Immunomodulatory Function of Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells during B Cell-Mediated Immune Responses
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. General Phenotype of MDSCs
3. MDSC-Mediated Regulation of B Cell Differentiation
4. Direct Regulation of B Cell Responses by Effector Molecules Expressed by MDSCs
4.1. Arginase-1
4.2. NO/ROS
4.3. TGF-β
4.4. PGE2
4.5. Cysteine
5. Direct Regulation of B Cell Responses by MDSCs via Expression of Cell Surface Molecules
6. Indirect Regulation of B Cell Responses by MDSCs
6.1. Regulatory B Cells
6.2. Treg Cells
7. MDSC Signaling Pathways Involved in B Cell Regulation
7.1. TNF-α Signaling
7.2. Stat3 Pathway
7.3. TGF-β Signaling
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Breg | Regulatory B cell |
| CIA | Collagen-induced arthritis |
| DC | Dendritic cell |
| iNOS | Inducible nitric oxide synthase |
| MDSC | Myeloid-derived suppressor cell |
| M-MDSC NF-κB | Monocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cell Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells |
| NK | Natural killer |
| NO | Nitric oxide |
| PD-1 | Programmed cell death protein 1 |
| PD-L1 | Programmed cell death ligand 1 |
| PGE2 | Prostaglandin E2 |
| PMN-MDSC | Polymorphonuclear myeloid-derived suppressor cell |
| PNT | Peroxynitrite |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| SLE | Systemic lupus erythematosus |
| SOD | Superoxide dismutase |
| Stat | Signal transducer and activator of transcription |
| sTNF | Secretory tumor necrosis factor |
| tBreg | Tumor-evoked regulatory B cell |
| TGF-β | Transforming growth factor-beta |
| tmTNF | Transmembrane tumor necrosis factor |
| TNF | Tumor necrosis factor |
| TNFR | Tumor necrosis factor receptor |
| Treg | Regulatory T cell |
| VISTA | V-domain immunoglobulin suppressor of T cell activation |
References
- Young, M.R.; Newby, M.; Wepsic, H.T. Hematopoiesis and suppressor bone marrow cells in mice bearing large metastatic Lewis lung carcinoma tumors. Cancer Res. 1987, 47, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Paraiso, K.H.; Ghansah, T.; Costello, A.; Engelman, R.W.; Kerr, W.G. Induced SHIP deficiency expands myeloid regulatory cells and abrogates graft-versus-host disease. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 2893–2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawanobori, Y.; Ueha, S.; Kurachi, M.; Shimaoka, T.; Talmadge, J.E.; Abe, J.; Shono, Y.; Kitabatake, M.; Kakimi, K.; Mukaida, N.; et al. Chemokine-mediated rapid turnover of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in tumor-bearing mice. Blood 2008, 111, 5457–5466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ochoa, A.C.; Zea, A.H.; Hernandez, C.; Rodriguez, P.C. Arginase, prostaglandins, and myeloid-derived suppressor cells in renal cell carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 721s–726s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fricke, I.; Mirza, N.; Dupont, J.; Lockhart, C.; Jackson, A.; Lee, J.H.; Sosman, J.A.; Gabrilovich, D.I. Vascular endothelial growth factor-trap overcomes defects in dendritic cell differentiation but does not improve antigen-specific immune responses. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 4840–4848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youn, J.I.; Nagaraj, S.; Collazo, M.; Gabrilovich, D.I. Subsets of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in tumor-bearing mice. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 5791–5802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabrilovich, D.I.; Nagaraj, S. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells as regulators of the immune system. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 162–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goh, C.; Narayanan, S.; Hahn, Y.S. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells: The dark knight or the joker in viral infections? Immunol. Rev. 2013, 255, 210–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trikha, P.; Carson, W.E., III. Signaling pathways involved in MDSC regulation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1846, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostrand-Rosenberg, S.; Sinha, P. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells: Linking inflammation and cancer. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 4499–4506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, K.H.; Beury, D.W.; Ostrand-Rosenberg, S. Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells: Critical Cells Driving Immune Suppression in the Tumor Microenvironment. Adv. Cancer Res. 2015, 128, 95–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Velez-Delgado, A.; Mathew, E.; Li, D.; Mendez, F.M.; Flannagan, K.; Rhim, A.D.; Simeone, D.M.; Beatty, G.L.; Pasca di Magliano, M. Myeloid cells are required for PD-1/PD-L1 checkpoint activation and the establishment of an immunosuppressive environment in pancreatic cancer. Gut 2017, 66, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.R.; Kwak, Y.; Yang, T.; Han, J.H.; Park, S.H.; Ye, M.B.; Lee, W.; Sim, K.Y.; Kang, J.A.; Kim, Y.C.; et al. Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells Are Controlled by Regulatory T Cells via TGF-β during Murine Colitis. Cell Rep. 2016, 17, 3219–3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shurin, G.V.; Ma, Y.; Shurin, M.R. Immunosuppressive mechanisms of regulatory dendritic cells in cancer. Cancer Microenviron. Off. J. Int. Cancer Microenviron. Soc. 2013, 6, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, Y.; Sarhan, D.; Steven, A.; Seliger, B.; Kiessling, R.; Lundqvist, A. Inhibition of tumor-derived prostaglandin-e2 blocks the induction of myeloid-derived suppressor cells and recovers natural killer cell activity. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 4096–4106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crook, K.R.; Jin, M.; Weeks, M.F.; Rampersad, R.R.; Baldi, R.M.; Glekas, A.S.; Shen, Y.; Esserman, D.A.; Little, P.; Schwartz, T.A.; et al. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells regulate T cell and B cell responses during autoimmune disease. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2015, 97, 573–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rastad, J.L.; Green, W.R. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells in murine AIDS inhibit B-cell responses in part via soluble mediators including reactive oxygen and nitrogen species, and TGF-β. Virology 2016, 499, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunt, S.K.; Clements, V.K.; Hanson, E.M.; Sinha, P.; Ostrand-Rosenberg, S. Inflammation enhances myeloid-derived suppressor cell cross-talk by signaling through Toll-like receptor 4. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2009, 85, 996–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youn, J.I.; Gabrilovich, D.I. The biology of myeloid-derived suppressor cells: The blessing and the curse of morphological and functional heterogeneity. Eur. J. Immunol. 2010, 40, 2969–2975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youm, Y.H.; Kanneganti, T.D.; Vandanmagsar, B.; Zhu, X.; Ravussin, A.; Adijiang, A.; Owen, J.S.; Thomas, M.J.; Francis, J.; Parks, J.S.; et al. The NLRP3 inflammasome promotes age-related thymic demise and immunosenescence. Cell Rep. 2012, 1, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lechner, M.G.; Megiel, C.; Russell, S.M.; Bingham, B.; Arger, N.; Woo, T.; Epstein, A.L. Functional characterization of human Cd33+ and Cd11b+ myeloid-derived suppressor cell subsets induced from peripheral blood mononuclear cells co-cultured with a diverse set of human tumor cell lines. J. Transl. Med. 2011, 9, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gustafson, M.P.; Lin, Y.; Maas, M.L.; Van Keulen, V.P.; Johnston, P.B.; Peikert, T.; Gastineau, D.A.; Dietz, A.B. A method for identification and analysis of non-overlapping myeloid immunophenotypes in humans. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohanbash, G.; McKaveney, K.; Sakaki, M.; Ueda, R.; Mintz, A.H.; Amankulor, N.; Fujita, M.; Ohlfest, J.R.; Okada, H. GM-CSF promotes the immunosuppressive activity of glioma-infiltrating myeloid cells through interleukin-4 receptor-α. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 6413–6423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obermajer, N.; Muthuswamy, R.; Odunsi, K.; Edwards, R.P.; Kalinski, P. PGE(2)-induced CXCL12 production and CXCR4 expression controls the accumulation of human MDSCs in ovarian cancer environment. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 7463–7470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Idorn, M.; Kollgaard, T.; Kongsted, P.; Sengelov, L.; Thor Straten, P. Correlation between frequencies of blood monocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cells, regulatory T cells and negative prognostic markers in patients with castration-resistant metastatic prostate cancer. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2014, 63, 1177–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, A.; Zhang, B.; Wang, B.; Zhang, F.; Fan, K.X.; Guo, Y.J. Increased CD14+HLA-DR-/low myeloid-derived suppressor cells correlate with extrathoracic metastasis and poor response to chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer patients. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2013, 62, 1439–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandau, S.; Trellakis, S.; Bruderek, K.; Schmaltz, D.; Steller, G.; Elian, M.; Suttmann, H.; Schenck, M.; Welling, J.; Zabel, P.; et al. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells in the peripheral blood of cancer patients contain a subset of immature neutrophils with impaired migratory properties. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2011, 89, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilwani, F.A.; Knight, K.L. Adipocyte-derived soluble factor(s) inhibits early stages of B lymphopoiesis. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 4379–4386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, D.E.; Knight, K.L. Inhibition of B Lymphopoiesis by Adipocytes and IL-1-Producing Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 2666–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenberg, A.S.; Obin, M.S. Obesity and the role of adipose tissue in inflammation and metabolism. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 83, 461s–465s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruchard, M.; Mignot, G.; Derangere, V.; Chalmin, F.; Chevriaux, A.; Vegran, F.; Boireau, W.; Simon, B.; Ryffel, B.; Connat, J.L.; et al. Chemotherapy-triggered cathepsin B release in myeloid-derived suppressor cells activates the NLRP3 inflammasome and promotes tumor growth. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, D.E.; Witte, P.L.; Knight, K.L. Bone marrow fat and the decline of B lymphopoiesis in rabbits. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2016, 58, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lelis, F.J.N.; Jaufmann, J.; Singh, A.; Fromm, K.; Teschner, A.C.; Poschel, S.; Schafer, I.; Beer-Hammer, S.; Rieber, N.; Hartl, D. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells modulate B-cell responses. Immunol. Lett. 2017, 188, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bronte, V.; Zanovello, P. Regulation of immune responses by L-arginine metabolism. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 5, 641–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, P.C.; Ochoa, A.C. Arginine regulation by myeloid derived suppressor cells and tolerance in cancer: Mechanisms and therapeutic perspectives. Immunol. Rev. 2008, 222, 180–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connor, M.A.; Fu, W.W.; Green, K.A.; Green, W.R. Subpopulations of M-MDSCs from mice infected by an immunodeficiency-causing retrovirus and their differential suppression of T- vs. B-cell responses. Virology 2015, 485, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, K.A.; Cook, W.J.; Green, W.R. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells in murine retrovirus-induced AIDS inhibit T- and B-cell responses in vitro that are used to define the immunodeficiency. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 2058–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bingisser, R.M.; Tilbrook, P.A.; Holt, P.G.; Kees, U.R. Macrophage-derived nitric oxide regulates T cell activation via reversible disruption of the Jak3/STAT5 signaling pathway. J. Immunol. 1998, 160, 5729–5734. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mannick, J.B.; Hausladen, A.; Liu, L.; Hess, D.T.; Zeng, M.; Miao, Q.X.; Kane, L.S.; Gow, A.J.; Stamler, J.S. Fas-induced caspase denitrosylation. Science 1999, 284, 651–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusmartsev, S.; Nefedova, Y.; Yoder, D.; Gabrilovich, D.I. Antigen-specific inhibition of CD8+ T cell response by immature myeloid cells in cancer is mediated by reactive oxygen species. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 989–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagaraj, S.; Gupta, K.; Pisarev, V.; Kinarsky, L.; Sherman, S.; Kang, L.; Herber, D.L.; Schneck, J.; Gabrilovich, D.I. Altered recognition of antigen is a mechanism of CD8+ T cell tolerance in cancer. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 828–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusmartsev, S.; Gabrilovich, D.I. Inhibition of myeloid cell differentiation in cancer: The role of reactive oxygen species. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2003, 74, 186–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, T.; Gabrilovich, D.I. Molecular pathways: Tumor-infiltrating myeloid cells and reactive oxygen species in regulation of tumor microenvironment. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 4877–4882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Huang, J.; Ren, X.; Gorska, A.E.; Chytil, A.; Aakre, M.; Carbone, D.P.; Matrisian, L.M.; Richmond, A.; Lin, P.C.; et al. Abrogation of TGF β signaling in mammary carcinomas recruits Gr-1+CD11b+ myeloid cells that promote metastasis. Cancer Cell 2008, 13, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, P.; Clements, V.K.; Fulton, A.M.; Ostrand-Rosenberg, S. Prostaglandin E2 promotes tumor progression by inducing myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 4507–4513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obermajer, N.; Kalinski, P. Generation of myeloid-derived suppressor cells using prostaglandin E2. Transpl. Res. 2012, 1, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rodriguez, P.C.; Hernandez, C.P.; Quiceno, D.; Dubinett, S.M.; Zabaleta, J.; Ochoa, J.B.; Gilbert, J.; Ochoa, A.C. Arginase I in myeloid suppressor cells is induced by COX-2 in lung carcinoma. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 202, 931–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phipps, R.P.; Stein, S.H.; Roper, R.L. A new view of prostaglandin E regulation of the immune response. Immunol. Today 1991, 12, 349–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, M.K.; Sinha, P.; Clements, V.K.; Rodriguez, P.; Ostrand-Rosenberg, S. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells inhibit T-cell activation by depleting cystine and cysteine. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.; Hathcock, K.; Zheng, B.; Kepler, T.B.; Hodes, R.; Kelsoe, G. Cellular interaction in germinal centers. Roles of CD40 ligand and B7-2 in established germinal centers. J. Immunol. 1995, 155, 556–567. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kansas, G.S. Structure and function of L-selectin. Acta Pathol. Microbiol. Immunol. Scand. 1992, 100, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steeber, D.A.; Subramanian, H.; Grailer, J.J.; Conway, R.M.; Storey, T.J. L-selectin-mediated leukocyte adhesion and migration. In Adhesion Molecules: Function and Inhibition; Ley, K., Ed.; Birkhäuser: Basel, Switzerland, 2007; pp. 27–70. [Google Scholar]
- Hanson, E.M.; Clements, V.K.; Sinha, P.; Ilkovitch, D.; Ostrand-Rosenberg, S. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells down-regulate L-selectin expression on CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 937–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, K.A.; Wang, L.; Noelle, R.J.; Green, W.R. Selective Involvement of the Checkpoint Regulator VISTA in Suppression of B-Cell, but Not T-Cell, Responsiveness by Monocytic Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells from Mice Infected with an Immunodeficiency-Causing Retrovirus. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 9693–9698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ku, A.W.; Muhitch, J.B.; Powers, C.A.; Diehl, M.; Kim, M.; Fisher, D.T.; Sharda, A.P.; Clements, V.K.; O’Loughlin, K.; Minderman, H.; et al. Tumor-induced MDSC act via remote control to inhibit L-selectin-dependent adaptive immunity in lymph nodes. eLife 2016, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Mercier, I.; Chen, W.; Lines, J.L.; Day, M.; Li, J.; Sergent, P.; Noelle, R.J.; Wang, L. VISTA Regulates the Development of Protective Antitumor Immunity. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 1933–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosser, E.C.; Mauri, C. Regulatory B cells: Origin, phenotype, and function. Immunity 2015, 42, 607–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauri, C.; Bosma, A. Immune regulatory function of B cells. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 30, 221–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosser, E.C.; Blair, P.A.; Mauri, C. Cellular targets of regulatory B cell-mediated suppression. Mol. Immunol. 2014, 62, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitale, G.; Mion, F.; Pucillo, C. Regulatory B cells: Evidence, developmental origin and population diversity. Mol. Immunol. 2010, 48, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, M.; Miles, K.; Salter, D.; Gray, D.; Savill, J. Apoptotic cells protect mice from autoimmune inflammation by the induction of regulatory B cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 14080–14085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, J.G.; Chavez-Rueda, K.A.; Eddaoudi, A.; Meyer-Bahlburg, A.; Rawlings, D.J.; Ehrenstein, M.R.; Mauri, C. Novel suppressive function of transitional 2 B cells in experimental arthritis. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 7868–7878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, M.J.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, E.K.; Lee, E.J.; Park, S.H.; Kwok, S.K.; Cho, M.L. Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells Induce the Expansion of Regulatory B Cells and Ameliorate Autoimmunity in the Sanroque Mouse Model of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Arthr. Rheumatol. 2016, 68, 2717–2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, H.W.; Hillsamer, P.; Banham, A.H.; Kim, C.H. Cutting edge: Direct suppression of B cells by CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 4180–4183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iikuni, N.; Lourenco, E.V.; Hahn, B.H.; La Cava, A. Cutting edge: Regulatory T cells directly suppress B cells in systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 1518–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, A.; Liu, Y.; Chen, W.; Wang, J.; Xue, Y.; Huang, F.; Rong, L.; Lin, J.; Liu, D.; Yan, M.; et al. TGF-beta-Induced Regulatory T Cells Directly Suppress B Cell Responses through a Noncytotoxic Mechanism. J. Immunol. 2016, 196, 3631–3641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.M.; Thornton, A.M.; DiPaolo, R.J.; Shevach, E.M. Activated CD4+CD25+ T cells selectively kill B lymphocytes. Blood 2006, 107, 3925–3932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serafini, P.; Mgebroff, S.; Noonan, K.; Borrello, I. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells promote cross-tolerance in B-cell lymphoma by expanding regulatory T cells. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 5439–5449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, B.; Pan, P.Y.; Li, Q.; Sato, A.I.; Levy, D.E.; Bromberg, J.; Divino, C.M.; Chen, S.H. Gr-1+CD115+ immature myeloid suppressor cells mediate the development of tumor-induced T regulatory cells and T-cell anergy in tumor-bearing host. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 1123–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, M.R.; Ledgerwood, L.; Yang, Y.; Xu, J.; Lal, G.; Burrell, B.; Ma, G.; Hashimoto, D.; Li, Y.; Boros, P.; et al. Monocytic suppressive cells mediate cardiovascular transplantation tolerance in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 2486–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luan, Y.; Mosheir, E.; Menon, M.C.; Wilson, D.; Woytovich, C.; Ochando, J.; Murphy, B. Monocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cells accumulate in renal transplant patients and mediate CD4+Foxp3+ Treg expansion. Am. J. Transpl. Off. J. Am. Soc. Transpl. Am. Soc. Transpl. Surg. 2013, 13, 3123–3131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Rong, L.; Zhao, X.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Deng, J.; Wu, H.; Xu, X.; Erben, U.; Wu, P.; et al. TNF signaling drives myeloid-derived suppressor cell accumulation. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 4094–4104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Li, L.; Shi, W.; Jiang, X.; Xu, Y.; Gong, F.; Zhou, M.; Edwards, C.K., 3rd; Li, Z. Mechanism of action differences in the antitumor effects of transmembrane and secretory tumor necrosis factor-alpha in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2006, 55, 1470–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doss, G.P.; Agoramoorthy, G.; Chakraborty, C. TNF/TNFR: Drug target for autoimmune diseases and immune-mediated inflammatory diseases. Front. Biosci. 2014, 19, 1028–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ba, H.; Li, B.; Li, X.; Li, C.; Feng, A.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Yin, B. Transmembrane tumor necrosis factor-α promotes the recruitment of MDSCs to tumor tissue by upregulating CXCR4 expression via TNFR2. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2017, 44, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Meng, Q.; Erben, U.; Wang, P.; Glauben, R.; Kuhl, A.A.; Wu, H.; Ma, C.W.; Hu, M.; Wang, Y.; et al. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells promote B-cell production of IgA in a TNFR2-dependent manner. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2017, 14, 597–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polz, J.; Remke, A.; Weber, S.; Schmidt, D.; Weber-Steffens, D.; Pietryga-Krieger, A.; Muller, N.; Ritter, U.; Mostbock, S.; Mannel, D.N. Myeloid suppressor cells require membrane TNFR2 expression for suppressive activity. Immunity Inflamm. Dis. 2014, 2, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Li, B.; Li, X.; Zhao, X.; Wan, L.; Lin, G.; Yu, M.; Wang, J.; Jiang, X.; Feng, W.; et al. Transmembrane TNF-alpha promotes suppressive activities of myeloid-derived suppressor cells via TNFR2. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 1320–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yazdani, Y.; Mohammadnia-Afrouzi, M.; Yousefi, M.; Anvari, E.; Ghalamfarsa, G.; Hasannia, H.; Sadreddini, S.; Jadidi-Niaragh, F. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells in B cell malignancies. Tumour Biol. J. Int. Soc. Oncodev. Biol. Med. 2015, 36, 7339–7353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Liu, Y.; McFarland, B.C.; Deshane, J.S.; Hurst, D.R.; Ponnazhagan, S.; Benveniste, E.N.; Qin, H. SOCS3 Deficiency in Myeloid Cells Promotes Tumor Development: Involvement of STAT3 Activation and Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2015, 3, 727–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Eksioglu, E.A.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, L.; Djeu, J.; Fortenbery, N.; Epling-Burnette, P.; Van Bijnen, S.; Dolstra, H.; Cannon, J.; et al. Induction of myelodysplasia by myeloid-derived suppressor cells. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 4595–4611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Olkhanud, P.B.; Damdinsuren, B.; Bodogai, M.; Gress, R.E.; Sen, R.; Wejksza, K.; Malchinkhuu, E.; Wersto, R.P.; Biragyn, A. Tumor-evoked regulatory B cells promote breast cancer metastasis by converting resting CD4+ T cells to T-regulatory cells. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 3505–3515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodogai, M.; Moritoh, K.; Lee-Chang, C.; Hollander, C.M.; Sherman-Baust, C.A.; Wersto, R.P.; Araki, Y.; Miyoshi, I.; Yang, L.; Trinchieri, G.; et al. Immunosuppressive and Prometastatic Functions of Myeloid-Derived Suppressive Cells Rely upon Education from Tumor-Associated B Cells. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 3456–3465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryzhov, S.V.; Pickup, M.W.; Chytil, A.; Gorska, A.E.; Zhang, Q.; Owens, P.; Feoktistov, I.; Moses, H.L.; Novitskiy, S.V. Role of TGF-β signaling in generation of CD39+CD73+ myeloid cells in tumors. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 3155–3164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauri, C.; Gray, D.; Mushtaq, N.; Londei, M. Prevention of arthritis by interleukin 10-producing B cells. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 197, 489–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee-Chang, C.; Bodogai, M.; Martin-Montalvo, A.; Wejksza, K.; Sanghvi, M.; Moaddel, R.; de Cabo, R.; Biragyn, A. Inhibition of breast cancer metastasis by resveratrol-mediated inactivation of tumor-evoked regulatory B cells. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 4141–4151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
 , positive effect;
, positive effect;  , negative effect.
, negative effect.
 , positive effect;
, positive effect;  , negative effect.
, negative effect.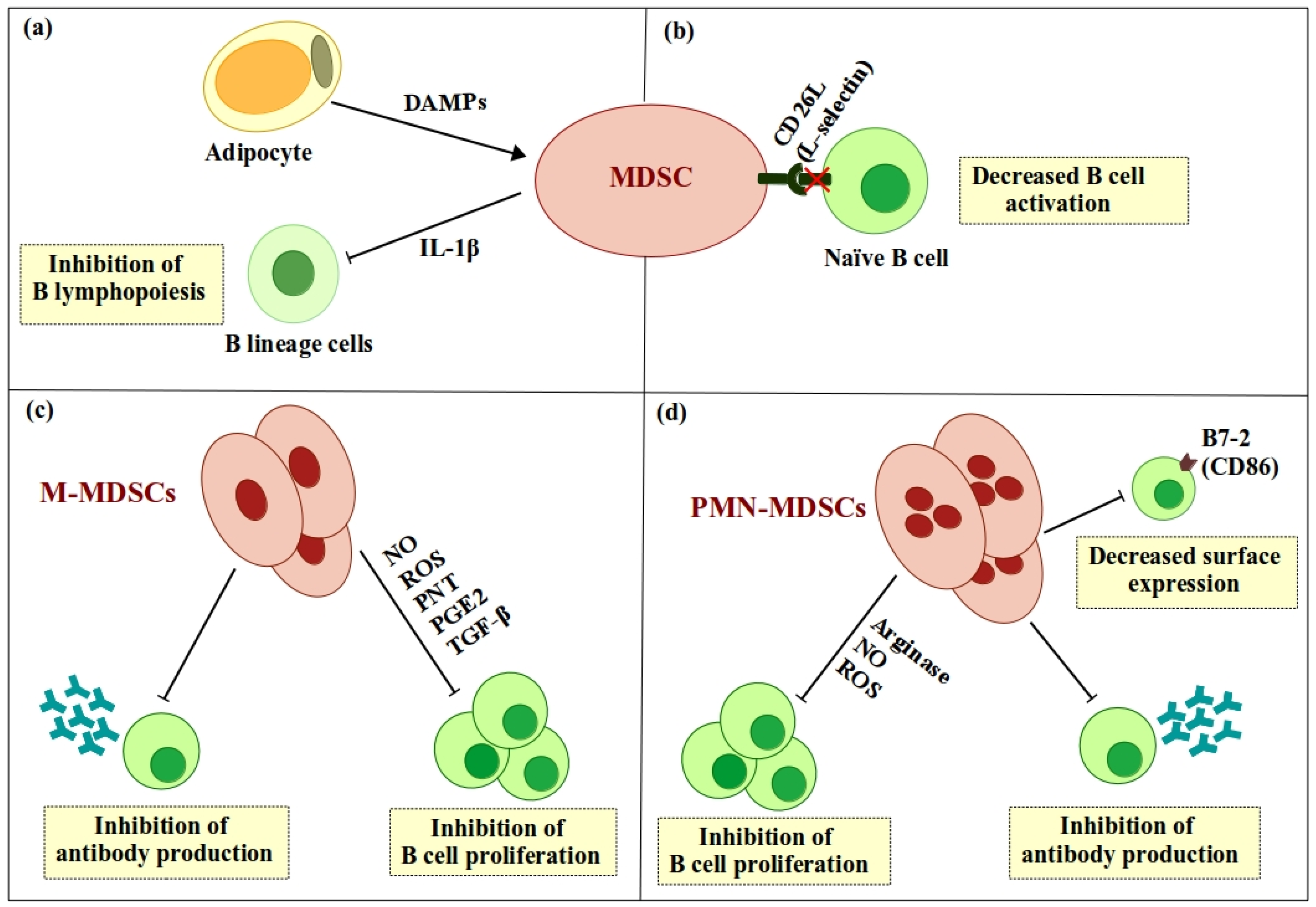
 , positive effect;
, positive effect;  , negative effect.
, negative effect.
 , positive effect;
, positive effect;  , negative effect.
, negative effect.
 , positive effect;
, positive effect;  , negative effect;
, negative effect;  , differentiation.
, differentiation.
 , positive effect;
, positive effect;  , negative effect;
, negative effect;  , differentiation.
, differentiation.
 , positive effect;
, positive effect;  , negative effect;
, negative effect;  , differentiation.
, differentiation.
 , positive effect;
, positive effect;  , negative effect;
, negative effect;  , differentiation.
, differentiation.
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Özkan, B.; Lim, H.; Park, S.-G. Immunomodulatory Function of Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells during B Cell-Mediated Immune Responses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1468. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19051468
Özkan B, Lim H, Park S-G. Immunomodulatory Function of Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells during B Cell-Mediated Immune Responses. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(5):1468. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19051468
Chicago/Turabian StyleÖzkan, Bilgenaz, Heejin Lim, and Sung-Gyoo Park. 2018. "Immunomodulatory Function of Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells during B Cell-Mediated Immune Responses" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 5: 1468. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19051468
APA StyleÖzkan, B., Lim, H., & Park, S.-G. (2018). Immunomodulatory Function of Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells during B Cell-Mediated Immune Responses. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(5), 1468. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19051468





