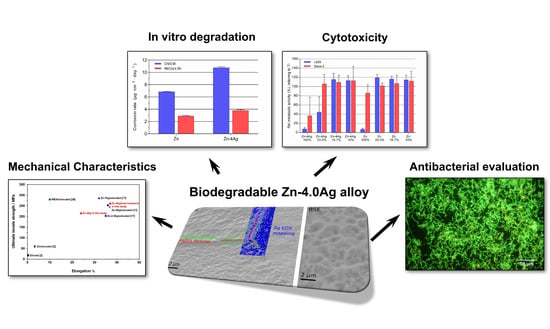
Mechanical Characteristics, In Vitro Degradation, Cytotoxicity, and Antibacterial Evaluation of Zn-4.0Ag Alloy as a Biodegradable Material
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials Preparation
2.2. Microstructure Observation and Mechanical Characteristic Test
2.3. Extract Preparation
2.4. Corrosion Rate Determination
2.5. Cytotoxicity Tests
2.6. Antibacterial Effect Evaluation
2.7. Statistical Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties
3.2. Corrosion Properties
3.3. Cytocompatibility
3.4. Antibacterial Evaluation
4. Conclusions
- After thermomechanical treatment, the yield strength (YS), ultimate tensile strength (UTS) and elongation of the alloy are 157 MPa, 261 MPa, and 37%, respectively, rendering this alloy a promising material for bioresorbable stents. Future alloy development will focus on the optimization of the microstructure to ensure a safe application.
- The corrosion rate of Zn-4Ag calculated from the released Zn ions in DMEM extract was approximately 10.75 ± 0.16 μg cm–2 day–1, which is higher than that of pure Zn.
- A cytotoxic effect decreasing viability and proliferation of L929 and Saos-2 cells was observed, but only in the undiluted extracts of the Zn-4Ag alloy. However, this finding should not be overestimated, since the suitability of the used ISO 10993-5 standard method has to be discussed for degradable materials, according to each application.
- In vitro antibacterial evaluation showed the Zn-4Ag alloy has the potential to inhibit initial S. gordonii adhesion.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zheng, Y.; Gu, X.; Witte, F. Biodegradable metals. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2014, 77, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katarivas Levy, G.; Goldman, J.; Aghion, E. The prospects of zinc as a structural material for biodegradable implants—A review paper. Metals 2017, 7, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moravej, M.; Mantovani, D. Biodegradable metals for cardiovascular stent application: Interests and new opportunities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 4250–4270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraus, T.; Fischerauer, S.F.; Hänzi, A.C.; Uggowitzer, P.J.; Löffler, J.F.; Weinberg, A.M. Magnesium alloys for temporary implants in osteosynthesis: In vivo studies of their degradation and interaction with bone. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 1230–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geis-Gerstorfer, J.; Schille, C.; Schweizer, E.; Rupp, F.; Scheideler, L.; Reichel, H.-P.; Hort, N.; Nolte, A.; Wendel, H.-P. Blood triggered corrosion of magnesium alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2011, 176, 1761–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierson, D.; Edick, J.; Tauscher, A.; Pokorney, E.; Bowen, P.; Gelbaugh, J.; Stinson, J.; Getty, H.; Lee, C.H.; Drelich, J. A simplified in vivo approach for evaluating the bioabsorbable behavior of candidate stent materials. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2012, 100, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drynda, A.; Hassel, T.; Bach, F.W.; Peuster, M. In vitro and in vivo corrosion properties of new iron–manganese alloys designed for cardiovascular applications. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2015, 103, 649–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Liu, B.; Wu, Y.; Zheng, Y. Comparative in vitro study on pure metals (Fe, Mn, Mg, Zn and W) as biodegradable metals. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2013, 29, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, P.K.; Guillory, R.J.; Shearier, E.R.; Seitz, J.-M.; Drelich, J.; Bocks, M.; Zhao, F.; Goldman, J. Metallic zinc exhibits optimal biocompatibility for bioabsorbable endovascular stents. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 56, 467–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beyersmann, D.; Haase, H. Functions of zinc in signaling, proliferation and differentiation of mammalian cells. Biometals 2001, 14, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, A.S. Zinc in human health: Effect of zinc on immune cells. Mol. Med. 2008, 14, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schenck, J.F. The role of magnetic susceptibility in magnetic resonance imaging: MRI magnetic compatibility of the first and second kinds. Med. Phys. 1996, 23, 815–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vojtěch, D.; Kubásek, J.; Šerák, J.; Novák, P. Mechanical and corrosion properties of newly developed biodegradable Zn-based alloys for bone fixation. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 3515–3522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubásek, J.; Vojtěch, D. Zn-based alloys as an alternative biodegradable materials. Proc. Metal 2012, 5, 23–25. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Yang, H.; Zheng, Y.; Zhou, F.; Qiu, K.; Wang, X. Design and characterizations of novel biodegradable ternary Zn-based alloys with IIA nutrient alloying elements Mg, Ca and Sr. Mater. Des. 2015, 83, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Liu, X.; Fan, B.; Lan, P.; Zhou, F.; Li, X.; Wang, H.; Xiao, X.; Li, L.; Zhao, S. Mechanical properties, in vitro degradation behavior, hemocompatibility and cytotoxicity evaluation of Zn–1.2 Mg alloy for biodegradable implants. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 86410–86419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikora-Jasinska, M.; Mostaed, E.; Mostaed, A.; Beanland, R.; Mantovani, D.; Vedani, M. Fabrication, mechanical properties and in vitro degradation behavior of newly developed Zn Ag alloys for degradable implant applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 77, 1170–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tie, D.; Feyerabend, F.; Müller, W.-D.; Schade, R.; Liefeith, K.; Kainer, K.U.; Willumeit, R. Antibacterial biodegradable Mg-Ag alloys. Eur. Cells Mater. 2012, 25, 284–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Organization for Standardization. ISO 10993-12: 2012. Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices–Part 12: Sample Preparation and Reference Materials; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Witte, F.; Xi, T.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, K.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, D.; Meng, J.; Li, Y.; Li, W. Recommendation for modifying current cytotoxicity testing standards for biodegradable magnesium-based materials. Acta Biomater. 2015, 21, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubásek, J.; Vojtěch, D.; Jablonská, E.; Pospíšilová, I.; Lipov, J.; Ruml, T. Structure, mechanical characteristics and in vitro degradation, cytotoxicity, genotoxicity and mutagenicity of novel biodegradable Zn–Mg alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 58, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jablonská, E.; Vojtěch, D.; Fousová, M.; Kubásek, J.; Lipov, J.; Fojt, J.; Ruml, T. Influence of surface pre-treatment on the cytocompatibility of a novel biodegradable ZnMg alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 68, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Čapek, J.; Jablonská, E.; Lipov, J.; Kubatík, T.F.; Vojtěch, D. Preparation and characterization of porous zinc prepared by spark plasma sintering as a material for biodegradable scaffolds. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 203, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zheng, Y. Effects of alloying elements (Mn, Co, Al, W, Sn, B, C and S) on biodegradability and in vitro biocompatibility of pure iron. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 1407–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Organization for Standardization. ISO 10993–5: 2009 Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices–Part 5: Tests for In Vitro Cytotoxicity; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Kirkland, N.; Lespagnol, J.; Birbilis, N.; Staiger, M. A survey of bio-corrosion rates of magnesium alloys. Corros. Sci. 2010, 52, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, P.K.; Drelich, J.; Goldman, J. Zinc exhibits ideal physiological corrosion behavior for bioabsorbable stents. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 2577–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, X.-N.; Zheng, Y.-F. A review on magnesium alloys as biodegradable materials. Front. Mater. Sci. China 2010, 4, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostaed, E.; Sikora-Jasinska, M.; Ramirez-Ledesma, A.L.; Levesque, L.; Mantovani, D.; Vedani, M. Development of Zn-Ag-Mn alloys for future bioabsorbable vascular stents. In Proceedings of the 9th Symposium on Biodegradable Metals, Bertinoro, Italy, 27 August–1 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Xin, Y.; Hu, T.; Chu, P. In vitro studies of biomedical magnesium alloys in a simulated physiological environment: A review. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 1452–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, A.H.M.; Luthringer, B.J.; Feyerabend, F.; Willumeit, R. Mg and Mg alloys: How comparable are in vitro and in vivo corrosion rates? A review. Acta Biomater. 2015, 13, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patterson, M.K.; Dell’orco, R.T. Preparation of McCoy’s medium 5A. Methods Cell Sci. 1978, 4, 737–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheideler, L.; Füger, C.; Schille, C.; Rupp, F.; Wendel, H.-P.; Hort, N.; Reichel, H.; Geis-Gerstorfer, J. Comparison of different in vitro tests for biocompatibility screening of Mg alloys. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 8740–8745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Sun, J.; Yang, Y.; Pu, Z.; Zheng, Y. In vitro investigation of ultra-pure Zn and its mini-tube as potential bioabsorbable stent material. Mater. Lett. 2015, 161, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, W.; Maitz, M.F.; Chen, M.; Zhang, H.; Mao, J.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, N.; Wan, G. Comparative corrosion behavior of Zn with Fe and Mg in the course of immersion degradation in phosphate buffered saline. Corros. Sci. 2016, 111, 541–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, J.; Prosenc, M.H.; Wolff, M.; Hort, N.; Willumeit, R.; Feyerabend, F. Interference of magnesium corrosion with tetrazolium-based cytotoxicity assays. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 1813–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hambidge, K.M.; Krebs, N.F. Zinc deficiency: A special challenge. J. Nutr. 2007, 137, 1101–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plum, L.M.; Rink, L.; Haase, H. The essential toxin: Impact of zinc on human health. Int. J. Environ. Res. Publ. Health 2010, 7, 1342–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadrup, N.; Lam, H.R. Oral toxicity of silver ions, silver nanoparticles and colloidal silver—A review. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2014, 68, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murni, N.; Dambatta, M.; Yeap, S.; Froemming, G.; Hermawan, H. Cytotoxicity evaluation of biodegradable Zn–3Mg alloy toward normal human osteoblast cells. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 49, 560–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Yang, H.; Li, X.; Zheng, Y. In vitro evaluation of the feasibility of commercial Zn alloys as biodegradable metals. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2016, 32, 909–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhsheshi-Rad, H.; Hamzah, E.; Low, H.; Kasiri-Asgarani, M.; Farahany, S.; Akbari, E.; Cho, M. Fabrication of biodegradable Zn-Al-Mg alloy: Mechanical properties, corrosion behavior, cytotoxicity and antibacterial activities. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 73, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misch, C. Vertical Alveolar Ridge Augmentation in Implant Dentistry: A Surgical Manual; LWW: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2017; p. 85. [Google Scholar]
- Goudouri, O.-M.; Kontonasaki, E.; Lohbauer, U.; Boccaccini, A.R. Antibacterial properties of metal and metalloid ions in chronic periodontitis and peri-implantitis therapy. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 3795–3810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noronha, V.T.; Paula, A.J.; Durán, G.; Galembeck, A.; Cogo-Müller, K.; Franz-Montan, M.; Durán, N. Silver nanoparticles in dentistry. Dent. Mater. 2017, 33, 1110–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafeeq, S.; Kuipers, O.P.; Kloosterman, T.G. The role of zinc in the interplay between pathogenic streptococci and their hosts. Mol. Microbiol. 2013, 88, 1047–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Zhang, W.; Qiao, Y.; Jiang, X.; Liu, X.; Ding, C. Antibacterial activity and increased bone marrow stem cell functions of Zn-incorporated TiO2 coatings on titanium. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 904–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









| Alloy/Processing | Mechanical Properties | References | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yield Strength (YS0.2) (MPa) | Ultimate Tensile Strength (UTS) (MPa) | Elongation to Failure (%) | Hardness (HV1) | ||
| Zn-4Ag * | 157 | 261 | 37 | 73 | In this study |
| Zn-4Ag ** | 149 | 215 | 24 | 82 | In this study |
| WE43/extruded | 195 | 280 | 10 | - | [28] |
| Zn/cast | 10 | 18 | 0.32 | 38 | [2] |
| Zn/extruded | 35 | 60 | 3.5 | - | [2] |
| Zn/hot rolled | 30–110 | 50–140 | 5.8–36 | 39 | [2] |
| Zn-2.5Ag/extruded | 147 | 203 | 35 | - | [17,29] |
| Zn-5Ag/extruded | 205 | 253 | 36 | - | [17,29] |
| Zn-7Ag/extruded | 236 | 287 | 32 | - | [17] |
| Inorganic Ions (mmol L−1) | Organic Components | Concentrations of Buffering Agents (mmol L−1) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Composition Title | Na | K | Mg | Cl | Ca | HPO4 | SO4 | HCO3 | Protein (g L−1) | Glucose (mmol L−1) | Amino Acids (g L−1) | |
| Blood plasma | 142 | 5.0 | 1.5 | 103.0 | 2.5 | 1.0 | 0.5 | 27.0 | 63–80 | 3.6–5.2 | Variable | 43.5–45.5 |
| DMEM | 127.3 | 5.3 | 0.8 | 90.8 | 1.8 | 0.9 | 0.8 | 44.1 | - | 4.5 | 1.6 | 70 |
| McCoy’s 5A | 141.0 | 5.4 | 0.8 | 117.2 | 1.2 | 4.2 | 0.8 | 26.2 | - | 16.6 | 0.4 | 30.4 |
| Cell Medium | Samples | Zn Ion Concentration (μmol/L) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100% Extracts | 33.3% Extracts | 16.7% Extracts | 10% Extracts | ||
| DMEM | Pure Zn | 314.4 | 107.4 | 55.5 | 34.7 |
| Zn-4Ag | 493.4 | 167.2 | 85.4 | 52.6 | |
| McCoy’s 5A | Pure Zn | 132.8 | 51.5 | 31.1 | 22.9 |
| Zn-4Ag | 174.4 | 65.4 | 38.0 | 27.0 | |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, P.; Schille, C.; Schweizer, E.; Rupp, F.; Heiss, A.; Legner, C.; Klotz, U.E.; Geis-Gerstorfer, J.; Scheideler, L. Mechanical Characteristics, In Vitro Degradation, Cytotoxicity, and Antibacterial Evaluation of Zn-4.0Ag Alloy as a Biodegradable Material. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 755. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19030755
Li P, Schille C, Schweizer E, Rupp F, Heiss A, Legner C, Klotz UE, Geis-Gerstorfer J, Scheideler L. Mechanical Characteristics, In Vitro Degradation, Cytotoxicity, and Antibacterial Evaluation of Zn-4.0Ag Alloy as a Biodegradable Material. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(3):755. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19030755
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Ping, Christine Schille, Ernst Schweizer, Frank Rupp, Alexander Heiss, Claudia Legner, Ulrich E. Klotz, Jürgen Geis-Gerstorfer, and Lutz Scheideler. 2018. "Mechanical Characteristics, In Vitro Degradation, Cytotoxicity, and Antibacterial Evaluation of Zn-4.0Ag Alloy as a Biodegradable Material" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 3: 755. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19030755
APA StyleLi, P., Schille, C., Schweizer, E., Rupp, F., Heiss, A., Legner, C., Klotz, U. E., Geis-Gerstorfer, J., & Scheideler, L. (2018). Mechanical Characteristics, In Vitro Degradation, Cytotoxicity, and Antibacterial Evaluation of Zn-4.0Ag Alloy as a Biodegradable Material. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(3), 755. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19030755