Mechanisms and Functions of Long Non-Coding RNAs at Multiple Regulatory Levels
Abstract
1. Introduction
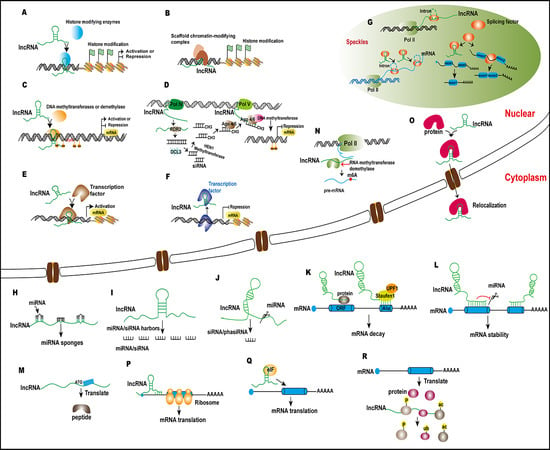
2. lncRNAs Are Involved in Regulating Histone Modifications at the Chromatin Level
2.1. lncRNAs Interact with Histone-Modified Complexes or Enzymes to Regulate Histone Methylation
2.2. lncRNAs Interact with Histone-Modified Complexes or Enzymes to Regulate Histone Acetylation
2.3. lncRNAs Act as Scaffold Regulating Histone Methylation and Acetylation
3. lncRNAs Are Involved in Regulating DNA Methylation at the DNA Level
3.1. lncRNA Are Involved in RdDM
3.2. lncRNAs Regulate DNA Methylation by Interacting with DNA Methyltransferase
4. lncRNAs Involved in the Process of Transcriptional Regulation
4.1. lncRNAs Function in Transcription Activation
4.2. lncRNAs Function in Transcriptional Interference
5. lncRNAs Are Involved in Post-Transcriptional Regulation
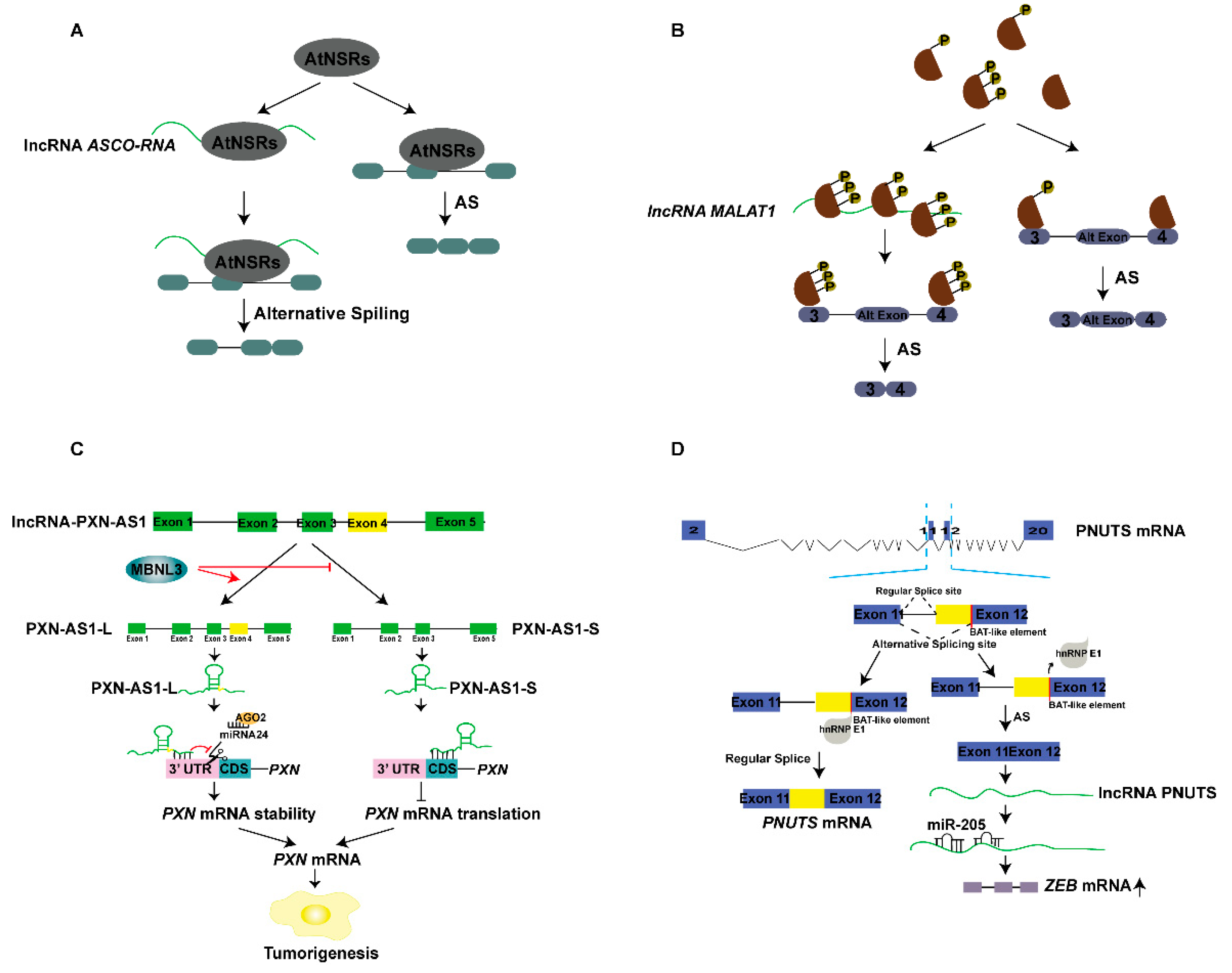
5.1. lncRNAs and Alternative Splicing
5.2. lncRNA, miRNAs, and siRNAs
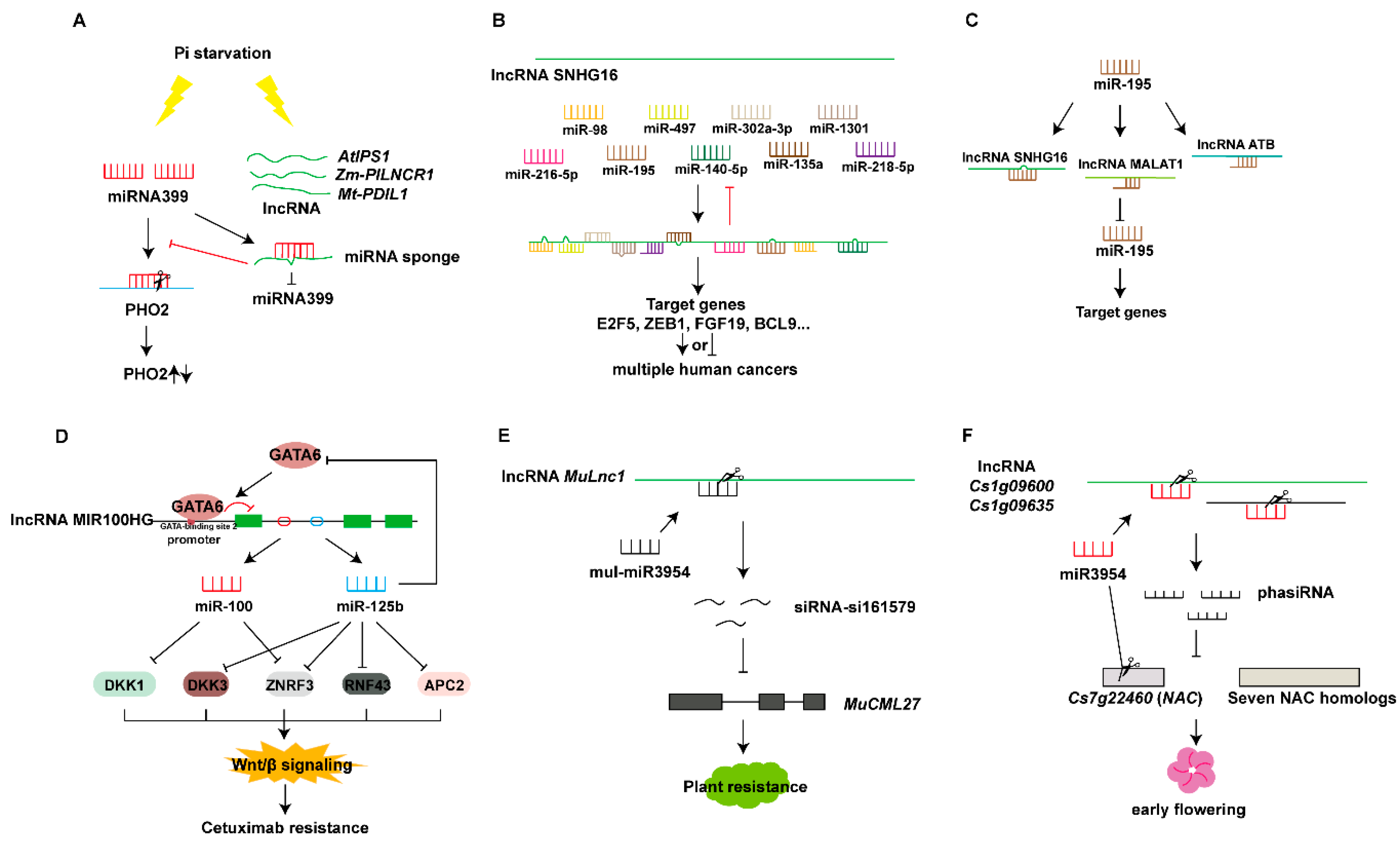
5.2.1. lncRNAs Act as miRNA Sponges
5.2.2. lncRNAs Act as Precursors of miRNAs And siRNAs
5.2.3. miRNAs Target lncRNAs to Produce Small RNAs
5.3. lncRNAs Mediate RNA Decay
5.4. lncRNAs Regulate RNA Stability
5.5. lncRNAs Encode Peptides
5.6. lncRNAs Are Involved in Protein Relocalization
5.7. lncRNAs Regulate RNA Methylation of mRNA
6. lncRNAs Are Involved in Translational Regulation
7. LncRNAs Are Involved in Post-translational Modification
7.1. lncRNAs Are Involved in Regulating Protein Phosphorylation
7.2. lncRNAs Are Involved in Regulating Protein Ubiquitinlation
7.3. lncRNAs Are Involved in Regulating Protein Acetylation
8. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Matzke, M.A.; Mosher, R.A. RNA-directed DNA methylation: An epigenetic pathway of increasing complexity. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2014, 15, 394–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wierzbicki, A.T.; Haag, J.R.; Pikaard, C.S. Noncoding transcription by RNA polymerase pol IVb/Pol V mediates transcriptional silencing of overlapping and adjacent genes. Cell 2008, 135, 635–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derrien, T.; Johnson, R.; Bussotti, G.; Tanzer, A.; Djebali, S.; Tilgner, H.; Guernec, G.; Martin, D.; Merkel, A.; Knowles, D.G.; et al. The GENCODE v7 catalog of human long noncoding RNAs: Analysis of their gene structure, evolution, and expression. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 1775–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafiq, S.; Li, J.; Sun, Q. Functions of plants long non-coding RNAs. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gene Regul. Mech. 2016, 1859, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopp, F.; Mendell, J.T. Functional classification and experimental dissection of long noncoding RNAs. Cell 2018. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, J.B.; Lee, Y.S.; Sung, S. Epigenetic regulation by long noncoding RNAs in plants. Chromosom. Res. 2013, 338, 1435–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vance, K.W.; Ponting, C.P. Transcriptional regulatory functions of nuclear long noncoding RNAs. Trends Genet. 2014, 30, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dykes, I.M.; Emanueli, C. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional gene regulation by long non-coding RNA. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2017, 15, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.A.; Shah, N.; Wang, K.C.; Kim, J.; Horlings, H.M.; Wong, D.J.; Tsai, M.C.; Hung, T.; Argani, P.; Rinn, J.L.; et al. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR reprograms chromatin state to promote cancer metastasis. Nature 2010, 464, 1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilik, I.A.; Quinn, J.J.; Georgiev, P.; Tavares-Cadete, F.; Maticzka, D.; Toscano, S.; Wan, Y.; Spitale, R.C.; Luscombe, N.; Backofen, R.; et al. Tandem stem-loops in roX RNAs act together to mediate X Chromosome dosage compensation in Drosophila. Mol. Cell 2013, 51, 156–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanduri, C. Long noncoding RNAs: Lessons from genomic imprinting. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gene Regul. Mech. 2016, 1859, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, V.; Ellis, J.D.; Shen, Z.; Song, D.Y.; Pan, Q.; Watt, A.T.; Freier, S.M.; Bennett, C.F.; Sharma, A.; Bubulya, P.A.; et al. The nuclear-retained noncoding RNA MALAT1 regulates alternative splicing by modulating SR splicing factor phosphorylation. Mol. Cell 2010, 39, 925–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatica, A.; Bozzoni, I. Long non-coding RNAs: New players in cell differentiation and development. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2014, 15, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitagawa, M.; Kitagawa, K.; Kotake, Y.; Niida, H.; Ohhata, T. Cell cycle regulation by long non-coding RNAs. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2013, 70, 4785–4794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Lu, X.; Yuan, L. LncRNA: A link between RNA and cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gene Regul. Mech. 2014, 1839, 1097–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berry, S.; Dean, C. Environmental perception and epigenetic memory: Mechanistic insight through FLC. Plant J. 2015, 83, 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Fan, X.; Lin, F.; He, G.; Terzaghi, W.; Zhu, D.; Deng, X.W. Arabidopsis noncoding RNA mediates control of photomorphogenesis by red light. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 10359–10364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.C.; Liao, J.Y.; Li, Z.Y.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, J.P.; Li, Q.F.; Qu, L.H.; Shu, W.S.; Chen, Y.Q. Genome-wide screening and functional analysis identify a large number of long noncoding RNAs involved in the sexual reproduction of rice. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Luo, X.; Sun, F.; Hu, J.; Zha, X.; Su, W.; Yang, J. Overexpressing lncRNA LAIR increases grain yield and regulates neighbouring gene cluster expression in rice. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouzarides, T. Histone methylation in transcriptional control. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2002, 12, 198–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portela, A.; Esteller, M. Epigenetic modifications and human disease. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 1057–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, J.B.; Sung, S. Vernalization-mediated epigenetic silencing by a long intronic noncoding RNA. Science 2011, 331, 76–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, A.K.; Xi, Y.; McCarthy, R.; Allton, K.; Akdemir, K.C.; Patel, L.R.; Aronow, B.; Lin, C.; Li, W.; Yang, L.; et al. LncPRESS1 Is a p53-Regulated LncRNA that Safeguards Pluripotency by Disrupting SIRT6-Mediated De-acetylation of Histone H3K56. Mol. Cell 2016, 64, 967–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, T.-T.; He, J.; Liang, Q.; Ren, L.-L.; Yan, T.-T.; Yu, T.-C.; Tang, J.-Y.; Bao, Y.-J.; Hu, Y.; Lin, Y.; et al. LncRNA GClnc1 Promotes gastric carcinogenesis and may act as a modular scaffold of WDR5 and KAT2A complexes to specify the histone modification pattern. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, 784–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, R.J.; Nishioka, K.; Reinberg, D. Histone lysine methylation: A signature for chromatin function. Trends Genet. 2003, 19, 629–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trojer, P.; Reinberg, D. Histone lysine demethylases and their impact on epigenetics. Cell 2006, 125, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margueron, R.; Reinberg, D. The Polycomb complex PRC2 and its mark in life. Nature 2011, 469, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Kong, N.C.; Gu, X.; Li, Z.; He, Y. Arabidopsis COMPASS-like complexes mediate histone H3 lysine-4 trimethylation to control floral transition and plant development. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1001330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Xi, Y.; Sung, S. Modular function of long noncoding RNA, COLDAIR, in the vernalization response. PLoS Genet. 2017, 13, e1006939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Li, J.; Lian, B.; Gu, H.; Li, Y.; Qi, Y. Global identification of Arabidopsis lncRNAs reveals the regulation of MAF4 by a natural antisense RNA. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Shan, Y.; Ma, J.; Pan, Y.; Zhou, H.; Jiang, L.; Jia, L. LncRNA ST3Gal6-AS1/ST3Gal6 axis mediates colorectal cancer progression by regulating α-2,3 sialylation via PI3K/Akt signaling. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 145, 450–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Xia, R.; Lu, K.; Xie, M.; Yang, F.; Sun, M.; De, W.; Wang, C.; Ji, G. LincRNAFEZF1-AS1 represses p21 expression to promote gastric cancer proliferation through LSD1-Mediated H3K4me2 demethylation. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menzies, K.J.; Zhang, H.; Katsyuba, E.; Auwerx, J. Protein acetylation in metabolism-metabolites and cofactors. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2016, 12, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michishita, E.; McCord, R.A.; Berber, E.; Kioi, M.; Padilla-Nash, H.; Damian, M.; Cheung, P.; Kusumoto, R.; Kawahara, T.L.A.; Barrett, J.C.; et al. SIRT6 is a histone H3 lysine 9 deacetylase that modulates telomeric chromatin. Nature 2008, 452, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercer, T.R.; Dinger, M.E.; Mattick, J.S. Long non-coding RNAs: Insights into functions. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 10, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhmdorfer, G.; Rowley, M.J.; Kuciński, J.; Zhu, Y.; Amies, I.; Wierzbicki, A.T. RNA-directed DNA methylation requires stepwise binding of silencing factors to long non-coding RNA. Plant. J. 2014, 79, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daxinger, L.; Kanno, T.; Bucher, E.; van der Winden, J.; Naumann, U.; Matzke, A.J.M.; Matzke, M. A stepwise pathway for biogenesis of 24-nt secondary siRNAs and spreading of DNA methylation. EMBO J. 2009, 28, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Johansen, L.K.; Gustafson, A.M.; Kasschau, K.D.; Lellis, A.D.; Zilberman, D.; Jacobsen, S.E.; Carrington, J.C. Genetic and Functional Diversification of Small RNA Pathways in Plants. PLoS Biol. 2004, 2, e104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhu, J.-K. RNA-directed DNA methylation. Curr. Opin. Plant. Biol. 2011, 14, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wierzbicki, A.T. The role of long non-coding RNA in transcriptional gene silencing. Curr. Opin. Plant. Biol. 2012, 15, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Amor, B.; Wirth, S.; Merchan, F.; Laporte, P.; d’Aubenton-Carafa, Y.; Hirsch, J.; Maizel, A.; Mallory, A.; Lucas, A.; Deragon, J.M.; et al. Novel long non-protein coding RNAs involved in Arabidopsis differentiation and stress responses. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ariel, F.; Jegu, T.; Latrasse, D.; Romero-Barrios, N.; Christ, A.; Benhamed, M.; Crespi, M. Noncoding transcription by alternative RNA polymerases dynamically regulates an auxin-driven chromatin loop. Mol. Cell 2014, 55, 383–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgia, S.; Kanji, M.; Bhushan, A. DNMT1 represses p53 to maintain progenitor cell survival during pancreatic organogenesis. Genes Dev. 2013, 27, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.; Xiong, Y.; Liao, W.; Meng, L.; Yang, S. Long noncoding RNA ATB participates in the development of renal cell carcinoma by downregulating p53 via binding to DNMT1. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 12910–12917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Hu, X. Downregulated long noncoding RNA LINC00313 inhibits the epithelial–mesenchymal transition, invasion, and migration of thyroid cancer cells through inhibiting the methylation of ALX4. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 20992–21004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Bi, C.; Clark, B.S.; Mady, R.; Shah, P.; Kohtz, J.D. The Evf-2 noncoding RNA is transcribed from the Dlx-5/6 ultraconserved region and functions as a Dlx-2 transcriptional coactivator. Genes Dev. 2006, 20, 1470–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, W.; Li, B.; Chen, P.; Qu, J.; Shi, L.; Zhuang, W.; Fu, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Sun, Y. Activation of LTBP3 gene by a long noncoding RNA (IncRNA) MALAT1 transcript in mesenchymal stem cells from multiple myeloma. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 29365–29375. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, J.S.; Sun, H.-X.; Park, B.S.; Huang, C.-H.; Yeh, S.-D.; Jung, C.; Chua, N.-H. ELF18-induced long-noncoding RNA associates with mediator to enhance expression of innate immune response genes in arabidopsis. Plant. Cell 2017, 29, 1024–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.S.; Diloknawarit, P.; Park, B.S.; Chua, N. ELF18-induced long noncoding RNA 1 evicts fibrillarin from mediator subunit to enhance pathogenesis-related gene 1 (PR1) expression. New Phytol. 2019, 221, 2067–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Yan, X.; Wu, D.; Yang, Y.; Li, M.; Su, Y.; Yang, W.; Shan, Z.; Gao, Y.; Jin, Z. High expression of Ras-related protein 1A promotes an aggressive phenotype in colorectal cancer via PTEN/FOXO3/CCND1 pathway. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 1, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, B.; Kong, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, K.; Yang, X.; Zhai, J.; Gao, R.; Qi, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; et al. LINC01355 suppresses breast cancer growth through FOXO3-mediated transcriptional repression of CCND1. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina, J.; Catalá, R.; Salinas, J. The CBFs: Three arabidopsis transcription factors to cold acclimate. Plant. Sci. 2011, 180, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kindgren, P.; Ard, R.; Ivanov, M.; Marquardt, S. Transcriptional read-through of the long non-coding RNA SVALKA governs plant cold acclimation. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keren, H.; Lev-Maor, G.; Ast, G. Alternative splicing and evolution: Diversification, exon definition and function. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2010, 11, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erkelenz, S.; Mueller, W.F.; Evans, M.S.; Busch, A.; Schöneweis, K.; Hertel, K.J.; Schaal, H. Position-dependent splicing activation and repression by SR and hnRNP proteins rely on common mechanisms. RNA 2013, 19, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, D.; Qian, H.; Tsai, Y.S.; Shao, S.; Liu, Q.; Dominguez, D.; Wang, Z. The splicing factor RBM4 controls apoptosis, proliferation, and migration to suppress tumor progression. Cancer Cell 2014, 26, 374–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardou, F.; Ariel, F.; Simpson, C.G.; Romero-Barrios, N.; Laporte, P.; Balzergue, S.; Brown, J.W.S.; Crespi, M. Long noncoding RNA modulates alternative splicing regulators in arabidopsis. Dev. Cell 2014, 30, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.H.; Liu, X.N.; Wang, T.T.; Pan, W.; Tao, Q.F.; Zhou, W.P.; Wang, F.; Sun, S.H. The MBNL3 splicing factor promotes hepatocellular carcinoma by increasing PXN expression through the alternative splicing of lncRNA-PXN-AS1. Nat. Cell Biol. 2017, 19, 820–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akker, S.A.; Misra, S.; Aslam, S.; Morgan, E.L.; Smith, P.J.; Khoo, B.; Chew, S.L. Pre-Spliceosomal Binding of U1 Small Nuclear Ribonucleoprotein (RNP) and Heterogenous Nuclear RNP E1 Is Associated with Suppression of a Growth Hormone Receptor Pseudoexon. Mol. Endocrinol. 2007, 21, 2529–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grelet, S.; Link, L.A.; Howley, B.; Obellianne, C.; Palanisamy, V.; Gangaraju, V.K.; Diehl, J.A.; Howe, P.H. A regulated PNUTS mRNA to lncRNA splice switch mediates EMT and tumour progression. Nat. Cell Biol. 2017, 19, 1105–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, Biogenesis, Mechanism, and Function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, D.W.; Dinger, M.E. Endogenous microRNA sponges: Evidence and controversy. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2016, 17, 272–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.-H.; Liu, S.; Zhou, H.; Qu, L.-H.; Yang, J.-H. starBase v2.0: Decoding miRNA-ceRNA, miRNA-ncRNA and protein–RNA interaction networks from large-scale CLIP-Seq data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D92–D97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Zhi, H.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Gao, Y.; Guo, M.; Ning, S.; Li, X. miRSponge: A manually curated database for experimentally supported miRNA sponges and ceRNAs. Database J. Biol. Databases Curation 2015, 2015, bav098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karakülah, G.; Yücebilgili Kurtoğlu, K.; Unver, T. PeTMbase: A Database of Plant Endogenous Target Mimics (eTMs). PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denzler, R.; Agarwal, V.; Stefano, J.; Bartel, D.P.; Stoffel, M. Assessing the ceRNA hypothesis with quantitative measurements of miRNA and target abundance. Mol. Cell 2014, 54, 766–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denzler, R.; McGeary, S.E.; Title, A.C.; Agarwal, V.; Bartel, D.P.; Stoffel, M. Impact of MicroRNA levels, target-site complementarity, and cooperativity on competing endogenous RNA-regulated gene expression. Mol. Cell 2016, 64, 565–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco-Zorrilla, J.M.; Valli, A.; Todesco, M.; Mateos, I.; Puga, M.I.; Rubio-Somoza, I.; Leyva, A.; Weigel, D.; García, J.A.; Paz-Ares, J. Target mimicry provides a new mechanism for regulation of microRNA activity. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 1033–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Q.; Wang, K.; Zou, C.; Xu, C.; Li, W.-X. The PILNCR1-miR399 regulatory module is important for low-phosphate tolerance in maize. Plant. Physiol. 2018, 177, 1743–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, X.; Liu, M.; Yang, C.; Chen, Y.; Chen, R.; Wen, J.; Mysore, K.S.; Zhang, W.H. Novel phosphate deficiency-responsive long non-coding RNAs in the legume model plant Medicago truncatula. J. Exp. Bot. 2017, 68, 5937–5948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.; Cui, J.; Shi, Y.; Yang, G.; Zhou, X.; Hou, X.; Meng, J.; Luan, Y. Tomato lncRNA23468 functions as a competing endogenous RNA to modulate NBS-LRR genes by decoying miR482b in the tomato-Phytophthora infestans interaction. Hortic. Res. 2019, 6, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, C.; Huo, Q.; Wang, X.; Chen, B.; Yang, Q. SNHG16 contributes to breast cancer cell migration by competitively binding miR-98 with E2F5. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 485, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Zeng, Y.; Zhou, C.; Ye, W. SNHG16/miR-216-5p/ZEB1 signal pathway contributes to the tumorigenesis of cervical cancer cells. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2018, 637, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Xu, W.; Song, J.S.; Wu, T.; Wang, W.X. LncRNA SNHG16 promotes cell proliferation through miR-302a-3p/FGF19 axis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Neoplasma 2019, 66, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; Xu, X.; Sun, C.; Yu, Z. Long intergenic noncoding RNA SNHG16 interacts with miR-195 to promote proliferation, invasion and tumorigenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Exp. Cell Res. 2019, 383, 111501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Q.; Zhao, L.; Wang, T.; Lv, N.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, G.; Bai, L. LncRNA SNHG16 drives proliferation and invasion of papillary thyroid cancer through modulation of miR-497. Onco. Targets 2019, 12, 699–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Hu, C.; Wang, Y.; Liu, S. Long noncoding RNA SNHG16 promotes human retinoblastoma progression via sponging miR-140-5p. Biomed. Pharm. 2019, 117, 109153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, F.; Chen, A.; Huang, J.; Xia, Q.; Chen, Y.; Jin, X. Long noncoding RNA SNHG16 contributes to the development of bladder cancer via regulating miR-98/STAT3/Wnt/β-catenin pathway axis. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 9408–9418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Hu, K.; Chao, Y.; Wang, L. LncRNA SNHG16 promotes proliferation, migration and invasion of osteosarcoma cells by targeting miR-1301/BCL9 axis. Biomed. Pharm. 2019, 114, 108798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, W.; Liu, K.; Liu, Y. LncRNA SNHG16 promotes tumor growth of pancreatic cancer by targeting miR-218-5p. Biomed. Pharm. 2019, 114, 108862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Kan, J.; Han, J.; Zhang, W.; Bai, L.; Wu, H. LncRNA SNHG16 Functions as an Oncogene by Sponging MiR-135a and Promotes JAK2/STAT3 Signal Pathway in Gastric Cancer. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 1013–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Li, F.; Sun, J.; Li, D.; Li, W.; Jiang, R.; Li, Z.; Liu, X.; Han, R.; Li, G.; et al. LncRNA IMFNCR Promotes Intramuscular Adipocyte Differentiation by Sponging miR-128-3p and miR-27b-3p. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Huang, T.; Liu, Z.; Sun, M.; Luo, S. LncRNA SNHG7 contributes to tumorigenesis and progression in breast cancer by interacting with miR-34a through EMT initiation and the Notch-1 pathway. Eur. J. Pharm. 2019, 856, 172407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Zhang, L.; Qiao, Y.; Song, R. Long noncoding RNA LINC00662 functions as miRNA sponge to promote the prostate cancer tumorigenesis through targeting miR-34a. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 23, 3688–3698. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, A.; Sun, Y.; Ma, Q.; Xu, F. lncRNA-ATB promotes viability, migration, and angiogenesis in human microvascular endothelial cells by sponging microRNA-195. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 14360–14371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.-M.; Lian, G.-Y.; Song, Y.; Huang, Y.-F.; Gong, Y. LncRNA MALAT1 promotes tumorigenesis and immune escape of diffuse large B cell lymphoma by sponging miR-195. Life Sci. 2019, 231, 116335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Cullen, B.R. The imprinted H19 noncoding RNA is a primary microRNA precursor. RNA 2007, 13, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keniry, A.; Oxley, D.; Monnier, P.; Kyba, M.; Dandolo, L.; Smits, G.; Reik, W. The H19 lincRNA is a developmental reservoir of miR-675 that suppresses growth and Igf1r. Nat. Cell Biol. 2012, 14, 659–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Liu, Q.; Li, C.; Graves-Deal, R.; Cao, Z.; Singh, B.; Franklin, J.L.; Wang, J.; Hu, H.; et al. lncRNA MIR100HG-derived miR-100 and miR-125b mediate cetuximab resistance via Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 1331–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.; Kasprzewska, A.; Tennessen, K.; Fernandes, J.; Nan, G.-L.; Walbot, V.; Sundaresan, V.; Vance, V.; Bowman, L.H. Clusters and superclusters of phased small RNAs in the developing inflorescence of rice. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 1429–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, Y.-P.; Yuan, S.-S.; Zhao, Y.-N.; Zhao, H.-N.; Zhang, H.-L.; Ji, X.-L. A Novel LncRNA, MuLnc1, Associated With Environmental Stress in Mulberry (Morus multicaulis). Front. Plant. Sci. 2018, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Ke, L.; Wu, G.; Xu, Y.; Wu, X.; Xia, R.; Deng, X.; Xu, Q. miR3954 is a trigger of phasiRNAs that affects flowering time in citrus. Plant. J. 2017, 92, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, C.; Maquat, L.E. lncRNAs transactivate STAU1-mediated mRNA decay by duplexing with 3′ UTRs via Alu elements. Nature 2011, 470, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Gong, C.; Maquat, L.E. Control of myogenesis by rodent SINE-containing lncRNAs. Genes Dev. 2013, 27, 793–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, X.; Klibanski, A. MEG3 noncoding RNA: A tumor suppressor. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2012, 48, R45–R53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawicka, K.; Bushell, M.; Spriggs, K.A.; Willis, A.E. Polypyrimidine-tract-binding protein: A multifunctional RNA-binding protein. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2008, 36, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, Z.; Trottier, J.; Barbier, O.; Wang, L. Long noncoding RNA MEG3 induces cholestatic liver injury by interaction with PTBP1 to facilitate shp mRNA decay. Hepatology 2017, 65, 604–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Hu, X.; Liu, Y.; Dong, S.; Wen, Z.; He, W.; Zhang, S.; Huang, Q.; Shi, M. ROS signaling under metabolic stress: Cross-talk between AMPK and AKT pathway. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Lin, L.; Huang, Q.; He, W.; Zhang, S.; Dong, S.; Wen, Z.; Rao, J.; Liao, W.; et al. The lncRNA MACC1-AS1 promotes gastric cancer cell metabolic plasticity via AMPK/Lin28 mediated mRNA stability of MACC1. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Wang, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Chen, X.-C.; Ma, M.; Cai, R.; Gao, Y.; Sun, Y.; Yang, G.-S.; Pang, W.-J. Sirt1 AS lncRNA interacts with its mRNA to inhibit muscle formation by attenuating function of miR-34a. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.M.; Anderson, K.M.; Chang, C.-L.; Makarewich, C.A.; Nelson, B.R.; McAnally, J.R.; Kasaragod, P.; Shelton, J.M.; Liou, J.; Bassel-Duby, R.; et al. A micropeptide encoded by a putative long noncoding RNA regulates muscle performance. Cell 2015, 160, 595–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoncu, R.; Bar-Peled, L.; Efeyan, A.; Wang, S.; Sancak, Y.; Sabatini, D.M. mTORC1 senses lysosomal amino acids through an inside-out mechanism that requires the vacuolar H+-ATPase. Science 2011, 334, 678–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, A.; Pasut, A.; Matsumoto, M.; Yamashita, R.; Fung, J.; Monteleone, E.; Saghatelian, A.; Nakayama, K.I.; Clohessy, J.G.; Pandolfi, P.P. MTORC1 and muscle regeneration are regulated by the LINC00961-encoded SPAR polypeptide. Nature 2017, 541, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.-C.; Katinakis, P.; Hendriks, P.; Smolders, A.; de Vries, F.; Spee, J.; van Kammen, A.; Bisseling, T.; Franssen, H. Characterization of GmENOD40, a gene showing novel patterns of cell-specific expression during soybean nodule development. Plant. J. 1993, 3, 573–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohrig, H.; Schmidt, J.; Miklashevichs, E.; Schell, J.; John, M. Soybean ENOD40 encodes two peptides that bind to sucrose synthase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 1915–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crespi, M.D.; Jurkevitch, E.; Poiret, M.; D’Aubenton-Carafa, Y.; Petrovics, G.; Kondorosi, E.; Kondorosi, A. enod40, a gene expressed during nodule organogenesis, codes for a non-translatable RNA involved in plant growth. Embo J. 1994, 13, 5099–5112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compaan, B.; Yang, W.C.; Bisseling, T.; Franssen, H. ENOD40 expression in the pericycle precedes cortical cell division in rhizobium-legume interaction and the highly conserved internal region of the gene does not encode a peptide. Proc. Plant Soil 2001, 230, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campalans, A. Enod40, a short open reading frame-containing mRNA, induces cytoplasmic localization of a nuclear RNA binding protein in medicago truncatula. Plant. Cell Online 2004, 16, 1047–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Parisien, M.; Dai, Q.; Zheng, G.; He, C.; Pan, T. Probing N6-methyladenosine RNA modification status at single nucleotide resolution in mRNA and long noncoding RNA. RNA 2013, 19, 1848–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Liu, J.; He, C. RNA N6-methyladenosine methylation in post-transcriptional gene expression regulation. Genes Dev. 2015, 29, 1343–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhao, B.S.; Zhou, A.; Lin, K.; Zheng, S.; Lu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Sulman, E.P.; Xie, K.; Bögler, O.; et al. The m6A demethylase ALKBH5 maintains tumorigenicity of glioblastoma stem-like cells by sustaining FOXM1 expression and Cell proliferation program. Cancer Cell 2017, 31, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huarte, M.; Guttman, M.; Feldser, D.; Garber, M.; Koziol, M.J.; Kenzelmann-Broz, D.; Khalil, A.M.; Zuk, O.; Amit, I.; Rabani, M.; et al. A large intergenic noncoding RNA induced by p53 mediates global gene repression in the p53 response. Cell 2010, 142, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, J.-H.; Abdelmohsen, K.; Srikantan, S.; Yang, X.; Martindale, J.L.; De, S.; Huarte, M.; Zhan, M.; Becker, K.G.; Gorospe, M. LincRNA-p21 suppresses target mRNA translation. Mol. Cell 2012, 47, 648–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, G.; Lou, Z.; Gupta, M. The long non-coding RNA GAS5 cooperates with the eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E to regulate c-Myc translation. Plos ONE 2014, 9, e107016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, A.E.; Row, P.E.; Dudley, E. Post-translation modification of proteins; methodologies and applications in plant sciences. Phytochemistry 2011, 72, 975–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Xue, Y.; Han, Y.; Lin, L.; Wu, C.; Xu, S.; Jiang, Z.; Xu, J.; Liu, Q.; Cao, X. The STAT3-binding long noncoding RNA lnc-DC controls human dendritic cell differentiation. Science 2014, 344, 310–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Liu, J.; Ben, Q.; Qu, Y.; Li, M.; Wang, Y.; Chen, W.; Zhang, J. The aspirin-induced long non-coding RNA OLA1P2 blocks phosphorylated STAT3 homodimer formation. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Liu, X.; Zhou, J.; Hu, J.; Zhang, D.; Liu, J.; Qiao, Y.; Zhan, Q. Long noncoding RNA HULC modulates the phosphorylation of YB-1 through serving as a scaffold of extracellular signal–regulated kinase and YB-1 to enhance hepatocarcinogenesis. Hepatology 2017, 65, 1612–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.-H.; Abdelmohsen, K.; Kim, J.; Yang, X.; Martindale, J.L.; Tominaga-Yamanaka, K.; White, E.J.; Orjalo, A.V.; Rinn, J.L.; Kreft, S.G.; et al. Scaffold function of long non-coding RNA HOTAIR in protein ubiquitination. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Cooper, J.; Zhou, L.; Yang, C.; Erdjument-Bromage, H.; Zagzag, D.; Snuderl, M.; Ladanyi, M.; Hanemann, C.O.; Zhou, P.; et al. Merlin/NF2 loss-driven tumorigenesis linked to CRL4DCAF1-mediated inhibition of the hippo pathway kinases lats1 and 2 in the nucleus. Cancer Cell 2014, 26, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhan, Z.; Ye, F.; Liang, Y.; Huang, J.; Chen, K.; Chen, L.; Ding, Y. A novel lncRNA uc.134 represses hepatocellular carcinoma progression by inhibiting CUL4A-mediated ubiquitination of LATS1. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2017, 10, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narita, T.; Weinert, B.T.; Choudhary, C. Functions and mechanisms of non-histone protein acetylation. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 156–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.E.; Chen, J.; Lou, Z. DBC1 is a negative regulator of SIRT1. Nature 2008, 451, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Kruse, J.P.; Tang, Y.; Jung, S.Y.; Qin, J.; Gu, W. Negative regulation of the deacetylase SIRT1 by DBC1. Nature 2008, 451, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Liu, Y.; Zhuang, H.; Yang, B.; Hei, K.; Xiao, M.; Hou, C.; Gao, H.; Zhang, X.; Jia, C.; et al. Quantitative proteomics reveals that long non-coding RNA MALAT1 interacts with DBC1 to regulate p53 acetylation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 9947–9959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Wang, W.; Zhu, W.; Dong, J.; Cheng, Y.; Yin, Z.; Shen, F. Mechanisms and Functions of Long Non-Coding RNAs at Multiple Regulatory Levels. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5573. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20225573
Zhang X, Wang W, Zhu W, Dong J, Cheng Y, Yin Z, Shen F. Mechanisms and Functions of Long Non-Coding RNAs at Multiple Regulatory Levels. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(22):5573. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20225573
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xiaopei, Wei Wang, Weidong Zhu, Jie Dong, Yingying Cheng, Zujun Yin, and Fafu Shen. 2019. "Mechanisms and Functions of Long Non-Coding RNAs at Multiple Regulatory Levels" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 22: 5573. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20225573
APA StyleZhang, X., Wang, W., Zhu, W., Dong, J., Cheng, Y., Yin, Z., & Shen, F. (2019). Mechanisms and Functions of Long Non-Coding RNAs at Multiple Regulatory Levels. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(22), 5573. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20225573