Targeting Cytokines as Evolving Treatment Strategies in Chronic Inflammatory Airway Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Mediators of Chronic Inflammatory Airway Diseases
2.1. COPD
2.2. Bronchiectasis
2.3. Allergic Asthma
2.4. Current Therapeutic Strategies and Their Effect on Airway Inflammation
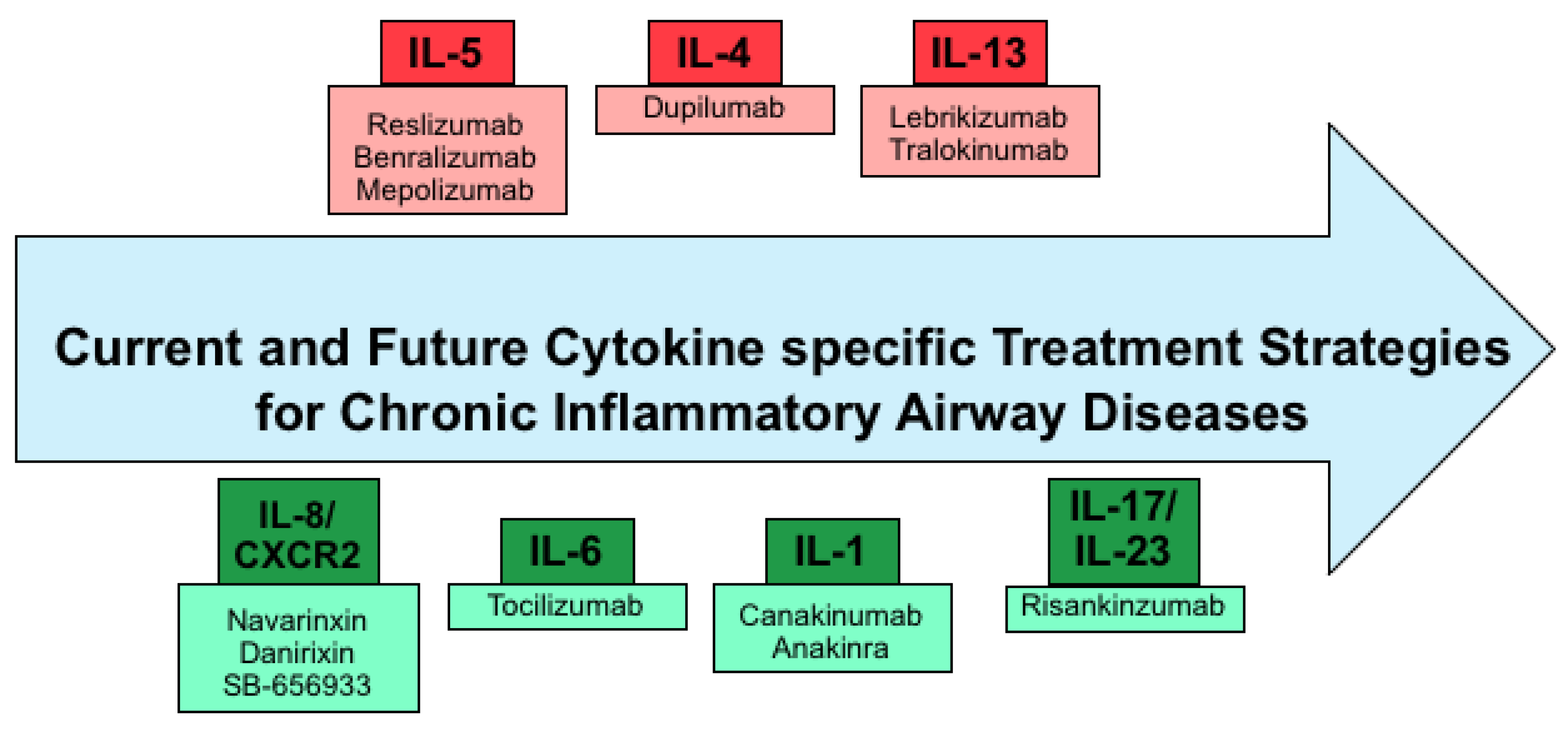
3. Current Cytokine Specific Treatment Strategies
4. Future Therapeutic Strategies
4.1. Inhibition of IL-1β as Therapeutic Strategy
4.2. IL-6 Blocking Antibody Therapy
4.3. Inhibition of IL-8 Signaling as an Anti-Inflammatory Therapy Approach
4.4. Future Approaches Targeting IL-17 and IL-23
5. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Murray, C.J.; Vos, T.; Lozano, R.; Naghavi, M.; Flaxman, A.D.; Michaud, C.; Ezzati, M.; Shibuya, K.; Salomon, J.A.; Abdalla, S.; et al. Disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) for 291 diseases and injuries in 21 regions, 1990–2010: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 2012, 380, 2197–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdoganoglu, T.; Songu, M. The burden of allergic rhinitis and asthma. Ther. Adv. Respir. Dis. 2012, 6, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakata, K.; Gotoh, H.; Watanabe, J.; Uetake, T.; Komuro, I.; Yuasa, K.; Watanabe, S.; Ieki, R.; Sakamaki, H.; Akiyama, H.; et al. Augmented proliferation of human alveolar macrophages after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Blood 1999, 93, 667–673. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bender, A.T.; Ostenson, C.L.; Wang, E.H.; Beavo, J.A. Selective up-regulation of PDE1B2 upon monocyte-to-macrophage differentiation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 497–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burns, A.R.; Smith, C.W.; Walker, D.C. Unique structural features that influence neutrophil emigration into the lung. Physiol. Rev. 2003, 83, 309–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yazdanbakhsh, M.; Kremsner, P.G.; van Ree, R. Allergy, parasites, and the hygiene hypothesis. Science 2002, 296, 490–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tesmer, L.A.; Lundy, S.K.; Sarkar, S.; Fox, D.A. Th17 cells in human disease. Immunol. Rev. 2008, 223, 87–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adler, K.B.; Fischer, B.M.; Wright, D.T.; Cohn, L.A.; Becker, S. Interactions between respiratory epithelial cells and cytokines: Relationships to lung inflammation. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1994, 725, 128–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suratt, B.T.; Parsons, P.E. Mechanisms of acute lung injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome. Clin. Chest Med. 2006, 27, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallstrand, T.S.; Hackett, T.L.; Altemeier, W.A.; Matute-Bello, G.; Hansbro, P.M.; Knight, D.A. Airway epithelial regulation of pulmonary immune homeostasis and inflammation. Clin. Immunol. 2014, 151, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ince, L.M.; Zhang, Z.; Beesley, S.; Vonslow, R.M.; Saer, B.R.; Matthews, L.C.; Begley, N.; Gibbs, J.E.; Ray, D.W.; Loudon, A.S.I. Circadian variation in pulmonary inflammatory responses is independent of rhythmic glucocorticoid signaling in airway epithelial cells. FASEB J. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krick, S.; Grabner, A.; Baumlin, N.; Yanucil, C.; Helton, S.; Grosche, A.; Sailland, J.; Geraghty, P.; Viera, L.; Russell, D.W.; et al. Fibroblast growth factor 23 and Klotho contribute to airway inflammation. Eur. Respir. J. 2018, 52, 1800236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krick, S.; Baumlin, N.; Aller, S.P.; Aguiar, C.; Grabner, A.; Sailland, J.; Mendes, E.; Schmid, A.; Qi, L.; David, N.V.; et al. Klotho Inhibits Interleukin-8 Secretion from Cystic Fibrosis Airway Epithelia. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, D.; Prince, A. Type I interferon response to extracellular bacteria in the airway epithelium. Trends Immunol. 2011, 32, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gras, D.; Chanez, P.; Vachier, I.; Petit, A.; Bourdin, A. Bronchial epithelium as a target for innovative treatments in asthma. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 140, 290–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knight, D.A.; Holgate, S.T. The airway epithelium: Structural and functional properties in health and disease. Respirology 2003, 8, 432–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crystal, R.G.; Randell, S.H.; Engelhardt, J.F.; Voynow, J.; Sunday, M.E. Airway epithelial cells: Current concepts and challenges. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2008, 5, 772–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, K.; Hori, A.; Kawamoto, K.; Thangudu, R.R.; Ishida, T.; Igarashi, K.; Samejima, M.; Yamada, C.; Arakawa, T.; Wakagi, T.; et al. Crystal structure of a feruloyl esterase belonging to the tannase family: A disulfide bond near a catalytic triad. Proteins 2014, 82, 2857–2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widdicombe, J.H.; Widdicombe, J.G. Regulation of human airway surface liquid. Respir. Physiol. 1995, 99, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corfield, A.P. Mucins: A biologically relevant glycan barrier in mucosal protection. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1850, 236–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, A.M.; Liao, H.I.; Stuchlik, O.; Tilan, J.; Pohl, J.; Ganz, T. Cationic polypeptides are required for antibacterial activity of human airway fluid. J. Immunol. 2002, 169, 6985–6991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Novo, C.A.; Watelet, J.B.; Claeys, C.; Van Cauwenberge, P.; Bachert, C. Prostaglandin, leukotriene, and lipoxin balance in chronic rhinosinusitis with and without nasal polyposis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2005, 115, 1189–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gohy, S.T.; Hupin, C.; Pilette, C.; Ladjemi, M.Z. Chronic inflammatory airway diseases: The central role of the epithelium revisited. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2016, 46, 529–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, W.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Adcock, I.M.; Barnes, P.J.; Huang, M.; Yao, X. Bronchial epithelial cells: The key effector cells in the pathogenesis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease? Respirology 2015, 20, 722–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moldoveanu, B.; Otmishi, P.; Jani, P.; Walker, J.; Sarmiento, X.; Guardiola, J.; Saad, M.; Yu, J. Inflammatory mechanisms in the lung. J. Inflamm. Res. 2009, 2, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Toossi, Z.; Hirsch, C.S.; Hamilton, B.D.; Knuth, C.K.; Friedlander, M.A.; Rich, E.A. Decreased production of TGF-beta 1 by human alveolar macrophages compared with blood monocytes. J. Immunol. 1996, 156, 3461–3468. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moore, S.A.; Strieter, R.M.; Rolfe, M.W.; Standiford, T.J.; Burdick, M.D.; Kunkel, S.L. Expression and regulation of human alveolar macrophage-derived interleukin-1 receptor antagonist. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 1992, 6, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, L.; Linsley, P.S.; Huang, L.Y.; Germain, R.N.; Shevach, E.M. IL-10 inhibits macrophage costimulatory activity by selectively inhibiting the up-regulation of B7 expression. J. Immunol. 1993, 151, 1224–1234. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Holgate, S.T. Pathogenesis of asthma. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2008, 38, 872–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurowska-Stolarska, M.; Kewin, P.; Murphy, G.; Russo, R.C.; Stolarski, B.; Garcia, C.C.; Komai-Koma, M.; Pitman, N.; Li, Y.; Niedbala, W.; et al. IL-33 induces antigen-specific IL-5+ T cells and promotes allergic-induced airway inflammation independent of IL-4. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 4780–4790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarir, H.; Henricks, P.A.; van Houwelingen, A.H.; Nijkamp, F.P.; Folkerts, G. Cells, mediators and Toll-like receptors in COPD. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 585, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suter, P.M.; Suter, S.; Girardin, E.; Roux-Lombard, P.; Grau, G.E.; Dayer, J.M. High bronchoalveolar levels of tumor necrosis factor and its inhibitors, interleukin-1, interferon, and elastase, in patients with adult respiratory distress syndrome after trauma, shock, or sepsis. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1992, 145, 1016–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samet, J.M. Tobacco smoking: The leading cause of preventable disease worldwide. Thorac. Surg. Clin. 2013, 23, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonough, J.E.; Yuan, R.; Suzuki, M.; Seyednejad, N.; Elliott, W.M.; Sanchez, P.G.; Wright, A.C.; Gefter, W.B.; Litzky, L.; Coxson, H.O.; et al. Small-airway obstruction and emphysema in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 1567–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, P.J.; Shapiro, S.D.; Pauwels, R.A. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: Molecular and cellular mechanisms. Eur. Respir. J. 2003, 22, 672–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, P.J. Mechanisms in COPD: Differences from asthma. Chest 2000, 117 (Suppl. 2), 10S–14S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bucchioni, E.; Kharitonov, S.A.; Allegra, L.; Barnes, P.J. High levels of interleukin-6 in the exhaled breath condensate of patients with COPD. Respir. Med. 2003, 97, 1299–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sommerhoff, C.P.; Nadel, J.A.; Basbaum, C.B.; Caughey, G.H. Neutrophil elastase and cathepsin G stimulate secretion from cultured bovine airway gland serous cells. J. Clin. Investig. 1990, 85, 682–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Retamales, I.; Elliott, W.M.; Meshi, B.; Coxson, H.O.; Pare, P.D.; Sciurba, F.C.; Rogers, R.M.; Hayashi, S.; Hogg, J.C. Amplification of inflammation in emphysema and its association with latent adenoviral infection. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 164, 469–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finkelstein, R.; Fraser, R.S.; Ghezzo, H.; Cosio, M.G. Alveolar inflammation and its relation to emphysema in smokers. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1995, 152 Pt 1, 1666–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banchereau, J.; Briere, F.; Caux, C.; Davoust, J.; Lebecque, S.; Liu, Y.J.; Pulendran, B.; Palucka, K. Immunobiology of dendritic cells. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2000, 18, 767–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mio, T.; Romberger, D.J.; Thompson, A.B.; Robbins, R.A.; Heires, A.; Rennard, S.I. Cigarette smoke induces interleukin-8 release from human bronchial epithelial cells. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1997, 155, 1770–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellermann, G.R.; Nagy, S.B.; Kong, X.; Lockey, R.F.; Mohapatra, S.S. Mechanism of cigarette smoke condensate-induced acute inflammatory response in human bronchial epithelial cells. Respir. Res. 2002, 3, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Floreani, A.A.; Wyatt, T.A.; Stoner, J.; Sanderson, S.D.; Thompson, E.G.; Allen-Gipson, D.; Heires, A.J. Smoke and C5a induce airway epithelial intercellular adhesion molecule-1 and cell adhesion. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2003, 29, 472–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miotto, D.; Ruggieri, M.P.; Boschetto, P.; Cavallesco, G.; Papi, A.; Bononi, I.; Piola, C.; Murer, B.; Fabbri, L.M.; Mapp, C.E. Interleukin-13 and -4 expression in the central airways of smokers with chronic bronchitis. Eur. Respir. J. 2003, 22, 602–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imaoka, H.; Hoshino, T.; Takei, S.; Kinoshita, T.; Okamoto, M.; Kawayama, T.; Kato, S.; Iwasaki, H.; Watanabe, K.; Aizawa, H. Interleukin-18 production and pulmonary function in COPD. Eur. Respir. J. 2008, 31, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakanishi, K.; Yoshimoto, T.; Tsutsui, H.; Okamura, H. Interleukin-18 regulates both Th1 and Th2 responses. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2001, 19, 423–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitasato, Y.; Hoshino, T.; Okamoto, M.; Kato, S.; Koda, Y.; Nagata, N.; Kinoshita, M.; Koga, H.; Yoon, D.Y.; Asao, H.; et al. Enhanced expression of interleukin-18 and its receptor in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2004, 31, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoshino, T.; Kato, S.; Oka, N.; Imaoka, H.; Kinoshita, T.; Takei, S.; Kitasato, Y.; Kawayama, T.; Imaizumi, T.; Yamada, K.; et al. Pulmonary inflammation and emphysema: Role of the cytokines IL-18 and IL-13. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 176, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoshino, T.; Yagita, H.; Ortaldo, J.R.; Wiltrout, R.H.; Young, H.A. In vivo administration of IL-18 can induce IgE production through Th2 cytokine induction and up-regulation of CD40 ligand (CD154) expression on CD4+ T cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 2000, 30, 1998–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshino, T.; Wiltrout, R.H.; Young, H.A. IL-18 is a potent coinducer of IL-13 in NK and T cells: A new potential role for IL-18 in modulating the immune response. J. Immunol. 1999, 162, 5070–5077. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Barker, A.F. Bronchiectasis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 346, 1383–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalmers, J.D.; Aliberti, S.; Blasi, F. Management of bronchiectasis in adults. Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 45, 1446–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aksamit, T.R.; O’Donnell, A.E.; Barker, A.; Olivier, K.N.; Winthrop, K.L.; Daniels, M.L.A.; Johnson, M.; Eden, E.; Griffith, D.; Knowles, M.; et al. Adult Patients With Bronchiectasis: A First Look at the US Bronchiectasis Research Registry. Chest 2017, 151, 982–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weycker, D.; Hansen, G.L.; Seifer, F.D. Prevalence and incidence of noncystic fibrosis bronchiectasis among US adults in 2013. Chronic Respir. Dis. 2017, 14, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidhu, M.K.; Mandal, P.; Hill, A.T. Bronchiectasis: An update on current pharmacotherapy and future perspectives. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2014, 15, 505–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamutcu, R.; Rowland, J.M.; Horn, M.V.; Kaminsky, C.; MacLaughlin, E.F.; Starnes, V.A.; Woo, M.S. Clinical findings and lung pathology in children with cystic fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 165, 1172–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatakrishnan, A.; Stecenko, A.A.; King, G.; Blackwell, T.R.; Brigham, K.L.; Christman, J.W.; Blackwell, T.S. Exaggerated activation of nuclear factor-kappaB and altered IkappaB-beta processing in cystic fibrosis bronchial epithelial cells. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2000, 23, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koehler, D.R.; Downey, G.P.; Sweezey, N.B.; Tanswell, A.K.; Hu, J. Lung inflammation as a therapeutic target in cystic fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2004, 31, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verhaeghe, C.; Delbecque, K.; de Leval, L.; Oury, C.; Bours, V. Early inflammation in the airways of a cystic fibrosis foetus. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2007, 6, 304–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, T.Z.; Wagener, J.S.; Bost, T.; Martinez, J.; Accurso, F.J.; Riches, D.W. Early pulmonary inflammation in infants with cystic fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1995, 151, 1075–1082. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sly, P.D.; Brennan, S.; Gangell, C.; de Klerk, N.; Murray, C.; Mott, L.; Stick, S.M.; Robinson, P.J.; Robertson, C.F.; Ranganathan, S.C.; et al. Lung disease at diagnosis in infants with cystic fibrosis detected by newborn screening. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 180, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, D.S.; Hook, S.M.; Jamsen, K.M.; Nixon, G.M.; Carzino, R.; Carlin, J.B.; Robertson, C.F.; Grimwood, K. Lower airway inflammation in infants with cystic fibrosis detected by newborn screening. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2005, 40, 500–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagel, S.D.; Wagner, B.D.; Anthony, M.M.; Emmett, P.; Zemanick, E.T. Sputum biomarkers of inflammation and lung function decline in children with cystic fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 186, 857–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rincon, M.; Irvin, C.G. Role of IL-6 in asthma and other inflammatory pulmonary diseases. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2012, 8, 1281–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broide, D.H. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of allergic disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2001, 108 (Suppl. 2), S65–S71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vignola, A.M.; Kips, J.; Bousquet, J. Tissue remodeling as a feature of persistent asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2000, 105, 1041–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, D.K.; Shao, Z. Pathogenesis of allergic airway inflammation. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2010, 10, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berton, M.T.; Uhr, J.W.; Vitetta, E.S. Synthesis of germ-line gamma 1 immunoglobulin heavy-chain transcripts in resting B cells: Induction by interleukin 4 and inhibition by interferon gamma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 2829–2833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wills-Karp, M. Immunologic basis of antigen-induced airway hyperresponsiveness. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1999, 17, 255–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whittaker, L.; Niu, N.; Temann, U.A.; Stoddard, A.; Flavell, R.A.; Ray, A.; Homer, R.J.; Cohn, L. Interleukin-13 mediates a fundamental pathway for airway epithelial mucus induced by CD4 T cells and interleukin-9. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2002, 27, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walter, D.M.; McIntire, J.J.; Berry, G.; McKenzie, A.N.; Donaldson, D.D.; DeKruyff, R.H.; Umetsu, D.T. Critical role for IL-13 in the development of allergen-induced airway hyperreactivity. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 4668–4675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherry, W.B.; Yoon, J.; Bartemes, K.R.; Iijima, K.; Kita, H. A novel IL-1 family cytokine, IL-33, potently activates human eosinophils. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2008, 121, 1484–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondo, Y.; Yoshimoto, T.; Yasuda, K.; Futatsugi-Yumikura, S.; Morimoto, M.; Hayashi, N.; Hoshino, T.; Fujimoto, J.; Nakanishi, K. Administration of IL-33 induces airway hyperresponsiveness and goblet cell hyperplasia in the lungs in the absence of adaptive immune system. Int. Immunol. 2008, 20, 791–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agusti, A.; Fabbri, L.M.; Singh, D.; Vestbo, J.; Celli, B.; Franssen, F.M.; Rabe, K.F.; Papi, A. Inhaled corticosteroids in COPD: Friend or foe? Eur. Respir. J. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, P.J. Targeting cytokines to treat asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 454–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, A.; Khirani, S.; Cazzola, M. Long-acting β(2)-agonists (LABA) in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: Efficacy and safety. Int. J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2008, 3, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alagha, K.; Palot, A.; Sofalvi, T.; Pahus, L.; Gouitaa, M.; Tummino, C.; Martinez, S.; Charpin, D.; Bourdin, A.; Chanez, P. Long-acting muscarinic receptor antagonists for the treatment of chronic airway diseases. Ther. Adv. Chronic Dis. 2014, 5, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garth, J.M.; Mackel, J.J.; Reeder, K.M.; Blackburn, J.P.; Dunaway, C.W.; Yu, Z.; Matalon, S.; Fitz, L.; Steele, C. Acidic mammalian chitinase negatively affects immune responses during acute and chronic Aspergillus fumigatus exposure. Infect. Immunity 2018, 86, e00944-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, K.R.; Chmiel, J.F.; Konstan, M.W. The Role of Inhaled Corticosteroids in the Management of Cystic Fibrosis. Paediatr. Drugs 2009, 11, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albert, R.K.; Connett, J.; Bailey, W.C.; Casaburi, R.; Cooper, J.A., Jr.; Criner, G.J.; Curtis, J.L.; Dransfield, M.T.; Han, M.K.; Lazarus, S.C.; et al. Azithromycin for prevention of exacerbations of COPD. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 689–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Southern, K.W.; Barker, P.M.; Solis-Moya, A.; Patel, L. Macrolide antibiotics for cystic fibrosis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, 11, CD002203. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chong, J.; Leung, B.; Poole, P. Phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitors for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 9, CD002309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, P.J. Theophylline. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 188, 901–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, D.; Chakraborty, S.; Singh, S.; Mishra, B. Doxofylline: A promising methylxanthine derivative for the treatment of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2009, 10, 2343–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livraghi, A.; Randell, S.H. Cystic fibrosis and other respiratory diseases of impaired mucus clearance. Toxicol. Pathol. 2007, 35, 116–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sloane, P.A.; Shastry, S.; Wilhelm, A.; Courville, C.; Tang, L.P.; Backer, K.; Levin, E.; Raju, S.V.; Li, Y.; Mazur, M.; et al. A pharmacologic approach to acquired cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator dysfunction in smoking related lung disease. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flume, P.A.; Mogayzel, P.J., Jr.; Robinson, K.A.; Goss, C.H.; Rosenblatt, R.L.; Kuhn, R.J.; Marshall, B.C.; Clinical Practice Guidelines for Pulmonary Therapies Committee. Cystic fibrosis pulmonary guidelines: Treatment of pulmonary exacerbations. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 180, 802–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konstan, M.W.; Ratjen, F. Effect of dornase alfa on inflammation and lung function: Potential role in the early treatment of cystic fibrosis. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2012, 11, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubin, B.K. Aerosol Medications for Treatment of Mucus Clearance Disorders. Respir. Care 2015, 60, 825–829; discussion 830–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leckie, M.J.; ten Brinke, A.; Khan, J.; Diamant, Z.; O’Connor, B.J.; Walls, C.M.; Mathur, A.K.; Cowley, H.C.; Chung, K.F.; Djukanovic, R.; et al. Effects of an interleukin-5 blocking monoclonal antibody on eosinophils, airway hyper-responsiveness, and the late asthmatic response. Lancet 2000, 356, 2144–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavord, I.D.; Korn, S.; Howarth, P.; Bleecker, E.R.; Buhl, R.; Keene, O.N.; Ortega, H.; Chanez, P. Mepolizumab for severe eosinophilic asthma (DREAM): A multicentre, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2012, 380, 651–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, M.; Wenzel, S.E.; Bleecker, E.R.; Pizzichini, E.; Kuna, P.; Busse, W.W.; Gossage, D.L.; Ward, C.K.; Wu, Y.; Wang, B.; et al. Benralizumab, an anti-interleukin 5 receptor alpha monoclonal antibody, versus placebo for uncontrolled eosinophilic asthma: A phase 2b randomised dose-ranging study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2014, 2, 879–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeks, E.D.; Brusselle, G. Reslizumab in Eosinophilic Asthma: A Review. Drugs 2017, 77, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brightling, C.E.; Bleecker, E.R.; Panettieri, R.A., Jr.; Bafadhel, M.; She, D.; Ward, C.K.; Xu, X.; Birrell, C.; van der Merwe, R. Benralizumab for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and sputum eosinophilia: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2a study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2014, 2, 891–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavord, I.D.; Chanez, P.; Criner, G.J.; Kerstjens, H.A.M.; Korn, S.; Lugogo, N.; Martinot, J.-B.; Sagara, H.; Albers, F.C.; Bradford, E.S.; et al. Mepolizumab for Eosinophilic Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1613–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenzel, S.; Castro, M.; Corren, J.; Maspero, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, B.; Pirozzi, G.; Sutherland, E.R.; Evans, R.R.; Joish, V.N.; et al. Dupilumab efficacy and safety in adults with uncontrolled persistent asthma despite use of medium-to-high-dose inhaled corticosteroids plus a long-acting beta2 agonist: A randomised double-blind placebo-controlled pivotal phase 2b dose-ranging trial. Lancet 2016, 388, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzel, S.; Ford, L.; Pearlman, D.; Spector, S.; Sher, L.; Skobieranda, F.; Wang, L.; Kirkesseli, S.; Rocklin, R.; Bock, B.; et al. Dupilumab in persistent asthma with elevated eosinophil levels. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 2455–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wechsler, M.E. Current and Emerging Biologic Therapies for Asthma and COPD. Respir. Care 2018, 63, 699–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lappalainen, U.; Whitsett, J.A.; Wert, S.E.; Tichelaar, J.W.; Bry, K. Interleukin-1beta causes pulmonary inflammation, emphysema, and airway remodeling in the adult murine lung. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2005, 32, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinarello, C.A. Immunological and inflammatory functions of the interleukin-1 family. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 27, 519–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamkanfi, M. Emerging inflammasome effector mechanisms. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, E.A.; Ernst, R.K.; Dors, M.; Mao, D.P.; Aderem, A. Pseudomonas aeruginosa activates caspase 1 through Ipaf. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 2562–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douglas, T.A.; Brennan, S.; Gard, S.; Berry, L.; Gangell, C.; Stick, S.M.; Clements, B.S.; Sly, P.D. Acquisition and eradication of P. aeruginosa in young children with cystic fibrosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2009, 33, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, H.; Murphy, A.; Zou, F.; Gerard, C.; Klanderman, B.; Schuemann, B.; Lazarus, R.; Garcia, K.C.; Celedon, J.C.; Drumm, M.; et al. IL1B polymorphisms modulate cystic fibrosis lung disease. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2009, 44, 580–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muselet-Charlier, C.; Roque, T.; Boncoeur, E.; Chadelat, K.; Clement, A.; Jacquot, J.; Tabary, O. Enhanced IL-1beta-induced IL-8 production in cystic fibrosis lung epithelial cells is dependent of both mitogen-activated protein kinases and NF-kappaB signaling. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 357, 402–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palomo, J.; Marchiol, T.; Piotet, J.; Fauconnier, L.; Robinet, M.; Reverchon, F.; Le Bert, M.; Togbe, D.; Buijs-Offerman, R.; Stolarczyk, M.; et al. Role of IL-1beta in experimental cystic fibrosis upon P. aeruginosa infection. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e114884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iannitti, R.G.; Napolioni, V.; Oikonomou, V.; De Luca, A.; Galosi, C.; Pariano, M.; Massi-Benedetti, C.; Borghi, M.; Puccetti, M.; Lucidi, V.; et al. IL-1 receptor antagonist ameliorates inflammasome-dependent inflammation in murine and human cystic fibrosis. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, P.; Gibson, P.G.; Baines, K.J.; Yang, I.A.; Upham, J.W.; Reynolds, P.N.; Hodge, S.; James, A.L.; Jenkins, C.; Peters, M.J.; et al. Anti-inflammatory deficiencies in neutrophilic asthma: Reduced galectin-3 and IL-1RA/IL-1beta. Respir. Res. 2015, 16, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Peng, S.; Xiong, W.; Xu, Y.; Liu, J. Association between polymorphism of interleukin-1 beta and interleukin-1 receptor antagonist gene and asthma risk: A meta-analysis. ScientificWorldJournal 2015, 2015, 685684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besnard, A.G.; Togbe, D.; Couillin, I.; Tan, Z.; Zheng, S.G.; Erard, F.; Le Bert, M.; Quesniaux, V.; Ryffel, B. Inflammasome-IL-1-Th17 response in allergic lung inflammation. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 4, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whelan, R.; Kim, C.; Chen, M.; Leiter, J.; Grunstein, M.M.; Hakonarson, H. Role and regulation of interleukin-1 molecules in pro-asthmatic sensitised airway smooth muscle. Eur. Respir. J. 2004, 24, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogliani, P.; Calzetta, L.; Ora, J.; Matera, M.G. Canakinumab for the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 31, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez, M.L.; Mills, K.; Almond, M.; Todoric, K.; Aleman, M.M.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, H.; Peden, D.B. IL-1 receptor antagonist reduces endotoxin-induced airway inflammation in healthy volunteers. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 135, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montgomery, S.T.; Mall, M.A.; Kicic, A.; Stick, S.M.; Arest, C.F. Hypoxia and sterile inflammation in cystic fibrosis airways: Mechanisms and potential therapies. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 49, 1600903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marini, M.; Vittori, E.; Hollemborg, J.; Mattoli, S. Expression of the potent inflammatory cytokines, granulocyte-macrophage-colony-stimulating factor and interleukin-6 and interleukin-8, in bronchial epithelial cells of patients with asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1992, 89, 1001–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadnyk, A.W. Cytokine production by epithelial cells. FASEB J. 1994, 8, 1041–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokoyama, A.; Kohno, N.; Fujino, S.; Hamada, H.; Inoue, Y.; Fujioka, S.; Ishida, S.; Hiwada, K. Circulating interleukin-6 levels in patients with bronchial asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1995, 151, 1354–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franceschi, C.; Capri, M.; Monti, D.; Giunta, S.; Olivieri, F.; Sevini, F.; Panourgia, M.P.; Invidia, L.; Celani, L.; Scurti, M.; et al. Inflammaging and anti-inflammaging: A systemic perspective on aging and longevity emerged from studies in humans. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2007, 128, 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, P.J. Future treatments for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and its comorbidities. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2008, 5, 857–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, A.; Tay, J.; Ton, S.; Agrawal, S.; Gupta, S. Increased reactivity of dendritic cells from aged subjects to self-antigen, the human DNA. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 1138–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, G.; Hanania, N.A.; Shim, Y.M. The aging immune system and its relationship to the development of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2009, 6, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehrotra, N.; Freire, A.X.; Bauer, D.C.; Harris, T.B.; Newman, A.B.; Kritchevsky, S.B.; Meibohm, B.; Health, A.B.C.S. Predictors of mortality in elderly subjects with obstructive airway disease: The PILE score. Ann. Epidemiol. 2010, 20, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nixon, L.S.; Yung, B.; Bell, S.C.; Elborn, J.S.; Shale, D.J. Circulating immunoreactive interleukin-6 in cystic fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1998, 157, 1764–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neveu, W.A.; Bernardo, E.; Allard, J.L.; Nagaleekar, V.; Wargo, M.J.; Davis, R.J.; Iwakura, Y.; Whittaker, L.A.; Rincon, M. Fungal allergen beta-glucans trigger p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase-mediated IL-6 translation in lung epithelial cells. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2011, 45, 1133–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dienz, O.; Rincon, M. The effects of IL-6 on CD4 T cell responses. Clin. Immunol. 2009, 130, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dienz, O.; Eaton, S.M.; Bond, J.P.; Neveu, W.; Moquin, D.; Noubade, R.; Briso, E.M.; Charland, C.; Leonard, W.J.; Ciliberto, G.; et al. The induction of antibody production by IL-6 is indirectly mediated by IL-21 produced by CD4+ T cells. J. Exp. Med. 2009, 206, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tillie-Leblond, I.; Pugin, J.; Marquette, C.H.; Lamblin, C.; Saulnier, F.; Brichet, A.; Wallaert, B.; Tonnel, A.B.; Gosset, P. Balance between proinflammatory cytokines and their inhibitors in bronchial lavage from patients with status asthmaticus. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1999, 159, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virchow, J.C., Jr.; Kroegel, C.; Walker, C.; Matthys, H. Inflammatory determinants of asthma severity: Mediator and cellular changes in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of patients with severe asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1996, 98, S27–S33; discussion S33–S40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, A.E.; Raymond, D.M.; Suratt, B.T.; Bourassa, L.M.; Irvin, C.G. Lower airway disease in asthmatics with and without rhinitis. Lung 2008, 186, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morjaria, J.B.; Babu, K.S.; Vijayanand, P.; Chauhan, A.J.; Davies, D.E.; Holgate, S.T. Sputum IL-6 concentrations in severe asthma and its relationship with FEV1. Thorax 2011, 66, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, A.E.; Shade, D.M.; Cohen, R.I.; Skloot, G.S.; Holbrook, J.T.; Smith, L.J.; Lima, J.J.; Allayee, H.; Irvin, C.G.; Wise, R.A.; et al. Effect of obesity on clinical presentation and response to treatment in asthma. J. Asthma 2006, 43, 553–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishimoto, T. IL-6: From its discovery to clinical applications. Int. Immunol. 2010, 22, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, E.; Greene, C.M.; McElvaney, N.G. Targeting neutrophil elastase in cystic fibrosis. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2008, 12, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, H.; Yoshimura, K.; McElvaney, N.G.; Crystal, R.G. Neutrophil elastase in respiratory epithelial lining fluid of individuals with cystic fibrosis induces interleukin-8 gene expression in a human bronchial epithelial cell line. J. Clin. Investig. 1992, 89, 1478–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lampronti, I.; Manzione, M.G.; Sacchetti, G.; Ferrari, D.; Spisani, S.; Bezzerri, V.; Finotti, A.; Borgatti, M.; Dechecchi, M.C.; Miolo, G.; et al. Differential Effects of Angelicin Analogues on NF-kappaB Activity and IL-8 Gene Expression in Cystic Fibrosis IB3-1 Cells. Mediat. Inflamm. 2017, 2017, 2389487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaudszus, A.; Arnold, C.; Hentschel, J.; Hunniger, K.; Baier, M.; Mainz, J.G. Increased cytokines in cystic fibrosis patients’ upper airways during a new P. aeruginosa colonization. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2018, 53, 881–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, A.; Wasiliew, P.; Kracht, M. Interleukin-1beta (IL-1beta) processing pathway. Sci. Signal. 2010, 3, cm2. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Scheid, P.; Kempster, L.; Griesenbach, U.; Davies, J.C.; Dewar, A.; Weber, P.P.; Colledge, W.H.; Evans, M.J.; Geddes, D.M.; Alton, E.W. Inflammation in cystic fibrosis airways: Relationship to increased bacterial adherence. Eur. Respir. J. 2001, 17, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsson, K. Inflammatory markers in COPD. Clin. Respir. J. 2008, 2 (Suppl. 1), 84–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bautista, M.V.; Chen, Y.; Ivanova, V.S.; Rahimi, M.K.; Watson, A.M.; Rose, M.C. IL-8 regulates mucin gene expression at the posttranscriptional level in lung epithelial cells. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 2159–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, D.; Ganesan, S.; Comstock, A.T.; Meldrum, C.A.; Mahidhara, R.; Goldsmith, A.M.; Curtis, J.L.; Martinez, F.J.; Hershenson, M.B.; Sajjan, U. Increased cytokine response of rhinovirus-infected airway epithelial cells in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 182, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarir, H.; Mortaz, E.; Janse, W.T.; Givi, M.E.; Nijkamp, F.P.; Folkerts, G. IL-8 production by macrophages is synergistically enhanced when cigarette smoke is combined with TNF-alpha. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2010, 79, 698–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, H.; Ma, W.; Wang, F.; Liu, C.; He, S. Increased interleukin (IL)-8 and decreased IL-17 production in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) provoked by cigarette smoke. Cytokine 2011, 56, 717–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiemstra, P.S. Altered macrophage function in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2013, 10, S180–S185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dibbert, B.; Weber, M.; Nikolaizik, W.H.; Vogt, P.; Schoni, M.H.; Blaser, K.; Simon, H.U. Cytokine-mediated Bax deficiency and consequent delayed neutrophil apoptosis: A general mechanism to accumulate effector cells in inflammation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 13330–13335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, A.X.; Lu, L.W.; Liu, W.J.; Huang, M. Plasma Inflammatory Cytokine IL-4, IL-8, IL-10, and TNF-alpha Levels Correlate with Pulmonary Function in Patients with Asthma-Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Overlap Syndrome. Med. Sci. Monit. 2016, 22, 2800–2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jatakanon, A.; Uasuf, C.; Maziak, W.; Lim, S.; Chung, K.F.; Barnes, P.J. Neutrophilic inflammation in severe persistent asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1999, 160 Pt 1, 1532–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordonez, C.L.; Shaughnessy, T.E.; Matthay, M.A.; Fahy, J.V. Increased neutrophil numbers and IL-8 levels in airway secretions in acute severe asthma: Clinical and biologic significance. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 161 Pt 1, 1185–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamblin, C.; Gosset, P.; Tillie-Leblond, I.; Saulnier, F.; Marquette, C.H.; Wallaert, B.; Tonnel, A.B. Bronchial neutrophilia in patients with noninfectious status asthmaticus. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1998, 157, 394–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosoki, K.; Ying, S.; Corrigan, C.; Qi, H.; Kurosky, A.; Jennings, K.; Sun, Q.; Boldogh, I.; Sur, S. Analysis of a Panel of 48 Cytokines in BAL Fluids Specifically Identifies IL-8 Levels as the Only Cytokine that Distinguishes Controlled Asthma from Uncontrolled Asthma, and Correlates Inversely with FEV1. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahler, D.A.; Huang, S.; Tabrizi, M.; Bell, G.M. Efficacy and safety of a monoclonal antibody recognizing interleukin-8 in COPD: A pilot study. Chest 2004, 126, 926–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazaar, A.L.; Miller, B.E.; Tabberer, M.; Yonchuk, J.; Leidy, N.; Ambery, C.; Bloomer, J.; Watz, H.; Tal-Singer, R. Effect of the CXCR2 antagonist danirixin on symptoms and health status in COPD. Eur. Respir. J. 2018, 52, 1801020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rennard, S.I.; Dale, D.C.; Donohue, J.F.; Kanniess, F.; Magnussen, H.; Sutherland, E.R.; Watz, H.; Lu, S.; Stryszak, P.; Rosenberg, E.; et al. CXCR2 Antagonist MK-7123. A Phase 2 Proof-of-Concept Trial for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 191, 1001–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moss, R.B.; Mistry, S.J.; Konstan, M.W.; Pilewski, J.M.; Kerem, E.; Tal-Singer, R.; Lazaar, A.L. Safety and early treatment effects of the CXCR2 antagonist SB-656933 in patients with cystic fibrosis. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2013, 12, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linden, A.; Laan, M.; Anderson, G.P. Neutrophils, interleukin-17A and lung disease. Eur. Respir. J. 2005, 25, 159–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nembrini, C.; Marsland, B.J.; Kopf, M. IL-17-producing T cells in lung immunity and inflammation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009, 123, 986–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Stefano, A.; Caramori, G.; Gnemmi, I.; Contoli, M.; Vicari, C.; Capelli, A.; Magno, F.; D’Anna, S.E.; Zanini, A.; Brun, P.; et al. T helper type 17-related cytokine expression is increased in the bronchial mucosa of stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2009, 157, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Huang, L.; Vergis, A.L.; Ye, H.; Bajwa, A.; Narayan, V.; Strieter, R.M.; Rosin, D.L.; Okusa, M.D. IL-17 produced by neutrophils regulates IFN-gamma-mediated neutrophil migration in mouse kidney ischemia-reperfusion injury. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eustace, A.; Smyth, L.J.C.; Mitchell, L.; Williamson, K.; Plumb, J.; Singh, D. Identification of cells expressing IL-17A and IL-17F in the lungs of patients with COPD. Chest 2011, 139, 1089–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doe, C.; Bafadhel, M.; Siddiqui, S.; Desai, D.; Mistry, V.; Rugman, P.; McCormick, M.; Woods, J.; May, R.; Sleeman, M.A.; et al. Expression of the T helper 17-associated cytokines IL-17A and IL-17F in asthma and COPD. Chest 2010, 138, 1140–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pridgeon, C.; Bugeon, L.; Donnelly, L.; Straschil, U.; Tudhope, S.J.; Fenwick, P.; Lamb, J.R.; Barnes, P.J.; Dallman, M.J. Regulation of IL-17 in chronic inflammation in the human lung. Clin. Sci. 2011, 120, 515–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiehler, S.; Proud, D. Interleukin-17A modulates human airway epithelial responses to human rhinovirus infection. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2007, 293, L505-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujisawa, T.; Velichko, S.; Thai, P.; Hung, L.Y.; Huang, F.; Wu, R. Regulation of airway MUC5AC expression by IL-1beta and IL-17A; the NF-kappaB paradigm. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 6236–6243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brodlie, M.; McKean, M.C.; Johnson, G.E.; Anderson, A.E.; Hilkens, C.M.; Fisher, A.J.; Corris, P.A.; Lordan, J.L.; Ward, C. Raised interleukin-17 is immunolocalised to neutrophils in cystic fibrosis lung disease. Eur. Respir. J. 2011, 37, 1378–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, D.; Taylor, P.; Fletcher, D.; van Heeckeren, R.; Eastman, J.; van Heeckeren, A.; Davis, P.; Chmiel, J.F.; Pearlman, E.; Bonfield, T.L. Interleukin-17 Pathophysiology and Therapeutic Intervention in Cystic Fibrosis Lung Infection and Inflammation. Infect. Immun. 2016, 84, 2410–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcorn, J.F.; Crowe, C.R.; Kolls, J.K. TH17 cells in asthma and COPD. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2010, 72, 495–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, Y.R.; Chen, K.; Duncan, S.R.; Lathrop, K.L.; Latoche, J.D.; Logar, A.J.; Pociask, D.A.; Wahlberg, B.J.; Ray, P.; Ray, A.; et al. Patients with cystic fibrosis have inducible IL-17+IL-22+ memory cells in lung draining lymph nodes. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 131, 1117–1129.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAleer, J.P.; Kolls, J.K. Directing traffic: IL-17 and IL-22 coordinate pulmonary immune defense. Immunol. Rev. 2014, 260, 129–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busse, W.W.; Holgate, S.; Kerwin, E.; Chon, Y.; Feng, J.; Lin, J.; Lin, S.L. Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of brodalumab, a human anti-IL-17 receptor monoclonal antibody, in moderate to severe asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 188, 1294–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eich, A.; Urban, V.; Jutel, M.; Vlcek, J.; Shim, J.J.; Trofimov, V.I.; Liam, C.K.; Kuo, P.H.; Hou, Y.; Xiao, J.; et al. A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Phase 2 Trial of CNTO 6785 in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. COPD 2017, 14, 476–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Garth, J.; Barnes, J.W.; Krick, S. Targeting Cytokines as Evolving Treatment Strategies in Chronic Inflammatory Airway Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3402. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113402
Garth J, Barnes JW, Krick S. Targeting Cytokines as Evolving Treatment Strategies in Chronic Inflammatory Airway Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(11):3402. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113402
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarth, Jaleesa, Jarrod W. Barnes, and Stefanie Krick. 2018. "Targeting Cytokines as Evolving Treatment Strategies in Chronic Inflammatory Airway Diseases" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 11: 3402. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113402
APA StyleGarth, J., Barnes, J. W., & Krick, S. (2018). Targeting Cytokines as Evolving Treatment Strategies in Chronic Inflammatory Airway Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(11), 3402. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113402




