Abstract
Calcium (Ca2+) is a universal second messenger involved in various cellular processes, leading to plant development and to biotic and abiotic stress responses. Intracellular variation in free Ca2+ concentration is among the earliest events following the plant perception of environmental change. These Ca2+ variations differ in their spatio-temporal properties according to the nature, strength and duration of the stimulus. However, their conversion into biological responses requires Ca2+ sensors for decoding and relaying. The occurrence in plants of calmodulin (CaM) but also of other sets of plant-specific Ca2+ sensors such as calmodulin-like proteins (CMLs), Ca2+-dependent protein kinases (CDPKs) and calcineurin B-like proteins (CBLs) indicate that plants possess specific tools and machineries to convert Ca2+ signals into appropriate responses. Here, we focus on recent progress made in monitoring the generation of Ca2+ signals at the whole plant or cell level and their long distance propagation during biotic interactions. The contribution of CaM/CMLs and CDPKs in plant immune responses mounted against bacteria, fungi, viruses and insects are also presented.
Keywords:
biotic stress responses; calcium; calcium signature; calmodulin; CMLs; CDPKs; plant immunity; symbiosis 1. Introduction
Like all living organisms, plants face environmental challenges that can be either of a biotic nature such as interactions with pathogens (e.g., bacteria, fungi, oomycetes, viruses, insects) or of an abiotic nature such as drought, soil salinity, air pollution, extreme temperatures and mechanical injury [1]. These adverse conditions often limit growth and productivity of crops worldwide. The expected global temperature elevation in the coming years and associated climate modifications are creating ever-greater challenges for agriculture [2,3]. To adapt to adverse growth conditions, plants must be able to detect the nature and strength of environmental stimuli, interpret them and activate appropriate physiological responses [3]. Among signalling elements that are involved in plant stress responses and particularly during immune responses to pathogens, reactive oxygen species (ROS) and Ca2+ ions are among the earliest actors that coordinate plant adaptive responses [4,5,6,7]. The oxidative burst was first described in 1983 following Potato infection by the oomycete Phytophtora infestans [8], whereas the importance of Ca2+ signalling in plant immunity was reported in tobacco following Pseudomonas syringae inoculation in 1990 [9]. A close connection was then established between ROS and Ca2+ signalling pathways in plant immunity [10].
In this review, we will focus on the importance of Ca2+, a ubiquitous and versatile second messenger [11], in plant biotic interactions. To become informative, the Ca2+ message needs to be decoded and relayed in order to activate the appropriate cell response and this is carried out by Ca2+-binding proteins termed Ca2+ sensors [12]. The complex spatiotemporal patterns of Ca2+ changes at cellular and tissue levels (frequency, amplitude, and distribution within the cell) are proposed to carry information and are denoted as the Ca2+ signature [13,14] (Figure 1). The Ca2+ signature encodes a first layer of specificity and will be considered first, with a particular emphasis on how methods to monitor Ca2+ signatures have evolved and brought new information. Ca2+-binding proteins and their downstream targets provide a second layer of specificity. Most Ca2+-binding proteins are characterized by the presence in their sequence of the canonical Ca2+-binding motif called the EF-hand [15]. For example, the plant model Arabidopsis thaliana encodes at least 250 EF-hand-containing proteins [16]. This number is much higher than in mammals and notably, the majority of plant Ca2+ sensors do not have homologs in others organisms [17,18]. However, only about half of them have been considered as Ca2+ sensors [17]. These plant Ca2+ sensors are classified into four major groups: the calcineurin B-like (CBL), the Ca2+-dependent protein kinases (CDPK), the calmodulin (CaM) group and its closely related group, the Calmodulin-like protein (CML) family [17,19]. Calmodulin (CaM) is one of the most studied eukaryotic proteins and has been shown to interact with and modulate the activity of numerous target proteins [20]. Plants also possess a remarkable repertoire of CaM-related proteins termed CMLs (7 CaM and 50 CMLs genes in Arabidopsis) that are not present in animals, as is also the case for CBLs and CDPKs (ten and 34 genes in Arabidopsis, respectively) [21,22]. To date, the roles of most of these Ca2+ sensors remain unknown but recent studies have pointed out the roles for some of them in physiological processes associated with development, abiotic plant stress responses and plant immunity [23,24,25]. Here, we present recent and relevant data about CaM, CMLs and CDPKs and their involvement in plant responses to various biotic stresses.
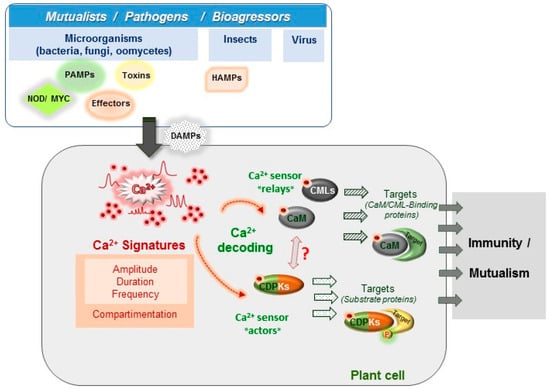
Figure 1.
Key steps in Ca2+ signaling pathways during plant biotic interactions. Plants are exposed to diverse microorganisms, pests or other aggressors leading to beneficial or detrimental interactions. Plant cells possess a large repertoire of sensors that allow to perceive, discriminate and transduce different signals during plant immunity (Pathogen-Associated Molecular Patterns (PAMPs) , effectors, toxins, Damage-Associated Molecular Patterns (DAMPs) or Herbivory-Associated Molecular Patterns (HAMPs)) or during the interaction with mutualistic organisms (Nod and Myc Factors). In response to different stimuli, the earliest steps rely on specific cytosolic Ca2+ rises termed calcium signatures occurring in the cytosol and in organelles, including nucleus (Section 2.1). These calcium signatures differ by their spatio-temporal properties and encode a first layer of specificity. A second layer of specificity, relies on the decoding of these calcium transients (Section 3). Ca2+ binds to a plethora of sensors such as calmodulin (CaM), CaM-like proteins (CML), calcium-dependent protein kinases (CDPK) that activate target proteins either by direct binding or through phosphorylation (P).
2. Ca2+ Signatures as the Earliest Signalling Events in Plant-Organism Interactions
2.1. Discovering the Importance of Ca2+ Signalling in Biotic Interactions
Free Ca2+ is a universal second messenger, and increases in cytosolic Ca2+ concentration are among the earliest signalling events occurring in plants challenged with mutualistic or pathogenic partners. If we consider plant-pathogen interactions, the plant immune system is schematically organized as a two-tiered system composed of Pathogen-Associated Molecular Patterns (PAMP)-Triggered Immunity (PTI) and Effector-Triggered Immunity (ETI) [26]. Activation of PTI enhances overall plant defence and protects plants from subsequent pathogen attack [27] while activation of ETI often culminates in a localized programmed cell death (PCD) also referred to as the Hypersensitive Response (HR), which blocks pathogen invasion. These immune layers also differ in their Ca2+ signature. For instance, PTI activation involves Ca2+ transients that returns to basal levels within minutes [28] whereas ETI is associated with a prolonged cytosolic Ca2+ increase that can last for hours [29]. The generic Ca2+ channel blocker lanthanum strongly impairs the immune responses associated with both types of plant immunity [29,30], thereby placing Ca2+ signals and their decoders at the centre of immune signalling pathways.
Ca2+ elevations during immune signalling are critical for the control of gene reprogramming which is required to mount the adequate responses (e.g., symbiosis or defence). Such widely acknowledged importance of these Ca2+ variations in plant signalling has been made possible through the emergence in the early 1990s of tools allowing the monitoring of the dynamics of Ca2+ changes in plant cells. The pioneering work of Trewavas’s group and his collaborators demonstrated the occurrence of Ca2+ variations in plant cells using the fluorescent Fluo3 Ca2+ indicator and caged Ca2+ or IP3 as triggers [31]. His group then opened a new research avenue mainly through the application, for the first time in plants, of the non-invasive, organelle-addressable and highly dynamic Ca2+ probe aequorin [32]. The use of aequorin allowed tremendous progress in our current understanding of how Ca2+ controls plant adaptive responses. In the seminal paper reporting the use of aequorin in plants, Knight et al. established for the first time that biotic stimuli consisting of various yeast preparations were able, like abiotic stimuli, to trigger Ca2+ signals in tobacco seedlings [32]. This result suggested that the Ca2+ cation should be taken into consideration as an important second messenger in studies dealing with plant-microbe or plant-pest interactions. Due to the numerous studies available in the literature, we will focus in this section, more specifically on several well-documented examples illustrating how exploiting the diversity of Ca2+ probes has contributed to increasing our knowledge on the role of Ca2+ during plant immunity, symbiosis and response to herbivory attacks.
Chandra and Low pointed out the advantages of the aequorin probe versus other available Ca2+ sensors [33]. Using a suspension of aequorin-transformed tobacco cells, they reported that oligogalacturonic acid, a pectin-derived component, was able to induce plant defence and to generate a Ca2+ response followed by a delayed oxidative burst [34,35]. Using a pharmacological approach, they demonstrated that the oxidative burst was fully dependent on the Ca2+ response. This result was among the first to suggest a possible role of Ca2+ transients in the ROS-mediated defence signalling pathway [33]. At the same time, Mithoefer et al. established a similar link between cytosolic Ca2+ increases and defence responses using chitotetraose, a fungal cell wall component and β-glucans. A sustained high Ca2+ concentration response was observed in the case of β-glucans while this was not the case with the chitotetraose [36]. The sustained Ca2+ increase generated after β-glucan application was linked to the increase of a major soybean phytolalexin glyceollin [36]. One year later, Blume et al. demonstrated that a Phytophtora sojae-derived peptide (Pep 13) elicited a biphasic Ca2+ variation due to an influx of extracellular Ca2+ in parsley cells stably expressing aequorin. Only the sustained Ca2+ variation reaching a concentration around 250–300 nM could be associated with ROS and phytoalexin production [37]. Interestingly, stimuli that triggered only the first transient peak were unable to stimulate phytoalexin production [37]. Similarly, the use of Nicotiana plumbaginifolia cells stably expressing cytosolic aequorin challenged with the Phytophtora cryptogea elicitin “cryptogein” allowed us to demonstrate that oligogalacturonic acids and cryptogein each elicit a very specific cytosolic Ca2+ response [38]. After a lag phase of 1–2 min, the cryptogein-induced Ca2+ response appeared as a biphasic Ca2+ increase with a first transient peak lasting 10 min followed by a sustained increase. Suppression of this sustained Ca2+ phase using the Ca2+ channel blocker lanthanum chloride just after the first Ca2+ transient, resulted in the suppression of MAPK activation, accumulation of PAL and hsr203j immune-related gene transcripts and induced cell death [38].
Most of the above studies were performed with elicitors of various nature and origin coming from fungal or bacterial pathogens such as Microbe Associated Molecular Patterns (MAMPs) or compounds derived from the activity of pathogens on plant cell walls, the Damage-Associated Molecular Patterns (DAMPs) [39,40]. Similarly, elicitors can originate from herbivores and are named Herbivore Associated-Molecular Patterns (HAMPS). They are found in oral secretions or oviposition fluids of insects (for a review see [41]). HAMPs have also been shown to induce cytosolic Ca2+ variations, for example in lima bean leaves incubated with the fluorescent Ca2+ probe Fluo3-AM or in soybean cell cultures expressing cytosolic aequorin. Spodoptera littoralis larvae bites elicited a Ca2+ response on the margin of the leaves within a delimited region of 30 to 200 µm from the bite zone whereas several components from the larvae regurgitate such as linolenoyl-L-Glutamine or volicitin were able to elicit Ca2+ transients in soybean cells [42]. These Ca2+ transients are correlated with early membrane depolarization/hyperpolarization events that are known to be linked to plant defence responses through systemin synthesis, ROS and jasmonate signalling (for a review see [43]).
These few examples showing that different elicitors trigger different Ca2+ variations reinforced the concept of the Ca2+ signature [13,14]. This concept postulates that a specific Ca2+ variation is defined by its form, amplitude, frequency, duration, spatial localization and the Ca2+ pool involved. All these parameters are tightly linked to the nature and strength of the stimulus perceived by the cell. Subsequent studies performed on guard cells largely corroborated this concept. Artificial modulation of the frequency, transient number of spikes, duration and amplitude of Ca2+ oscillations were found to control the degree of long-term steady-state stomata closure [44]. Other findings supporting the Ca2+ signature concept come from work performed with Medicago truncatula plants expressing the Ca2+ probe cameleon YC2.1. Using a pharmacological approach modulating Ca2+ homeostasis, the authors were able to demonstrate a link between the bacterial Nod factor-induced Ca2+ oscillations and the activation of some selected nodulation markers genes. For example, the induction of the ENOD11 nodulin gene required about 30 consecutive Ca2+ spikes [45].
2.2. Monitoring Ca2+ Transients at the Whole Tissue or Organism Level
Most of the initial studies on Ca2+ variations in plant immunity were performed with elicitors and cultured cells. Although convenient, this model cannot inform us about the downstream events activated during genuine plant-microorganism or plant-pest interactions, such as cell-to-cell communication leading to long distance and systemic signalling. Pathogen elicitors only mimic the recognition step when surface motifs of pathogens are recognized by pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) of the host [7]. In addition to this recognition of surface motifs, pathogens also inject effectors into the plant cell to modulate plant defence responses [46]. Therefore, if we consider pathogenic bacteria, both compatible and incompatible strains possess the same PAMPs but in the first case the interaction leads to plant susceptibility while in the second case the interaction may lead to plant resistance through the execution of the HR due to effector recognition by plant resistance (R) genes [47,48]. Aequorin allows long kinetic studies due to its stability in the cell [49]. It has enabled the analysis of Ca2+ signalling in whole plants challenged with a microorganism (pathogen, symbiont) or insect, in a non-destructive manner. One of the first examples of such studies, was the monitoring of Ca2+ response in Arabidopsis leaves stably expressing aequorin under control of the 35S promoter challenged either with the compatible strain of Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000 or with incompatible strains carrying the avirulence genes avrRPM1 or avrB, both detected by the resistance Arabidopsis RPM1 protein [29]. In this study, the authors showed that the compatible strain elicited a transient Ca2+ peak lasting about 10 min and peaking between 8–12 min whereas the incompatible strains avrRPM1 and avrB induced an additional delayed peak giving a maximal increase at around 105 ± 10 and 137 ± 7 min, respectively [29]. This second peak was dependent on a functional type III secretion apparatus because DC3000 mutants in this secretion system did not induce this second Ca2+ response. In addition, Arabidopsis rpm1 mutant failed to generate the second Ca2+ peak and the HR. Thus, the aequorin technology allowed, in this specific case, to make a clear correlation between the delayed Ca2+ peak and the gene for gene interactions responsible for the HR response.
In symbiotic interaction studies, the use of Oregon-dextran dye injected in root hair cells by iontophoresis demonstrated that two important genes in the rhizobia symbiosis were involved upstream of the Ca2+ spikes [50]. Using the same fluorescent Ca2+ probe, this group demonstrated two years later that spatiotemporal Ca2+ spiking studies were helpful in understanding the regulation of nod gene expression. Indeed, they showed that strains differing by their ability to produce Nod factor could be differentiated by the Ca2+ oscillations they induce. Thus, two strains derived from the same parent displayed large differences in the kinetics of Ca2+ spiking; Rm1021 triggered a robust Ca2+ spiking after a lag phase of 10–15 min in more than 50% of the root hair cells whereas Rm2011 did not [51]. The new generation of available genetically encoded Ca2+ probes [52] facilitated the measurement of Ca2+ responses at the organ and cell level during symbiotic relationships with rhizobia and mycorrhizal fungi. Kosuta et al. [53] were able to compare and discriminate the two types of symbiosis through their induced Ca2+ oscillations. They demonstrated that the two symbiotic pathways require both DMI1 and DMI2 for both the establishment of functional symbiosis and also for the generation of Ca2+ oscillations. This result indicates that Ca2+ oscillations are also required for plant colonization by rhizobia or mycorrhizal fungi. Interestingly, the symbiotic fungus induced a Ca2+ oscillation that differs from the Nod-factor-induced Ca2+ oscillations by its amplitude and its periodicity [53]. In the bacterial symbiotic model, the use of nucleoplasmin-tagged cameleon (NupYC2.1) Ca2+ probe demonstrated a regular nuclear Ca2+ spiking in Medicago root hairs challenged with Nod Factors [54].
2.3. Systemic Ca2+ Signalling during Plant Defence
The whole plant approach allowed researchers to detect long-range Ca2+ waves, but most of these studies were performed in response to abiotic stimuli and were exploiting either cameleon derivatives such as the YCNano-65 FRET sensor [55,56] or Bioluminescence Resonance Energy Transfer (BRET) [57]. Using the BRET system, Ca2+ waves propagating from the root to the shoot were reported in response to salt [57]. A similar study reported comparable Ca2+ waves and that the Two-Pore Channel (TPC1) vacuolar plant Ca2+ channel appeared to be a main player in this spreading [55]. To our knowledge, in response to biotic stimuli, the most significant data displaying systemic Ca2+ responses have come from plant–insect interactions [58]. Wounding or caterpillar feeding on a specific Arabidopsis leaf was found to elicit Ca2+ signals on the neighbouring leaves. Interestingly, TPC1 appeared to be involved in the systemic propagation of the Ca2+ wave but not to be involved in the generation of the primary Ca2+ transient observed at the feeding point [58]. The recent emergence of intensity-based Ca2+ sensors has made it possible to evaluate the spatio-temporal specificity of immune responses as well as the direction in which the PAMP-induced Ca2+ waves propagate [59]. Using R-GECO as an intensity-based Ca2+ sensor, Keinath et al. studied Ca2+ responses induced by Pathogen-Associated Molecular Patterns (PAMPS) such as flagellin and chitin [60]. They showed that flagellin, known to induce monophasic Ca2+ variations in cultured cells when Ca2+ changes are monitored with aequorin, was also able to induce Ca2+ variations in roots. They localized these variations to the elongation zone where callose deposition takes place and immune-responsive genes are upregulated supporting a clear correlation between Ca2+ changes and defence responses [60].
Overall, these few examples highlight the complexity of Ca2+ signalling and illustrate how monitoring Ca2+ signals at the cell tissue or whole plant level and the use of alternative Ca2+ probes from the available panel can be very helpful to decipher both immune and symbiotic responses.
3. Ca2+ Decoding Processes and Plant Immunity
The information encrypted by Ca2+ signals previously described (Section 2.1) needs to be decoded and relayed by Ca2+ binding proteins in order to be converted into biological responses (Figure 1). Following Ca2+ binding, sensors undergo conformational changes leading either to the regulation of their own catalytic activity or to their interaction with target proteins [61]. In plants, Ca2+ sensors are classified into three sub-groups including calmodulin (CaM) and calmodulin-like proteins (CMLs), Ca2+-dependent protein kinases (CDPKs) and calcineurin B-Like proteins (CBLs) (for reviews see [62,63,64,65]). In this review, we will focus and present information on CaM, CMLs and CDPKs, due to increasing evidence for their involvement in plant immunity. The importance of Ca2+ signalling in symbiosis has been recently reviewed, as well as the function of CBLs, which are mainly related to the regulation of membrane proteins involved in plant development, nutrition and abiotic stress [65].
3.1. CaM and CaM Binding Proteins in Plant Immune Responses
CaM is the prototype of a Ca2+-binding protein and is found in all eukaryotic cells. CaM acts as part of a Ca2+ signalling pathway by modifying its interactions with various CaM-binding proteins (CaMBP). Genome analysis of the model plant A. thaliana revealed the presence of 3 distinct CaM isoforms (encoded by seven genes) [17,66]. Until now, most of our knowledge about CaM mainly relies on the identification of the repertoire of CaMBPs [67]. During the last decade, the development of large scale yeast two-hybrid protein array screens, as well as proteomic analyses, increased our knowledge of CaM targets [67,68,69]. We can conclude from these analyses that CaM exerts a regulatory role on a wide variety of cellular processes by modulating the activity of various proteins such as channels, enzymes and transcriptional regulators [5,68,70,71]. Although many CaM-binding transcription factors (TFs) have been identified in diverse families of DNA binding proteins including plant-specific TFs [5,72], in most cases, the biological significance of the interaction with CaM remains to be elucidated.
CaMBPs with predicted or demonstrated functions during plant immunity have been reported [5,24]. For example, several pathogen-induced CaM-binding TFs have been associated with plant defence responses by acting on homeostasis regulation by salicylic acid (SA), a defence-associated hormone in plants [63,73]. The production of SA in A. thaliana infected cells is enhanced by up-regulation of the expression of ICS1 (Isochorismate synthase 1) and EDS1 (Enhanced Disease Susceptibility 1) genes and the expression of ICS1 and EDS1 is positively and negatively controlled by CBP60g and CAMTA3/AtSR1, respectively, two CaM-binding TFs [73,74,75].
CBP60g belongs to a plant-specific DNA-binding protein family comprising eight members in Arabidopsis [74,76,77]. The cbp60g knock-out mutant exhibits defects in pathogen-induced SA accumulation and shows enhanced susceptibility to the Pseudomonas syringae phytopathogenic bacteria [74]. A variant of CBP60g unable to bind CaM, does not restore SA production and defence and failed to complement the cbp60g mutant. This shows the importance of CaM in regulating CBP60g function and its contribution to plant immunity [74]. The role of other CBP60g-related proteins have been explored during plant–microbe interaction and to date, only CBP60a seems to contribute to plant immunity [77]. If CaM-binding is also crucial for the biological function of CBP60a, cbp60a mutations reduced P. syringae growth in planta, indicating that CBP60a acts as a negative regulator of immunity whereas CPB60g acts as a positive regulator [77]. Moreover, it was recently demonstrated that CML46 and CML47 negatively control SA accumulation in Arabidopsis and that this effect is genetically linked and additive to that of CBP60a [78]. Altogether, these data indicate a complex regulation of SA-dependent processes involving related TFs possessing (or not) CaM-binding activity and highlight the importance of the Ca2+-CaM/CML complex in the activation of immune responses.
The CBP60 transcriptional regulator family is not the only one regulated by Ca2+ and CaM. Indeed, the CaM-binding Transcription Activator (CAMTA) family certainly constitutes one of the most important Ca2+/CaM-regulated TF families in plants [79,80]. CAMTAs are key players in various plant biological processes including disease resistance and abiotic stress tolerance [81]. One of the pioneer studies concerned the functional analysis of CAMTA3, also known as AtSR1 (Arabidopsis thaliana Signal Responsive 1), in plant defence responses against pathogens [82] and its contribution as a negative regulator of the SA pathway [75]. Arabidopsis camta3/Atsr1 Knock-Out mutants display elevated SA levels, high expression of EDS1 and constitutive defence responses. CaM binding is crucial for the function of CAMTA3 in the control of SA production and defence [75]. Surprisingly, camta3 mutants are more resistant to P. syringae, Botrytis cinerea and Sclerotinia sclerotiorum [82,83] but are more susceptible to insect attack (i.e., Trichophusia) [83]. These data suggest that CAMTA3 negatively regulates plant defence against biotrophic and necrotrophic pathogens by controlling endogenous levels of SA [75,82]. In addition, CAMTA3 was proposed to control plant resistance to herbivory insects through the regulation of glucosinolates metabolism [84,85].
Other studies revealed additional roles for CAMTA3/AtSR1 in defence. For instance, AtCAMTA3 negatively regulates plant immunity following PAMP recognition as well as non-host resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae [80]. CAMTA3 may negatively regulate PTI (PAMP-triggered Immunity) by targeting BAK1 [83]. More recently, a transcriptome comparative analysis using CAMTA modified transgenic plants has demonstrated activation of defence genes involved in both PTI and ETI (Effector-Triggered Immunity), suggesting that CAMTA could define an early convergence point in these two signalling pathways [86]. To date, it has not yet been elucidated how CaM can balance the activation of CBP60g and/or CAMTA3 upon pathogen attack with how the Ca2+ signatures are integrated in this transcriptional pathway. Efforts are being made in this perspective and dynamic mathematical models incorporating several parameters are being developed with the aim of predicting regulation networks according to the generated Ca2+ signatures [87,88].
Although the CaM contribution in plant immunity was mainly revealed by the identification of CaMBP, it is now clear how CaM plays a pivotal role in the fine tuning of immune responses by acting either as a positive or a negative regulator of defence responses. Identification of the whole set of CaMBPs is certainly not complete and other CaM-binding TFs including several members of TGA, WRKY, MYB and NAC families also contribute to plant immunity either positively or negatively [63,88,89]. For example, TGA3 and several WRKY transcription factors such as WRKY7 and WRKY53 can interact with CaM in a Ca2+-dependent manner [68] but the effects of this interaction on the physiological and/or biochemical function of these TFs remain unknown.
3.2. CMLs: Emerging Plant Ca2+ Sensors in Immunity
In addition to the presence of the typical CaMs, plants also possess a broad range of divergent forms of CaM called CaM-like proteins (CMLs, with 50 members in A. thaliana) [17,19]. Like CaMs, CMLs contain several EF-hand motifs, are predicted to bind Ca2+ ions and do not possess other known functional domains [17,19]. Whereas CaM encoding genes are uniformly and highly expressed, the expression patterns of CMLs vary according to plant developmental stages, tissues and environmental stimuli, indicating that each CML may have a specific role in plants [17]. Indeed, data on the physiological relevance of CMLs during plant physiology and more specifically in plant immunity have emerged during the last decade (reviewed in [6,90,91,92]).
Although we cannot rule out functional redundancy between members of the CaM/CML family, accumulating evidence indicate that deregulation of individual CaM/CML gene expression or loss of a CML function in mutated plants affect plant defence responses to various pathogens. The first report involving CMLs in plant defence came from gain-of-function experiments by overexpressing CMLs. The over-expression of soybean CMLs (i.e., SCaM-4/-5) in tobacco confers enhanced resistance to a wide spectrum of virulent and avirulent pathogens, including bacteria, fungi and viruses [93]. When constitutively expressed in Arabidopsis, SCaM-5 confers enhanced resistance to Pseudomonas syringae infection [94] whereas over-expression of SCaM-1 (a typical CaM) does not, which suggests that SCAM-4/-5 are specifically recruited in response to pathogens [94]. Although obtained in heterologous plant systems, these results suggest that CaM/CML isoforms are components of signal transduction pathways leading to disease resistance. Interestingly, it was later shown that the overexpression of SCaM-4 in soybean stimulated resistance to the oomycete Phytophtora sojae and to two necrotrophic fungal pathogens (Alternaria tenuissima and Phomopsis longicolla) supporting the idea that CaM/CMLs do take part in plant immune responses [95].
Loss-of- function genetic approaches also demonstrated roles in plant immunity for several CMLs. For instance, silencing APR134 in tomato suppresses the hypersensitive response (HR), whereas overexpression of the APR134 orthologue from Arabidopsis CML43 stimulates the HR in response to an avirulent strain of P. syringae [96]. Similarly, cml24 knockout in Arabidopsis impairs the HR response and reduces nitric oxide production following PAMP recognition [97]. Gain- and loss-of-function strategies were also developed on Arabidopsis CML8 and CML9 to evaluate their physiological function in plant stress responses. These two CMLs are positive regulators of plant defence against different strains of P. syringae [98,99,100]. CML9 was first described to be involved in plant responses to abiotic stress [101] and later shown to also contribute to plant immune responses [97]. The cml9 mutants and CML9 overexpressing lines exhibit enhanced or reduced susceptibility to virulent strains of P. syringae, respectively [98]. These phenotypes can be explained by alterations of flagellin-induced responses, including deposition of callose papillae and modifications of defence-related genes expression [98]. CML8 also takes part in plant immune responses against P. syringae but compared to CML9, the enhanced resistance observed in CML8 overexpressing lines relies mainly on SA-dependent responses [99]. Emerging data indicate that the regulation of plasmodesmata by plant cells is critical for the establishment of plant defence signalling [102]. Indeed, plasmodesmata are plasma membrane pores that establish cytoplasmic and membrane continuity between cells [102]. It was recently identified that closure of plasmodesmata in response to bacterial flagellin is mediated by the plasmodesmatal-localized CML41 [103]. CML41 is transcriptionally upregulated by PAMPs and facilitates callose deposition at plasmodesmata following flagellin treatment. Using amiRNA and CML41 overexpressing lines, Xu et al. reported that CML41 acts as a positive regulator of defence against Pseudomonas syringae [103].
Ca2+ signalling is not only required for defence mechanisms upon microbial pathogen attack but also in response to herbivores [58,104,105,106]. Data from Mithoefer’s group indicate that the loss of function of Arabidopsis CML42 enhances resistance to Spodoptera littoralis which is correlated with the up-regulation of jasmonic acid-responsive genes and to an accumulation of aliphatic glucosinolates [107]. In contrast to CML42, CML37 acts positively on defence against S. littoralis [108]. Indeed, a cml37 Knock-Out mutant exhibits an enhanced susceptibility to herbivory which is correlated to a lower level of the bioactive form of jasmonate (i.e., JA-Ile) known to be crucial in plant defence coordination against insects [108]. These data suggest opposite roles for CML37 and CML42 in insect herbivory resistance. We cannot exclude that other CMLs such as CML9, CML11, CML12, CML16, CML17 and CML23 could participate in insect defence responses since the corresponding genes are significantly up-regulated in plants treated with oral secretion of the lepidopteran herbivore [109].
Among the range of processes regulated by CaM/CMLs, CMLs are also involved in the suppression of post-transcriptional gene silencing (PTGS), a regulatory mechanism targeting mRNA content [110]. Plant viruses can act both as inducers and as targets of PTGS and this led to the idea that PTGS evolved as a defence mechanism against viruses in plants [110]. Interestingly, a tobacco CML termed rgs-CaM (for regulator of gene silencing) has been reported to act as a suppressor of PTGS [110] and to play a role in antiviral defence by modulating virus-induced RNA silencing [111,112]. The rgs-CaM exerts its antiviral activity by binding and controlling the degradation of viral RNA silencing suppressors. This constitutes the first example of an interaction between a CML and a pathogen protein [111]. Recently, the role of this rgs-CaM in systemic acquired resistance against cucumber mosaic virus has been described in tobacco plants [113]. It was proposed that rgs-CaM functions as an immune receptor that induces salicylic acid signalling by simultaneously perceiving both viral RNA silencing suppressors and Ca2+ influx [113].
To date, most of the data describing the involvement of CMLs in different cellular processes associated with plant physiology remain descriptive and new research is now required to decipher the molecular mechanisms controlled by these CMLs. The identification of CML-interacting partners will be crucial to clarify how these CMLs exert their action at the molecular level in plant immunity. For example, CML9, previously described to positively regulate plant immunity, was reported to interact with transcription factors such as the WRKYs and the TGAs, two classes of transcription factors known to play key roles in the regulation of defence processes [69]. PRR2 (PSEUDO-RESPONSE REGULATOR 2), a plant specific transcription factor was also described to interact in planta with CML9 but not with the typical CaM [114]. Using a reverse genetic strategy in A. thaliana, PRR2 was shown to act as a positive regulator of plant immunity through SA-dependent responses [115].
In many cases, the regulation of these TFs by CML9 or by other CMLs remain presumptive. The next challenge will be to elucidate if all CMLs really act as Ca2+ sensors/Ca2+ relay proteins, are able to interact with CML-binding proteins and to modulate their activity, as demonstrated for the CaMs. Several questions remain unanswered: Do CaM and CMLs share the same targets? What could be the consequences of such interactions? Interestingly, Yoo et al. showed that the typical CaM (SCaM-1) and the CML (SCaM-4) physically interact with MYB2, a TF that regulates the expression of salt- and dehydration-responsive genes in Arabidopsis [116]. However, SCaM-4 enhances the DNA binding properties of MYB2 whereas SCaM-1 inhibits MYB2 DNA binding [116]. Although these data need validation, different modes of regulation are suggested depending on the interaction with either a CaM or a CML. CaM/CMLs have been reported to interact with different nuclear proteins [68] but do these interactions help to recruit other actors into transcriptional complexes and regulate their activity? What is the contribution of Ca2+ in these interactions? Efforts are now made to answer these questions and to better understand the contribution of these sensors in Ca2+ signalling with a particular interest on plant specific CMLs.
3.3. CDPKs: Positive Regulators of Plant Immune Responses
Beside CaMs and CMLs, plants also possess another class of Ca2+ sensors referred to as Ca2+ dependent protein kinases or CDPKs. Found only in green algae, land plants and unicellular protists, CDPKs are important Ca2+ decoders and relays in plant defence signalling against various types of pathogens (for review: [4]). Their number expanded during evolution of land plants to reach ~30 members in angiosperms (e.g., 34 in A. thaliana—29 in S. lycopersicum) [117]. The family architecture is nonetheless conserved from mosses to angiosperms, and formed of four distinct groups [22,118]. In contrast to CaMs and CMLs, CDPKs are unique in the repertoire of Ca2+ decoders since they combine into a single module Ca2+ sensing and downstream signal propagation capabilities. They are composed of a variable N-terminal part, a kinase domain and an activation domain. The activation domain contains an auto-inhibitory pseudo-substrate linked to a CaM-like domain typically containing four EF-hands [119,120]. Upon Ca2+ binding by the CaM-like domain, a conformational change displaces the pseudo-substrate from the kinase to allow for downstream phosphorylation events. The dynamic range of Ca2+ concentrations that activate a given CDPK therefore depends on the CaM-like domain affinity for Ca2+. This likely accounts in part for the specific decoding of different Ca2+ variations. Of note, some CDPKs do not show strict Ca2+-dependent kinase activity. For example, Arabidopsis thaliana CPK7, 8, 13, and CPK30 showed more than half-maximal in vitro syntide-2 phosphorylation activity at very low Ca2+ concentrations (1 to 10 nM), with little to no additional kinase activity at higher Ca2+ concentrations [121,122]. Whether this reflects true Ca2+-independence in vivo or specific Ca2+ requirements depending on substrates remains to be clarified [121].
Functional analyses in planta revealed that CDPKs are important components of the plant immune system. Acting alongside and in synergy with the Mitogen Activated Protein Kinases (MAPKs)-dependent signalling cascade, Arabidopsis CPK4, 5, 6 and 11 positively regulate defence gene expression upon bacterial flagellin perception [30]. CPK4, 5, 6 and 11 collectively and redundantly contribute to PTI-induced resistance against Pseudomonas syringae [30]. CPK5, but also CPK4, 6 and 11, are able to phosphorylate AtRBOHD, the main ROS producing enzyme acting in immunity [122,123]. A model was proposed in which CPK5 and RBOHD sustain a ROS-mediated cell-to-cell communication to reach distal sites from the initial PAMP perception area [124]. Through phosphorylation of the HsfB2a transcription factor, Arabidopsis CPK3 and CPK13 are important regulators of the PDF1.2 defence gene induction after wounding by the caterpillar Sodoptera littoralis [122]. These positive immune regulatory functions of CDPKs prompted their biotechnological use in crop protection against pathogens. For example, overexpression of full length OsCPK4 in rice leads to enhanced disease resistance against Magnaporthe oryzae [125]. This enhanced disease resistance in transformed plants is likely due to their higher basal levels of salicylic acid and the resulting potentiation of defence gene induction [125].
In addition to the control of defence gene induction, another important aspect of CDPK function is the control of plant cell death in response to pathogens. Early work on CDPKs in Nicotiana sp. showed that CDPK2 and CDPK3 are required for the PCD response triggered after perception of the Cladosporium fulvum race-specific Avr4 or Avr9 elicitors [126]. This pioneering work was further expanded in Arabidopsis with the demonstration that CPK1 and 2 control the onset of HR upon challenge with avirulent Pseudomonas syringae and subsequent NLR-mediated effector recognition [127]. In line with this, several constitutively active CDPKs harbour cell death inducing activity. Auto-active CDPKs (CDPK-VKs) are devoid of their activation domains and therefore do not need Ca2+ inputs to be in an active state. Expression of CPK5-VK in Arabidopsis leaf protoplasts leads to cell death and this requires kinase activity [123]. Similar results were obtained in transgenic potato plants stably expressing StCPK5-VK under a pathogen inducible promoter [128]. This latter approach led to increased plant resistance against the hemi-biotrophic oomycete Phytophthora infestans. As a trade-off however, plants became more susceptible to the necrotrophic fungus Alternaria solani [128]. This contrasted outcome in plant defence toward pathogens with different lifestyles might prevent wider use of these genetic tools in crop protection. PCD induction can also be observed in heterologous expression systems, as demonstrated by the cell death inducing activity of transiently expressed barley CDPK4-VK or Arabidopsis CPK5-VK in tobacco leaves [123,129]. Activation of any given CDPK does not seem sufficient per se to provoke PCD since not all CDPKs tested under their auto-active configuration induce PCD [123,129]. The kinase and auto-inhibitory domains of CDPKs being under strong purifying selection [22], it is therefore likely that the specific properties of CDPKs lie, in part, in other features such as their hypervariable termini ends. For example, swapping the N-terminal variable domains of tomato SlCDPK2 and SlCDPK5 exchanged their respective subcellular localizations and their ability to phosphorylate StRBOHB [130]. The existence of cross-species PCD-inducing properties supports nonetheless some degree of functional conservation in CDPKs mode(s) of action through the evolution of land plants.
As already, mentioned, functional redundancy can be problematic when studying particular gene functions within a large family. Although gain-of-function auto-active CDPKs proved of immense value in this context, cdpk mutants remain necessary tools and high-order cdpk mutants are often required to observe a phenotype of interest such as pathogen susceptibility [30,127]. In contrast to that, a suppressor screen of the exo70B1 autoimmune phenotype uncovered several cpk5 loss-of-function alleles [131]. The exo70B1-mediated cell death and enhanced resistance to Golovinomyces cichoracearum phenotypes were lost in the absence of a functional CPK5, but not of CPK4, 6, or 11 [131]. This advocates for a specific function of CPK5 that cannot be fulfilled here by its otherwise functionally redundant close homologues. In addition to CPK5, the exo70B1-mediated autoimmunity also requires the atypical truncated NLR resistance gene TN2 [132]. A tripartite interaction between Exo70B1, CPK5 and TN2 therefore controls cell death. CPK5 kinase activity and its membrane association are both required although the exact mechanism is not completely understood [131]. Whether other CDPKs are also involved in similar interactions, and whether this mechanism represents an innovation present only in Arabidopsis, remain open questions.
3.4. CDPKs: Also Negative Regulators of Plant Immune Responses
In addition to these positive roles, CDPKs also perform negative functions in plant defence. For example, overexpression of OsCPK12 increased rice susceptibility to avirulent and virulent Magnaporthe grisae strains [133] while in barley, overexpressing an auto-active variant of HvCDPK3 increased susceptibility to powdery mildew (B. graminis f. sp. hordei) [129]. In Arabidopsis, perception of several PAMPs by their cognate receptors requires the activity of Somatic Embryogenesis Receptor Kinases 3 (SERK3), a plasma membrane localized receptor and co-regulator also referred to as BAK1 (BRI1-Associated Kinase 1) [134]. In a forward genetic screen set to discover modifiers of the bak1–5 loss-of-function allele [135], Monaghan and colleagues recovered cpk28 mutants. The loss of CPK28 reverted the impaired ROS production phenotype observed in bak1–5 after PAMP treatments [136]. CPK28 buffers immune responses by modulating the proteasome-mediated turnover of the BIK1 receptor-like cytoplasmic kinase, a shared component of signalling pathways controlled by several PRRs [136]. The search for E3 ligases targeting BIK1 led to the identification of PUB25 and 26, two related E3 ligases of the U-box family whose enzymatic activities towards BIK1 are activated through CPK28-dependent phosphorylation [136]. It is tempting to speculate that the Ca2+ influx resulting from PRR activation first participates in ROS production through CPK5 activity, before CPK28 dampens immune outputs. In line with this hypothesis, in vitro assays determined that CPK28 is indeed Ca2+ responsive [137]. Interestingly, CPK28 is also able to bind Ca2+/CaM, however, this interaction negatively affects its kinase activity in vitro [138]. Ca2+ therefore seems to have a dual role in regulating CPK28 activity, thereby, adding another layer of complexity that has yet to be resolved.
Globally, plants have a wide repertoire of Ca2+-binding proteins whose functions in plant physiology start to be unravelled. Far from being exhaustive, we have summarized here some examples that describe the importance of certain CaM/CMLs and CDPKs in plant immunity [17,18]. The picture remains nevertheless complex as duplications events and the expected neo-functionalization is sometimes confronted with functional redundancy observed in higher plants. Plants belonging to a sister clade of angiosperms such as liverworts or hornworts could be of interest in discovering yet hidden functions of some calcium sensors. The pursuit of research efforts on these plant specific sensors and particularly the identification of novel CaM/CML-binding proteins and CDPK substrates will be important milestones to get a better view of the many Ca2+-regulated events.
4. Concluding Remarks and Outlooks
Increasing data support that Ca2+, Ca2+ sensors and their targets are positioned among the first actors setting up the plant response to biotic interactions. One of the challenges of the coming years will be to understand and expect plant behaviour in a changing environment, with the long-term goal to breed stress-tolerant crops for agriculture. However, although Ca2+ signals are the very first step in the signaling pathway, it appears that their manipulation to improve plant resistance could be very challenging. Indeed, calcium signals result from the intricate interaction between pathways and components involved in both their generation and their dissipation such as calcium channels, exchangers or calcium pumps [139]. Nevertheless, some reverse genetic approaches have demonstrated that plant immunity can be modulated through the control of calcium signals by interfering with their generation [140,141] or their dissipation through the activity modulation of calcium pumps [142,143]. Such examples in the literature are rather scarce. Envisioning strategies based on calcium variation modulation to improve plant resistance could be hazardous due to a lack of knowledge concerning actors involved in calcium homeostasis associated to specific plant-microorganism interactions.
An alternative and more amenable approach would be rather to interfere with the function of the Ca2+ sensors or their targets that decode Ca2+ messages. To date, studies about CaM/CML and CDPKs focus mainly on their interaction with plant target proteins. However, recent and promising data indicate that Ca2+ signalling components can be themselves the direct targets of pathogen effectors. In the context of plant immunity, studies on these specifically targeted plant calcium sensors by pathogen effectors might provide a new way for breeding plant resistance. Indeed, it was recently demonstrated that plant CaM is required by the HopE1 effector from Pseudomonas syringae to target MAP65, a microtubule-associated protein, to reduce plant immune responses [144]. In a similar way, the Xanthomonas AvrBsT effector, able to acetylate ACIP1, a microtubule-associated protein in Arabidopsis and required for both PTI and ETI, possesses a CaM-binding region. AvrBsT is the first member of the YopJ family known to suppress effector-triggered plant immunity [145]. It was reported that AvrBsT is able to interact with CaM in a Ca2+-dependent manner and that a mutation of the AvrBsT CaM-binding domain alters or delays the hypersensitive response phenotype (MB Mudgett, personal communication and reports from MPMI meeting 2016 [146]). Whereas CaM has long been known to be a co-factor for mammalian pathogen toxins [147]; these new data obtained with plants support new roles for CaM in plant immunity.
In this review, we focused on Ca2+ signalling and biotic stress responses. We point out that CMLs and CDPKs can exhibit a dual function as either positive and/or negative regulators in plant biotic stresses. Moreover, many other data highlight the contribution of Ca2+ and Ca2+ decoding processes following abiotic stress perception [6,23,63,148]. Studies deciphering plant responses to simultaneously applied abiotic and biotic stress remain sparse. More importantly, these different types of stress are often interrelated in the field and several forms of abiotic stress significantly affect the resistance of plants to bacteria, fungi, viruses and insects [149]. Therefore, is it really attractive to hypothesize that Ca2+, Ca2+ sensors and their respective targets can be at the crossroads of various signalling pathways and that they could be good candidates to act as central integrators involved in the fine tuning of plant physiological responses to pathogens under fluctuating environmental conditions. As stated in the introduction, it is obvious that Ca2+ signalling is not acting as a unique contributor in plant stress responses and we cannot rule out crosstalk between Ca2+ and ROS, as well as other second messengers. The next mid and long-term challenges should better characterize the interplay between these signalling pathways.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Julie Cullimore for proofreading and corrections and Julie Mazard for her comments on this manuscript. This work was supported by the Université Paul Sabatier (Toulouse, France), the CNRS (France), the French Laboratory of Excellence project “TULIP” (ANR-10-LABX-41; ANR-11-IDEX-0002-02) and by the Agence Nationale de la Recherche (ANR) (ANR-17-CE20-0017-01) thanks to the CaPPTure project.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Van Loon, L.C. The intelligent behavior of plants. Trends Plant Sci. 2016, 21, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kissoudis, C.; van de Wiel, C.; Visser, R.G.; van der Linden, G. Future-proof crops: Challenges and strategies for climate resilience improvement. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2016, 30, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kissoudis, C.; van de Wiel, C.; Visser, R.G.; van der Linden, G. Enhancing crop resilience to combined abiotic and biotic stress through the dissection of physiological and molecular crosstalk. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boudsocq, M.; Sheen, J. CDPKs in immune and stress signaling. Trends Plant Sci. 2013, 18, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poovaiah, B.W.; Du, L.; Wang, H.; Yang, T. Recent advances in calcium/calmodulin-mediated signaling with an emphasis on plant-microbe interactions. Plant Physiol. 2013, 163, 531–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranty, B.; Aldon, D.; Cotelle, V.; Galaud, J.P.; Thuleau, P.; Mazars, C. Calcium sensors as key hubs in plant responses to biotic and abiotic stresses. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zipfel, C.; Oldroyd, G.E. Plant signalling in symbiosis and immunity. Nature 2017, 543, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doke, N. Involvement of superoxide anion generation in the hypersensitive response of potato tuber tissues to infection with an incompatible race of phytophthora infestans and to the hyphal wall components. Physiol. Plant Pathol. 1983, 23, 345–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, M.M.; Keppler, L.D.; Orlandi, E.W.; Baker, C.J.; Mischke, C.F. Involvement of plasma membrane calcium influx in bacterial induction of the K+/H+ and hypersensitive responses in tobacco. Plant Physiol. 1990, 92, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stael, S.; Kmiecik, P.; Willems, P.; Van Der Kelen, K.; Coll, N.S.; Teige, M.; Van Breusegem, F. Plant innate immunity—Sunny side up? Trends Plant Sci. 2015, 20, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berridge, M.J.; Lipp, P.; Bootman, M.D. The versatility and universality of calcium signalling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2000, 1, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinhorst, L.; Kudla, J. Signaling in cells and organisms—calcium holds the line. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2014, 22, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAinsh, M.R.; Brownlee, C.; Hetherington, A.M. Visualizing changes in cytosolic-free Ca2+ during the response of stomatal guard cells to abscisic acid. Plant Cell 1992, 4, 1113–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- McAinsh, M.R.; Hetherington, A.M. Encoding specificity in Ca2+ signalling systems. Trends Plant Sci. 1998, 3, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, K.L.; Ames, J.B.; Swindells, M.B.; Ikura, M. Diversity of conformational states and changes within the ef-hand protein superfamily. Proteins 1999, 37, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, I.S.; Reddy, V.S.; Shad Ali, G.; Reddy, A.S. Analysis of EF-hand-containing proteins in Arabidopsis. Genome Biol. 2002, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Dunand, C.; Snedden, W.; Galaud, J.P. Cam and cml emergence in the green lineage. Trends Plant Sci. 2015, 20, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edel, K.H.; Marchadier, E.; Brownlee, C.; Kudla, J.; Hetherington, A.M. The evolution of calcium-based signalling in plants. Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, R667–R679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCormack, E.; Tsai, Y.C.; Braam, J. Handling calcium signaling: Arabidopsis CaMs and CMLs. Trends Plant Sci. 2005, 10, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snedden, W.A.; Fromm, H. Calmodulin as a versatile calcium signal transducer in plants. New Phytol. 2001, 151, 35–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batistic, O.; Kudla, J. Plant calcineurin B-like proteins and their interacting protein kinases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1793, 985–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valmonte, G.R.; Arthur, K.; Higgins, C.M.; MacDiarmid, R.M. Calcium-dependent protein kinases in plants: Evolution, expression and function. Plant Cell Physiol. 2014, 55, 551–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, H.; Xu, L.; Singh, A.; Wang, H.; Du, L.; Poovaiah, B.W. Involvement of calmodulin and calmodulin-like proteins in plant responses to abiotic stresses. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, P.; Jauregui, E.; Du, L.; Tanaka, K.; Poovaiah, B.W. Calcium signatures and signaling events orchestrate plant-microbe interactions. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2017, 38, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Du, L.; Poovaiah, B.W. Calcium signalling and biotic defense responses in plants. Plant Signal Behav. 2014, 9, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, J.D.; Dangl, J.L. The plant immune system. Nature 2006, 444, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zipfel, C.; Robatzek, S.; Navarro, L.; Oakeley, E.J.; Jones, J.D.; Felix, G.; Boller, T. Bacterial disease resistance in arabidopsis through flagellin perception. Nature 2004, 428, 764–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lecourieux, D.; Lamotte, O.; Bourque, S.; Wendehenne, D.; Mazars, C.; Ranjeva, R.; Pugin, A. Proteinaceous and oligosaccharidic elicitors induce different calcium signatures in the nucleus of tobacco cells. Cell Calcium 2005, 38, 527–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, M.; Brown, I.; Adams, S.; Knight, M.; Ainslie, A.; Mansfield, J. The RPM1 plant disease resistance gene facilitates a rapid and sustained increase in cytosolic calcium that is necessary for the oxidative burst and hypersensitive cell death. Plant J. 2000, 23, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boudsocq, M.; Willmann, M.R.; McCormack, M.; Lee, H.; Shan, L.; He, P.; Bush, J.; Cheng, S.H.; Sheen, J. Differential innate immune signalling via Ca2+ sensor protein kinases. Nature 2010, 464, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilroy, S.; Read, N.D.; Trewavas, A.J. Elevation of cytoplasmic calcium by caged calcium or caged inositol triphosphate initiates stomatal closure. Nature 1990, 346, 769–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knight, M.R.; Campbell, A.K.; Smith, S.M.; Trewavas, A.J. Transgenic plant aequorin reports the effects of touch and cold-shock and elicitors on cytoplasmic calcium. Nature 1991, 352, 524–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra, S.; Stennis, M.; Low, P.S. Measurement of Ca2+ fluxes during elicitation of the oxidative burst in aequorin-transformed tobacco cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 28274–28280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, M.G. Microbial elicitors and their receptors in plants. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 1996, 34, 387–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, M.G.; Darvill, A.G.; Albersheim, P. Host-pathogen interactions: XIX. The endogenous elicitor, a fragment of a plant cell wall polysaccharide that elicits phytoalexin accumulation in soybeans. Plant Physiol. 1981, 68, 1161–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mithofer, A.; Fliegmann, J.; Ebel, J. Isolation of a french bean (phaseolus vulgaris L.) homolog to the beta-glucan elicitor-binding protein of soybean (glycine max L.). Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1999, 1418, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blume, B.; Nurnberger, T.; Nass, N.; Scheel, D. Receptor-mediated increase in cytoplasmic free calcium required for activation of pathogen defense in parsley. Plant Cell 2000, 12, 1425–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lecourieux, D.; Mazars, C.; Pauly, N.; Ranjeva, R.; Pugin, A. Analysis and effects of cytosolic free calcium increases in response to elicitors in nicotiana plumbaginifolia cells. Plant Cell 2002, 14, 2627–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, W.G.; Hilleary, R.; Swanson, S.J.; Kim, S.H.; Gilroy, S. Rapid, long-distance electrical and calcium signaling in plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2016, 67, 287–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, M.A.; Sundelin, T.; Nielsen, J.T.; Erbs, G. Mamp (microbe-associated molecular pattern) triggered immunity in plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2013, 4, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mithofer, A.; Boland, W. Recognition of herbivory-associated molecular patterns. Plant Physiol. 2008, 146, 825–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maffei, M.; Bossi, S.; Spiteller, D.; Mithofer, A.; Boland, W. Effects of feeding spodoptera littoralis on lima bean leaves. I. Membrane potentials, intracellular calcium variations, oral secretions, and regurgitate components. Plant Physiol. 2004, 134, 1752–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arimura, G.; Ozawa, R.; Shimoda, T.; Nishioka, T.; Boland, W.; Takabayashi, J. Herbivory-induced volatiles elicit defence genes in lima bean leaves. Nature 2000, 406, 512–515. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Allen, G.J.; Chu, S.P.; Harrington, C.L.; Schumacher, K.; Hoffmann, T.; Tang, Y.Y.; Grill, E.; Schroeder, J.I. A defined range of guard cell calcium oscillation parameters encodes stomatal movements. Nature 2001, 411, 1053–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miwa, H.; Sun, J.; Oldroyd, G.E.; Downie, J.A. Analysis of calcium spiking using a cameleon calcium sensor reveals that nodulation gene expression is regulated by calcium spike number and the developmental status of the cell. Plant J. 2006, 48, 883–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collmer, A.; Badel, J.L.; Charkowski, A.O.; Deng, W.L.; Fouts, D.E.; Ramos, A.R.; Rehm, A.H.; Anderson, D.M.; Schneewind, O.; van Dijk, K.; et al. Pseudomonas Syringae Hrp type III secretion system and effector proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 8770–8777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heath, M.C. Hypersensitive response-related death. Plant Mol. Biol. 2000, 44, 321–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keen, N.T. Gene-for-gene complementarity in plant-pathogen interactions. Annu. Rev. Genet. 1990, 24, 447–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badminton, M.N.; Sala-Newby, G.B.; Kendall, J.M.; Campbell, A.K. Differences in stability of recombinant apoaequorin within subcellular compartments. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1995, 217, 950–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wais, R.J.; Galera, C.; Oldroyd, G.; Catoira, R.; Penmetsa, R.V.; Cook, D.; Gough, C.; Denarie, J.; Long, S.R. Genetic analysis of calcium spiking responses in nodulation mutants of medicago truncatula. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 13407–13412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wais, R.J.; Keating, D.H.; Long, S.R. Structure-function analysis of nod factor-induced root hair calcium spiking in rhizobium-legume symbiosis. Plant Physiol. 2002, 129, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyawaki, A.; Llopis, J.; Heim, R.; McCaffery, J.M.; Adams, J.A.; Ikura, M.; Tsien, R.Y. Fluorescent indicators for Ca2+ based on green fluorescent proteins and calmodulin. Nature 1997, 388, 882–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosuta, S.; Hazledine, S.; Sun, J.; Miwa, H.; Morris, R.J.; Downie, J.A.; Oldroyd, G.E. Differential and chaotic calcium signatures in the symbiosis signaling pathway of legumes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 9823–9828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sieberer, B.J.; Chabaud, M.; Timmers, A.C.; Monin, A.; Fournier, J.; Barker, D.G. A nuclear-targeted cameleon demonstrates intranuclear Ca2+ spiking in medicago truncatula root hairs in response to rhizobial nodulation factors. Plant Physiol. 2009, 151, 1197–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, W.G.; Gilroy, S. Plant biologists fret over stress. eLife 2014, 3, e02763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horikawa, K.; Yamada, Y.; Matsuda, T.; Kobayashi, K.; Hashimoto, M.; Matsu-ura, T.; Miyawaki, A.; Michikawa, T.; Mikoshiba, K.; Nagai, T. Spontaneous network activity visualized by ultrasensitive Ca2+ indicators, yellow cameleon-nano. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 729–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, T.C.; Ronzier, E.; Sanchez, F.; Corratge-Faillie, C.; Mazars, C.; Thibaud, J.B. Imaging long distance propagating calcium signals in intact plant leaves with the BRET-based GFP-aequorin reporter. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiep, V.; Vadassery, J.; Lattke, J.; Maass, J.P.; Boland, W.; Peiter, E.; Mithofer, A. Systemic cytosolic Ca2+ elevation is activated upon wounding and herbivory in arabidopsis. New Phytol. 2015, 207, 996–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akerboom, J.; Carreras Calderon, N.; Tian, L.; Wabnig, S.; Prigge, M.; Tolo, J.; Gordus, A.; Orger, M.B.; Severi, K.E.; Macklin, J.J.; et al. Genetically encoded calcium indicators for multi-color neural activity imaging and combination with optogenetics. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2013, 6, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keinath, N.F.; Waadt, R.; Brugman, R.; Schroeder, J.I.; Grossmann, G.; Schumacher, K.; Krebs, M. Live cell imaging with R-GECO1 sheds light on flg22- and chitin-induced transient [Ca2+]cyt patterns in arabidopsis. Mol. Plant 2015, 8, 1188–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, K.; Kudla, J. Calcium decoding mechanisms in plants. Biochimie 2011, 93, 2054–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Defalco, T.A.; Bender, K.W.; Snedden, W.A. Breaking the code: Ca2+ sensors in plant signalling. Biochem. J. 2010, 425, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, A.S.; Ali, G.S.; Celesnik, H.; Day, I.S. Coping with stresses: Roles of calcium- and calcium/calmodulin-regulated gene expression. Plant Cell 2011, 23, 2010–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudla, J.; Batistic, O.; Hashimoto, K. Calcium signals: The lead currency of plant information processing. Plant Cell 2010, 22, 541–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudla, J.; Becker, D.; Grill, E.; Hedrich, R.; Hippler, M.; Kummer, U.; Parniske, M.; Romeis, T.; Schumacher, K. Advances and current challenges in calcium signaling. New Phytol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCormack, E.; Braam, J. Calmodulins and related potential calcium sensors of arabidopsis. New Phytol. 2003, 159, 585–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouche, N.; Yellin, A.; Snedden, W.A.; Fromm, H. Plant-specific calmodulin-binding proteins. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2005, 56, 435–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popescu, S.C.; Popescu, G.V.; Bachan, S.; Zhang, Z.; Seay, M.; Gerstein, M.; Snyder, M.; Dinesh-Kumar, S.P. Differential binding of calmodulin-related proteins to their targets revealed through high-density arabidopsis protein microarrays. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 4730–4735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popescu, S.C.; Snyder, M.; Dinesh-Kumar, S. Arabidopsis protein microarrays for the high-throughput identification of protein-protein interactions. Plant Signal Behav. 2007, 2, 416–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Hua, B.-G.; Mercier, R.W.; Zielinski, R.E.; Berkowitz, G.A. Functional interaction of calmodulin with a plant cyclic nucleotide gated cation channel. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2003, 41, 945–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeFalco, T.A.; Marshall, C.B.; Munro, K.; Kang, H.G.; Moeder, W.; Ikura, M.; Snedden, W.A.; Yoshioka, K. Multiple calmodulin-binding sites positively and negatively regulate Arabidopsis cyclic nucleotide-gated channel12. Plant Cell 2016, 28, 1738–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galon, Y.; Finkler, A.; Fromm, H. Calcium-regulated transcription in plants. Mol. Plant 2010, 3, 653–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pieterse, C.M.; Van der Does, D.; Zamioudis, C.; Leon-Reyes, A.; Van Wees, S.C. Hormonal modulation of plant immunity. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2012, 28, 489–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Tsuda, K.; Sato, M.; Cohen, J.D.; Katagiri, F.; Glazebrook, J. Arabidopsis cam binding protein CBP60g contributes to MAMP-induced SA accumulation and is involved in disease resistance against pseudomonas syringae. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, L.; Ali, G.S.; Simons, K.A.; Hou, J.; Yang, T.; Reddy, A.S.; Poovaiah, B.W. Ca2+/calmodulin regulates salicylic-acid-mediated plant immunity. Nature 2009, 457, 1154–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Tsuda, K.; Truman, W.; Sato, M.; Nguyen le, V.; Katagiri, F.; Glazebrook, J. CBP60g and SARD1 play partially redundant critical roles in salicylic acid signaling. Plant J. 2011, 67, 1029–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truman, W.; Sreekanta, S.; Lu, Y.; Bethke, G.; Tsuda, K.; Katagiri, F.; Glazebrook, J. The calmodulin-binding protein60 family includes both negative and positive regulators of plant immunity. Plant Physiol. 2013, 163, 1741–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Truman, W.; Liu, X.; Bethke, G.; Zhou, M.; Myers, C.L.; Katagiri, F.; Glazebrook, J. Different modes of negative regulation of plant immunity by calmodulin-related genes. Plant Physiol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finkler, A.; Ashery-Padan, R.; Fromm, H. Camtas: Calmodulin-binding transcription activators from plants to human. FEBS Lett. 2007, 581, 3893–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, H.; Yang, J.; Xu, Y.P.; Munyampundu, J.P.; Cai, X.Z. Phylogeny of plant camtas and role of atcamtas in nonhost resistance to xanthomonas oryzae pv. Oryzae. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, C.; Yang, Y.; Du, L.; Wang, H. Calmodulin-binding transcription activators and perspectives for applications in biotechnology. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 10379–10385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galon, Y.; Nave, R.; Boyce, J.M.; Nachmias, D.; Knight, M.R.; Fromm, H. Calmodulin-binding transcription activator (CAMTA) 3 mediates biotic defense responses in arabidopsis. FEBS Lett. 2008, 582, 943–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, H.; Xu, Y.P.; Zhang, X.R.; Cai, X.Z. Brassica napus genome possesses extraordinary high number of CAMTA genes and CAMTA3 contributes to pamp triggered immunity and resistance to sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laluk, K.; Prasad, K.V.; Savchenko, T.; Celesnik, H.; Dehesh, K.; Levy, M.; Mitchell-Olds, T.; Reddy, A.S. The calmodulin-binding transcription factor signal responsive1 is a novel regulator of glucosinolate metabolism and herbivory tolerance in arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol. 2012, 53, 2008–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Y.; Xi, J.; Du, L.; Suttle, J.C.; Poovaiah, B.W. Coupling calcium/calmodulin-mediated signaling and herbivore-induced plant response through calmodulin-binding transcription factor atsr1/camta3. Plant Mol. Biol. 2012, 79, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, F.; Kracher, B.; Mine, A.; Seyfferth, C.; Blanvillain-Baufume, S.; Parker, J.E.; Tsuda, K.; Schulze-Lefert, P.; Maekawa, T. A dominant-interfering CAMTA3 mutation compromises primary transcriptional outputs mediated by both cell surface and intracellular immune receptors in arabidopsis thaliana. New Phytol. 2018, 217, 1667–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Whalley, H.J.; Knight, M.R. Combining modelling and experimental approaches to explain how calcium signatures are decoded by calmodulin-binding transcription activators (CAMTAs) to produce specific gene expression responses. New Phytol. 2015, 208, 174–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenzoni, G.; Liu, J.; Knight, M.R. Predicting plant immunity gene expression by identifying the decoding mechanism of calcium signatures. New Phytol. 2018, 217, 1598–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, C.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Yoo, J.H.; Moon, B.C.; Choi, M.S.; Kang, Y.H.; Lee, S.M.; Kim, H.S.; Kang, K.Y.; Chung, W.S.; et al. WRKY group IId transcription factors interact with calmodulin. FEBS Lett. 2005, 579, 1545–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, J.W.; Loake, G.J.; Spoel, S.H. Transcription dynamics in plant immunity. Plant Cell 2011, 23, 2809–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bender, K.W.; Snedden, W.A. Calmodulin-related proteins step out from the shadow of their namesake. Plant Physiol. 2013, 163, 486–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheval, C.; Aldon, D.; Galaud, J.P.; Ranty, B. Calcium/calmodulin-mediated regulation of plant immunity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1833, 1766–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, W.D.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, M.C.; Kim, J.C.; Chung, W.S.; Chun, H.J.; Lee, K.J.; Park, C.Y.; Park, H.C.; Choi, J.Y.; et al. Involvement of specific calmodulin isoforms in salicylic acid-independent activation of plant disease resistance responses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 766–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, C.Y.; Heo, W.D.; Yoo, J.H.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, M.C.; Chun, H.J.; Moon, B.C.; Kim, I.H.; Park, H.C.; Choi, M.S.; et al. Pathogenesis-related gene expression by specific calmodulin isoforms is dependent on nim1, a key regulator of systemic acquired resistance. Mol. Cells 2004, 18, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rao, S.S.; El-Habbak, M.H.; Havens, W.M.; Singh, A.; Zheng, D.; Vaughn, L.; Haudenshield, J.S.; Hartman, G.L.; Korban, S.S.; Ghabrial, S.A. Overexpression of GmCaM4 in soybean enhances resistance to pathogens and tolerance to salt stress. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2014, 15, 145–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiasson, D.; Ekengren, S.K.; Martin, G.B.; Dobney, S.L.; Snedden, W.A. Calmodulin-like proteins from arabidopsis and tomato are involved in host defense against pseudomonas syringae pv. Tomato. Plant Mol. Biol. 2005, 58, 887–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, W.; Smigel, A.; Tsai, Y.C.; Braam, J.; Berkowitz, G.A. Innate immunity signaling: Cytosolic Ca2+ elevation is linked to downstream nitric oxide generation through the action of calmodulin or a calmodulin-like protein. Plant Physiol. 2008, 148, 818–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leba, L.J.; Cheval, C.; Ortiz-Martin, I.; Ranty, B.; Beuzon, C.R.; Galaud, J.P.; Aldon, D. Cml9, an arabidopsis calmodulin-like protein, contributes to plant innate immunity through a flagellin-dependent signalling pathway. Plant J. 2012, 71, 976–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Robe, E.; Jomat, L.; Aldon, D.; Mazars, C.; Galaud, J.P. Cml8, an arabidopsis calmodulin-like protein, plays a role in pseudomonas syringae plant immunity. Plant Cell Physiol. 2017, 58, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Perez, M.; Aldon, D.; Galaud, J.P. Respective contribution of CML8 and CML9, two arabidopsis calmodulin-like proteins, to plant stress responses. Plant Signal Behav. 2017, 12, e1322246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magnan, F.; Ranty, B.; Charpenteau, M.; Sotta, B.; Galaud, J.P.; Aldon, D. Mutations in atcml9, a calmodulin-like protein from arabidopsis thaliana, alter plant responses to abiotic stress and abscisic acid. Plant J. 2008, 56, 575–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheval, C.; Faulkner, C. Plasmodesmal regulation during plant-pathogen interactions. New Phytol. 2018, 217, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; Cheval, C.; Laohavisit, A.; Hocking, B.; Chiasson, D.; Olsson, T.S.G.; Shirasu, K.; Faulkner, C.; Gilliham, M. A calmodulin-like protein regulates plasmodesmal closure during bacterial immune responses. New Phytol. 2017, 215, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arimura, G.; Ozawa, R.; Maffei, M.E. Recent advances in plant early signaling in response to herbivory. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 3723–3739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arimura, G.; Maffei, M.E. Calcium and secondary cpk signaling in plants in response to herbivore attack. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 400, 455–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verrillo, F.; Occhipinti, A.; Kanchiswamy, C.N.; Maffei, M.E. Quantitative analysis of herbivore-induced cytosolic calcium by using a cameleon (YC 3.6) calcium sensor in arabidopsis thaliana. J. Plant Physiol. 2014, 171, 136–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vadassery, J.; Reichelt, M.; Hause, B.; Gershenzon, J.; Boland, W.; Mithofer, A. Cml42-mediated calcium signaling coordinates responses to spodoptera herbivory and abiotic stresses in arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2012, 159, 1159–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholz, S.S.; Vadassery, J.; Heyer, M.; Reichelt, M.; Bender, K.W.; Snedden, W.A.; Boland, W.; Mithofer, A. Mutation of the arabidopsis calmodulin-like protein CML37 deregulates the jasmonate pathway and enhances susceptibility to herbivory. Mol. Plant 2014, 7, 1712–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vadassery, J.; Scholz, S.S.; Mithofer, A. Multiple calmodulin-like proteins in Arabidopsis are induced by insect-derived (spodoptera littoralis) oral secretion. Plant Signal Behav. 2012, 7, 1277–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anandalakshmi, R.; Marathe, R.; Ge, X.; Herr, J.M., Jr.; Mau, C.; Mallory, A.; Pruss, G.; Bowman, L.; Vance, V.B. A calmodulin-related protein that suppresses posttranscriptional gene silencing in plants. Science 2000, 290, 142–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakahara, K.S.; Masuta, C.; Yamada, S.; Shimura, H.; Kashihara, Y.; Wada, T.S.; Meguro, A.; Goto, K.; Tadamura, K.; Sueda, K.; et al. Tobacco calmodulin-like protein provides secondary defense by binding to and directing degradation of virus RNA silencing suppressors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 10113–10118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Huang, C.; Li, Z.; Zhou, X. Suppression of RNA silencing by a plant DNA virus satellite requires a host calmodulin-like protein to repress RDR6 expression. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1003921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, E.J.; Tadamura, K.; Murakami, T.; Inaba, J.I.; Kim, B.M.; Sato, M.; Atsumi, G.; Kuchitsu, K.; Masuta, C.; Nakahara, K.S. Rgs-cam detects and counteracts viral RNA silencing suppressors in plant immune priming. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e00761-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perochon, A.; Dieterle, S.; Pouzet, C.; Aldon, D.; Galaud, J.P.; Ranty, B. Interaction of a plant pseudo-response regulator with a calmodulin-like protein. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 398, 747–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheval, C.; Perez, M.; Leba, L.J.; Ranty, B.; Perochon, A.; Reichelt, M.; Mithofer, A.; Robe, E.; Mazars, C.; Galaud, J.P.; et al. Prr2, a pseudo-response regulator, promotes salicylic acid and camalexin accumulation during plant immunity. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, J.H.; Park, C.Y.; Kim, J.C.; Heo, W.D.; Cheong, M.S.; Park, H.C.; Kim, M.C.; Moon, B.C.; Choi, M.S.; Kang, Y.H.; et al. Direct interaction of a divergent CaM isoform and the transcription factor, MYB2, enhances salt tolerance in Arabidopsis. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 3697–3706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Lv, X.; Xia, X.; Zhou, J.; Shi, K.; Yu, J.; Zhou, Y. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of calcium-dependent protein kinase in tomato. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamel, L.P.; Sheen, J.; Seguin, A. Ancient signals: Comparative genomics of green plant CDPKs. Trends Plant Sci. 2014, 19, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harper, J.F.; Sussman, M.R.; Schaller, G.E.; Putnam-Evans, C.; Charbonneau, H.; Harmon, A.C. A calcium-dependent protein kinase with a regulatory domain similar to calmodulin. Science 1991, 252, 951–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satterlee, J.S.; Sussman, M.R. Unusual membrane-associated protein kinases in higher plants. J. Membr. Biol. 1998, 164, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boudsocq, M.; Droillard, M.J.; Regad, L.; Lauriere, C. Characterization of arabidopsis calcium-dependent protein kinases: Activated or not by calcium? Biochem. J. 2012, 447, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanchiswamy, C.N.; Takahashi, H.; Quadro, S.; Maffei, M.E.; Bossi, S.; Bertea, C.; Zebelo, S.A.; Muroi, A.; Ishihama, N.; Yoshioka, H.; et al. Regulation of arabidopsis defense responses against spodoptera littoralis by cpk-mediated calcium signaling. BMC Plant Biol. 2010, 10, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubiella, U.; Seybold, H.; Durian, G.; Komander, E.; Lassig, R.; Witte, C.P.; Schulze, W.X.; Romeis, T. Calcium-dependent protein kinase/nadph oxidase activation circuit is required for rapid defense signal propagation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 8744–8749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadota, Y.; Sklenar, J.; Derbyshire, P.; Stransfeld, L.; Asai, S.; Ntoukakis, V.; Jones, J.D.; Shirasu, K.; Menke, F.; Jones, A.; et al. Direct regulation of the NADPH oxidase RBOHD by the PRR-associated kinase BIK1 during plant immunity. Mol. Cell 2014, 54, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bundo, M.; Coca, M. Enhancing blast disease resistance by overexpression of the calcium-dependent protein kinase oscpk4 in rice. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2016, 14, 1357–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romeis, T.; Ludwig, A.A.; Martin, R.; Jones, J.D. Calcium-dependent protein kinases play an essential role in a plant defence response. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 5556–5567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Chen, X.; Lin, W.; Chen, S.; Lu, D.; Niu, Y.; Li, L.; Cheng, C.; McCormack, M.; Sheen, J.; et al. Bifurcation of arabidopsis nlr immune signaling via Ca2+-dependent protein kinases. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, M.; Yoshioka, M.; Asai, S.; Nomura, H.; Kuchimura, K.; Mori, H.; Doke, N.; Yoshioka, H. Stcdpk5 confers resistance to late blight pathogen but increases susceptibility to early blight pathogen in potato via reactive oxygen species burst. New Phytol. 2012, 196, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freymark, G.; Diehl, T.; Miklis, M.; Romeis, T.; Panstruga, R. Antagonistic control of powdery mildew host cell entry by barley calcium-dependent protein kinases (CDPKs). Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2007, 20, 1213–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asai, S.; Ichikawa, T.; Nomura, H.; Kobayashi, M.; Kamiyoshihara, Y.; Mori, H.; Kadota, Y.; Zipfel, C.; Jones, J.D.; Yoshioka, H. The variable domain of a plant calcium-dependent protein kinase (CDPK) confers subcellular localization and substrate recognition for NADPH oxidase. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 14332–14340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Hake, K.; Wang, W.; Zhao, T.; Romeis, T.; Tang, D. Calcium-dependent protein kinase5 associates with the truncated NLR protein TIR-nbs2 to contribute to exo70b1-mediated immunity. Plant Cell 2017, 29, 746–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, T.; Rui, L.; Li, J.; Nishimura, M.T.; Vogel, J.P.; Liu, N.; Liu, S.; Zhao, Y.; Dangl, J.L.; Tang, D. A truncated nlr protein, tir-nbs2, is required for activated defense responses in the exo70b1 mutant. PLoS Genet. 2015, 11, e1004945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asano, T.; Hayashi, N.; Kobayashi, M.; Aoki, N.; Miyao, A.; Mitsuhara, I.; Ichikawa, H.; Komatsu, S.; Hirochika, H.; Kikuchi, S.; et al. A rice calcium-dependent protein kinase OSCPK12 oppositely modulates salt-stress tolerance and blast disease resistance. Plant J. 2012, 69, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roux, M.; Schwessinger, B.; Albrecht, C.; Chinchilla, D.; Jones, A.; Holton, N.; Malinovsky, F.G.; Tor, M.; de Vries, S.; Zipfel, C. The arabidopsis leucine-rich repeat receptor-like kinases BAK1/SERK3 and BKK1/SERK4 are required for innate immunity to hemibiotrophic and biotrophic pathogens. Plant Cell 2011, 23, 2440–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwessinger, B.; Roux, M.; Kadota, Y.; Ntoukakis, V.; Sklenar, J.; Jones, A.; Zipfel, C. Phosphorylation-dependent differential regulation of plant growth, cell death, and innate immunity by the regulatory receptor-like kinase bak1. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1002046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monaghan, J.; Matschi, S.; Shorinola, O.; Rovenich, H.; Matei, A.; Segonzac, C.; Malinovsky, F.G.; Rathjen, J.P.; MacLean, D.; Romeis, T.; et al. The calcium-dependent protein kinase CPK28 buffers plant immunity and regulates bik1 turnover. Cell Host Microbe 2014, 16, 605–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Grubb, L.E.; Wang, J.; Liang, X.; Li, L.; Gao, C.; Ma, M.; Feng, F.; Li, M.; Li, L.; et al. A regulatory module controlling homeostasis of a plant immune kinase. Mol. Cell 2018, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bender, K.W.; Blackburn, R.K.; Monaghan, J.; Derbyshire, P.; Menke, F.L.; Zipfel, C.; Goshe, M.B.; Zielinski, R.E.; Huber, S.C. Autophosphorylation-based calcium (Ca2+) sensitivity priming and Ca2+/calmodulin inhibition of arabidopsis thaliana Ca2+-dependent protein kinase 28 (cpk28). J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 3988–4002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAinsh, M.R.; Pittman, J.K. Shaping the calcium signature. New Phytol. 2009, 181, 275–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, W.; Yoshioda, K.; Berkowitz, G.A. Cyclic nucleotide gated channel and Ca2+-mediated signal transduction during plant innate immune responses to pathogen. Plant Signal Behav. 2007, 2, 548–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, R.; Ma, W.; Lemtiri-Chlieh, F.; Tsaltas, D.; Leng, Q.; von Bodman, S.; Berkowitz, G.A. Death don’t have no mercy and neither does calcium: Arabidopsis CYCLIC NUCLEOTIDE GATED CHANNEL2 and innate immunity. Plant Cell 2007, 19, 1081–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonza, M.C.; Morandini, P.; Luoni, L.; Geisler, M.; Palmgreen, M.G.; De Michelis, M.I. At-ACA8 encodes a plasma membrane-localized calcium ATPase of Arabidopsis with a calmodulin-binding domain at the N-terminus. Plant Physiol. 2000, 123, 1495–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frei dit Frey, N.; Mbengue, M.; Kwaaitaal, M.; Nitsch, L.; Attenbach, D.; Haweker, H.; Lozano-Duran, R.; Njo, M.F.; Beeckman, T.; Huettel, B.; et al. Plasma membrane calcium ATPases are important components of receptor-mediated signalling in plant immune responses and development. Plant Physiol. 2012, 159, 789–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, M.; Kim, P.; Li, G.; Elowsky, C.G.; Alfano, J.R. A bacterial effector co-opts calmodulin to target the plant microtubule network. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 19, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buttner, D.; Bonas, U. Regulation and secretion of xanthomonas virulence factors. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 34, 107–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ameen, G.; Mechan, M. XVI congress on molecular plant-microbe interactions meeting report. In Proceedings of the Travel Awardees for the 2016 is-MPMI XVII Congress, Portland, OR, USA, 16–21 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wolff, J.; Cook, G.H.; Goldhammer, A.R.; Berkowitz, S.A. Calmodulin activates prokaryotic adenylate cyclase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1980, 77, 3841–3844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knight, H. Calcium signaling during abiotic stress in plants. Int. Rev. Cytol. 2000, 195, 269–324. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.; Gao, X.; Feng, B.; Sheen, J.; Shan, L.; He, P. Plant immune response to pathogens differs with changing temperatures. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).