Opioid Addiction, Genetic Susceptibility, and Medical Treatments: A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Opioid Addiction, Biological Mechanism and Medications
Opioid Receptors
3. Medications for Opioid Addiction
3.1. Methadone, Buprenorphine, and Naloxone
3.2. Pharmacogenomics for Opioid Addiction
4. Genetic Susceptibility on Addiction
4.1. Classic Genetic Research and Molecular Genetic Research on Addiction
4.2. The Highest Heritability: Opioid Addiction
4.3. Genetic Susceptibility and Psychological Traits
4.4. Polygenic Risk Score for Opioid Addiction
5. CRISPR Gene Editing for Opioid Addition
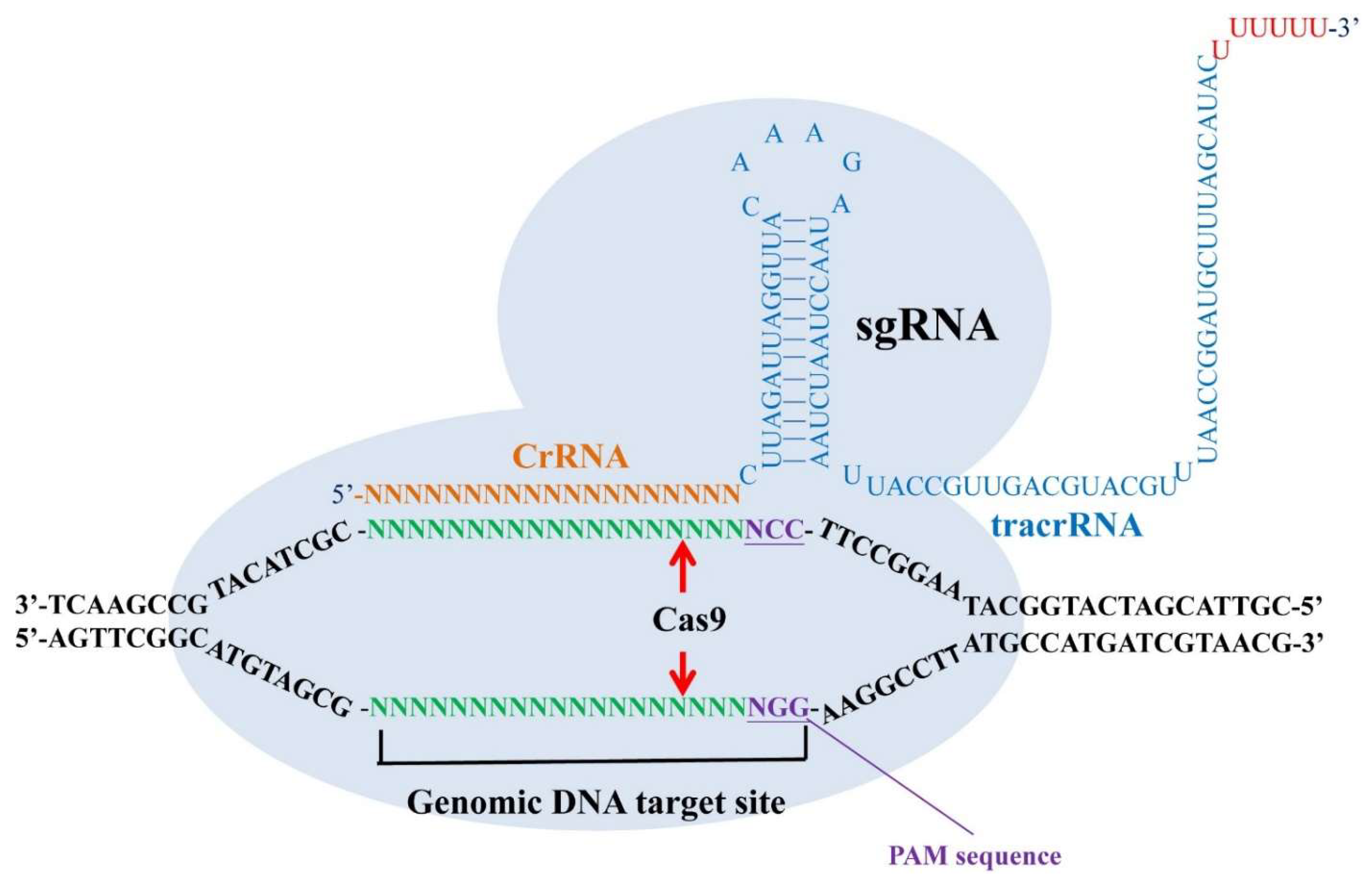
5.1. CRISPR/Cas9 as a Tool for Studying Mental Illness
5.2. Potential Treatment for Opioid Addiction Based on CRISPR
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5®); American Psychiatric Pub: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- McLellan, A.T.; Lewis, D.C.; O’brien, C.P.; Kleber, H.D. Drug dependence, a chronic medical illness: Implications for treatment, insurance, and outcomes evaluation. JAMA 2000, 284, 1689–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, B.F.; Goldstein, R.B.; Saha, T.D.; Chou, S.P.; Jung, J.; Zhang, H.; Pickering, R.P.; Ruan, W.J.; Smith, S.M.; Huang, B. Epidemiology of DSM-5 alcohol use disorder: Results from the National Epidemiologic Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions III. JAMA Psychiatry 2015, 72, 757–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamal, A.; Agaku, I.T.; O’Connor, E.; King, B.A.; Kenemer, J.B.; Neff, L. Current Cigarette Smoking among Adults—United States, 2005–2013; Center for Disease Control and Prevention: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2014; pp. 1108–1112.
- Ahern, J.; Stuber, J.; Galea, S. Stigma, discrimination and the health of illicit drug users. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2007, 88, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douaihy, A.B.; Kelly, T.M.; Sullivan, C. Medications for substance use disorders. Soc. Work Public Health 2013, 28, 264–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedegaard, H.; Warner, M.; Miniño, A.M. Drug Overdose Deaths in the United States, 1999–2015; US Department of Health and Human Services: Washington, DC, USA; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Atlanta, GA, USA; National Center for Health Statistics: Hyattsville, MD, USA, 2017.
- Clark, A.K.; Wilder, C.M.; Winstanley, E.L. A systematic review of community opioid overdose prevention and naloxone distribution programs. J. Addict. Med. 2014, 8, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrell, M.; Ward, J.; Mattick, R.; Hall, W.; Stimson, G.V.; Des Jarlais, D.; Gossop, M.; Strang, J. Methadone maintenance treatment in opiate dependence: A review. Br. Med. J. 1994, 309, 997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connock, M.; Juarez-Garcia, A.; Jowett, S.; Frew, E.; Liu, Z.; Taylor, R.J.; Fry-Smith, A.; Day, E.; Lintzeris, N.; Roberts, T.; et al. Methadone and Buprenorphine for the Management of Opioid Dependence: A Systematic Review and Economic Evaluation; 2007/02/23 ed.; NIHR Journals Library: Southampton, UK, 2007; Volume 11, pp. 1–171. [Google Scholar]
- Thomasson, H.R.; Edenberg, H.J.; Crabb, D.W.; Mai, X.L.; Jerome, R.E.; Li, T.K.; Wang, S.P.; Lin, Y.T.; Lu, R.B.; Yin, S.J. Alcohol and aldehyde dehydrogenase genotypes and alcoholism in Chinese men. Am. J. Human Genet. 1991, 48, 677. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, K.G.; White, H.R.; Chung, I.-J.; Hawkins, J.D.; Catalano, R.F. Early adult outcomes of adolescent binge drinking: Person-and variable-centered analyses of binge drinking trajectories. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2000, 24, 892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, K.M.; Sher, K.J. Similarities and differences of longitudinal phenotypes across alternate indices of alcohol involvement: A methodologic comparison of trajectory approaches. Psychol. Addict. Behav. 2005, 19, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genberg, B.L.; Gange, S.J.; Go, V.F.; Celentano, D.D.; Kirk, G.D.; Mehta, S.H. Trajectories of injection drug use over 20 years (1988–2008) in Baltimore, Maryland. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ries, R.K.; Miller, S.C.; Fiellin, D.A. Principles of Addiction Medicine; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Spahn, V.; Fischer, O.; Endres-Becker, J.; Schäfer, M.; Stein, C.; Zöllner, C. Opioid withdrawal increases transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 activity in a protein kinase A-dependent manner. Pain 2013, 154, 598–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zöllner, C.; Stein, C. Opioids. In Analgesia; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 31–63. [Google Scholar]
- Volkow, N.D.; McLellan, A.T. Opioid abuse in chronic pain—misconceptions and mitigation strategies. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 1253–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christie, M. Cellular neuroadaptations to chronic opioids: Tolerance, withdrawal and addiction. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 154, 384–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalivas, P.W.; Volkow, N.D. The neural basis of addiction: A pathology of motivation and choice. Am. J. Psychiatry 2005, 162, 1403–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volkow, N.; Morales, M. The brain on drugs: From reward to addiction. Cell 2015, 162, 712–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomson, A.D. Mechanisms of vitamin deficiency in chronic alcohol misusers and the development of the Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome. Alcohol Alcohol. 2000, 35, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victor, M.; Adams, R.D.; Collins, G.H. The Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome. A clinical and pathological study of 245 patients, 82 with post-mortem examinations. Contemp. Neurol. Ser. 1971, 7, 1. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ersche, K.D.; Clark, L.; London, M.; Robbins, T.W.; Sahakian, B.J. Profile of executive and memory function associated with amphetamine and opiate dependence. Neuropsychopharmacology 2006, 31, 1036–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruneau, J.; Ahamad, K.; Goyer, M.-È.; Poulin, G.; Selby, P.; Fischer, B.; Wild, T.C.; Wood, E. Management of opioid use disorders: A national clinical practice guideline. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 2018, 190, E247–E257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, H.; Stancliff, S.; Langrod, J. Methadone maintenance treatment (MMT): A review of historical and clinical issues. Mount Sinai J. Med. N. Y. 2000, 67, 347–364. [Google Scholar]
- Fudala, P.J.; Bridge, T.P.; Herbert, S.; Williford, W.O.; Chiang, C.N.; Jones, K.; Collins, J.; Raisch, D.; Casadonte, P.; Goldsmith, R.J. Office-based treatment of opiate addiction with a sublingual-tablet formulation of buprenorphine and naloxone. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 949–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skolnick, P. The opioid epidemic: Crisis and solutions. Ann. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2018, 58, 143–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janecka, A.; Fichna, J.; Janecki, T. Opioid receptors and their ligands. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2004, 4, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, C. Opioid receptors. Ann. Rev. Med. 2016, 67, 433–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waldhoer, M.; Bartlett, S.E.; Whistler, J.L. Opioid receptors. Ann. Rev. Biochem. 2004, 73, 953–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S. Historical review: Opiate addiction and opioid receptors. Cell Transplant. 2019, 28, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansour, A.; Khachaturian, H.; Lewis, M.E.; Akil, H.; Watson, S.J. Anatomy of CNS opioid receptors. Trends Neurosci. 1988, 11, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wood, P.L. The significance of multiple CNS opioid receptor types: A review of critical considerations relating to technical details and anatomy in the study of central opioid actions. Peptides 1988, 9, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contet, C.; Kieffer, B.L.; Befort, K. Mu opioid receptor: A gateway to drug addiction. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2004, 14, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Merrer, J.; Becker, J.A.; Befort, K.; Kieffer, B.L. Reward processing by the opioid system in the brain. Physiol. Rev. 2009, 89, 1379–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pert, C.B.; Snyder, S.H. Opiate receptor: Demonstration in nervous tissue. Science 1973, 179, 1011–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wassum, K.; Ostlund, S.; Maidment, N.; Balleine, B. Distinct opioid circuits determine the palatability and the desirability of rewarding EVENTS. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 12512–12517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wassum, K.M.; Cely, I.C.; Balleine, B.W.; Maidment, N.T. μ-opioid receptor activation in the basolateral amygdala mediates the learning of increases but not decreases in the incentive value of a food reward. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 1591–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troisi, A.; Frazzetto, G.; Carola, V.; Di Lorenzo, G.; Coviello, M.; D’Amato, F.R.; Moles, A.; Siracusano, A.; Gross, C. Social hedonic capacity is associated with the A118G polymorphism of the mu-opioid receptor gene (OPRM1) in adult healthy volunteers and psychiatric patients. Soc. Neurosci. 2011, 6, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cinque, C.; Pondiki, S.; Oddi, D.; Di Certo, M.; Marinelli, S.; Troisi, A.; Moles, A.; D’amato, F. Modeling socially anhedonic syndromes: Genetic and pharmacological manipulation of opioid neurotransmission in mice. Transl. Psychiatry 2012, 2, e155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Der-Avakian, A.; Markou, A. The neurobiology of anhedonia and other reward-related deficits. Trends Neurosci. 2012, 35, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schramm-Sapyta, N.L.; Walker, Q.D.; Caster, J.M.; Levin, E.D.; Kuhn, C.M. Are adolescents more vulnerable to drug addiction than adults? Evidence from animal models. Psychopharmacology 2009, 206, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Doherty, J.M.; Frantz, K.J. Heroin self-administration and reinstatement of heroin-seeking in adolescent vs. adult male rats. Psychopharmacology 2012, 219, 763–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wee, S.; Koob, G.F. The role of the dynorphin–κ opioid system in the reinforcing effects of drugs of abuse. Psychopharmacology 2010, 210, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruchas, M.; Land, B.; Chavkin, C. The dynorphin/kappa opioid system as a modulator of stress-induced and pro-addictive behaviors. Brain Res. 2010, 1314, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Veer, A.V.T.; Yano, J.M.; Carroll, F.I.; Cohen, B.M.; Carlezon, W.A., Jr. Corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF)-induced disruption of attention in rats is blocked by the κ-opioid receptor antagonist JDTic. Neuropsychopharmacology 2012, 37, 2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, A.J.; Gold, L.H.; Polis, I.; McDonald, J.S.; Filliol, D.; Kieffer, B.L.; Koob, G.F. Increased ethanol self-administration in δ-opioid receptor knockout mice. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2001, 25, 1249–1256. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Inturrisi, C.E.; Max, M.B.; Foley, K.M.; Schultz, M.; Shin, S.-U.; Houde, R.W. The pharmacokinetics of heroin in patients with chronic pain. N. Engl. J. Med. 1984, 310, 1213–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazoit, J.-X.; Sandouk, P.; Zetlaoui, P.; Scherrmann, J.-M. Pharmacokinetics of unchanged morphine in normal and cirrhotic subjects. Anesth. Analg. 1987, 66, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, M.P.; Glare, P.A.; Hardy, J. Opioids in Cancer Pain; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, R.; Kraus, C.; Fleming, M.; Reddy, S. Methadone: Applied pharmacology and use as adjunctive treatment in chronic pain. Postgrad. Med. J. 2004, 80, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, G.; Oliveto, A.; Kosten, T.R. Combating opiate dependence: A comparison among the available pharmacological options. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2004, 5, 713–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattick, R.P.; Kimber, J.; Breen, C.; Davoli, M. Buprenorphine maintenance versus placebo or methadone maintenance for opioid dependence. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2008, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, C.P.; Fullerton, C.A.; Kim, M.; Montejano, L.; Lyman, D.R.; Dougherty, R.H.; Daniels, A.S.; Ghose, S.S.; Delphin-Rittmon, M.E. Medication-assisted treatment with buprenorphine: Assessing the evidence. Psychiatr. Serv. 2014, 65, 158–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahan, A.; Aarts, L.; Smith, T.W. Incidence, reversal, and prevention of opioid-induced respiratory depression. Anesthesiol. J. Am. Soc. Anesthesiol. 2010, 112, 226–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heel, R.; Brogden, R.; Speight, T.; Avery, G. Buprenorphine: A review of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic efficacy. Drugs 1979, 17, 81–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mello, N.K.; Mendelson, J.H. Behavioral pharmacology of buprenorphine. Drug Alcohol Depend. 1985, 14, 283–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, S.L.; Preston, K.L.; Stitzer, M.L.; Cone, E.J.; Bigelow, G.E. Clinical pharmacology of buprenorphine: Ceiling effects at high doses. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 1994, 55, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, R.D.; Potter, J.S.; Fiellin, D.A.; Byrne, M.; Connery, H.S.; Dickinson, W.; Gardin, J.; Griffin, M.L.; Gourevitch, M.N.; Haller, D.L. Adjunctive counseling during brief and extended buprenorphine-naloxone treatment for prescription opioid dependence: A 2-phase randomized controlled trial. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2011, 68, 1238–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodrich, P. Naloxone hydrochloride: A review. AANA J. 1990, 58, 14–16. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Johansson, B.A.; Berglund, M.; Lindgren, A. Efficacy of maintenance treatment with naltrexone for opioid dependence: A meta-analytical review. Addiction 2006, 101, 491–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapham, S.C.; McMillan, G.P. Open-label pilot study of extended-release naltrexone to reduce drinking and driving among repeat offenders. J. Addict. Med. 2011, 5, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, R.A.; Hotham, E.; Hall, C.; Williams, M.; Suppiah, V. Pharmacogenomics and patient treatment parameters to opioid treatment in chronic pain: A focus on morphine, oxycodone, tramadol, and fentanyl. Pain Med. 2017, 18, 2369–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yiannakopoulou, E. Pharmacogenomics and opioid analgesics: Clinical implications. Int. J. Genom. 2015, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendler, K.S.; Jacobson, K.C.; Prescott, C.A.; Neale, M.C. Specificity of genetic and environmental risk factors for use and abuse/dependence of cannabis, cocaine, hallucinogens, sedatives, stimulants, and opiates in male twins. Am. J. Psychiatry 2003, 160, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuang, M.T.; Lyons, M.J.; Meyer, J.M.; Doyle, T.; Eisen, S.A.; Goldberg, J.; True, W.; Lin, N.; Toomey, R.; Eaves, L. Co-occurrence of abuse of different drugs in men: The role of drug-specific and shared vulnerabilities. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1998, 55, 967–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornelis, M.C.; Monda, K.L.; Yu, K.; Paynter, N.; Azzato, E.M.; Bennett, S.N.; Berndt, S.I.; Boerwinkle, E.; Chanock, S.; Chatterjee, N. Genome-wide meta-analysis identifies regions on 7p21 (AHR) and 15q24 (CYP1A2) as determinants of habitual caffeine consumption. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1002033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crabb, D.W.; Edenberg, H.J.; Bosron, W.F.; Li, T.-K. Genotypes for aldehyde dehydrogenase deficiency and alcohol sensitivity. The inactive ALDH2 (2) allele is dominant. J. Clin. Investig. 1989, 83, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sulem, P.; Gudbjartsson, D.F.; Geller, F.; Prokopenko, I.; Feenstra, B.; Aben, K.K.; Franke, B.; den Heijer, M.; Kovacs, P.; Stumvoll, M. Sequence variants at CYP1A1–CYP1A2 and AHR associate with coffee consumption. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2011, 20, 2071–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobacco and Genetics Consortium. Genome-wide meta-analyses identify multiple loci associated with smoking behavior. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, P.; Kranzler, H.R.; Krauthammer, M.; Cosgrove, K.P.; Oslin, D.; Anton, R.F.; Farrer, L.A.; Picciotto, M.R.; Krystal, J.H.; Zhao, H. Rare nonsynonymous variants in alpha-4 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor gene protect against nicotine dependence. Biol. Psychiatry 2011, 70, 528–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burton, P.R.; Tobin, M.D.; Hopper, J.L. Key concepts in genetic epidemiology. Lancet 2005, 366, 941–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreek, M.J.; Nielsen, D.A.; LaForge, K.S. Genes associated with addiction: Alcoholism, opiate, and cocaine addiction. Neuromol. Med. 2004, 5, 85–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaij, L.; Rosenthal, D. Alcoholism in twins. Studies on the etiology and sequels of abuse of alcohol. J. Nerv. Ment. Dis. 1961, 133, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partanen, J.; Bruun, K.; Markkanen, T. Inheritance of Drinking Behavior: A study on Intelligence, Personality, and Use of Alcohol of Adult Twins; Finnish Foundation for Alcohol Studies: Stockholm, Sweden, 1966; Volume 14. [Google Scholar]
- Cloninger, C.R.; Bohman, M.; Sigvardsson, S. Inheritance of alcohol abuse: Cross-fostering analysis of adopted men. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1981, 38, 861–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merikangas, K.R.; Stolar, M.; Stevens, D.E.; Goulet, J.; Preisig, M.A.; Fenton, B.; Zhang, H.; O’Malley, S.S.; Rounsaville, B.J. Familial transmission of substance use disorders. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1998, 55, 973–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilens, T.E.; Biederman, J.; Bredin, E.; Hahesy, A.L.; Abrantes, A.; Neft, D.; Millstein, R.; Spencer, T.J. A family study of the high-risk children of opioid-and alcohol-dependent parents. Am. J. Addic. 2002, 11, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadoret, R.J.; Troughton, E.; O’Gorman, T.W.; Heywood, E. An adoption study of genetic and environmental factors in drug abuse. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1986, 43, 1131–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teare, M.D.; Barrett, J.H. Genetic linkage studies. Lancet 2005, 366, 1036–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelernter, J.; Panhuysen, C.; Wilcox, M.; Hesselbrock, V.; Rounsaville, B.; Poling, J.; Weiss, R.; Sonne, S.; Zhao, H.; Farrer, L. Genomewide linkage scan for opioid dependence and related traits. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2006, 78, 759–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lachman, H.M.; Fann, C.S.; Bartzis, M.; Evgrafov, O.V.; Rosenthal, R.N.; Nunes, E.V.; Miner, C.; Santana, M.; Gaffney, J.; Riddick, A. Genomewide suggestive linkage of opioid dependence to chromosome 14q. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2007, 16, 1327–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Psychiatric GWAS Consortium Coordinating Committee. Genomewide association studies: History, rationale, and prospects for psychiatric disorders. Am. J. Psychiatry 2009, 166, 540–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.Y.; Barratt, B.J.; Clayton, D.G.; Todd, J.A. Genome-wide association studies: Theoretical and practical concerns. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2005, 6, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetherill, L.; Agrawal, A.; Kapoor, M.; Bertelsen, S.; Bierut, L.J.; Brooks, A.; Dick, D.; Hesselbrock, M.; Hesselbrock, V.; Koller, D.L. Association of substance dependence phenotypes in the COGA sample. Addict. Biol. 2015, 20, 617–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelernter, J.; Kranzler, H.R.; Sherva, R.; Koesterer, R.; Almasy, L.; Zhao, H.; Farrer, L.A. Genome-wide association study of opioid dependence: Multiple associations mapped to calcium and potassium pathways. Biol. Psychiatry 2014, 76, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreek, M.J.; Nielsen, D.A.; Butelman, E.R.; LaForge, K.S. Genetic influences on impulsivity, risk taking, stress responsivity and vulnerability to drug abuse and addiction. Nat. Neurosci. 2005, 8, 1450–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Q.-F.; Li, S.-B. Potential association of DRD2 and DAT1 genetic variation with heroin dependence. Neurosci. Lett. 2009, 464, 127–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vereczkei, A.; Demetrovics, Z.; Szekely, A.; Sarkozy, P.; Antal, P.; Szilagyi, A.; Sasvari-Szekely, M.; Barta, C. Multivariate analysis of dopaminergic gene variants as risk factors of heroin dependence. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; Xu, L.; Liu, H.; Chen, W.; Zhuang, D.; Zhang, J.; Duan, S.; Zhou, W. Positive association between− 1021TT genotype of dopamine beta hydroxylase gene and progressive behavior of injection heroin users. Neurosci. Lett. 2013, 541, 258–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lusher, J.; Chandler, C.; Ball, D. Dopamine D4 receptor gene (DRD4) is associated with Novelty Seeking (NS) and substance abuse: The saga continues. Mol. Psychiatry 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schinka, J.; Letsch, E.; Crawford, F. DRD4 and novelty seeking: Results of meta-analyses. Am. J. Med. Genet. 2002, 114, 643–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergen, A.; Kokoszka, J.; Peterson, R.; Long, J.; Virkkunen, M.; Linnoila, M.; Goldman, D. Mu opioid receptor gene variants: Lack of association with alcohol dependence. Mol. Psychiatry 1996, 2, 490–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garriock, H.A.; Tanowitz, M.; Kraft, J.B.; Dang, V.C.; Peters, E.J.; Jenkins, G.D.; Reinalda, M.S.; McGrath, P.J.; von Zastrow, M.; Slager, S.L. Association of mu-opioid receptor variants and response to citalopram treatment in major depressive disorder. Am. J. Psychiatry 2010, 167, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haerian, B.S.; Haerian, M.S. OPRM1 rs1799971 polymorphism and opioid dependence: Evidence from a meta-analysis. Pharmacogenomics 2013, 14, 813–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudbridge, F. Power and predictive accuracy of polygenic risk scores. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, S.M.; Wray, N.R.; Stone, J.L.; Visscher, P.M.; O’Donovan, M.C.; Sullivan, P.F.; Sklar, P. Common polygenic variation contributes to risk of schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Nature 2009, 460, 748–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Multiple Sclerosis Genetics Consortium. Evidence for polygenic susceptibility to multiple sclerosis—The shape of things to come. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2010, 86, 621–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonson, M.A.; Wills, A.G.; Keller, M.C.; McQueen, M.B. Recent methods for polygenic analysis of genome-wide data implicate an important effect of common variants on cardiovascular disease risk. BMC Med. Genet. 2011, 12, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stahl, E.A.; Wegmann, D.; Trynka, G.; Gutierrez-Achury, J.; Do, R.; Voight, B.F.; Kraft, P.; Chen, R.; Kallberg, H.J.; Kurreeman, F.A. Bayesian inference analyses of the polygenic architecture of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-C.; Sheng, J.; Trang, P.; Liu, F. Potential application of the CRISPR/Cas9 system against herpesvirus infections. Viruses 2018, 10, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-C. Introductory Chapter: Gene Editing Technologies and Applications. In Gene Editing-Technologies and Applications; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Homberg, J.R.; Wöhr, M.; Alenina, N. Comeback of the rat in biomedical research. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2017, 8, 900–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bäck, S.; Necarsulmer, J.; Whitaker, L.R.; Coke, L.M.; Koivula, P.; Heathward, E.J.; Fortuno, L.V.; Zhang, Y.; Yeh, C.G.; Baldwin, H.A. Neuron-specific genome modification in the adult rat brain using CRISPR-Cas9 transgenic rats. Neuron 2019, 102, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Q.; Liu, Y.-Z.; Zhu, Y.-B.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Li, Q.; Yin, D.-M. Genetic labeling reveals temporal and spatial expression pattern of D2 dopamine receptor in rat forebrain. Brain Struct. Funct. 2019, 224, 1035–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zallar, L.; Tunstall, B.; Richie, C.; Zhang, Y.; You, Z.; Gardner, E.; Heilig, M.; Pickel, J.; Koob, G.; Vendruscolo, L. Development and initial characterization of a novel ghrelin receptor CRISPR/Cas9 knockout wistar rat model. Int. J. Obes. 2019, 43, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Kong, Q.; Yue, J.; Gou, X.; Xu, M.; Wu, X. Genome-edited skin epidermal stem cells protect mice from cocaine-seeking behaviour and cocaine overdose. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 3, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulligan, M.K.; Abreo, T.J.; Neuner, S.M.; Parks, C.L.; Watkins, C.E.; Houseal, M.T.; Shapaker, T.; Hook, M.; Tan, H.; Wang, X. Identification of a functional non-coding variant in the GABAA Receptor α2 subunit of the C57BL/6J mouse reference genome: Major implications for neuroscience research. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komor, A.C.; Badran, A.H.; Liu, D.R. CRISPR-based technologies for the manipulation of eukaryotic genomes. Cell 2017, 168, 20–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaudelli, N.M.; Komor, A.C.; Rees, H.A.; Packer, M.S.; Badran, A.H.; Bryson, D.I.; Liu, D.R. Programmable base editing of A• T to G• C in genomic DNA without DNA cleavage. Nature 2017, 551, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haapaniemi, E.; Botla, S.; Persson, J.; Schmierer, B.; Taipale, J. CRISPR–Cas9 genome editing induces a p53-mediated DNA damage response. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ihry, R.J.; Worringer, K.A.; Salick, M.R.; Frias, E.; Ho, D.; Theriault, K.; Kommineni, S.; Chen, J.; Sondey, M.; Ye, C. p53 inhibits CRISPR–Cas9 engineering in human pluripotent stem cells. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brokowski, C.; Adli, M. CRISPR ethics: Moral considerations for applications of a powerful tool. J. Mol. Biol. 2019, 431, 88–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J. The birth of CRISPR Inc. Science 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contreras, J.L.; Sherkow, J.S. CRISPR, surrogate licensing, and scientific discovery. Science 2017, 355, 698–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abubakar, I.; Tillmann, T.; Banerjee, A. Global, regional, and national age-sex specific all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 240 causes of death, 1990–2013: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet 2015, 385, 117–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birnbaum, H.G.; White, A.G.; Schiller, M.; Waldman, T.; Cleveland, J.M.; Roland, C.L. Societal costs of prescription opioid abuse, dependence, and misuse in the United States. Pain Med. 2011, 12, 657–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merikangas, K.R.; McClair, V.L. Epidemiology of substance use disorders. Hum. Genet. 2012, 131, 779–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reginsson, G.W.; Ingason, A.; Euesden, J.; Bjornsdottir, G.; Olafsson, S.; Sigurdsson, E.; Oskarsson, H.; Tyrfingsson, T.; Runarsdottir, V.; Hansdottir, I. Polygenic risk scores for schizophrenia and bipolar disorder associate with addiction. Addict. Biol. 2018, 23, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohn, T.T.; Kim, N.; Isho, N.F.; Mack, J.M. The potential of CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing as a treatment strategy for Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimer Dis. Parkinsonism 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Gene | Protein | System/Function | Chromosomal Location | Associated SNP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OPRM1 | µ opioid receptor | Opioid | 6q24-25 | rs1799971 |
| OPRK1 | κ opioid receptor | Opioid | 8q11.2 | rs963549 rs1051660 |
| DRD4 | Dopamine receptor D4 | Dopaminergic | 11q15.5 | rs1800955, rs747302, rs936462 |
| TPH2 | Tryptophan hydroxylase 2 | Serotonergic | 12q.21.1 | rs4290270 rs7963720 |
| HTR1B | Serotonin receptor 1B | Serotonergic | 6q13 | rs130058 rs11568817 |
| SLC6A4 | Serotonin transporter | Serotonergic | 17q11.1-q12 | |
| COMT | Catechol-O-methyl transferase | Catecholaminergic | 22q11.2 | rs4680 |
| CYP2D6 | Cytochrome CYP450 | Drug metabolism | 22q13.1 |
| Challenge | Issue |
|---|---|
| Technique | Nonspecific target and cleavage (off target) Localization of function with the availability of NGG sequence Difficulty in the selection of delivery tools |
| Safety | Gene mutation caused by off target effects Tumorigenesis induced by p53 gene suppression Possible insertion of foreign genes into self-body |
| Ethics | Complexity of risk assessment Imbalance between public interests and private interests Commercialization of therapeutics in humans Random manipulation of germline genes |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.-C.; Chen, Y.-C.; Lee, C.-H.; Cheng, C.-M. Opioid Addiction, Genetic Susceptibility, and Medical Treatments: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4294. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20174294
Wang S-C, Chen Y-C, Lee C-H, Cheng C-M. Opioid Addiction, Genetic Susceptibility, and Medical Treatments: A Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(17):4294. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20174294
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Shao-Cheng, Yuan-Chuan Chen, Chun-Hung Lee, and Ching-Ming Cheng. 2019. "Opioid Addiction, Genetic Susceptibility, and Medical Treatments: A Review" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 17: 4294. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20174294
APA StyleWang, S.-C., Chen, Y.-C., Lee, C.-H., & Cheng, C.-M. (2019). Opioid Addiction, Genetic Susceptibility, and Medical Treatments: A Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(17), 4294. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20174294






