Revisiting the Advances in Isolation, Characterization and Secretome of Adipose-Derived Stromal/Stem Cells
Abstract
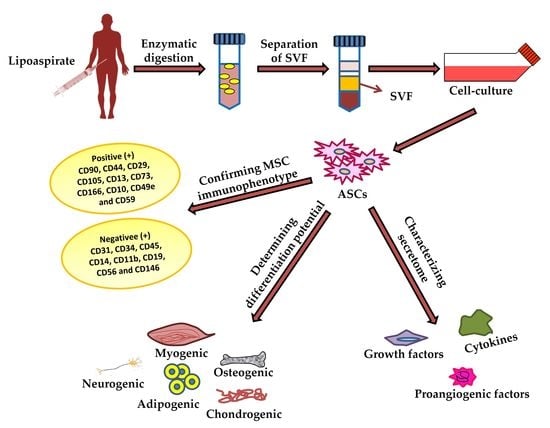
:1. Introduction
2. Adipose Tissues as Source of ASCs
2.1. Harvesting of Adipose Tissues
2.2. Isolation of ASCs from Harvested Adipose Tissues
3. Characterization of ASCs
3.1. Differentiation Potential of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells
3.1.1. Osteogenic Differentiation of ASCs
3.1.2. Chondrogenic Differentiation of ASCs
3.1.3. Adipogenic Differentiation of ASCs
4. ASC Secretome and Its Therapeutic Effect
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mitchell, J.B.; McIntosh, K.; Zvonic, S.; Garrett, S.; Floyd, Z.E.; Kloster, A.; Di Halvorsen, Y.; Storms, R.W.; Goh, B.; Kilroy, G.; et al. Immunophenotype of human adipose-derived cells: Temporal changes in stromal-associated and stem cell-associated markers. Stem Cells 2006, 24, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wankhade, U.D.; Shen, M.; Kolhe, R.; Fulzele, S. Advances in Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Isolation, Characterization, and Application in Regenerative Tissue Engineering. Stem Cells Int. 2016, 2016, 3206807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crisan, M.; Yap, S.; Casteilla, L.; Chen, C.-W.; Corselli, M.; Park, T.S.; Andriolo, G.; Sun, B.; Zheng, B.; Zhang, L.; et al. A Perivascular Origin for Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Multiple Human Organs. Cell Stem Cell 2008, 3, 301–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kishi, K.; Imanishi, N.; Ohara, H.; Ninomiya, R.; Okabe, K.; Hattori, N.; Kubota, Y.; Nakajima, H.; Nakajima, T. Distribution of adipose-derived stem cells in adipose tissues from human cadavers. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2010, 63, 1717–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baer, P.C.; Geiger, H. Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal/Stem Cells: Tissue Localization, Characterization, and Heterogeneity. Stem Cells Int. 2012, 2012, 812693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuk, P.A.; Zhu, M.; Ashjian, P.; De Ugarte, D.A.; Huang, J.I.; Mizuno, H.; Alfonso, Z.C.; Fraser, J.K.; Benhaim, P.; Hedrick, M.H. Human Adipose Tissue Is a Source of Multipotent Stem Cells. Mol. Biol. Cell 2002, 13, 4279–4295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bajek, A.; Gurtowska, N.; Gackowska, L.; Kubiszewska, I.; Bodnar, M.; Marszałek, A.; Januszewski, R.; Michalkiewicz, J.; Drewa, T. Does the liposuction method influence the phenotypic characteristic of human adipose-derived stem cells? Biosci. Rep. 2015, 35, e00212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.-Y.; Chiou, J.-F.; Wu, A.T.H.; Tsai, C.-Y.; Leu, J.-D.; Ting, L.-L.; Wang, M.-F.; Chen, H.-Y.; Lin, C.-T.; Williams, D.F.; et al. The effect of diminished osteogenic signals on reduced osteoporosis recovery in aged mice and the potential therapeutic use of adipose-derived stem cells. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 6105–6112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brzoska, M.; Geiger, H.; Gauer, S.; Baer, P. Epithelial differentiation of human adipose tissue-derived adult stem cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 330, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; Zhao, P.; Lin, C.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Yang, D.; Wang, X.; Xu, H.; Zhou, F.; et al. Differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells into neuron-like cells which are compatible with photocurable three-dimensional scaffolds. Tissue Eng. Part A 2014, 20, 1271–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, T.; Sun, J.; Zhao, Z.; Lei, W.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Yang, J.; Shen, Z. A brief review: Adipose-derived stem cells and their therapeutic potential in cardiovascular diseases. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2017, 8, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, B.-Y.; Dubey, N.K.; Mishra, V.K.; Tsai, F.-C.; Dubey, R.; Deng, W.-P.; Wei, H.-J. Addressing Stem Cell Therapeutic Approaches in Pathobiology of Diabetes and Its Complications. J. Diabetes Res. 2018, 2018, 7806435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, N.K.; Mishra, V.K.; Dubey, R.; Syed-Abdul, S.; Wang, J.R.; Wang, P.D.; Deng, W.-P. Combating Osteoarthritis through Stem Cell Therapies by Rejuvenating Cartilage: A Review. Stem Cells Int. 2018, 2018, 5421019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erba, P.; Terenghi, G.; Kingham, P.J. Neural differentiation and therapeutic potential of adipose tissue derived stem cells. Curr. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2010, 5, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.; He, D.; Kleiner, G.; Kuluz, J. Neuron-like Differentiation of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells From Infant Piglets In Vitro. J. Spinal Cord Med. 2007, 30 (Suppl. 1), S35–S40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.-H.; Jung, M.; Kim, H.-S.; Kim, Y.-M.; Choi, E.-H. Adipose-derived stem cells as a new therapeutic modality for ageing skin. Exp. Dermatol. 2011, 20, 383–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagami, H.; Maeda, K.; Morishita, R.; Iguchi, S.; Nishikawa, T.; Takami, Y.; Kikuchi, Y.; Saito, Y.; Tamai, K.; Ogihara, T.; et al. Novel Autologous Cell Therapy in Ischemic Limb Disease Through Growth Factor Secretion by Cultured Adipose Tissue–Derived Stromal Cells. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2005, 25, 2542–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zeppieri, M.; Salvetat, M.; Beltrami, A.; Cesselli, D.; Russo, R.; Alcalde, I.; Merayo-Lloves, J.; Brusini, P.; Parodi, P. Adipose Derived Stem Cells for Corneal Wound Healing after Laser Induced Corneal Lesions in Mice. J. Clin. Med. 2017, 6, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-W.; Scutaru, T.T.; Ghetu, N.; Carasevici, E.; Lupascu, C.D.; Ferariu, D.; Pieptu, D.; Coman, C.-G.; Danciu, M. The Effects of Adipose-Derived Stem Cell–Differentiated Adipocytes on Skin Burn Wound Healing in Rats. J. Burn Care Res. 2017, 38, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, W.-S.; Park, B.-S.; Sung, J.-H. The wound-healing and antioxidant effects of adipose-derived stem cells. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2009, 9, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frese, L.; Dijkman, P.E.; Hoerstrup, S.P. Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells in Regenerative Medicine. Transfus. Med. Hemother. 2016, 43, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, Y.; Liu, T.; Song, K.; Fan, X.; Ma, X.; Cui, Z. Adipose-derived stem cell: A better stem cell than BMSC. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2008, 26, 664–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casteilla, L.; Planat-Benard, V.; Laharrague, P.; Cousin, B. Adipose-derived stromal cells: Their identity and uses in clinical trials, an update. World J. Stem Cells 2011, 3, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarte, K.; Gaillard, J.; Lataillade, J.-J.; Fouillard, L.; Becker, M.; Mossafa, H.; Tchirkov, A.; Rouard, H.; Henry, C.; Splingard, M.; et al. Clinical-grade production of human mesenchymal stromal cells: Occurrence of aneuploidy without transformation. Blood 2010, 115, 1549–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurgens, W.J.; Oedayrajsingh-Varma, M.J.; Helder, M.N.; Zandiehdoulabi, B.; Schouten, T.E.; Kuik, D.J.; Ritt, M.J.; van Milligen, F.J. Effect of tissue-harvesting site on yield of stem cells derived from adipose tissue: Implications for cell-based therapies. Cell Tissue Res. 2008, 332, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schäffler, A.; Büchler, C. Concise Review: Adipose Tissue-Derived Stromal Cells—Basic and Clinical Implications for Novel Cell-Based Therapies. Stem Cells 2007, 25, 818–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobita, M.; Tajima, S.; Mizuno, H. Adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells and platelet-rich plasma: Stem cell transplantation methods that enhance stemness. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2015, 6, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuk, P.A.; Zhu, M.; Mizuno, H.; Huang, J.; Futrell, J.W.; Katz, A.J.; Benhaim, P.; Lorenz, H.P.; Hedrick, M.H. Multilineage cells from human adipose tissue: Implications for cell-based therapies. Tissue Eng. 2001, 7, 211–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuk, P.A. The Adipose-derived Stem Cell: Looking Back and Looking Ahead. Mol. Biol. Cell 2010, 21, 1783–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, C.S.; Xin, Z.C.; Deng, C.H.; Ning, H.; Lin, G.; Lue, T.F. Defining adipose tissue-derived stem cells in tissue and in culture. Histol. Histopathol. 2010, 25, 807–815. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lafontan, M. Historical perspectives in fat cell biology: The fat cell as a model for the investigation of hormonal and metabolic pathways. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2012, 302, C327–C359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, V.M.; Stransky, C.A.; Bucky, L.P.; Percec, I. Fat Grafting’s Past, Present, and Future: Why Adipose Tissue Is Emerging as a Critical Link to the Advancement of Regenerative Medicine. Aesthet. Surg. J. 2012, 32, 892–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Laharrague, P.; Casteilla, L. The emergence of adipocytes. Endocr. Dev. 2010, 19, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bai, X.; Alt, E. Myocardial regeneration potential of adipose tissue-derived stem cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 401, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaquero, A.; Sternglanz, R.; Reinberg, D. NAD+-dependent deacetylation of H4 lysine 16 by class III HDACs. Oncogene 2007, 26, 5505–5520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Casteilla, L.; Dani, C. Adipose tissue-derived cells: From physiology to regenerative medicine. Diabetes Metab. 2006, 32 Pt 1, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himms-Hagen, J. Brown adipose tissue thermogenesis: Interdisciplinary studies. FASEB J. 1990, 4, 2890–2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ailhaud, G.; Grimaldi, P.; Negrel, R. Cellular and molecular aspects of adipose tissue development. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 1992, 12, 207–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gimble, J.M.; Robinson, C.E.; Wu, X.; Kelly, K.A. The function of adipocytes in the bone marrow stroma: An update. Bone 1996, 19, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaus, S.; Casteilla, L.; Bouillaud, F.; Ricquier, D. The uncoupling protein UCP: A membraneous mitochondrial ion carrier exclusively expressed in brown adipose tissue. Int. J. Biochem. 1991, 23, 791–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, B.; Nedergaard, J. Brown adipose tissue: Function and physiological significance. Physiol. Rev. 2004, 84, 277–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casteilla, L.; Penicaud, L.; Cousin, B.; Calise, D. Choosing an adipose tissue depot for sampling: Factors in selection and depot specificity. Methods Mol. Biol. 2008, 456, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bjorntorp, P.; Bengtsson, C.; Blohme, G.; Jonsson, A.; Sjostrom, L.; Tibblin, E.; Tibblin, G.; Wilhelmsen, L. Adipose tissue fat cell size and number in relation to metabolism in randomly selected middle-aged men and women. Metabolism 1971, 20, 927–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salans, L.B.; Cushman, S.W.; Weismann, R.E. Studies of Human Adipose Tissue Adipose Cell Size and Number in Nonobese and Obese Patients. J. Clin. Investig. 1973, 52, 929–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berry, D.C.; Stenesen, D.; Zeve, D.; Graff, J.M. The developmental origins of adipose tissue. Development 2013, 140, 3939–3949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kajimura, S.; Seale, P.; Spiegelman, B.M. Transcriptional Control of Brown Fat Development. Cell Metab. 2010, 11, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Iyyanki, T.; Hubenak, J.; Liu, J.; Chang, E.I.; Beahm, E.K.; Zhang, Q. Harvesting Technique Affects Adipose-Derived Stem Cell Yield. Aesthet. Surg. J. 2015, 35, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kornicka, K.; Marycz, K.; Tomaszewski, K.A.; Marędziak, M.; Śmieszek, A. The Effect of Age on Osteogenic and Adipogenic Differentiation Potential of Human Adipose Derived Stromal Stem Cells (hASCs) and the Impact of Stress Factors in the Course of the Differentiation Process. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2015, 2015, 309169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, R.; Wang, Z.; Samanipour, R.; Koo, K.-I.; Kim, K. Adipose-Derived Stem Cells for Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine Applications. Stem Cells Int. 2016, 2016, 6737345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nedergaard, J.; Bengtsson, T.; Cannon, B. Unexpected evidence for active brown adipose tissue in adult humans. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 293, E444–E452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gesta, S.; Tseng, Y.-H.; Kahn, C.R. Developmental Origin of Fat: Tracking Obesity to Its Source. Cell 2007, 131, 242–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kocan, B.; Maziarz, A.; Tabarkiewicz, J.; Ochiya, T.; Banaś-Ząbczyk, A. Trophic Activity and Phenotype of Adipose Tissue-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells as a Background of Their Regenerative Potential. Stem Cells Int. 2017, 2017, 1653254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunnell, B.A.; Flaat, M.; Gagliardi, C.; Patel, B.; Ripoll, C. Adipose-derived stem cells: Isolation, expansion and differentiation. Methods 2008, 45, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraser, J.K.; Wulur, I.; Alfonso, Z.; Hedrick, M.H. Fat tissue: An underappreciated source of stem cells for biotechnology. Trends in Biotechnol. 2006, 24, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauner, H.; Entenmann, G. Regional variation of adipose differentiation in cultured stromal-vascular cells from the abdominal and femoral adipose tissue of obese women. Int. J. Obes. 1991, 15, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Di Taranto, G.; Cicione, C.; Visconti, G.; Isgrò, M.A.; Barba, M.; Di Stasio, E.; Stigliano, E.; Bernardini, C.; Michetti, F.; Salgarello, M.; et al. Qualitative and quantitative differences of adipose-derived stromal cells from superficial and deep subcutaneous lipoaspirates: A matter of fat. Cytotherapy 2015, 17, 1076–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsekouras, A.; Mantas, D.; Tsilimigras, I.D.; Moris, D.; Kontos, M.; Zografos, C.G. Comparison of the Viability and Yield of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells (ASCs) from Different Donor Areas. In Vivo 2017, 31, 1229–1234. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rezai Rad, M.; Bohloli, M.; Akhavan Rahnama, M.; Anbarlou, A.; Nazeman, P.; Khojasteh, A. Impact of Tissue Harvesting Sites on the Cellular Behaviors of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells: Implication for Bone Tissue Engineering. Stem Cells Int. 2017, 2017, 2156478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oedayrajsingh-Varma, M.J.; van Ham, S.M.; Knippenberg, M.; Helder, M.N.; Klein-Nulend, J.; Schouten, T.E.; Ritt, M.J.; van Milligen, F.J. Adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cell yield and growth characteristics are affected by the tissue-harvesting procedure. Cytotherapy 2006, 8, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Vollenstee, F.A.; Hoffmann, D.; Pepper, M.S. Harvesting and Collection of Adipose Tissue for the Isolation of Adipose-Derived Stromal/Stem Cells. In Stem Cell Processing; Pham, P.V., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 199–220. [Google Scholar]
- Beane, O.S.; Fonseca, V.C.; Cooper, L.L.; Koren, G.; Darling, E.M. Impact of Aging on the Regenerative Properties of Bone Marrow-, Muscle-, and Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e115963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varghese, J.; Griffin, M.; Mosahebi, A.; Butler, P. Systematic review of patient factors affecting adipose stem cell viability and function: Implications for regenerative therapy. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2017, 8, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, X.; Liao, C.; Liu, G.; Xu, Y.; Tan, J.; Song, Z. Age-Related Changes in the Regenerative Potential of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Isolated from the Prominent Fat Pads in Human Lower Eyelids. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Niklason, L.; Steinbacher, D.M. The effect of age on human adipose-derived stem cells. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2013, 131, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dufrane, D. Impact of Age on Human Adipose Stem Cells for Bone Tissue Engineering. Cell Transplant. 2017, 26, 1496–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.; Lee, K.S.; Kim, C.-L.; Byeon, J.S.; Gu, N.-Y.; Cho, I.-S.; Cha, S.-H. Effect of donor age on the proliferation and multipotency of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells. J. Vet. Sci. 2017, 18, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreml, S.; Babilas, P.; Fruth, S.; Orsó, E.; Schmitz, G.; Mueller, M.B.; Nerlich, M.; Prantl, L. Harvesting human adipose tissue-derived adult stem cells: Resection versus liposuction. Cytotherapy 2009, 11, 947–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gnanasegaran, N.; Govindasamy, V.; Musa, S.; Kasim, N.H.A. Different Isolation Methods Alter the Gene Expression Profiling of Adipose Derived Stem Cells. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2014, 11, 391–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dominici, M.; Le Blanc, K.; Mueller, I.; Slaper-Cortenbach, I.; Marini, F.; Krause, D.; Deans, R.; Keating, A.; Prockop, D.; Horwitz, E. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy 2006, 8, 315–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellini, E.; Grieco, M.P.; Raposio, E. A journey through liposuction and liposculture: Review. Ann. Med. Surg. 2017, 24, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, A.J.; Llull, R.; Hedrick, M.H.; Futrell, J.W. Emerging approaches to the tissue engineering of fat. Clin. Plast. Surg. 1999, 26, 587–603. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Agostini, T.; Lazzeri, D.; Pini, A.; Marino, G.; Li Quattrini, A.; Bani, D.; Dini, M. Wet and Dry Techniques for Structural Fat Graft Harvesting: Histomorphometric and Cell Viability Assessments of Lipoaspirated Samples. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2012, 130, 331e–339e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, J.A. The Tumescent Technique for Lipo-Suction Surgery. Am. J. Cosmet. Surg. 1987, 4, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonacci, F.; Bertozzi, N.; Grieco, M.P.; Grignaffini, E.; Raposio, E. Procedure, applications, and outcomes of autologous fat grafting. Ann. Med. Surg. 2017, 20, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Illouz, Y. Une nouvelle technique pour les lipodystrophies localisées. Rev. Chir. Esthet. Fr. 1980, 4, 19. [Google Scholar]
- Kakagia, D.; Pallua, N. Autologous fat grafting: In search of the optimal technique. Surg. Innov. 2014, 21, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, L.L.; Coleman, S.R.; Cui, X.; Ferguson, R.E., Jr.; Vasconez, H.C. Autologous fat grafts harvested and refined by the Coleman technique: A comparative study. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2008, 122, 932–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozsoy, Z.; Kul, Z.; Bilir, A. The role of cannula diameter in improved adipocyte viability: A quantitative analysis. Aesthet. Surg. J. 2006, 26, 287–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Erdim, M.; Tezel, E.; Numanoglu, A.; Sav, A. The effects of the size of liposuction cannula on adipocyte survival and the optimum temperature for fat graft storage: An experimental study. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2009, 62, 1210–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gimble, J.M.; Katz, A.J.; Bunnell, B.A. Adipose-Derived Stem Cells for Regenerative Medicine. Circ. Res. 2007, 100, 1249–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Campbell, G.L.; Laudenslager, N.; Newman, J. The Effect of Mechanical Stress on Adipocyte Morphology and Metabolism. Am. J. Cosmet. Surg. 1987, 4, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, Z.; Oplander, C.; Almakadi, S.; Fritz, A.; Vogt, M.; Pallua, N. Conventional vs. micro-fat harvesting: How fat harvesting technique affects tissue-engineering approaches using adipose tissue-derived stem/stromal cells. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2013, 66, 1271–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, P.S.; Desouches, C.; Gay, A.M.; Hautier, A.; Magalon, G. Development of micro-injection as an innovative autologous fat graft technique: The use of adipose tissue as dermal filler. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2012, 65, 1692–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zocchi, M. Ultrasonic liposculpturing. Aesthet. Plast. Surg. 1992, 16, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apfelberg, D.B.; Rosenthal, S.; Hunstad, J.P.; Achauer, B.; Fodor, P.B. Progress report on multicenter study of laser-assisted liposuction. Aesthet. Plast. Surg. 1994, 18, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apfelberg, D. Laser-assisted liposuction may benefit surgeons, patients. Clin. Laser Mon. 1992, 10, 193–194. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Coleman, S.R. Hand rejuvenation with structural fat grafting. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2002, 110, 1731–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodbell, M. Metabolism of isolated fat cells. II. The similar effects of phospholipase C (Clostridium perfringens alpha toxin) and of insulin on glucose and amino acid metabolism. J. Biol. Chem. 1966, 241, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rodbell, M. The metabolism of isolated fat cells. IV. Regulation of release of protein by lipolytic hormones and insulin. J. Biol. Chem. 1966, 241, 3909–3917. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rodbell, M.; Jones, A.B. Metabolism of isolated fat cells. 3. The similar inhibitory action of phospholipase C (Clostridium perfringens alpha toxin) and of insulin on lipolysis stimulated by lipolytic hormones and theophylline. J. Biol. Chem. 1966, 241, 140–142. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Van, R.L.; Bayliss, C.E.; Roncari, D.A. Cytological and enzymological characterization of adult human adipocyte precursors in culture. J. Clin. Investig. 1976, 58, 699–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjorntorp, P.; Karlsson, M.; Pertoft, H.; Pettersson, P.; Sjostrom, L.; Smith, U. Isolation and characterization of cells from rat adipose tissue developing into adipocytes. J. Lipid Res. 1978, 19, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Deslex, S.; Negrel, R.; Vannier, C.; Etienne, J.; Ailhaud, G. Differentiation of human adipocyte precursors in a chemically defined serum-free medium. Int. J. Obes. 1987, 11, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hauner, H.; Wabitsch, M.; Pfeiffer, E.F. Differentiation of adipocyte precursor cells from obese and nonobese adult women and from different adipose tissue sites. Horm. Metab. Res. Suppl. 1988, 19, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hauner, H.; Entenmann, G.; Wabitsch, M.; Gaillard, D.; Ailhaud, G.; Negrel, R.; Pfeiffer, E.F. Promoting effect of glucocorticoids on the differentiation of human adipocyte precursor cells cultured in a chemically defined medium. J. Clin. Investig. 1989, 84, 1663–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurita, M.; Matsumoto, D.; Shigeura, T.; Sato, K.; Gonda, K.; Harii, K.; Yoshimura, K. Influences of Centrifugation on Cells and Tissues in Liposuction Aspirates: Optimized Centrifugation for Lipotransfer and Cell Isolation. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2008, 121, 1033–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, M.; Heydarkhan-Hagvall, S.; Hedrick, M.; Benhaim, P.; Zuk, P. Manual Isolation of Adipose-derived Stem Cells from Human Lipoaspirates. J. Vis. Exp. 2013, e50585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, S.; Unger, M.; van Griensven, M.; Balmayor, E.R. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells from liposuction and resected fat are feasible sources for regenerative medicine. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2017, 22, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markarian, C.F.; Frey, G.Z.; Silveira, M.D.; Milani, A.R.; Ely, P.B.; Horn, A.P.; Nardi, N.B.; Camassola, M. Isolation of adipose-derived stem cells: A comparison among different methods. Biotechnol. Lett. 2014, 36, 693–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, P.P.; Gimble, J.M.; Dias, I.R.; Gomes, M.E.; Reis, R.L. Xenofree enzymatic products for the isolation of human adipose-derived stromal/stem cells. Tissue Eng. Part C Methods 2013, 19, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirkpatrick, C.; Melzner, I.; Göller, T. Comparative effects of trypsin, collagenase and mechanical harvesting on cell membrane lipids studied in monolayer-cultured endothelial cells and a green monkey kidney cell line. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Mol. Cell Res. 1985, 846, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadler, G.; Hennerbichler, S.; Lindenmair, A.; Peterbauer, A.; Hofer, K.; Van Griensven, M.; Gabriel, C.; Redl, H.; Wolbank, S. Phenotypic shift of human amniotic epithelial cells in culture is associated with reduced osteogenic differentiation in vitro. Cytotherapy 2008, 10, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellei, B.; Migliano, E.; Tedesco, M.; Caputo, S.; Picardo, M. Maximizing non-enzymatic methods for harvesting adipose-derived stem from lipoaspirate: Technical considerations and clinical implications for regenerative surgery. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hélène, B.; Cécile, D.B.; Frédéric, U.; Mehdi, N.; Karlien, P.; Gordana, R.; Nathalie, M.; Dominique, B.; Laurence, L. Isolation of Adipose-Derived Stromal Cells Without Enzymatic Treatment: Expansion, Phenotypical, and Functional Characterization. Stem Cells Dev. 2014, 23, 2390–2400. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Shah, F.S.; Wu, X.; Dietrich, M.; Rood, J.; Gimble, J.M. A non-enzymatic method for isolating human adipose tissue-derived stromal stem cells. Cytotherapy 2013, 15, 979–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghorbani, A.; Jalali, S.A.; Varedi, M. Isolation of adipose tissue mesenchymal stem cells without tissue destruction: A non-enzymatic method. Tissue Cell 2014, 46, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oberbauer, E.; Steffenhagen, C.; Wurzer, C.; Gabriel, C.; Redl, H.; Wolbank, S. Enzymatic and non-enzymatic isolation systems for adipose tissue-derived cells: Current state of the art. Cell Regen. 2015, 4, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pamphilon, D.; Selogie, E.; McKenna, D.; Cancelas-Peres, J.; Szczepiorkowski, Z.M.; Sacher, R.; McMannis, J.; Eichler, H.; Garritsen, H.; Takanashi, M.; et al. Current practices and Prospects for Standardization of the Hematopoietic Colony-Forming-Unit (CFU) assay: A Report by the Cellular Therapy Team of the Biomedical Excellence for Safer Transfusion (BEST) Collaborative. Cytotherapy 2013, 15, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarma, N.J.; Takeda, A.; Yaseen, N.R. Colony Forming Cell (CFC) Assay for Human Hematopoietic Cells. J. Vis. Exp. 2010, 2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedenstein, A.J.; Chailakhyan, R.K.; Latsinik, N.V.; Panasyuk, A.F.; Keiliss-Borok, I.V. Stromal cells responsible for transferring the microenvironment of the hemopoietic tissues. Cloning in vitro and retransplantation in vivo. Transplantation 1974, 17, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pochampally, R. Colony forming unit assays for MSCs. Methods Mol. Biol. 2008, 449, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Javazon, E.H.; Colter, D.C.; Schwarz, E.J.; Prockop, D.J. Rat marrow stromal cells are more sensitive to plating density and expand more rapidly from single-cell-derived colonies than human marrow stromal cells. Stem Cells 2001, 19, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peister, A.; Mellad, J.A.; Larson, B.L.; Hall, B.M.; Gibson, L.F.; Prockop, D.J. Adult stem cells from bone marrow (MSCs) isolated from different strains of inbred mice vary in surface epitopes, rates of proliferation, and differentiation potential. Blood 2004, 103, 1662–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rodeheffer, M.S.; Birsoy, K.; Friedman, J.M. Identification of white adipocyte progenitor cells in vivo. Cell 2008, 135, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, G.; Garcia, M.; Ning, H.; Banie, L.; Guo, Y.-L.; Lue, T.F.; Lin, C.-S. Defining Stem and Progenitor Cells within Adipose Tissue. Stem Cells Dev. 2008, 17, 1053–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaiba, S.; França, L.P.D.; França, J.P.D.; Ferreira, L.M. Characterization of human adipose-derived stem cells. Acta Cir. Bras. 2012, 27, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mildmay-White, A.; Khan, W. Cell Surface Markers on Adipose-Derived Stem Cells: A Systematic Review. Curr. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2017, 12, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.-S.; Ning, H.; Lin, G.; Lue, T.F. Is CD34 Truly a Negative Marker for Mesenchymal Stem Cells? Cytotherapy 2012, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strem, B.M.; Hicok, K.C.; Zhu, M.; Wulur, I.; Alfonso, Z.; Schreiber, R.E.; Fraser, J.K.; Hedrick, M.H. Multipotential differentiation of adipose tissue-derived stem cells. Keio J. Med. 2005, 54, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowan, C.M.; Shi, Y.-Y.; Aalami, O.O.; Chou, Y.-F.; Mari, C.; Thomas, R.; Quarto, N.; Contag, C.H.; Wu, B.; Longaker, M.T. Adipose-derived adult stromal cells heal critical-size mouse calvarial defects. Nat. Biotechnol. 2004, 22, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grottkau, B.E.; Lin, Y. Osteogenesis of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells. Bone Res. 2013, 1, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Girolamo, L.; Sartori, M.F.; Albisetti, W.; Brini, A.T. Osteogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells: Comparison of two different inductive media. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2007, 1, 154–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Girolamo, L.; Sartori, M.F.; Arrigoni, E.; Rimondini, L.; Albisetti, W.; Weinstein, R.L.; Brini, A.T. Human adipose-derived stem cells as future tools in tissue regeneration: Osteogenic differentiation and cell-scaffold interaction. Int. J. Artif. Organs 2008, 31, 467–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arrigoni, E.; Lopa, S.; de Girolamo, L.; Stanco, D.; Brini, A.T. Isolation, characterization and osteogenic differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells: From small to large animal models. Cell Tissue Res. 2009, 338, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedenstein, A.J.; Chailakhyan, R.K.; Gerasimov, U.V. Bone marrow osteogenic stem cells: In vitro cultivation and transplantation in diffusion chambers. Cell Prolif. 1987, 20, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, T.; Aoyama, T.; Nakayama, T.; Nakamata, T.; Hosaka, T.; Nishijo, K.; Nakamura, T.; Kiyono, T.; Toguchida, J. Clonal heterogeneity in differentiation potential of immortalized human mesenchymal stem cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 295, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Lin, Y. Osteogenic differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells promoted by quercetin. Cell Prolif. 2014, 47, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.J.; Bae, Y.C.; Suh, K.T.; Jung, J.S. Quercetin, a flavonoid, inhibits proliferation and increases osteogenic differentiation in human adipose stromal cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2006, 72, 1268–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almalki, S.G.; Agrawal, D.K. Key Transcription Factors in the Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Differ. Res. Biol. Divers. 2016, 92, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langenbach, F.; Handschel, J. Effects of dexamethasone, ascorbic acid and β-glycerophosphate on the osteogenic differentiation of stem cells in vitro. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2013, 4, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behr, B.; Tang, C.; Germann, G.; Longaker, M.T.; Quarto, N. Locally applied VEGFA increases the osteogenic healing capacity of human adipose derived stem cells by promoting osteogenic and endothelial differentiation. Stem Cells 2011, 29, 286–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.L.; Liu, Y.B.; Ma, E.G.; Shen, W.X.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.N. Synergistic effect of BMP9 and TGF-β in the proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts. Genet. Mol. Res. 2015, 14, 7605–7615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Madhu, V.; Dighe, A.S.; Irvine, J.N., Jr.; Cui, Q. Osteogenic response of human adipose-derived stem cells to BMP-6, VEGF, and combined VEGF plus BMP-6 in vitro. Growth Factors 2012, 30, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuk, P.; Chou, Y.F.; Mussano, F.; Benhaim, P.; Wu, B.M. Adipose-derived stem cells and BMP2: Part 2. BMP2 may not influence the osteogenic fate of human adipose-derived stem cells. Connect. Tissue Res. 2011, 52, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz, A.C.C.; Silva, M.L.; Caon, T.; SimÕEs, C.M.O. Addition of bone morphogenetic protein type 2 to ascorbate and β-glycerophosphate supplementation did not enhance osteogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells. J. Appl. Oral Sci. 2012, 20, 628–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Song, I.; Kim, B.S.; Kim, C.S.; Im, G.I. Effects of BMP-2 and vitamin D3 on the osteogenic differentiation of adipose stem cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 408, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdollahi, H.; Harris, L.J.; Zhang, P.; McIlhenny, S.; Tulenko, T.; DiMuzio, P.J. The Role of Hypoxia in Stem Cell Differentiation and Therapeutics. J. Surg. Res. 2011, 165, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Valorani, M.G.; Montelatici, E.; Germani, A.; Biddle, A.; D’Alessandro, D.; Strollo, R.; Patrizi, M.P.; Lazzari, L.; Nye, E.; Otto, W.R.; et al. Pre-culturing human adipose tissue mesenchymal stem cells under hypoxia increases their adipogenic and osteogenic differentiation potentials. Cell Prolif. 2012, 45, 225–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Sun, X.; Cao, K.; Wu, Y.; Zou, D.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, G.; Huang, Q.; et al. Hypoxia induces osteogenesis in rabbit adipose-derived stem cells overexpressing bone morphogenic protein-2. Oral Dis. 2014, 20, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skubis, A.; Sikora, B.; Zmarzły, N.; Wojdas, E.; Mazurek, U. Adipose-derived stem cells: A review of osteogenesis differentiation. Folia Biol. Oecol. 2016, 12, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Yoon, S.M.; Song, S.U.; Park, S.G.; Kim, W.-S.; Park, I.G.; Lee, J.; Sung, J.-H. Hypoxia Suppresses Spontaneous Mineralization and Osteogenic Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells via IGFBP3 Up-Regulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, S.H.; Chen, C.T.; Wei, Y.H. Inhibitory effects of hypoxia on metabolic switch and osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells 2013, 31, 2779–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Gao, Z.; Chen, Y.; Guan, M.-X. The role of mitochondria in osteogenic, adipogenic and chondrogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Protein Cell 2017, 8, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, H.; Guan, D.; Liu, X.; Li, J.; Wang, L.; Wu, J.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, W.; Ren, R.; Zhang, W.; et al. SIRT6 safeguards human mesenchymal stem cells from oxidative stress by coactivating NRF2. Cell Res. 2016, 26, 190–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Min-Wen, J.C.; Jun-Hao, E.T.; Shyh-Chang, N. Stem cell mitochondria during aging. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2016, 52, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Guo, J.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, G. The Roles of Bone Morphogenetic Proteins and Their Signaling in the Osteogenesis of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 2014, 20, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reddi, A.H. BMPs: From bone morphogenetic proteins to body morphogenetic proteins. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2005, 16, 249–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levi, B.; Hyun, J.S.; Nelson, E.R.; Li, S.; Montoro, D.T.; Wan, D.C.; Jia, F.J.; Glotzbach, J.C.; James, A.W.; Lee, M.; et al. Nonintegrating Knockdown and Customized Scaffold Design Enhances Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cells in Skeletal Repair. Stem Cells 2011, 29, 2018–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mizrahi, O.; Sheyn, D.; Tawackoli, W.; Kallai, I.; Oh, A.; Su, S.; Da, X.; Zarrini, P.; Cook-Wiens, G.; Gazit, D.; et al. BMP-6 is more efficient in bone formation than BMP-2 when overexpressed in mesenchymal stem cells. Gene Ther. 2013, 20, 370–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knippenberg, M.; Helder, M.N.; Zandieh Doulabi, B.; Wuisman, P.I.; Klein-Nulend, J. Osteogenesis versus chondrogenesis by BMP-2 and BMP-7 in adipose stem cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 342, 902–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Wu, G.; Zhao, J.; Wang, L.; Sun, P.; Gu, Z. rhBMP2/7 heterodimer: An osteoblastogenesis inducer of not higher potency but lower effective concentration compared with rhBMP2 and rhBMP7 homodimers. Tissue Eng. Part A 2010, 16, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vicente Lopez, M.A.; Vazquez Garcia, M.N.; Entrena, A.; Olmedillas Lopez, S.; Garcia-Arranz, M.; Garcia-Olmo, D.; Zapata, A. Low doses of bone morphogenetic protein 4 increase the survival of human adipose-derived stem cells maintaining their stemness and multipotency. Stem Cells Dev. 2011, 20, 1011–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panetta, N.J.; Gupta, D.M.; Lee, J.K.; Wan, D.C.; Commons, G.W.; Longaker, M.T. Human adipose-derived stromal cells respond to and elaborate bone morphogenetic protein-2 during in vitro osteogenic differentiation. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2010, 125, 483–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, D.C.; Shi, Y.-Y.; Nacamuli, R.P.; Quarto, N.; Lyons, K.M.; Longaker, M.T. Osteogenic differentiation of mouse adipose-derived adult stromal cells requires retinoic acid and bone morphogenetic protein receptor type IB signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 12335–12340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ducy, P.; Zhang, R.; Geoffroy, V.; Ridall, A.L.; Karsenty, G. Osf2/Cbfa1: A transcriptional activator of osteoblast differentiation. Cell 1997, 89, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.; Bakker, A.D.; de Blieck-Hogervorst, J.M.; Klein-Nulend, J. WNT5A induces osteogenic differentiation of human adipose stem cells via rho-associated kinase ROCK. Cytotherapy 2010, 12, 924–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takada, I.; Kouzmenko, A.P.; Kato, S. Molecular switching of osteoblastogenesis versus adipogenesis: Implications for targeted therapies. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2009, 13, 593–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chillakuri, C.R.; Sheppard, D.; Lea, S.M.; Handford, P.A. Notch receptor–ligand binding and activation: Insights from molecular studies. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2012, 23, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gimble, J.; Guilak, F. Adipose-derived adult stem cells: Isolation, characterization, and differentiation potential. Cytotherapy 2003, 5, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estes, B.T.; Wu, A.W.; Guilak, F. Potent induction of chondrocytic differentiation of human adipose-derived adult stem cells by bone morphogenetic protein 6. Arthritis Rheum. 2006, 54, 1222–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.J.; Im, G.I. Chondrogenic differentiation of adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells: Greater doses of growth factor are necessary. J. Orthop. Res. 2009, 27, 612–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sottile, V.; Halleux, C.; Bassilana, F.; Keller, H.; Seuwen, K. Stem cell characteristics of human trabecular bone-derived cells. Bone 2002, 30, 699–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suva, D.; Garavaglia, G.; Menetrey, J.; Chapuis, B.; Hoffmeyer, P.; Bernheim, L.; Kindler, V. Non-hematopoietic human bone marrow contains long-lasting, pluripotential mesenchymal stem cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2004, 198, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puetzer, J.L.; Petitte, J.N.; Loboa, E.G. Comparative review of growth factors for induction of three-dimensional in vitro chondrogenesis in human mesenchymal stem cells isolated from bone marrow and adipose tissue. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 2010, 16, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Sun, X.; Wang, W.; Hu, Y. Adipose-derived stem cells and chondrogenesis. Cytotherapy 2007, 9, 712–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stromps, J.P.; Paul, N.E.; Rath, B.; Nourbakhsh, M.; Bernhagen, J.; Pallua, N. Chondrogenic Differentiation of Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cells: A New Path in Articular Cartilage Defect Management? BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 740926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Wang, W.; Ludeman, M.; Cheng, K.; Hayami, T.; Lotz, J.C.; Kapila, S. Chondrogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells in three-dimensional alginate gels. Tissue Eng. Part A 2008, 14, 667–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erickson, G.R.; Gimble, J.M.; Franklin, D.M.; Rice, H.E.; Awad, H.; Guilak, F. Chondrogenic potential of adipose tissue-derived stromal cells in vitro and in vivo. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 290, 763–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awad, H.A.; Wickham, M.Q.; Leddy, H.A.; Gimble, J.M.; Guilak, F. Chondrogenic differentiation of adipose-derived adult stem cells in agarose, alginate, and gelatin scaffolds. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 3211–3222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baptista, L.S.; Silva, K.R.; Pedrosa, C.S.; Amaral, R.J.; Belizário, J.V.; Borojevic, R.; Granjeiro, J.M. Bioengineered Cartilage in a Scaffold-Free Method by Human Cartilage-Derived Progenitor Cells: A Comparison With Human Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells. Artif. Organs 2013, 37, 1068–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, M.A.; Nguyen, V.T.; Levi, B.; James, A.W. Current Methods of Adipogenic Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2011, 20, 1793–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Higuchi, M.; Dusting, G.J.; Peshavariya, H.; Jiang, F.; Hsiao, S.T.-F.; Chan, E.C.; Liu, G.-S. Differentiation of Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cells into Fat Involves Reactive Oxygen Species and Forkhead Box O1 Mediated Upregulation of Antioxidant Enzymes. Stem Cells Dev. 2013, 22, 878–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cristancho, A.G.; Lazar, M.A. Forming functional fat: A growing understanding of adipocyte differentiation. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2011, 12, 722–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, L.; Li, Y.B.; Wang, Y.S. Dexamethasone-induced adipogenesis in primary marrow stromal cell cultures: Mechanism of steroid-induced osteonecrosis. Chin. Med. J. 2006, 119, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ailhaud, G. Adipose cell differentiation in culture. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 1982, 49, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosen, E.D.; Walkey, C.J.; Puigserver, P.; Spiegelman, B.M. Transcriptional regulation of adipogenesis. Genes Dev. 2000, 14, 1293–1307. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gurriarán-Rodríguez, U.; Al-Massadi, O.; Roca-Rivada, A.; Crujeiras, A.B.; Gallego, R.; Pardo, M.; Seoane, L.M.; Pazos, Y.; Casanueva, F.F.; Camiña, J.P. Obestatin as a regulator of adipocyte metabolism and adipogenesis. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2011, 15, 1927–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.P.; Ha, J.M.; Yun, S.J.; Kim, E.K.; Chung, S.W.; Hong, K.W.; Kim, C.D.; Bae, S.S. Transcriptional activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma requires activation of both protein kinase A and Akt during adipocyte differentiation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 399, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scioli, M.G.; Bielli, A.; Gentile, P.; Mazzaglia, D.; Cervelli, V.; Orlandi, A. The Biomolecular Basis of Adipogenic Differentiation of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 6517–6526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hemmingsen, M.; Vedel, S.; Skafte-Pedersen, P.; Sabourin, D.; Collas, P.; Bruus, H.; Dufva, M. The Role of Paracrine and Autocrine Signaling in the Early Phase of Adipogenic Differentiation of Adipose-derived Stem Cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miyamoto, Y.; Ikeuchi, M.; Noguchi, H.; Yagi, T.; Hayashi, S. Enhanced Adipogenic Differentiation of Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cells in an in vitro Microenvironment: The Preparation of Adipose-Like Microtissues Using a Three-Dimensional Culture. Cell Med. 2017, 9, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- White, U.A.; Tchoukalova, Y.D. Adipose Stem Cells and Adipogenesis. In Adipose Tissue and Adipokines in Health and Disease; Fantuzzi, G., Braunschweig, C., Eds.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 15–32. [Google Scholar]
- Otto, T.C.; Lane, M.D. Adipose development: From stem cell to adipocyte. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2005, 40, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Z.; Li, Q.; Luo, S.; Liu, Z.; Luo, D.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, D.; Rao, P.; Xiao, J. PPARgamma and Wnt Signaling in Adipogenic and Osteogenic Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Curr. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2016, 11, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salgado, A.J.; Reis, R.L.; Sousa, N.; Gimble, J.M. Adipose tissue derived stem cells secretome: Soluble factors and their roles in regenerative medicine. Curr. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2010, 5, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maumus, M.; Jorgensen, C.; Noël, D. Mesenchymal stem cells in regenerative medicine applied to rheumatic diseases: Role of secretome and exosomes. Biochimie 2013, 95, 2229–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakanishi, C.; Nagaya, N.; Ohnishi, S.; Yamahara, K.; Takabatake, S.; Konno, T.; Hayashi, K.; Kawashiri, M.A.; Tsubokawa, T.; Yamagishi, M. Gene and protein expression analysis of mesenchymal stem cells derived from rat adipose tissue and bone marrow. Circ. J. 2011, 75, 2260–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kachgal, S.; Putnam, A.J. Mesenchymal stem cells from adipose and bone marrow promote angiogenesis via distinct cytokine and protease expression mechanisms. Angiogenesis 2011, 14, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapur, S.K.; Katz, A.J. Review of the adipose derived stem cell secretome. Biochimie 2013, 95, 2222–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helena, S.; Jan, M.; Jivan, G.S.; Hana, K. Mapping of the secretome of primary isolates of mammalian cells, stem cells and derived cell lines. Proteomics 2011, 11, 691–708. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, D.; Suenaga, N.; Edelmann, M.J.; Fridman, R.; Muschel, R.J.; Kessler, B.M. Novel MMP-9 Substrates in Cancer Cells Revealed by a Label-free Quantitative Proteomics Approach. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2008, 7, 2215–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brini, A.T.; Amodeo, G.; Ferreira, L.M.; Milani, A.; Niada, S.; Moschetti, G.; Franchi, S.; Borsani, E.; Rodella, L.F.; Panerai, A.E.; et al. Therapeutic effect of human adipose-derived stem cells and their secretome in experimental diabetic pain. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, W.-S.; Park, B.-S.; Sung, J.-H. Protective role of adipose-derived stem cells and their soluble factors in photoaging. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2009, 301, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.Y.; Xia, Y.; Kim, W.S.; Kim, M.H.; Kim, T.H.; Kim, K.J.; Park, B.S.; Sung, J.H. Hypoxia-enhanced wound-healing function of adipose-derived stem cells: Increase in stem cell proliferation and up-regulation of VEGF and bFGF. Wound Repair Regen. 2009, 17, 540–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakudo, N.; Morimoto, N.; Ogawa, T.; Taketani, S.; Kusumoto, K. Hypoxia Enhances Proliferation of Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cells via HIF-1a Activation. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0139890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Zachar, V.; Pennisi, C.P.; Fink, T.; Maeda, Y.; Emmersen, J. Hypoxia Enhances Differentiation of Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells toward the Smooth Muscle Phenotype. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thangarajah, H.; Vial, I.N.; Chang, E.; El-Ftesi, S.; Januszyk, M.; Chang, E.I.; Paterno, J.; Neofytou, E.; Longaker, M.T.; Gurtner, G.C. IFATS collection: Adipose stromal cells adopt a proangiogenic phenotype under the influence of hypoxia. Stem Cells 2009, 27, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, C.A.; Fraga, J.S.; Grãos, M.; Neves, N.M.; Reis, R.L.; Gimble, J.M.; Sousa, N.; Salgado, A.J. The secretome of stem cells isolated from the adipose tissue and Wharton jelly acts differently on central nervous system derived cell populations. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2012, 3, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marfia, G.; Navone, S.E.; Hadi, L.A.; Paroni, M.; Berno, V.; Beretta, M.; Gualtierotti, R.; Ingegnoli, F.; Levi, V.; Miozzo, M.; et al. The Adipose Mesenchymal Stem Cell Secretome Inhibits Inflammatory Responses of Microglia: Evidence for an Involvement of Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Signalling. Stem Cells Dev. 2016, 25, 1095–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Constantin, G.; Marconi, S.; Rossi, B.; Angiari, S.; Calderan, L.; Anghileri, E.; Gini, B.; Bach, S.D.; Martinello, M.; Bifari, F.; et al. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate chronic experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Stem Cells 2009, 27, 2624–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehman, J.; Traktuev, D.; Li, J.; Merfeld-Clauss, S.; Temm-Grove, C.J.; Bovenkerk, J.E.; Pell, C.L.; Johnstone, B.H.; Considine, R.V.; March, K.L. Secretion of angiogenic and antiapoptotic factors by human adipose stromal cells. Circulation 2004, 109, 1292–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egashira, Y.; Sugitani, S.; Suzuki, Y.; Mishiro, K.; Tsuruma, K.; Shimazawa, M.; Yoshimura, S.; Iwama, T.; Hara, H. The conditioned medium of murine and human adipose-derived stem cells exerts neuroprotective effects against experimental stroke model. Brain Res. 2012, 1461, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Du, Z.; Zhao, L.; Feng, D.; Wei, G.; He, Y.; Tan, J.; Lee, W.H.; Hampel, H.; Dodel, R.; et al. IFATS collection: The conditioned media of adipose stromal cells protect against hypoxia-ischemia-induced brain damage in neonatal rats. Stem Cells 2009, 27, 478–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, B.; Luan, Z.; Wei, X.; He, Y.; Wei, G.; Johnstone, B.H.; Farlow, M.; Du, Y. AMP-activated kinase mediates adipose stem cell-stimulated neuritogenesis of PC12 cells. Neuroscience 2011, 181, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, L.F.; Costa, R.O.; Pedro, J.R.; Aguiar, P.; Serra, S.C.; Teixeira, F.G.; Sousa, N.; Salgado, A.J.; Almeida, R.D. Mesenchymal stem cells secretome-induced axonal outgrowth is mediated by BDNF. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palomares, T.; Cordero, M.; Bruzos-Cidon, C.; Torrecilla, M.; Ugedo, L.; Alonso-Varona, A. The Neuroprotective Effect of Conditioned Medium from Human Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells is Impaired by N-acetyl Cysteine Supplementation. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Cesare Mannelli, L.; Tenci, B.; Micheli, L.; Vona, A.; Corti, F.; Zanardelli, M.; Lapucci, A.; Clemente, A.M.; Failli, P.; Ghelardini, C. Adipose-derived stem cells decrease pain in a rat model of oxaliplatin-induced neuropathy: Role of VEGF-A modulation. Neuropharmacology 2018, 131, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bravo, B.; de Durango, C.G.; González, Á.; Gortázar, A.R.; Santos, X.; Forteza-Vila, J.; Vidal-Vanaclocha, F. Opposite Effects of Mechanical Action of Fluid Flow on Proangiogenic Factor Secretion From Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cells with and without Oxidative Stress. J. Cell. Physiol. 2017, 232, 2158–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilroy, G.E.; Foster, S.J.; Wu, X.; Ruiz, J.; Sherwood, S.; Heifetz, A.; Ludlow, J.W.; Stricker, D.M.; Potiny, S.; Green, P.; et al. Cytokine profile of human adipose-derived stem cells: Expression of angiogenic, hematopoietic, and pro-inflammatory factors. J. Cell. Physiol. 2007, 212, 702–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krumboeck, A.; Giovanoli, P.; Plock, J.A. Fat grafting and stem cell enhanced fat grafting to the breast under oncological aspects–recommendations for patient selection. Breast 2013, 22, 579–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Halloran, N.; Courtney, D.; Kerin, M.J.; Lowery, A.J. Adipose-Derived Stem Cells in Novel Approaches to Breast Reconstruction: Their Suitability for Tissue Engineering and Oncological Safety. Breast Cancer Basic Clin. Res. 2017, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Yao, F.; Yao, X.; Yi, C.; Tan, C.; Wei, L.; Sun, S. Role of CCL5 in invasion, proliferation and proportion of CD44+/CD24− phenotype of MCF-7 cells and correlation of CCL5 and CCR5 expression with breast cancer progression. Oncol. Rep. 2009, 21, 1113–1121. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ryu, H.; Oh, J.-E.; Rhee, K.-J.; Baik, S.K.; Kim, J.; Kang, S.J.; Sohn, J.H.; Choi, E.; Shin, H.C.; Kim, Y.M. Adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured at high density express IFN-β and suppress the growth of MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2014, 352, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmerlin, L.; Donnenberg, A.D.; Rubin, J.P.; Basse, P.; Landreneau, R.J.; Donnenberg, V.S. Regenerative therapy and cancer: In vitro and in vivo studies of the interaction between adipose-derived stem cells and breast cancer cells from clinical isolates. Tissue Eng. Part A 2010, 17, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Guo, S.; Liu, X.; Xv, N.; Zhang, S. Protective effects of adipose-derived stem cells secretome on human dermal fibroblasts from ageing damages. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 15739–15748. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cho, J.W.; Kang, M.C.; Lee, K.S. TGF-beta1-treated ADSCs-CM promotes expression of type I collagen and MMP-1, migration of human skin fibroblasts, and wound healing in vitro and in vivo. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2010, 26, 901–906. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, E.-J.; Bang, S.-I. Effects of conditioned medium from LL-37 treated adipose stem cells on human fibroblast migration. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 14, 723–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, B.S.; Jang, K.A.; Sung, J.H.; Park, J.S.; Kwon, Y.H.; Kim, K.J.; Kim, W.S. Adipose-derived stem cells and their secretory factors as a promising therapy for skin aging. Dermatol. Surg. 2008, 34, 1323–1326. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.C.; Kim, J.O.; Kim, S.-J. Secretome from human adipose-derived stem cells protects mouse liver from hepatic ischemia–reperfusion injury. Surgery 2015, 157, 934–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, X.; Chiu, P.W.Y.; Lam, P.K.; Chin, W.C.; Ng, E.K.W.; Lau, J.Y.W. Secretome from hypoxia-conditioned adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells promotes the healing of gastric mucosal injury in a rodent model. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Mol. Basis Dis. 2018, 1864, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, E.W.; Seo, M.K.; Woo, E.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Park, E.J.; Kim, S. Exosomes from human adipose-derived stem cells promote proliferation and migration of skin fibroblasts. Exp. Dermatol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, R.C.; Arslan, F.; Lee, M.M.; Sze, N.S.; Choo, A.; Chen, T.S.; Salto-Tellez, M.; Timmers, L.; Lee, C.N.; El Oakley, R.M.; et al. Exosome secreted by MSC reduces myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Stem Cell Res. 2010, 4, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vyas, N.; Dhawan, J. Exosomes: Mobile platforms for targeted and synergistic signaling across cell boundaries. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2017, 74, 1567–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Xie, X.; Lian, W.; Shi, R.; Han, S.; Zhang, H.; Lu, L.; Li, M. Exosomes from adipose-derived stem cells overexpressing Nrf2 accelerate cutaneous wound healing by promoting vascularization in a diabetic foot ulcer rat model. Exp. Mol. Med. 2018, 50, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- García-Contreras, M.; Vera-Donoso, C.D.; Hernández-Andreu, J.M.; García-Verdugo, J.M.; Oltra, E. Therapeutic Potential of Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cells (ADSCs) from Cancer Patients: A Pilot Study. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, L.; Wang, J.; Zhou, X.; Xiong, Z.; Zhao, J.; Yu, R.; Huang, F.; Zhang, H.; Chen, L. Exosomes derived from human adipose mensenchymal stem cells accelerates cutaneous wound healing via optimizing the characteristics of fibroblasts. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Hu, L.; Zhou, X.; Xiong, Z.; Zhang, C.; Shehada, H.M.A.; Hu, B.; Song, J.; Chen, L. Exosomes secreted by human adipose mesenchymal stem cells promote scarless cutaneous repair by regulating extracellular matrix remodelling. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, M.; Liu, T.; Wooseok, I.; Manho, K. Exosomes from adipose-derived stem cells ameliorate phenotype of Huntington’s disease in vitro model. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2016, 44, 2114–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, G.; Song, X.; Yang, F.; Wu, S.; Wang, J.; Chen, Z.; Liu, Y. Exosomes derived from miR-122-modified adipose tissue-derived MSCs increase chemosensitivity of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2015, 8, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Salomon, C.; Freeman, D.J. Extracellular Vesicles from Adipose Tissue—A Potential Role in Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes? Front. Endocrinol. 2017, 8, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| ASC Immunophenotypic Surface Markers | |
|---|---|
| Positive (+ve) | CD90, CD44, CD29, CD105, CD13, CD73, CD166, CD10, CD49e and CD59 |
| Negative (−ve) | CD31, CD34, CD45, CD14, CD11b, CD19, CD56 and CD146 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dubey, N.K.; Mishra, V.K.; Dubey, R.; Deng, Y.-H.; Tsai, F.-C.; Deng, W.-P. Revisiting the Advances in Isolation, Characterization and Secretome of Adipose-Derived Stromal/Stem Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2200. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19082200
Dubey NK, Mishra VK, Dubey R, Deng Y-H, Tsai F-C, Deng W-P. Revisiting the Advances in Isolation, Characterization and Secretome of Adipose-Derived Stromal/Stem Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(8):2200. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19082200
Chicago/Turabian StyleDubey, Navneet Kumar, Viraj Krishna Mishra, Rajni Dubey, Yue-Hua Deng, Feng-Chou Tsai, and Win-Ping Deng. 2018. "Revisiting the Advances in Isolation, Characterization and Secretome of Adipose-Derived Stromal/Stem Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 8: 2200. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19082200
APA StyleDubey, N. K., Mishra, V. K., Dubey, R., Deng, Y.-H., Tsai, F.-C., & Deng, W.-P. (2018). Revisiting the Advances in Isolation, Characterization and Secretome of Adipose-Derived Stromal/Stem Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(8), 2200. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19082200