNAi Silencing
4.6. Membrane Isolation
4.7. Western Blot
4.8. Proliferation Assay
4.9. Anti-Apoptosis Assay
4.10. Migration Assay
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADAM | A disintegrin and metalloproteinase |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium |
| DMSO | Dimethylsulfoxide |
| ERK | Extracellular signal-regulated kinase (p42/p44) |
| FBS | Fetal bovine serum |
| GAPDH | Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase |
| GBM | Glioblastoma multiforme |
| ICC | Immunocytochemistry |
| qRT-PCR | Quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction |
References
- Eissner, G.; Kolch, W.; Scheurich, P. Ligands working as receptors: Reverse signaling by members of the TNF superfamily enhance the plasticity of the immune system. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2004, 1, 353–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, R. Bidirectional modulation of synaptic functions by Eph/ephrin signaling. Nat. Neurosci. 2009, 12, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Gunput, R.A.; Pasterkamp, R.J. Semaphorin signaling: Progress made and promises ahead. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2008, 33, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juhasz, K.; Buzas, K.; Duda, E. Importance of reverse signaling of the TNF superfamily in immune regulation. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2013, 9, 335–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, Z.; Schwarz, H. CD137 ligand, a member of the tumor necrosis factor family, regulates immune responses via reverse signal transduction. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2011, 89, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, N.J.; Henkemeyer, M. Ephrin reverse signaling in axon guidance and synaptogenesis. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2012, 23, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Zhou, Y.; Cheng, S.; Rao, Y. Plexin A-Semaphorin-1a reverse signaling regulates photoreceptor axon guidance in Drosophila. J. Neurosci. 2011, 30, 12151–12156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuo, K.; Otaki, N. Bone cell interactions through Eph/ephrin: Bone modeling, remodeling and associated diseases. Cell Adh. Migr. 2012, 6, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawamiphak, S.; Seidel, S.; Essmann, C.L.; Wilkinson, G.A.; Pitulescu, M.E.; Acker, T.; Acker-Palmer, A. Ephrin-B2 regulates VEGFR2 function in developmental and tumour angiogenesis. Nature 2010, 465, 487–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garton, K.J.; Gough, P.J.; Blobel, C.P.; Murphy, G.; Greaves, D.R.; Dempsey, P.J.; Raines, E.W. Tumor necrosis factor-α-converting enzyme (ADAM17) mediates the cleavage and shedding of fractalkine (CX3CL1). J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 37993–38001. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Abel, S.; Hundhausen, C.; Mentlein, R.; Schulte, A.; Berkhout, T.A.; Broadway, N.; Hartmann, D.; Sedlacek, R.; Dietrich, S.; Muetze, B.; et al. The transmembrane CXC-chemokine ligand 16 is induced by IFN-γ and TNF-α and shed by the activity of the disintegrin-like metalloproteinase ADAM10. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 6362–6372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludwig, A.; Schulte, A.; Schnack, C.; Hundhausen, C.; Reiss, K.; Brodway, N.; Held-Feindt, J.; Mentlein, R. Enhanced expression and shedding of the transmembrane chemokine CXCL16 by reactive astrocytes and glioma cells. J. Neurochem. 2005, 93, 1293–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hattermann, K.; Gebhardt, H.; Krossa, S.; Ludwig, A.; Lucius, R.; Held-Feindt, J.; Mentlein, R. Transmembrane chemokines act as receptors in a novel mechanism termed inverse signaling. Elife 2016, 5, e10820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hattermann, K.; Bartsch, K.; Gebhardt, H.; Mehdorn, H.M.; Synowitz, M.; Schmitt, A.D.; Mentlein, R.; Held-Feindt, J. “Inverse signaling” of the transmembrane chemokine CXCL16 contributes to proliferative and anti-apoptotic effects in cultured human meningioma cells. Cell Commun. Signal. 2016, 14, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matloubian, M.; David, A.; Engel, S.; Ryan, J.E.; Cyster, J.G. A transmembrane CXC chemokine is a ligand for HIV-coreceptor Bonzo. Nat. Immunol. 2000, 1, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Voort, R.; van Lieshout, A.W.; Toonen, L.W.; Slöetjes, A.W.; van den Berg, W.B.; Figdor, C.G.; Radstake, T.R.; Adema, G.J. Elevated CXCL16 expression by synovial macrophages recruits memory T cells into rheumatoid joints. Arthritis Rheum. 2005, 52, 1381–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, G.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Zu, L.; Cheng, G.; Hao, M.; Sun, X.; Xue, Y.; Lu, J.; Wang, J. CXCL16/CXCR6 chemokine signaling mediates breast cancer progression by pERK1/2-dependent mechanisms. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 14165–14178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.; Kapur, N.; Mir, H.; Singh, N.; Lillard, J.W., Jr.; Singh, S. CXCR6-CXCL16 axis promotes prostate cancer by mediating cytoskeleton rearrangement via Ezrin activation and αvβ3 integrin clustering. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 7343–7353. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Takiguchi, G.; Nishita, M.; Kurita, K.; Kakeji, Y.; Minami, Y. Wnt5a-Ror2 signaling in mesenchymal stem cells promotes proliferation of gastric cancer cells by activating CXCL16-CXCR6 axis. Cancer Sci. 2016, 107, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hattermann, K.; Held-Feindt, J.; Ludwig, A.; Mentlein, R. The CXCL16-CXCR6 chemokine axis in glial tumors. J. Neuroimmunol. 2013, 260, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Held-Feindt, J.; Rehmke, B.; Mentlein, R.; Hattermann, K.; Knerlich, F.; Hugo, H.-H.; Ludwig, A.; Mehdorn, H.M. Overexpression of CXCL16 and its receptor CXCR6/Bonzo promotes growth of human schwannomas. Glia 2008, 56, 764–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Hattermann, K.; Mentlein, R.; Mehdorn, H.M.; Held-Feindt, J. The transmembrane chemokines CXCL16 and CX3CL1 and their receptors are expressed in human meningiomas. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 29, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Veinotte, L.; Gebremeskel, S.; Johnston, B. CXCL16-positive dendritic cells enhance invariant natural killer T cell-dependent IFNγ production and tumor control. Oncoimmunology 2016, 5, e1160979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, M.S.; Pham, C.T.; Phan, M.T.; Shin, D.J.; Jang, Y.Y.; Park, M.H.; Kim, S.K.; Kim, S.; Cho, D. Irradiation of breast cancer cells enhances CXCL16 ligand expression and induces the migration of natural killer cells expressing the CXCR6 receptor. Cytotherapy 2016, 18, 1532–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kee, J.Y.; Ito, A.; Hojo, S.; Hashimoto, I.; Igarashi, Y.; Tsuneyama, K.; Tsukada, K.; Irimura, T.; Shibahara, N.; Takasaki, I.; Inujima, A.; et al. CXCL16 suppresses liver metastasis of colorectal cancer by promoting TNF-α-induced apoptosis by tumor-associated macrophages. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamski, V.; Schmitt, A.D.; Flüh, C.; Synowitz, M.; Hattermann, K.; Held-Feindt, J. Isolation and characterization of fast-migrating human glioma cells in the progression of malignant gliomas. Oncol. Res. 2016, 25, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimaoka, T.; Nakayama, T.; Fukumoto, N.; Kume, N.; Takahashi, S.; Yamaguchi, J.; Minami, M.; Hayashida, K.; Kita, T.; Ohsumi, J.; et al. Cell surface-anchored SR-PSOX/CXC chemokine ligand 16 mediates firm adhesion of CXC chemokine receptor 6-expressing cells. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2004, 75, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hattermann, K.; Ludwig, A.; Gieselmann, V.; Held-Feindt, J.; Mentlein, R. The chemokine CXCL16 induces migration and invasion of glial precursor cells via its receptor CXCR6. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2008, 39, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuge, X.; Murayama, T.; Arai, H.; Yamauchi, R.; Tanaka, M.; Shimaoka, T.; Yonehara, S.; Kume, N.; Yokode, M.; Kita, T. CXCL16 is a novel angiogenic factor for human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 331, 1295–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.; Fink, P.J. A new class of reverse signaling costimulators belongs to the TNF family. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 4307–4312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battistini, C.; Tamagnone, L. Transmembrane semaphorins, forward and reverse signaling: Have a look both ways. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 1609–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daar, I.O. Non-SH2/PDZ reverse signaling by ephrins. Semin. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2012, 23, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kisiswa, L.; Osorio, C.; Erice, C.; Vizard, T.; Wyatt, S.; Davies, A.M. TNFα reverse signaling promotes sympathetic axon growth and target innervation. Nat. Neurosci. 2012, 16, 865–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noren, N.K.; Lu, M.; Freeman, A.L.; Koolpe, M.; Pasquale, E.B. Interplay between EphB4 on tumor cells and vascular ephrin-B2 regulates tumor growth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 5583–5588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakada, M.; Anderson, E.M.; Demuth, T.; Nakada, S.; Reavie, L.B.; Drake, K.L.; Hoelzinger, D.B.; Berens, M.E. The phosphorylation of ephrin-B2 ligand promotes glioma cell migration and invasion. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 126, 1155–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Law, J.W.; Lee, A.Y. Semaphorin 5A and plexin-B3 regulate human glioma cell motility and morphology through Rac1 and the actin cytoskeleton. Oncogene 2012, 31, 595–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, T.R.; Rouslathi, E.; Schold, S.C.; Bigner, D.D. Fibronectin and glial fibrillary acidic protein expression in normal brain and anaplastic human gliomas. Cancer Res. 1982, 42, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nishiguchi, D.J.; Stephens, R.E.; Yates, A.J. Application of flow cytometry to analyses of cultured human glioma and fetal brain cells. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 1985, 44, 254–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thies, A.; Mauer, S.; Fodstad, O.; Schumacher, U. Clinically proven markers of metastasis predict metastatic spread of human melanoma cells engrafted in scid mice. Br. J. Cancer 2007, 96, 609–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hattermann, K.; Held-Feindt, J.; Lucius, R.; Sebens Müerköster, S.; Penfold, M.E.; Schall, T.J.; Mentlein, R. The chemokine receptor CXCR7 is highly expressed in human glioma cells and mediates anti-apoptotic effects. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 3299–3308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Adamski, V.; Mentlein, R.; Lucius, R.; Synowitz, M.; Held-Feindt, J.; Hattermann, K. The Chemokine Receptor CXCR6 Evokes Reverse Signaling via the Transmembrane Chemokine CXCL16. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1468. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18071468
Adamski V, Mentlein R, Lucius R, Synowitz M, Held-Feindt J, Hattermann K. The Chemokine Receptor CXCR6 Evokes Reverse Signaling via the Transmembrane Chemokine CXCL16. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(7):1468. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18071468
Chicago/Turabian StyleAdamski, Vivian, Rolf Mentlein, Ralph Lucius, Michael Synowitz, Janka Held-Feindt, and Kirsten Hattermann. 2017. "The Chemokine Receptor CXCR6 Evokes Reverse Signaling via the Transmembrane Chemokine CXCL16" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 7: 1468. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18071468
APA StyleAdamski, V., Mentlein, R., Lucius, R., Synowitz, M., Held-Feindt, J., & Hattermann, K. (2017). The Chemokine Receptor CXCR6 Evokes Reverse Signaling via the Transmembrane Chemokine CXCL16. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(7), 1468. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18071468