Serum MicroRNAs as Biomarkers in Hepatitis C: Preliminary Evidence of a MicroRNA Panel for the Diagnosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Patient Characteristics
2.2. Differential miRNA Expression in Chronic Hepatitis C (CHC)
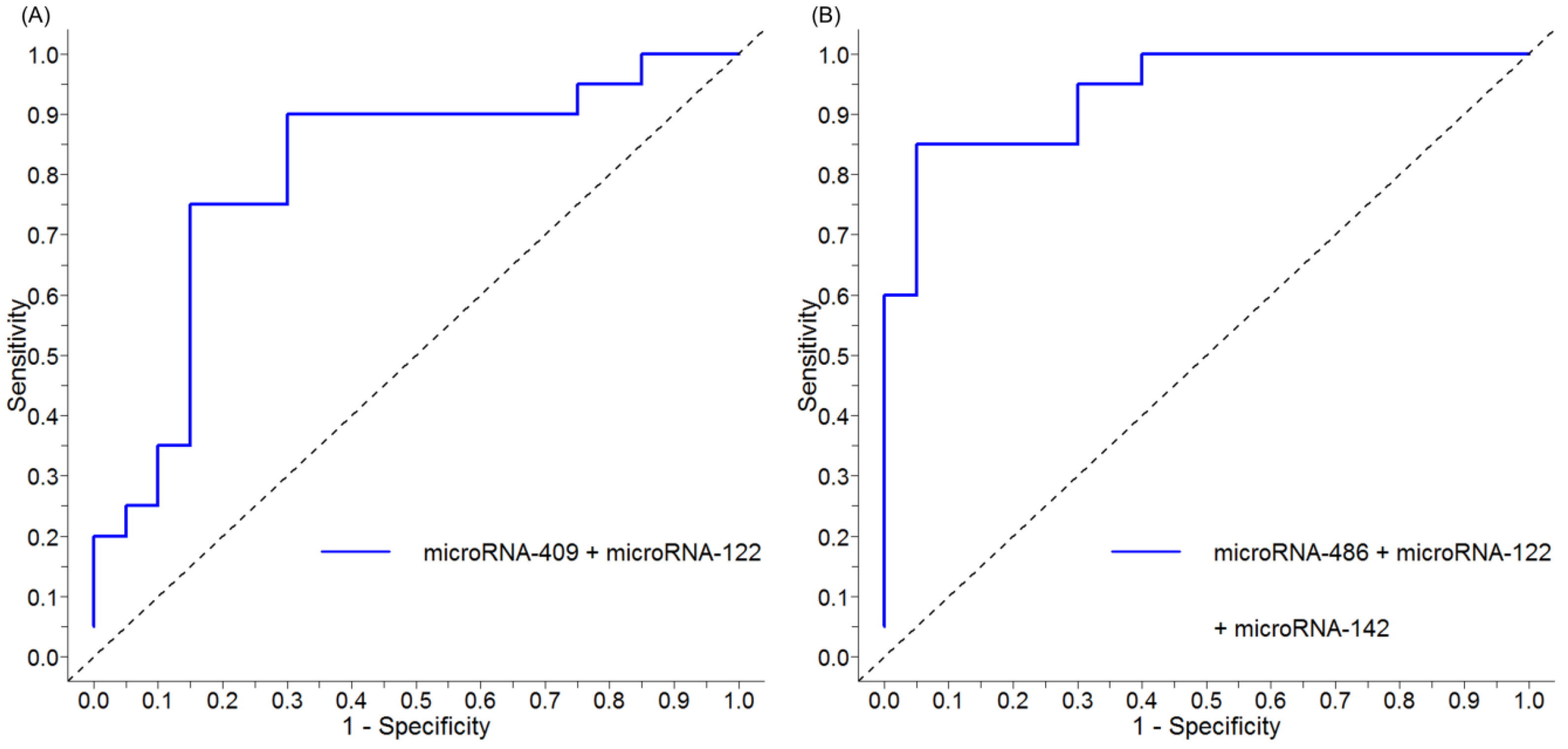
2.3. Discriminating Cirrhosis and Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) Using Serum miRNA Panels
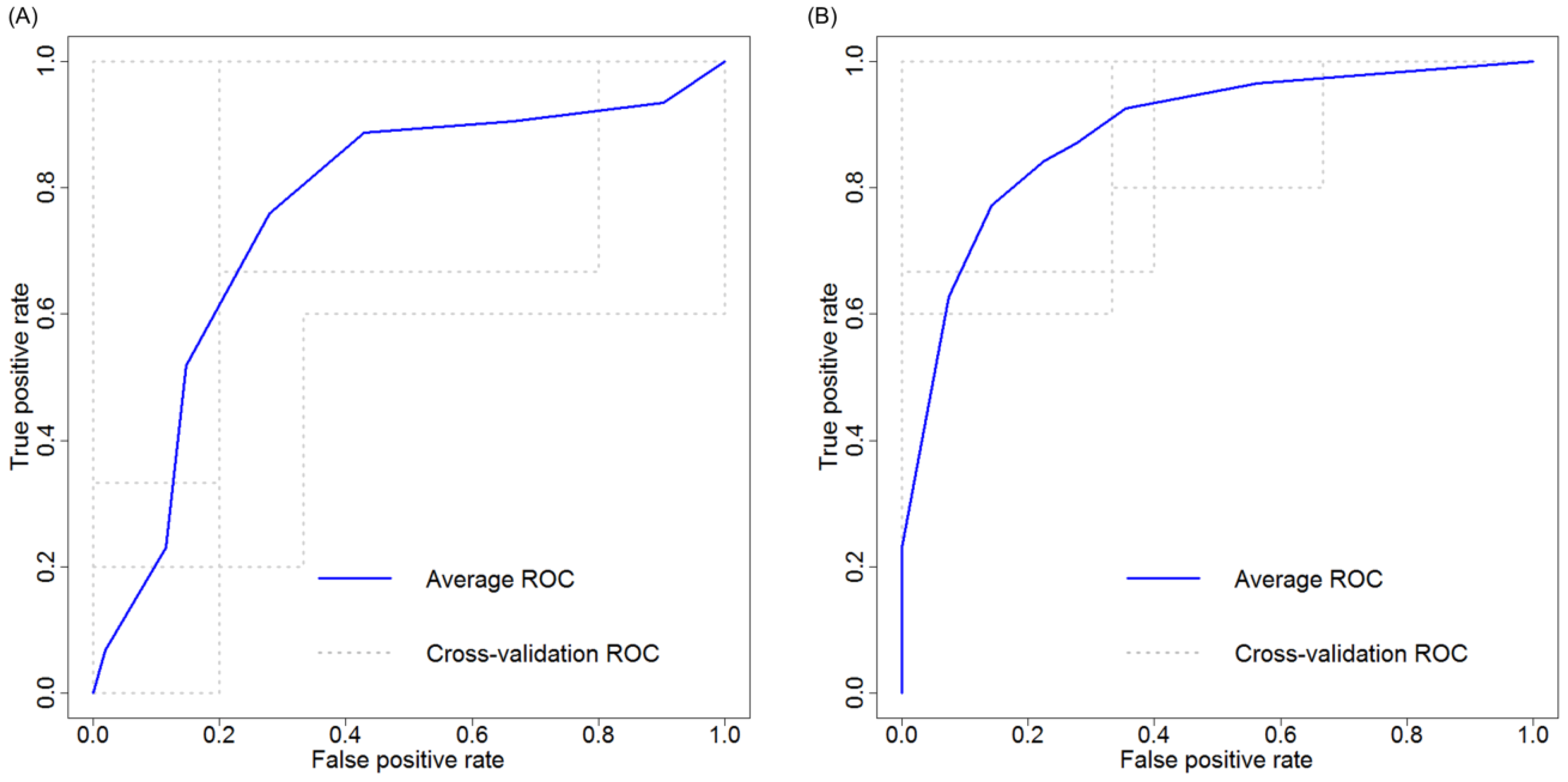
2.4. Cross Validation of Serum miRNA Panels
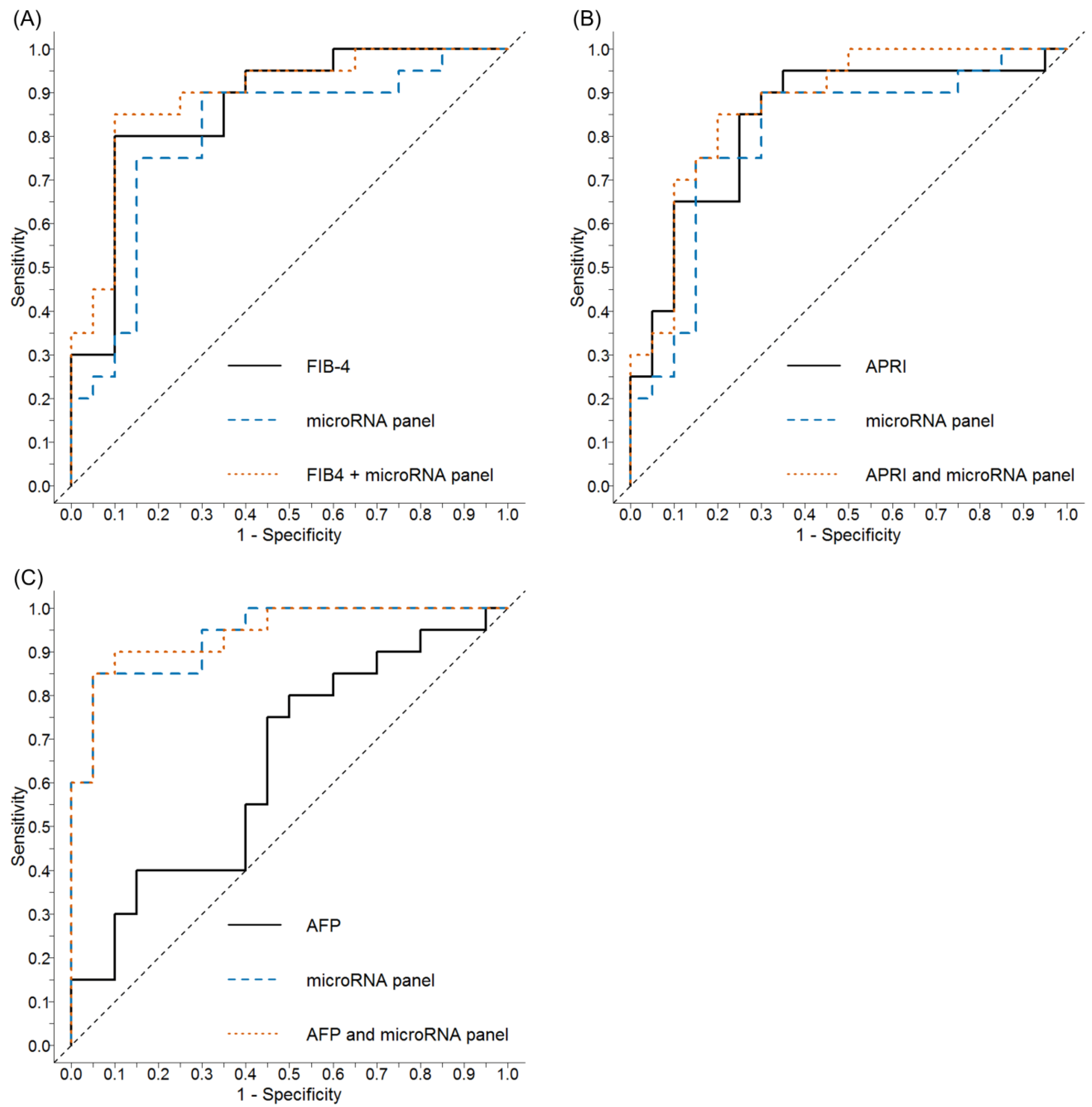
2.5. Comparative Performance of the Aspartate Aminotransferase-to-Platelet Ratio (APRI) and Fibrosis 4 (FIB-4) ± Serum miRNA Panel to Discriminate Cirrhosis
2.6. Comparative Performance of Alpha-Fetoprotein (AFP) ± Serum miRNA Panel to Discriminate HCC
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patient Recruitment and Characteristics
4.2. RNA Extractions and Reverse Transcription
4.3. miRNA PCR Array, qRT-PCR, and Data Analysis
4.4. Panel Design and k-Fold Cross Validation
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AFP | Alpha-fetoprotein |
| ALT | Alanine aminotransferase |
| APRI | Aspartate aminotransferase to platelet ratio |
| AST | Aspartate aminotransferase |
| AUC | Area under the curve |
| CHC | Chronic Hepatitis C |
| 95% CI | 95% Confidence interval |
| DAA | Direct acting antivirals |
| FAK | Focal adhesion kinase |
| FIB-4 | Fibrosis-4 |
| HCC | Hepatocellular carcinoma |
| IQR | Interquartile range |
| miRNA | MicroRNA |
| NEK2 | NIMA-related kinase 2 |
| NIMA | Never in mitosis gene a |
| NPV | Negative predictive value |
| PIK3R1 | Phosphoinositide-3-Kinase Regulatory Subunit 1 |
| PPV | Positive predictive value |
| qRT-PCR | Real-time quantitative reverse transcription PCR |
| ROC | Receiver operating characteristic |
| SVR | Sustained virologic response |
References
- Valery, P.C.; Laversanne, M.; Clark, P.J.; Petrick, J.L.; McGlynn, K.A.; Bray, F. Projections of primary liver cancer to 2030 in 30 countries worldwide. Hepatology 2018, 67, 600–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawlotsky, J.M.; Negro, F.; Aghemo, A.; Berengue, M.; Dalgard, O.; Dusheiko, G.; Marra, F.; Puoti, M.; Wedemeyer, H. EASL Recommendations on Treatment of Hepatitis C 2018. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 461–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wedemeyer, H.; Dore, G.J.; Ward, J.W. Estimates on HCV disease burden worldwide-filling the gaps. J. Viral Hepat 2015, 22, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, G.R.; Irving, W.L.; Cheung, M.C.; Walker, A.J.; Hudson, B.E.; Verma, S.; McLauchlan, J.; Mutimer, D.J.; Brown, A.; Gelson, W.T.; et al. Impact of direct acting antiviral therapy in patients with chronic hepatitis C and decompensated cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 1224–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Verveer, C.; Zondervan, P.E.; ten Kate, F.J.; Hansen, B.E.; Janssen, H.L.; de Knegt, R.J. Evaluation of transient elastography for fibrosis assessment compared with large biopsies in chronic hepatitis B and C. Liver Int. 2012, 32, 622–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.H.; Xin, Y.N.; Dong, Q.J.; Wang, Q.; Jiang, X.J.; Zhan, S.H.; Sun, Y.; Xuan, S.Y. Performance of the aspartate aminotransferase-to-platelet ratio index for the staging of hepatitis C-related fibrosis: An updated meta-analysis. Hepatology 2011, 53, 726–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallet-Pichard, A.; Mallet, V.; Nalpas, B.; Verkarre, V.; Nalpas, A.; Dhalluin-Venier, V.; Fontaine, H.; Pol, S. FIB-4: An inexpensive and accurate marker of fibrosis in HCV infection. comparison with liver biopsy and fibrotest. Hepatology 2007, 46, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singal, A.; Volk, M.L.; Waljee, A.; Salgia, R.; Higgins, P.; Rogers, M.A.; Marrero, J.A. Meta-analysis: Surveillance with ultrasound for early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with cirrhosis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2009, 30, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, G.; Kirschner, M.B.; van Zandwijk, N. Circulating microRNAs: Association with disease and potential use as biomarkers. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2011, 80, 193–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cermelli, S.; Ruggieri, A.; Marrero, J.A.; Ioannou, G.N.; Beretta, L. Circulating microRNAs in patients with chronic hepatitis C and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bihrer, V.; Friedrich-Rust, M.; Kronenberger, B.; Forestier, N.; Haupenthal, J.; Shi, Y.; Peveling-Oberhag, J.; Radeke, H.H.; Sarrazin, C.; Herrmann, E.; et al. Serum miR-122 as a biomarker of necroinflammation in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 106, 1663–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruix, J.; Sherman, M.; American Association for the Study of Liver, D. Management of hepatocellular carcinoma: An update. Hepatology 2011, 53, 1020–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Angileri, F.; Morrow, G.; Scoazec, J.Y.; Gadot, N.; Roy, V.; Huang, S.; Wu, T.; Tanguay, R.M. Identification of circulating microRNAs during the liver neoplastic process in a murine model of hereditary tyrosinemia type 1. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Josson, S.; Gururajan, M.; Hu, P.; Shao, C.; Chu, G.Y.; Zhau, H.E.; Liu, C.; Lao, K.; Lu, C.L.; Lu, Y.T.; et al. miR-409-3p/-5p promotes tumorigenesis, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition, and bone metastasis of human prostate cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 4636–4646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Liu, Z.; Xu, H.; Yang, Q. miR-409-3p suppresses breast cancer cell growth and invasion by targeting Akt1. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 469, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, J.; Lin, L.; Zhou, W.; Wang, Z.; Ding, G.; Dong, Q.; Qin, L.; Wu, X.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, Y.; et al. Identification of miRNomes in human liver and hepatocellular carcinoma reveals miR-199a/b-3p as therapeutic target for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Cell 2011, 19, 232–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bala, S.; Tilahun, Y.; Taha, O.; Alao, H.; Kodys, K.; Catalano, D.; Szabo, G. Increased microRNA-155 expression in the serum and peripheral monocytes in chronic HCV infection. J. Transl. Med. 2012, 10, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koberle, V.; Kronenberger, B.; Pleli, T.; Trojan, J.; Imelmann, E.; Peveling-Oberhag, J.; Welker, M.W.; Elhendawy, M.; Zeuzem, S.; Piiper, A.; et al. Serum microRNA-1 and microRNA-122 are prognostic markers in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur. J. Cancer 2013, 49, 3442–3449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulouarn, C.; Factor, V.M.; Andersen, J.B.; Durkin, M.E.; Thorgeirsson, S.S. Loss of miR-122 expression in liver cancer correlates with suppression of the hepatic phenotype and gain of metastatic properties. Oncogene 2009, 28, 3526–3536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Varnholt, H.; Drebber, U.; Schulze, F.; Wedemeyer, I.; Schirmacher, P.; Dienes, H.P.; Odenthal, M. MicroRNA gene expression profile of hepatitis C virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2008, 47, 1223–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Cui, C.; Xiao, F.; Wang, H.; Xu, J.; Shi, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zheng, X.; Yang, X.; et al. miR-486 regulates metastasis and chemosensitivity in hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting CLDN10 and CITRON. Hepatol. Res. 2015, 45, 1312–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, M.; Zhu, H.; Rong, W.; Wu, F.; An, S.; Liu, F.; Feng, L.; Wu, J.; Xu, N. Identification of recurrence-related serum microRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma following hepatectomy. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2015, 16, 1445–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, X.P.; Hou, J.; Shen, X.Y.; Huang, C.Y.; Zhang, X.H.; Xie, Y.A.; Luo, X.L. MicroRNA-486-5p, which is downregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma, suppresses tumor growth by targeting PIK3R1. FEBS J. 2015, 282, 579–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.J.; Chen, J.; Ji, F.; Ju, W.Q.; Zhao, Q.; Chen, M.G.; Guo, Z.Y.; Wu, L.W.; Ma, Y.; Wang, D.P.; et al. MiR-486-5p negatively regulates oncogenic NEK2 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 52948–52959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, J.; Huang, S.; Wu, S.; Zhao, Y.; Liang, L.; Yan, M.; Ge, C.; Yao, J.; Chen, T.; Wan, D.; et al. Gain of miR-151 on chromosome 8q24.3 facilitates tumour cell migration and spreading through downregulating RhoGDIA. Nat. Cell Biol. 2010, 12, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okajima, W.; Komatsu, S.; Ichikawa, D.; Miyamae, M.; Kawaguchi, T.; Hirajima, S.; Ohashi, T.; Imamura, T.; Kiuchi, J.; Arita, T.; et al. Circulating microRNA profiles in plasma: Identification of miR-224 as a novel diagnostic biomarker in hepatocellular carcinoma independent of hepatic function. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 53820–53836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.M.; Zhang, C.; Burchard, J.; Fan, S.T.; Wong, K.F.; Dai, H.; Poon, R.T.; Luk, J.M. Global regulation on microRNA in hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. OMICS 2011, 15, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Li, W.; Hu, L.; Zhou, H.; Zheng, L.; Yu, L.; Liang, W. Diagnostic value of circulating microRNAs for liver cirrhosis: A meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 5397–5405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Yan, J.L.; Fang, A.N.; Zhou, W.F.; Huang, L. Circulating miRNAs as novel diagnostic biomarkers in hepatocellular carcinoma detection: A meta-analysis based on 24 articles. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 66402–66413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.H.; Liang, K.H.; Chien, R.N.; Hu, T.H.; Lin, K.H.; Hsu, C.W.; Lin, C.L.; Pan, T.L.; Ke, P.Y.; Yeh, C.T. A Circulating MicroRNA Signature Capable of Assessing the Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Cirrhotic Patients. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Team, R.C. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2013; ISBN 3-900051-07-0. [Google Scholar]
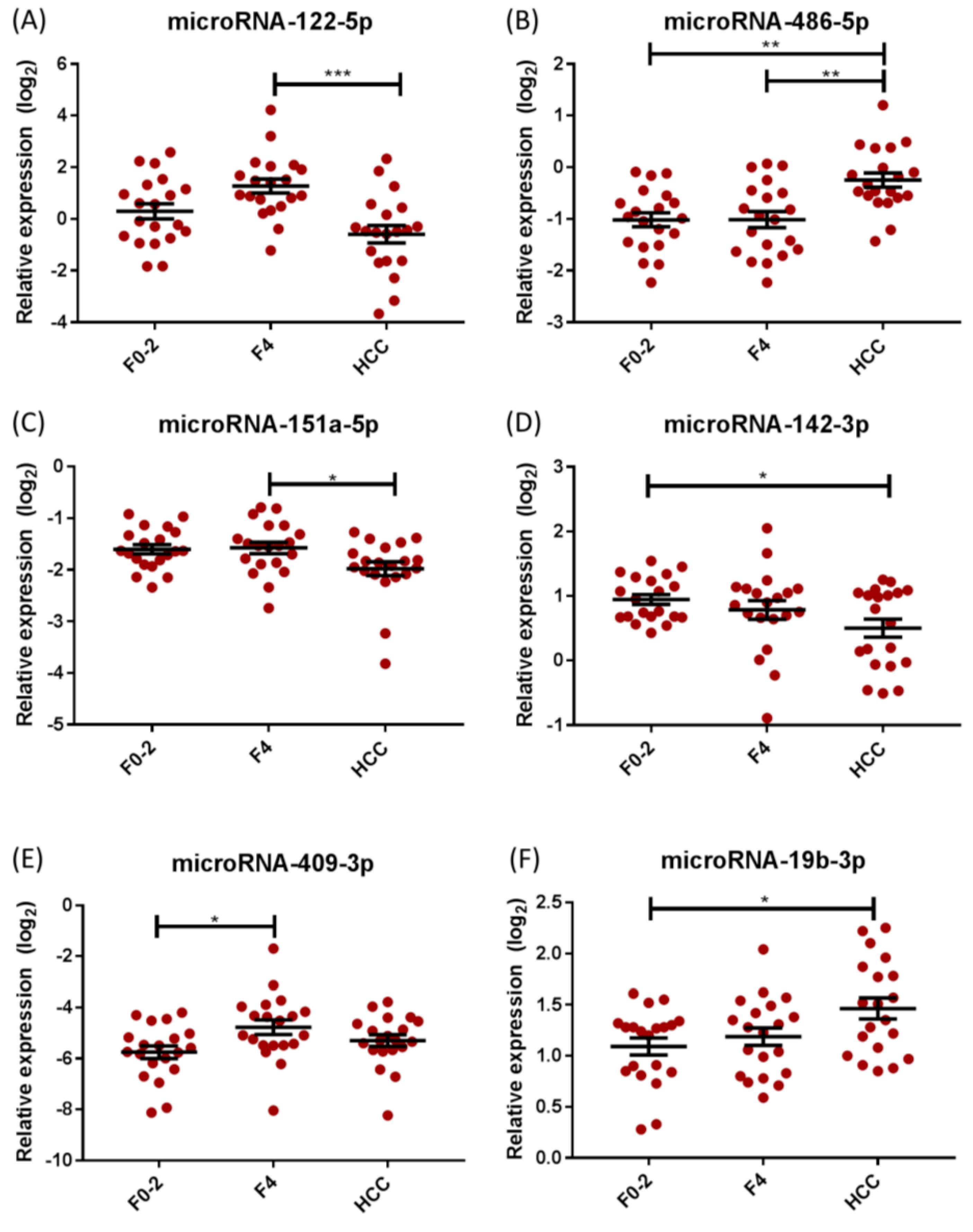

| miRNA | Overall p-Value (ANOVA) | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F0-2 vs. F4 | F0-2 vs. HCC | F4 vs. HCC | ||
| miRNA-122-5p | <0.001 | 0.066 | 0.103 | <0.001 |
| miRNA-486-5p | <0.001 | 0.999 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| miRNA-151a-5p | 0.025 | 0.986 | 0.056 | 0.039 |
| miRNA-409-3p | 0.030 | 0.023 | 0.417 | 0.320 |
| miRNA-19b-3p | 0.015 | 0.734 | 0.015 | 0.089 |
| miRNA-142-3p | 0.047 | 0.636 | 0.039 | 0.253 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Weis, A.; Marquart, L.; Calvopina, D.A.; Genz, B.; Ramm, G.A.; Skoien, R. Serum MicroRNAs as Biomarkers in Hepatitis C: Preliminary Evidence of a MicroRNA Panel for the Diagnosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 864. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20040864
Weis A, Marquart L, Calvopina DA, Genz B, Ramm GA, Skoien R. Serum MicroRNAs as Biomarkers in Hepatitis C: Preliminary Evidence of a MicroRNA Panel for the Diagnosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(4):864. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20040864
Chicago/Turabian StyleWeis, Anna, Louise Marquart, Diego A. Calvopina, Berit Genz, Grant A. Ramm, and Richard Skoien. 2019. "Serum MicroRNAs as Biomarkers in Hepatitis C: Preliminary Evidence of a MicroRNA Panel for the Diagnosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 4: 864. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20040864
APA StyleWeis, A., Marquart, L., Calvopina, D. A., Genz, B., Ramm, G. A., & Skoien, R. (2019). Serum MicroRNAs as Biomarkers in Hepatitis C: Preliminary Evidence of a MicroRNA Panel for the Diagnosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(4), 864. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20040864





