IL-8 Secreted from M2 Macrophages Promoted Prostate Tumorigenesis via STAT3/MALAT1 Pathway
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
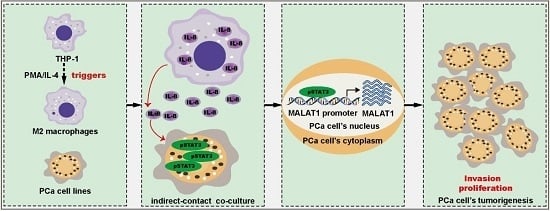
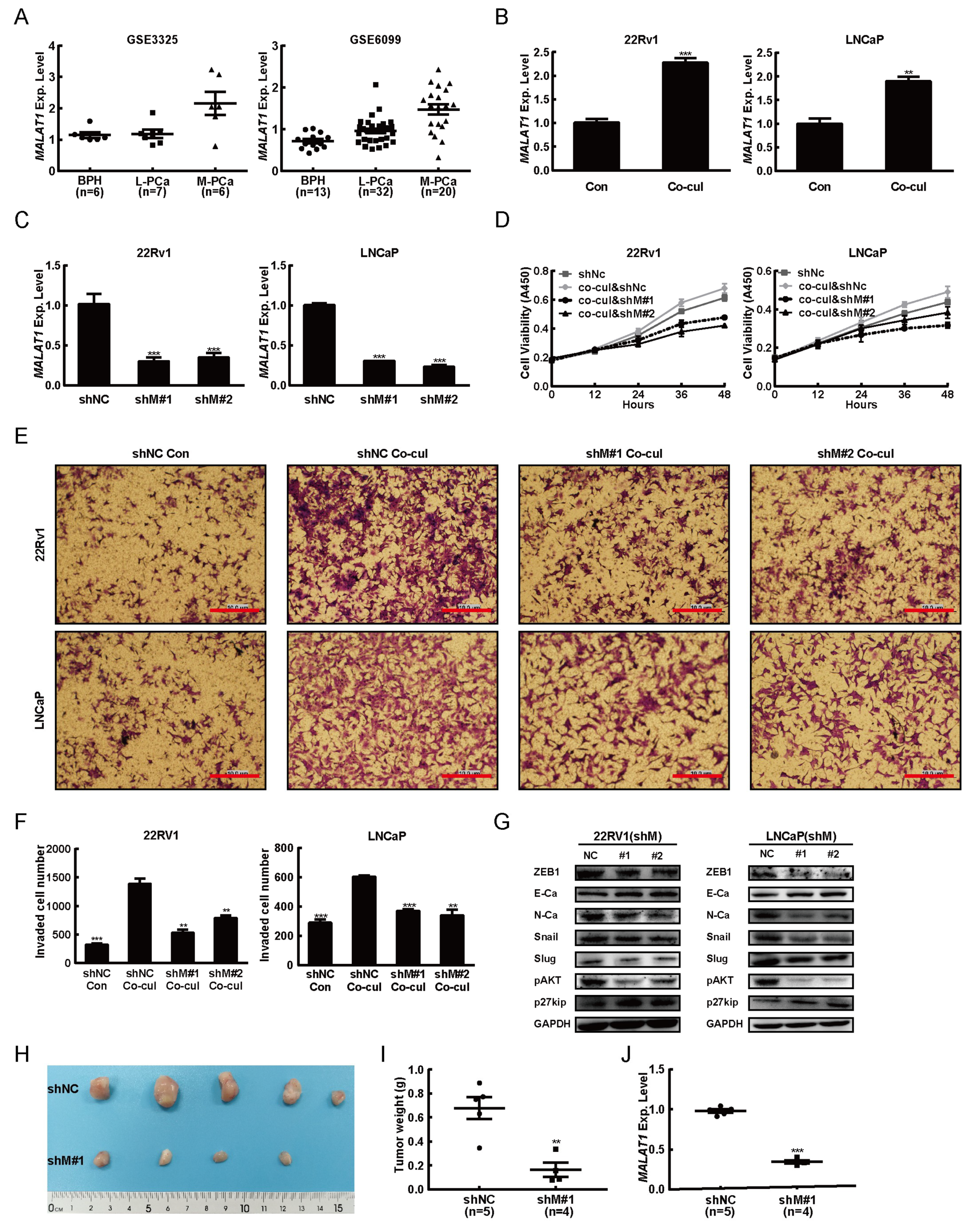
2.1. M2 Macrophages Driven From THP-1 Cells Promoted the PCa Tumorigenesis
2.2. MALAT1 was Potential Mediator for M2 Macrophage-Mediated Prostate Tumorigenesis
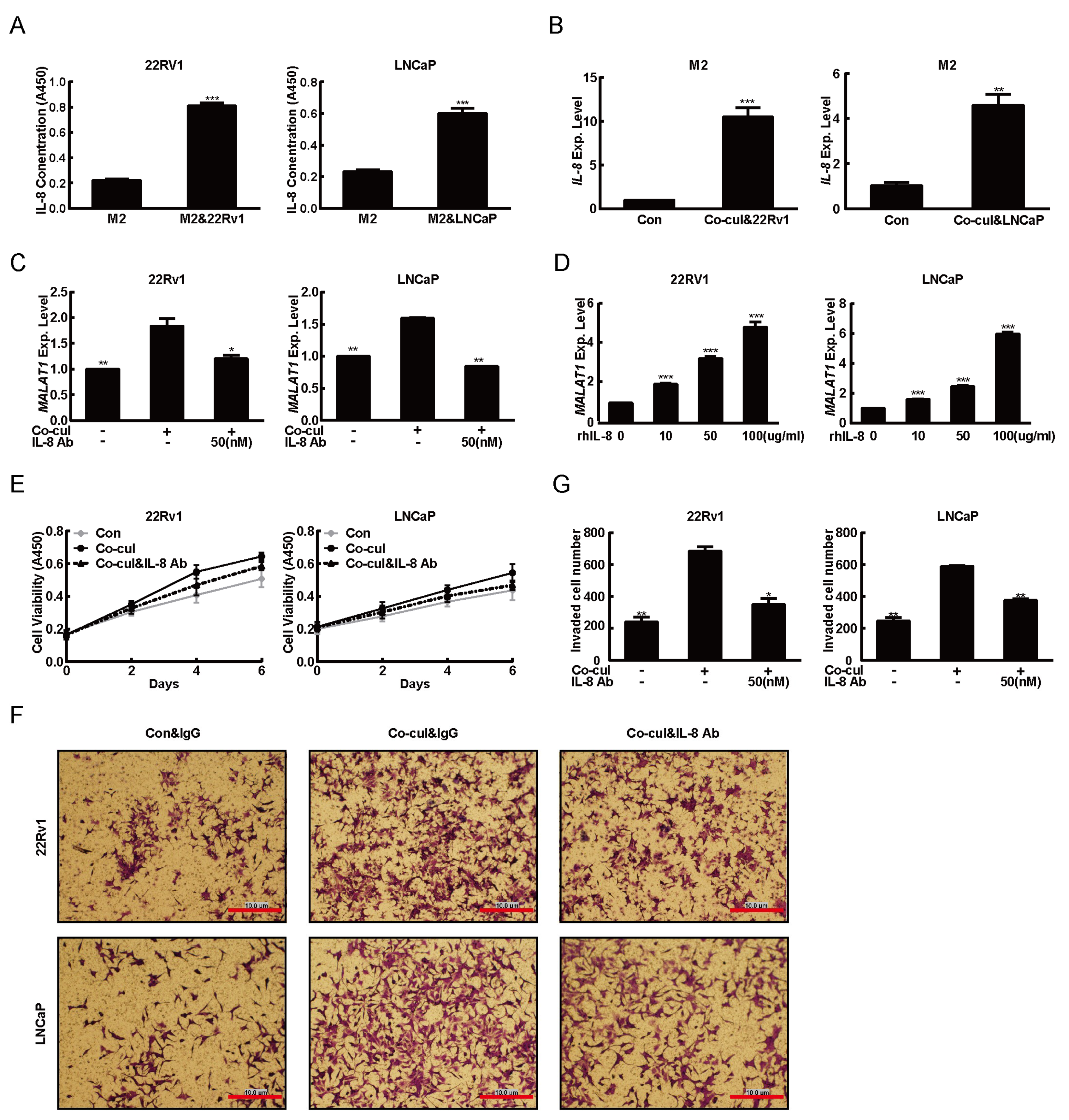
2.3. M2 Macrophages Derived IL-8 to Induced MALAT1 Expression
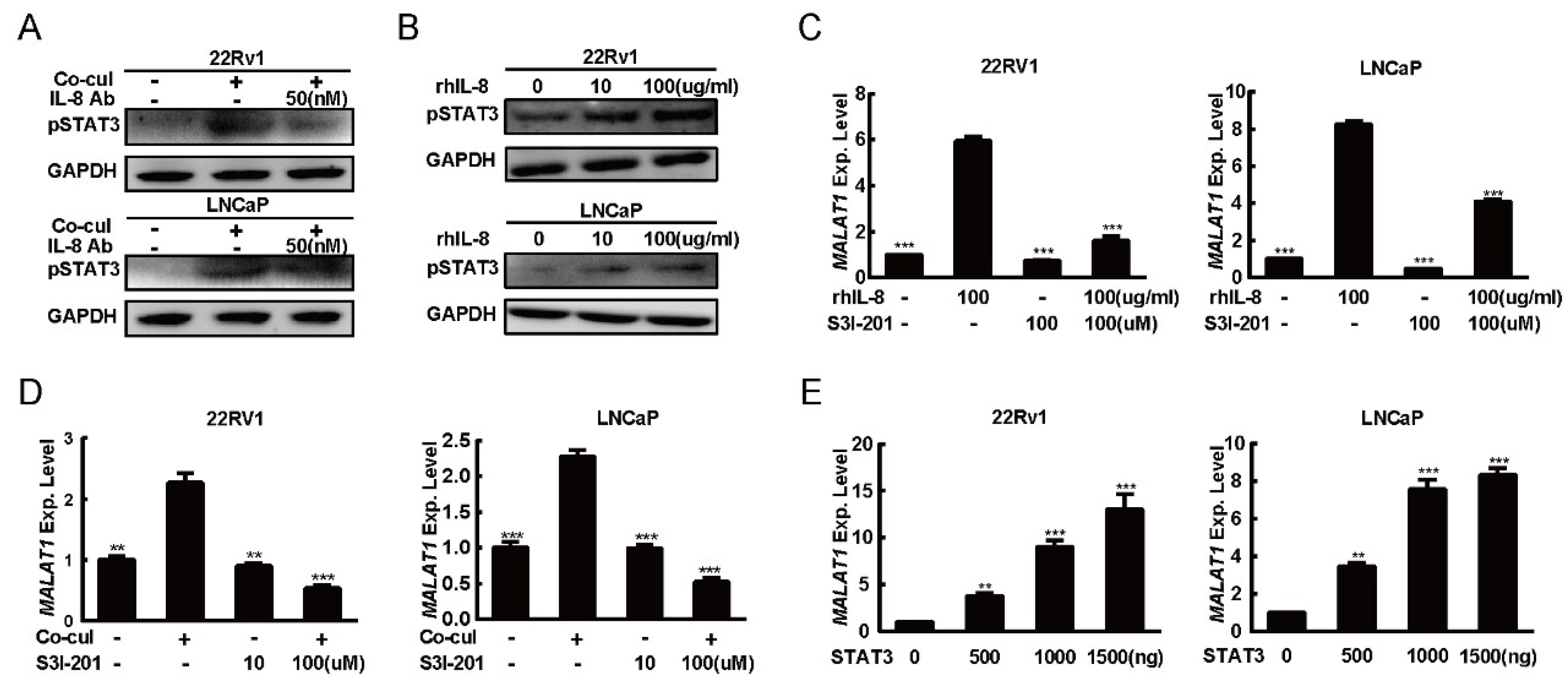
2.4. IL-8 Modified the Expression of MALAT1 Through STAT3 Phosphorylation
2.5. STAT3 Induced Expression of MALAT1 by Directly Binding to its Promoter
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. Plasmids and Reagents
4.3. Cell Proliferation Assay
4.4. Invasion Assay
4.5. In Silico Analysis Using the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO)
4.6. Total RNA Extraction and Real-Time Quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR)
4.7. Lentiviral Transduction and Infection shRNA
4.8. In Vivo Tumorigenicity Assay
4.9. ELISA Assay
4.10. Western Blotting
4.11. Luciferase Assay
4.12. Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP)
4.13. Statistical Analyses
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PCa | Prostate cancer |
| MALAT1 | Metastasis-associated with lung adenocarcinoma transcript-1 |
| EMT | epithelial-mesenchymal transition |
| IL-8 | interleukin-8 |
| STAT3 | Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 |
References
- Attard, G.; Parker, C.; Eeles, R.A.; Schröder, F.; Tomlins, S.A.; Tannock, I.; Drake, C.G.; de Bono, J.S. Prostate cancer. The Lancet 2016, 387, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonnenburg, D.W.; Morgans, A.K. Emerging Therapies in Metastatic Prostate Cancer. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 20, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Efstathiou, E.; Logothetis, C.J. A new therapy paradigm for prostate cancer founded on clinical observations. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 1100–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlecnik, B.; Bindea, G.; Kirilovsky, A.; Angell, H.K.; Obenauf, A.C.; Tosolini, M.; Church, S.E.; Maby, P.; Vasaturo, A.; Angelova, M.; et al. The tumor microenvironment and Immunoscore are critical determinants of dissemination to distant metastasis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 326r–327r. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, F.; Hu, C.; Tai, Z.; Yao, C.; Tian, J.; Zhang, L.; Xia, Q.; Gong, C.; Gao, Y.; Gao, S. Tumour microenvironment-responsive lipoic acid nanoparticles for targeted delivery of docetaxel to lung cancer. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hartmann, S.; Bhola, N.E.; Grandis, J.R. HGF/Met Signaling in Head and Neck Cancer: Impact on the Tumor Microenvironment. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 4005–4013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruffell, B.; Coussens, L.M. Macrophages and Therapeutic Resistance in Cancer. Cancer Cell 2015, 27, 462–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Josson, S.; Matsuoka, Y.; Chung, L.W.; Zhau, H.E.; Wang, R. Tumor-stroma co-evolution in prostate cancer progression and metastasis. Semin Cell Dev. Biol. 2010, 21, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhao, D.; Spring, D.J.; DePinho, R.A. Genetics and biology of prostate cancer. Genes Dev. 2018, 32, 1105–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Donato, M.; Giovannelli, P.; Cernera, G.; Di Santi, A.; Marino, I.; Bilancio, A.; Galasso, G.; Auricchio, F.; Migliaccio, A.; Castoria, G. Non-genomic androgen action regulates proliferative/migratory signaling in stromal cells. Front. Endocrinol. 2014, 5, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condeelis, J.; Pollard, J.W. Macrophages: Obligate partners for tumor cell migration, invasion, and metastasis. Cell 2006, 124, 263–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comito, G.; Giannoni, E.; Segura, C.P.; Barcellos-de-Souza, P.; Raspollini, M.R.; Baroni, G.; Lanciotti, M.; Serni, S.; Chiarugi, P. Cancer-associated fibroblasts and M2-polarized macrophages synergize during prostate carcinoma progression. Oncogene 2014, 33, 2423–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Wang, L.; Zou, C.; Xia, Y.; Qin, S.; Keller, E.; Mizokami, A.; Zhang, J.; Lu, Y. Tumor microenvironment promotes prostate cancer cell dissemination via the Akt/mTOR pathway. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 9206–9218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehai, C.; Bo, P.; Qiang, T.; Lihua, S.; Fang, L.; Shi, J.; Jingyan, C.; Yan, Y.; Guangbin, W.; Zhenjun, Y. Enhanced invasion of lung adenocarcinoma cells after co-culture with THP-1-derived macrophages via the induction of EMT by IL-6. Immunol. Lett. 2014, 160, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Shen, B.; Tan, M.; Mu, X.; Qin, Y.; Zhang, F.; Liu, Y. TGF-beta-induced upregulation of malat1 promotes bladder cancer metastasis by associating with suz12. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 1531–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veltri, R.W.; Miller, M.C.; Zhao, G.; Ng, A.; Marley, G.M.; Wright, G.J.; Vessella, R.L.; Ralph, D. Interleukin-8 serum levels in patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia and prostate cancer. Urology 1999, 53, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorpe, L.; Araujo, J.C.; Parikh, N.U.; Eli, M.B.; Gallick, G.E. Abstract A65: Contribution of stromal-derived IL-8 on prostate cancer progression. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, A65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Lv, M.; Niu, H.; Tian, Y. Tumor-suppressive function of long noncoding RNA MALAT1 in glioma cells by suppressing miR-155 expression and activating FBXW7 function. AM J. Cancer Res. 2016, 6, 2561–2574. [Google Scholar]
- Kwok, Z.H.; Roche, V.; Chew, X.H.; Fadieieva, A.; Tay, Y. A non-canonical tumor suppressive role for the long non-coding RNA MALAT1 in colon and breast cancers. Int. J. Cancer 2018, 143, 668–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latorre, E.; Carelli, S.; Raimondi, I.; D’Agostino, V.; Castiglioni, I.; Zucal, C.; Moro, G.; Luciani, A.; Ghilardi, G.; Monti, E.; et al. The Ribonucleic Complex HuR-MALAT1 Represses CD133 Expression and Suppresses Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Breast Cancer. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 2626–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hirata, H.; Hinoda, Y.; Shahryari, V.; Deng, G.; Nakajima, K.; Tabatabai, Z.L.; Ishii, N.; Dahiya, R. Long Noncoding RNA MALAT1 Promotes Aggressive Renal Cell Carcinoma through Ezh2 and Interacts with miR-205. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 1322–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gutschner, T.; Hammerle, M.; Eissmann, M.; Hsu, J.; Kim, Y.; Hung, G.; Revenko, A.; Arun, G.; Stentrup, M.; Gross, M.; et al. The noncoding RNA MALAT1 is a critical regulator of the metastasis phenotype of lung cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 1180–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, M.C.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, L.; Zhu, Q.Q.; Xie, H.Y.; Zhang, F.; Wu, L.M.; Chen, L.M.; Zheng, S.S. Long non-coding RNA MALAT-1 overexpression predicts tumor recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after liver transplantation. Med. Oncol. 2012, 29, 1810–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Liu, Y.; Xu, W.; Sun, Y.; Lu, J.; Wang, F.; Wei, M.; Shen, J.; Hou, J.; Gao, X.; et al. Long noncoding RNA MALAT-1 is a new potential therapeutic target for castration resistant prostate cancer. J. Urol. 2013, 190, 2278–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Ren, S.; Chen, R.; Lu, J.; Shi, X.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Jing, T.; Zhang, C.; Shen, J.; et al. Development and prospective multicenter evaluation of the long noncoding RNA MALAT-1 as a diagnostic urinary biomarker for prostate cancer. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 11091–11102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, R.; Sun, Y.; Li, L.; Niu, Y.; Lin, W.; Lin, C.; Antonarakis, E.S.; Luo, J.; Yeh, S.; Chang, C. Preclinical Study using Malat1 Small Interfering RNA or Androgen Receptor Splicing Variant 7 Degradation Enhancer ASC-J9® to Suppress Enzalutamide-resistant Prostate Cancer Progression. Eur. Urol. 2017, 72, 835–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Tang, M.; Wu, Y.; Xu, X.; Pan, F.; Xu, R. LncRNAs and miRNAs: Potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets for prostate cancer. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2016, 8, 5141–5150. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, M.M.K.; Chui, R.K.S.; Tam, I.Y.S.; Lau, A.H.Y.; Wong, Y.H. CCR1-Mediated STAT3 Tyrosine Phosphorylation and CXCL8 Expression in THP-1 Macrophage-like Cells Involve Pertussis Toxin-Insensitive Gα14/16 Signaling and IL-6 Release. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 5266–5276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.T.; Dai, Z.; Song, K.; Zhang, Z.J.; Zhou, Z.J.; Zhou, S.L.; Zhao, Y.M.; Xiao, Y.S.; Sun, Q.M.; Ding, Z.B.; et al. Macrophage-secreted IL-8 induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma cells by activating the JAK2/STAT3/snail pathway. Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 46, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genin, M.; Clement, F.; Fattaccioli, A.; Raes, M.; Michiels, C. M1 and M2 macrophages derived from THP-1 cells differentially modulate the response of cancer cells to etoposide. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Lai, W.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, L.; Luo, X.; Zeng, Y.; Wu, H.; Lan, Q.; Chu, Z. Tumor-associated macrophage-derived IL-6 and IL-8 enhance invasive activity of LoVo cells induced by PRL-3 in a KCNN4 channel-dependent manner. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagemann, T.; Robinson, S.C.; Schulz, M.; Trumper, L.; Balkwill, F.R.; Binder, C. Enhanced invasiveness of breast cancer cell lines upon co-cultivation with macrophages is due to TNF-alpha dependent up-regulation of matrix metalloproteases. Carcinogenesis 2004, 25, 1543–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, H.; Huang, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Pang, X.; Li, K.; Dang, W.; Tang, H.; Wei, L.; Su, M.; et al. Leptin promotes migration and invasion of breast cancer cells by stimulating IL-8 production in M2 macrophages. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 65441–65453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Horoszewicz, J.S.; Leong, S.S.; Kawinski, E.; Karr, J.P.; Rosenthal, H.; Chu, T.M.; Mirand, E.A.; Murphy, G.P. LNCaP model of human prostatic carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1983, 43, 1809–1818. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Peng, H.Y.; Jiang, S.S.; Hsiao, J.R.; Hsiao, M.; Hsu, Y.M.; Wu, G.H.; Chang, W.M.; Chang, J.Y.; Jin, S.L.; Shiah, S.G. IL-8 induces miR-424-5p expression and modulates SOCS2/STAT5 signaling pathway in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Mol. Oncol. 2016, 10, 895–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, K.; Slaton, J.W.; Eve, B.Y.; Kim, S.J.; Perrotte, P.; Balbay, M.D.; Yano, S.; Bar-Eli, M.; Radinsky, R.; Pettaway, C.A.; et al. Interleukin 8 expression regulates tumorigenicity and metastases in androgen-independent prostate cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2000, 6, 2104–2119. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, B.B.; Arenberg, D.A.; Stoy, K.; Morgan, T.; Addison, C.L.; Morris, S.B.; Glass, M.; Wilke, C.; Xue, Y.Y.; Sitterding, S.; et al. Distinct CXC chemokines mediate tumorigenicity of prostate cancer cells. Am. J. Pathol. 1999, 154, 1503–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pencik, J.; Schlederer, M.; Gruber, W.; Unger, C.; Walker, S.M.; Chalaris, A.; Marie, I.J.; Hassler, M.R.; Javaheri, T.; Aksoy, O.; et al. STAT3 regulated ARF expression suppresses prostate cancer metastasis. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarron, S.L.; Edwards, S.; Evans, P.R.; Gibbs, R.; Dearnaley, D.P.; Dowe, A.; Southgate, C.; Easton, D.F.; Eeles, R.A.; Howell, W.M. Influence of cytokine gene polymorphisms on the development of prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 3369–3372. [Google Scholar]
- Lapeire, L.; Hendrix, A.; Lambein, K.; Van Bockstal, M.; Braems, G.; Van Den Broecke, R.; Limame, R.; Mestdagh, P.; Vandesompele, J.; Vanhove, C.; et al. Cancer-associated adipose tissue promotes breast cancer progression by paracrine oncostatin M and Jak/STAT3 signaling. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 6806–6819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, Y.; Cui, Y.; Li, X.; Cao, X.; Chen, A.; Xu, C.; Cao, J.; Luo, X. Co-culture of ovarian cancer stem-like cells with macrophages induced SKOV3 cells stemness via IL-8/STAT3 signaling. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 103, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, D.; Lu, H.; Xu, H.Y.; Zhou, C.X.; He, X.Z. Long noncoding RNA MALAT1 enhances the docetaxel resistance of prostate cancer cells via miR-145-5p-mediated regulation of AKAP12. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 3223–3237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.; Xu, W.; Du, X.; Hou, J. MALAT1 silencing suppresses prostate cancer progression by upregulating miR-1 and downregulating KRAS. Onco. Targets Ther. 2018, 11, 3461–3473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Ding, L.; Wang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, Z.; Karnes, R.J.; Zhang, J.; Huang, H. LncRNA MALAT1 enhances oncogenic activities of EZH2 in castration-resistant prostate cancer. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 41045–41055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mantovani, A.; Allavena, P.; Sica, A.; Balkwill, F. Cancer-related inflammation. Nature 2008, 454, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, W.; Qian, Y.; Yu, F.; Liu, W.; Wu, Y.; Fang, X.; Hao, W. Alternatively activated macrophages are associated with metastasis and poor prognosis in prostate adenocarcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2015, 10, 1390–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shimura, S.; Yang, G.; Ebara, S.; Wheeler, T.M.; Frolov, A.; Thompson, T.C. Reduced infiltration of tumor-associated macrophages in human prostate cancer: Association with cancer progression. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 5857–5861. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Murphy, C.; McGurk, M.; Pettigrew, J.; Santinelli, A.; Mazzucchelli, R.; Johnston, P.G.; Montironi, R.; Waugh, D.J. Nonapical and cytoplasmic expression of interleukin-8, CXCR1, and CXCR2 correlates with cell proliferation and microvessel density in prostate cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 4117–4127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seaton, A.; Scullin, P.; Maxwell, P.J.; Wilson, C.; Pettigrew, J.; Gallagher, R.; O’Sullivan, J.M.; Johnston, P.G.; Waugh, D.J. Interleukin-8 signaling promotes androgen-independent proliferation of prostate cancer cells via induction of androgen receptor expression and activation. Carcinogenesis 2008, 29, 1148–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gutschner, T.; Hammerle, M.; Diederichs, S. MALAT1—A paradigm for long noncoding RNA function in cancer. J. Mol. Med. 2013, 91, 791–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amodio, N.; Raimondi, L.; Juli, G.; Stamato, M.A.; Caracciolo, D.; Tagliaferri, P.; Tassone, P. MALAT1: A druggable long non-coding RNA for targeted anti-cancer approaches. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 11, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilusz, J.E.; Freier, S.M.; Spector, D.L. 3′ end processing of a long nuclear-retained noncoding RNA yields a tRNA-like cytoplasmic RNA. Cell 2008, 135, 919–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koshimizu, T.A.; Fujiwara, Y.; Sakai, N.; Shibata, K.; Tsuchiya, H. Oxytocin stimulates expression of a noncoding RNA tumor marker in a human neuroblastoma cell line. Life Sci. 2010, 86, 455–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Lin, D.C.; Cao, Q.; Pang, B.; Gae, D.D.; Lee, V.; Lim, H.J.; Doan, N.; Said, J.W.; Gery, S.; et al. Identification of a Novel SYK/c-MYC/MALAT1 Signaling Pathway and Its Potential Therapeutic Value in Ewing Sarcoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 4376–4387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, C.; Zhang, C.; Li, Z.; Zhu, T.; Chen, J.; Ren, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, X. TGF-beta-induced STAT3 overexpression promotes human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma invasion and metastasis through malat1/miR-30a interactions. Cancer Lett. 2018, 436, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, T.; Ma, G.; Tang, M.; Li, Z.; Xu, R. IL-8 Secreted from M2 Macrophages Promoted Prostate Tumorigenesis via STAT3/MALAT1 Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 98. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20010098
Zheng T, Ma G, Tang M, Li Z, Xu R. IL-8 Secreted from M2 Macrophages Promoted Prostate Tumorigenesis via STAT3/MALAT1 Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(1):98. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20010098
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Tingjin, Guoxing Ma, Mingqing Tang, Zhongwan Li, and Ruian Xu. 2019. "IL-8 Secreted from M2 Macrophages Promoted Prostate Tumorigenesis via STAT3/MALAT1 Pathway" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 1: 98. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20010098
APA StyleZheng, T., Ma, G., Tang, M., Li, Z., & Xu, R. (2019). IL-8 Secreted from M2 Macrophages Promoted Prostate Tumorigenesis via STAT3/MALAT1 Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(1), 98. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20010098