The Kinase CIPK11 Functions as a Negative Regulator in Drought Stress Response in Arabidopsis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
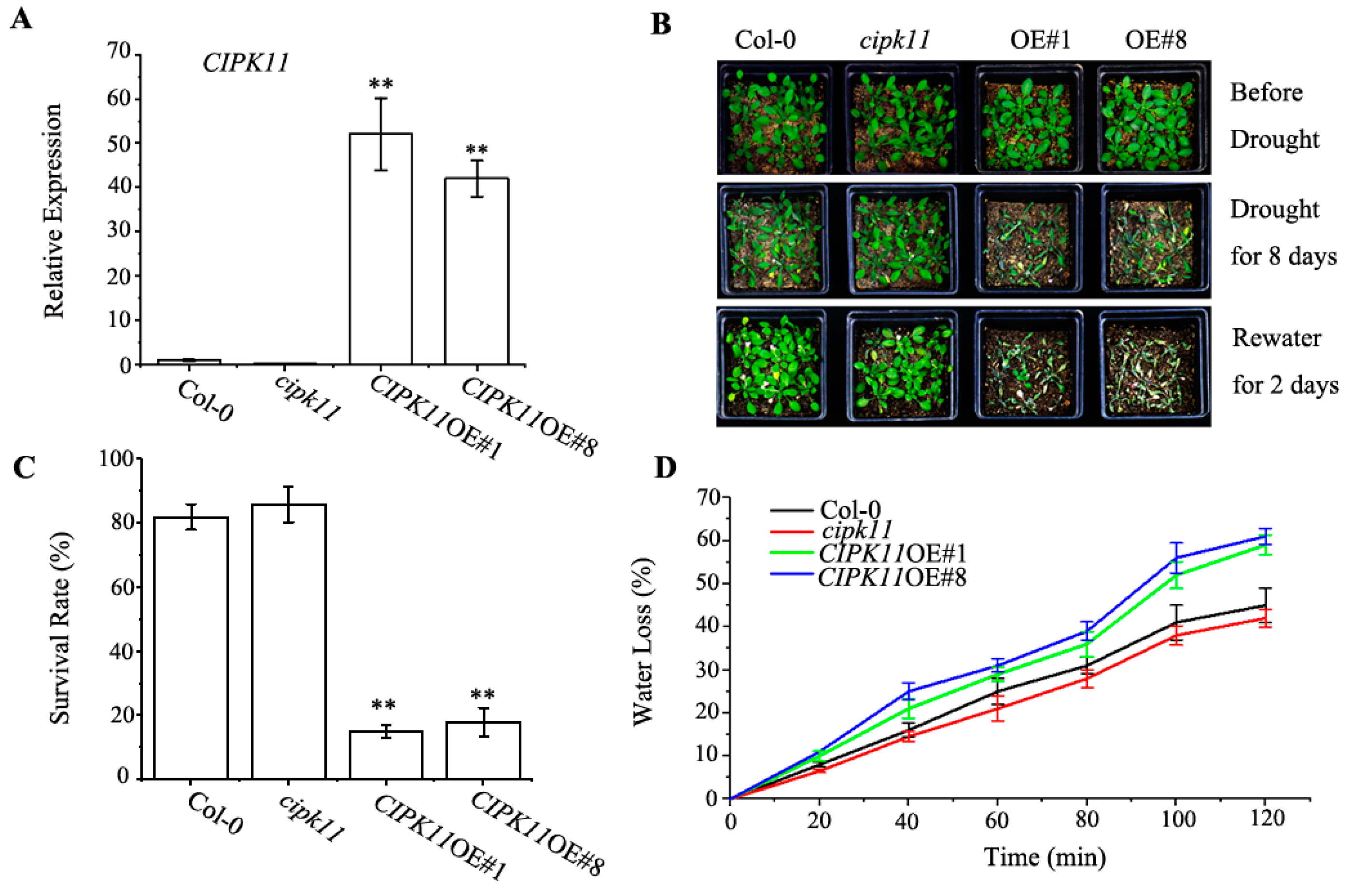
2.1. Expression of CIPK11 is Induced by Drought
2.2. Overexpression of CIPK11 Confers Drought Hypersensitivity
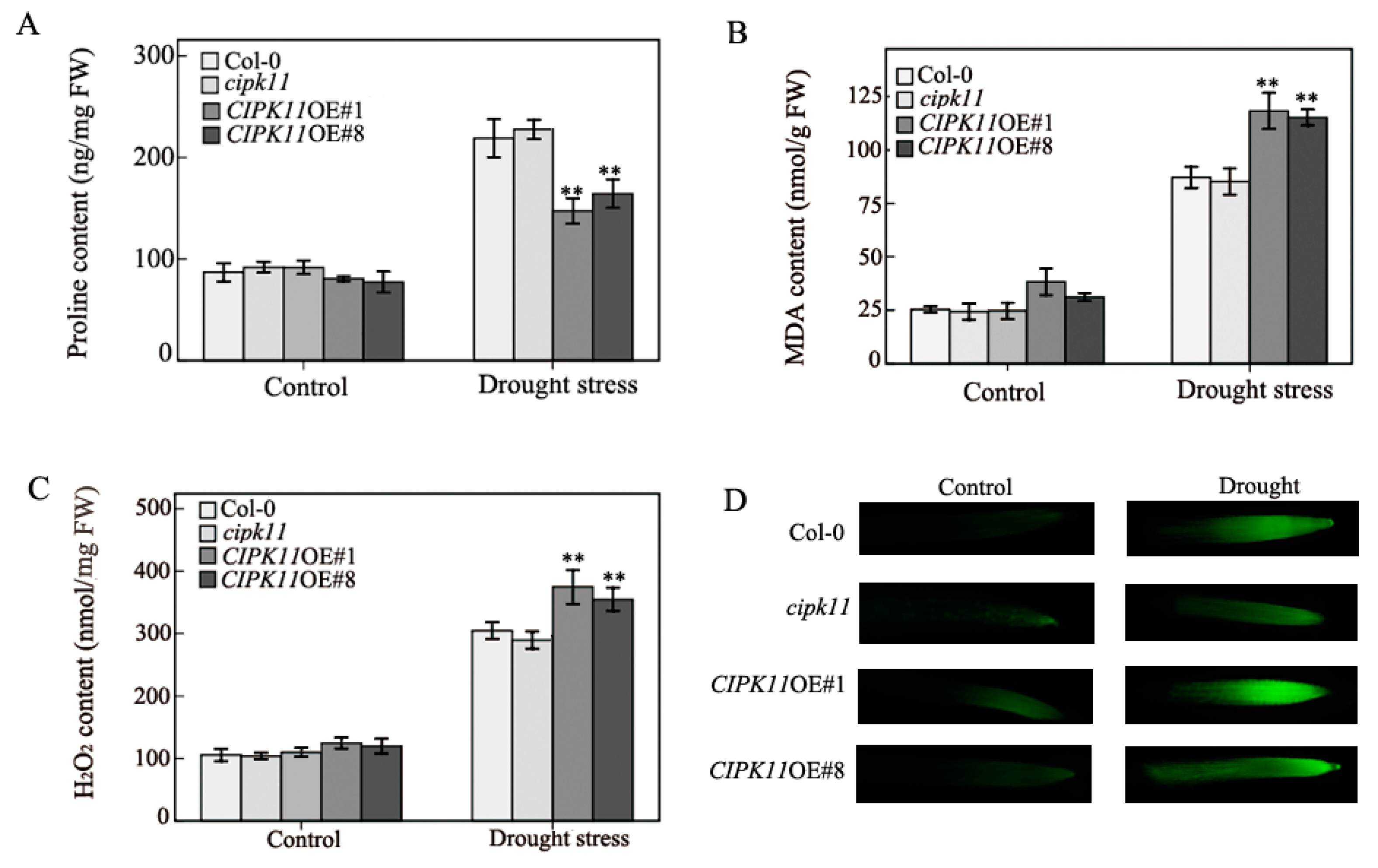
2.3. Physiological Properties in CIPK11-Overexpressing Arabidopsis under Drought Treatment
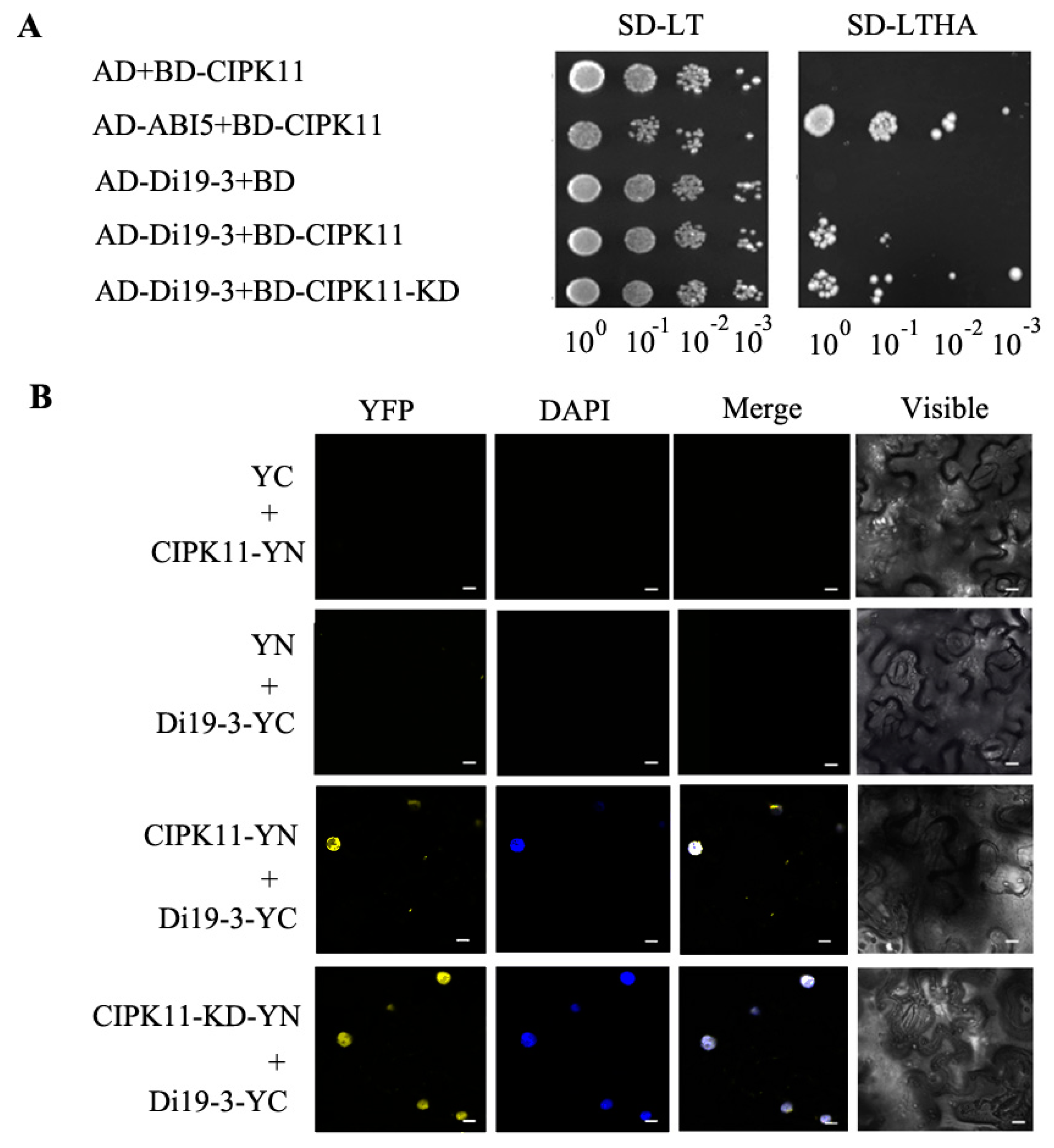
2.4. Identification of Di19-3 as A CIPK11-Interacting Protein
2.5. CIPK11 Phosphorylates Di19-3 In Vitro
2.6. Genetic Interaction between CIPK11 and Di19-3 under Drought Stress
3. Discussion
3.1. CIPK11 is A Negative Regulator for Plant Tolerance to Drought
3.2. How does CIPK11 Participate in Regulating Drought Response?
3.3. Identification of a Downstream Target of CIPK11
3.4. Possible Activation Mechanisms of CIPK11 by Upstream Regulators
3.5. CIPK11-Di19-3 Regulatory Pathway may be a Potential Target in Agricultural Production
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Growth
4.2. Quantitative Real-Time PCR Analysis
4.3. Constructs and Generation of Transgenic Plants
4.4. Yeast Two-Hybrid Assay
4.5. Monitoring ROS in the Root Cells under Drought Stress
4.6. Determination of Drought Responsive Physiological Indices
4.7. Bimolecular Fluorescence Complementation Assay
4.8. Protein Purification and Protein Phosphorylation Assay
4.9. Abiotic Stress Tolerance Assays
4.10. DAB Staining
4.11. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, J.K. Abiotic Stress Signaling and Responses in Plants. Cell 2016, 167, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Yin, Y.; Liu, X.; Tong, S.; Xing, J.; Zhang, Y.; Pudake, R.N.; Izquierdo, E.M.; Peng, H.; Xin, M.; et al. The E3 Ligase TaSAP5 Alters Drought Stress Responses by Promoting the Degradation of DRIP Proteins. Plant Physiol. 2017, 175, 1878–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osakabe, Y.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K.; Shinozaki, K.; Tran, L.S. Sensing the environment: Key roles of membrane-localized kinases in plant perception and response to abiotic stress. J. Exp. Bot. 2013, 64, 445–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.-H. Mechanism of ABA Signal Transduction_ Agricultural Highlights for Improving Drought Tolerance. J. Plant Biol. 2014, 57, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Xiong, L. Genetic engineering and breeding of drought-resistant crops. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2014, 65, 715–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rentel, M.C.; Knight, M.R. Oxidative stress-induced calcium signaling in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2004, 135, 1471–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudla, J.; Batistic, O.; Hashimoto, K. Calcium signals: The lead currency of plant information processing. Plant Cell 2010, 22, 541–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, D.; Guo, Y.; Schumaker, K.S.; Zhu, J.K. The SOS3 family of calcium sensors and SOS2 family of protein kinases in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2004, 134, 919–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolukisaoglu, U.; Weinl, S.; Blazevic, D.; Batistic, O.; Kudla, J. Calcium sensors and their interacting protein kinases: Genomics of the Arabidopsis and rice CBL-CIPK signaling networks. Plant Physiol. 2004, 134, 43–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanwar, P.; Sanyal, S.K.; Tokas, I.; Yadav, A.K.; Pandey, A.; Kapoor, S.; Pandey, G.K. Comprehensive structural, interaction and expression analysis of CBL and CIPK complement during abiotic stresses and development in rice. Cell Calcium 2014, 56, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Q.S.; Guo, Y.; Dietrich, M.A.; Schumaker, K.S.; Zhu, J.K. Regulation of SOS1, a plasma membrane Na+/H+ exchanger in Arabidopsis thaliana, by SOS2 and SOS3. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci USA 2002, 99, 8436–8441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H. The Putative Plasma Membrane Na+/H+ Antiporter SOS1 Controls Long-Distance Na+ Transport in Plants. Plant Cell Online 2002, 14, 465–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragel, P.; Rodenas, R.; Garcia-Martin, E.; Andres, Z.; Villalta, I.; Nieves-Cordones, M.; Rivero, R.M.; Martinez, V.; Pardo, J.M.; Quintero, F.J.; et al. The CBL-Interacting Protein Kinase CIPK23 Regulates HAK5-Mediated High-Affinity K+ Uptake in Arabidopsis Roots. Plant Physiol. 2015, 169, 2863–2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiger, D.; Scherzer, S.; Mumm, P.; Stange, A.; Marten, I.; Bauer, H.; Ache, P.; Matschi, S.; Liese, A.; Al-Rasheid, K.A.; et al. Activity of guard cell anion channel SLAC1 is controlled by drought-stress signaling kinase-phosphatase pair. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 21425–21430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Held, K.; Pascaud, F.; Eckert, C.; Gajdanowicz, P.; Hashimoto, K.; Corratge-Faillie, C.; Offenborn, J.N.; Lacombe, B.; Dreyer, I.; Thibaud, J.B.; et al. Calcium-dependent modulation and plasma membrane targeting of the AKT2 potassium channel by the CBL4/CIPK6 calcium sensor/protein kinase complex. Cell Res. 2011, 21, 1116–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, G.K.; Kanwar, P.; Singh, A.; Steinhorst, L.; Pandey, A.; Yadav, A.K.; Tokas, I.; Sanyal, S.K.; Kim, B.G.; Lee, S.C.; et al. Calcineurin B-Like Protein-Interacting Protein Kinase CIPK21 Regulates Osmotic and Salt Stress Responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2015, 169, 780–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.-P.; Agarwal, M.; Ohta, M.; Guo, Y.; Halfter, U.; Wang, P.; Zhu, J.-K. Role of an Arabidopsis AP2_EREBP-Type Transcriptional Repressor in Abscisic Acid and Drought Stress Responses. Plant. Cell 2016, 17, 2384–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Hao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Bai, Y.; Zhu, W.; Qin, Y.; Yuan, F.; Zhao, F.; Wang, M.; Hu, J.; et al. SOS2-LIKE PROTEIN KINASE5, an SNF1-RELATED PROTEIN KINASE3-Type Protein Kinase, Is Important for Abscisic Acid Responses in Arabidopsis through Phosphorylation of ABSCISIC ACID-INSENSITIVE5. Plant Physiol. 2015, 168, 659–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milla, M.A.; Townsend, J.; Chang, I.F.; Cushman, J.C. The Arabidopsis AtDi19 gene family encodes a novel type of Cys2/His2 zinc-finger protein implicated in ABA-independent dehydration, high-salinity stress and light signaling pathways. Plant Mol. Biol. 2006, 61, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.X.; Zhang, F.C.; Zhang, W.Z.; Song, L.F.; Wu, W.H.; Chen, Y.F. Arabidopsis Di19 functions as a transcription factor and modulates PR1, PR2, and PR5 expression in response to drought stress. Mol. Plant 2013, 6, 1487–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Gupta, P.; Rajabhoj, M.P.; Maruthachalam, R.; Nandi, A.K. The Polycomb-Group Repressor MEDEA Attenuates Pathogen Defense. Plant Physiol. 2018, 177, 1728–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.X.; Li, Y.; Li, D.D.; Xu, W.L.; Zheng, Y.; Li, X.B. Arabidopsis drought-induced protein Di19-3 participates in plant response to drought and high salinity stresses. Plant Mol. Biol. 2014, 86, 609–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, X.; Chong, J.; Ni, M. HYPERSENSITIVE TO RED AND BLUE 1, a ZZ-type zinc finger protein, regulates phytochrome B-mediated red and cryptochrome-mediated blue light responses. Plant Cell 2005, 17, 822–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez Milla, M.A.; Uno, Y.; Chang, I.F.; Townsend, J.; Maher, E.A.; Quilici, D.; Cushman, J.C. A novel yeast two-hybrid approach to identify CDPK substrates: Characterization of the interaction between AtCPK11 and AtDi19, a nuclear zinc finger protein. FEBS Lett. 2006, 580, 904–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Tai, F.J.; Zheng, Y.; Luo, J.; Gong, S.Y.; Zhang, Z.T.; Li, X.B. Two cotton Cys2/His2-type zinc-finger proteins, GhDi19-1 and GhDi19-2, are involved in plant response to salt/drought stress and abscisic acid signaling. Plant Mol. Biol. 2010, 74, 437–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yu, C.; Xu, S.; Zhu, Y.; Huang, W. OsDi19-4 acts downstream of OsCDPK14 to positively regulate ABA response in rice. Plant Cell Environ. 2016, 39, 2740–2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuglsang, A.T.; Guo, Y.; Cuin, T.A.; Qiu, Q.; Song, C.; Kristiansen, K.A.; Bych, K.; Schulz, A.; Shabala, S.; Schumaker, K.S.; et al. Arabidopsis protein kinase PKS5 inhibits the plasma membrane H+ -ATPase by preventing interaction with 14-3-3 protein. Plant Cell 2007, 19, 1617–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winter, D.; Vinegar, B.; Nahal, H.; Ammar, R.; Wilson, G.V.; Provart, N.J. An "Electronic Fluorescent Pictograph" browser for exploring and analyzing large-scale biological data sets. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAinsh, M.R.; Pittman, J.K. Shaping the calcium signature. New Phytol. 2009, 181, 275–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, Q.Q.; Zhou, L.; Ren, F.; Li, D.D.; Li, X.B. Arabidopsis CBL-interacting protein kinase (CIPK6) is involved in plant response to salt/osmotic stress and ABA. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2013, 40, 4759–4767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Niu, F.; Liu, W.Z.; Zhang, H.; Wang, B.; Lan, W.; Che, Y.; Yang, B.; Luan, S.; Jiang, Y.Q. Arabidopsis CIPK14 positively regulates glucose response. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 450, 1679–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, T.; Li, T.; Wang, M.; Yang, G.; He, G. A CBL-Interacting Protein Kinase TaCIPK2 Confers Drought Tolerance in Transgenic Tobacco Plants through Regulating the Stomatal Movement. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, S. The CBL-CIPK network in plant calcium signaling. Trends Plant Sci. 2009, 14, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, H.; Ishitani, M.; Kim, C.; Zhu, J.K. The Arabidopsis thaliana salt tolerance gene SOS1 encodes a putative Na+/H+ antiporter. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 6896–6901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.Y.; Ali, Z.; Park, H.J.; Park, S.J.; Cha, J.Y.; Perez-Hormaeche, J.; Quintero, F.J.; Shin, G.; Kim, M.R.; Qiang, Z.; et al. Release of SOS2 kinase from sequestration with GIGANTEA determines salt tolerance in Arabidopsis. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albrecht, V.; Weinl, S.; Blazevic, D.; D’Angelo, C.; Batistic, O.; Kolukisaoglu, U.; Bock, R.; Schulz, B.; Harter, K.; Kudla, J. The calcium sensor CBL1 integrates plant responses to abiotic stresses. Plant J. 2003, 36, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Angelo, C.; Weinl, S.; Batistic, O.; Pandey, G.K.; Cheong, Y.H.; Schultke, S.; Albrecht, V.; Ehlert, B.; Schulz, B.; Harter, K.; et al. Alternative complex formation of the Ca-regulated protein kinase CIPK1 controls abscisic acid-dependent and independent stress responses in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2006, 48, 857–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, S.; Sopory, S.K.; Tuteja, N. Cloning and characterization of CBL-CIPK signalling components from a legume (Pisum sativum). FEBS J. 2006, 273, 907–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Xia, Z.; Yan, Y.; Ding, Z.; Tie, W.; Wang, L.; Zou, M.; Wei, Y.; Lu, C.; Hou, X.; et al. Genome-wide gene phylogeny of CIPK family in cassava and expression analysis of partial drought-induced genes. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Zhang, J.; Wu, G.; Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; Wei, J. HbCIPK2, a novel CBL-interacting protein kinase from halophyte Hordeum brevisubulatum, confers salt and osmotic stress tolerance. Plant Cell Environ. 2012, 35, 1582–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdula, S.E.; Lee, H.J.; Ryu, H.; Kang, K.K.; Nou, I.; Sorrells, M.E.; Cho, Y.G. Overexpression of BrCIPK1 Gene Enhances Abiotic Stress Tolerance by Increasing Proline Biosynthesis in Rice. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Xiong, L.; Song, C.-P.; Gong, D.; Halfter, U.; Zhu, J.-K. A Calcium Sensor and Its Interacting Protein Kinase Are Global Regulators of Abscisic Acid Signaling in Arabidopsis. Dev. Cell 2002, 3, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Zhou, X.; Deng, X.; Guo, Y. PKS5, a SNF1-related kinase, interacts with and phosphorylates NPR1, and modulates expression of WRKY38 and WRKY62. J. Genet. Genomics 2010, 37, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Lin, H.; Chen, S.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Fuglsang, A.T.; Palmgren, M.G.; Wu, W.; Guo, Y. Phosphorylation of SOS3-like calcium-binding proteins by their interacting SOS2-like protein kinases is a common regulatory mechanism in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2011, 156, 2235–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Du, W.; Yang, Y.; Schumaker, K.S.; Guo, Y. A calcium-independent activation of the Arabidopsis SOS2-like protein kinase24 by its interacting SOS3-like calcium binding protein1. Plant Physiol. 2014, 164, 2197–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Yang, Y.; Quan, R.; Mendoza, I.; Wu, Y.; Du, W.; Zhao, S.; Schumaker, K.S.; Pardo, J.M.; Guo, Y. Phosphorylation of SOS3-LIKE calcium binding protein8 by SOS2 protein kinase stabilizes their protein complex and regulates salt tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2009, 21, 1607–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, M.; Guo, Y.; Halfter, U.; Zhu, J.K. A novel domain in the protein kinase SOS2 mediates interaction with the protein phosphatase 2C ABI2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 11771–11776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyzenga, W.J.; Liu, H.; Schofield, A.; Muise-Hennessey, A.; Stone, S.L. Arabidopsis CIPK26 interacts with KEG, components of the ABA signalling network and is degraded by the ubiquitin-proteasome system. J. Exp. Bot 2013, 64, 2779–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furihata, T.; Maruyama, K.; Fujita, Y.; Umezawa, T.; Yoshida, R.; Shinozaki, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. Abscisic acid-dependent multisite phosphorylation regulates the activity of a transcription activator AREB1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 1988–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clough, S.J.; Bent, A.F. Floral dip: A simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation ofArabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 1998, 16, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Zheng, S.; Wang, X. Lanthanum regulates the reactive oxygen species in the roots of rice seedlings. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sparkes, I.A.; Runions, J.; Kearns, A.; Hawes, C. Rapid, transient expression of fluorescent fusion proteins in tobacco plants and generation of stably transformed plants. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 2019–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, W.; Zou, Y.; Liu, Q.; Liu, J.; Luo, X.; Huang, Q.; Chen, S.; Zhu, L.; Bi, R.; Hao, Q.; et al. The structural basis for activation of plant immunity by bacterial effector protein AvrPto. Nature 2007, 449, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.J.; Li, X.D.; Ratnasekera, D.; Wang, C.; Liu, W.X.; Song, L.F.; Zhang, W.Z.; Wu, W.H. Arabidopsis CALCIUM-DEPENDENT PROTEIN KINASE8 and CATALASE3 Function in Abscisic Acid-Mediated Signaling and H2O2 Homeostasis in Stomatal Guard Cells under Drought Stress. Plant Cell 2015, 27, 1445–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, Y.; Cao, J.; Chen, Q.; He, J.; Liu, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Yang, Y. The Kinase CIPK11 Functions as a Negative Regulator in Drought Stress Response in Arabidopsis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2422. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20102422
Ma Y, Cao J, Chen Q, He J, Liu Z, Wang J, Li X, Yang Y. The Kinase CIPK11 Functions as a Negative Regulator in Drought Stress Response in Arabidopsis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(10):2422. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20102422
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Yanlin, Jing Cao, Qiaoqiao Chen, Jiahan He, Zhibin Liu, Jianmei Wang, Xufeng Li, and Yi Yang. 2019. "The Kinase CIPK11 Functions as a Negative Regulator in Drought Stress Response in Arabidopsis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 10: 2422. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20102422
APA StyleMa, Y., Cao, J., Chen, Q., He, J., Liu, Z., Wang, J., Li, X., & Yang, Y. (2019). The Kinase CIPK11 Functions as a Negative Regulator in Drought Stress Response in Arabidopsis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(10), 2422. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20102422



