Long-Term Vemurafenib Exposure Induced Alterations of Cell Phenotypes in Melanoma: Increased Cell Migration and Its Association with EGFR Expression
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
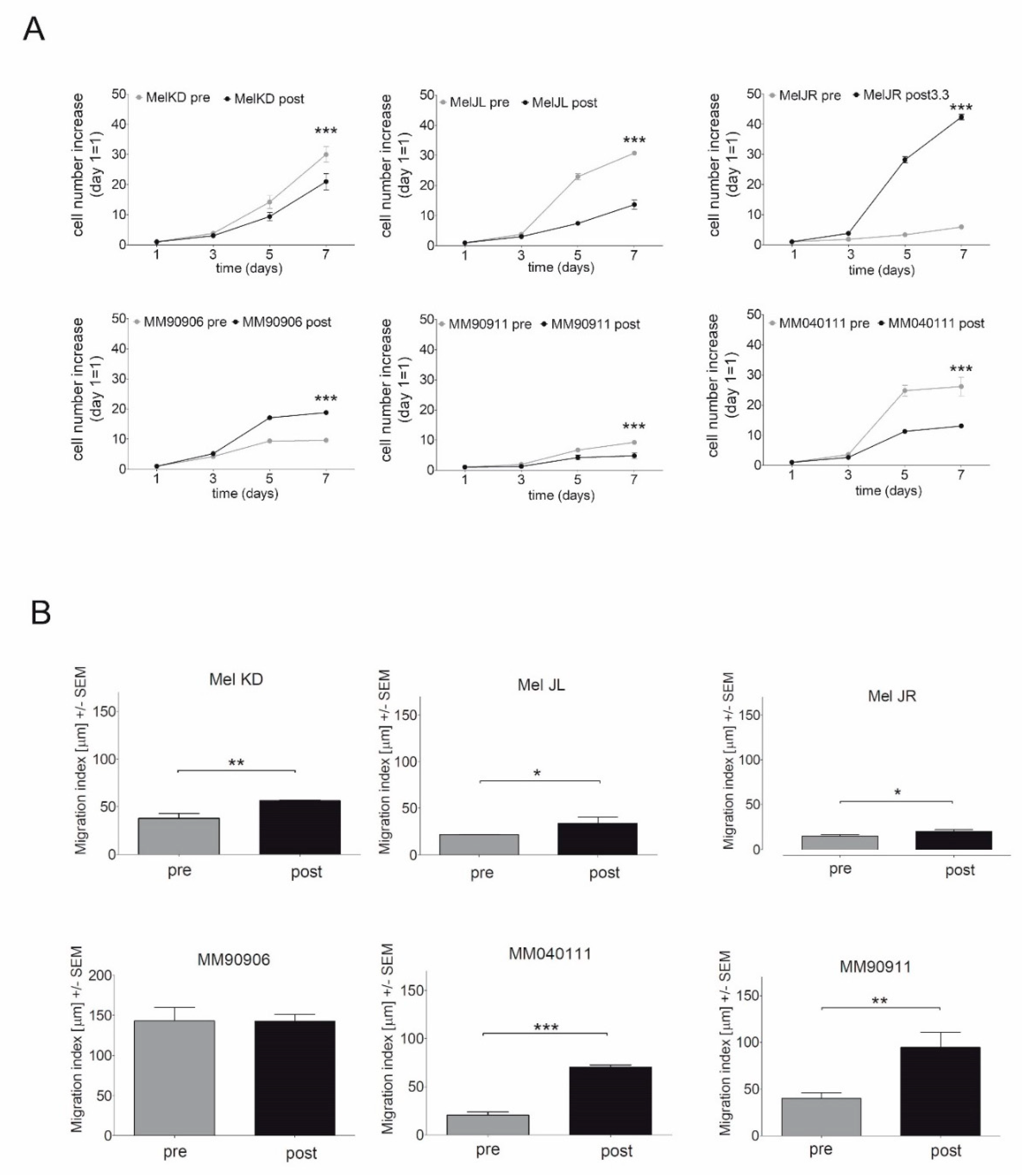
2.1. Proliferation and Migration of the Melanoma Cell Line Pairs
2.2. Evaluation of EMT Marker Expression by q-RT-PCR
2.3. Signaling Pathway Activation and EGFR, PTEN, MITF, FRA-1, and PD-L1 Expression of the Cell Line Pairs
2.4. High-EGFR-Expressing Cells Are More Resistant to Erlotinib Treatment
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Lines and Reagents
4.2. Cell Proliferation Assay
4.3. Time-Lapse Microscopy
4.4. Gene Expression Analysis
4.5. Immunoblot
4.6. Statistics
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Corrie, P.; Hategan, M.; Fife, K.; Parkinson, C. Management of melanoma. Br. Med. Bull. 2014, 111, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.B.; Sosman, J.A. Therapeutic advances and treatment options in metastatic melanoma. JAMA Oncol. 2015, 1, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpe, V.O.; Klufas, D.M.; Hegde, U.; Grant-Kels, J.M. The new paradigm of systemic therapies for metastatic melanoma. J. Am. Acad. Derm. 2017, 77, 356–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dummer, R.; Ascierto, P.A.; Gogas, H.J.; Arance, A.; Mandala, M.; Liszkay, G.; Garbe, C.; Schadendorf, D.; Krajsova, I.; Gutzmer, R.; et al. Overall survival in patients with BRAF-mutant melanoma receiving encorafenib plus binimetinib versus vemurafenib or encorafenib (COLUMBUS): A multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 1315–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, C.; Karaszewska, B.; Schachter, J.; Rutkowski, P.; Mackiewicz, A.; Stroiakovski, D.; Lichinitser, M.; Dummer, R.; Grange, F.; Mortier, L.; et al. Improved overall survival in melanoma with combined dabrafenib and trametinib. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzies, A.M.; Long, G.V. Systemic treatment for BRAF-mutant melanoma: Where do we go next? Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, e371–e381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girotti, M.R.; Pedersen, M.; Sanchez-Laorden, B.; Viros, A.; Turajlic, S.; Niculescu-Duvaz, D.; Zambon, A.; Sinclair, J.; Hayes, A.; Gore, M.; et al. Inhibiting EGF receptor or SRC family kinase signaling overcomes BRAF inhibitor resistance in melanoma. Cancer Discov. 2013, 3, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Huang, S.K.; Marzese, D.M.; Hsu, S.C.; Kawas, N.P.; Chong, K.K.; Long, G.V.; Menzies, A.M.; Scolyer, R.A.; Izraely, S.; et al. Epigenetic changes of EGFR have an important role in BRAF inhibitor-resistant cutaneous melanomas. J. Investig. Derm. 2015, 135, 532–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glitza, I.C.; Davies, M.A. Genotyping of cutaneous melanoma. Chin. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 3, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paraiso, K.H.; Xiang, Y.; Rebecca, V.W.; Abel, E.V.; Chen, Y.A.; Munko, A.C.; Wood, E.; Fedorenko, I.V.; Sondak, V.K.; Anderson, A.R.; et al. PTEN loss confers BRAF inhibitor resistance to melanoma cells through the suppression of BIM expression. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 2750–2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizos, H.; Menzies, A.M.; Pupo, G.M.; Carlino, M.S.; Fung, C.; Hyman, J.; Haydu, L.E.; Mijatov, B.; Becker, T.M.; Boyd, S.C.; et al. BRAF inhibitor resistance mechanisms in metastatic melanoma: Spectrum and clinical impact. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 1965–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villanueva, J.; Vultur, A.; Lee, J.T.; Somasundaram, R.; Fukunaga-Kalabis, M.; Cipolla, A.K.; Wubbenhorst, B.; Xu, X.; Gimotty, P.A.; Kee, D.; et al. Acquired resistance to BRAF inhibitors mediated by a RAF kinase switch in melanoma can be overcome by cotargeting MEK and IGF-1R/PI3K. Cancer Cell 2010, 18, 683–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagle, N.; Emery, C.; Berger, M.F.; Davis, M.J.; Sawyer, A.; Pochanard, P.; Kehoe, S.M.; Johannessen, C.M.; Macconaill, L.E.; Hahn, W.C.; et al. Dissecting therapeutic resistance to RAF inhibition in melanoma by tumor genomic profiling. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 3085–3096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagle, N.; Van Allen, E.M.; Treacy, D.J.; Frederick, D.T.; Cooper, Z.A.; Taylor-Weiner, A.; Rosenberg, M.; Goetz, E.M.; Sullivan, R.J.; Farlow, D.N.; et al. MAP kinase pathway alterations in BRAF-mutant melanoma patients with acquired resistance to combined RAF/MEK inhibition. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, H.; Kong, X.; Ribas, A.; Lo, R.S. Combinatorial treatments that overcome PDGFRbeta-driven resistance of melanoma cells to V600EB-RAF inhibition. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 5067–5074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Audrito, V.; Serra, S.; Stingi, A.; Orso, F.; Gaudino, F.; Bologna, C.; Neri, F.; Garaffo, G.; Nassini, R.; Baroni, G.; et al. PD-L1 up-regulation in melanoma increases disease aggressiveness and is mediated through miR-17-5p. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 15894–15911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordaro, F.G.; De Presbiteris, A.L.; Camerlingo, R.; Mozzillo, N.; Pirozzi, G.; Cavalcanti, E.; Manca, A.; Palmieri, G.; Cossu, A.; Ciliberto, G.; et al. Phenotype characterization of human melanoma cells resistant to dabrafenib. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 38, 2741–2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.Z.; Dhillon, A.S.; Anderson, R.L.; McArthur, G.; Ferrao, P.T. Phenotype switching in melanoma: Implications for progression and therapy. Front. Oncol. 2015, 5, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulitschke, V.; Berger, W.; Paulitschke, P.; Hofstatter, E.; Knapp, B.; Dingelmaier-Hovorka, R.; Fodinger, D.; Jager, W.; Szekeres, T.; Meshcheryakova, A.; et al. Vemurafenib resistance signature by proteome analysis offers new strategies and rational therapeutic concepts. Mol. Cancer 2015, 14, 757–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearlman, R.L.; Montes de Oca, M.K.; Pal, H.C.; Afaq, F. Potential therapeutic targets of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in melanoma. Cancer Lett. 2017, 391, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paluncic, J.; Kovacevic, Z.; Jansson, P.J.; Kalinowski, D.; Merlot, A.M.; Huang, M.L.; Lok, H.C.; Sahni, S.; Lane, D.J.; Richardson, D.R. Roads to melanoma: Key pathways and emerging players in melanoma progression and oncogenic signaling. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1863, 770–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tulchinsky, E.; Pringle, J.H.; Caramel, J.; Ansieau, S. Plasticity of melanoma and EMT-TF reprogramming. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyd, S.C.; Mijatov, B.; Pupo, G.M.; Tran, S.L.; Gowrishankar, K.; Shaw, H.M.; Goding, C.R.; Scolyer, R.A.; Mann, G.J.; Kefford, R.F.; et al. Oncogenic B-RAF(V600E) signaling induces the T-Box3 transcriptional repressor to repress E-cadherin and enhance melanoma cell invasion. J. Investig. Derm. 2013, 133, 1269–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, M.B.; Abel, E.V.; Mayberry, M.M.; Basile, K.J.; Berger, A.C.; Aplin, A.E. TWIST1 is an ERK1/2 effector that promotes invasion and regulates MMP-1 expression in human melanoma cells. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 6382–6392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartman, M.L.; Czyz, M. MITF in melanoma: Mechanisms behind its expression and activity. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2015, 72, 1249–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donia, M.; Fagone, P.; Nicoletti, F.; Andersen, R.S.; Høgdall, E.; Straten, P.T.; Andersen, M.H.; Svane, I.M. BRAF inhibition improves tumor recognition by the immune system: Potential implications for combinatorial therapies against melanoma involving adoptive T-cell transfer. Oncoimmunology 2012, 1, 1476–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, F.; Jiang, C.C.; Farrelly, M.L.; Zhang, X.D.; Hersey, P. Evidence for upregulation of Bim and the splicing factor SRp55 in melanoma cells from patients treated with selective BRAF inhibitors. Melanoma Res. 2012, 22, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, J.; Krijgsman, O.; Tsoi, J.; Robert, L.; Hugo, W.; Song, C.; Kong, X.; Possik, P.A.; Cornelissen-Steijger, P.D.; Geukes Foppen, M.H.; et al. Low MITF/AXL ratio predicts early resistance to multiple targeted drugs in melanoma. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eccles, M.R.; He, S.; Ahn, A.; Slobbe, L.J.; Jeffs, A.R.; Yoon, H.S.; Baguley, B.C. MITF and PAX3 Play Distinct Roles in Melanoma Cell Migration; Outline of a “Genetic Switch” Theory Involving MITF and PAX3 in Proliferative and Invasive Phenotypes of Melanoma. Front. Oncol. 2013, 3, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnarsdóttir, M.; Ponten, F.; Garmo, H.; Wagenius, G.; Mucci, L.; Magnusson, K.; Holmberg, L.; Eaker-Fält, S. MITF Expression in Cutaneous Malignant Melanoma. Mol. Biomark. Diagn. 2012, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirsat, N.V.; Shaikh, S.A. Overexpression of the immediate early gene fra-1 inhibits proliferation, induces apoptosis, and reduces tumourigenicity of c6 glioma cells. Exp. Cell Res. 2003, 291, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belguise, K.; Kersual, N.; Galtier, F.; Chalbos, D. FRA-1 expression level regulates proliferation and invasiveness of breast cancer cells. Oncogene 2005, 24, 1434–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernards, R. A price to pay for tumor regression. Cell Res. 2015, 25, 763–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Obenauf, A.C.; Zou, Y.; Ji, A.L.; Vanharanta, S.; Shu, W.; Shi, H.; Kong, X.; Bosenberg, M.C.; Wiesner, T.; Rosen, N.; et al. Therapy-induced tumour secretomes promote resistance and tumour progression. Nature 2015, 520, 368–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prahallad, A.; Sun, C.; Huang, S.; Di Nicolantonio, F.; Salazar, R.; Zecchin, D.; Beijersbergen, R.L.; Bardelli, A.; Bernards, R. Unresponsiveness of colon cancer to BRAF(V600E) inhibition through feedback activation of EGFR. Nature 2012, 483, 100–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Wang, L.; Huang, S.; Heynen, G.J.; Prahallad, A.; Robert, C.; Haanen, J.; Blank, C.; Wesseling, J.; Willems, S.M.; et al. Reversible and adaptive resistance to BRAF(V600E) inhibition in melanoma. Nature 2014, 508, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szasz, I.; Koroknai, V.; Kiss, T.; Vizkeleti, L.; Adany, R.; Balazs, M. Molecular alterations associated with acquired resistance to BRAFV600E targeted therapy in melanoma cells. Melanoma Res. 2019, 29, 390–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inno, A.; Di Noia, V.; Martini, M.; D’Argento, E.; Di Salvatore, M.; Arena, V.; Schinzari, G.; Orlandi, A.; Larocca, L.M.; Cassano, A.; et al. Erlotinib for Patients with EGFR Wild-Type Metastatic NSCLC: A Retrospective Biomarkers Analysis. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2019, 25, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, K.Y.; Shia, J.; Kemeny, N.E.; Shah, M.; Schwartz, G.K.; Tse, A.; Hamilton, A.; Pan, D.; Schrag, D.; Schwartz, L.; et al. Cetuximab shows activity in colorectal cancer patients with tumors that do not express the epidermal growth factor receptor by immunohistochemistry. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 1803–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlyarik, A.; Piurko, V.; Vizkeleti, L.; Papai, Z.; Raso, E.; Lahm, E.; Kiss, E.; Sikter, M.; Vachaja, J.; Kenessey, I.; et al. EGFR Protein Expression of KRAS Wild-Type Colorectal Cancer: Predictive Value of the Sidedness for Efficacy of Anti-EGFR Therapy. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2019, 2019, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcoran, R.B.; Andre, T.; Atreya, C.E.; Schellens, J.H.M.; Yoshino, T.; Bendell, J.C.; Hollebecque, A.; McRee, A.J.; Siena, S.; Middleton, G.; et al. Combined BRAF, EGFR, and MEK Inhibition in Patients with BRAF(V600E)-Mutant Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2018, 8, 428–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Cutsem, E.; Huijberts, S.; Grothey, A.; Yaeger, R.; Cuyle, P.-J.; Elez, E.; Fakih, M.; Montagut, C.; Peeters, M.; Yoshino, T.; et al. Binimetinib, Encorafenib, and Cetuximab Triplet Therapy for Patients With BRAF V600E–Mutant Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: Safety Lead-In Results From the Phase III BEACON Colorectal Cancer Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 1460–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenessey, I.; Kramer, Z.; Istvan, L.; Cserepes, M.T.; Garay, T.; Hegedus, B.; Dobos, J.; Timar, J.; Tovari, J. Inhibition of epidermal growth factor receptor improves antitumor efficacy of vemurafenib in BRAF-mutant human melanoma in preclinical model. Melanoma Res. 2018, 28, 536–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbay, E.A.; Koyama, S.; Carretero, J.; Altabef, A.; Tchaicha, J.H.; Christensen, C.L.; Mikse, O.R.; Cherniack, A.D.; Beauchamp, E.M.; Pugh, T.J.; et al. Activation of the PD-1 pathway contributes to immune escape in EGFR-driven lung tumors. Cancer Discov. 2013, 3, 1355–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Vanderbilt, C.M.; Cotzia, P.; Arias Stella, J.A., 3rd; Chang, J.C.; Chen, Y.; Tang, L.H.; DeLair, D.F.; Yao, J.; Ladanyi, M.; et al. JAK2, PD-L1, and PD-L2 (9p24.1) amplification in metastatic mucosal and cutaneous melanomas with durable response to immunotherapy. Hum. Pathol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koopmans, I.; Hendriks, D.; Samplonius, D.F.; van Ginkel, R.J.; Heskamp, S.; Wierstra, P.J.; Bremer, E.; Helfrich, W. A novel bispecific antibody for EGFR-directed blockade of the PD-1/PD-L1 immune checkpoint. Oncoimmunology 2018, 7, e1466016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richman, S.D.; Seymour, M.T.; Chambers, P.; Elliott, F.; Daly, C.L.; Meade, A.M.; Taylor, G.; Barrett, J.H.; Quirke, P. KRAS and BRAF Mutations in Advanced Colorectal Cancer Are Associated With Poor Prognosis but Do Not Preclude Benefit From Oxaliplatin or Irinotecan: Results From the MRC FOCUS Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 5931–5937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garay, T.; Juhasz, E.; Molnar, E.; Eisenbauer, M.; Czirok, A.; Dekan, B.; Laszlo, V.; Hoda, M.A.; Dome, B.; Timar, J.; et al. Cell migration or cytokinesis and proliferation?—Revisiting the “go or grow” hypothesis in cancer cells in vitro. Exp. Cell Res. 2013, 319, 3094–3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of Image Analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Cell Line | Pre-TX IC50 [µM] | Post-TX IC50 [µM] | Sex | Age | Response to Vemurafenib | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mel KD | 6.7 | 18.6 | M | 35 | PR | Patient 1 in [27] |
| Mel JL | 14.2 | 16.5 | F | 53 | PR | Patient 4 in [27] |
| Mel JR | 1 | 7.1 | F | 54 | PR | Patient 3 in [27] |
| MM90906 | 8.8 | 14.8 | M | 36 | n.a. | Patient 5 in [26] |
| MM90911 | 1.5 | 37.1 | M | 41 | n.a. | Patient 4 in [26] |
| MM040111 | 0.7 | 3.5 | F | 78 | n.a. | Patient 3 in [26] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Molnár, E.; Garay, T.; Donia, M.; Baranyi, M.; Rittler, D.; Berger, W.; Tímár, J.; Grusch, M.; Hegedűs, B. Long-Term Vemurafenib Exposure Induced Alterations of Cell Phenotypes in Melanoma: Increased Cell Migration and Its Association with EGFR Expression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4484. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20184484
Molnár E, Garay T, Donia M, Baranyi M, Rittler D, Berger W, Tímár J, Grusch M, Hegedűs B. Long-Term Vemurafenib Exposure Induced Alterations of Cell Phenotypes in Melanoma: Increased Cell Migration and Its Association with EGFR Expression. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(18):4484. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20184484
Chicago/Turabian StyleMolnár, Eszter, Tamás Garay, Marco Donia, Marcell Baranyi, Dominika Rittler, Walter Berger, József Tímár, Michael Grusch, and Balázs Hegedűs. 2019. "Long-Term Vemurafenib Exposure Induced Alterations of Cell Phenotypes in Melanoma: Increased Cell Migration and Its Association with EGFR Expression" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 18: 4484. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20184484
APA StyleMolnár, E., Garay, T., Donia, M., Baranyi, M., Rittler, D., Berger, W., Tímár, J., Grusch, M., & Hegedűs, B. (2019). Long-Term Vemurafenib Exposure Induced Alterations of Cell Phenotypes in Melanoma: Increased Cell Migration and Its Association with EGFR Expression. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(18), 4484. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20184484








