Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Increase in Lysine Content of Waxy Maize through the Introgression of the opaque2 Allele
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. The Kernel Morphological Characteristics and Lysine Content of Pyramided Progenies
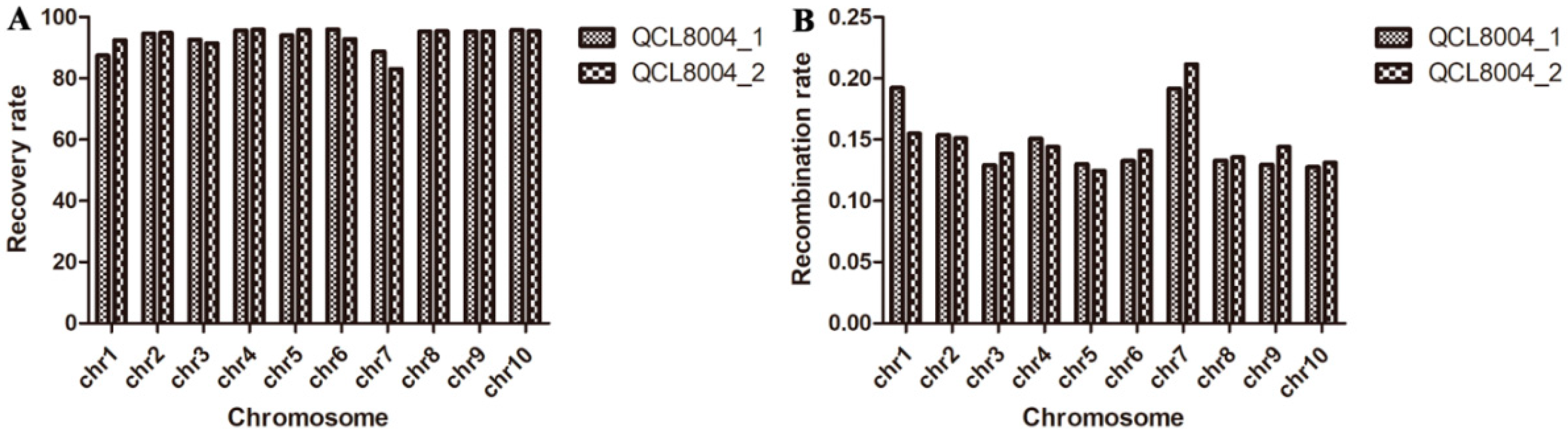
2.2. The Recovery Rate of the Genetic Background of o2o2wxwx Lines
2.3. The Quality of RNA-Seq and Biological Replicates
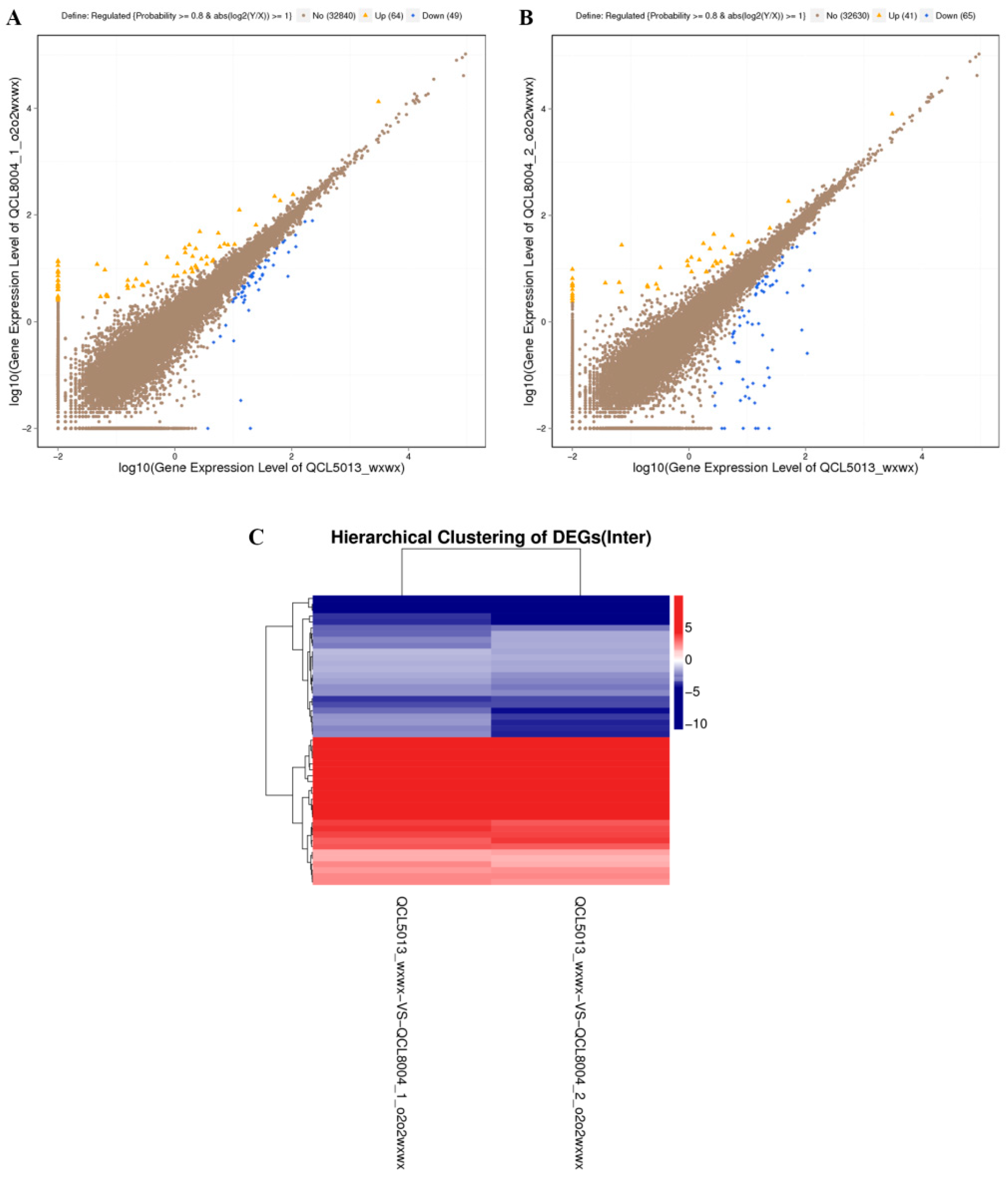
2.4. Identification of Differentially Expressed Genes
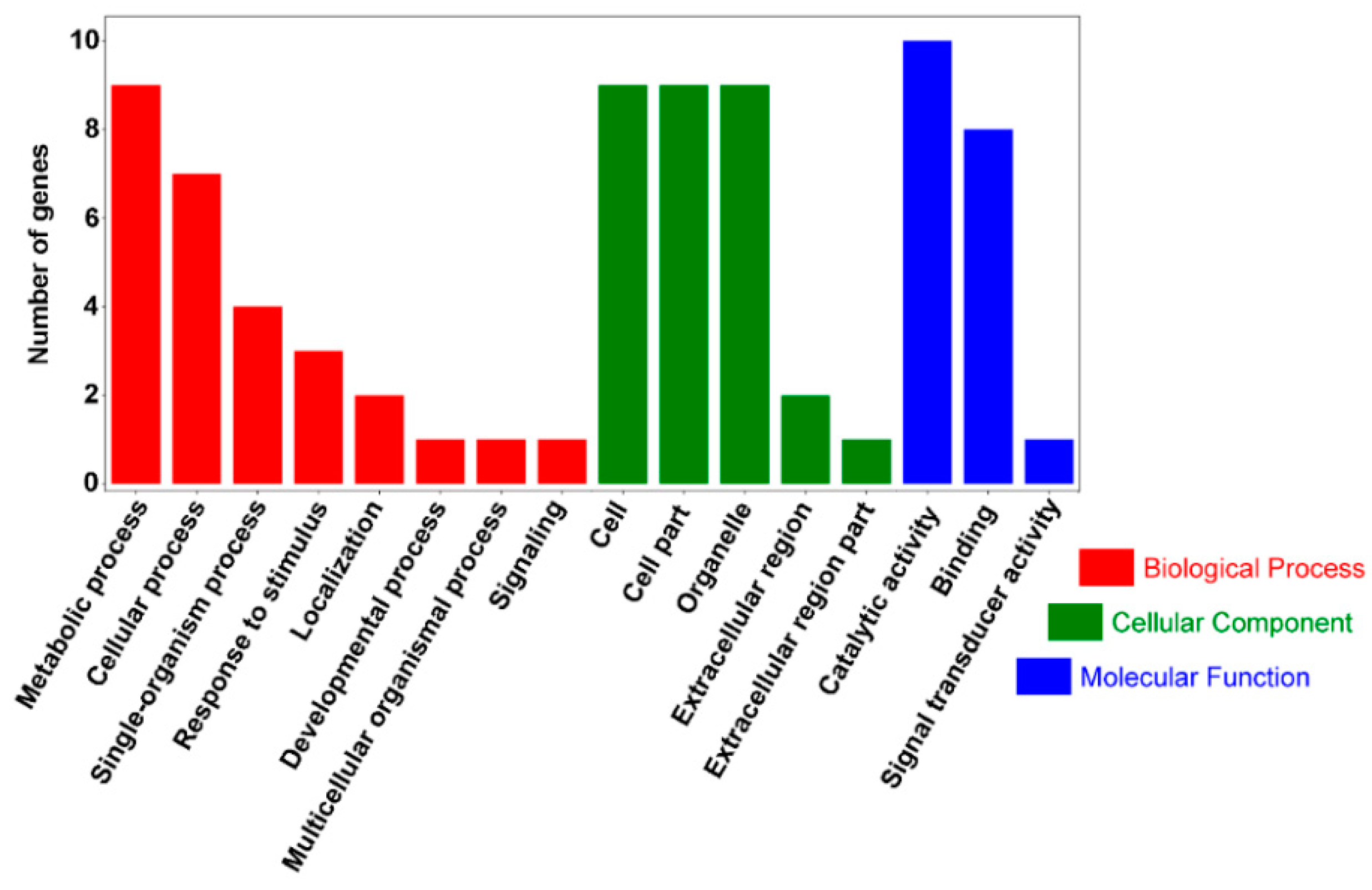
2.5. GO Annotation and KEGG Analysis
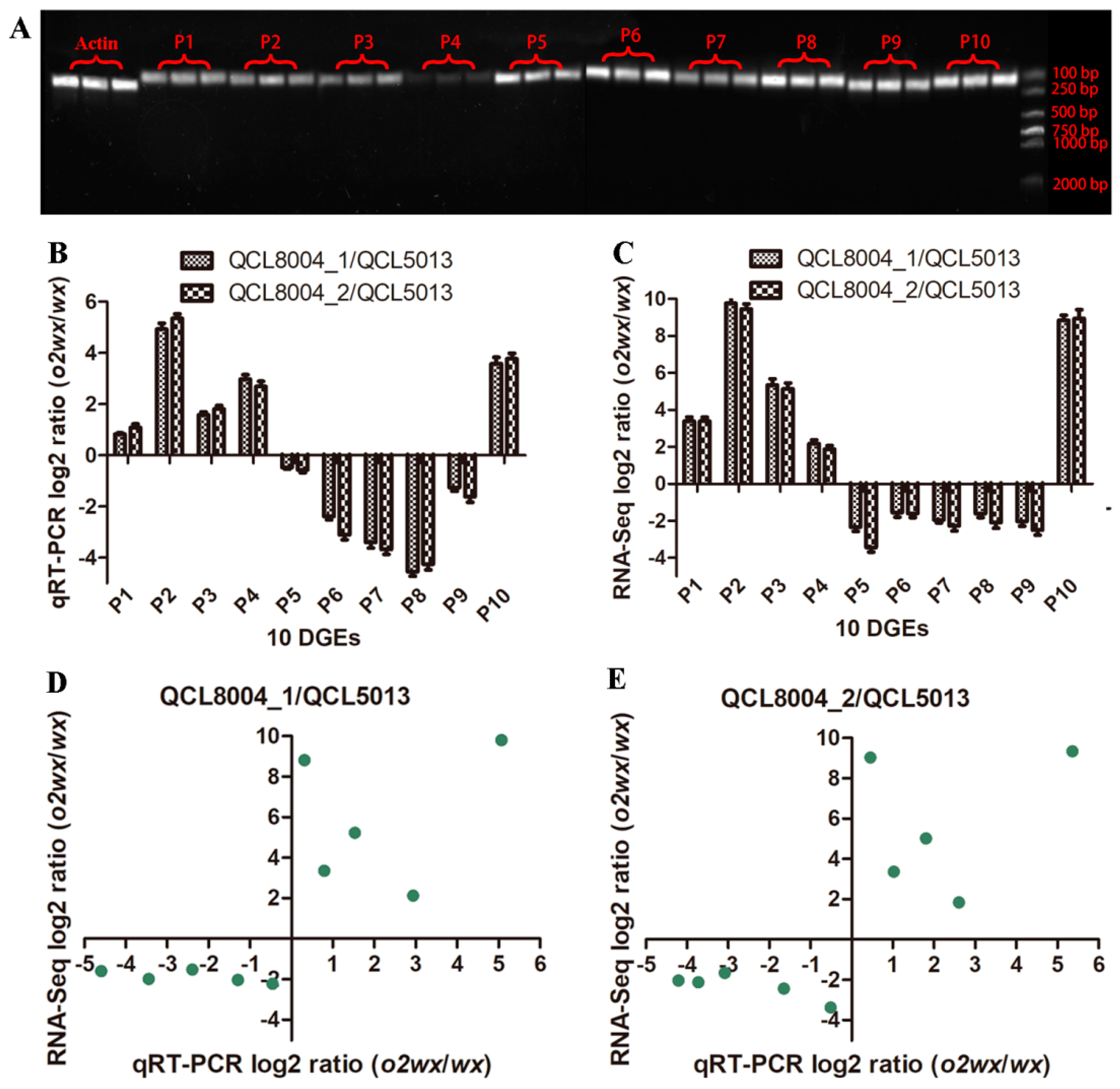
2.6. qRT-PCR Validation
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. DNA Extraction and Genetic Background Analysis
4.3. RNA-Seq Library Construction and Sequencing
4.4. Identification of Differentially Expressed Genes
4.5. GO and Pathway Enrichment Analysis of DEGs
4.6. qRT-PCR Validation
4.7. Accession Numbers
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GBSS-I | Granule-bound starch synthase I |
| MABS | Marker-assisted backcrossing selection |
| DAP | Day after pollination |
| SNP | Single nucleotide polymorphism |
| SSR | Simple Sequence Repeats |
| qRT-PCR | Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction |
| FPKM | Fragments Per Kilobase Million |
| GO | Gene Ontology |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| hct3 | Hydroxycinnamoyl transferase 3 |
| LHT1 | Lysine histidine transporter 1 |
| DHN13 | Dehydrin 13 |
| EF-1α | Elongation factor 1-alpha |
| MF | Molecular function |
| BP | Biological processes |
| CC | Cell components |
| ChIP-Seq | Chromatin immune-precipitation follow by sequencing |
| HSP | heat shock protein |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscopy |
References
- Tian, Q.Z.; Li, X.H.; Li, M.S.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, S.H. Molecular markers assisted selection to quality protein maize. J. Maize Sci. 2004, 12, 108–110+113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertz, E.T.; Bates, L.S.; Nelson, O.E. Mutant gene that changes protein composition and increases lysine content of maize endosperm. Science 1964, 145, 279–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gavazzi, F.; Lazzari, B.; Ciceri, P.; Gianazza, E.; Viotti, A. Wild-type Opaque2 and defective opaque2 polypeptides form complexes in maize endosperm cells and bind the opaque2-zein target site. Plant Physiol 2007, 145, 933–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, V.; Motto, M.; Pellegrini, L. Analysis of the methylation pattern of the maize Opaque-2 (O2) promoter and in vitro binding studies indicate that the O2 B-Zip protein and other endosperm factors can bind to methylated target sequences. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 13758–13765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, M.Q. Blood relationship of Chinese waxy maize. China Seeds 1987, 3, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.J.; Wang, H.; Yang, H.; Wu, J.H.; Shi, B.; Cai, R.; Xu, Y.B.; Wu, A.Z.; Luo, L.J. Genetic diversity and molecular evolution of Chinese waxy maize germplasm. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.Y.; Chen, D.; Lu, Y.Q.; Liu, W.H.; Yang, X.M.; Du, J.; Li, L.H. Molecular characteristics of two new waxy mutations in China waxy maize. Mol. Breed. 2017, 37, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, G.N. A New Type of Indian Corn from China; US Department of Agriculture, Bureau of Plant Industry: Washington, DC, USA, 1909; Volume 161, pp. 1–30.
- Wicker, T.; Sabot, F.; Hua-Van, A.; Bennetzen, J.; Capy, P.; Chalhoub, B.; Flavell, A.; Leroy, P.; Morgante, M.; Panaud, O.; et al. A unified classification system for eukaryotic transposable elements. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2007, 8, 973–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.J.; Quan, L.Y.; Leng, X.D.; Guo, X.Y.; Hu, W.M.; Ruan, S.; Ma, H.; Zeng, M. Molecular evidence for post-domestication selection in the Waxy gene of Chinese waxy maize. Mol. Breed. 2008, 22, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, J.D.; Yao, J.Q.; Zhu, J.Q.; Hu, W.M.; Cai, D.G.; Li, Y.; Shu, Q.Y.; Fan, L.J. Identification of glutinous maize landraces and inbred lines with altered transcription of waxy gene. Mol. Breed. 2012, 30, 1707–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Lu, W.P. Effects of protein removal on the physicochemical properties of waxy maize flours. Starch-Stärke 2012, 64, 874–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.L.; Yang, W.P.; Wang, M.C.; Wang, W.; Zeng, G.P.; Chen, Z.W.; Cai, Y.L. Increasing lysine content of waxy maize through introgression of opaque-2 and opaque-16 genes using molecular assisted and biochemical development. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.Q.; Song, L.Y.; Zhang, X.X.; Li, X.H.; Yan, N.; Xia, R.P.; Zhu, H.; Weng, J.F.; Hao, Z.F.; Zhang, D.G.; et al. Introgression of opaque2 into waxy maize causes extensive biochemical and proteomic changes in endosperm. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0158971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misra, P.S.; Mertz, E.T.; Glover, D.V. Studies on corn proteins. VI. Endosperm protein changes in single and double endosperm mutants of maize. Cereal Chem. 1975, 52, l–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.K.; Teng, H.S.; Su, Q.; Yang, Y.J. Selection of waxy-QPM maize lines with SSR markers. Guangxi Agric. Sci. 2009, 10, 1279–1283. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.Q.; Wang, W.; Yang, W.P.; Wang, M.C. Marker-assisted selection for pyramiding the waxy and opaque-16 genes in maize using cross and backcross schemes. Mol. Breed. 2013, 31, 767–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, N.C.; Munsch, M.; Aulinger, I.; Renlai, W.; Stamp, P. Inducer line generated double haploid seeds for combined waxy and opaque 2 grain quality in subtropical maize (Zea mays. L.). Euphytica 2012, 183, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Nettleton, D.; Peterson, J.M.; Vazquez-Carrillo, G.; Jannink, J.L.; Scott, M.P. Comparison of transcript profiles in wild-type and o2 maize endosperm in different genetic backgrounds. Crop Sci. 2007, 47, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Zheng, X.X.; Yang, J.; Messing, J.; Wu, Y.R. Maize endosperm-specific transcription factors O2 and PBF network the regulation of protein and starch synthesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 10842–10847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, N.P.; Hughes, P.A.; Larkins, B.A. The eEFlA gene family is differentially expressed in maize endosperm. Plant Mol. Biol. 1999, 41, 801–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habben, J.E.; Moro, G.L.; Hunter, B.G.; Hamaker, B.R.; Larkins, B.A. Elongation factor 1 alpha concentration is highly correlated with the lysine content of maize endosperm. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 8640–8644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Ma, C.Q.; Pan, Y.; Gong, S.L.; Zhao, C.X.; Chen, S.X.; Li, H.Y. Sugar beet M14 glyoxalase I gene can enhance plant tolerance to abiotic stresses. J. Plant Res. 2013, 126, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.B.; Qiao, Z.Y.; Qi, W.W.; Wang, Q.; Yuan, Y.; Yang, X.; Tang, Y.P.; Mei, B.; Lu, Y.D.; Zhao, H.; et al. Genome-wide characterization of cis-acting DNA targets reveals the transcriptional regulatory framework of Opaque2 in maize. Plant Cell 2015, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bush, D.R. Proton-coupled sugar and amino acid transporters in plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 1993, 44, 513–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frommer, W.B.; Hummel, S.; Riesmeier, J.W. Expression cloning in yeast of a cDNA encoding a broad specificity amino acid permease from Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 5944–5948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, L.C.; Chiou, T.J.; Chen, L.; Bush, D.R. Cloning a plant amino acid transporter by functional complementation of a yeast amino acid transport mutant. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 7441–7445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwart, M.; Hirner, B.; Hummel, S.; Frommer, W.B. Differential expression of two related amino acid transporters with differing substrate specificity in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 1993, 4, 993–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, W.N.; Kwart, M.; Hummel, S.; Frommer, W.B. Substrate specificity and expression profile of amino acid transporters (AAPs) in Arabidopsis. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 16315–16320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rentsch, D.; Hirner, B.; Schmelzer, E.; Frommer, W.B. Salt stress-induced proline transporters and salt stress-repressed broad specificity amino acid permeases identified by suppression of a yeast amino acid permease-targeting mutant. Plant Cell 1996, 8, 1437–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Bush, D.R. LHT1, a lysine-and histidine-specific amino acid transporter in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 1997, 115, 1127–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svennerstam, H.; Ganeteg, U.; Bellini, C.; Näsholm, T. Comprehensive screening of Arabidopsis mutants suggests the lysine histidine transporter 1 to be involved in plant uptake of amino acids. Plant Physiol. 2007, 143, 1853–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, T.P.; Yang, X.H.; Li, D.Q. Functional characterization of KS-type dehydrin ZmDHN13 and its related conserved domains under oxidative stress. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirihara, J.A.; Petri, J.B.; Messing, J. Isolation and sequence of a gene encoding a methionine-rich 10-kDa zein protein from maize. Gene 1988, 71, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, K.; Argos, P.; Naravana, S.V.; Larkins, B.A. Sequence analysis and characterization of a maize gene encoding a high-sulfur zein protein of Mr 15,000. J. Biol. Chem. 1986, 261, 6279–6284. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.P.; Zheng, Y.L.; Zheng, W.T.; Feng, R. Molecular genetic mapping of a high-lysine mutant gene (opaque-16) and the double recessive effect with opaque-2 in maize. Mol. Breed. 2005, 15, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Ren, Y.H.; Jian, Y.Q.; Guo, Z.F.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, C.X.; Fu, J.J.; Wang, H.W.; Wang, G.Y.; Xu, Y.B.; et al. Development of a maize 55 K SNP array with improved genome coverage for molecular breeding. Mol. Breed. 2017, 37, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hospital, F.; Chevalet, C.; Mulsant, P. Using markers in gene introgression breeding programs. Genetics 1992, 132, 199–210. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, J.H.; Zheng, Y.L. Molecular marker-assisted backcross breeding of maize Rf3 NIL and its efficient analysis. Acta Agron. Sin. 2002, 28, 339–344. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, M.J.; Ding, D.; Yang, W.P.; Xu, S.Z.; Zheng, Y.L. The linkage drag analysis of flanked opaque2 by SSR marker in two maize BC1F1 population. Acta Agron. Sin. 2005, 31, 1359–1364. [Google Scholar]
- Langmead, B.; Trapnell, C.; Pop, M.; Salzberg, S.L. Ultrafast and memory-efficient alignment of short DNA sequences to the human genome. Genome Biol. 2009, 10, R25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. HISAT: A fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Dewey, C.N. RSEM: Accurate transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a reference genome. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarazona, S.; Furio-Tari, P.; Turra, D.; Pietro, A.D.; Nueda, M.J.; Ferrer, A.; Conesa, A. Data quality aware analysis of differential expression in RNA-seq with NOISeq R/Bioc package. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, e140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdi, H. Bonferroni and Šidák Corrections for Multiple Comparisons. In Encyclopedia of Measurement and Statistics; Salkind, M.J., Ed.; Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Kanehisa, M.; Araki, M.; Goto, S.; Hattori, M.; Hirakawa, M.; Itoh, M.; Katayama, T.; Kawashima, S.; Okuda, S.; Tokimatsu, T.; et al. KEGG for linking genomes to life and the environment. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, 480–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.B.; Qin, L.J.; Han, L.Z.; Xiang, Y.; Zhao, D.G. Overexpression of maize SDD1 (ZmSDD1) improves drought resistance in Zea mays L. by reducing stomatal density. Plant Cell 2015, 122, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephen, A.B.; Vladimir, B.; Jeremy, A.G.; Jan, H.; Jim, H.; Mikael, K.; Reinhold, M.; Tania, N.; Michael, W.P.; Gregory, L.S.; et al. The MIQE guidelines: Minimum information for publication of quantitative real-time PCR experiments. Clin. Chem. 2009, 55, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
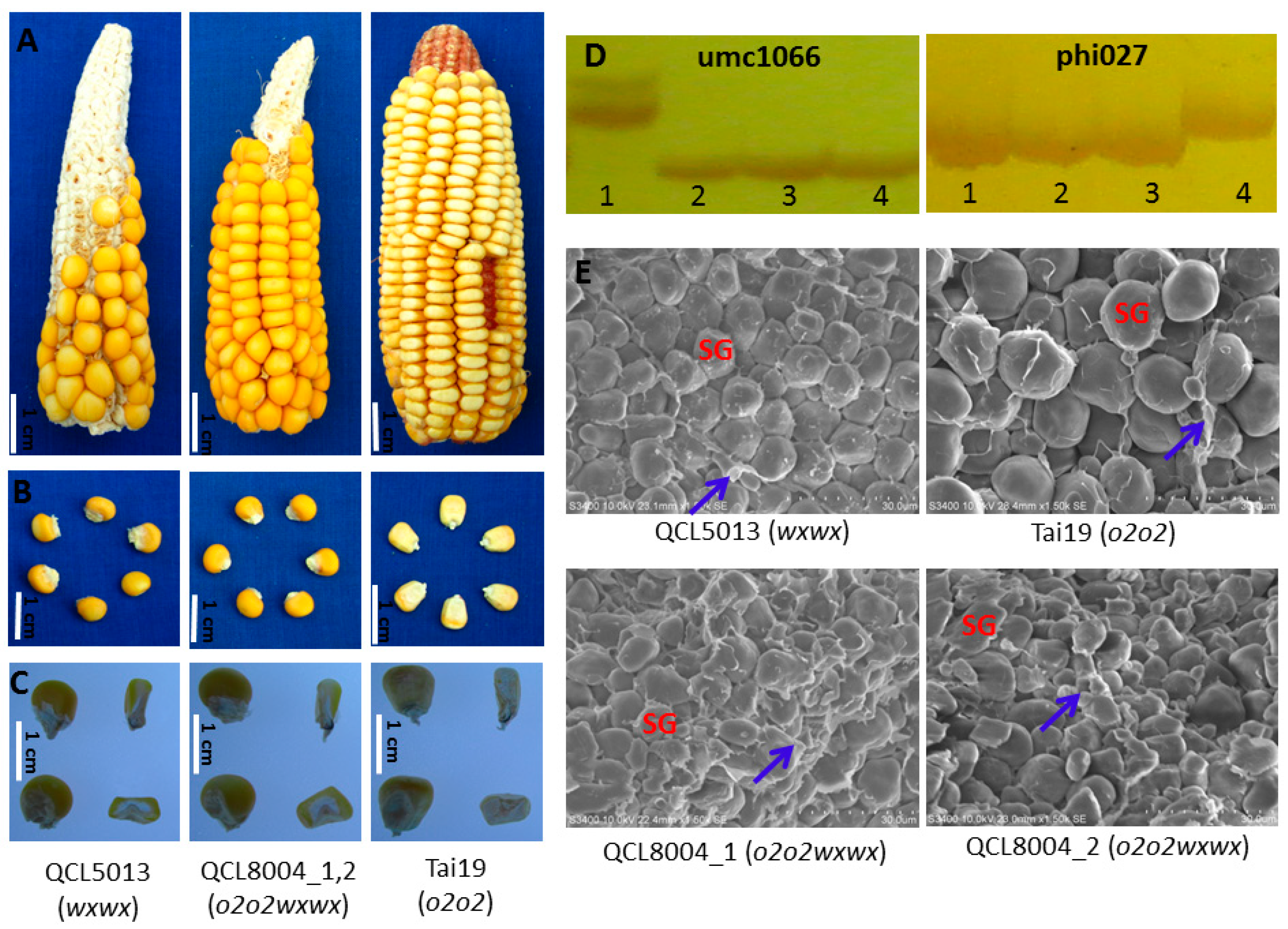



| No. | Name | Genotype | Lysine (%) | ±% to QCL5013 | Amylopectin (%) | ±% to QCL5013 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Tai19 | o2o2 | 0.43 | / | / | / |
| 2 | QCL5013 | wxwx | 0.32 | / | 100 | / |
| 3 | QCL8004_1 | o2o2wxwx | 0.37 | 15.63 | 98.95 | −1.05 |
| 4 | QCL8004_2 | o2o2wxwx | 0.38 | 18.75 | 98.64 | −1.36 |
| NO. | Gene ID | Primer Sequences (5′-3′) | Location of Primer | Amplicon Length (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | Zm00001d034771.1 | F: TGGTGGTGGTTGACTGTATTG | Exon 2 | 95 |
| R: CACGGTAAGAACTGGCCTAATC | ||||
| P2 | Zm00001d029385.1 | F: CCGATGCATCAAACAGAGAGA | Exon 4 | 120 |
| R: TCAGGTCGCTTCCTGAATAAC | ||||
| P3 | Zm00001d012262.1 | F: AGTAAAGCAGCTCGTGTTCTAA | Exon 2 | 103 |
| R: CAATGTGGTAGTGTCGCAAATC | ||||
| P4 | Zm00001d033483.1 | F: GGCATCGTGGAGAAGATCAA | Exon 1 | 101 |
| R: TCGCCGTGCTTCTTCTTT | ||||
| P5 | Zm00001d011063.1 | F: CAACTATGTAGCGGCGTCTAA | Exon 2 | 138 |
| R: ACAGACACAGGCGGTAATG | ||||
| P6 | Zm00001d028561.1 | F: AGGAGCACGAGGAGAAGAA | Exon 1 | 108 |
| R: CCTTGATCTGGTCTGCCTTG | ||||
| P7 | Zm00001d039935.1 | F: TCTGGTTGAGCATCCAATCC | Exon 1 | 102 |
| R: TCGTAGAAGACACAGGAAACATC | ||||
| P8 | Zm00001d039936.1 | F: GAGAACACCAAGGTGGATCAG | Exon 1 and 2 | 113 |
| R: CCAGAGATCTCAATAGCCTTCAC | ||||
| P9 | Zm00001d028408.1 | F: CAGGAGAACAGGGACAACAG | Exon 2 | 149 |
| R: GGCGACATCGGATCAACTAA | ||||
| P10 | Zm00001d030185.1 | F: GAGGCTAAAGAGAAGTGCAAGA | Exon 1 | 117 |
| R: CTCCTCTCCAACCCTAGATACA |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, W.; Niu, S.; Dai, Y.; Zhai, X.; Wang, M.; Ding, Y.; Yang, W.; Zhao, D. Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Increase in Lysine Content of Waxy Maize through the Introgression of the opaque2 Allele. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 684. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20030684
Wang W, Niu S, Dai Y, Zhai X, Wang M, Ding Y, Yang W, Zhao D. Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Increase in Lysine Content of Waxy Maize through the Introgression of the opaque2 Allele. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(3):684. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20030684
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Wei, Suzhen Niu, Yi Dai, Xinmi Zhai, Mingchun Wang, Yanqin Ding, Wenpeng Yang, and Degang Zhao. 2019. "Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Increase in Lysine Content of Waxy Maize through the Introgression of the opaque2 Allele" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 3: 684. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20030684
APA StyleWang, W., Niu, S., Dai, Y., Zhai, X., Wang, M., Ding, Y., Yang, W., & Zhao, D. (2019). Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Increase in Lysine Content of Waxy Maize through the Introgression of the opaque2 Allele. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(3), 684. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20030684





