Understanding Platelets in Infectious and Allergic Lung Diseases
Abstract
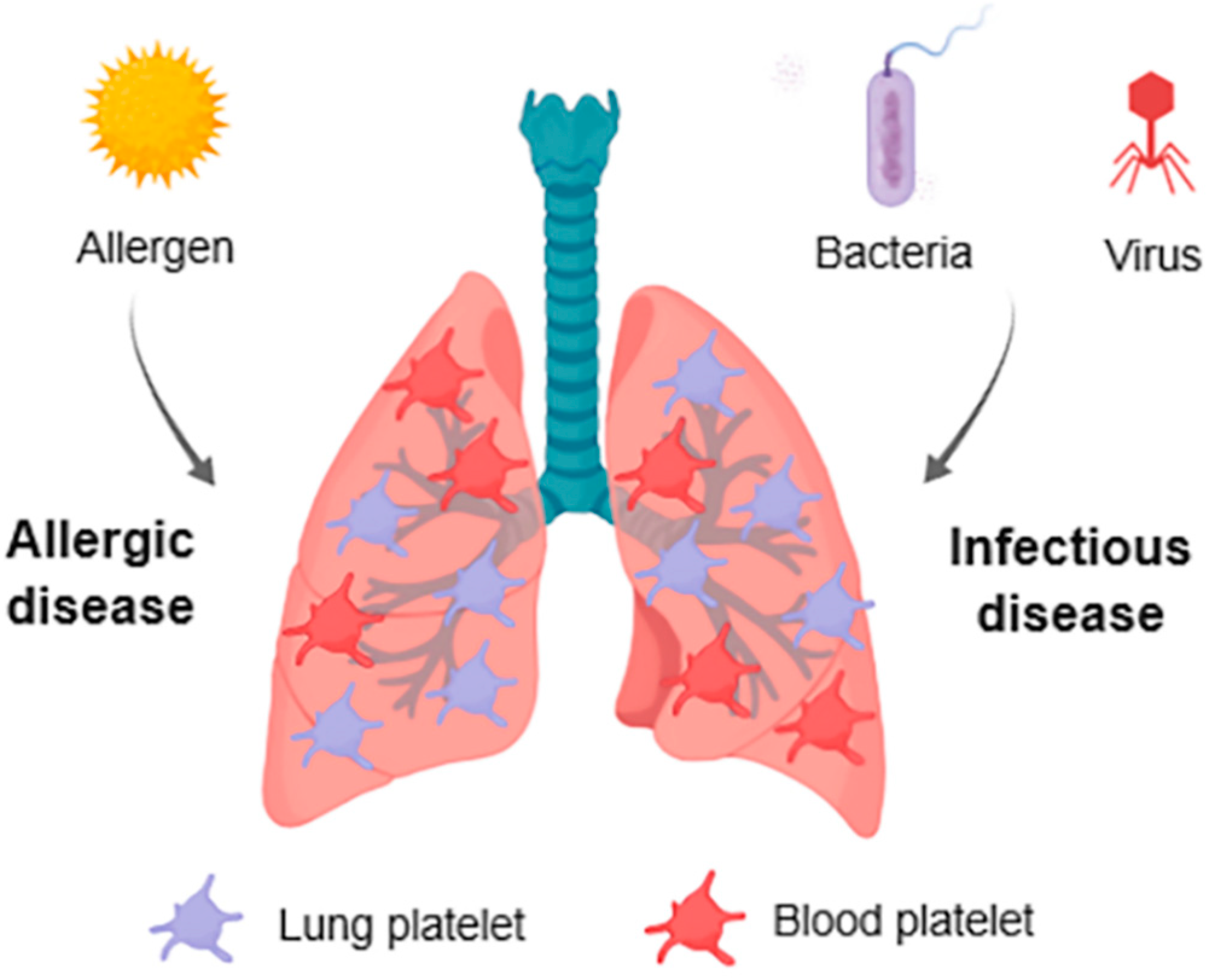
1. Introduction
2. Platelet Biology
2.1. Platelets as Coagulation Factors
2.2. Platelets as Immune Mediators
2.3. Metabolic Plasticity of Platelets
3. Platelets in Respiratory Allergic Inflammation
3.1. Alterations in Platelet Functions
3.2. Platelet Contribution in Lung Allergic Sensitization and Inflammation
3.3. Lung Platelets
4. Platelets in Infectious Diseases
4.1. Platelets in Bacterial Infection
4.2. Platelets in Viral Infection
5. Systemic Biomarkers of Platelet Activation with Predictive Potential
6. Considerations in Human Platelet Research
7. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rondina, M.T.; Garraud, O. Emerging evidence for platelets as immune and inflammatory effector cells. Front Immunol. 2014, 5, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machlus, K.R.; Italiano, J.E., Jr. The incredible journey: From megakaryocyte development to platelet formation. J. Cell. Biol. 2013, 201, 785–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grozovsky, R.; Giannini, S.; Falet, H.; Hoffmeister, K.M. Regulating billions of blood platelets: Glycans and beyond. Blood 2015, 126, 1877–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrell, C.N.; Aggrey, A.A.; Chapman, L.M.; Modjeski, K.L. Emerging roles for platelets as immune and inflammatory cells. Blood 2014, 123, 2759–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, K.D.; Carpinelli, M.R.; Fletcher, J.I.; Collinge, J.E.; Hilton, A.A.; Ellis, S.; Kelly, P.N.; Ekert, P.G.; Metcalf, D.; Roberts, A.W.; et al. Programmed anuclear cell death delimits platelet life span. Cell 2007, 128, 1173–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McArthur, K.; Chappaz, S.; Kile, B.T. Apoptosis in megakaryocytes and platelets: The life and death of a lineage. Blood 2018, 131, 605–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coller, B.S.; Shattil, S.J. The GPIIb/IIIa (integrin αIIbβ3) odyssey: A technology-driven saga of a receptor with twists, turns, and even a bend. Blood 2008, 112, 3011–3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plow, E.F.; Meller, J.; Byzova, T.V. Integrin function in vascular biology: A view from 2013. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2014, 21, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deppermann, C.; Kubes, P. Platelets and infection. Semin. Immunol. 2016, 28, 536–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.R.; Storey, R.F. The role of platelets in inflammation. Thromb. Haemost. 2015, 114, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho-Tin-Noe, B.; Demers, M.; Wagner, D.D. How platelets safeguard vascular integrity. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2011, 9, S56–S65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenen, R.R. The prowess of platelets in immunity and inflammation. Thromb. Haemost. 2016, 116, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, P.R.; Rawnsley, D.R.; Jakus, Z.; Yang, Y.; Sweet, D.T.; Fu, J.; Herzog, B.; Lu, M.; Nieswandt, B.; Oliver, G.; et al. Platelets mediate lymphovenous hemostasis to maintain blood-lymphatic separation throughout life. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, A.T.; Corken, A.; Ware, J. Platelets at the interface of thrombosis, inflammation, and cancer. Blood 2015, 126, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, C.M.; Fingerlin, T.E.; Schwarz, M.I.; Lynch, D.; Kurche, J.; Warg, L.; Yang, I.V.; Schwartz, D.A. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Genetic Disease That Involves Mucociliary Dysfunction of the Peripheral Airways. Physiol. Rev. 2016, 96, 1567–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsh, J.D.; Kahn, M.L.; Sweet, D.T. Lymphovenous hemostasis and the role of platelets in regulating lymphatic flow and lymphatic vessel maturation. Blood 2016, 128, 1169–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondina, M.T.; Weyrich, A.S.; Zimmerman, G.A. Platelets as cellular effectors of inflammation in vascular diseases. Circ. Res. 2013, 112, 1506–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, T.; Wakasawa, T.; Shima, Y.; Tsuboi, I.; Aizawa, S.; Tamai, I. Role of polyamines derived from arginine in differentiation and proliferation of human blood cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2006, 29, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapata, J.C.; Cox, D.; Salvato, M.S. The role of platelets in the pathogenesis of viral hemorrhagic fevers. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyth, S.S.; McEver, R.P.; Weyrich, A.S.; Morrell, C.N.; Hoffman, M.R.; Arepally, G.M.; French, P.A.; Dauerman, H.L.; Becker, R.C.; Platelet Colloquium, P. Platelet functions beyond hemostasis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2009, 7, 1759–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thon, J.N.; Peters, C.G.; Machlus, K.R.; Aslam, R.; Rowley, J.; Macleod, H.; Devine, M.T.; Fuchs, T.A.; Weyrich, A.S.; Semple, J.W.; et al. T granules in human platelets function in TLR9 organization and signaling. J. Cell Biol. 2012, 198, 561–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maynard, D.M.; Heijnen, H.F.; Horne, M.K.; White, J.G.; Gahl, W.A. Proteomic analysis of platelet α-granules using mass spectrometry. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2007, 5, 1945–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koseoglu, S.; Flaumenhaft, R. Advances in platelet granule biology. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2013, 20, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurden, A.T. Platelets, inflammation and tissue regeneration. Thromb. Haemost. 2011, 105, S13–S33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, P.; Flaumenhaft, R. Platelet alpha-granules: Basic biology and clinical correlates. Blood Rev. 2009, 23, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deppermann, C.; Cherpokova, D.; Nurden, P.; Schulz, J.N.; Thielmann, I.; Kraft, P.; Vogtle, T.; Kleinschnitz, C.; Dutting, S.; Krohne, G.; et al. Gray platelet syndrome and defective thrombo-inflammation in Nbeal2-deficient mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, N.; Soga, F.; Nara, T.; Tamagawa-Mineoka, R.; Nin, M.; Kotani, H.; Masuda, K.; Kishimoto, S. Effect of serotonin on the differentiation of human monocytes into dendritic cells. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2006, 146, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leon-Ponte, M.; Ahern, G.P.; O’Connell, P.J. Serotonin provides an accessory signal to enhance T-cell activation by signaling through the 5-HT7 receptor. Blood 2007, 109, 3139–3146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langer, H.F.; Daub, K.; Braun, G.; Schonberger, T.; May, A.E.; Schaller, M.; Stein, G.M.; Stellos, K.; Bueltmann, A.; Siegel-Axel, D.; et al. Platelets recruit human dendritic cells via Mac-1/JAM-C interaction and modulate dendritic cell function in vitro. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc. Biol. 2007, 27, 1463–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagihara, M.; Higuchi, A.; Tamura, N.; Ueda, Y.; Hirabayashi, K.; Ikeda, Y.; Kato, S.; Sakamoto, S.; Hotta, T.; Handa, S.; et al. Platelets, after exposure to a high shear stress, induce IL-10-producing, mature dendritic cells in vitro. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 5297–5303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danese, S.; de la Motte, C.; Reyes, B.M.; Sans, M.; Levine, A.D.; Fiocchi, C. Cutting edge: T cells trigger CD40-dependent platelet activation and granular RANTES release: A novel pathway for immune response amplification. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 2011–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elzey, B.D.; Tian, J.; Jensen, R.J.; Swanson, A.K.; Lees, J.R.; Lentz, S.R.; Stein, C.S.; Nieswandt, B.; Wang, Y.; Davidson, B.L.; et al. Platelet-mediated modulation of adaptive immunity. A communication link between innate and adaptive immune compartments. Immunity 2003, 19, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindemann, S.; Tolley, N.D.; Dixon, D.A.; McIntyre, T.M.; Prescott, S.M.; Zimmerman, G.A.; Weyrich, A.S. Activated platelets mediate inflammatory signaling by regulated interleukin 1beta synthesis. J. Cell Biol. 2001, 154, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, G.T.; McIntyre, T.M. Lipopolysaccharide signaling without a nucleus: Kinase cascades stimulate platelet shedding of proinflammatory IL-1β-rich microparticles. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 5489–5496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.; Field, D.J.; Ko, K.A.; Ture, S.; Srivastava, K.; Levy, S.; Kowalska, M.A.; Poncz, M.; Fowell, D.J.; Morrell, C.N. Platelet factor 4 limits Th17 differentiation and cardiac allograft rejection. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi, S.; Chacko, B.; Sawada, H.; Kramer, P.A.; Johnson, M.S.; Benavides, G.A.; O′Donnell, V.; Marques, M.B.; Darley-Usmar, V.M. Metabolic plasticity in resting and thrombin activated platelets. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obeso, D.; Mera-Berriatua, L.; Rodriguez-Coira, J.; Rosace, D.; Fernandez, P.; Martin-Antoniano, I.A.; Santaolalla, M.; Marco Martin, G.; Chivato, T.; Fernandez-Rivas, M.; et al. Multi-omics analysis points to altered platelet functions in severe food-associated respiratory allergy. Allergy 2018, 73, 2137–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Cardenes, N.; Corey, C.; Erzurum, S.C.; Shiva, S. Platelets from Asthmatic Individuals Show Less Reliance on Glycolysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0132007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, C.; Pitchford, S. Platelets and allergic inflammation. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2014, 44, 901–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caspary, E.A.; Comaish, J.S. Release of serotonin from human platelets in hypersensitivity states. Nature 1967, 214, 286–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audera, C.; Rocklin, R.; Vaillancourt, R.; Jakubowski, J.A.; Deykin, D. Altered arachidonic acid metabolism and platelet size in atopic subjects. Clin. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1988, 46, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczeklik, A.; Milner, P.C.; Birch, J.; Watkins, J.; Martin, J.F. Prolonged bleeding time, reduced platelet aggregation, altered PAF-acether sensitivity and increased platelet mass are a trait of asthma and hay fever. Thromb. Haemost. 1986, 56, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taytard, A.; Guenard, H.; Vuillemin, L.; Bouvot, J.L.; Vergeret, J.; Ducassou, D.; Piquet, Y.; Freour, P. Platelet kinetics in stable atopic asthmatic patients. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1986, 134, 983–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ind, P.W.; Peters, A.M.; Malik, F.; Lavender, J.P.; Dollery, C.T. Pulmonary platelet kinetics in asthma. Thorax 1985, 40, 412–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmendinger, S.; Pauli, G.; Tenabene, A.; Pujol, J.L.; Bessot, J.C.; Eber, M.; Cazenave, J.P. Platelet function: Aggregation by PAF or sequestration in lung is not modified during immediate or late allergen-induced bronchospasm in man. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1989, 83, 990–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, J.S.; Bernstein, I.L.; Maccia, C.A.; Splansky, G.L.; Glueck, H.I. Cyclic platelet dysfunction in IgE-mediated allergy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1978, 62, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gresele, P.; Dottorini, M.; Selli, M.L.; Iannacci, L.; Canino, S.; Todisco, T.; Romano, S.; Crook, P.; Page, C.P.; Nenci, G.G. Altered platelet function associated with the bronchial hyperresponsiveness accompanying nocturnal asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1993, 91, 894–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pareti, F.I.; Capitanio, A.; Mannucci, L.; Ponticelli, C.; Mannucci, P.M. Acquired dysfunction due to the circulation of “exhausted” platelets. Am. J. Med. 1980, 69, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maccia, C.A.; Gallagher, J.S.; Ataman, G.; Glueck, H.I.; Brooks, S.M.; Bernstein, I.L. Platelet thrombopathy in asthmatic patients with elevated immunoglobulin E. J. Allergy. Clin. Immunol. 1977, 59, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loftus, R.M.; Finlay, D.K. Immunometabolism: Cellular Metabolism Turns Immune Regulator. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, L.A.; Kishton, R.J.; Rathmell, J. A guide to immunometabolism for immunologists. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 553–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostroukhova, M.; Goplen, N.; Karim, M.Z.; Michalec, L.; Guo, L.; Liang, Q.; Alam, R. The role of low-level lactate production in airway inflammation in asthma. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2012, 302, L300–L307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigo, G.J.; Rodrigo, C. Elevated plasma lactate level associated with high dose inhaled albuterol therapy in acute severe asthma. Emerg. Med. J. 2005, 22, 404–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shime, H.; Yabu, M.; Akazawa, T.; Kodama, K.; Matsumoto, M.; Seya, T.; Inoue, N. Tumor-secreted lactic acid promotes IL-23/IL-17 proinflammatory pathway. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 7175–7183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcus, A.J.; Broekman, M.J.; Safier, L.B.; Ullman, H.L.; Islam, N.; Serhan, C.N.; Weissmann, G. Production of arachidonic acid lipoxygenase products during platelet–neutrophil interactions. Clin. Physiol. Biochem 1984, 2, 78–83. [Google Scholar]
- Marcus, A.J.; Safier, L.B.; Ullman, H.L.; Islam, N.; Broekman, M.J.; von Schacky, C. Studies on the mechanism of omega-hydroxylation of platelet 12-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid (12-HETE) by unstimulated neutrophils. J. Clin. Investig. 1987, 79, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roviezzo, F.; Sorrentino, R.; Bertolino, A.; De Gruttola, L.; Terlizzi, M.; Pinto, A.; Napolitano, M.; Castello, G.; D’Agostino, B.; Ianaro, A.; et al. S1P-induced airway smooth muscle hyperresponsiveness and lung inflammation in vivo: Molecular and cellular mechanisms. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 1882–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivera, A. Unraveling the complexities of sphingosine-1-phosphate function: The mast cell model. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2008, 86, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitchford, S.C.; Riffo-Vasquez, Y.; Sousa, A.; Momi, S.; Gresele, P.; Spina, D.; Page, C.P. Platelets are necessary for airway wall remodeling in a murine model of chronic allergic inflammation. Blood 2004, 103, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, M.; Ogura, M.; Tsutsumi, T.; Tsuji, H.; Yamashita, T. Presence of platelet-activating factor in nasal polyps and eosinophils. Acta Otolaryngol. 2002, 122, 872–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laidlaw, T.M.; Boyce, J.A. Cysteinyl leukotriene receptors, old and new; implications for asthma. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2012, 42, 1313–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benveniste, J.; Henson, P.M.; Cochrane, C.G. Leukocyte-dependent histamine release from rabbit platelets. The role of IgE, basophils, and a platelet-activating factor. J. Exp. Med. 1972, 136, 1356–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, S.; Wanke, K.; Wawrzyniak, P.; Meng, Y.; Kast, J.I.; Ruckert, B.; Rebane, A.; Xian, M.; Bindslev-Jensen, C.; Broesby-Olsen, S.; et al. Platelet-activating factor decreases skin keratinocyte tight junction barrier integrity. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 138, 1725–1728 e1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, T.; Unno, H.; Morita, H.; Futamura, K.; Emi-Sugie, M.; Arae, K.; Shoda, T.; Okada, N.; Igarashi, A.; Inoue, E.; et al. Platelets constitutively express IL-33 protein and modulate eosinophilic airway inflammation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 138, 1395–1403 e1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darius, H.; Lefer, D.J.; Smith, J.B.; Lefer, A.M. Role of platelet-activating factor-acether in mediating guinea pig anaphylaxis. Science 1986, 232, 58–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, S.; Kuwaki, T.; Nagase, T.; Maki, K.; Tashiro, F.; Sunaga, S.; Cao, W.H.; Kume, K.; Fukuchi, Y.; Ikuta, K.; et al. Impaired anaphylactic responses with intact sensitivity to endotoxin in mice lacking a platelet-activating factor receptor. J. Exp. Med. 1998, 187, 1779–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadas, P.; Gold, M.; Perelman, B.; Liss, G.M.; Lack, G.; Blyth, T.; Simons, F.E.; Simons, K.J.; Cass, D.; Yeung, J. Platelet-activating factor, PAF acetylhydrolase, and severe anaphylaxis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, K.; Baig, M.; Colangelo, M.; Chu, D.; Walker, T.; Goncharova, S.; Coyle, A.; Vadas, P.; Waserman, S.; Jordana, M. Concurrent blockade of platelet-activating factor and histamine prevents life-threatening peanut-induced anaphylactic reactions. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009, 124, 307–314, 314 e301–314-e302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escribese, M.M.; Rosace, D.; Chivato, T.; Fernandez, T.D.; Corbi, A.L.; Barber, D. Alternative Anaphylactic Routes: The Potential Role of Macrophages. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez-Saiz, R.; Ellenbogen, Y.; Koenig, J.F.E.; Gordon, M.E.; Walker, T.D.; Rosace, D.; Spill, P.; Bruton, K.; Kong, J.; Monteiro, K.; et al. IgG1+ B-cell immunity predates IgE responses in epicutaneous sensitization to foods. Allergy 2019, 74, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodoun, M.V.; Strait, R.; Armstrong, L.; Yanase, N.; Finkelman, F.D. Identification of markers that distinguish IgE- from IgG-mediated anaphylaxis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 12413–12418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amison, R.T.; Cleary, S.J.; Riffo-Vasquez, Y.; Bajwa, M.; Page, C.P.; Pitchford, S.C. Platelets Play a Central Role in Sensitization to Allergen. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2018, 59, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemetson, K.J.; Clemetson, J.M.; Proudfoot, A.E.; Power, C.A.; Baggiolini, M.; Wells, T.N. Functional expression of CCR1, CCR3, CCR4, and CXCR4 chemokine receptors on human platelets. Blood 2000, 96, 4046–4054. [Google Scholar]
- Joseph, M.; Gounni, A.S.; Kusnierz, J.P.; Vorng, H.; Sarfati, M.; Kinet, J.P.; Tonnel, A.B.; Capron, A.; Capron, M. Expression and functions of the high-affinity IgE receptor on human platelets and megakaryocyte precursors. Eur. J. Immunol. 1997, 27, 2212–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cognasse, F.; Nguyen, K.A.; Damien, P.; McNicol, A.; Pozzetto, B.; Hamzeh-Cognasse, H.; Garraud, O. The Inflammatory Role of Platelets via Their TLRs and Siglec Receptors. Front Immunol. 2015, 6, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitchford, S.C.; Momi, S.; Giannini, S.; Casali, L.; Spina, D.; Page, C.P.; Gresele, P. Platelet P-selectin is required for pulmonary eosinophil and lymphocyte recruitment in a murine model of allergic inflammation. Blood 2005, 105, 2074–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semple, J.W.; Freedman, J. Platelets and innate immunity. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2010, 67, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Vandenbriele, C.; Kauskot, A.; Verhamme, P.; Hoylaerts, M.F.; Wright, G.J. A Human Platelet Receptor Protein Microarray Identifies the High Affinity Immunoglobulin E Receptor Subunit α (FcepsilonR1α) as an Activating Platelet Endothelium Aggregation Receptor 1 (PEAR1) Ligand. Mol. Cell Proteomics 2015, 14, 1265–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, H.J.; Sutton, B.J. IgE in allergy and asthma today. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ind, P.W. Platelet and clotting abnormalities in asthma. Clin. Exp. Allergy 1991, 21, 395–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma-Carlos, A.G.; Palma-Carlos, M.L.; Santos, M.C.; de Sousa, J.R. Platelet aggregation in allergic reactions. Int. Arch. Allergy Appl. Immunol. 1991, 94, 251–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harwell, W.B.; Patterson, J.T.; Lieberman, P.; Beachey, E. Platelet aggregation in atopic and normal patients. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1973, 51, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, J.R.; Tan, E.M.; Stevenson, D.D.; Vaughan, J.H. Platelet aggregation in asthmatic and normal subjects. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1974, 54, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieberman, J.A.; Chehade, M. Use of omalizumab in the treatment of food allergy and anaphylaxis. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2013, 13, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacGlashan, D.W., Jr.; Bochner, B.S.; Adelman, D.C.; Jardieu, P.M.; Togias, A.; McKenzie-White, J.; Sterbinsky, S.A.; Hamilton, R.G.; Lichtenstein, L.M. Down-regulation of Fc(epsilon)RI expression on human basophils during in vivo treatment of atopic patients with anti-IgE antibody. J. Immunol. 1997, 158, 1438–1445. [Google Scholar]
- Holgate, S.; Casale, T.; Wenzel, S.; Bousquet, J.; Deniz, Y.; Reisner, C. The anti-inflammatory effects of omalizumab confirm the central role of IgE in allergic inflammation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2005, 115, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.K.; Hartzema, A.G. Assessing the association between omalizumab and arteriothrombotic events through spontaneous adverse event reporting. J. Asthma Allergy 2012, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everds, N.E.; Tarrant, J.M. Unexpected hematologic effects of biotherapeutics in nonclinical species and in humans. Toxicol. Pathol. 2013, 41, 280–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefrancais, E.; Ortiz-Munoz, G.; Caudrillier, A.; Mallavia, B.; Liu, F.; Sayah, D.M.; Thornton, E.E.; Headley, M.B.; David, T.; Coughlin, S.R.; et al. The lung is a site of platelet biogenesis and a reservoir for haematopoietic progenitors. Nature 2017, 544, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, W.H.; Donahue, D.D. The Production of Blood Platelets in the Lungs. J. Exp. Med. 1937, 65, 177–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallinikos-Maniatis, A. Megakaryocytes and platelets in central venous and arterial blood. Acta Haematol. 1969, 42, 330–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunois-Larde, C.; Capron, C.; Fichelson, S.; Bauer, T.; Cramer-Borde, E.; Baruch, D. Exposure of human megakaryocytes to high shear rates accelerates platelet production. Blood 2009, 114, 1875–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, K.; de Waard, V.; Fearns, C.; Loskutoff, D.J. Tissue distribution and regulation of murine von Willebrand factor gene expression in vivo. Blood 1998, 92, 2791–2801. [Google Scholar]
- Aslam, R.; Speck, E.R.; Kim, M.; Crow, A.R.; Bang, K.W.; Nestel, F.P.; Ni, H.; Lazarus, A.H.; Freedman, J.; Semple, J.W. Platelet Toll-like receptor expression modulates lipopolysaccharide-induced thrombocytopenia and tumor necrosis factor-alpha production in vivo. Blood 2006, 107, 637–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, O.; Hoshino, K.; Kawai, T.; Sanjo, H.; Takada, H.; Ogawa, T.; Takeda, K.; Akira, S. Differential roles of TLR2 and TLR4 in recognition of gram-negative and gram-positive bacterial cell wall components. Immunity 1999, 11, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, S.R.; Ma, A.C.; Tavener, S.A.; McDonald, B.; Goodarzi, Z.; Kelly, M.M.; Patel, K.D.; Chakrabarti, S.; McAvoy, E.; Sinclair, G.D.; et al. Platelet TLR4 activates neutrophil extracellular traps to ensnare bacteria in septic blood. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, F.Y.; Davidson, S.J.; Moraes, L.A.; Traves, S.L.; Paul-Clark, M.; Bishop-Bailey, D.; Warner, T.D.; Mitchell, J.A. Role of nuclear receptor signaling in platelets: Antithrombotic effects of PPARbeta. FASEB J. 2006, 20, 326–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andonegui, G.; Kerfoot, S.M.; McNagny, K.; Ebbert, K.V.; Patel, K.D.; Kubes, P. Platelets express functional Toll-like receptor-4. Blood 2005, 106, 2417–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, A.E.; Bayer, C.R.; Chen, R.Y.; Guth, P.H.; Wallace, R.J.; Stevens, D.L. Vascular dysfunction and ischemic destruction of tissue in Streptococcus pyogenes infection: The role of streptolysin O-induced platelet/neutrophil complexes. J. Infect. Dis. 2005, 192, 1014–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, S.M.; Lutay, N.; Holmqvist, B.; Shannon, O. The Dynamics of Platelet Activation during the Progression of Streptococcal Sepsis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, O. Platelet interaction with bacterial toxins and secreted products. Platelets 2015, 26, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. The Top 10 Causes of Death. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/the-top-10-causes-of-death (accessed on 7 March 2016).
- Sanz Herrero, F.; Blanquer Olivas, J. Microbiology and risk factors for community-acquired pneumonia. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 33, 220–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rae, N.; Finch, S.; Chalmers, J.D. Cardiovascular disease as a complication of community-acquired pneumonia. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2016, 22, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guckian, J.C. Effect of pneumococci on blood clotting, platelets, and polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect. Immun. 1975, 12, 910–918. [Google Scholar]
- Tunjungputri, R.N.; van de Heijden, W.; Urbanus, R.T.; de Groot, P.G.; van der Ven, A.; de Mast, Q. Higher platelet reactivity and platelet-monocyte complex formation in Gram-positive sepsis compared to Gram-negative sepsis. Platelets 2017, 28, 595–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Violi, F.; Cangemi, R.; Falcone, M.; Taliani, G.; Pieralli, F.; Vannucchi, V.; Nozzoli, C.; Venditti, M.; Chirinos, J.A.; Corrales-Medina, V.F.; et al. Cardiovascular Complications and Short-term Mortality Risk in Community-Acquired Pneumonia. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 64, 1486–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferroni, P.; Riondino, S.; Vazzana, N.; Santoro, N.; Guadagni, F.; Davi, G. Biomarkers of platelet activation in acute coronary syndromes. Thromb. Haemost. 2012, 108, 1109–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunjungputri, R.N.; Mobegi, F.M.; Cremers, A.J.; van der Gaast-de Jongh, C.E.; Ferwerda, G.; Meis, J.F.; Roeleveld, N.; Bentley, S.D.; Pastura, A.S.; van Hijum, S.A.; et al. Phage-Derived Protein Induces Increased Platelet Activation and Is Associated with Mortality in Patients with Invasive Pneumococcal Disease. MBio 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaudewitz, D.; Skroblin, P.; Bender, L.H.; Barwari, T.; Willeit, P.; Pechlaner, R.; Sunderland, N.P.; Willeit, K.; Morton, A.C.; Armstrong, P.C.; et al. Association of MicroRNAs and YRNAs With Platelet Function. Circ. Res. 2016, 118, 420–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunderland, N.; Skroblin, P.; Barwari, T.; Huntley, R.P.; Lu, R.; Joshi, A.; Lovering, R.C.; Mayr, M. MicroRNA Biomarkers and Platelet Reactivity: The Clot Thickens. Circ. Res. 2017, 120, 418–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.; Feldman, C. Review manuscript: Mechanisms of platelet activation by the pneumococcus and the role of platelets in community-acquired pneumonia. J. Infect. 2017, 75, 473–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssefian, T.; Drouin, A.; Masse, J.M.; Guichard, J.; Cramer, E.M. Host defense role of platelets: Engulfment of HIV and Staphylococcus aureus occurs in a specific subcellular compartment and is enhanced by platelet activation. Blood 2002, 99, 4021–4029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Stoppelaar, S.F.; Van’t Veer, C.; Claushuis, T.A.; Albersen, B.J.; Roelofs, J.J.; van der Poll, T. Thrombocytopenia impairs host defense in gram-negative pneumonia-derived sepsis in mice. Blood 2014, 124, 3781–3790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Stoppelaar, S.F.; Van’t Veer, C.; Roelofs, J.J.; Claushuis, T.A.; de Boer, O.J.; Tanck, M.W.; Hoogendijk, A.J.; van der Poll, T. Platelet and endothelial cell P-selectin are required for host defense against Klebsiella pneumoniae-induced pneumosepsis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2015, 13, 1128–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, B.P.; Linden, M.D.; Frelinger, A.L., 3rd; Barnard, M.R.; Spencer-Manzon, M.; Morris, J.E.; Salem, R.O.; Laposata, M.; Michelson, A.D. Platelet activation in cystic fibrosis. Blood 2005, 105, 4635–4641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thachil, J. What is the evidence for platelet transfusion thresholds? Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2014, 25, e37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerrigan, S.W.; Cox, D. Platelet–bacterial interactions. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2010, 67, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amison, R.T.; O’Shaughnessy, B.G.; Arnold, S.; Cleary, S.J.; Nandi, M.; Pitchford, S.C.; Bragonzi, A.; Page, C.P. Platelet Depletion Impairs Host Defense to Pulmonary Infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Mice. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2018, 58, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeaman, M.R.; Tang, Y.Q.; Shen, A.J.; Bayer, A.S.; Selsted, M.E. Purification and in vitro activities of rabbit platelet microbicidal proteins. Infect. Immun. 1997, 65, 1023–1031. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Y.Q.; Yeaman, M.R.; Selsted, M.E. Antimicrobial peptides from human platelets. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 6524–6533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukour, S.; Masse, J.M.; Benit, L.; Dubart-Kupperschmitt, A.; Cramer, E.M. Lentivirus degradation and DC-SIGN expression by human platelets and megakaryocytes. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2006, 4, 426–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondina, M.T.; Brewster, B.; Grissom, C.K.; Zimmerman, G.A.; Kastendieck, D.H.; Harris, E.S.; Weyrich, A.S. In vivo platelet activation in critically ill patients with primary 2009 influenza A(H1N1). Chest 2012, 141, 1490–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandaker, G.; Dierig, A.; Rashid, H.; King, C.; Heron, L.; Booy, R. Systematic review of clinical and epidemiological features of the pandemic influenza A (H1N1) 2009. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses 2011, 5, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terada, H.; Baldini, M.; Ebbe, S.; Madoff, M.A. Interaction of influenza virus with blood platelets. Blood 1966, 28, 213–228. [Google Scholar]
- Nair, H.; Nokes, D.J.; Gessner, B.D.; Dherani, M.; Madhi, S.A.; Singleton, R.J.; O’Brien, K.L.; Roca, A.; Wright, P.F.; Bruce, N.; et al. Global burden of acute lower respiratory infections due to respiratory syncytial virus in young children: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 2010, 375, 1545–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrottmaier, W.C.; Kral, J.B.; Badrnya, S.; Assinger, A. Aspirin and P2Y12 Inhibitors in platelet-mediated activation of neutrophils and monocytes. Thromb. Haemost. 2015, 114, 478–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kullaya, V.I.; de Mast, Q.; van der Ven, A.; elMoussaoui, H.; Kibiki, G.; Simonetti, E.; de Jonge, M.I.; Ferwerda, G. Platelets Modulate Innate Immune Response Against Human Respiratory Syncytial Virus In Vitro. Viral. Immunol. 2017, 30, 576–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejias, A.; Dimo, B.; Suarez, N.M.; Garcia, C.; Suarez-Arrabal, M.C.; Jartti, T.; Blankenship, D.; Jordan-Villegas, A.; Ardura, M.I.; Xu, Z.; et al. Whole blood gene expression profiles to assess pathogenesis and disease severity in infants with respiratory syncytial virus infection. PLoS Med. 2013, 10, e1001549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsui, C.; Kajiwara, K.; Hayashi, H.; Ito, J.; Mita, H.; Ono, E.; Higashi, N.; Fukutomi, Y.; Sekiya, K.; Tsuburai, T.; et al. Platelet activation markers overexpressed specifically in patients with aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 137, 400–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gremmel, T.; Ay, C.; Riedl, J.; Kopp, C.W.; Eichelberger, B.; Koppensteiner, R.; Panzer, S. Platelet-specific markers are associated with monocyte-platelet aggregate formation and thrombin generation potential in advanced atherosclerosis. Thromb. Haemost. 2016, 115, 615–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freynhofer, M.K.; Gruber, S.C.; Grove, E.L.; Weiss, T.W.; Wojta, J.; Huber, K. Antiplatelet drugs in patients with enhanced platelet turnover: Biomarkers versus platelet function testing. Thromb. Haemost. 2015, 114, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.H.; Sim, E.H.; Goh, R.Y.; Park, J.I.; Han, J.Y. Platelet Activation: The Mechanisms and Potential Biomarkers. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 9060143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Lin, Z.; Xiao, X.; He, C.; Bihl, J.C.; Zhao, B.; Ma, X.; Chen, Y. The Role of Circulating Platelets Microparticles and Platelet Parameters in Acute Ischemic Stroke Patients. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2015, 24, 2313–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Directorate for the Quality of Medicines and HealthCare. Guide to the Preparation, Use and Quality Assurance of Blood Components, 19th ed.; Council of Europe: Strasbourg, France, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Bueno, J.L.; Barea, L.; Garcia, F.; Castro, E. A comparison of PLT collections from two apheresis devices. Transfusion 2004, 44, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, J.L.; Garcia, F.; Castro, E.; Barea, L.; Gonzalez, R. A randomized crossover trial comparing three plateletpheresis machines. Transfusion 2005, 45, 1373–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeiffer, I.A.; Zinser, E.; Strasser, E.; Stein, M.F.; Dorrie, J.; Schaft, N.; Steinkasserer, A.; Knippertz, I. Leukoreduction system chambers are an efficient, valid, and economic source of functional monocyte-derived dendritic cells and lymphocytes. Immunobiology 2013, 218, 1392–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, J.L.; Ynigo, M.; de Miguel, C.; Gonzalo-Daganzo, R.M.; Richart, A.; Vilches, C.; Regidor, C.; Garcia-Marco, J.A.; Flores-Ballester, E.; Cabrera, J.R. Growth differentiation factor 11 (GDF11)—A promising anti-ageing factor—Is highly concentrated in platelets. Vox. Sang. 2016, 111, 434–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, J.E.; Zurakowski, D.; Italiano, J.E., Jr.; Michel, L.V.; Connors, S.; Oenick, M.; D’Amato, R.J.; Klement, G.L.; Folkman, J. VEGF, PF4 and PDGF are elevated in platelets of colorectal cancer patients. Angiogenesis 2012, 15, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dymicka-Piekarska, V.; Matowicka-Karna, J.; Osada, J.; Kemona, H.; Butkiewicz, A.M. Changes in platelet CD 62P expression and soluble P-selectin concentration in surgically treated colorectal carcinoma. Adv. Med. Sci. 2006, 51, 304–308. [Google Scholar]

| α-Granules | ||
| No. | Molecule | Function |
| 1 | PF4 (CXCL4) | Chemokine: Induce leukocyte pro-inflammatory cytokine release in monocyte, neutrophil, and T-cell recruitment; Th differentiation |
| 2 | P-selectin | Adhesion molecule: Formation of platelet-leukocyte aggregate; Formation of bridges between leukocytes and endothelium |
| 3 | CD40L | TNF superfamily: antigen-presenting cell activation, B-cell responses, endothelial cell activation |
| 4 | MIP-1a (CCL3) | Cytokine: neutrophil and eosinophil activation, B-cell immunoglobulin production |
| 5 | IL-1β | Cytokine: acute phase response, leukocyte and endothelial activation |
| 6 | RANTES (CCL5) | Chemokine: Promotes monocyte, macrophage and T cell recruitment |
| 7 | TGF-β | Cytokine: cell proliferation, T-cell differentiation, B-cell and macrophage phenotype regulation |
| 8 | PDGF | Growth factor: cell growth and differentiation, monocyte/macrophage differentiation |
| 9 | VWF | Platelet adhesion, PMN extravasation |
| 10 | CD63 | Tetraspanin: transmembrane adaptor protein, leukocyte recruitment |
| 11 | SDF-1 | Chemokine: T-cell, monocyte, and PMN chemotaxis |
| 12 | VEGF | Growth factor: angiogenesis, adhesion molecule expression |
| 13 | Ppbp β-thromboglobulin (NAP-2) | Chemokine: neutrophil activation and recruitment, macrophage phagocytic activity |
| 14 | Thrombospondins | Apoptosis, endothelial cell inflammation, macrophage-platelet aggregates |
| 15 | MMP-2, MMP-9 | Protease: extracellular matrix breakdown, platelet-leukocyte aggregate formation |
| 16 | Cyclophilin A | Vascular smooth muscle cell growth factor |
| 18 | CXCL1, CXCL5, CXCL7, CXCL12 | Chemokines |
| 19 | Microbial proteins | Cationic proteins: disrupt cell membrane |
| Dense Granule | ||
| No. | Molecule | Immune/Inflammatory Role |
| 1 | Serotonin | DC and T-cell functions |
| 2 | Glutamate | T-cell trafficking |
| 3 | Polyphosphates | Inflammatory response amplification |
| 4 | ADP | Platelet, leukocyte, endothelial cell activation |
| 5 | Histamine | Increased vessel reactivity and degranulation |
| 6 | ATP, phosphate, calcium | Fuel cell and co-factors in thrombosis |
| 7 | Eicosanoids | Pro-inflammatory signals |
| Produced Metabolites | ||
| No. | Molecule | Immune/Inflammatory Role |
| 1 | Thromboxane | Eicosanoid: T-cell differentiation, monocyte activation |
| 2 | Nitric oxide | Reactive oxygen species: anti-inflammatory and antithrombotic |
| 3 | GPIbα | Adhesion molecule: binds Mac-1 on leukocytes |
| 4 | TXA2 | Mediator that enhance platelet activation |
| 5 | S1P | Active metabolite which activate platelets and stimulate mitogenesis |
| 6 | PAF | Bioactive lipid: induce endothelial migration |
| 7 | Chrondroitin sulfate | Metabolite released by platelets after trigger complement activation |
| 8 | LPA | Lipid: ligand of G protein-coupled receptors |
| Membrane Receptors | ||
| No. | Molecule | Immune/Inflammatory Role |
| 1 | TLR1, TLR2, TLR4, TLR6, TRL8 and TLR9 | Receptors that recognize pathogen-associated molecular patterns and mediate inflammatory events |
| 2 | CD40, CD40L | Receptor: Mediator of interactions between lymphocytes and antigen presenting cells |
| 3 | GPIa, GPIIb/IIIa, GPIc-IIa (VLA-6) | Platelet glycoprotein: adhesion molecules |
| 4 | GPVI | Collagen receptor: induces powerful platelet activation |
| 5 | P2X1 | Receptor is involved in platelet shape change and in activation by collagen |
| 6 | P2Y1, P2Y12 | G-protein receptors: sustain platelet activation in response to ADP |
| 7 | PAR-1, PAR-4 | Thrombin activates platelets through proteolytic cleavage of PAR receptors |
| 8 | ICAM-2, | Adhesion molecule |
| 10 | JAM-A, | Protects from thrombosis by suppressing integrin αIIbβ3 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gomez-Casado, C.; Villaseñor, A.; Rodriguez-Nogales, A.; Bueno, J.L.; Barber, D.; Escribese, M.M. Understanding Platelets in Infectious and Allergic Lung Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1730. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20071730
Gomez-Casado C, Villaseñor A, Rodriguez-Nogales A, Bueno JL, Barber D, Escribese MM. Understanding Platelets in Infectious and Allergic Lung Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(7):1730. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20071730
Chicago/Turabian StyleGomez-Casado, Cristina, Alma Villaseñor, Alba Rodriguez-Nogales, Jose Luis Bueno, Domingo Barber, and Maria M. Escribese. 2019. "Understanding Platelets in Infectious and Allergic Lung Diseases" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 7: 1730. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20071730
APA StyleGomez-Casado, C., Villaseñor, A., Rodriguez-Nogales, A., Bueno, J. L., Barber, D., & Escribese, M. M. (2019). Understanding Platelets in Infectious and Allergic Lung Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(7), 1730. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20071730








