Recurrent Stimulation of Natural Killer Cell Clones with K562 Expressing Membrane-Bound Interleukin-21 Affects Their Phenotype, Interferon-γ Production, and Lifespan
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. NK Cell Cloning Conditions
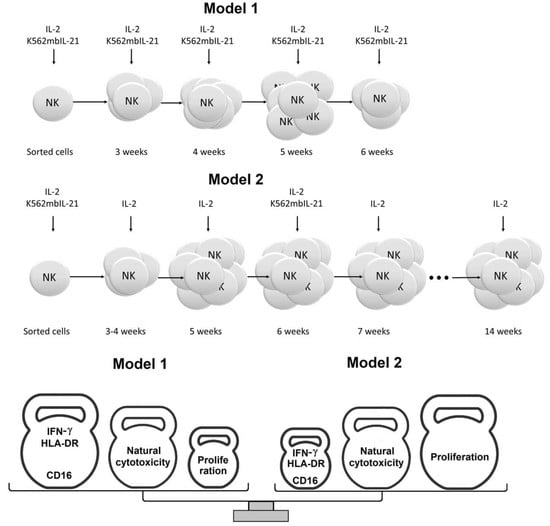
2.2. Restimulation Frequency Affects NK Cell Clones Lifespan, Phenotype, and Functional State
2.3. Changes in Certain Clone Characteristics are Associated with the Addition of Feeder Cells
2.4. Long-Lived NK Cell Clones Obtained Using Model 2 were Capable of Natural Cytotoxicity
2.5. Freezing NK Cell Clones Retains Their Functional Potential
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Cell Lines
4.2. NK Cell Isolation
4.3. Preparation of Plates with Feeder Cells for Cell Sorting
4.4. Fluorescence-Activated Single Cell Sorting and Generation of NK Cell Clones
4.5. Cultivation of NK Cell Clones
4.5.1. Model 1
4.5.2. Model 2
4.6. Estimation of NK Cell Clone Generation Frequency and Lifespan
4.7. Surface Fluorescent Immunostaining and Flow Cytometry
4.8. Natural Cytotoxicity Evaluation
4.8.1. Registration of Caspase-6 Activity in Target Cells
4.8.2. Registration of NK Cell Degranulation by CD107a Expression
4.9. Antibody-Dependent Cytotoxicity Evaluation
4.10. Analysis of IFN-γ Production Assessment
4.10.1. ELISA
4.10.2. Intracellular Staining
4.11. Intracellular Granzyme B Evaluation
4.12. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IFN-γ | interferon-γ |
| IL | interleukin |
| K562-mbIL21 | gene-modified K562 cells expressing membrane-bound IL-21 |
| NK cells | natural killer cells |
| PBMC | peripheral blood mononuclear cells |
References
- Bjorkstrom, N.K.; Riese, P.; Heuts, F.; Andersson, S.; Fauriat, C.; Ivarsson, M.A.; Bjorklund, A.T.; Flodstrom-Tullberg, M.; Michaelsson, J.; Rottenberg, M.E.; et al. Expression patterns of NKG2A, KIR, and CD57 define a process of CD56dim NK-cell differentiation uncoupled from NK-cell education. Blood 2010, 116, 3853–3864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Long, E.O.; Kim, H.S.; Liu, D.; Peterson, M.E.; Rajagopalan, S. Controlling natural killer cell responses: Integration of signals for activation and inhibition. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 31, 227–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovalenko, E.I.; Streltsova, M.A. Adaptive Features of Natural Killer Cells—Lymphocytes of Innate Immunity. Russ. J. Bioorg. Chem. 2016, 42, 649–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guma, M.; Angulo, A.; Vilches, C.; Gomez-Lozano, N.; Malats, N.; Lopez-Botet, M. Imprint of human cytomegalovirus infection on the NK cell receptor repertoire. Blood 2004, 104, 3664–3671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pérez-Villar, J.J.; Melero, I.; Rodríguez, A.; Carretero, M.; Aramburu, J.; Sivori, S.; Orengo, A.M.; Moretta, A.; López-Botet, M. Functional ambivalence of the Kp43 (CD94) NK cell-associated surface antigen. J. Immunol. 1995, 154, 5779–5788. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sobanov, Y.; Brostjan, C.; Bello, T.; Lo, M. Differential expression of inhibitory and activating CD94/NKG2 receptors on NK cell clones. J. Immunol. Methods 2002, 264, 109–119. [Google Scholar]
- Ruggeri, L.; Capanni, M.; Casucci, M.; Volpi, I.; Tosti, A.; Perruccio, K.; Urbani, E.; Negrin, R.S.; Martelli, M.F.; Velardi, A. Role of natural killer cell alloreactivity in HLA-mismatched hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Blood 1999, 94, 333–339. [Google Scholar]
- Feuchtinger, T.; Pfeiffer, M.; Pfaffle, A.; Teltschik, H.-M.; Wernet, D.; Schumm, M.; Lotfi, R.; Handgretinger, R.; Lang, P. Cytolytic activity of NK cell clones against acute childhood precursor-B-cell leukaemia is influenced by HLA class I expression on blasts and the differential KIR phenotype of NK clones. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2009, 43, 875–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmidt, R.E.; Hercend, T.; Fox, D.A.; Bensussan, A.; Bartley, G.; Daley, J.F.; Schlossman, S.F.; Reinherz, E.L.; Ritz, J. The role of interleukin 2 and T11 E rosette antigen in activation and proliferation of human NK clones. J. Immunol. 1985, 135, 672–678. [Google Scholar]
- Moretta, A.; Bottino, C.; Pende, D.; Tripodi, G.; Tambussi, G.; Viale, O.; Orengo, A.; Barbaresi, M.; Merli, A.; Ciccone, E. Identification of four subsets of human CD3-CD16+ natural killer (NK) cells by the expression of clonally distributed functional surface molecules: Correlation between subset assignment of NK clones and ability to mediate specific alloantigen recognition. J. Exp. Med. 1990, 172, 1589–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferlazzo, G.; Tsang, M.L.; Moretta, L.; Melioli, G.; Steinman, R.M.; Münz, C. Human dendritic cells activate resting natural killer (NK) cells and are recognized via the NKp30 receptor by activated NK cells. J. Exp. Med. 2002, 195, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semino, C.; Ceccarelli, J.; Lotti, L.V.; Torrisi, M.R.; Angelini, G.; Rubartelli, A. The maturation potential of NK cell clones toward autologous dendritic cells correlates with HMGB1 secretion. J. Leuk. Biol. 2007, 81, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cella, M.; Colonna, M. Cloning human natural killer cells. Methods Mol. Biol. 2000, 121, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litwin, V.; Gumperz, J.; Parham, P.; Phillips, J.H.; Lanier, L.L. Specificity of HLA class I antigen recognition by human NK clones: Evidence for clonal heterogeneity, protection by self and non-self alleles, and influence of the target cell type. J. Exp. Med. 1993, 178, 1321–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, J.H.; Chang, C.; Mattson, J.; Gumperz, J.E.; Parham, P.; Lanier, L.L. CD94 and a novel associated protein (94AP) form a NK cell receptor involved in the recognition of HLA-A, HLA-B, and HLA-C allotypes. Immunity 1996, 5, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spits, H.; Yssel, H. Cloning of human T and natural killer cells. Methods 1996, 9, 416–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carr, W. NK Cell-Mediated Lysis of Autologous HCMV-Infected Skin Fibroblasts Is Highly Variable among NK Cell Clones and Polyclonal NK Cell Lines. Clin. Immunol. 2002, 105, 126–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denman, C.J.; Senyukov, V.V.; Somanchi, S.S.; Phatarpekar, P.V.; Kopp, L.M.; Johnson, J.L.; Singh, H.; Hurton, L.; Maiti, S.N.; Huls, M.H.; et al. Membrane-bound IL-21 promotes sustained Ex Vivo proliferation of human natural killer cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Somanchi, S.S.; Lee, D.A. Ex vivo expansion of human NK cells using K562 engineered to express membrane bound IL21. Methods Mol. Biol. 2016, 1441, 175–193. [Google Scholar]
- Romee, R.; Leong, J.W.; Fehniger, T.A. Utilizing cytokines to function-enable human NK cells for the immunotherapy of cancer. Scientifica 2014, 2014, 205796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dybkaer, K.; Iqbal, J.; Zhou, G.; Geng, H.; Xiao, L.; Schmitz, A.; d’Amore, F.; Chan, W.C. Genome wide transcriptional analysis of resting and IL2 activated human natural killer cells: Gene expression signatures indicative of novel molecular signaling pathways. BMC Genom. 2007, 8, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasaian, M.T.; Whitters, M.J.; Carter, L.L.; Lowe, L.D.; Jussif, J.M.; Deng, B.; Johnson, K.A.; Witek, J.S.; Senices, M.; Konz, R.F.; et al. IL-21 limits NK cell responses and promotes antigen-specific T cell activation: A mediator of the transition from innate to adaptive immunity. Immunity 2002, 16, 559–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erokhina, S.A.; Streltsova, M.A.; Kanevskiy, L.M.; Telford, W.G.; Sapozhnikov, A.M.; Kovalenko, E.I. HLA-DR+ NK cells are mostly characterized by less mature phenotype and high functional activity. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2018, 96, 212–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roda, J.M.; Parihar, R.; Lehman, A.; Mani, A.; Tridandapani, S.; Carson, W.E. Interleukin-21 enhances NK cell activation in response to antibody-coated targets. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croce, M.; Rigo, V.; Ferrini, S. IL-21: A pleiotropic cytokine with potential applications in oncology. J. Immunol. Res. 2015, 2015, 696578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciurea, S.O.; Schafer, J.R.; Bassett, R.; Denman, C.J.; Cao, K.; Willis, D.; Rondon, G.; Chen, J.; Soebbing, D.; Kaur, I.; et al. Phase 1 clinical trial using mbIL21 ex vivo–expanded donor-derived NK cells after haploidentical transplantation. Blood 2017, 130, 1857–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domogala, A.; Madrigal, J.A.; Saudemont, A. Cryopreservation has no effect on function of natural killer cells differentiated in vitro from umbilical cord blood CD34 + cells. Cytotherapy 2016, 18, 754–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dominguez, E.; Lowdell, M.W.; Perez-Cruz, I.; Madrigal, A.; Cohen, S.B. Natural killer cell function is altered by freezing in DMSO. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 1997, 25, 175S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holubova, M.; Miklikova, M.; Leba, M.; Georgiev, D.; Jindra, P.; Caprnda, M.; Ciccocioppo, R.; Kruzliak, P.; Lysak, D. Cryopreserved NK cells in the treatment of haematological malignancies: Preclinical study. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 142, 2561–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, D.-P.; Jang, Y.-Y.; Kim, S.; Koh, S.S.; Lee, J.-J.; Kim, J.-S.; Thi Phan, M.-T.; Shin, D.-J.; Shin, M.-G.; Lee, S.-H.; et al. Effect of exposure to interleukin-21 at various time points on human natural killer cell culture. Cytotherapy 2014, 16, 1419–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benlahrech, A.; Donaghy, H.; Rozis, G.; Goodier, M.; Klavinskis, L.; Gotch, F.; Patterson, S. Human NK Cell up-regulation of CD69, HLA-DR, Interferon γ secretion and cytotoxic activity by plasmacytoid dendritic cells is regulated through overlapping but different pathways. Sensors 2009, 9, 386–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayakawa, K.; Salmeron, M.A.; Kornbluth, J.; Bucana, C.; Itoh, K. The role of IL-4 in proliferation and differentiation of human natural killer cells. Study of an IL-4-dependent versus an IL-2-dependent natural killer cell clone. J. Immunol. 1991, 146, 2453–2460. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fujisaki, H.; Kakuda, H.; Imai, C.; Mullighan, C.; Campana, D. Replicative Potential of Human Natural Killer Cells. Br. J. Haematol. 2009, 145, 606–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapteva, N.; Parihar, R.; Rollins, L.A.; Gee, A.P.; Rooney, C.M. Large-Scale Culture and Genetic Modification of Human Natural Killer Cells for Cellular Therapy. Methods Mol. Biol. 2016, 1441, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wendt, K.; Wilk, E.; Buyny, S.; Schmidt, R.E.; Jacobs, R. Interleukin-21 differentially affects human natural killer cell subsets. Immunology 2007, 122, 486–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melero, I.; Johnston, J.V.; Shufford, W.W.; Mittler, R.S.; Chen, L. NK1.1 cells express 4-1BB (CDw137) costimulatory molecule and are required for tumor immunity elicited by anti-4-1BB monoclonal antibodies. Cell. Immunol. 1998, 190, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parrish-Novak, J.; Dillon, S.R.; Nelson, A.; Hammond, A.; Sprecher, C.; Gross, J.A.; Johnston, J.; Madden, K.; Xu, W.; West, J.; et al. Interleukin 21 and its receptor are involved in NK cell expansion and regulation of lymphocyte function. Nature 2000, 408, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brady, J.; Carotta, S.; Thong, R.P.L.; Chan, C.J.; Hayakawa, Y.; Smyth, M.J.; Nutt, S.L. The interactions of multiple cytokines control NK cell maturation. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 6679–6688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granzin, M.; Stojanovic, A.; Miller, M.; Childs, R.; Huppert, V.; Cerwenka, A. Highly efficient IL-21 and feeder cell-driven ex vivo expansion of human NK cells with therapeutic activity in a xenograft mouse model of melanoma. Oncoimmunology 2016, 5, e1219007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Evans, J.H.; Horowitz, A.; Mehrabi, M.; Wise, E.L.; Pease, J.E.; Riley, E.M.; Davis, D.M. A distinct subset of human NK cells expressing HLA-DR expand in response to IL-2 and can aid immune responses to BCG. Eur. J. Immunol. 2011, 41, 1924–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Loyon, R.; Picard, E.; Mauvais, O.; Queiroz, L.; Mougey, V.; Pallandre, J.-R.; Galaine, J.; Mercier-Letondal, P.; Kellerman, G.; Chaput, N.; et al. IL-21-induced MHC Class II+ NK Cells promote the expansion of human uncommitted CD4+ central memory T cells in a macrophage migration inhibitory factor-dependent manner. J. Immunol. 2016, 197, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skak, K.; Frederiksen, K.S.; Lundsgaard, D. Interleukin-21 activates human natural killer cells and modulates their surface receptor expression. Immunology 2008, 123, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Q.; Ye, L.-J.; Ren, H.-L.; Huyan, T.; Li, J.; Shi, J.-L.; Huang, Q.-S. Multiple effects of IL-21 on human NK cells in ex vivo expansion. Immunobiology 2015, 220, 876–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romee, R.; Schneider, S.E.; Leong, J.W.; Chase, J.M.; Keppel, C.R.; Sullivan, R.P.; Cooper, M.A.; Fehniger, T.A. Cytokine activation induces human memory-like NK cells. Blood 2012, 120, 4751–4760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alter, G.; Malenfant, J.M.; Altfeld, M. CD107a as a functional marker for the identification of natural killer cell activity. J. Immunol. Methods 2004, 294, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanevskiy, L.M.; Erokhina, S.A.; Streltsova, M.A.; Telford, W.G.; Sapozhnikov, A.M.; Kovalenko, E.I. Bacterial lipopolysaccharide activates CD57-negative human NK cells. Biochemistry 2014, 79, 1339–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Model | Survival (Mean ± SD) | Total Cell Number in Well Proliferation Clones (Mean ± SD) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Week 5 | Week 7 | Week 5 (19 Clones) | Week 7 (25 Clones) | Week 12 (10 Clones) | |
| Model 1 (3 collections) | 42% ± 5% | 1.2 × 106 ± 1.14 × 106 | |||
| Model 2 (6 collections) | 30% ± 18% | 2.8 × 106 ± 4.0 × 106 | 3.9 × 106 ± 5.84 × 106 | ||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Streltsova, M.A.; Erokhina, S.A.; Kanevskiy, L.M.; Grechikhina, M.V.; Kobyzeva, P.A.; Lee, D.A.; Telford, W.G.; Sapozhnikov, A.M.; Kovalenko, E.I. Recurrent Stimulation of Natural Killer Cell Clones with K562 Expressing Membrane-Bound Interleukin-21 Affects Their Phenotype, Interferon-γ Production, and Lifespan. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 443. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20020443
Streltsova MA, Erokhina SA, Kanevskiy LM, Grechikhina MV, Kobyzeva PA, Lee DA, Telford WG, Sapozhnikov AM, Kovalenko EI. Recurrent Stimulation of Natural Killer Cell Clones with K562 Expressing Membrane-Bound Interleukin-21 Affects Their Phenotype, Interferon-γ Production, and Lifespan. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(2):443. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20020443
Chicago/Turabian StyleStreltsova, Maria A., Sofya A. Erokhina, Leonid M. Kanevskiy, Maria V. Grechikhina, Polina A. Kobyzeva, Dean A. Lee, William G. Telford, Alexander M. Sapozhnikov, and Elena I. Kovalenko. 2019. "Recurrent Stimulation of Natural Killer Cell Clones with K562 Expressing Membrane-Bound Interleukin-21 Affects Their Phenotype, Interferon-γ Production, and Lifespan" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 2: 443. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20020443
APA StyleStreltsova, M. A., Erokhina, S. A., Kanevskiy, L. M., Grechikhina, M. V., Kobyzeva, P. A., Lee, D. A., Telford, W. G., Sapozhnikov, A. M., & Kovalenko, E. I. (2019). Recurrent Stimulation of Natural Killer Cell Clones with K562 Expressing Membrane-Bound Interleukin-21 Affects Their Phenotype, Interferon-γ Production, and Lifespan. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(2), 443. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20020443