Dual Convolutional Neural Network Based Method for Predicting Disease-Related miRNAs
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Performance Evaluation Metrics
2.2. Comparison with Other Methods
2.3. Comparison between the Individual Networks and the Integrated Network
2.4. Case Studies on Breast Cancer, Colorectal Cancer and Lung Cancer
2.5. Predicting Novel Disease-Related miRNAs
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Dataset
3.2. Construction of a miRNA–Disease Heterogeneous Network
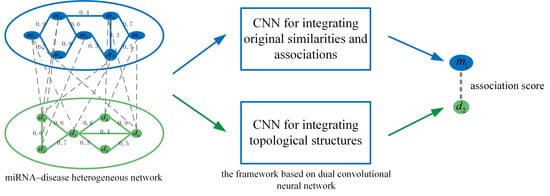
3.3. Prediction Model Based on Dual CNN
3.3.1. Embedding Layer
3.3.2. Convolutional Module on the Left
3.3.3. Convolutional Module on the Right
3.3.4. Combined Strategy
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meister, G.; Tuschl, T. Mechanisms of gene silencing by double-stranded RNA. Nature 2004, 431, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambros, V. microRNAs: Tiny regulators with great potential. Cell 2001, 107, 823–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambros, V. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature 2004, 431, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Guo, M.; Liu, X.; Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; Liu, G. Identify bilayer modules via pseudo-3D clustering: Applications to miRNA-gene bilayer networks. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, e152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calin, G.A.; Croce, C.M. MicroRNA-cancer connection: The beginning of a new tale. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 7390–7394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meola, N.; Gennarino, V.A.; Banfi, S. MicroRNAs and genetic diseases. Pathogenetics 2009, 2, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayed, D.; Abdellatif, M. MicroRNAs in development and disease. Physiol. Rev. 2011, 91, 827–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasquinelli, A.E. MicroRNAs and their targets: Recognition, regulation and an emerging reciprocal relationship. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2012, 13, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Q.; Hao, Y.; Wang, G.; Juan, L.; Zhang, T.; Teng, M.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y. Prioritization of disease microRNAs through a human phenome-microRNAome network. BMC Syst. Boil. 2010, 4, S2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Wang, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Lv, S.; Ning, S.; Sun, J.; Huang, T.; Zheng, Q.; Ren, H.; Xu, J.; et al. Prioritizing human cancer microRNAs based on genes’ functional consistency between microRNA and cancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, e153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, B.P.; Shih, I.H.; Jones-Rhoades, M.W.; Bartel, D.P.; Burge, C.B. Prediction of mammalian microRNA targets. Cell 2003, 115, 787–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, B.; Enright, A.J.; Aravin, A.; Tuschl, T.; Sander, C.; Marks, D.S. Human microRNA targets. PLoS Biol. 2004, 2, e363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kertesz, M.; Iovino, N.; Unnerstall, U.; Gaul, U.; Segal, E. The role of site accessibility in microRNA target recognition. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Yan, C.C.; Zhang, X.; You, Z.H.; Deng, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Dai, Q. WBSMDA: Within and between score for miRNA-disease association prediction. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasquier, C.; Gardès, J. Prediction of miRNA-disease associations with a vector space model. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, J.Q.; Rong, Z.H.; Chen, X.; Yan, G.Y.; You, Z.H. MCMDA: Matrix completion for miRNA-disease association prediction. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 21187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, W.; Wang, J.; Li, M.; Liu, J.; Wu, F.X.; Pan, Y. Predicting microRNA-disease associations based on improved microRNA and disease similarities. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Boil. Bioinform. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Y.; Xuan, P.; Wang, X.; Zhang, T.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, W. A non-negative matrix factorization based method for predicting disease-associated miRNAs in miRNA-disease bilayer network. Bioinformatics 2017, 34, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Q.; Luo, J.; Liang, C.; Cai, J.; Ding, P. A graph regularized non-negative matrix factorization method for identifying microRNA-disease associations. Bioinformatics 2017, 34, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zeng, X.; He, Z.; Zou, Q. Inferring microRNA-disease associations by random walk on a heterogeneous network with multiple data sources. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Boil. Bioinform. 2017, 14, 905–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Liao, B.; Li, Z. Global Similarity Method Based on a Two-tier Random Walk for the Prediction of microRNA–Disease Association. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, X.; Liu, L.; Lü, L.; Zou, Q.; Valencia, A. Prediction of potential disease-associated microRNAs using structural perturbation method. Bioinformatics 2018, 1, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, Z.H.; Huang, Z.A.; Zhu, Z.; Yan, G.Y.; Li, Z.W.; Wen, Z.; Chen, X. PBMDA: A novel and effective path-based computational model for miRNA-disease association prediction. PLoS Comput. Boil. 2017, 13, e1005455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zou, Q.; Rodriguez-Paton, A. Meta-path methods for prioritizing candidate disease miRNAs. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Boil. Bioinform. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Wang, M.; Sun, D.; Li, A. A novel method for identifying potential disease-related miRNAs via a disease–miRNA–target heterogeneous network. Mol. BioSyst. 2017, 13, 2328–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, X.; Zhang, X.; Zou, Q. Integrative approaches for predicting microRNA function and prioritizing disease-related microRNA using biological interaction networks. Brief. Bioinform. 2015, 17, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zou, Q.; Li, J.; Song, L.; Zeng, X.; Wang, G. Similarity computation strategies in the microRNA-disease network: A survey. Brief. Funct. Genom. 2015, 15, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Q.; Chen, L.; Huang, T.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, Y. Machine learning and graph analytics in computational biomedicine. Artif. Intell. Med. 2017, 83, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Luo, J.; Zhao, W.; Zhou, X. Deep learning of the splicing (epi)genetic code reveals a novel candidate mechanism linking histone modifications to ESC fate decision. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 12100–12112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, Z.; Ren, F.; Liu, C.; He, S.; Sun, G.; Gao, Q.; Yao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Miao, R.; Cao, Y.; et al. dbDEMC: A database of differentially expressed miRNAs in human cancers. BMC Genom. 2010, 11, S5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, B.; Ding, Q.; Han, H.; Wu, D. miRCancer: A microRNA–cancer association database constructed by text mining on literature. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 638–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruepp, A.; Kowarsch, A.; Schmidl, D.; Buggenthin, F.; Brauner, B.; Dunger, I. PhenomiR: A knowledgebase for microRNA expression in diseases and biological processes. Genome Boil. 2010, 11, R6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Jiang, D.R.; Xu, C.C.; Zhu, G.L.; Wu, Z.S.; Wu, Q. Differential expression profile analysis of miRNAs with HER-2 overexpression and intervention in breast cancer cells. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2017, 10, 5039–5062. [Google Scholar]
- Maltseva, D.V.; Galatenko, V.V.; Samatov, T.R.; Zhikrivetskaya, S.O.; Khaustova, N.A.; Nechaev, I.N.; Shkurnikov, M.U.; Lebedev, A.E.; Mityakina, I.A.; Kaprin, A.D.; et al. miRNome of inflammatory breast cancer. BMC Res. Notes 2014, 7, 871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.Y.; Yi, W.; Zhang, M.Y.; Xu, R.; Zeng, L.S.; Long, X.R.; Zhou, X.; Zheng, X.; Kang, Y.; Wang, H.Y. MicroRNA-711 is a prognostic factor for poor overall survival and has an oncogenic role in breast cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 11, 2155–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, J.; Zhou, X.; Wong, C.W. Genome-wide identification of estrogen receptor alpha regulated miRNAs using transcription factor binding data. Bioinform.-Trends Methodol. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Su, B.; Zhang, P.; Xie, H.; Zheng, H.; Xu, Y.; Du, Q.; Zeng, H.; Zhou, X.; Chen, C.; et al. Expression of miR-150 and miR-3940-5p is reduced in non-small cell lung carcinoma and correlates with clinicopathological features. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 29, 704–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Qiu, C.; Tu, J.; Geng, B.; Yang, J.; Jiang, T.; Cui, Q. HMDD v2.0: A database for experimentally supported human microRNA and disease associations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 42, D1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Wang, J.; Lu, M.; Song, F.; Cui, Q. Inferring the human microRNA functional similarity and functional network based on microRNA-associated diseases. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 1644–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xuan, P.; Han, K.; Guo, Y.; Li, J.; Li, X.; Zhong, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Ding, J. Prediction of potential disease-associated microRNAs based on random walk. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1805–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.9 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ROC-AUC | 0.890 | 0.918 | 0.934 | 0.939 | 0.946 | 0.950 | 0.952 | 0.954 | 0.956 |
| PR-AUC | 0.340 | 0.401 | 0.442 | 0.462 | 0.491 | 0.503 | 0.513 | 0.521 | 0.538 |
| Disease Name | ROC-AUC CNNDMP | GSTRW | DMPred | PBMDA | Liu’s Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Breast neoplasm | 0.987 | 0.822 | 0.938 | 0.852 | 0.863 |
| Hepatocellular carcinoma | 0.986 | 0.779 | 0.900 | 0.803 | 0.845 |
| Renal cell carcinoma | 0.950 | 0.816 | 0.903 | 0.813 | 0.832 |
| Squamous cell carcinoma | 0.936 | 0.817 | 0.908 | 0.881 | 0.890 |
| Colorectal neoplasm | 0.910 | 0.737 | 0.842 | 0.826 | 0.857 |
| Glioblastoma | 0.926 | 0.814 | 0.904 | 0.803 | 0.842 |
| Heart failure | 0.972 | 0.817 | 0.987 | 0.791 | 0.828 |
| Acute myeloid leukemia | 0.961 | 0.788 | 0.890 | 0.844 | 0.874 |
| Lung neoplasm | 0.962 | 0.791 | 0.948 | 0.905 | 0.920 |
| Melanoma | 0.978 | 0.789 | 0.913 | 0.836 | 0.860 |
| Ovarian neoplasm | 0.958 | 0.830 | 0.929 | 0.889 | 0.897 |
| Pancreatic neoplasm | 0.945 | 0.838 | 0.916 | 0.891 | 0.904 |
| Prostatic neoplasm | 0.964 | 0.822 | 0.951 | 0.843 | 0.855 |
| Stomach neoplasm | 0.954 | 0.762 | 0.908 | 0.821 | 0.836 |
| Urinary bladder neoplasm | 0.956 | 0.816 | 0.919 | 0.854 | 0.865 |
| Average AUC | 0.956 | 0.802 | 0.917 | 0.844 | 0.865 |
| Diseases Name | PR-AUC CNNDMP | GSTRW | DMPred | PBMDA | Liu’s Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Breast neoplasm | 0.894 | 0.322 | 0.699 | 0.574 | 0.573 |
| Hepatocellular carcinoma | 0.893 | 0.279 | 0.501 | 0.454 | 0.498 |
| Renal cell carcinoma | 0.365 | 0.150 | 0.293 | 0.181 | 0.186 |
| Squamous cell carcinoma | 0.287 | 0.109 | 0.213 | 0.211 | 0.208 |
| Colorectal neoplasm | 0.367 | 0.141 | 0.186 | 0.367 | 0.371 |
| Glioblastoma | 0.330 | 0.151 | 0.219 | 0.217 | 0.243 |
| Heart failure | 0.602 | 0.191 | 0.700 | 0.168 | 0.189 |
| Acute myeloid leukemia | 0.368 | 0.140 | 0.211 | 0.191 | 0.236 |
| Lung neoplasms | 0.636 | 0.147 | 0.511 | 0.537 | 0.503 |
| Melanoma | 0.657 | 0.171 | 0.389 | 0.363 | 0.397 |
| Ovarian neoplasm | 0.490 | 0.169 | 0.404 | 0.361 | 0.361 |
| Pancreatic neoplasm | 0.555 | 0.137 | 0.329 | 0.364 | 0.354 |
| Prostatic neoplasm | 0.568 | 0.166 | 0.463 | 0.282 | 0.264 |
| Stomach neoplasm | 0.608 | 0.220 | 0.446 | 0.344 | 0.346 |
| Urinary bladder neoplasm | 0.470 | 0.163 | 0.315 | 0.252 | 0.280 |
| Average AUC | 0.538 | 0.177 | 0.392 | 0.324 | 0.334 |
| p-Value | DMPred | GSTRW | PBMDA | Liu’s Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| p-value of ROC-AUC between CNNDMP and other methods | 6.44998 × 10−4 | 9.60973 × 10−16 | 2.65553 × 10−10 | 1.25344 × 10−10 |
| p-value of PR-AUC between CNNDMP and other methods | 0.02972 | 1.75747 × 10−6 | 0.00111 | 0.00151 |
| Rank | miRNA Name | Evidence | Rank | miRNA Name | Evidence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | hsa-mir-1266 | dbDEMC | 26 | hsa-mir-663 | dbDEMC |
| 2 | hsa-mir-942 | dbDEMC | 27 | hsa-mir-545 | dbDEMC |
| 3 | hsa-mir-384 | dbDEMC | 28 | hsa-mir-525 | dbDEMC |
| 4 | hsa-mir-374b | dbDEMC | 29 | hsa-mir-520f | dbDEMC |
| 5 | hsa-mir-1293 | dbDEMC | 30 | hsa-mir-520g | dbDEMC |
| 6 | hsa-mir-3148 | Literature [34] | 31 | hsa-mir-659 | dbDEMC |
| 7 | hsa-mir-569 | Literature [35] | 32 | hsa-mir-150 | miRCancer, PhenomiR |
| 8 | hsa-mir-431 | dbDEMC | 33 | hsa-mir-592 | dbDEMC |
| 9 | hsa-mir-711 | Literature [36] | 34 | hsa-mir-1254 | dbDEMC |
| 10 | hsa-mir-325 | dbDEMC | 35 | hsa-mir-548c | dbDEMC |
| 11 | hsa-mir-1302 | Literature [37] | 36 | hsa-mir-675 | miRCancer |
| 12 | hsa-mir-33a | dbDEMC | 37 | hsa-mir-3940 | Literature [38] |
| 13 | hsa-mir-1246 | dbDEMC | 38 | hsa-mir-1299 | dbDEMC |
| 14 | hsa-mir-376b | dbDEMC | 39 | hsa-mir-377 | dbDEMC |
| 15 | hsa-mir-487a | dbDEMC | 40 | hsa-mir-519a | dbDEMC |
| 16 | hsa-mir-1236 | dbDEMC | 41 | hsa-mir-1180 | dbDEMC |
| 17 | hsa-mir-548a | dbDEMC | 42 | hsa-mir-1184 | dbDEMC |
| 18 | hsa-mir-624 | dbDEMC | 43 | hsa-mir-3151 | dbDEMC |
| 19 | hsa-mir-633 | dbDEMC | 44 | hsa-mir-627 | dbDEMC |
| 20 | hsa-mir-1181 | dbDEMC | 45 | hsa-mir-1273a | dbDEMC |
| 21 | hsa-mir-382 | dbDEMC | 46 | hsa-mir-1972 | dbDEMC |
| 22 | hsa-mir-448 | dbDEMC | 47 | hsa-mir-208a | dbDEMC, PhenomiR |
| 23 | hsa-mir-583 | dbDEMC | 48 | hsa-mir-668 | dbDEMC |
| 24 | hsa-mir-518a | dbDEMC | 49 | hsa-mir-635 | dbDEMC |
| 25 | hsa-mir-433 | dbDEMC | 50 | hsa-mir-619 | dbDEMC |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xuan, P.; Dong, Y.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, T.; Liu, Y. Dual Convolutional Neural Network Based Method for Predicting Disease-Related miRNAs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3732. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19123732
Xuan P, Dong Y, Guo Y, Zhang T, Liu Y. Dual Convolutional Neural Network Based Method for Predicting Disease-Related miRNAs. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(12):3732. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19123732
Chicago/Turabian StyleXuan, Ping, Yihua Dong, Yahong Guo, Tiangang Zhang, and Yong Liu. 2018. "Dual Convolutional Neural Network Based Method for Predicting Disease-Related miRNAs" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 12: 3732. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19123732
APA StyleXuan, P., Dong, Y., Guo, Y., Zhang, T., & Liu, Y. (2018). Dual Convolutional Neural Network Based Method for Predicting Disease-Related miRNAs. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(12), 3732. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19123732