Extended Cleavage Specificities of Rabbit and Guinea Pig Mast Cell Chymases: Two Highly Specific Leu-Ases
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Phylogenetic and Primary Structure Analysis
2.2. Purification and Activation of the Recombinant Rabbit and Guinea Pig Enzymes
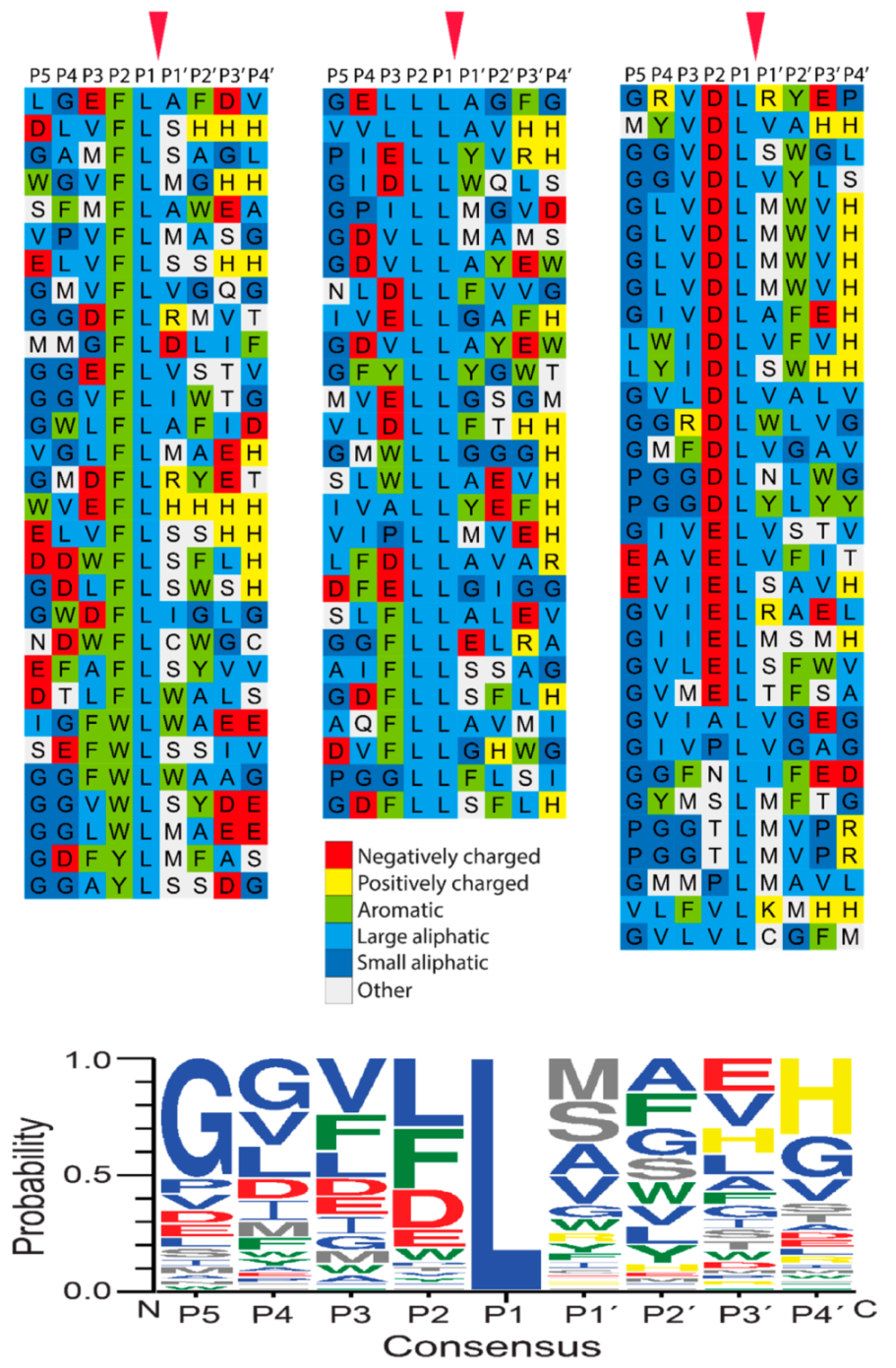
2.3. Determination of the Extended Cleavage Specificity of the Rabbit Cma1-Like Enzyme by Substrate Phage Display
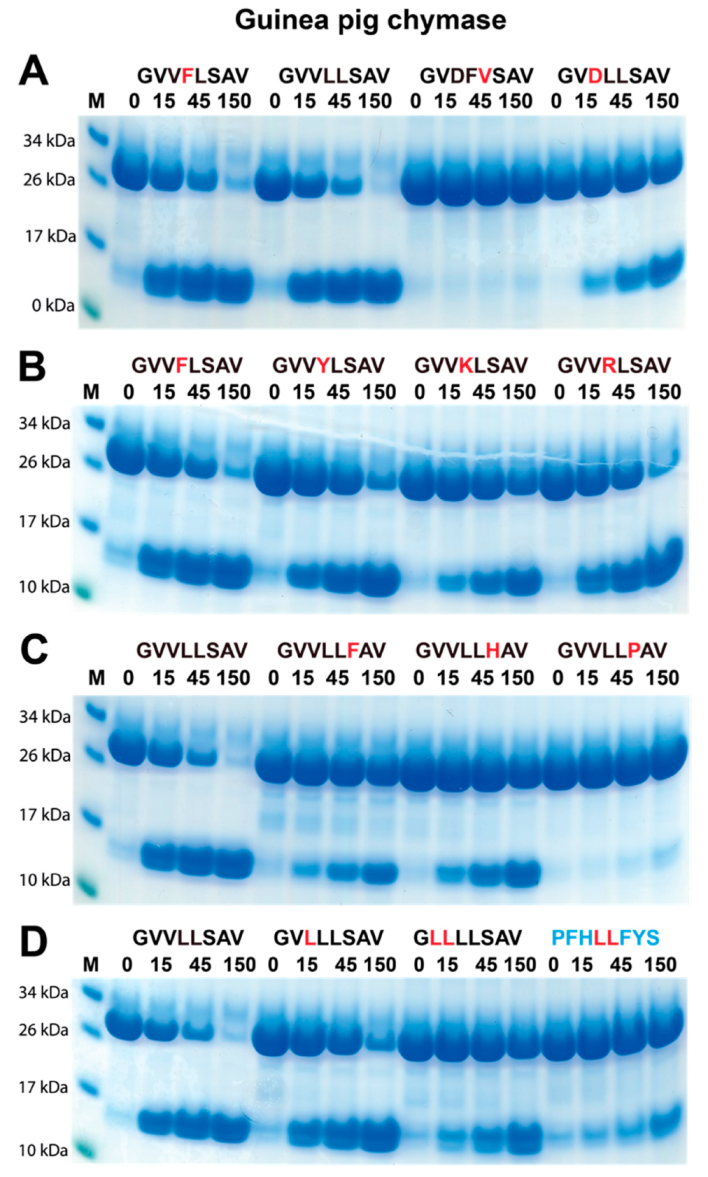
2.4. Verifying the Consensus Sequence by the Use of Recombinant Protein Substrates
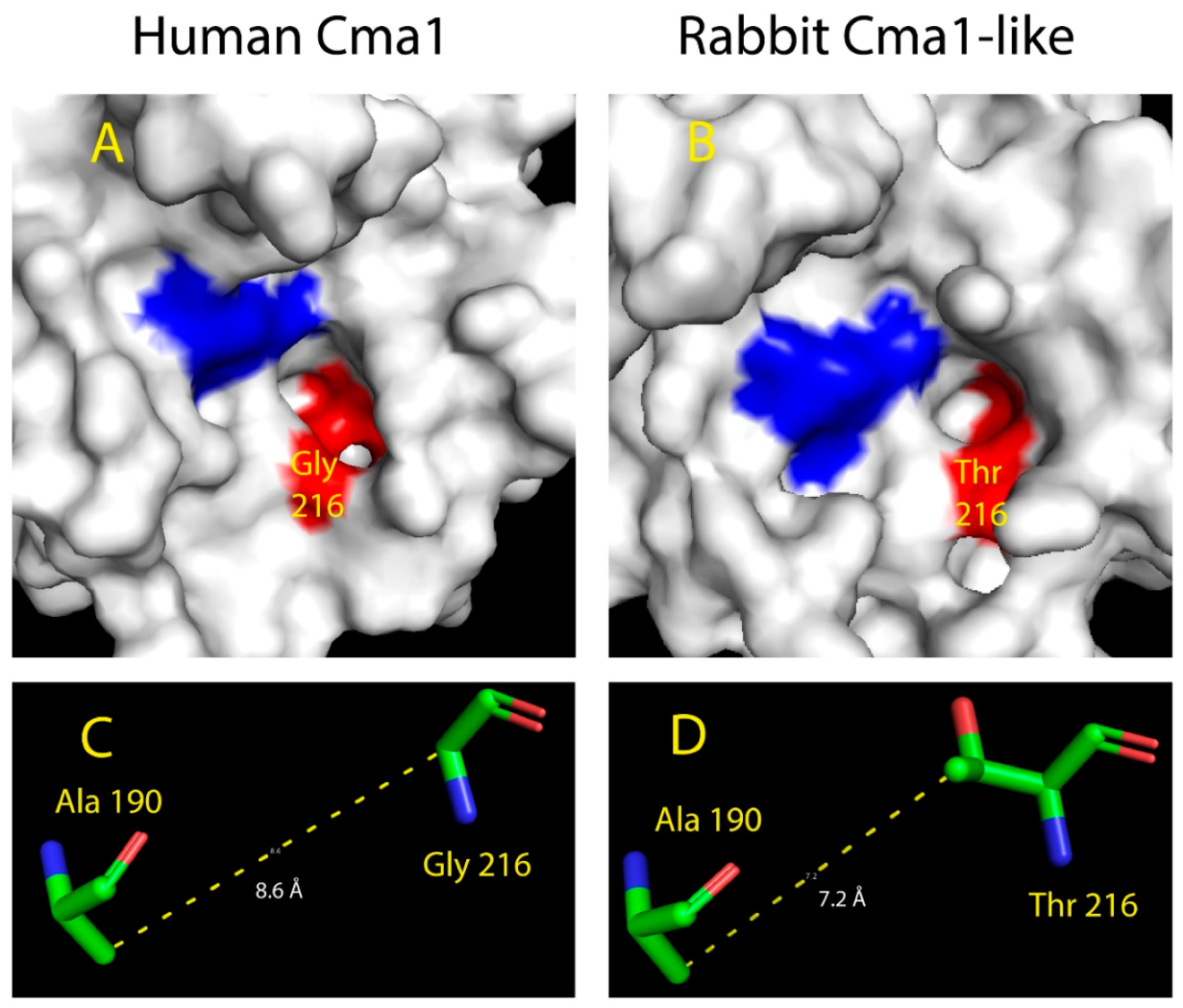
2.5. Structural Modeling of the Active Site of Rabbit Cma1-Like
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Production and Purification of Recombinant Rabbit and Guinea Pig Enzymes
4.2. Determination of Cleavage Specificity by Phage-Displayed Nonapeptide Library
4.3. Generation of Recombinant Substrates for the Analysis of the Cleavage Specificity
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kunder, C.A.; St John, A.L.; Abraham, S.N. Mast cell modulation of the vascular and lymphatic endothelium. Blood 2011, 118, 5383–5393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galli, S.J.; Grimbaldeston, M.; Tsai, M. Immunomodulatory mast cells: Negative, as well as positive, regulators of immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 478–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caughey, G.H. Mast cell tryptases and chymases in inflammation and host defense. Immunol. Rev. 2007, 217, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pejler, G.; Ronnberg, E.; Waern, I.; Wernersson, S. Mast cell proteases: Multifaceted regulators of inflammatory disease. Blood 2010, 115, 4981–4990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akula, S.; Thorpe, M.; Boinapally, V.; Hellman, L. Granule Associated Serine Proteases of Hematopoietic Cells—An Analysis of Their Appearance and Diversification during Vertebrate Evolution. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0143091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallwitz, M.; Reimer, J.M.; Hellman, L. Expansion of the mast cell chymase locus over the past 200 million years of mammalian evolution. Immunogenetics 2006, 58, 655–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallwitz, M.; Hellman, L. Rapid lineage-specific diversification of the mast cell chymase locus during mammalian evolution. Immunogenetics 2006, 58, 641–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, M.K.; Karlson, U.; Hellman, L. The extended cleavage specificity of the rodent beta-chymases rMCP-1 and mMCP-4 reveal major functional similarities to the human mast cell chymase. Mol. Immunol. 2008, 45, 766–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlson, U.; Pejler, G.; Froman, G.; Hellman, L. Rat mast cell protease 4 is a beta-chymase with unusually stringent substrate recognition profile. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 18579–18585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellman, L.; Thorpe, M. Granule proteases of hematopoietic cells, a family of versatile inflammatory mediators—An update on their cleavage specificity, in vivo substrates, and evolution. Biol. Chem. 2014, 395, 15–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanker, S.; Chandrasekharan, U.M.; Wilk, D.; Glynias, M.J.; Karnik, S.S.; Husain, A. Distinct multisite synergistic interactions determine substrate specificities of human chymase and rat chymase-1 for angiotensin II formation and degradation. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 2963–2968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caughey, G.H.; Raymond, W.W.; Wolters, P.J. Angiotensin II generation by mast cell alpha- and beta-chymases. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta 2000, 1480, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunori, Y.; Muroga, Y.; Iidaka, M.; Mitsuhashi, H.; Kamimura, T.; Fukamizu, A. Species differences in angiotensin II generation and degradation by mast cell chymases. J. Recept Signal Transduct. Res. 2005, 25, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Z.; Thorpe, M.; Alemayehu, R.; Roy, A.; Kervinen, J.; de Garavilla, L.; Abrink, M.; Hellman, L. Highly Selective Cleavage of Cytokines and Chemokines by the Human Mast Cell Chymase and Neutrophil Cathepsin G. J. Immunol. 2017, 198, 1474–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pat, B.; Chen, Y.; Killingsworth, C.; Gladden, J.D.; Shi, K.; Zheng, J.; Powell, P.C.; Walcott, G.; Ahmed, M.I.; Gupta, H.; et al. Chymase inhibition prevents fibronectin and myofibrillar loss and improves cardiomyocyte function and LV torsion angle in dogs with isolated mitral regurgitation. Circulation 2010, 122, 1488–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okumura, K.; Takai, S.; Muramatsu, M.; Katayama, S.; Sakaguchi, M.; Kishi, K.; Jin, D.; Miyazaki, M. Human chymase degrades human fibronectin. Clin. Chim. Acta 2004, 347, 223–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caughey, G.H.; Beauchamp, J.; Schlatter, D.; Raymond, W.W.; Trivedi, N.N.; Banner, D.; Mauser, H.; Fingerle, J. Guinea pig chymase is leucine-specific: A novel example of functional plasticity in the chymase/granzyme family of serine peptidases. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 13943–13951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kervinen, J.; Crysler, C.; Bayoumy, S.; Abad, M.C.; Spurlino, J.; Deckman, I.; Greco, M.N.; Maryanoff, B.E.; de Garavilla, L. Potency variation of small-molecule chymase inhibitors across species. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2010, 80, 1033–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kervinen, J.; Abad, M.; Crysler, C.; Kolpak, M.; Mahan, A.D.; Masucci, J.A.; Bayoumy, S.; Cummings, M.D.; Yao, X.; Olson, M.; et al. Structural basis for elastolytic substrate specificity in rodent alpha-chymases. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkin, M.A.; Blackshields, G.; Brown, N.P.; Chenna, R.; McGettigan, P.A.; McWilliam, H.; Valentin, F.; Wallace, I.M.; Wilm, A.; Lopez, R.; et al. Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2947–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crooks, G.E.; Hon, G.; Chandonia, J.M.; Brenner, S.E. WebLogo: A sequence logo generator. Genome Res. 2004, 14, 1188–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorpe, M.; Fu, Z.; Albat, E.; Akula, S.; de Garavilla, L.; Kervinen, J.; Hellman, L. Extended cleavage specificities of mast cell proteases 1 and 2 from golden hamster: Classical chymase and an elastolytic protease comparable to rat and mouse MCP-5. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0207826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, Y.; Kakuda, S.; Koizumi, M.; Mizuno, T.; Muroga, Y.; Kawamura, T.; Takimoto-Kamimura, M. Crystal structure of a complex of human chymase with its benzimidazole derived inhibitor. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 2013, 20, 914–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reimer, J.M.; Enoksson, M.; Samollow, P.B.; Hellman, L. Extended substrate specificity of opossum chymase-Implications for the origin of mast cell chymases. Mol. Immunol. 2008, 45, 2116–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, M.K.; Enoksson, M.; Gallwitz, M.; Hellman, L. The extended substrate specificity of the human mast cell chymase reveals a serine protease with well-defined substrate recognition profile. Int. Immunol. 2009, 21, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, M.K.; Thorpe, M.; Hellman, L. Arg143 and Lys192 of the human mast cell chymase mediate the preference for acidic amino acids in position P2′ of substrates. FEBS J. 2010, 277, 2255–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, L.A.; Mezulis, S.; Yates, C.M.; Wass, M.N.; Sternberg, M.J. The Phyre2 web portal for protein modeling, prediction and analysis. Nat. Protoc. 2015, 10, 845–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooers, B.H.M. Shortcuts for faster image creation in PyMOL. Protein Sci. Publ. Protein Soc. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metz, M.; Piliponsky, A.M.; Chen, C.C.; Lammel, V.; Abrink, M.; Pejler, G.; Tsai, M.; Galli, S.J. Mast cells can enhance resistance to snake and honeybee venoms. Science 2006, 313, 526–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellon, M.B.; Frank, B.T.; Fang, K.C. Mast cell alpha-chymase reduces IgE recognition of birch pollen profilin by cleaving antibody-binding epitopes. J. Immunol. 2002, 168, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuhoff, V.; Arold, N.; Taube, D.; Ehrhardt, W. Improved staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels including isoelectric focusing gels with clear background at nanogram sensitivity using Coomassie Brilliant Blue G-250 and R-250. Electrophoresis 1988, 9, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlson, U.; Pejler, G.; Tomasini-Johansson, B.; Hellman, L. Extended substrate specificity of rat mast cell protease 5, a rodent alpha-chymase with elastase-like primary specificity. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 39625–39631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorpe, M.; Yu, J.; Boinapally, V.; Ahooghalandari, P.; Kervinen, J.; Garavilla, L.D.; Hellman, L. Extended cleavage specificity of the mast cell chymase from the crab-eating macaque (Macaca fascicularis): An interesting animal model for the analysis of the function of the human mast cell chymase. Int. Immunol. 2012, 12, 771–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhongwei, Y.; Akula, S.; Fu, Z.; de Garavilla, L.; Kervinen, J.; Thorpe, M.; Hellman, L. Extended Cleavage Specificities of Rabbit and Guinea Pig Mast Cell Chymases: Two Highly Specific Leu-Ases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6340. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20246340
Zhongwei Y, Akula S, Fu Z, de Garavilla L, Kervinen J, Thorpe M, Hellman L. Extended Cleavage Specificities of Rabbit and Guinea Pig Mast Cell Chymases: Two Highly Specific Leu-Ases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(24):6340. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20246340
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhongwei, Yuan, Srinivas Akula, Zhirong Fu, Lawrence de Garavilla, Jukka Kervinen, Michael Thorpe, and Lars Hellman. 2019. "Extended Cleavage Specificities of Rabbit and Guinea Pig Mast Cell Chymases: Two Highly Specific Leu-Ases" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 24: 6340. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20246340
APA StyleZhongwei, Y., Akula, S., Fu, Z., de Garavilla, L., Kervinen, J., Thorpe, M., & Hellman, L. (2019). Extended Cleavage Specificities of Rabbit and Guinea Pig Mast Cell Chymases: Two Highly Specific Leu-Ases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(24), 6340. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20246340





