The Role of ApoE in HCV Infection and Comorbidity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
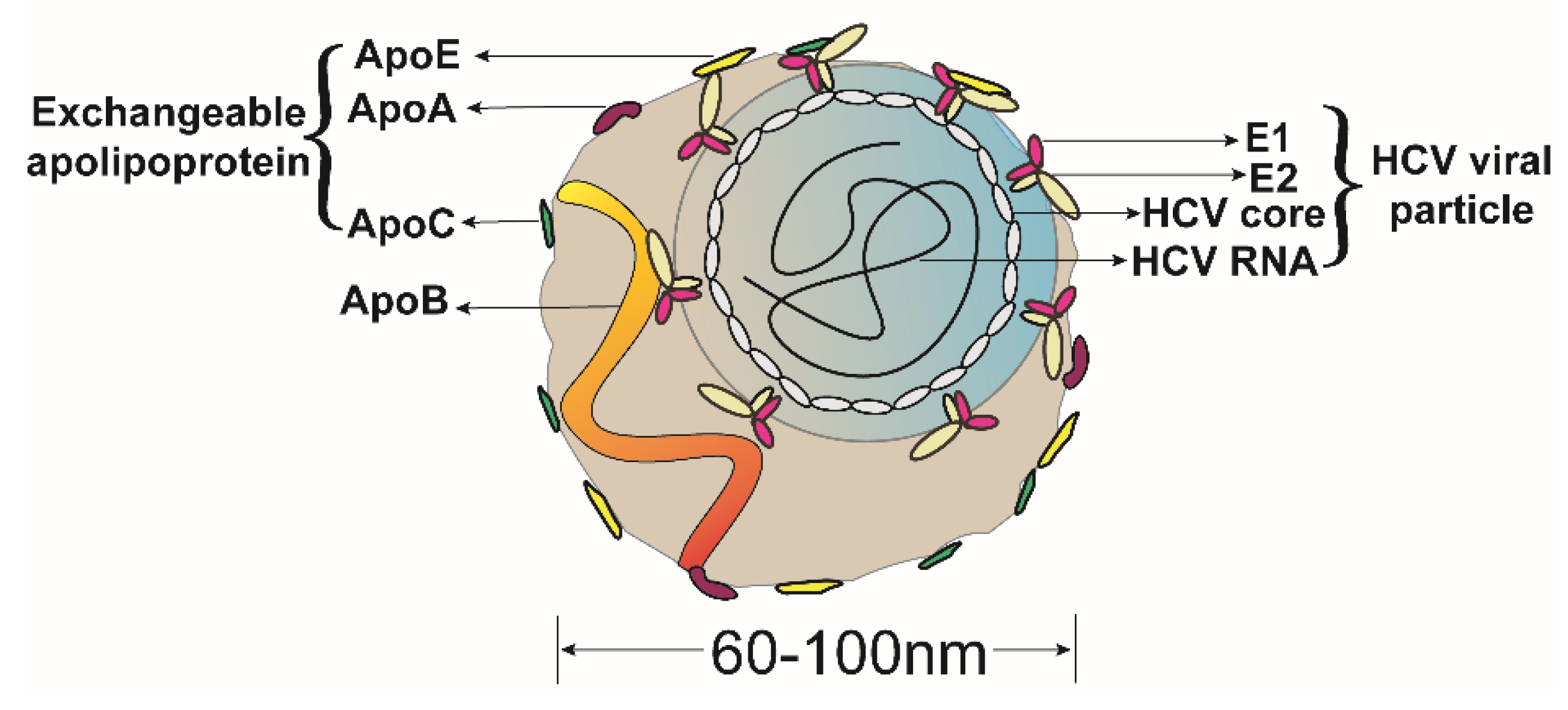
2. The Morphological Association of ApoE and HCV LVPs
2.1. The Function of ApoE Dictated by Its Structure
2.2. HCV Infection
2.3. ApoE Is a Morphological Component of the HCV LVPs
3. Role of ApoE in the HCV Infection
3.1. Apolipoprotein E Is Required for Production of HCV
3.2. HCV Infectivity Is Influenced by ApoE
3.3. ApoE Is Essential for Efficient Cell-to-Cell Transmission of HCV
3.4. Alteration of HCV Infectivity by Extracellular ApoE
4. Function of ApoE and HCV-Associated Comorbidities
4.1. ApoE Promotes Immune Evasion for HCV Chronic Infection
4.2. Hints Regarding Persistently Hijacked ApoE and HCV-Associated Comorbidities
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Getz, G.S.; Reardon, C.A. Apoprotein E as a lipid transport and signaling protein in the blood, liver, and artery wall. J. Lipid Res. 2009, 50, S156–S161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Mahley, R.W. Apolipoprotein E: Structure and function in lipid metabolism, neurobiology, and Alzheimer’s diseases. Neurobiol. Dis. 2014, 72, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, M.C. Apolipoprotein E isoforms and lipoprotein metabolism. IUBMB Life 2014, 66, 616–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jofre-Monseny, L.; Minihane, A.; Rimbach, G. Impact of apoE genotype on oxidative stress, inflammation and disease risk. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2008, 52, 131–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisgraber, K. Apolipoprotein E: Structure-function relationships. Adv. Protein Chem. 1994, 45, 249–302. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wilson, C.; Wardell, M.; Weisgraber, K.; Mahley, R.; Agard, D. Three-dimensional structure of the LDL receptor-binding domain of human apolipoprotein E. Science 1991, 252, 1817–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holtzman, D.M.; Herz, J.; Bu, G. Apolipoprotein E and Apolipoprotein E Receptors: Normal Biology and Roles in Alzheimer Disease. Perspect. Med. 2012, 2, a006312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatters, D.M.; Peters-Libeu, C.A.; Weisgraber, K.H. Apolipoprotein E structure: Insights into function. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2006, 31, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindenbach, B.D.; Rice, C.M. The ins and outs of hepatitis C virus entry and assembly. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 688–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Douam, F.; Lavillette, D.; Cosset, F.-L. The Mechanism of HCV Entry into Host Cells. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2015, 129, 63–107. [Google Scholar]
- Collaborators, T.; Blach, S.; Zeuzem, S.; Manns, M.; Altraif, I.; Duberg, A.-S.; Muljono, D.H.; Waked, I.; Alavian, S.M.; Lee, M.-H.; et al. Global prevalence and genotype distribution of hepatitis C virus infection in 2015: A modelling study. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 2, 161–176. [Google Scholar]
- Bradley, D.; McCaustland, K.; Krawczynski, K.; Spelbring, J.; Humphey, C.; Cook, E. Hepatitis C virus: Buoyant density if the factor VIII-derived isolate in sucrose. J. Med. Virol. 1991, 34, 206–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- André, P.; Komurian-Pradel, F.; Deforges, S.; Perret, M.; Berland, J.; Sodoyer, M.; Pol, S.; Bréchot, C.; Paranhos-Baccalà, G.; Lotteau, V. Characterization of Low- and Very-Low-Density Hepatitis C Virus RNA-Containing Particles. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 6919–6928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gastaminza, P.; Kapadia, S.B.; Chisari, F.V. Differential Biophysical Properties of Infectious Intracellular and Secreted Hepatitis C Virus Particles. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 11074–11081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Sun, F.; Owen, D.M.; Li, W.; Chen, Y.; Gale, M.; Ye, J. Hepatitis C virus production by human hepatocytes dependent on assembly and secretion of very low-density lipoproteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 5848–5853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhong, J.; Gastaminza, P.; Cheng, G.; Kapadia, S.; Kato, T.; Burton, D.R.; Wieland, S.F.; Uprichard, S.L.; Wakita, T.; Chisari, F.V. Robust hepatitis C virus infection in vitro. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakita, T.; Pietschmann, T.; Kato, T.; Date, T.; Miyamoto, M.; Zhao, Z.; Murthy, K.; Habermann, A.; Kräusslich, H.-G.; Mizokami, M.; et al. Production of infectious hepatitis C virus in tissue culture from a cloned viral genome. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 791–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cai, Z.; Zhang, C.; Chang, K.-S.; Jiang, J.; Ahn, B.-C.; Wakita, T.; Liang, J.T.; Luo, G. Robust Production of Infectious Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) from Stably HCV cDNA-Transfected Human Hepatoma Cells. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 13963–13973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lindenbach, B.D.; Evans, M.J.; Syder, A.J.; Wölk, B.; Tellinghuisen, T.L.; Liu, C.C.; Maruyama, T.; Hynes, R.O.; Burton, D.R.; McKeating, J.A.; et al. Complete Replication of Hepatitis C Virus in Cell Culture. Science 2005, 309, 623–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gastaminza, P.; Dryden, K.A.; Boyd, B.; Wood, M.R.; Law, M.; Yeager, M.; Chisari, F.V. Ultrastructural and Biophysical Characterization of Hepatitis C Virus Particles Produced in Cell Culture. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 10999–11009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merz, A.; Long, G.; Hiet, M.-S.; Brügger, B.; Chlanda, P.; Andre, P.; Wieland, F.; Krijnse-Locker, J.; Bartenschlager, R. Biochemical and Morphological Properties of Hepatitis C Virus Particles and Determination of Their Lipidome. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 3018–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catanese, M.; Uryu, K.; Kopp, M.; Edwards, T.J.; Andrus, L.; Rice, W.J.; Silvestry, M.; Kuhn, R.J.; Rice, C.M. Ultrastructural analysis of hepatitis C virus particles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 9505–9510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Piver, E.; Boyer, A.; Gaillard, J.; Bull, A.; Beaumont, E.; Roingeard, P.; Meunier, J.-C. Ultrastructural organisation of HCV from the bloodstream of infected patients revealed by electron microscopy after specific immunocapture. Gut 2017, 66, 1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, B.-K.; Kim, H.-R.; Park, G.-N.; Luo, G.; Chang, K.-S. Roles of human apolipoprotein E in the infectivity and replication of hepatitis C virus genotype 2a. J. Microbiol. 2016, 54, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Luo, G. Apolipoprotein E but Not B Is Required for the Formation of Infectious Hepatitis C Virus Particles. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 12680–12691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-Y.; Acosta, E.G.; Stoeck, I.; Long, G.; Hiet, M.-S.; Mueller, B.; Fackler, O.T.; Kallis, S.; Bartenschlager, R. Apolipoprotein E Likely Contributes to a Maturation Step of Infectious Hepatitis C Virus Particles and Interacts with Viral Envelope Glycoproteins. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 12422–12437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hueging, K.; Doepke, M.; Vieyres, G.; Bankwitz, D.; Frentzen, A.; Doerrbecker, J.; Gumz, F.; Haid, S.; Wölk, B.; Kaderali, L.; et al. Apolipoprotein E Codetermines Tissue Tropism of Hepatitis C Virus and Is Crucial for Viral Cell-to-Cell Transmission by Contributing to a Postenvelopment Step of Assembly. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 1433–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cun, W.; Jiang, J.; Luo, G. The C-Terminal α-Helix Domain of Apolipoprotein E Is Required for Interaction with Nonstructural Protein 5A and Assembly of Hepatitis C Virus. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 11532–11541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hishiki, T.; Shimizu, Y.; Tobita, R.; Sugiyama, K.; Ogawa, K.; Funami, K.; Ohsaki, Y.; Fujimoto, T.; Takaku, H.; Wakita, T.; et al. Infectivity of Hepatitis C Virus Is Influenced by Association with Apolipoprotein E Isoforms. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 12048–12057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.-S.; Jiang, J.; Cai, Z.; Luo, G. Human Apolipoprotein E Is Required for Infectivity and Production of Hepatitis C Virus in Cell Culture. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 13783–13793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Ou, J. Regulation of Apolipoprotein E Trafficking by Hepatitis C Virus-Induced Autophagy. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e00211-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benga, W.J.; Krieger, S.E.; Dimitrova, M.; Zeisel, M.B.; Parnot, M.; Lupberger, J.; Hildt, E.; Luo, G.; McLauchlan, J.; Baumert, T.F.; et al. Apolipoprotein E interacts with hepatitis C virus nonstructural protein 5A and determines assembly of infectious particles. Hepatology 2010, 51, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyer, A.; Dumans, A.; Beaumont, E.; Etienne, L.; Roingeard, P.; Meunier, J.-C. The Association of Hepatitis C Virus Glycoproteins with Apolipoproteins E and B Early in Assembly Is Conserved in Lipoviral Particles. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 18904–18913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rösch, K.; Kwiatkowski, M.; Hofmann, S.; Schöbel, A.; Grüttner, C.; Wurlitzer, M.; Schlüter, H.; Herker, E. Quantitative Lipid Droplet Proteome Analysis Identifies Annexin A3 as a Cofactor for HCV Particle Production. Cell Rep. 2016, 16, 3219–3231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weller, R.; Hueging, K.; Brown, R.J.; Todt, D.; Joecks, S.; Vondran, F.W.; Pietschmann, T. Hepatitis C Virus Strain-Dependent Usage of Apolipoprotein E Modulates Assembly Efficiency and Specific Infectivity of Secreted Virions. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e00422-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, D.; Turek, M.; Felmlee, D.J.; Girardi, E.; Pfeffer, S.; Long, G.; Bartenschlager, R.; Zeisel, M.B.; Baumert, T.F. Reconstitution of the Entire Hepatitis C Virus Life Cycle in Nonhepatic Cells. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 11919–11925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murayama, A.; Sugiyama, N.; Wakita, T.; Kato, T. Completion of the Entire Hepatitis C Virus Life Cycle in Vero Cells Derived from Monkey Kidney. Mbio 2016, 7, e00273-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, G.; Hiet, M.; Windisch, M.P.; Lee, J.; Lohmann, V.; Bartenschlager, R. Mouse Hepatic Cells Support Assembly of Infectious Hepatitis C Virus Particles. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 1057–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Bi, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yao, Y.; Li, Q.; Cun, W.; Dong, S. Extracellular Interactions between Hepatitis C Virus and Secreted Apolipoprotein E. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e02227-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuhara, T.; Tamura, T.; Ono, C.; Shiokawa, M.; Mori, H.; Uemura, K.; Yamamoto, S.; Kurihara, T.; Okamoto, T.; Suzuki, R.; et al. Host-derived apolipoproteins play comparable roles with viral secretory proteins Erns and NS1 in the infectious particle formation of Flaviviridae. Plos Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuhara, T.; Wada, M.; Nakamura, S.; Ono, C.; Shiokawa, M.; Yamamoto, S.; Motomura, T.; Okamoto, T.; Okuzaki, D.; Yamamoto, M.; et al. Amphipathic α-Helices in Apolipoproteins Are Crucial to the Formation of Infectious Hepatitis C Virus Particles. Plos Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puig-Basagoiti, F.; Fukuhara, T.; Tamura, T.; Ono, C.; Uemura, K.; Kawachi, Y.; Yamamoto, S.; Mori, H.; Kurihara, T.; Okamoto, T.; et al. Human Cathelicidin Compensates for the Role of Apolipoproteins in Hepatitis C Virus Infectious Particle Formation. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 8464–8477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, J.; Cun, W.; Wu, X.; Shi, Q.; Tang, H.; Luo, G. Hepatitis C Virus Attachment Mediated by Apolipoprotein E Binding to Cell Surface Heparan Sulfate. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 7256–7267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, S.; McCormick, K.D.; Zhao, W.; Zhao, T.; Fan, D.; Wang, T. Human apolipoprotein E peptides inhibit hepatitis C virus entry by blocking virus binding. Hepatology 2012, 56, 484–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, G.; Montero, A.; Gastaminza, P.; Whitten-Bauer, C.; Wieland, S.F.; Isogawa, M.; Fredericksen, B.; Selvarajah, S.; Gallay, P.A.; Ghadiri, R.M.; et al. A virocidal amphipathic α-helical peptide that inhibits hepatitis C virus infection in vitro. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 3088–3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, J.; Wu, X.; Tang, H.; Luo, G. Apolipoprotein E Mediates Attachment of Clinical Hepatitis C Virus to Hepatocytes by Binding to Cell Surface Heparan Sulfate Proteoglycan Receptors. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefèvre, M.; Felmlee, D.J.; Parnot, M.; Baumert, T.F.; Schuster, C. Syndecan 4 Is Involved in Mediating HCV Entry through Interaction with Lipoviral Particle-Associated Apolipoprotein E. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Jiang, J.; Luo, G. Syndecan-1 Serves as the Major Receptor for Attachment of Hepatitis C Virus to the Surfaces of Hepatocytes. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 6866–6875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thi, V.; Granier, C.; Zeisel, M.B.; Guérin, M.; Mancip, J.; Granio, O.; Penin, F.; Lavillette, D.; Bartenschlager, R.; Baumert, T.F.; et al. Characterization of Hepatitis C Virus Particle Subpopulations Reveals Multiple Usage of the Scavenger Receptor BI for Entry Steps. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 31242–31257. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, S.S.; Connor, T.E.; Weeber, E.J.; Rebeck, W. Similarities and differences in structure, expression, and functions of VLDLR and ApoER. Mol. Neurodegener. 2011, 6, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, D.M.; Huang, H.; Ye, J.; Gale, M. Apolipoprotein E on hepatitis C virion facilitates infection through interaction with low-density lipoprotein receptor. Virology 2009, 394, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albecka, A.; Belouzard, S.; de Beeck, A.; Descamps, V.; Goueslain, L.; Bertrand-Michel, J.; Tercé, F.; Duverlie, G.; Rouillé, Y.; Dubuisson, J. Role of low-density lipoprotein receptor in the hepatitis C virus life cycle. Hepatology 2012, 55, 998–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carreau, A.; Hafny-Rahbi, B.; Matejuk, A.; Grillon, C.; Kieda, C. Why is the partial oxygen pressure of human tissues a crucial parameter? Small molecules and hypoxia. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2011, 15, 1239–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ujino, S.; Nishitsuji, H.; Hishiki, T.; Sugiyama, K.; Takaku, H.; Shimotohno, K. Hepatitis C virus utilizes VLDLR as a novel entry pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, S.; Fukuhara, T.; Ono, C.; Uemura, K.; Kawachi, Y.; Shiokawa, M.; Mori, H.; Wada, M.; Shima, R.; Okamoto, T.; et al. Lipoprotein Receptors Redundantly Participate in Entry of Hepatitis C Virus. PloS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weisgraber, K.; Rall, S.; Mahley, R. Human E apoprotein heterogeneity. Cysteine-arginine interchanges in the amino acid sequence of the apo-E isoforms. J. Biol. Chem. 1981, 256, 9077–9083. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bartosch, B.; Cosset, F.-L. Hepatitis C, Methods and Protocols. Methods Mol. Biol. 2009, 510, 279–293. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wozniak, M.A.; Itzhaki, R.F.; Faragher, B.E.; James, M.W.; Ryder, S.D.; Irving, W.L.; Group, T. Apolipoprotein E-epsilon 4 protects against severe liver disease caused by hepatitis C virus. Hepatology 2002, 36, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, D.; Bassendine, M.; Norris, S.M.; Golding, C.; Toms, G.; Schmid, M.; Morris, C.; Burt, A.; Donaldson, P. Apolipoprotein epsilon3 allele is associated with persistent hepatitis C virus infection. Gut 2005, 715–718. [Google Scholar]
- Gomaa, H.E.; Mahmoud, M.; Saad, N.E.; Saad-Hussein, A.; Ismail, S.; Thabet, E.H.; Farouk, H.; Kandil, D.; Heiba, A.; Hafez, W. Impact of Apo E gene polymorphism on HCV therapy related outcome in a cohort of HCV Egyptian patients. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2018, 16, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, T.; Fischer, J.; Gessner, R.; Rosendahl, J.; Böhm, S.; Bömmel, F.; Knop, V.; Sarrazin, C.; Witt, H.; Marques, A.; et al. Apolipoprotein E allele frequencies in chronic and self-limited hepatitis C suggest a protective effect of APOE4 in the course of hepatitis C virus infection. Liver Int. 2016, 36, 1267–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gondar, V.; Molina-Jiménez, F.; Hishiki, T.; García-Buey, L.; Koutsoudakis, G.; Shimotohno, K.; Benedicto, I.; Majano, P.L. Apolipoprotein E, but Not Apolipoprotein B, Is Essential for Efficient Cell-to-Cell Transmission of Hepatitis C Virus. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 9962–9973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barretto, N.; Sainz, B.; Hussain, S.; Uprichard, S.L. Determining the Involvement and Therapeutic Implications of Host Cellular Factors in Hepatitis C Virus Cell-to-Cell Spread. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 5050–5061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Z.; Wang, X.; Chi, X.; Zhao, F.; Guo, J.; Ma, P.; Zhong, J.; Niu, J.; Pan, X.; Long, G. Neglected but Important Role of Apolipoprotein E Exchange in Hepatitis C Virus Infection. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 9632–9643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bankwitz, D.; Doepke, M.; Hueging, K.; Weller, R.; Bruening, J.; Behrendt, P.; Lee, J.-Y.; Vondran, F.; Manns, M.P.; Bartenschlager, R.; et al. Maturation of secreted HCV particles by incorporation of secreted ApoE protects from antibodies by enhancing infectivity. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crouchet, E.; Lefèvre, M.; Verrier, E.R.; Oudot, M.A.; Baumert, T.F.; Schuster, C. Extracellular lipid-free apolipoprotein E inhibits HCV replication and induces ABCG1-dependent cholesterol efflux. Gut 2017, 66, 896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gal-Tanamy, M.; Keck, Z.-Y.; Yi, M.; McKeating, J.A.; Patel, A.H.; Foung, S.K.; Lemon, S.M. In vitro selection of a neutralization-resistant hepatitis C virus escape mutant. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 19450–19455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uebelhoer, L.; Han, J.-H.; Callendret, B.; Mateu, G.; Shoukry, N.H.; Hanson, H.L.; Rice, C.M.; Walker, C.M.; Grakoui, A. Stable Cytotoxic T Cell Escape Mutation in Hepatitis C Virus Is Linked to Maintenance of Viral Fitness. PloS Pathog. 2008, 4, e1000143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheridan, D.A.; Bridge, S.H.; Felmlee, D.J.; Crossey, M.; Thomas, H.C.; Taylor-Robinson, S.D.; Toms, G.L.; Neely, D.R.; Bassendine, M.F. Apolipoprotein-E and hepatitis C lipoviral particles in genotype 1 infection: Evidence for an association with interferon sensitivity. J. Hepatol. 2012, 57, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, P.; Tao, W.; Zhong, J.; Li, Q.; Zhang, X.-L. Ficolin-2 Inhibits Hepatitis C Virus Infection, whereas Apolipoprotein E3 Mediates Viral Immune Escape. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 783–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Timpe, J.M.; Stamataki, Z.; Jennings, A.; Hu, K.; Farquhar, M.J.; Harris, H.J.; Schwarz, A.; Desombere, I.; Roels, G.; Balfe, P.; et al. Hepatitis C virus cell-cell transmission in hepatoma cells in the presence of neutralizing antibodies. Hepatology 2008, 47, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fofana, I.; Fafi–Kremer, S.; Carolla, P.; Fauvelle, C.; Zahid, M.; Turek, M.; Heydmann, L.; Cury, K.; Hayer, J.; Combet, C.; et al. Mutations That Alter Use of Hepatitis C Virus Cell Entry Factors Mediate Escape From Neutralizing Antibodies. Gastroenterology 2012, 143, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauvelle, C.; Felmlee, D.J.; Crouchet, E.; Lee, J.; Heydmann, L.; Lefèvre, M.; Magri, A.; Hiet, M.-S.; Fofana, I.; Habersetzer, F.; et al. Apolipoprotein E Mediates Evasion from Hepatitis C Virus Neutralizing Antibodies. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negro, F. Facts and fictions of HCV and comorbidities: Steatosis, diabetes mellitus, and cardiovascular diseases. J. Hepatol. 2014, 61, S69–S78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lonardo, A.; Adinolfi, L.; Petta, S.; Craxì, A.; Loria, P. Hepatitis C and diabetes: The inevitable coincidence? Expert Rev. Anti-Infe. 2009, 7, 293–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olubamwo, O.O.; Onyeka, I.N.; Miettola, J.; Kauhanen, J.; Tuomainen, T. Hepatitis C as a risk factor for carotid atherosclerosis–a systematic review. Clin. Physiol. Funct. I 2016, 36, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, D.L.; Ratziu, V.; El-Serag, H.B. Hepatitis C infection and risk of diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Hepatol. 2008, 49, 831–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, H.; Kang, R.; Zhao, Z. Is Hepatitis C Associated with Atherosclerotic Burden? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamuta, M.; Yada, R.; Fujino, T.; Yada, M.; Higuchi, N.; Tanaka, M.; Miyazaki, M.; Kohjima, M.; Kato, M.; Yoshimoto, T.; et al. Changes in the expression of cholesterol metabolism-associated genes in HCV-infected liver: A novel target for therapy? Int. J. Mol. Med. 2009, 24, 825–828. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Onat, A.; Kaya, A.; Ademoglu, E. Modified risk associations of lipoproteins and apolipoproteins by chronic low-grade inflammation. Expert Rev. Cardiovasc. 2017, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujino, T.; Nakamuta, M.; Yada, R.; Aoyagi, Y.; Yasutake, K.; Kohjima, M.; Fukuizumi, K.; Yoshimoto, T.; Harada, N.; Yada, M.; et al. Expression profile of lipid metabolism-associated genes in hepatitis C virus-infected human liver. Hepatol. Res. 2010, 40, 923–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meir, K.S.; Leitersdorf, E. Atherosclerosis in the Apolipoprotein E–Deficient Mouse. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2004, 24, 1006–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gong, Y.; Cun, W. The Role of ApoE in HCV Infection and Comorbidity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2037. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20082037
Gong Y, Cun W. The Role of ApoE in HCV Infection and Comorbidity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(8):2037. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20082037
Chicago/Turabian StyleGong, Yue, and Wei Cun. 2019. "The Role of ApoE in HCV Infection and Comorbidity" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 8: 2037. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20082037
APA StyleGong, Y., & Cun, W. (2019). The Role of ApoE in HCV Infection and Comorbidity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(8), 2037. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20082037



