Clinical Applications of Natriuretic Peptides in Heart Failure and Atrial Fibrillation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Roles of NP: BNP and ANP
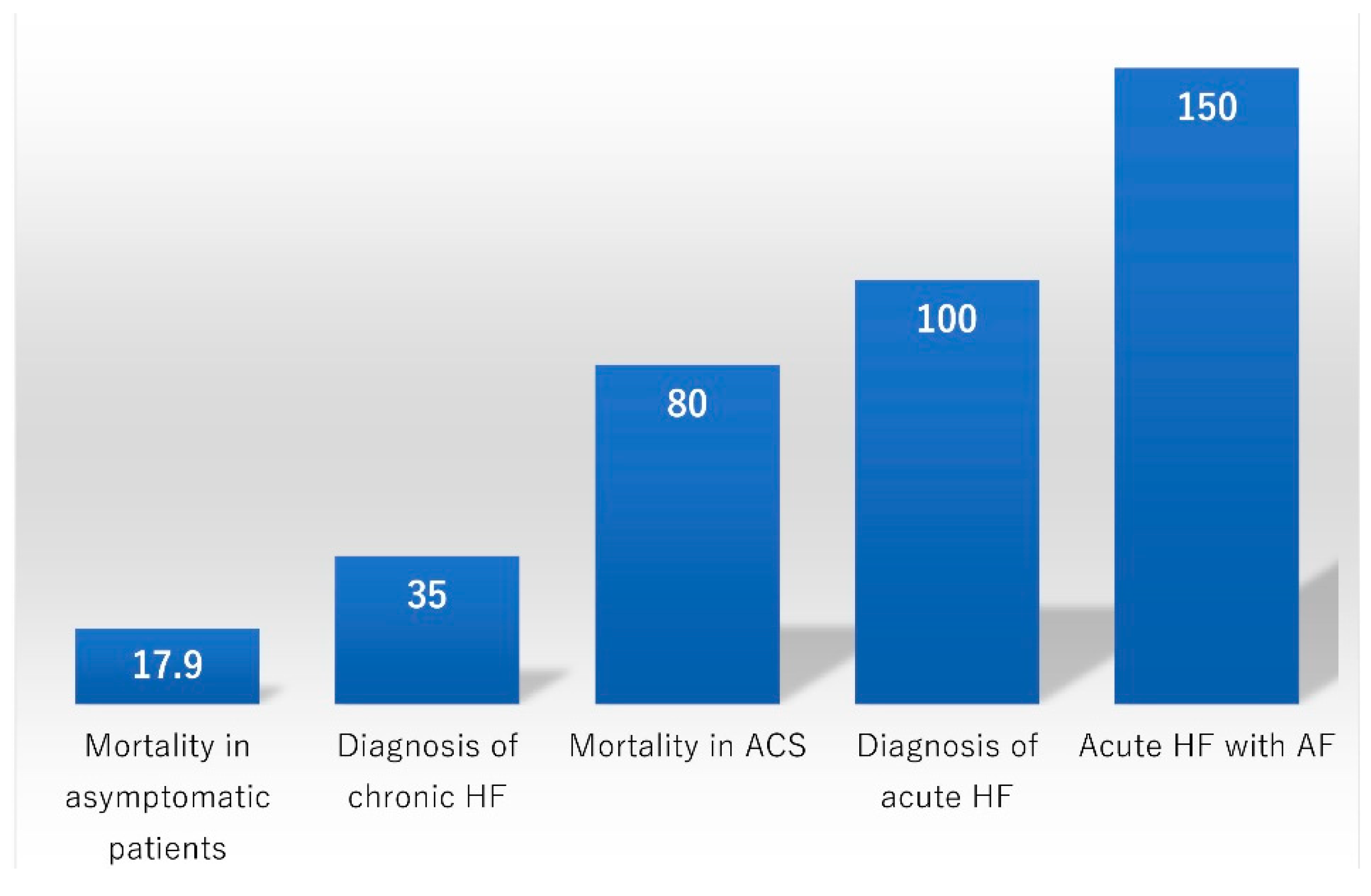
3. Screening for Asymptomatic Patients
4. Diagnosis of Acute HF
5. Diagnosis of Chronic Ambulatory HF
6. HF with Preserved versus Reduced EF (HFpEF vs. HFrEF)
7. Prognostication of HF
8. Prognostication of ACS
9. Interpretations of NP Levels in Different Populations
10. NP-Guided Therapy
11. Mid-Regional proANP
12. AF and NPs
13. Incident AF in Community Studies
14. Impact of Structural Heart Disease in AF patients
15. HF and AF
16. AF Recurrence after Cardioversion or Pulmonary Vein Isolation
17. Stroke in AF Patients
18. MR-proANP in AF Patients
19. Depletion of ANP in AF Patients with Atrial Remodeling
20. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Januzzi, J.L., Jr.; Camargo, C.A.; Anwaruddin, S.; Baggish, A.L.; Chen, A.A.; Krauser, D.G.; Tung, R.; Cameron, R.; Nagurney, J.T.; Chae, C.U.; et al. The N-terminal Pro-BNP investigation of dyspnea in the emergency department (PRIDE) study. Am. J. Cardiol. 2005, 95, 948–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hildebrandt, P.; Collinson, P.O. Amino-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide testing to assist the diagnostic evaluation of heart failure in symptomatic primary care patients. Am. J. Cardiol. 2008, 101, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maisel, A.S.; Krishnaswamy, P.; Nowak, R.M.; McCord, J.; Hollander, J.E.; Duc, P.; Omland, T.; Storrow, A.B.; Abraham, W.T.; Wu, A.H.; et al. Rapid measurement of B-type natriuretic peptide in the emergency diagnosis of heart failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 347, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Lemos, J.A.; Morrow, D.A.; Bentley, J.H.; Omland, T.; Sabatine, M.S.; McCabe, C.H.; Hall, C.; Cannon, C.P.; Braunwald, E. The prognostic value of B-type natriuretic peptide in patients with acute coronary syndromes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 345, 1014–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindahl, B.; Lindback, J.; Jernberg, T.; Johnston, N.; Stridsberg, M.; Venge, P.; Wallentin, L. Serial analyses of N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide in patients with non-ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndromes: A Fragmin and fast Revascularisation during In Stability in Coronary artery disease (FRISC)-II substudy. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2005, 45, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellinor, P.T.; Low, A.F.; Patton, K.K.; Shea, M.A.; Macrae, C.A. Discordant atrial natriuretic peptide and brain natriuretic peptide levels in lone atrial fibrillation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2005, 45, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Patton, K.K.; Ellinor, P.T.; Heckbert, S.R.; Christenson, R.H.; DeFilippi, C.; Gottdiener, J.S.; Kronmal, R.A. N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide is a major predictor of the development of atrial fibrillation: The Cardiovascular Health Study. Circulation 2009, 120, 1768–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breidthardt, T.; Noveanu, M.; Cayir, S.; Viglino, M.; Laule, K.; Hochholzer, W.; Reichlin, T.; Potocki, M.; Christ, M.; Mueller, C. The use of B-type natriuretic peptide in the management of patients with atrial fibrillation and dyspnea. Int. J. Cardiol. 2009, 136, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patton, K.K.; Heckbert, S.R.; Alonso, A.; Bahrami, H.; Lima, J.A.; Burke, G.; Kronmal, R.A. N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide as a predictor of incident atrial fibrillation in the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis: The effects of age, sex and ethnicity. Heart 2013, 99, 1832–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchhof, P.; Benussi, S.; Kotecha, D.; Ahlsson, A.; Atar, D.; Casadei, B.; Castella, M.; Diener, H.C.; Heidbuchel, H.; Hendriks, J.; et al. 2016 ESC Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with EACTS. Europace 2016, 18, 1609–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, B.S.; Zimmerman, R.S.; Schwab, T.R.; Heublein, D.M.; Burnett, J.C., Jr. Atrial stretch, not pressure, is the principal determinant controlling the acute release of atrial natriuretic factor. Circ. Res. 1988, 62, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cody, R.J.; Atlas, S.A.; Laragh, J.H.; Kubo, S.H.; Covit, A.B.; Ryman, K.S.; Shaknovich, A.; Pondolfino, K.; Clark, M.; Camargo, M.J.; et al. Atrial natriuretic factor in normal subjects and heart failure patients. Plasma levels and renal, hormonal, and hemodynamic responses to peptide infusion. J. Clin. Investig. 1986, 78, 1362–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakao, K.; Sugawara, A.; Morii, N.; Sakamoto, M.; Yamada, T.; Itoh, H.; Shiono, S.; Saito, Y.; Nishimura, K.; Ban, T.; et al. The pharmacokinetics of alpha-human atrial natriuretic polypeptide in healthy subjects. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1986, 31, 101–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollister, A.S.; Rodeheffer, R.J.; White, F.J.; Potts, J.R.; Imada, T.; Inagami, T. Clearance of atrial natriuretic factor by lung, liver, and kidney in human subjects and the dog. J. Clin. Investig. 1989, 83, 623–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, C. Essential biochemistry and physiology of (NT-pro)BNP. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2004, 6, 257–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abassi, Z.; Karram, T.; Ellaham, S.; Winaver, J.; Hoffman, A. Implications of the natriuretic peptide system in the pathogenesis of heart failure: Diagnostic and therapeutic importance. Pharmacol. Ther. 2004, 102, 223–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukoyama, M.; Nakao, K.; Hosoda, K.; Suga, S.; Saito, Y.; Ogawa, Y.; Shirakami, G.; Jougasaki, M.; Obata, K.; Yasue, H.; et al. Brain natriuretic peptide as a novel cardiac hormone in humans. Evidence for an exquisite dual natriuretic peptide system, atrial natriuretic peptide and brain natriuretic peptide. J. Clin. Investig. 1991, 87, 1402–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniels, L.B.; Maisel, A.S. Natriuretic peptides. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2007, 50, 2357–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lerman, A.; Gibbons, R.J.; Rodeheffer, R.J.; Bailey, K.R.; McKinley, L.J.; Heublein, D.M.; Burnett, J.C., Jr. Circulating N-terminal atrial natriuretic peptide as a marker for symptomless left-ventricular dysfunction. Lancet 1993, 341, 1105–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsutamoto, T.; Wada, A.; Maeda, K.; Hisanaga, T.; Maeda, Y.; Fukai, D.; Ohnishi, M.; Sugimoto, Y.; Kinoshita, M. Attenuation of compensation of endogenous cardiac natriuretic peptide system in chronic heart failure: Prognostic role of plasma brain natriuretic peptide concentration in patients with chronic symptomatic left ventricular dysfunction. Circulation 1997, 96, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukoyama, M.; Nakao, K.; Saito, Y.; Ogawa, Y.; Hosoda, K.; Suga, S.; Shirakami, G.; Jougasaki, M.; Imura, H. Human brain natriuretic peptide, a novel cardiac hormone. Lancet 1990, 335, 801–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukoyama, M.; Nakao, K.; Saito, Y.; Ogawa, Y.; Hosoda, K.; Suga, S.; Shirakami, G.; Jougasaki, M.; Imura, H. Increased human brain natriuretic peptide in congestive heart failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 1990, 323, 757–758. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ponikowski, P.; Voors, A.A.; Anker, S.D.; Bueno, H.; Cleland, J.G.F.; Coats, A.J.S.; Falk, V.; Gonzalez-Juanatey, J.R.; Harjola, V.P.; Jankowska, E.A.; et al. 2016 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure: The Task Force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC)Developed with the special contribution of the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur. Heart J. 2016, 37, 2129–2200. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yancy, C.W.; Jessup, M.; Bozkurt, B.; Butler, J.; Casey, D.E., Jr.; Drazner, M.H.; Fonarow, G.C.; Geraci, S.A.; Horwich, T.; Januzzi, J.L.; et al. 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of heart failure: A report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013, 62, e147–e239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonagh, T.A.; Cunningham, A.D.; Morrison, C.E.; McMurray, J.J.; Ford, I.; Morton, J.J.; Dargie, H.J. Left ventricular dysfunction, natriuretic peptides, and mortality in an urban population. Heart 2001, 86, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, T.J.; Larson, M.G.; Levy, D.; Benjamin, E.J.; Leip, E.P.; Omland, T.; Wolf, P.A.; Vasan, R.S. Plasma natriuretic peptide levels and the risk of cardiovascular events and death. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karmpaliotis, D.; Kirtane, A.J.; Ruisi, C.P.; Polonsky, T.; Malhotra, A.; Talmor, D.; Kosmidou, I.; Jarolim, P.; de Lemos, J.A.; Sabatine, M.S.; et al. Diagnostic and prognostic utility of brain natriuretic Peptide in subjects admitted to the ICU with hypoxic respiratory failure due to noncardiogenic and cardiogenic pulmonary edema. Chest 2007, 131, 964–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dao, Q.; Krishnaswamy, P.; Kazanegra, R.; Harrison, A.; Amirnovin, R.; Lenert, L.; Clopton, P.; Alberto, J.; Hlavin, P.; Maisel, A.S. Utility of B-type natriuretic peptide in the diagnosis of congestive heart failure in an urgent-care setting. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2001, 37, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koglin, J.; Pehlivanli, S.; Schwaiblmair, M.; Vogeser, M.; Cremer, P.; vonScheidt, W. Role of brain natriuretic peptide in risk stratification of patients with congestive heart failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2001, 38, 1934–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McMurray, J.J.; Adamopoulos, S.; Anker, S.D.; Auricchio, A.; Bohm, M.; Dickstein, K.; Falk, V.; Filippatos, G.; Fonseca, C.; Gomez-Sanchez, M.A.; et al. ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure 2012: The Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute and Chronic Heart Failure 2012 of the European Society of Cardiology. Developed in collaboration with the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur. Heart J. 2012, 33, 1787–1847. [Google Scholar]
- Tokola, H.; Hautala, N.; Marttila, M.; Magga, J.; Pikkarainen, S.; Kerkela, R.; Vuolteenaho, O.; Ruskoaho, H. Mechanical load-induced alterations in B-type natriuretic peptide gene expression. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2001, 79, 646–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwanaga, Y.; Nishi, I.; Furuichi, S.; Noguchi, T.; Sase, K.; Kihara, Y.; Goto, Y.; Nonogi, H. B-type natriuretic peptide strongly reflects diastolic wall stress in patients with chronic heart failure: Comparison between systolic and diastolic heart failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2006, 47, 742–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redfield, M.M.; Rodeheffer, R.J.; Jacobsen, S.J.; Mahoney, D.W.; Bailey, K.R.; Burnett, J.C., Jr. Plasma brain natriuretic peptide to detect preclinical ventricular systolic or diastolic dysfunction: A community-based study. Circulation 2004, 109, 3176–3181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maisel, A.S.; McCord, J.; Nowak, R.M.; Hollander, J.E.; Wu, A.H.B.; Duc, P.; Omland, T.; Storrow, A.B.; Krishnaswamy, P.; Abraham, W.T.; et al. Bedside B-Type natriuretic peptide in the emergency diagnosis of heart failure with reduced or preserved ejection fraction. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2003, 41, 2010–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.H.; Park, J.J.; Choi, D.J.; Yoon, C.H.; Oh, I.Y.; Kang, S.M.; Yoo, B.S.; Jeon, E.S.; Kim, J.J.; Cho, M.C.; et al. Prognostic value of NT-proBNP in heart failure with preserved versus reduced EF. Heart 2015, 101, 1881–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubien, E.; DeMaria, A.; Krishnaswamy, P.; Clopton, P.; Koon, J.; Kazanegra, R.; Gardetto, N.; Wanner, E.; Maisel, A.S. Utility of B-natriuretic peptide in detecting diastolic dysfunction: Comparison with Doppler velocity recordings. Circulation 2002, 105, 595–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, R.; Huelsman, M.; Strecker, K.; Bojic, A.; Moser, P.; Stanek, B.; Pacher, R. B-type natriuretic peptide predicts sudden death in patients with chronic heart failure. Circulation 2002, 105, 2392–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maisel, A.; Hollander, J.E.; Guss, D.; McCullough, P.; Nowak, R.; Green, G.; Saltzberg, M.; Ellison, S.R.; Bhalla, M.A.; Bhalla, V.; et al. Primary results of the Rapid Emergency Department Heart Failure Outpatient Trial (REDHOT). A multicenter study of B-type natriuretic peptide levels, emergency department decision making, and outcomes in patients presenting with shortness of breath. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2004, 44, 1328–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonarow, G.C.; Peacock, W.F.; Phillips, C.O.; Givertz, M.M.; Lopatin, M.; ADHERE Scientific Advisory Committee and Investigators. Admission B-type natriuretic peptide levels and in-hospital mortality in acute decompensated heart failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2007, 49, 1943–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Januzzi, J.L., Jr.; Sakhuja, R.; O’Donoghue, M.; Baggish, A.L.; Anwaruddin, S.; Chae, C.U.; Cameron, R.; Krauser, D.G.; Tung, R.; Camargo, C.A., Jr.; et al. Utility of amino-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide testing for prediction of 1-year mortality in patients with dyspnea treated in the emergency department. Arch. Intern. Med. 2006, 166, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omland, T.; Aakvaag, A.; Bonarjee, V.V.; Caidahl, K.; Lie, R.T.; Nilsen, D.W.; Sundsfjord, J.A.; Dickstein, K. Plasma brain natriuretic peptide as an indicator of left ventricular systolic function and long-term survival after acute myocardial infarction. Comparison with plasma atrial natriuretic peptide and N-terminal proatrial natriuretic peptide. Circulation 1996, 93, 1963–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mega, J.L.; Morrow, D.A.; De Lemos, J.A.; Sabatine, M.S.; Murphy, S.A.; Rifai, N.; Gibson, C.M.; Antman, E.M.; Braunwald, E. B-type natriuretic peptide at presentation and prognosis in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction: An ENTIRE-TIMI-23 substudy. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2004, 44, 335–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.J.; Larson, M.G.; Levy, D.; Leip, E.P.; Benjamin, E.J.; Wilson, P.W.; Sutherland, P.; Omland, T.; Vasan, R.S. Impact of age and sex on plasma natriuretic peptide levels in healthy adults. Am. J. Cardiol. 2002, 90, 254–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redfield, M.M.; Rodeheffer, R.J.; Jacobsen, S.J.; Mahoney, D.W.; Bailey, K.R.; Burnett, J.C. Plasma brain natriuretic peptide concentration: Impact of age and gender. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2002, 40, 976–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.J.; Larson, M.G.; Levy, D.; Benjamin, E.J.; Leip, E.P.; Wilson, P.W.; Vasan, R.S. Impact of obesity on plasma natriuretic peptide levels. Circulation 2004, 109, 594–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehra, M.R.; Uber, P.A.; Park, M.H.; Scott, R.L.; Ventura, H.O.; Harris, B.C.; Frohlich, E.D. Obesity and suppressed B-type natriuretic peptide levels in heart failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2004, 43, 1590–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bayes-Genis, A.; Lloyd-Jones, D.M.; van Kimmenade, R.R.; Lainchbury, J.G.; Richards, A.M.; Ordonez-Llanos, J.; Santalo, M.; Pinto, Y.M.; Januzzi, J.L., Jr. Effect of body mass index on diagnostic and prognostic usefulness of amino-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide in patients with acute dyspnea. Arch. Intern. Med. 2007, 167, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horwich, T.B.; Hamilton, M.A.; Fonarow, G.C. B-type natriuretic peptide levels in obese patients with advanced heart failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2006, 47, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
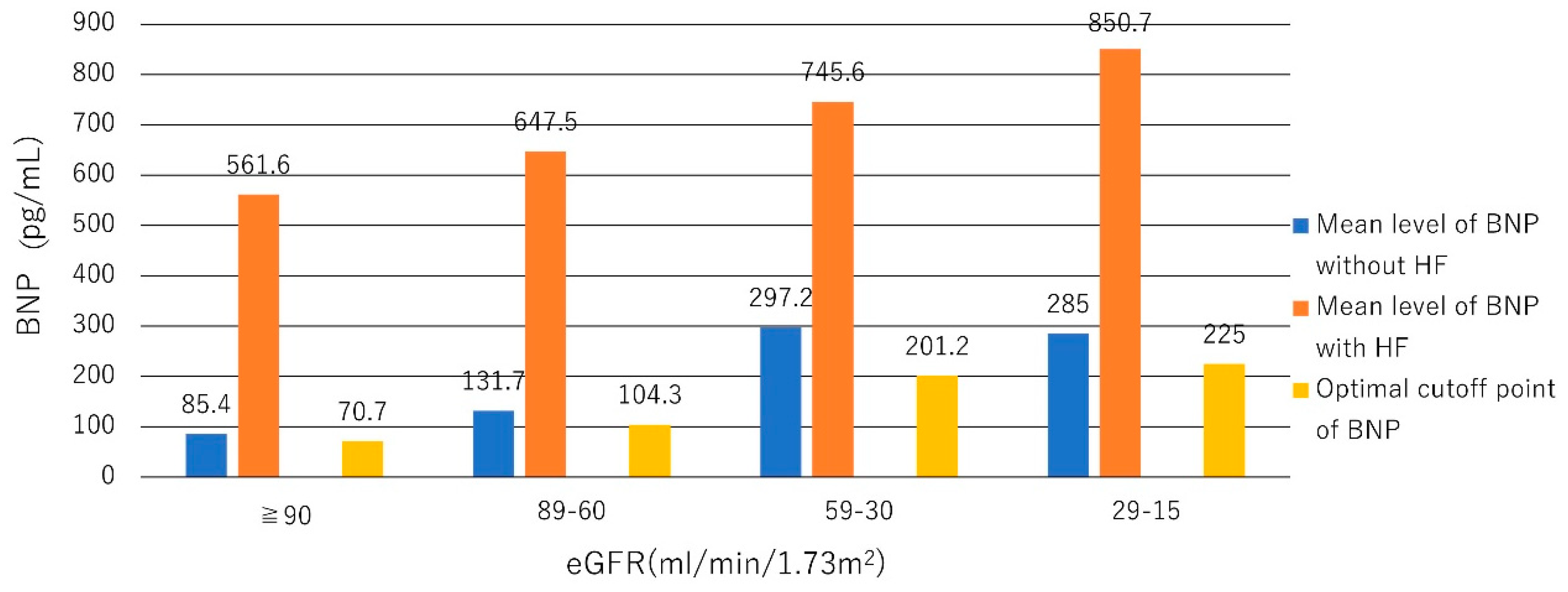
- Tsutamoto, T.; Wada, A.; Sakai, H.; Ishikawa, C.; Tanaka, T.; Hayashi, M.; Fujii, M.; Yamamoto, T.; Dohke, T.; Ohnishi, M.; et al. Relationship between renal function and plasma brain natriuretic peptide in patients with heart failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2006, 47, 582–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forfia, P.R.; Watkins, S.P.; Rame, J.E.; Stewart, K.J.; Shapiro, E.P. Relationship between B-type natriuretic peptides and pulmonary capillary wedge pressure in the intensive care unit. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2005, 45, 1667–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCullough, P.A.; Duc, P.; Omland, T.; McCord, J.; Nowak, R.M.; Hollander, J.E.; Herrmann, H.C.; Steg, P.G.; Westheim, A.; Knudsen, C.W.; et al. B-type natriuretic peptide and renal function in the diagnosis of heart failure: An analysis from the Breathing Not Properly Multinational Study. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2003, 41, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwaruddin, S.; Lloyd-Jones, D.M.; Baggish, A.; Chen, A.; Krauser, D.; Tung, R.; Chae, C.; Januzzi, J.L., Jr. Renal function, congestive heart failure, and amino-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide measurement: Results from the ProBNP Investigation of Dyspnea in the Emergency Department (PRIDE) Study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2006, 47, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, D.K.; de Lemos, J.A.; Ayers, C.R.; Berry, J.D.; Wang, T.J. Racial Differences in Natriuretic Peptide Levels: The Dallas Heart Study. JACC Heart Fail. 2015, 3, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, D.K.; Daniels, L.B.; Cheng, S.; deFilippi, C.R.; Criqui, M.H.; Maisel, A.S.; Lima, J.A.; Bahrami, H.; Greenland, P.; Cushman, M.; et al. Differences in Natriuretic Peptide Levels by Race/Ethnicity (From the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis). Am. J. Cardiol. 2017, 120, 1008–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jourdain, P.; Jondeau, G.; Funck, F.; Gueffet, P.; Le Helloco, A.; Donal, E.; Aupetit, J.F.; Aumont, M.C.; Galinier, M.; Eicher, J.C.; et al. Plasma brain natriuretic peptide-guided therapy to improve outcome in heart failure: The STARS-BNP Multicenter Study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2007, 49, 1733–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lainchbury, J.G.; Troughton, R.W.; Strangman, K.M.; Frampton, C.M.; Pilbrow, A.; Yandle, T.G.; Hamid, A.K.; Nicholls, M.G.; Richards, A.M. N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide-guided treatment for chronic heart failure: Results from the BATTLESCARRED (NT-proBNP-Assisted Treatment To Lessen Serial Cardiac Readmissions and Death) trial. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2009, 55, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunner-La Rocca, H.P.; Eurlings, L.; Richards, A.M.; Januzzi, J.L.; Pfisterer, M.E.; Dahlstrom, U.; Pinto, Y.M.; Karlstrom, P.; Erntell, H.; Berger, R.; et al. Which heart failure patients profit from natriuretic peptide guided therapy? A meta-analysis from individual patient data of randomized trials. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2015, 17, 1252–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfisterer, M.; Buser, P.; Rickli, H.; Gutmann, M.; Erne, P.; Rickenbacher, P.; Vuillomenet, A.; Jeker, U.; Dubach, P.; Beer, H.; et al. BNP-guided vs symptom-guided heart failure therapy: The Trial of Intensified vs Standard Medical Therapy in Elderly Patients With Congestive Heart Failure (TIME-CHF) randomized trial. JAMA 2009, 301, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgenthaler, N.G.; Struck, J.; Thomas, B.; Bergmann, A. Immunoluminometric assay for the midregion of pro-atrial natriuretic peptide in human plasma. Clin. Chem. 2004, 50, 234–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maisel, A.; Mueller, C.; Nowak, R.; Peacock, W.F.; Landsberg, J.W.; Ponikowski, P.; Mockel, M.; Hogan, C.; Wu, A.H.; Richards, M.; et al. Mid-region pro-hormone markers for diagnosis and prognosis in acute dyspnea: Results from the BACH (Biomarkers in Acute Heart Failure) trial. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2010, 55, 2062–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gegenhuber, A.; Struck, J.; Poelz, W.; Pacher, R.; Morgenthaler, N.G.; Bergmann, A.; Haltmayer, M.; Mueller, T. Midregional pro-A-type natriuretic peptide measurements for diagnosis of acute destabilized heart failure in short-of-breath patients: Comparison with B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) and amino-terminal proBNP. Clin. Chem. 2006, 52, 827–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chenevier-Gobeaux, C.; Guerin, S.; Andre, S.; Ray, P.; Cynober, L.; Gestin, S.; Pourriat, J.L.; Claessens, Y.E. Midregional pro-atrial natriuretic peptide for the diagnosis of cardiac-related dyspnea according to renal function in the emergency department: A comparison with B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) and N-terminal proBNP. Clin. Chem. 2010, 56, 1708–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seronde, M.F.; Gayat, E.; Logeart, D.; Lassus, J.; Laribi, S.; Boukef, R.; Sibellas, F.; Launay, J.M.; Manivet, P.; Sadoune, M.; et al. Comparison of the diagnostic and prognostic values of B-type and atrial-type natriuretic peptides in acute heart failure. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 168, 3404–3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masson, S.; Latini, R.; Carbonieri, E.; Moretti, L.; Rossi, M.G.; Ciricugno, S.; Milani, V.; Marchioli, R.; Struck, J.; Bergmann, A.; et al. The predictive value of stable precursor fragments of vasoactive peptides in patients with chronic heart failure: Data from the GISSI-heart failure (GISSI-HF) trial. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2010, 12, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.G.; Newton-Cheh, C.; Almgren, P.; Struck, J.; Morgenthaler, N.G.; Bergmann, A.; Platonov, P.G.; Hedblad, B.; Engstrom, G.; Wang, T.J.; et al. Assessment of conventional cardiovascular risk factors and multiple biomarkers for the prediction of incident heart failure and atrial fibrillation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2010, 56, 1712–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, L.B.; Clopton, P.; Potocki, M.; Mueller, C.; McCord, J.; Richards, M.; Hartmann, O.; Anand, I.S.; Wu, A.H.; Nowak, R.; et al. Influence of age, race, sex, and body mass index on interpretation of midregional pro atrial natriuretic peptide for the diagnosis of acute heart failure: Results from the BACH multinational study. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2012, 14, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burke, M.A.; Cotts, W.G. Interpretation of B-type natriuretic peptide in cardiac disease and other comorbid conditions. Heart Fail. Rev. 2007, 12, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Cao, H.; Su, L.; Ling, Z.; Liu, Z.; Lan, X.; Xu, Y.; Chen, W.; Yin, Y. NT-proBNP, but not ANP and C-reactive protein, is predictive of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation in patients undergoing pulmonary vein isolation. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. 2012, 33, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Rumayor, A.; Richards, A.M.; Burnett, J.C.; Januzzi, J.L., Jr. Biology of the natriuretic peptides. Am. J. Cardiol. 2008, 101, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arima, M.; Kanoh, T.; Kawano, Y.; Oigawa, T.; Yamagami, S.; Matsuda, S. Plasma levels of brain natriuretic peptide increase in patients with idiopathic bilateral atrial dilatation. Cardiology 2002, 97, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, S.; Murakami, Y.; Sano, K.; Katoh, H.; Shimada, T. Atrium as a source of brain natriuretic polypeptide in patients with atrial fibrillation. J. Card. Fail. 2000, 6, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, M.; Yang, J.; Li, Y. Serum N-terminal-pro-brain natriuretic peptide level and its clinical implications in patients with atrial fibrillation. Clin. Cardiol. 2009, 32, E1–E5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jourdain, P.; Bellorini, M.; Funck, F.; Fulla, Y.; Guillard, N.; Loiret, J.; Thebault, B.; Sadeg, N.; Desnos, M. Short-term effects of sinus rhythm restoration in patients with lone atrial fibrillation: A hormonal study. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2002, 4, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wozakowska-Kaplon, B. Effect of sinus rhythm restoration on plasma brain natriuretic peptide in patients with atrial fibrillation. Am. J. Cardiol. 2004, 93, 1555–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakowski, D.; Wozakowska-Kaplon, B.; Opolski, G. The influence of left ventricle diastolic function on natriuretic peptides levels in patients with atrial fibrillation. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2009, 32, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnabel, R.B.; Larson, M.G.; Yamamoto, J.F.; Sullivan, L.M.; Pencina, M.J.; Meigs, J.B.; Tofler, G.H.; Selhub, J.; Jacques, P.F.; Wolf, P.A.; et al. Relations of biomarkers of distinct pathophysiological pathways and atrial fibrillation incidence in the community. Circulation 2010, 121, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svennberg, E.; Lindahl, B.; Berglund, L.; Eggers, K.M.; Venge, P.; Zethelius, B.; Rosenqvist, M.; Lind, L.; Hijazi, Z. NT-proBNP is a powerful predictor for incident atrial fibrillation—Validation of a multimarker approach. Int. J. Cardiol. 2016, 223, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinner, M.F.; Stepas, K.A.; Moser, C.B.; Krijthe, B.P.; Aspelund, T.; Sotoodehnia, N.; Fontes, J.D.; Janssens, A.C.; Kronmal, R.A.; Magnani, J.W.; et al. B-type natriuretic peptide and C-reactive protein in the prediction of atrial fibrillation risk: The CHARGE-AF Consortium of community-based cohort studies. Europace 2014, 16, 1426–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelton, R.J.; Clark, A.L.; Goode, K.; Rigby, A.S.; Cleland, J.G. The diagnostic utility of N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide for the detection of major structural heart disease in patients with atrial fibrillation. Eur. Heart J. 2006, 27, 2353–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morello, A.; Lloyd-Jones, D.M.; Chae, C.U.; van Kimmenade, R.R.; Chen, A.C.; Baggish, A.L.; O’Donoghue, M.; Lee-Lewandrowski, E.; Januzzi, J.L., Jr. Association of atrial fibrillation and amino-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide concentrations in dyspneic subjects with and without acute heart failure: Results from the ProBNP Investigation of Dyspnea in the Emergency Department (PRIDE) study. Am. Heart J. 2007, 153, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
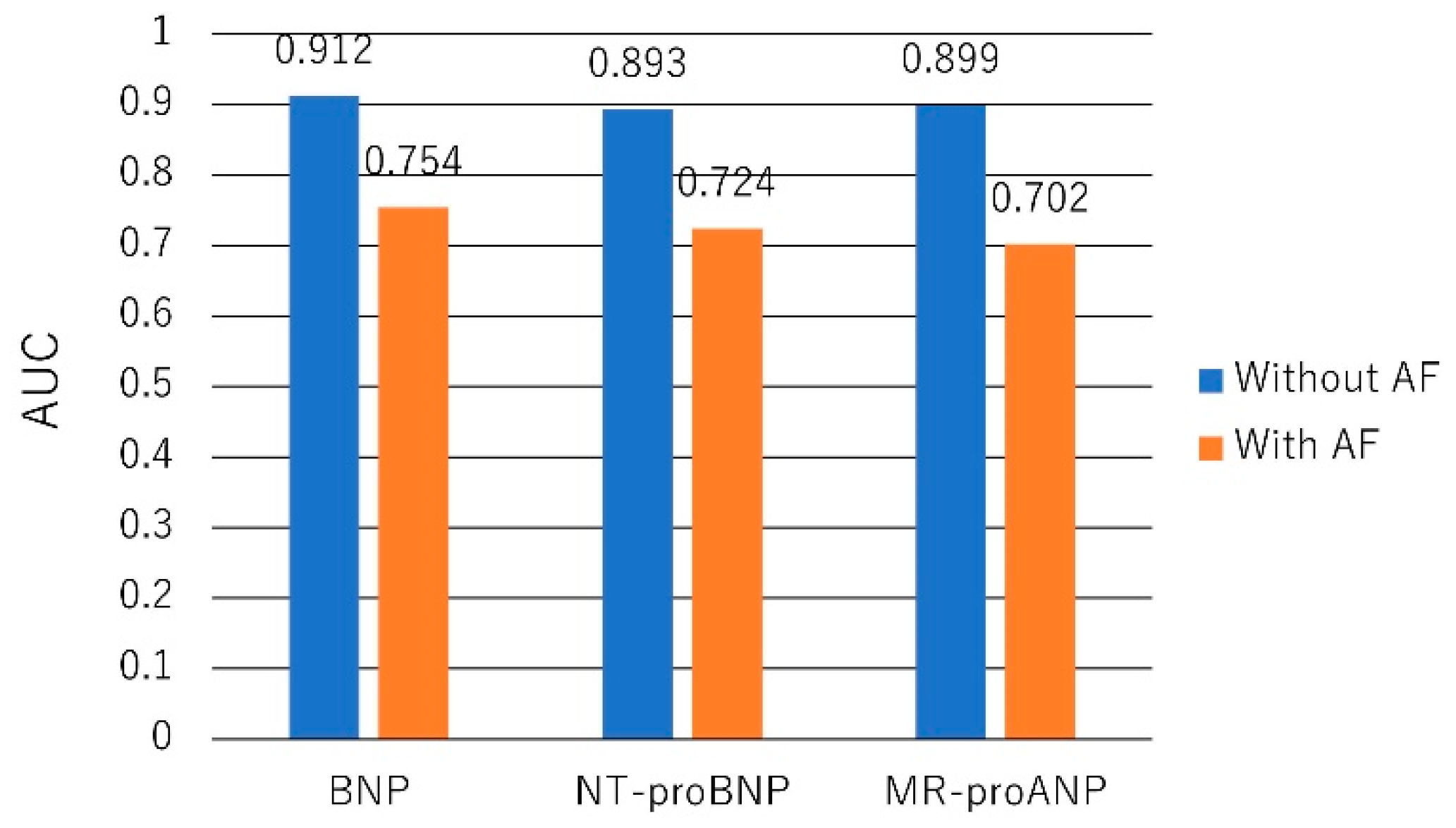
- Richards, M.; Di Somma, S.; Mueller, C.; Nowak, R.; Peacock, W.F.; Ponikowski, P.; Mockel, M.; Hogan, C.; Wu, A.H.; Clopton, P.; et al. Atrial fibrillation impairs the diagnostic performance of cardiac natriuretic peptides in dyspneic patients: Results from the BACH Study (Biomarkers in ACute Heart Failure). JACC Heart Fail. 2013, 1, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knudsen, C.W.; Omland, T.; Clopton, P.; Westheim, A.; Wu, A.H.; Duc, P.; McCord, J.; Nowak, R.M.; Hollander, J.E.; Storrow, A.B.; et al. Impact of atrial fibrillation on the diagnostic performance of B-type natriuretic peptide concentration in dyspneic patients: An analysis from the breathing not properly multinational study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2005, 46, 838–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, R.K.; Stoddard, G.J.; Greene, T.; Michaels, A.D.; Fernandez, G.; Freeman, A.; Nord, J.; Stehlik, J. Usefulness of adjusting for clinical covariates to improve the ability of B-type natriuretic peptide to distinguish cardiac from noncardiac dyspnea. Am. J. Cardiol. 2009, 104, 689–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Doorn, S.; Geersing, G.J.; Kievit, R.F.; van Mourik, Y.; Bertens, L.C.; van Riet, E.E.S.; Boonman-de Winter, L.J.; Moons, K.G.M.; Hoes, A.W.; Rutten, F.H. Opportunistic screening for heart failure with natriuretic peptides in patients with atrial fibrillation: A meta-analysis of individual participant data of four screening studies. Heart 2018, 104, 1236–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristensen, S.L.; Jhund, P.S.; Mogensen, U.M.; Rorth, R.; Abraham, W.T.; Desai, A.; Dickstein, K.; Rouleau, J.L.; Zile, M.R.; Swedberg, K.; et al. Prognostic Value of N-Terminal Pro-B-Type Natriuretic Peptide Levels in Heart Failure Patients With and Without Atrial Fibrillation. Circ. Heart Fail. 2017, 10, e004409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallergis, E.M.; Manios, E.G.; Kanoupakis, E.M.; Mavrakis, H.E.; Goudis, C.A.; Maliaraki, N.E.; Saloustros, I.G.; Milathianaki, M.E.; Chlouverakis, G.I.; Vardas, P.E. Effect of sinus rhythm restoration after electrical cardioversion on apelin and brain natriuretic Peptide prohormone levels in patients with persistent atrial fibrillation. Am. J. Cardiol. 2010, 105, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck-da-Silva, L.; de Bold, A.; Fraser, M.; Williams, K.; Haddad, H. Brain natriuretic peptide predicts successful cardioversion in patients with atrial fibrillation and maintenance of sinus rhythm. Can. J. Cardiol. 2004, 20, 1245–1248. [Google Scholar]
- Lellouche, N.; Berthier, R.; Mekontso-Dessap, A.; Braconnier, F.; Monin, J.L.; Duval, A.M.; Dubois-Rande, J.L.; Gueret, P.; Garot, J. Usefulness of plasma B-type natriuretic peptide in predicting recurrence of atrial fibrillation one year after external cardioversion. Am. J. Cardiol. 2005, 95, 1380–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solheim, E.; Off, M.K.; Hoff, P.I.; De Bortoli, A.; Schuster, P.; Ohm, O.J.; Chen, J. N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide level at long-term follow-up after atrial fibrillation ablation: A marker of reverse atrial remodelling and successful ablation. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. 2012, 34, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, A.; Song, L.; Li, M.; Chen, Y.; He, B. Association Between Baseline Natriuretic Peptides and Atrial Fibrillation Recurrence After Catheter Ablation. Int. Heart J. 2016, 57, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, H.; Wang, W.; Wang, C.; Xie, X.; Hou, Y. Association of pre-ablation level of potential blood markers with atrial fibrillation recurrence after catheter ablation: A meta-analysis. Europace 2017, 19, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, H.; Shantsila, A.; Guo, P.; Zhan, X.; Fang, X.; Liao, H.; Liu, Y.; Wei, W.; Fu, L.; Wu, S.; et al. Multiple biomarkers and arrhythmia outcome following catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation: The Guangzhou Atrial Fibrillation Project. J. Arrhythm. 2018, 34, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roldan, V.; Vilchez, J.A.; Manzano-Fernandez, S.; Jover, E.; Galvez, J.; Puche, C.M.; Valdes, M.; Vicente, V.; Lip, G.Y.; Marin, F. Usefulness of N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic Peptide levels for stroke risk prediction in anticoagulated patients with atrial fibrillation. Stroke 2014, 45, 696–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hijazi, Z.; Oldgren, J.; Andersson, U.; Connolly, S.J.; Ezekowitz, M.D.; Hohnloser, S.H.; Reilly, P.A.; Vinereanu, D.; Siegbahn, A.; Yusuf, S.; et al. Cardiac biomarkers are associated with an increased risk of stroke and death in patients with atrial fibrillation: A Randomized Evaluation of Long-term Anticoagulation Therapy (RE-LY) substudy. Circulation 2012, 125, 1605–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hijazi, Z.; Wallentin, L.; Siegbahn, A.; Andersson, U.; Christersson, C.; Ezekowitz, J.; Gersh, B.J.; Hanna, M.; Hohnloser, S.; Horowitz, J.; et al. N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide for risk assessment in patients with atrial fibrillation: Insights from the ARISTOTLE Trial (Apixaban for the Prevention of Stroke in Subjects With Atrial Fibrillation). J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013, 61, 2274–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oldgren, J.; Hijazi, Z.; Lindback, J.; Alexander, J.H.; Connolly, S.J.; Eikelboom, J.W.; Ezekowitz, M.D.; Granger, C.B.; Hylek, E.M.; Lopes, R.D.; et al. Performance and Validation of a Novel Biomarker-Based Stroke Risk Score for Atrial Fibrillation. Circulation 2016, 134, 1697–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hijazi, Z.; Lindback, J.; Alexander, J.H.; Hanna, M.; Held, C.; Hylek, E.M.; Lopes, R.D.; Oldgren, J.; Siegbahn, A.; Stewart, R.A.; et al. The ABC (age, biomarkers, clinical history) stroke risk score: A biomarker-based risk score for predicting stroke in atrial fibrillation. Eur. Heart J. 2016, 37, 1582–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckstein, J.; Potocki, M.; Murray, K.; Breidthardt, T.; Ziller, R.; Mosimann, T.; Klima, T.; Hoeller, R.; Moehring, B.; Sou, S.M.; et al. Direct comparison of mid-regional pro-atrial natriuretic peptide with N-terminal pro B-type natriuretic peptide in the diagnosis of patients with atrial fibrillation and dyspnoea. Heart 2012, 98, 1518–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darkner, S.; Goetze, J.P.; Chen, X.; Henningsen, K.; Pehrson, S.; Svendsen, J.H. Natriuretic Propeptides as Markers of Atrial Fibrillation Burden and Recurrence (from the AMIO-CAT Trial). Am. J. Cardiol. 2017, 120, 1309–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Berg, M.P.; van Gelder, I.C.; van Veldhuisen, D.J. Depletion of atrial natriuretic peptide during longstanding atrial fibrillation. Europace 2004, 6, 433–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, M.J.; Pomerance, A. Pathology of atrial fibrillation in man. Br. Heart J. 1972, 34, 520–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seino, Y.; Shimai, S.; Ibuki, C.; Itoh, K.; Takano, T.; Hayakawa, H. Disturbed secretion of atrial natriuretic peptide in patients with persistent atrial standstill: Endocrinologic silence. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1991, 18, 459–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoshihara, F.; Nishikimi, T.; Sasako, Y.; Hino, J.; Kobayashi, J.; Minatoya, K.; Bando, K.; Kosakai, Y.; Horio, T.; Suga, S.-I.; et al. Plasma atrial natriuretic peptide concentration inversely correlates with left atrial collagen volume fraction in patients with atrial fibrillation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2002, 39, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, K.; Tada, H.; Ogata, K.; Sekiguchi, Y.; Inaba, T.; Ito, Y.; Sato, Y.; Sato, A.; Seo, Y.; Kandori, A.; et al. Electrogram organization predicts left atrial reverse remodeling after the restoration of sinus rhythm by catheter ablation in patients with persistent atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm. 2012, 9, 1769–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakanishi, K.; Fukuda, S.; Yamashita, H.; Kosaka, M.; Shirai, N.; Tanaka, A.; Yoshikawa, J.; Shimada, K. Pre-procedural serum atrial natriuretic peptide levels predict left atrial reverse remodeling after catheter ablation in patients with atrial fibrillation. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2016, 2, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, K.; Yoshida, K.; Uehara, Y.; Ebine, M.; Kimata, A.; Nishina, H.; Takeyasu, N.; Noguchi, Y.; Ieda, M.; Aonuma, K.; et al. Mechanistic implication of decreased plasma atrial natriuretic peptide level for transient rise in the atrial capture threshold early after ICD or CRT-D implantation. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. 2018, 53, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Characteristic | BNP | NT-proBNP | ANP | MR-proANP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Localization within heart | Atrial and ventricular | Same as BNP | Atrial | Same as ANP |
| Storage | Minimal | Same as BNP | In intracellular granules | Same as ANP |
| Basal cardiac secretion | (+) | Same as BNP | ++ | Same as ANP |
| Gene transcription response to stretch | Rapid | Same as BNP | Slow | Same as ANP |
| Half-life (min) | 20 | 60-120 | 2 | 60–120 |
| Biologically active | Yes | No | Yes | No |
| Clinical range | 0–5000 pg/mL | 0–35,000 pg/mL | 0–2000 pg/mL | 0–1000 pmol/L |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baba, M.; Yoshida, K.; Ieda, M. Clinical Applications of Natriuretic Peptides in Heart Failure and Atrial Fibrillation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2824. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20112824
Baba M, Yoshida K, Ieda M. Clinical Applications of Natriuretic Peptides in Heart Failure and Atrial Fibrillation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(11):2824. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20112824
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaba, Masako, Kentaro Yoshida, and Masaki Ieda. 2019. "Clinical Applications of Natriuretic Peptides in Heart Failure and Atrial Fibrillation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 11: 2824. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20112824
APA StyleBaba, M., Yoshida, K., & Ieda, M. (2019). Clinical Applications of Natriuretic Peptides in Heart Failure and Atrial Fibrillation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(11), 2824. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20112824






