Luteolin-Mediated Inhibition of Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation via Suppression of the STAT3 Pathway
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
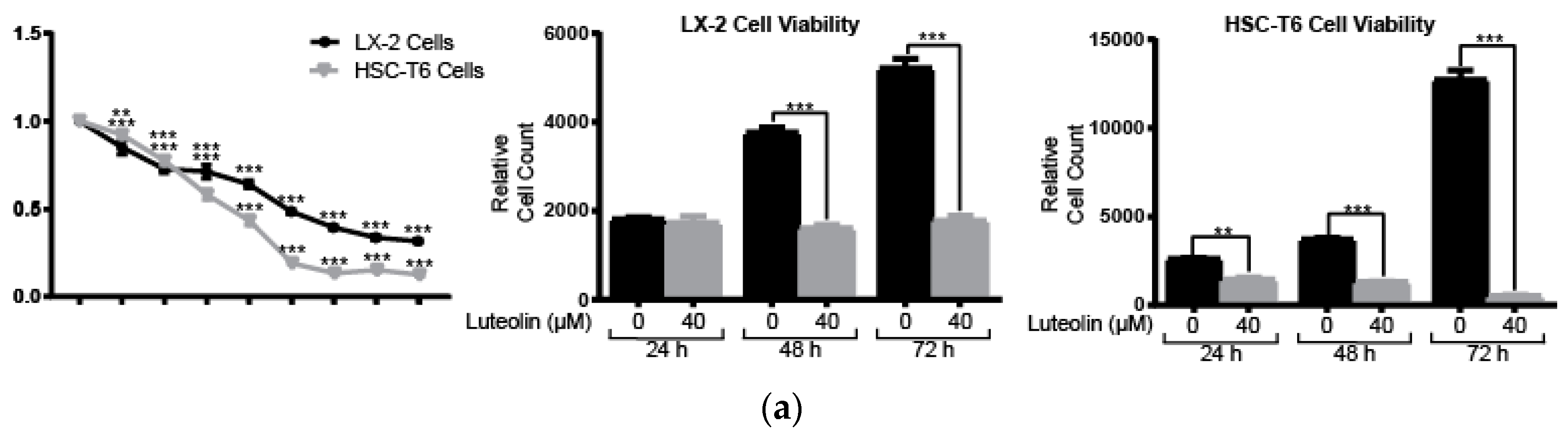
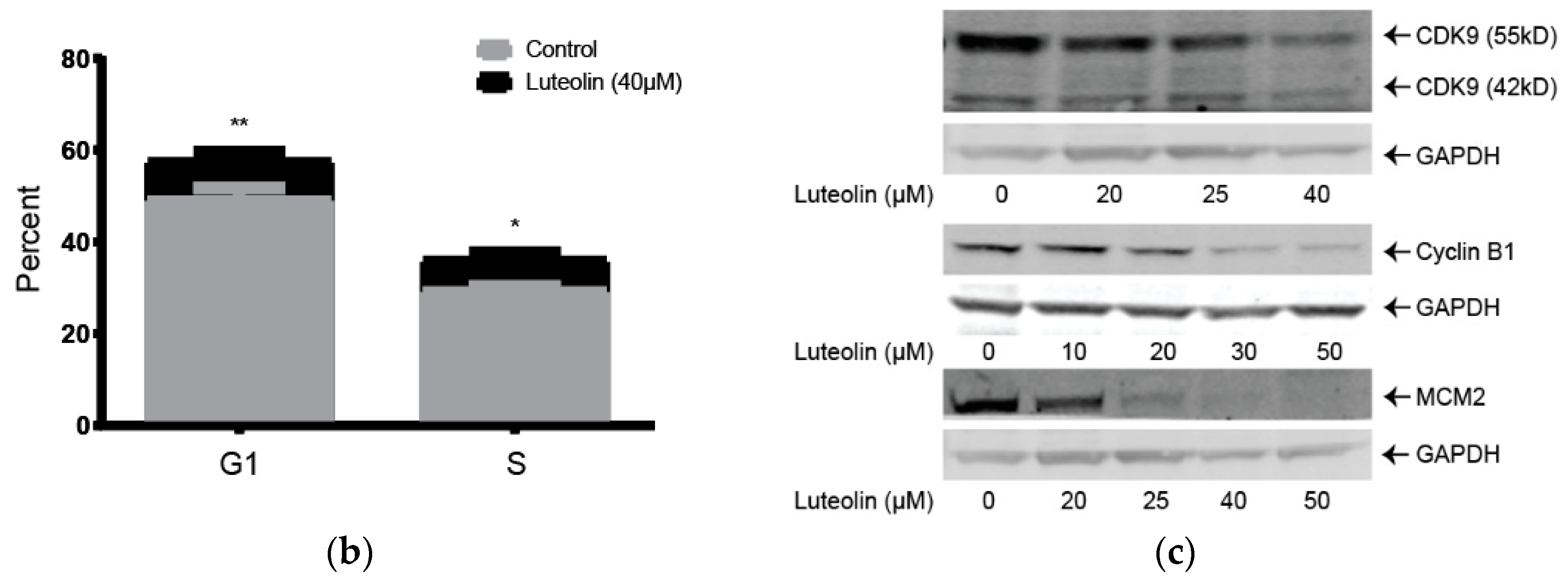
2.1. Lutelin Inhibits LX-2 and HSC-T6 Cell Proliferation
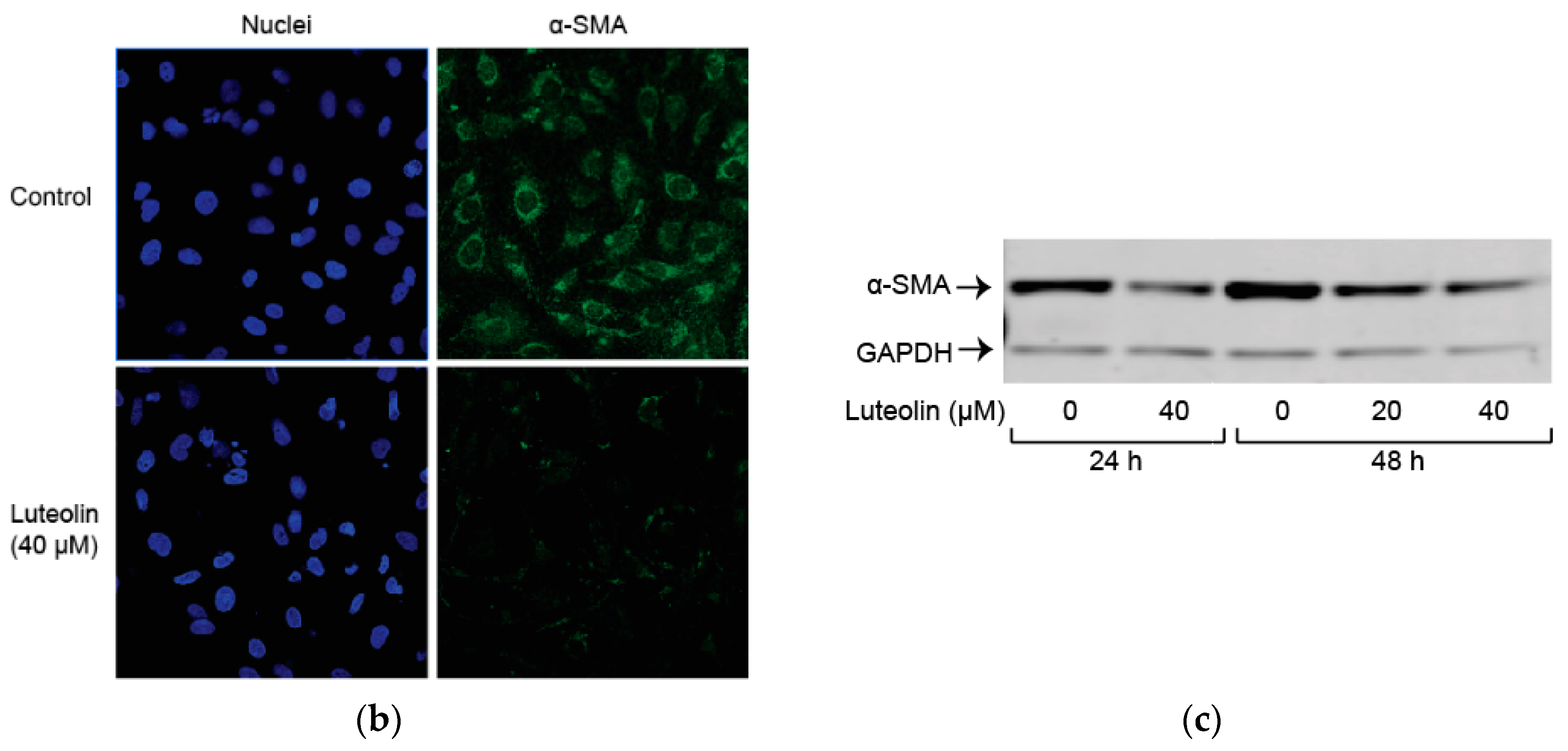
2.2. Luteolin Induces HSC Apoptosis and Attenuates α-SMA Expression
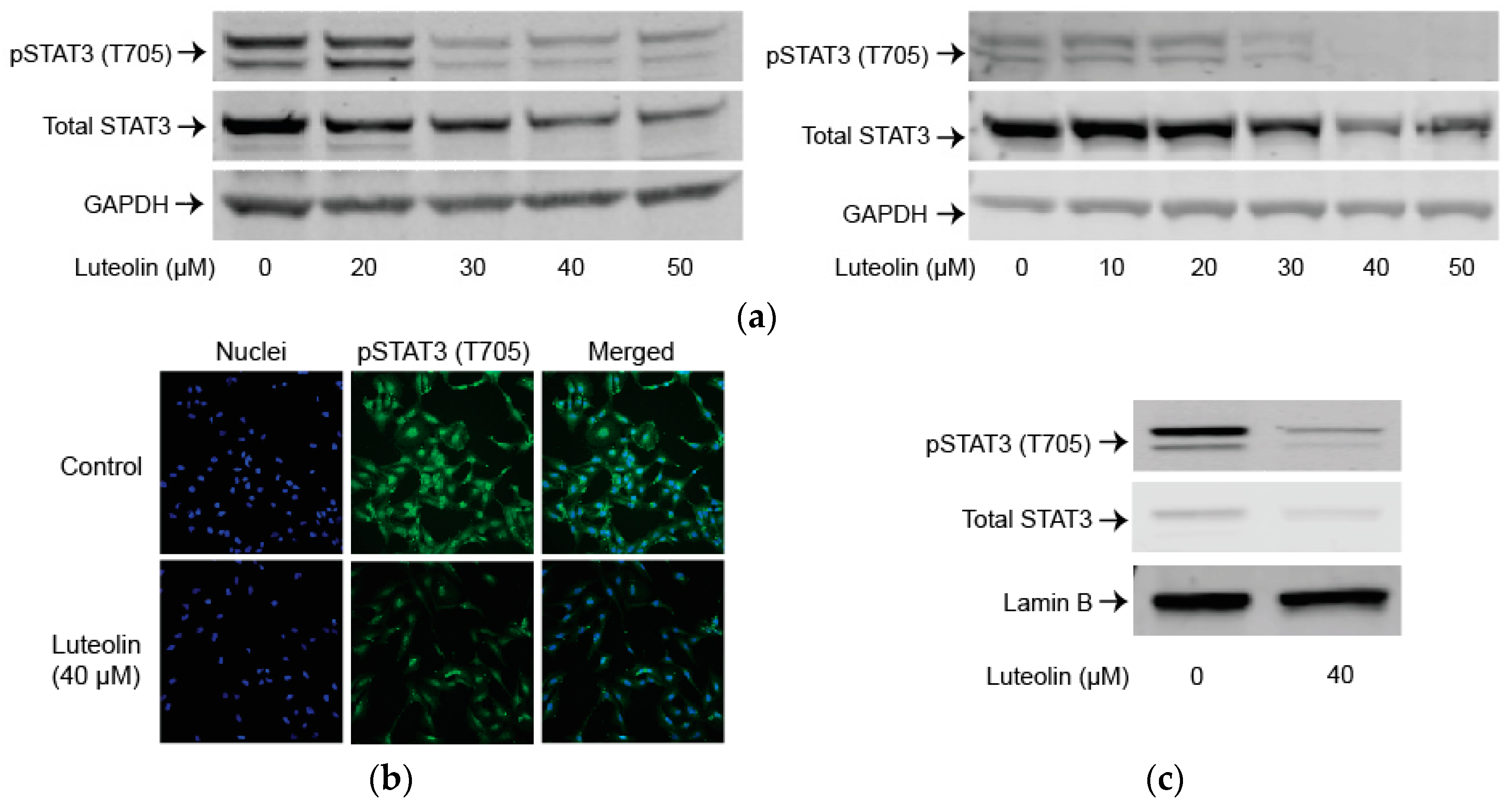
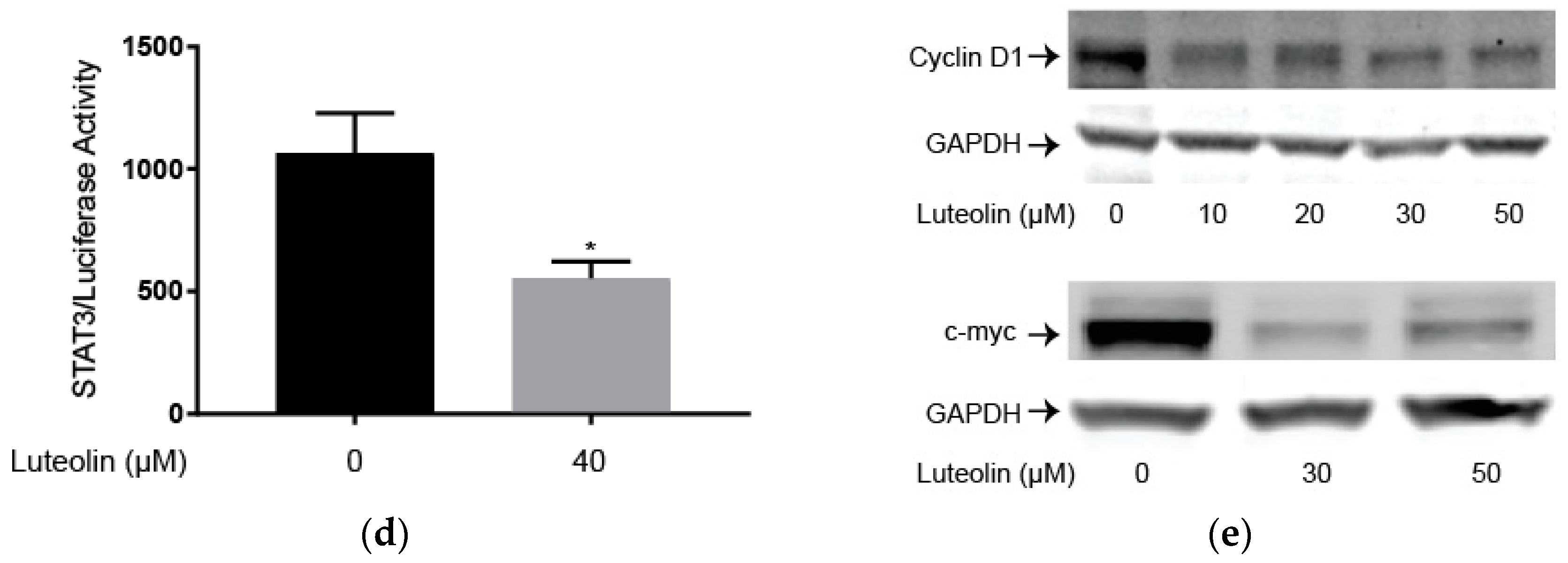
2.3. Luteolin Suppresses the STAT3 Pathway
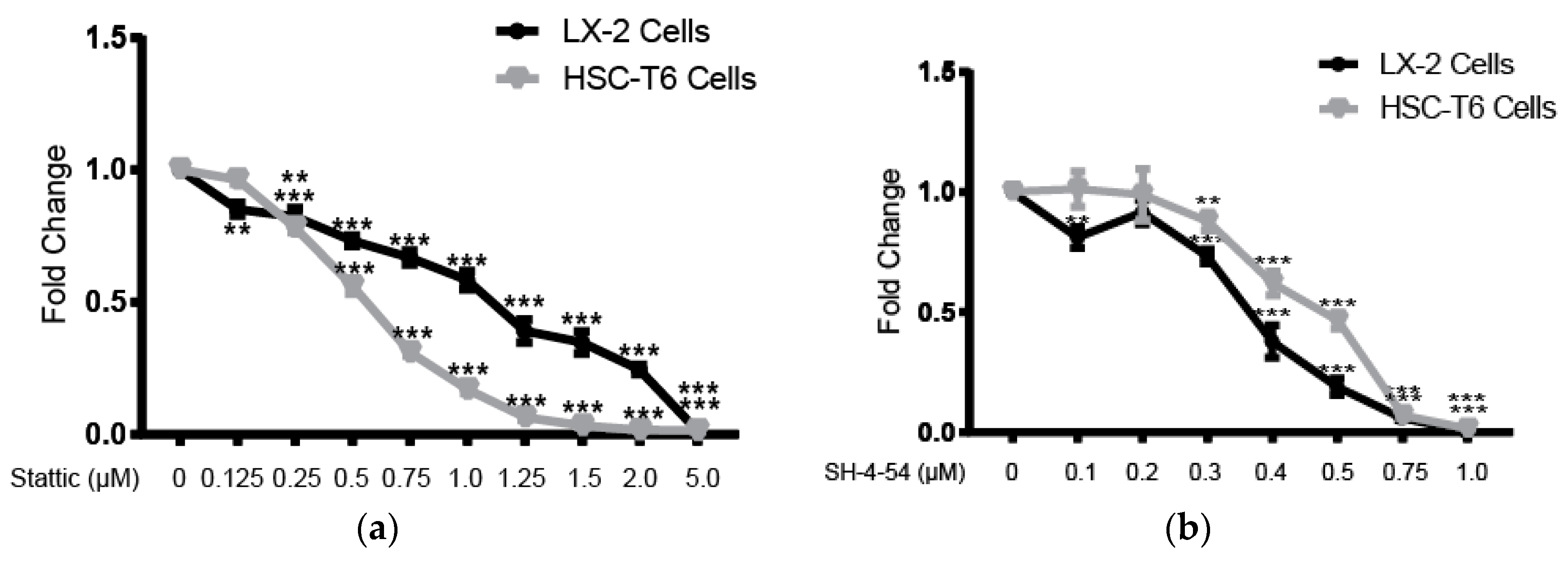
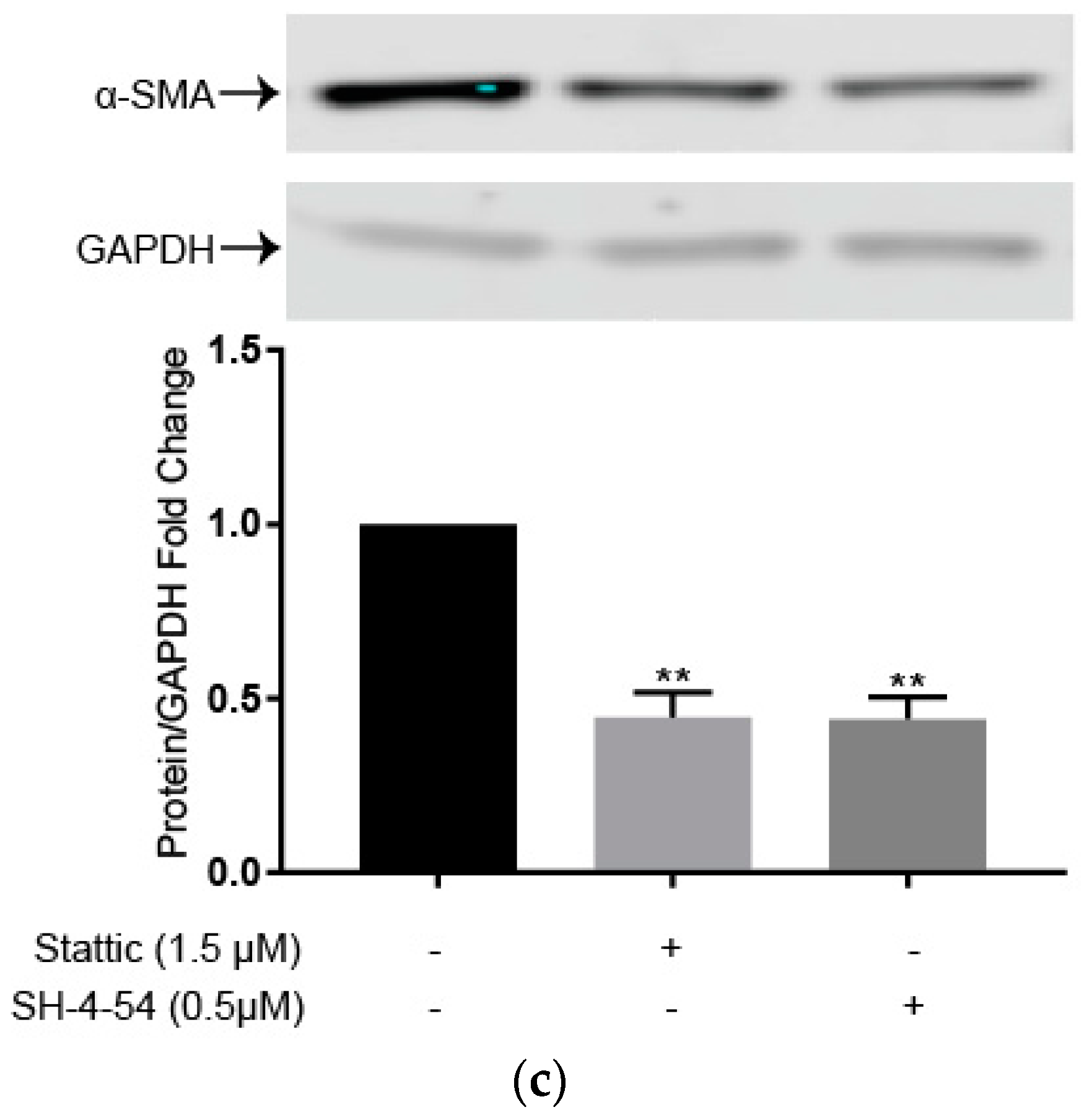
2.4. STAT3 Specific Inhibitors Suppress HSC Activation
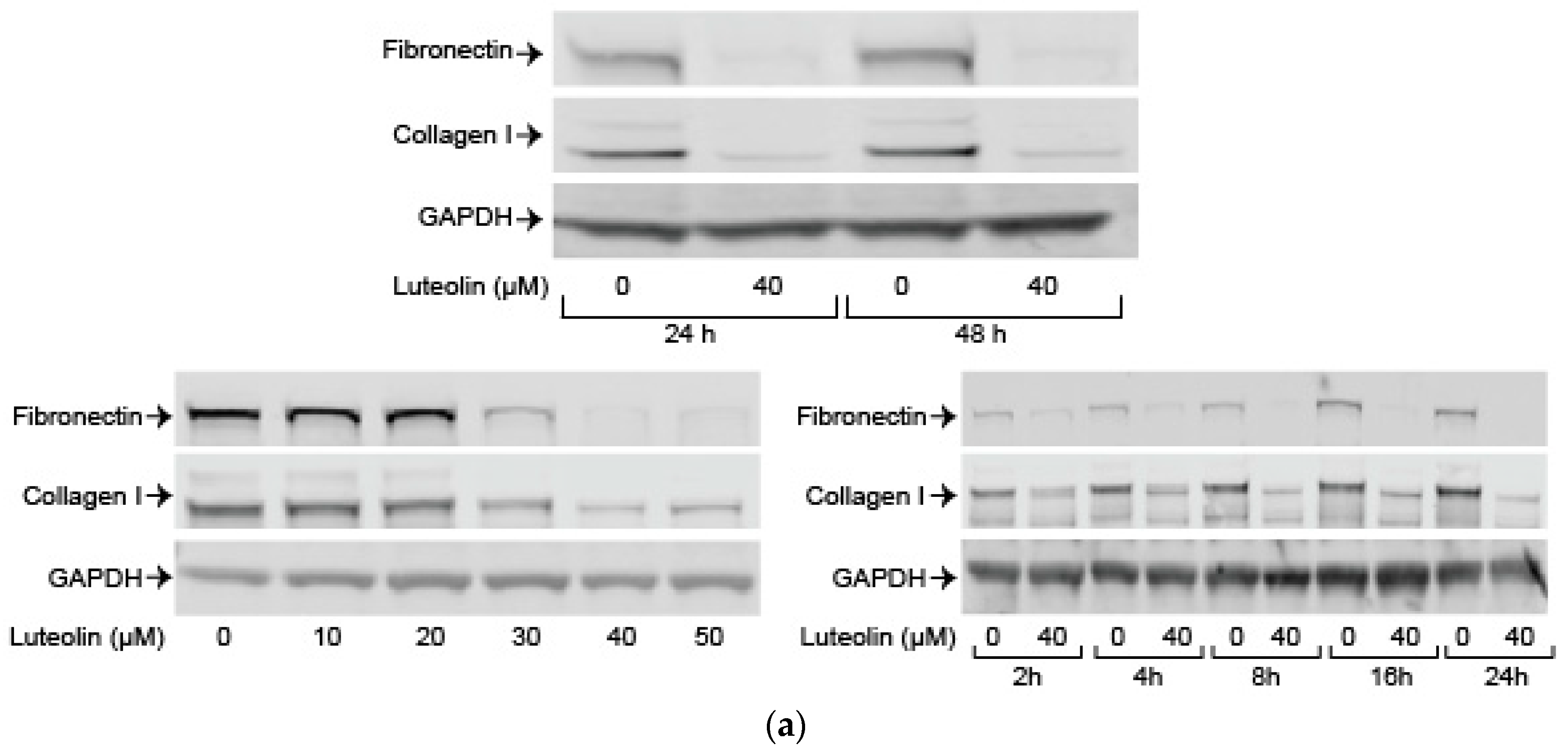
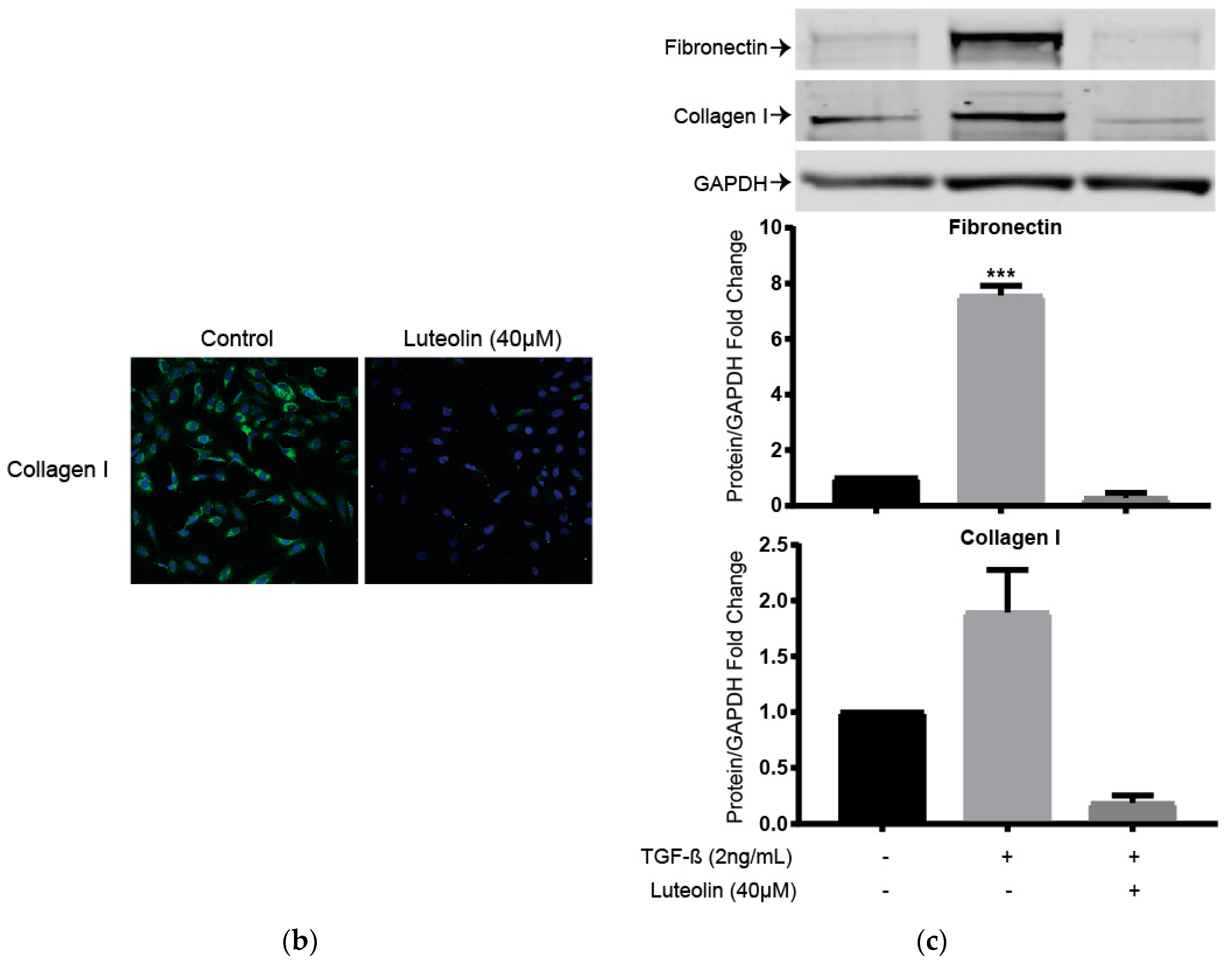
2.5. Luteolin Inhibits Endogenous and TGF-ß Induced ECM Proteins
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Cell Viability Assay
4.4. Detection of Apoptosis
4.5. Immunofluorescence Staining
4.6. Luciferase Assay
4.7. Western Immunoblotting
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HSC | Hepatic stellate cell |
| ECM | Extracellular matrix |
| TGF-ß | Transforming growth factor ß1 |
| STAT3 | Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 |
| IC50 | Half maximal inhibitory concentration |
| CDK9 | Cyclin dependent kinase 9 |
| MCM2 | Minichromosome maintenance protein 2 |
| PI | Propidium iodide |
References
- Roderfeld, M. Matrix metalloproteinase functions in hepatic injury and fibrosis. Matrix Biol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alter, G.; Heckerman, D.; Schneidewind, A.; Fadda, L.; Kadie, C.M.; Carlson, J.M.; Oniangue-Ndza, C.; Martin, M.; Li, B.; Khakoo, S.I.; et al. HIV-1 adaptation to NK-cell-mediated immune pressure. Nature 2011, 476, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemoinne, S.; Cadoret, A.; El Mourabit, H.; Thabut, D.; Housset, C. Origins and functions of liver myofibroblasts. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1832, 948–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Kwong, S.Q.; Lui, E.L.H.; Friedman, S.L.; Li, F.R.; Lam, R.W.C.; Zhang, G.C.; Zhang, H.; Ye, T. Inhibition of PDGF, TGF-beta, and Abl signaling and reduction of liver fibrosis by the small molecule Bcr-Abl tyrosine kinase antagonist Nilotinib. J. Hepatol. 2011, 55, 612–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Seo, G.S.; Park, Y.N.; Yoo, T.M.; Sohn, D.H. Effects and regulation of osteopontin in rat hepatic stellate cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2004, 68, 2367–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramm, G.A.; Shepherd, R.W.; Hoskins, A.C.; Greco, S.A.; Ney, A.D.; Pereira, T.N.; Bridle, K.R.; Doecke, J.D.; Meikle, P.J.; Turlin, B.; et al. Fibrogenesis in pediatric cholestatic liver disease: Role of taurocholate and hepatocyte-derived monocyte chemotaxis protein-1 in hepatic stellate cell recruitment. Hepatology 2009, 49, 533–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, S.; Yuan, J.; Shi, Q.; Xu, T.; Fu, Y.; Wu, Z.; Guo, W. Downregulation of UBC9 promotes apoptosis of activated human LX-2 hepatic stellate cells by suppressing the canonical NF-kappaB signaling pathway. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukamoto, H.; Zhu, N.L.; Wang, J.; Asahina, K.; Machida, K. Morphogens and hepatic stellate cell fate regulation in chronic liver disease. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 27 (Suppl. 2), 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, X.; Horiguchi, N.; Mori, M.; Gao, B. Cytokines and STATs in Liver Fibrosis. Front. Physiol. 2012, 3, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Lafdil, F.; Kong, X.; Gao, B. Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 in liver diseases: A novel therapeutic target. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2011, 7, 536–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.X.; Mikami, K.; Venugopal, S.; Li, Y.; Torok, N.J. Apoptotic body engulfment by hepatic stellate cells promotes their survival by the JAK/STAT and Akt/NF-kappaB-dependent pathways. J. Hepatol. 2009, 51, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parola, M.; Marra, F. Adipokines and redox signaling: Impact on fatty liver disease. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2011, 15, 461–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Su, T.H.; Shiau, C.W.; Jao, P.; Liu, C.H.; Liu, C.J.; Tai, W.T.; Jeng, Y.M.; Yang, H.C.; Tseng, T.C.; Huang, H.P.; et al. Sorafenib and its derivative SC-1 exhibit antifibrotic effects through signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 inhibition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 7243–7248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsharkawy, A.M.; Oakley, F.; Mann, D.A. The role and regulation of hepatic stellate cell apoptosis in reversal of liver fibrosis. Apoptosis 2005, 10, 927–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunez Lopez, O.; Bohanon, F.J.; Wang, X.; Ye, N.; Corsello, T.; Rojas-Khalil, Y.; Chen, H.; Chen, H.; Zhou, J.; Radhakrishnan, R.S. STAT3 Inhibition Suppresses Hepatic Stellate Cell Fibrogenesis: HJC0123, a Potential Therapeutic Agent for Liver Fibrosis. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 100652–100663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Lazaro, M. Distribution and biological activities of the flavonoid luteolin. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2009, 9, 31–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chun, O.K.; Chung, S.J.; Song, W.O. Estimated dietary flavonoid intake and major food sources of U.S. adults. J. Nutr. 2007, 137, 1244–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Cao, J.; Chen, W.; Yang, J.; Hao, D.; Zhang, Y.; Chang, P.; Zhao, X. Reproducibility and relative validity of a food frequency questionnaire to assess intake of dietary flavonol and flavone in Chinese university campus population. Nutr. Res. 2010, 30, 520–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Li, X.; Xu, W.; Wang, S.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Deng, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Guo, C. Antifibrotic effects of luteolin on hepatic stellate cells and liver fibrosis by targeting AKT/mTOR/p70S6K and TGFbeta/Smad signalling pathways. Liver Int. 2015, 35, 1222–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, N.S.; Bollen, C.; Perry, E.K.; Ballard, C. Salvia for dementia therapy: review of pharmacological activity and pilot tolerability clinical trial. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2003, 75, 651–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taliou, A.; Zintzaras, E.; Lykouras, L.; Francis, K. An open-label pilot study of a formulation containing the anti-inflammatory flavonoid luteolin and its effects on behavior in children with autism spectrum disorders. Clin. Ther. 2013, 35, 592–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, L.; Kwara, A.; Greenblatt, D.J. Metabolic interactions between acetaminophen (paracetamol) and two flavonoids, luteolin and quercetin, through in-vitro inhibition studies. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2017, 69, 1762–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, C.; Xu, D.; Zhang, R.; Cheng, Y.; Pan, Y.; Huang, C.; Chen, Y. Luteolin alleviates alcoholic liver disease induced by chronic and binge ethanol feeding in mice. J. Nutr. 2014, 144, 1009–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aneknan, P.; Kukongviriyapan, V.; Prawan, A.; Kongpetch, S.; Sripa, B.; Senggunprai, L. Luteolin arrests cell cycling, induces apoptosis and inhibits the JAK/STAT3 pathway in human cholangiocarcinoma cells. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 15, 5071–5076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Chen, D.; Zhao, B.; Zhao, Z.; Zhou, J.; Xu, Y.; Xin, Y.; Liu, C.; Luo, L.; Yin, Z. Luteolin induces carcinoma cell apoptosis through binding Hsp90 to suppress constitutive activation of STAT3. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e49194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Dai, S.; Dai, J.; Xiao, Y.; Bai, Y.; Chen, B.; Zhou, M. Luteolin decreases invasiveness, deactivates STAT3 signaling, and reverses interleukin-6 induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and matrix metalloproteinase secretion of pancreatic cancer cells. OncoTargets Ther. 2015, 8, 2989–3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonoki, H.; Tanimae, A.; Endo, S.; Matsunaga, T.; Furuta, T.; Ichihara, K.; Ikari, A. Kaempherol and Luteolin Decrease Claudin-2 Expression Mediated by Inhibition of STAT3 in Lung Adenocarcinoma A549 Cells. Nutrients 2017, 9, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, S.; Su, Z.; Xu, H.; Niu, M.; Chen, X.; Min, H.; Zhang, B.; Sun, G.; Xie, S.; Wang, H.; et al. Luteolin selectively kills STAT3 highly activated gastric cancer cells through enhancing the binding of STAT3 to SHP-1. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.Y.; Wang, C.J.; Chen, N.F.; Ho, W.H.; Lu, F.J.; Tseng, T.H. Luteolin enhances paclitaxel-induced apoptosis in human breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells by blocking STAT3. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2014, 213, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, U.E.; Friedman, S.L. Mechanisms of hepatic fibrogenesis. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2011, 25, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuppan, D.; Kim, Y.O. Evolving therapies for liver fibrosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 1887–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.W.; Sun, Y.M. The IL-6/JAK/STAT3 pathway: Potential therapeutic strategies in treating colorectal cancer (Review). Int. J. Oncol. 2014, 44, 1032–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, A.; Wang, J.; Wu, M.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H. The inhibition of activated hepatic stellate cells proliferation by arctigenin through G0/G1 phase cell cycle arrest: Persistent p27(Kip1) induction by interfering with PI3K/Akt/FOXO3a signaling pathway. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 747, 71–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, D.M.; Sun, W.; Ning, B.F.; Zhou, T.F.; Li, X.F.; Zhong, W.; Cheng, Z.; Xia, M.Y.; Wang, X.; Deng, X.; et al. The HLF/IL-6/STAT3 feedforward circuit drives hepatic stellate cell activation to promote liver fibrosis. Gut 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kagan, P.; Sultan, M.; Tachlytski, I.; Safran, M.; Ben-Ari, Z. Both MAPK and STAT3 signal transduction pathways are necessary for IL-6-dependent hepatic stellate cells activation. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Iness, A.; Yoon, J.; Grider, J.R.; Murthy, K.S.; Kellum, J.M.; Kuemmerle, J.F. Noncanonical STAT3 activation regulates excess TGF-beta1 and collagen I expression in muscle of stricturing Crohn’s disease. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 3422–3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Qiu, J.; Dong, S.; Redell, M.S.; Poli, V.; Mancini, M.A.; Tweardy, D.J. Stat3 isoforms, alpha and beta, demonstrate distinct intracellular dynamics with prolonged nuclear retention of Stat3beta mapping to its unique C-terminal end. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 34958–34967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wake, M.S.; Watson, C.J. STAT3 the oncogene—Still eluding therapy? FEBS J. 2015, 282, 2600–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schust, J.; Sperl, B.; Hollis, A.; Mayer, T.U.; Berg, T. Stattic: A small-molecule inhibitor of STAT3 activation and dimerization. Chem. Biol. 2006, 13, 1235–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haftchenary, S.; Luchman, H.A.; Jouk, A.O.; Veloso, A.J.; Page, B.D.; Cheng, X.R.; Dawson, S.S.; Grinshtein, N.; Shahani, V.M.; Kerman, K.; et al. Potent Targeting of the STAT3 Protein in Brain Cancer Stem Cells: A Promising Route for Treating Glioblastoma. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 4, 1102–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.Y.; Hu, J.J.; Shen, J.; Wang, M.L.; Zhang, Q.Q.; Qu, Y.; Lu, L.G. Stat3 signaling activation crosslinking of TGF-beta1 in hepatic stellate cell exacerbates liver injury and fibrosis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1842, 2237–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogata, H.; Chinen, T.; Yoshida, T.; Kinjyo, I.; Takaesu, G.; Shiraishi, H.; Iida, M.; Kobayashi, T.; Yoshimura, A. Loss of SOCS3 in the liver promotes fibrosis by enhancing STAT3-mediated TGF-beta1 production. Oncogene 2006, 25, 2520–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, B.; Wang, H.; Lafdil, F.; Feng, D. STAT proteins—Key regulators of anti-viral responses, inflammation, and tumorigenesis in the liver. J. Hepatol. 2012, 57, 430–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mair, M.; Zollner, G.; Schneller, D.; Musteanu, M.; Fickert, P.; Gumhold, J.; Schuster, C.; Fuchsbichler, A.; Bilban, M.; Tauber, S.; et al. Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 protects from liver injury and fibrosis in a mouse model of sclerosing cholangitis. Gastroenterology 2010, 138, 2499–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plum, W.; Tschaharganeh, D.F.; Kroy, D.C.; Corsten, E.; Erschfeld, S.; Dierssen, U.; Wasmuth, H.; Trautwein, C.; Streetz, K.L. Lack of glycoprotein 130/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3-mediated signaling in hepatocytes enhances chronic liver injury and fibrosis progression in a model of sclerosing cholangitis. Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 176, 2236–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, X.; Feng, D.; Wang, H.; Hong, F.; Bertola, A.; Wang, F.S.; Gao, B. Interleukin-22 induces hepatic stellate cell senescence and restricts liver fibrosis in mice. Hepatology 2012, 56, 1150–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casini, A.; Ceni, E.; Salzano, R.; Biondi, P.; Parola, M.; Galli, A.; Foschi, M.; Caligiuri, A.; Pinzani, M.; Surrenti, C. Neutrophil-derived superoxide anion induces lipid peroxidation and stimulates collagen synthesis in human hepatic stellate cells: role of nitric oxide. Hepatology 1997, 25, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canbay, A.; Friedman, S.; Gores, G.J. Apoptosis: The nexus of liver injury and fibrosis. Hepatology 2004, 39, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maher, J.J. Interactions between hepatic stellate cells and the immune system. Semin. Liver Dis. 2001, 21, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohanon, F.J.; Wang, X.; Ding, C.; Ding, Y.; Radhakrishnan, G.L.; Rastellini, C.; Zhou, J.; Radhakrishnan, R.S. Oridonin inhibits hepatic stellate cell proliferation and fibrogenesis. J. Surg. Res. 2014, 190, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cummins, C.B.; Wang, X.; Nunez Lopez, O.; Graham, G.; Tie, H.-Y.; Zhou, J.; Radhakrishnan, R.S. Luteolin-Mediated Inhibition of Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation via Suppression of the STAT3 Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1567. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19061567
Cummins CB, Wang X, Nunez Lopez O, Graham G, Tie H-Y, Zhou J, Radhakrishnan RS. Luteolin-Mediated Inhibition of Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation via Suppression of the STAT3 Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(6):1567. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19061567
Chicago/Turabian StyleCummins, Claire B., Xiaofu Wang, Omar Nunez Lopez, Gabriel Graham, Hong-Yan Tie, Jia Zhou, and Ravi S. Radhakrishnan. 2018. "Luteolin-Mediated Inhibition of Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation via Suppression of the STAT3 Pathway" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 6: 1567. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19061567
APA StyleCummins, C. B., Wang, X., Nunez Lopez, O., Graham, G., Tie, H.-Y., Zhou, J., & Radhakrishnan, R. S. (2018). Luteolin-Mediated Inhibition of Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation via Suppression of the STAT3 Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(6), 1567. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19061567





