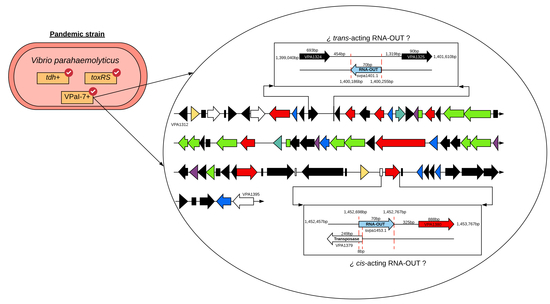
Conservation of Small Regulatory RNAs in Vibrio parahaemolyticus: Possible role of RNA-OUT Encoded by the Pathogenicity Island (VPaI-7) of Pandemic Strains
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
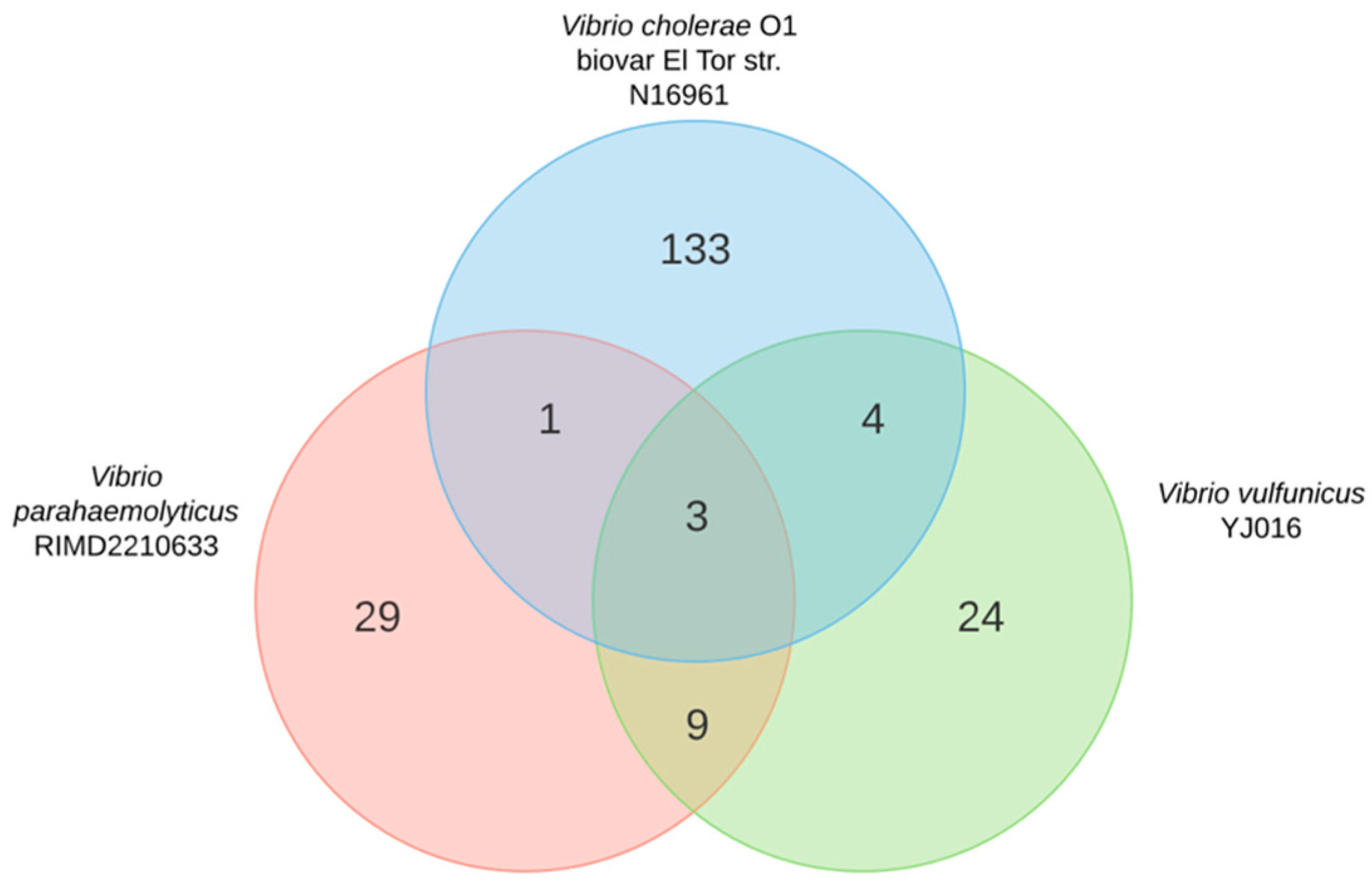
2.1. Gene Conservation across Human Pathogenic Vibrio Species
2.2. Small RNA Conservation and Distribution in Strains Differing in Pandemic Origin
2.3. Genomic Context of sRNAs Highly Conserved among Strains Differing in Pandemic Origin
2.4. Identification of Target Gene Regulated by svpa1401.1 and svpa1453.1
2.5. Adjustment to the Model of Antisense Regulation of IS10 Expression
2.6. VPA1379 mRNA and RNA-OUT svpa1401.1 Expression during in vitro Infection
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Strains
4.2. DNA Extraction, Sequencing, and Genome Data
4.3. SRNA Sequence Comparison between Human Pathogenic Vibrio Strains
4.4. Conservation and Distribution of sRNA in V. parahaemolyticus Strains
4.5. Infection Assay
4.6. RNA Extraction, cDNA Synthesis, and Real-Time Quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR)
4.7. Sequence-Based Analysis of RNA-OUT Target and Genomic-Context Visualization
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Tan, Y.; Guo, Z.; Yang, R.; Zhou, D. Transcriptional regulation of opaR, qrr2-4 and aphA by the master quorum-sensing regulator opaR in Vibrio parahaemolyticus. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta, T.; Srivastava, S. Small RNA-mediated regulation in bacteria: A growing palette of diverse mechanisms. Gene 2018, 656, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papenfort, K.; Vanderpool, C.K. Target activation by regulatory RNAs in bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 39, 362–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Perez-Reytor, D.; Plaza, N.; Espejo, R.T.; Navarrete, P.; Bastias, R.; Garcia, K. Role of non-coding regulatory RNA in the virulence of human pathogenic Vibrios. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, J.A.; Ellis, M.J.; Hossain, S.; Haniford, D.B. Hfq restructures RNA-IN and RNA-OUT and facilitates antisense pairing in the Tn 10/IS10 system. RNA 2013, 19, 670–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidelberg, J.F.; Heidelberg, K.B.; Colwell, R.R. Seasonality of chesapeake bay bacterioplankton species. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 5488–5497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Shao, Z. The pelagic bacterium Paraphotobacterium marinum has the smallest complete genome within the family vibrionaceae. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, F.L.; Iida, T.; Swings, J. Biodiveristy of Vibrios. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2004, 68, 403–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaza, N.; Castillo, D.; Pérez-Reytor, D.; Higuera, G.; García, K.; Bastías, R. Bacteriophages in the control of pathogenic Vibrios. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2018, 31, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, T.; Wai, S.N. A novel sRNA that modulates virulence and environmental fitness of Vibrio cholerae. RNA Biol. 2009, 6, 254–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, T.; Sabharwal, D.; Gurung, J.M.; Cheng, A.T.; Sjöström, A.E.; Yildiz, F.H.; Uhlin, B.E.; Wai, S.N. Vibrio cholerae utilizes direct sRNA regulation in expression of a biofilm matrix protein. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richard, A.L.; Withey, J.H.; Beyhan, S.; Yildiz, F.; DiRita, V.J. The Vibrio cholerae virulence regulatory cascade controls glucose uptake through activation of TarA, a small regulatory RNA. Mol. Microbiol. 2010, 78, 1171–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradley, E.S.; Bodi, K.; Ismail, A.M.; Camilli, A. A genome-wide approach to discovery of small RNAs involved in regulation of virulence in Vibrio cholerae. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García, K.; Bastías, R.; Higuera, G.; Torres, R.; Mellado, A.; Uribe, P.; Espejo, R.T. Rise and fall of pandemic Vibrio parahaemolyticus serotype O3: K6 in southern Chile. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 15, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillo, D.; Pérez-Reytor, D.; Plaza, N.; Ramírez-Araya, S.; Blondel, C.J.; Corsini, G.; Bastías, R.; Loyola, D.E.; Jaña, V.; Pavez, L.; et al. Exploring the genomic traits of non-toxigenic Vibrio parahaemolyticus strains isolated in southern Chile. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paranjpye, R.N.; Myers, M.S.; Yount, E.C.; Thompson, J.L. Zebrafish as a model for Vibrio parahaemolyticus virulence. Microbiol. (UK) 2013, 159, 2605–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottesman, S.; Storz, G. Bacterial small RNA regulators: Versatile roles and rapidly bacterial small RNA regulators. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2011, 3, a003798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanabe, T.; Funahashi, T.; Nakao, H.; Maki, J.; Yamamoto, S. The Vibrio parahaemolyticus small RNA ryhb promotes production of the siderophore vibrioferrin by stabilizing the polycistronic mRNA. J. Bacteriol. 2013, 195, 3692–3703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanabe, T.; Miyamoto, K.; Tsujibo, H.; Yamamoto, S.; Funahashi, T. The small RNA Spot 42 regulates the expression of the type III secretion system 1 (T3SS1) chaperone protein VP1682 in Vibrio parahaemolyticus. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2015, 362, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, K.; Yáñez, C.; Plaza, N.; Peña, F.; Sepúlveda, P.; Pérez-Reytor, D.; Espejo, R.T. Gene expression of Vibrio parahaemolyticus growing in laboratory isolation conditions compared to those common in its natural ocean environment. BMC Microbiol. 2017, 17, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livny, J.; Zhou, X.; Mandlik, A.; Hubbard, T.; Davis, B.M.; Waldor, M.K. Comparative RNA-Seq based dissection of the regulatory networks and environmental stimuli underlying Vibrio parahaemolyticus gene expression during infection. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 12212–12223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loyola, D.E.; Navarro, C.; Uribe, P.; García, K.; Mella, C.; Díaz, D.; Valdes, N.; Martínez-Urtaza, J.; Espejo, R.T. Genome diversification within a clonal population of pandemic Vibrio parahaemolyticus seems to depend on the life circumstances of each individual bacteria. BMC Genomics 2015, 16, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loyola, D.E.; Yañez, C.; Plaza, N.; Garcia, K.; Espejo, R.T. Genealogy of the Genome Components in the Highly Homogeneous Pandemic Vibrio parahaemolyticus Population. J. Phylogenetics Evol. Biol. 2016, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espejo, R.T.; García, K.; Plaza, N. Insight into the origin and evolution of the Vibrio parahaemolyticus pandemic strain. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhowmik, S.K. Study of Five Complete Genomes of Vibrio parahaemolyticus: Focusing Non-Pandemic to Pandemic Development. Int. J. Sci. Res. 2019, 8, 1994–2008. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, P.R.; Georg, J.; Mann, M.; Sorescu, D.A.; Richter, A.S.; Lott, S.; Kleinkauf, R.; Hess, W.R.; Backofen, R. CopraRNA and IntaRNA: Predicting small RNA targets, networks and interaction domains. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kery, M.B.; Feldman, M.; Livny, J.; Tjaden, B. TargetRNA2: Identifying targets of small regulatory RNAs in bacteria. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makino, K.; Oshima, K.; Kurokawa, K.; Yokoyama, K.; Uda, T.; Tagomori, K.; Iijima, Y.; Najima, M.; Nakano, M.; Yamashita, A.; et al. Genome sequence of Vibrio parahaemolyticus: A pathogenic mechanism distinct from that of V cholerae. Lancet 2003, 361, 743–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Gonzalez-Escalona, N.; Drees, K.P.; Sebra, R.P.; Cooper, V.S.; Jones, S.H.; Whistler, C.A. Parallel evolution of two clades of an Atlantic-Endemic Pathogenic Lineage of Vibrio parahaemolyticus by independent acquisition of related pathogenicity islands. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83, e01168-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nydam, S.D.; Shah, D.H.; Call, D.R. Transcriptome analysis of Vibrio parahaemolyticus in type III secretion system 1 inducing conditions. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2014, 4, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Lozano, M.; Marvig, R.L.; Molina-Santiago, C.; Tribelli, P.M.; Ramos, J.L.; Molin, S. Diversity of small RNAs expressed in Pseudomonas species. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2015, 7, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hnilicová, J.; Jirát Matějčková, J.; Šiková, M.; Pospíšil, J.; Halada, P.; Pánek, J.; Krásný, L. Ms1, a novel sRNA interacting with the RNA polymerase core in mycobacteria. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 11763–11776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Siguier, P.; Gourbeyre, E.; Chandler, M. Bacterial insertion sequences: Their genomic impact and diversity. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 38, 865–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craig, N. Transposition. In EcoSal—Escherichia coli and Salmonella: Cellular and Molecular Biology; Neidhardt, F., Ed.; ASM Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1996; pp. 2239–2262. [Google Scholar]
- Crow, J.F.; Dove, W.F. Perspectives on Genetics: Anecdotal, Historical, and Critical Commentaries, 1987–1998; The University of Wisconsin Press: Madison, WI, USA, 2000; pp. 147–152. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, C.; Simons, R.W. The IS10 antisense RNA blocks ribosome binding at the transposase translation initiation site. EMBO J. 1990, 9, 1267–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, J.A.; Wardle, S.J.; Haniford, D.B. Tn10/IS10 transposition is downregulated at the level of transposase expression by the RNA-binding protein Hfq. Mol. Microbiol. 2010, 78, 607–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Twiss, E.; Coros, A.M.; Tavakoli, N.P.; Derbyshire, K.M. Transposition is modulated by a diverse set of host factors in Escherichia coli and is stimulated by nutritional stress. Mol. Microbiol. 2005, 57, 1593–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, L.; Vargas, C.; Spear, B.B.; Cox, E.C. Transposable elements as mutator genes in evolution. Nature 1983, 303, 633–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichenbaum, Z.; Livneh, Z. UV light induces IS10 transposition in Escherichia coli. Genetics 1998, 149, 1173–1181. [Google Scholar]
- Fuenzalida, L.; Hernández, C.; Toro, J.; Rioseco, M.L.; Romero, J.; Espejo, R.T. Vibrio parahaemolyticus in shellfish and clinical samples during two large epidemics of diarrhoea in southern Chile. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 8, 675–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, K.; Torres, R.; Uribe, P.; Hernández, C.; Rioseco, M.L.; Romero, J.; Espejo, R.T. Dynamics of clinical and environmental Vibrio parahaemolyticus strains during seafood-related summer diarrhea outbreaks in southern Chile. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7482–7487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Huang, D.; Cheung, M.K.; Nong, W.; Huang, Q.; Kwan, H.S. BSRD: A repository for bacterial small regulatory RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D233–D238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rognes, T.; Flouri, T.; Nichols, B.; Quince, C.; Mahé, F. VSEARCH: A versatile open source tool for metagenomics. Peer J. 2016, 4, e2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurtz, S.; Phillippy, A.; Delcher, A.L.; Smoot, M.; Shumway, M.; Antonescu, C.; Salzberg, S.L.; Kurtz, S.; Phillippy, A.; Delcher, A.L.; et al. Versatile and open software for comparing large genomes. Genome Biol. 2004, 5, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrison, E.; Marth, G. Haplotype-based variant detection from short-read sequencing. arXiv 2012, arXiv:1207.3907. [Google Scholar]
- Quinlan, A.R.; Hall, I.M. BEDTools: A flexible suite of utilities for comparing genomic features. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 841–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carver, T.; Berriman, M.; Tivey, A.; Patel, C.; Böhme, U.; Barrell, B.G.; Parkhill, J.; Rajandream, M.A. Artemis and ACT: Viewing, annotating and comparing sequences stored in a relational database. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 2672–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, C.; Coulouris, G.; Avagyan, V.; Ma, N.; Papadopoulos, J.; Bealer, K.; Madden, T.L. BLAST+: Architecture and applications. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.J.; Sun, X.H.; Xu, X.Y.; Zhao, Y.; Pan, Y.J.; Hwang, C.A.; Wu, V.C.H. Investigation of reference genes in Vibrio parahaemolyticus for gene expression analysis using quantitative RT-PCR. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaffl, M.W.; Horgan, G.W.; Dempfle, L. Relative expression software tool (REST) for group-wise comparison and statistical analysis of relative expression results in real-time PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, e36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lott, S.C.; Schäfer, R.A.; Mann, M.; Backofen, R.; Hess, W.R.; Voß, B.; Georg, J. GLASSgo—Automated and reliable detection of sRNA homologs from a single input sequence. Front. Genet. 2018, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Strain | Isolate Year | Origin | Source | DGREA Classification | Accession Number and/or SRA | Sequencing Platform | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ATC210.98 | 1998 | Antofagasta, Chile | Stool | Pandemic | LFUN00000000 SRR1301223 | Ion Torrent | [22] |
| ATC220.98 | 1998 | Antofagasta, Chile | Stool | Pandemic | LFUQ00000000 SRR1293142 | Ion Torrent | [22] |
| PMC48.4 | 2004 | Puerto Montt, Chile | Stool | Pandemic | LFUP00000000 SRR1292943 | Ion Torrent | [22] |
| PMC58.5 | 2005 | Puerto Montt, Chile | Stool | Pandemic | LFUJ00000000 SRR1292941 | Ion Torrent | [22] |
| PMA37.5 | 2005 | Puerto Montt, Chile | Mussels | Pandemic | LFUL00000000 SRR1301224 | Ion Torrent | [22] |
| PMA109.5 | 2005 | Puerto Montt, Chile | Mussels | Pandemic | LFUK00000000 SRR1293140 | Ion Torrent | [22] |
| PMC14.7 | 2007 | Puerto Montt, Chile | Stool | Pandemic | LFUO00000000 SRR1293138 | Ion Torrent | [22] |
| PMC53.7 | 2007 | Puerto Montt, Chile | Stool | Nonpandemic | MKQF00000000 | Illumina MiSeq | [15] |
| PMC58.7 | 2007 | Puerto Montt, Chile | Stool | Pandemic | LFUM00000000 SRR1292939 | Ion Torrent | [22] |
| PMC54.13 | 2013 | Puerto Montt, Chile | Stool | Nonpandemic | MKQX00000000 | Illumina MiSeq | [15] |
| PMC81.13 | 2013 | Puerto Montt, Chile | Stool | Pandemic | SRR3002506 | Illumina MiSeq | [23] |
| PMA11.14 | 2014 | Puerto Montt, Chile | Mussels | Nonpandemic | MKQY00000000 | Illumina MiSeq | This study |
| PMA12.14 | 2014 | Puerto Montt, Chile | Mussels | Nonpandemic | MKQZ00000000 | Illumina MiSeq | This study |
| PMA14.14 | 2014 | Puerto Montt, Chile | Mussels | Nonpandemic | MKRA00000000 | Illumina MiSeq | [15] |
| PMA21.14 | 2014 | Puerto Montt, Chile | Mussels | Nonpandemic | MKRB00000000 | Illumina MiSeq | This study |
| PMA31.14 | 2014 | Puerto Montt, Chile | Mussels | Nonpandemic | MKRC00000000 | Illumina MiSeq | This study |
| PMA32.14 | 2014 | Puerto Montt, Chile | Mussels | Nonpandemic | MKRD00000000 | Illumina MiSeq | This study |
| PMA1.15 | 2015 | Puerto Montt, Chile | Mussels | Nonpandemic | MKQV00000000 | Ion Torrent | [15] |
| PMA2.15 | 2015 | Puerto Montt, Chile | Mussels | Nonpandemic | MKQT00000000 | Ion Torrent | [15] |
| PMA3.15 | 2015 | Puerto Montt, Chile | Mussels | Nonpandemic | MKQU00000000 | Ion Torrent | [15] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Plaza, N.; Pérez-Reytor, D.; Ramírez-Araya, S.; Pavón, A.; Corsini, G.; Loyola, D.E.; Jaña, V.; Pavéz, L.; Navarrete, P.; Bastías, R.; et al. Conservation of Small Regulatory RNAs in Vibrio parahaemolyticus: Possible role of RNA-OUT Encoded by the Pathogenicity Island (VPaI-7) of Pandemic Strains. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2827. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20112827
Plaza N, Pérez-Reytor D, Ramírez-Araya S, Pavón A, Corsini G, Loyola DE, Jaña V, Pavéz L, Navarrete P, Bastías R, et al. Conservation of Small Regulatory RNAs in Vibrio parahaemolyticus: Possible role of RNA-OUT Encoded by the Pathogenicity Island (VPaI-7) of Pandemic Strains. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(11):2827. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20112827
Chicago/Turabian StylePlaza, Nicolás, Diliana Pérez-Reytor, Sebastián Ramírez-Araya, Alequis Pavón, Gino Corsini, David E. Loyola, Víctor Jaña, Leonardo Pavéz, Paola Navarrete, Roberto Bastías, and et al. 2019. "Conservation of Small Regulatory RNAs in Vibrio parahaemolyticus: Possible role of RNA-OUT Encoded by the Pathogenicity Island (VPaI-7) of Pandemic Strains" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 11: 2827. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20112827
APA StylePlaza, N., Pérez-Reytor, D., Ramírez-Araya, S., Pavón, A., Corsini, G., Loyola, D. E., Jaña, V., Pavéz, L., Navarrete, P., Bastías, R., Castillo, D., & García, K. (2019). Conservation of Small Regulatory RNAs in Vibrio parahaemolyticus: Possible role of RNA-OUT Encoded by the Pathogenicity Island (VPaI-7) of Pandemic Strains. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(11), 2827. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20112827