The Biological Effects of Complete Gasoline Engine Emissions Exposure in a 3D Human Airway Model (MucilAirTM) and in Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells (BEAS-2B)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
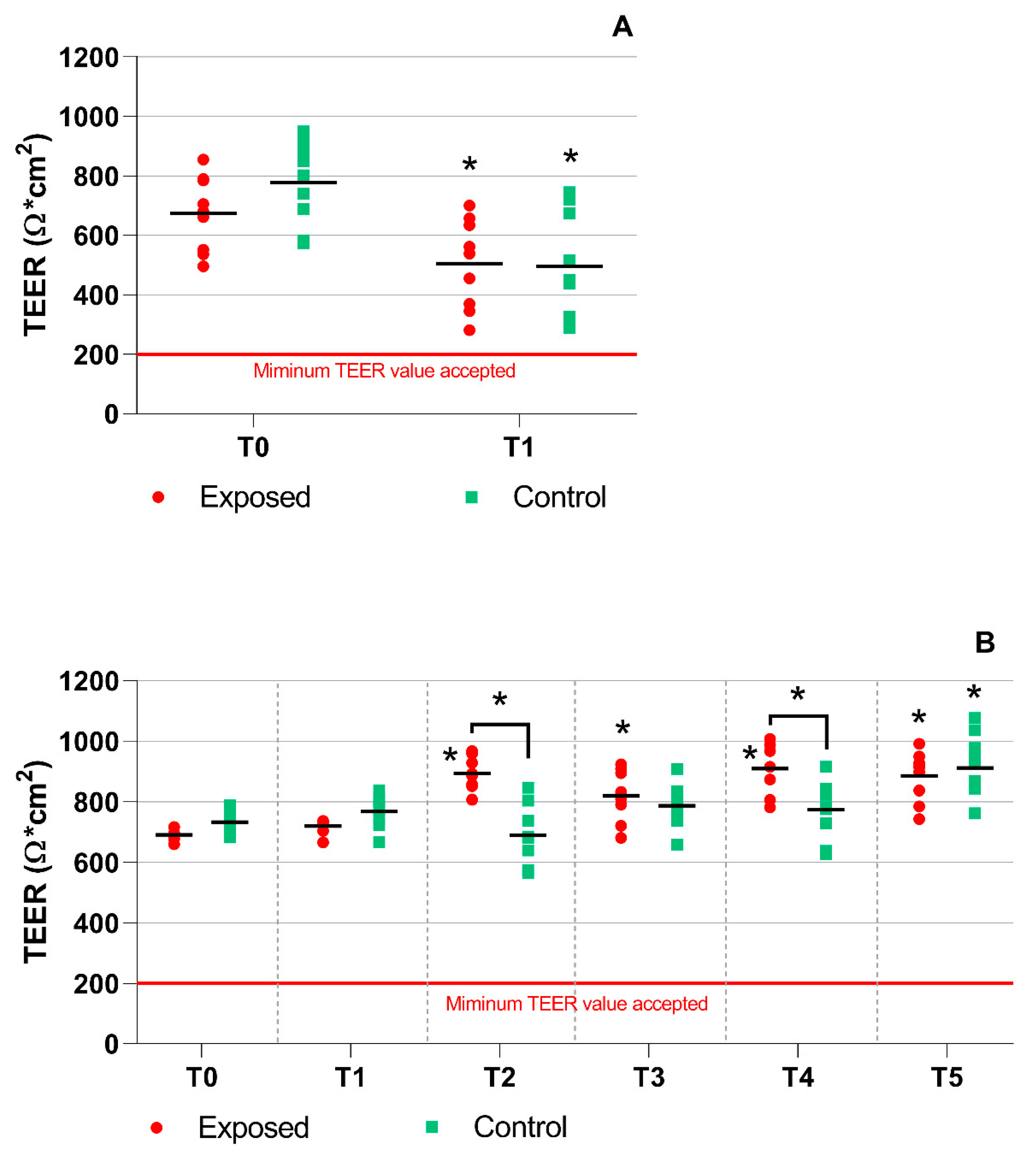
2.1. TEER Measurement, Mucin Production, and Cytotoxicity Analyses
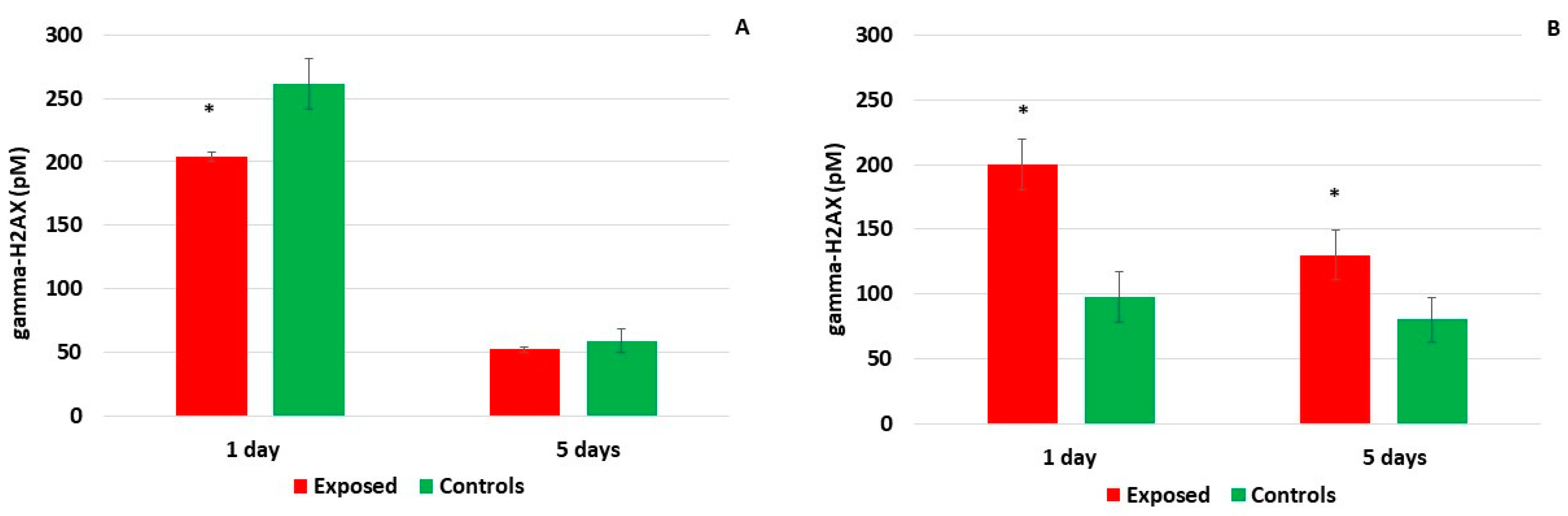
2.2. Detection of DNA Breaks
2.3. mRNA Expression Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Cultures
4.2. Exposure to Complete Emissions—Technical Aspects
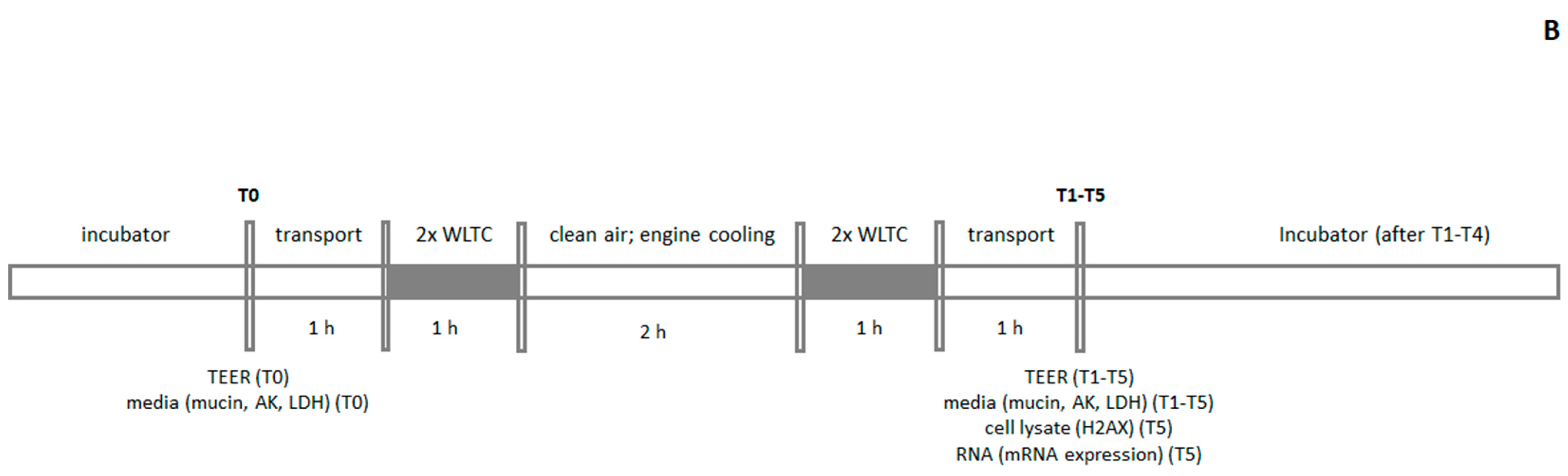
4.3. Exposure Scheme
4.4. Microscopy Analysis of the MucilAirTM Tissues and BEAS-2B Cells
4.5. TEER Assessment and Mucin Analysis
4.6. Cytotoxicity Determination
4.7. Phosphorylation of Histone H2AX
4.8. mRNA Expression Analysis
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AK | adenylate kinase |
| ALI | air–liquid interface |
| AQP4 | aquaporin 4 |
| CYP1A1 | cytochrome P450 family 1 subfamily A member 1 |
| EOM | extractable organic matter |
| HSPA5 | heat shock protein family A (Hsp70 |
| LDH | lactate dehydrogenase |
| PAH | polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon |
| SLC2A3 | solute carrier family 2 member 3 |
| TEER | transepithelial electrical resistance |
| WLTC | world harmonized light vehicle test cycle |
References
- Lewtas, J. Air pollution combustion emissions: Characterization of causative agents and mechanisms associated with cancer, reproductive, and cardiovascular effects. Mutat. Res. 2007, 636, 95–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Marini, D.M. Genotoxicity biomarkers associated with exposure to traffic and near-road atmospheres: A review. Mutagenesis 2013, 28, 485–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans. In Diesel and Gasoline Engine Exhausts and Some Nitroarenes; IARC Publications: Lyon, France, 2013; Volume 105. [Google Scholar]
- Eisenbrand, G.; Pool-Zobel, B.; Baker, V.; Balls, M.; Blaauboer, B.J.; Boobis, A.; Carere, A.; Kevekordes, S.; Lhuguenot, J.-C.; Pieters, R.; et al. Methods of in vitro toxicology. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2002, 40, 193–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, L. 4.3 In vitro genotoxicity tests to detect carcinogenicity: A systematic review. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2009, 28, 131–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, S.J.; Clift, M.J.D.; Singh, N.; de Oliveira Mallia, J.; Burgum, M.; Wills, J.W.; Wilkinson, T.S.; Jenkins, G.J.S.; Doak, S.H. Critical review of the current and future challenges associated with advanced in vitro systems towards the study of nanoparticle (secondary) genotoxicity. Mutagenesis 2017, 32, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Wiszniewski, L.; Derouette, J.-P.; Constant, S. In vitro organ culture models of asthma. Drug Discov. Today Dis. Models 2009, 6, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Wiszniewski, L.; Constant, S.; Roggen, E. Potential of in vitro reconstituted 3D human airway epithelia (MucilAirTM) to assess respiratory sensitizers. Toxicol. In Vitro 2013, 27, 1151–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, L.; Comte, P.; Czerwinski, J.; Kasper, M.; Mayer, A.C.R.; Gehr, P.; Burtscher, H.; Morin, J.-P.; Konstandopoulos, A.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B. New exposure system to evaluate the toxicity of (scooter) exhaust emissions in lung cells in vitro. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 2632–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, S.; Mueller, L.; Popovicheva, O.B.; Raemy, D.O.; Czerwinski, J.; Comte, P.; Mayer, A.; Gehr, P.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B.; Clift, M.J.D. Cerium dioxide nanoparticles can interfere with the associated cellular mechanistic response to diesel exhaust exposure. Toxicol. Lett. 2012, 214, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawley, B.; L’Orange, C.; Olsen, D.B.; Marchese, A.J.; Volckens, J. Oxidative stress and aromatic hydrocarbon response of human bronchial epithelial cells exposed to petro- or biodiesel exhaust treated with a diesel particulate filter. Toxicol. Sci. 2014, 141, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, S.; Czerwinski, J.; Comte, P.; Heeb, N.V.; Mayer, A.; Petri-Fink, A.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B. Effects of an iron-based fuel-borne catalyst and a diesel particle filter on exhaust toxicity in lung cells in vitro. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 5977–5986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oeder, S.; Kanashova, T.; Sippula, O.; Sapcariu, S.C.; Streibel, T.; Arteaga-Salas, J.M.; Passig, J.; Dilger, M.; Paur, H.-R.; Schlager, C.; et al. Particulate matter from both heavy fuel oil and diesel fuel shipping emissions show strong biological effects on human lung cells at realistic and comparable in vitro exposure conditions. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bisig, C.; Comte, P.; Güdel, M.; Czerwinski, J.; Mayer, A.; Müller, L.; Petri-Fink, A.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B. Assessment of lung cell toxicity of various gasoline engine exhausts using a versatile in vitro exposure system. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 235, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghio, A.J.; Dailey, L.A.; Soukup, J.M.; Stonehuerner, J.; Richards, J.H.; Devlin, R.B. Growth of human bronchial epithelial cells at an air-liquid interface alters the response to particle exposure. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2013, 10, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlofs-Nijland, M.E.; Totlandsdal, A.I.; Tzamkiozis, T.; Leseman, D.L.A.C.; Samaras, Z.; Låg, M.; Schwarze, P.; Ntziachristos, L.; Cassee, F.R. Cell toxicity and oxidative potential of engine exhaust particles: Impact of using particulate filter or biodiesel fuel blend. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 5931–5938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Totlandsdal, A.I.; Lag, M.; Lilleaas, E.; Cassee, F.; Schwarze, P. Differential proinflammatory responses induced by diesel exhaust particles with contrasting PAH and metal content. Environ. Toxicol. 2015, 30, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, N.; Lombard, M.; Jensen, K.R.; Kelley, P.; Pratt, T.; Traviss, N. Effect of biodiesel fuel on “real-world”, nonroad heavy duty diesel engine particulate matter emissions, composition and cytotoxicity. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 586, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-H.; Balasubramanian, R. Physicochemical and toxicological characteristics of particulate matter emitted from a non-road diesel engine: Comparative evaluation of biodiesel-diesel and butanol-diesel blends. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 264, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawal, A.O.; Zhang, M.; Dittmar, M.; Lulla, A.; Araujo, J.A. Heme oxygenase-1 protects endothelial cells from the toxicity of air pollutant chemicals. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2015, 284, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libalova, H.; Rossner, P.; Vrbova, K.; Brzicova, T.; Sikorova, J.; Vojtisek-Lom, M.; Beranek, V.; Klema, J.; Ciganek, M.; Neca, J.; et al. Comparative analysis of toxic responses of organic extracts from diesel and selected alternative fuels engine emissions in human lung BEAS-2B cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libalova, H.; Rossner, P.; Vrbova, K.; Brzicova, T.; Sikorova, J.; Vojtisek-Lom, M.; Beranek, V.; Klema, J.; Ciganek, M.; Neca, J.; et al. Transcriptional response to organic compounds from diverse gasoline and biogasoline fuel emissions in human lung cells. Toxicol. In Vitro 2018, 48, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, J.D.; Doyle-Eisele, M.; Seagrave, J.; Gigliotti, A.P.; Chow, J.; Zielinska, B.; Mauderly, J.L.; Seilkop, S.K.; Miller, R.A. HEI health review committee part 1. Assessment of carcinogenicity and biologic responses in rats after lifetime inhalation of new-technology diesel exhaust in the ACES bioassay. Res. Rep. Health Eff. Inst. 2015, 9, 141–171. [Google Scholar]
- Savary, C.C.; Bellamri, N.; Morzadec, C.; Langouët, S.; Lecureur, V.; Vernhet, L. Long term exposure to environmental concentrations of diesel exhaust particles does not impact the phenotype of human bronchial epithelial cells. Toxicol. In Vitro 2018, 52, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cervena, T.; Vrbova, K.; Rossnerova, A.; Topinka, J.; Rossner, P. Short-Term and long-term Exposure of the MucilAirTM Model to Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons. Altern. Lab. Anim. 2019, 47, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bisig, C.; Steiner, S.; Comte, P.; Czerwinski, J.; Mayer, A.; Petri-Fink, A.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B. Biological effects in lung cells in vitro of exhaust aerosols from a gasoline passenger car with and without particle filter. Emiss. Control Sci. Technol. 2015, 1, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisig, C.; Roth, M.; Müller, L.; Comte, P.; Heeb, N.; Mayer, A.; Czerwinski, J.; Petri-Fink, A.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B. Hazard identification of exhausts from gasoline-ethanol fuel blends using a multi-cellular human lung model. Environ. Res. 2016, 151, 789–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vojtisek-Lom, M.; Pechout, M.; Macoun, D.; Rameswaran, R.; Kumar Praharaj, K.; Cervena, T.; Topinka, J.; Rossner, P. Assessing exhaust toxicity with biological detector: configuration of portable air-liquid interface human lung cell model exposure system, sampling train and test conditions. SAE Tech. Pap. 2019, 24, 50. [Google Scholar]
- Stewart, C.E.; Torr, E.E.; Mohd Jamili, N.H.; Bosquillon, C.; Sayers, I. Evaluation of differentiated human bronchial epithelial cell culture systems for asthma research. J. Allergy 2012, 2012, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridley, C.; Thornton, D.J. Mucins: The frontline defence of the lung. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2018, 46, 1099–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, S.; Matsumura, K.; Kitamura, N.; Takanami, Y.; Ito, S. Multi-Omics analysis: Repeated exposure of a 3D bronchial tissue culture to whole-cigarette smoke. Toxicol. In Vitro 2019, 54, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuter, C.; Alzheimer, M.; Walles, H.; Oelschlaeger, T.A. An adherent mucus layer attenuates the genotoxic effect of colibactin. Cell. Microbiol. 2018, 20, e12812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Canton, C.; Anadón, A.; Meredith, C. γH2AX as a novel endpoint to detect DNA damage: Applications for the assessment of the in vitro genotoxicity of cigarette smoke. Toxicol. In Vitro 2012, 26, 1075–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barraud, C.; Corbière, C.; Pottier, I.; Estace, E.; Blanchard, K.; Logie, C.; Lagadu, S.; Kéravec, V.; Pottier, D.; Dionnet, F.; et al. Impact of after-treatment devices and biofuels on diesel exhausts genotoxicity in A549 cells exposed at air-liquid interface. Toxicol. In Vitro 2017, 45, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalska, M.; Wegierek-Ciuk, A.; Brzoska, K.; Wojewodzka, M.; Meczynska-Wielgosz, S.; Gromadzka-Ostrowska, J.; Mruk, R.; Øvrevik, J.; Kruszewski, M.; Lankoff, A. Genotoxic potential of diesel exhaust particles from the combustion of first- and second-generation biodiesel fuels—The FuelHealth project. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 24223–24234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Steiner, S.; Heeb, N.V.; Czerwinski, J.; Comte, P.; Mayer, A.; Petri-Fink, A.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B. Test-Methods on the test-bench: A comparison of complete exhaust and exhaust particle extracts for genotoxicity/mutagenicity assessment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 5237–5244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomašek, I.; Horwell, C.J.; Bisig, C.; Damby, D.E.; Comte, P.; Czerwinski, J.; Petri-Fink, A.; Clift, M.J.D.; Drasler, B.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B. Respiratory hazard assessment of combined exposure to complete gasoline exhaust and respirable volcanic ash in a multicellular human lung model at the air-liquid interface. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 238, 977–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarcone, M.C.; Duistermaat, E.; Alblas, M.J.; van Schadewijk, A.; Ninaber, D.K.; Clarijs, V.; Moerman, M.M.; Vaessen, D.; Hiemstra, P.S.; Kooter, I.M. Effect of diesel exhaust generated by a city bus engine on stress responses and innate immunity in primary bronchial epithelial cell cultures. Toxicol. In Vitro 2018, 48, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddel, R.R.; Ke, Y.; Gerwin, B.I.; McMenamin, M.G.; Lechner, J.F.; Su, R.T.; Brash, D.E.; Park, J.B.; Rhim, J.S.; Harris, C.C. Transformation of human bronchial epithelial cells by infection with SV40 or adenovirus-12 SV40 hybrid virus, or transfection via strontium phosphate coprecipitation with a plasmid containing SV40 early region genes. Cancer Res. 1988, 48, 1904–1909. [Google Scholar]
- Cervena, T.; Rossnerova, A.; Sikorova, J.; Beranek, V.; Vojtisek-Lom, M.; Ciganek, M.; Topinka, J.; Rossner, P. DNA damage potential of engine emissions measured in vitro by micronucleus test in human bronchial epithelial cells. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morin, J.P.; Fouquet, F.; Monteil, C.; Le Prieur, E.; Vaz, E.; Dionnet, F. Development of a new in vitro system for continuous in vitro exposure of lung tissue to complex atmospheres: Application to diesel exhaust toxicology. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 1999, 15, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewels, P.A.; Peltzer, A.; Fillinger, S.; Alneberg, J.; Patel, H.; Wilm, A.; Garcia, M.U.; Di Tommaso, P.; Nahnsen, S. Nf-core: Community curated bioinformatics pipelines. Bioinformatics 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]






| Exposure | Gene Name | Ensembl ID | Biological Pathway | Log2 FC | Adj. p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| One day | HSPA5 | ENSG00000044574 | Heat shock response | –0.877 | 0.001 |
| CYP1A1 | ENSG00000140465 | Cytochrome P450s and phase I drug metabolism Immunotoxicity | 2.634 | 0.042 | |
| Five days | CYP1A1 | ENSG00000140465 | Cytochrome P450s and phase I drug metabolism Immunotoxicity | 3.060 | 0.007 |
| Gene Name | Ensembl ID | Biological Pathway | Log2 FC | Adj. p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SLC2A3 | ENSG00000059804 | Phospholipidosis | –3.008 | 0.025 |
| AQP4 | ENSG00000171885 | Steatosis | –1.140 | 0.027 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rossner, P., Jr.; Cervena, T.; Vojtisek-Lom, M.; Vrbova, K.; Ambroz, A.; Novakova, Z.; Elzeinova, F.; Margaryan, H.; Beranek, V.; Pechout, M.; et al. The Biological Effects of Complete Gasoline Engine Emissions Exposure in a 3D Human Airway Model (MucilAirTM) and in Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells (BEAS-2B). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5710. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20225710
Rossner P Jr., Cervena T, Vojtisek-Lom M, Vrbova K, Ambroz A, Novakova Z, Elzeinova F, Margaryan H, Beranek V, Pechout M, et al. The Biological Effects of Complete Gasoline Engine Emissions Exposure in a 3D Human Airway Model (MucilAirTM) and in Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells (BEAS-2B). International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(22):5710. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20225710
Chicago/Turabian StyleRossner, Pavel, Jr., Tereza Cervena, Michal Vojtisek-Lom, Kristyna Vrbova, Antonin Ambroz, Zuzana Novakova, Fatima Elzeinova, Hasmik Margaryan, Vit Beranek, Martin Pechout, and et al. 2019. "The Biological Effects of Complete Gasoline Engine Emissions Exposure in a 3D Human Airway Model (MucilAirTM) and in Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells (BEAS-2B)" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 22: 5710. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20225710
APA StyleRossner, P., Jr., Cervena, T., Vojtisek-Lom, M., Vrbova, K., Ambroz, A., Novakova, Z., Elzeinova, F., Margaryan, H., Beranek, V., Pechout, M., Macoun, D., Klema, J., Rossnerova, A., Ciganek, M., & Topinka, J. (2019). The Biological Effects of Complete Gasoline Engine Emissions Exposure in a 3D Human Airway Model (MucilAirTM) and in Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells (BEAS-2B). International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(22), 5710. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20225710






