Quercetin Enhances the Anti-Tumor Effects of BET Inhibitors by Suppressing hnRNPA1
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
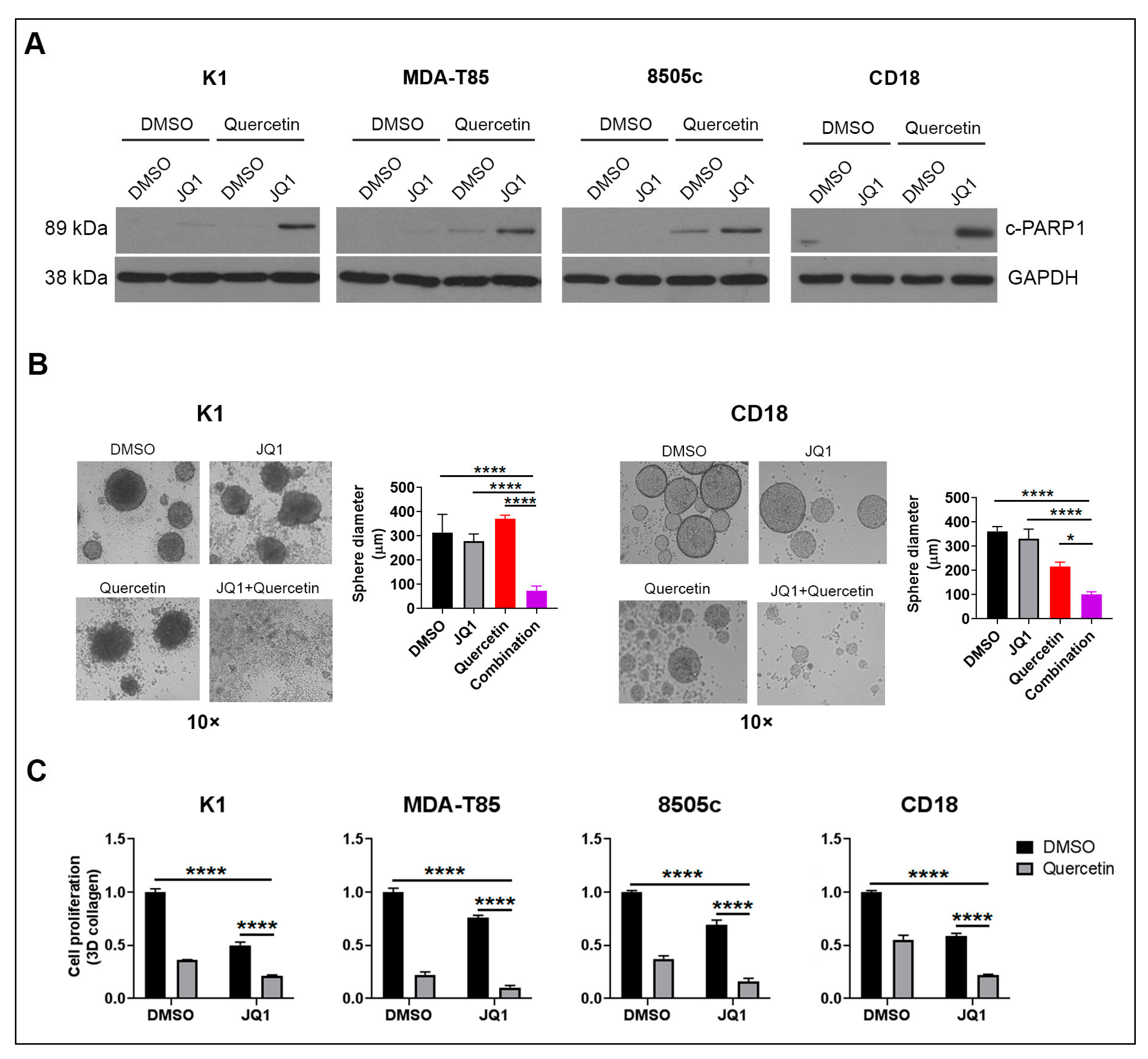
2.1. Quercetin Enhances the Anti-Tumor Effects of BET Inhibitors
2.2. hnRNPA1 Knockdown Enhances the Anti-Tumor Effects of BET Inhibitors
2.3. hnRNPA1 Mediates the Anti-Tumor Effects of Quercetin
2.4. Co-Treatment with Quercetin and JQ1 Decreases Survivin
2.5. Co-Treatment with hnRNPA1 Knockdown and JQ1 Decreases Survivin
2.6. Quercetin Enhances the Anti-Tumor Effects of JQ1 In Vivo
2.7. Expression of hnRNPA1 and BRD4 in Human Tumor Specimens
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Cell Culture
3.2. Chemicals
3.3. Embedding Cells in Three-Dimensional Type I Collagen Gels
3.4. Sphere Forming Assay
3.5. WST-1 Proliferation Assay
3.6. Transfection
3.7. Immunoblotting
3.8. Immunohistochemistry
3.9. Proteome Profiler Human Apoptosis
3.10. In Vivo Study
3.11. Statistical Analysis
3.12. Study Approval
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dutta, S.; Mahalanobish, S.; Saha, S.; Ghosh, S.; Sil, P.C. Natural products: An upcoming therapeutic approach to cancer. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 128, 240–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.; Sheng, Z.; Liang, S. Radiosensitization effects of curcumin plus cisplatin on non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 18, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Gao, W.; Zhang, M.J.; Chan, J.Y.; Wong, T.S. Curcumin enhances cisplatin sensitivity by suppressing NADPH oxidase 5 expression in human epithelial cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 18, 2132–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Martinez, D.; Soto, A.; Gil-Araujo, B.; Gallego, B.; Chiloeches, A.; Lasa, M. Resveratrol promotes apoptosis through the induction of dual specificity phosphatase 1 and sensitizes prostate cancer cells to cisplatin. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 124, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cipolletti, M.; Montalesi, E.; Nuzzo, M.T.; Fiocchetti, M.; Ascenzi, P.; Marino, M. Potentiation of paclitaxel effect by resveratrol in human breast cancer cells by counteracting the 17beta-estradiol/estrogen receptor alpha/neuroglobin pathway. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 3147–3157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanasekaran, S. Augmented cytotoxic effects of paclitaxel by curcumin induced overexpression of folate receptor-alpha for enhanced targeted drug delivery in HeLa cells. Phytomedicine 2019, 56, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Che, S.; Hui, B.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Qiang, Y.; Ma, H. Lung cancer therapy using doxorubicin and curcumin combination: Targeted prodrug based, pH sensitive nanomedicine. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 112, 108614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Wei, Y.; Liu, Y.; Lu, X.; Ding, F.; Wang, J.; Yang, S. Resveratrol promotes sensitization to Doxorubicin by inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition and modulating SIRT1/beta-catenin signaling pathway in breast cancer. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 1246–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouyafar, A.; Zadi Heydarabad, M.; Aghdam, S.B.; Khaksar, M.; Azimi, A.; Rahbarghazi, R.; Talebi, M. Resveratrol potentially increased the tumoricidal effect of doxorubicin on SKOV3 cancer stem cells in vitro. J. Cell Biochem. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, C.; Fu, L.; Huang, J.; Dai, Y.; Wang, B.; Xu, G.; Wu, L.; Zhou, H. Curcumin reverses doxorubicin resistance via inhibition the efflux function of ABCB4 in doxorubicinresistant breast cancer cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 19, 5162–5168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahai, V.; Redig, A.J.; Collier, K.A.; Eckerdt, F.D.; Munshi, H.G. Targeting BET bromodomain proteins in solid tumors. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 53997–54009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stathis, A.; Bertoni, F. BET Proteins as Targets for Anticancer Treatment. Cancer Discov. 2018, 8, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, K.; Raza, S.S.; Knab, L.M.; Chow, C.R.; Kwok, B.; Bentrem, D.J.; Popovic, R.; Ebine, K.; Licht, J.D.; Munshi, H.G. GLI2-dependent c-MYC upregulation mediates resistance of pancreatic cancer cells to the BET bromodomain inhibitor JQ1. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rathert, P.; Roth, M.; Neumann, T.; Muerdter, F.; Roe, J.S.; Muhar, M.; Deswal, S.; Cerny-Reiterer, S.; Peter, B.; Jude, J.; et al. Transcriptional plasticity promotes primary and acquired resistance to BET inhibition. Nature 2015, 525, 543–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fong, C.Y.; Gilan, O.; Lam, E.Y.; Rubin, A.F.; Ftouni, S.; Tyler, D.; Stanley, K.; Sinha, D.; Yeh, P.; Morison, J.; et al. BET inhibitor resistance emerges from leukaemia stem cells. Nature 2015, 525, 538–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, T.N.; Kumar, K.; DeCant, B.T.; Shang, M.; Munshi, S.Z.; Matsangou, M.; Ebine, K.; Munshi, H.G. Induction of MNK kinases-dependent eIF4E phosphorylation by inhibitors targeting BET proteins limits efficacy of BET inhibitors. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Tran, E.; Nguyen, T.H.; Do, P.T.; Huynh, T.H.; Huynh, H. The role of activated MEK-ERK pathway in quercetin-induced growth inhibition and apoptosis in A549 lung cancer cells. Carcinogenesis 2004, 25, 647–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.T.; Lee, Y.H.; Sharma, A.R.; Park, J.B.; Jagga, S.; Sharma, G.; Lee, S.S.; Nam, J.S. Quercetin induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in triple-negative breast cancer cells through modulation of Foxo3a activity. Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2017, 21, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, A.; Ghosh, S.; Chowdhury, S.; Pandey, B.; Sil, P.C. Targeted delivery of quercetin loaded mesoporous silica nanoparticles to the breast cancer cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1860, 2065–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, H.S.; Ku, J.M.; Choi, H.S.; Choi, Y.K.; Woo, J.K.; Kim, M.; Kim, I.; Na, C.H.; Hur, H.; Jang, B.H.; et al. Quercetin induces caspase-dependent extrinsic apoptosis through inhibition of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 signaling in HER2-overexpressing BT-474 breast cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 36, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baruah, M.M.; Khandwekar, A.P.; Sharma, N. Quercetin modulates Wnt signaling components in prostate cancer cell line by inhibiting cell viability, migration, and metastases. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 14025–14034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Liu, J.; Wei, T.; Ma, X.; Cheng, Q.; Huo, S.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Duan, X.; Liang, X.J. Quercetin-loaded nanomicelles to circumvent human castration-resistant prostate cancer in vitro and in vivo. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 5126–5138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, C.; Sun, L.; Mo, W.; Sun, L.; Luo, J.; Yang, Z.; Ran, Y. Quercetin Mediates beta-Catenin in Pancreatic Cancer Stem-Like Cells. Pancreas 2015, 44, 1334–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nwaeburu, C.C.; Bauer, N.; Zhao, Z.; Abukiwan, A.; Gladkich, J.; Benner, A.; Herr, I. Up-regulation of microRNA let-7c by quercetin inhibits pancreatic cancer progression by activation of Numbl. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 58367–58380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Guo, Q.; Chen, J.; Chen, Z. Quercetin Enhances Cisplatin Sensitivity of Human Osteosarcoma Cells by Modulating microRNA-217-KRAS Axis. Mol. Cells 2015, 38, 638–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Liang, X.; Wusiman, Z.; Yin, Y.; Shen, Q. Synergistic inhibition of migration and invasion of breast cancer cells by dual docetaxel/quercetin-loaded nanoparticles via Akt/MMP-9 pathway. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 523, 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Henning, S.M.; Magyar, C.E.; Elshimali, Y.; Heber, D.; Vadgama, J.V. Green tea and quercetin sensitize PC-3 xenograft prostate tumors to docetaxel chemotherapy. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 35, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, J.; Liu, L.; Sharma, S.; Dong, Q. Quercetin potentiates doxorubicin mediated antitumor effects against liver cancer through p53/Bcl-xl. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tummala, R.; Lou, W.; Gao, A.C.; Nadiminty, N. Quercetin Targets hnRNPA1 to Overcome Enzalutamide Resistance in Prostate Cancer Cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2017, 16, 2770–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jean-Philippe, J.; Paz, S.; Caputi, M. hnRNP A1: the Swiss army knife of gene expression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 18999–19024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, R.; Huang, Y.; Seckl, M.J.; Pardo, O.E. Emerging roles of hnRNPA1 in modulating malignant transformation. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patry, C.; Bouchard, L.; Labrecque, P.; Gendron, D.; Lemieux, B.; Toutant, J.; Lapointe, E.; Wellinger, R.; Chabot, B. Small interfering RNA-mediated reduction in heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoparticule A1/A2 proteins induces apoptosis in human cancer cells but not in normal mortal cell lines. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 7679–7688. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Lou, Y.; Zhong, H. Knockdown of HNRNPA1 inhibits lung adenocarcinoma cell proliferation through cell cycle arrest at G0/G1 phase. Gene 2016, 576, 791–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, S.M.; Veyrier, A.; Hosszu Ungureanu, N.; Bonnal, S.; Vagner, S.; Holcik, M. Subcellular relocalization of a trans-acting factor regulates XIAP IRES-dependent translation. Mol. Biol. Cell 2007, 18, 1302–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, R.; Durie, D.; Li, H.; Liu, B.Q.; Skehel, J.M.; Mauri, F.; Cuorvo, L.V.; Barbareschi, M.; Guo, L.; Holcik, M.; et al. hnRNPA1 couples nuclear export and translation of specific mRNAs downstream of FGF-2/S6K2 signalling. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 12483–12497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buxade, M.; Parra, J.L.; Rousseau, S.; Shpiro, N.; Marquez, R.; Morrice, N.; Bain, J.; Espel, E.; Proud, C.G. The Mnks are novel components in the control of TNF alpha biosynthesis and phosphorylate and regulate hnRNP A1. Immunity 2005, 23, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delmore, J.E.; Issa, G.C.; Lemieux, M.E.; Rahl, P.B.; Shi, J.; Jacobs, H.M.; Kastritis, E.; Gilpatrick, T.; Paranal, R.M.; Qi, J.; et al. BET bromodomain inhibition as a therapeutic strategy to target c-Myc. Cell 2011, 146, 904–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henssen, A.; Althoff, K.; Odersky, A.; Beckers, A.; Koche, R.; Speleman, F.; Schafers, S.; Bell, E.; Nortmeyer, M.; Westermann, F.; et al. Targeting MYCN-Driven Transcription By BET-Bromodomain Inhibition. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 2470–2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, Y.C.; Ahn, S.H.; Ryu, J.; Chen, Y.; Williams, M.D.; El-Naggar, A.K.; Gagea, M.; Schweppe, R.E.; Haugen, B.R.; Lai, S.Y.; et al. Development and characterization of six new human papillary thyroid carcinoma cell lines. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, E243–E252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahai, V.; Kumar, K.; Knab, L.M.; Chow, C.R.; Raza, S.S.; Bentrem, D.J.; Ebine, K.; Munshi, H.G. BET bromodomain inhibitors block growth of pancreatic cancer cells in three-dimensional collagen. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2014, 13, 1907–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shields, M.A.; Dangi-Garimella, S.; Krantz, S.B.; Bentrem, D.J.; Munshi, H.G. Pancreatic Cancer Cells Respond to Type I Collagen by Inducing Snail Expression to Promote Membrane Type 1 Matrix Metalloproteinase-dependent Collagen Invasion. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 10495–10504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shields, M.A.; Ebine, K.; Sahai, V.; Kumar, K.; Siddiqui, K.; Hwang, R.F.; Grippo, P.J.; Munshi, H.G. Snail Cooperates with KrasG12D to Promote Pancreatic Fibrosis. Mol. Cancer Res. 2013, 11, 1078–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, K.; DeCant, B.T.; Grippo, P.J.; Hwang, R.F.; Bentrem, D.J.; Ebine, K.; Munshi, H.G. BET inhibitors block pancreatic stellate cell collagen I production and attenuate fibrosis in vivo. JCI Insight 2017, 2, e88032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massard, C.; Soria, S.J.; Stathis, A.; Delord, J.P.; Awada, A.; Peters, S.; Lewin, J.; Bekradda, M.; Rezai, K.; Zeng, Z.; et al. A phase Ib trial with MK-8628/OTX015, a small molecule inhibitor of bromodomain (BRD) and extra-terminal (BET) proteins, in patients with selected advanced solid tumors. Eur. J. Cancer 2016, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauf, A.; Imran, M.; Khan, I.A.; Ur-Rehman, M.; Gilani, S.A.; Mehmood, Z.; Mubarak, M.S. Anticancer potential of quercetin: A comprehensive review. Phytother. Res. 2018, 32, 2109–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozsgai, E.; Bellyei, S.; Cseh, A.; Boronkai, A.; Racz, B.; Szabo, A.; Sumegi, B.; Hocsak, E. Quercetin increases the efficacy of glioblastoma treatment compared to standard chemoradiotherapy by the suppression of PI-3-kinase-Akt pathway. Nutr. Cancer 2013, 65, 1059–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granado-Serrano, A.B.; Martin, M.A.; Bravo, L.; Goya, L.; Ramos, S. Quercetin modulates NF-kappa B and AP-1/JNK pathways to induce cell death in human hepatoma cells. Nutr. Cancer 2010, 62, 390–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Long, C.; Junming, T.; Qihuan, L.; Youshun, Z.; Chan, Z. Quercetin-induced apoptosis of HL-60 cells by reducing PI3K/Akt. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2012, 39, 7785–7793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Li, L.U.; Fang, L.I.; Xie, H.; Yao, W.; Zhou, X.; Xiong, Z.; Wang, L.I.; Li, Z.; Luo, F. Quercetin reduces cyclin D1 activity and induces G1 phase arrest in HepG2 cells. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 12, 516–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Gao, N.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, G.; Budhraja, A.; Ke, Z.; Son, Y.O.; Wang, X.; Luo, J.; Shi, X. Quercetin induces tumor-selective apoptosis through downregulation of Mcl-1 and activation of Bax. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 5679–5691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duo, J.; Ying, G.G.; Wang, G.W.; Zhang, L. Quercetin inhibits human breast cancer cell proliferation and induces apoptosis via Bcl-2 and Bax regulation. Mol. Med. Rep. 2012, 5, 1453–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.H.; Szczepanski, M.; Lee, Y.J. Role of Bax in quercetin-induced apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2008, 75, 2345–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijayababu, M.R.; Kanagaraj, P.; Arunkumar, A.; Ilangovan, R.; Dharmarajan, A.; Arunakaran, J. Quercetin induces p53-independent apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells by modulating Bcl-2-related proteins: a possible mediation by IGFBP-3. Oncol. Res. 2006, 16, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegelin, M.D.; Reuss, D.E.; Habel, A.; Rami, A.; von Deimling, A. Quercetin promotes degradation of survivin and thereby enhances death-receptor-mediated apoptosis in glioma cells. Neuro Oncol. 2009, 11, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanc-Brude, O.P.; Mesri, M.; Wall, N.R.; Plescia, J.; Dohi, T.; Altieri, D.C. Therapeutic targeting of the survivin pathway in cancer: initiation of mitochondrial apoptosis and suppression of tumor-associated angiogenesis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2003, 9, 2683–2692. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Lyu, H.; Wang, J.; Liu, B. MicroRNA regulation and therapeutic targeting of survivin in cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2015, 5, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Taylor, W.F.; Jabbarzadeh, E. The use of natural products to target cancer stem cells. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2017, 7, 1588–1605. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.H.; Yu, C.C.; Wang, B.Y.; Chang, W.W. Tumorsphere as an effective in vitro platform for screening anti-cancer stem cell drugs. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 1215–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, S.N.; Singh, C.; Nall, D.; Meeker, D.; Shankar, S.; Srivastava, R.K. The dietary bioflavonoid quercetin synergizes with epigallocathechin gallate (EGCG) to inhibit prostate cancer stem cell characteristics, invasion, migration and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J. Mol. Signal. 2010, 5, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quagliariello, V.; Iaffaioli, R.V.; Armenia, E.; Clemente, O.; Barbarisi, M.; Nasti, G.; Berretta, M.; Ottaiano, A.; Barbarisi, A. Hyaluronic Acid Nanohydrogel Loaded With Quercetin Alone or in Combination to a Macrolide Derivative of Rapamycin RAD001 (Everolimus) as a New Treatment for Hormone-Responsive Human Breast Cancer. J. Cell Physiol. 2017, 232, 2063–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, P.C.; Yang, M.C.; Kulp, S.K.; Salunke, S.B.; Himmel, L.E.; Fang, C.S.; Jadhav, A.M.; Shan, Y.S.; Lee, C.T.; Lai, M.D.; et al. Regulation of oncogenic KRAS signaling via a novel KRAS-integrin-linked kinase-hnRNPA1 regulatory loop in human pancreatic cancer cells. Oncogene 2016, 35, 3897–3908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pham, T.N.D.; Stempel, S.; Shields, M.A.; Spaulding, C.; Kumar, K.; Bentrem, D.J.; Matsangou, M.; Munshi, H.G. Quercetin Enhances the Anti-Tumor Effects of BET Inhibitors by Suppressing hnRNPA1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4293. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20174293
Pham TND, Stempel S, Shields MA, Spaulding C, Kumar K, Bentrem DJ, Matsangou M, Munshi HG. Quercetin Enhances the Anti-Tumor Effects of BET Inhibitors by Suppressing hnRNPA1. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(17):4293. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20174293
Chicago/Turabian StylePham, Thao N.D., Sophie Stempel, Mario A. Shields, Christina Spaulding, Krishan Kumar, David J. Bentrem, Maria Matsangou, and Hidayatullah G. Munshi. 2019. "Quercetin Enhances the Anti-Tumor Effects of BET Inhibitors by Suppressing hnRNPA1" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 17: 4293. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20174293
APA StylePham, T. N. D., Stempel, S., Shields, M. A., Spaulding, C., Kumar, K., Bentrem, D. J., Matsangou, M., & Munshi, H. G. (2019). Quercetin Enhances the Anti-Tumor Effects of BET Inhibitors by Suppressing hnRNPA1. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(17), 4293. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20174293




