GTP Binding Is Necessary for the Activation of a Toxic Mutant Isoform of the Essential GTPase ObgE
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. The N-Terminal and G Domains of ObgE* Are Necessary for Toxicity
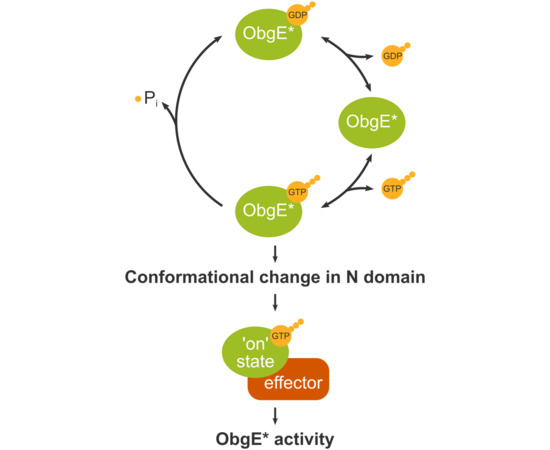
2.2. ObgE* Toxicity Is Influenced by Its Nucleotide Binding State
2.3. Altering the Linker Region between the N-Terminal and G Domains of ObgE* Neutralizes Toxicity
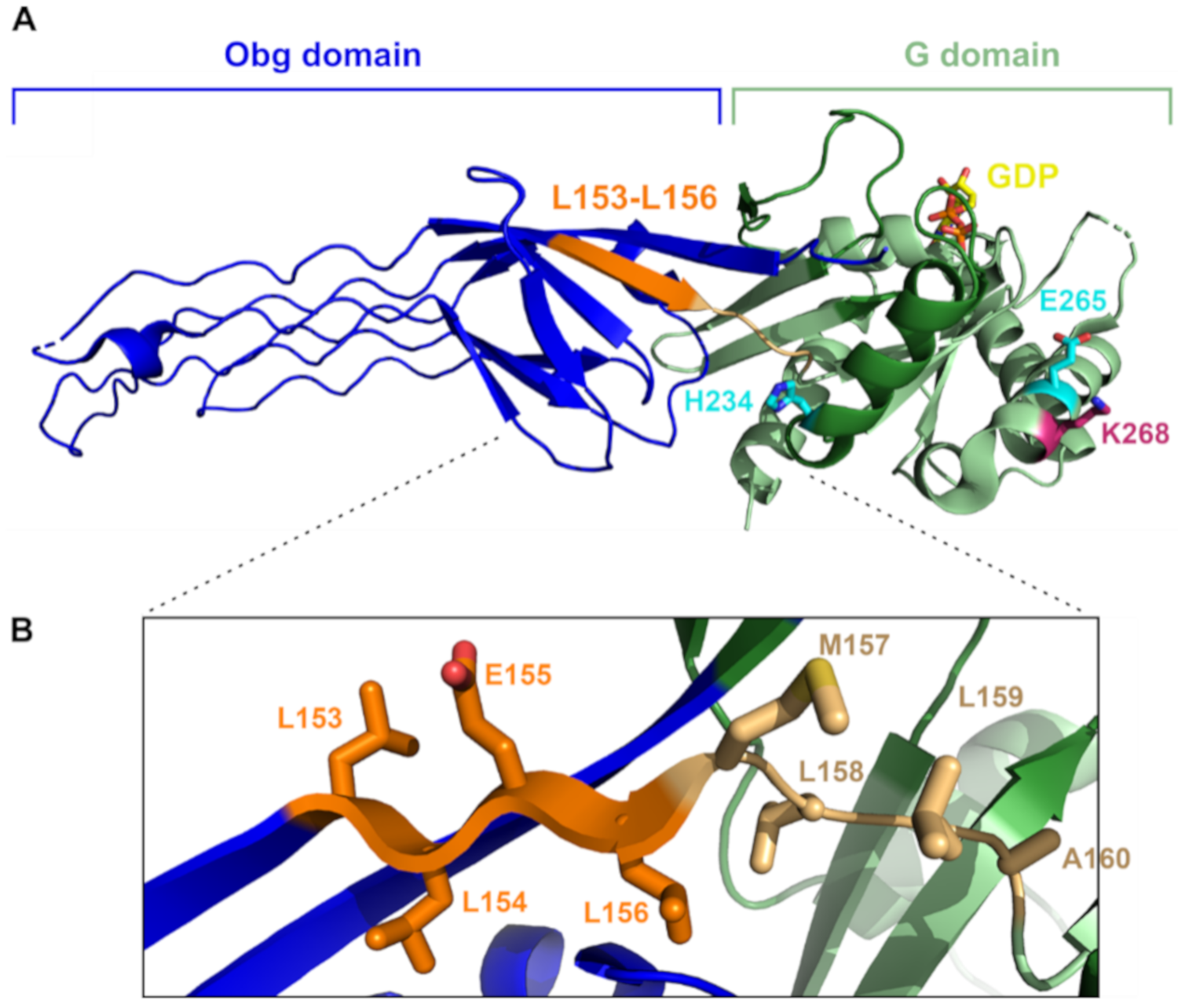
2.4. Spontaneous Mutations in ObgE* That Neutralize Toxicity Also Decrease GTP Binding
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Strains, Plasmids, and Growth Conditions
4.2. Survival Assay
4.3. Identification of Non-Toxic ObgE* Alleles
4.4. Identification of ObgE Mutant Alleles That Can Support Viability
4.5. Expression, Quantification, and Purification of ObgE Proteins
4.6. Isothermal Titration Calorimetry
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vetter, I.R.; Wittinghofer, A. The guanine nucleotide-binding switch in three dimensions. Science 2001, 294, 1299–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verstraeten, N.; Fauvart, M.; Versees, W.; Michiels, J. The universally conserved prokaryotic GTPases. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2011, 75, 507–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kint, C.; Verstraeten, N.; Hofkens, J.; Fauvart, M.; Michiels, J. Bacterial Obg proteins: GTPases at the nexus of protein and DNA synthesis. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 40, 207–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Covalle, K.L.; Maddock, J.R. The Caulobacter crescentus CgtA protein displays unusual guanine nucleotide binding and exchange properties. J. Bacteriol. 1999, 181, 5825–5832. [Google Scholar]
- Wout, P.; Pu, K.; Sullivan, S.M.; Reese, V.; Zhou, S.; Lin, B.; Maddock, J.R. The Escherichia coli GTPase CgtAE cofractionates with the 50S ribosomal subunit and interacts with SpoT. a ppGpp synthetase/hydrolase. J. Bacteriol. 2004, 186, 5249–5257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persky, N.S.; Ferullo, D.J.; Cooper, D.L.; Moore, H.R.; Lovett, S.T. The ObgE/CgtA GTPase influences the stringent response to amino acid starvation in Escherichia coli. Mol. Microbiol. 2009, 73, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verstraeten, N.; Gkekas, S.; Kint, C.I.; Deckers, B.; Van den Bergh, B.; Herpels, P.; Louwagie, E.; Knapen, W.; Wilmaerts, D.; Dewachter, L.; et al. Biochemical determinants of ObgE-mediated persistence. Mol. Microbiol. 2019, 112, 1593–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buglino, J.; Shen, V.; Hakimian, P.; Lima, C.D. Structural and biochemical analysis of the Obg GTP binding protein. Structure 2002, 10, 1581–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkekas, S.; Singh, R.K.; Shkumatov, A.V.; Messens, J.; Fauvart, M.; Verstraeten, N.; Michiels, J.; Versees, W. Structural and biochemical analysis of Escherichia coli ObgE. A central regulator of bacterial persistence. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 5871–5883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukimoto-Niino, M.; Murayama, K.; Inoue, M.; Terada, T.; Tame, J.R.; Kuramitsu, S.; Shirouzu, M.; Yokoyama, S. Crystal structure of the GTP-binding protein Obg from Thermus thermophilus HB8. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 337, 761–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Bang, W.Y.; Kim, S.; Lazar, P.; Kim, C.W.; Bahk, J.D.; Lee, K.W. Molecular modeling study for interaction between Bacillus subtilis Obg and Nucleotides. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, A.; Acharjee, A.; Das, S.; Datta, P.P. Deletion analyses reveal insights into the domain specific activities of an essential GTPase CgtA in Vibrio Cholerae. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2019, 665, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verstraeten, N.; Knapen, W.J.; Kint, C.I.; Liebens, V.; Van den Bergh, B.; Dewachter, L.; Michiels, J.E.; Fu, Q.; David, C.C.; Fierro, A.C.; et al. Obg and membrane depolarization are part of a microbial bet-hedging strategy that leads to antibiotic tolerance. Mol. Cell 2015, 59, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, B.; Mandava, C.S.; Guo, Q.; Wang, J.; Cao, W.; Li, N.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wu, J.; et al. Structural and functional insights into the mode of action of a universally conserved Obg GTPase. PLoS Biol. 2014, 12, e1001866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caldon, C.E.; March, P.E. Function of the universally conserved bacterial GTPases. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2003, 6, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikora, A.E.; Zielke, R.; Wegrzyn, A.; Wegrzyn, G. DNA replication defect in the Escherichia coli cgtA(ts) mutant arising from reduced DnaA levels. Arch. Microbiol. 2006, 185, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kobayashi, G.; Moriya, S.; Wada, C. Deficiency of essential GTP-binding protein ObgE in Escherichia coli inhibits chromosome partition. Mol. Microbiol. 2001, 41, 1037–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foti, J.J.; Persky, N.S.; Ferullo, D.J.; Lovett, S.T. Chromosome segregation control by Escherichia coli ObgE GTPase. Mol. Microbiol. 2007, 65, 569–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewachter, L.; Verstraeten, N.; Jennes, M.; Verbeelen, T.; Biboy, J.; Monteyne, D.; Perez-Morga, D.; Verstrepen, K.J.; Vollmer, W.; Fauvart, M.; et al. A mutant isoform of ObgE causes cell death by interfering with cell division. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewachter, L.; Verstraeten, N.; Fauvart, M.; Michiels, J. An integrative view of cell cycle control in Escherichia Coli. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 42, 116–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewachter, L.; Verstraeten, N.; Monteyne, D.; Kint, C.I.; Versees, W.; Perez-Morga, D.; Michiels, J.; Fauvart, M. A single-amino-acid substitution in Obg activates a new programmed cell death pathway in Escherichia coli. MBio 2015, 6, e01935-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, D.D.; Cebula, T.A. Fidelity of replication of repetitive DNA in mutS and repair proficient Escherichia coli. Mutat. Res. 2001, 474, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyson, H.J.; Wright, P.E. Intrinsically unstructured proteins and their functions. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 6, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewachter, L.; Herpels, P.; Verstraeten, N.; Fauvart, M.; Michiels, J. Reactive oxygen species do not contribute to ObgE*-mediated programmed cell death. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Datsenko, K.A.; Wanner, B.L. One-step inactivation of chromosomal genes in Escherichia coli K-12 using PCR products. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 6640–6645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Equilibrium Dissociation Constants | Ratios | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KD(GDP) | KD(GTPγS) | KD(ppGpp) | KD(GDP)/KD(ppGpp) | KD(GTPγS)/KD(GDP) | KD(GTPγS)/KD(ppGpp) | |
| Wildtype a | 0.44 ± 0.03 | 1.3 ± 0.1 | 0.63 ± 0.08 | 0.70 | 3.0 | 2.1 |
| G166V a | NMB | NMB | NMB | NMB | NMB | NMB |
| T174I | 115 ± 2 | 160 ± 11 | 81 ± 3 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 2.0 |
| T193A a | 0.53 ± 0.03 | 4.7 ± 0.4 | 0.8 ± 0.1 | 0.66 | 8.9 | 5.9 |
| D246G a | 4.1 ± 0.4 | 14.8 ± 0.9 | 7.8 ± 1.2 | 0.53 | 3.6 | 1.9 |
| S270I a | 0.45 ± 0.05 | 4.9 ± 0.5 | 1.14 ± 0.09 | 0.39 | 11 | 4.3 |
| N283I a | NMB | NMB | NMB | NMB | NMB | NMB |
| D286Y a | NMB | NMB | NMB | NMB | NMB | NMB |
| Type | Reference Sequence | Allele | AA Change | Frequency Found |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SNP | ATA | AAA | I268K | 5/9 |
| SNP | CAC | CGC | H234R | 1/9 |
| SNP | GAG | GAT | E265D | 1/9 |
| SNP | GAG | AAG | E265K | 1/9 |
| Deletion, 6 bp | GAA AGC | - | Δ298–299KA | 1/9 |
| Equilibrium Dissociation Constants | Ratios | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KD(GDP) | KD(GTPγS) | KD(ppGpp) | KD(GDP)/KD(ppGpp) | KD(GTPγS)/KD(GDP) | KD(GTPγS)/KD(ppGpp) | |
| Wildtype a | 0.44 ± 0.03 | 1.3 ± 0.1 | 0.63 ± 0.08 | 0.70 | 3.0 | 2.1 |
| Δ153–156 | 0.60 ± 0.05 | 3.4 ± 0.5 | 0.64 ± 0.06 | 0.94 | 5.7 | 5.3 |
| H234R | 0.43 ± 0.05 | 3.7 ± 0.5 | 0.60 ± 0.06 | 0.72 | 8.6 | 6.2 |
| E265K | 0.25 ± 0.03 | 5.7 ± 0.8 | 0.31 ± 0.03 | 0.81 | 23 | 18 |
| Name | Sequence (5′–3′) |
|---|---|
| SPI10603 | AGCCAAGCTTTTAACGCTTG |
| SPI10908 | CACCGGTACCCACCAGGAGGAATTAACCATGAAGTTTGTTGATGAAGCATCG |
| SPI10909 | AGCCAAGCTTCGAATTCTTA |
| SPI11077 | AAATCGATCTTTATTCGTGCGG |
| SPI11078 | AATAAAGATCGATTTACCCGCG |
| SPI11079 | ACCGCGCTGGTGCCAAGTCTGGGTG |
| SPI11080 | TGGCACCAGCGCGGTAAACGGATAATC |
| SPI11083 | CTGTTGCACCTCATCGGCATCG |
| SPI11084 | TCGATGCCGATGAGGTGCAAC |
| SPI11085 | AAGATCCTGCTGCTGGATAAGGT |
| SPI11086 | CAGCAGCAGGATCTTGTTGAACA |
| SPI11765 | GCGTAGCGCATCAGGCTGATTTGGCGTTTATCATCAGTGACATATGAATATCCTCCTTA |
| SPI11766 | ATCGCAACCCCGCGCAGGCGAATGATTTACGGAGAATAAAGTGTAGGCTGGAGCTGCTTC |
| SPI12297 | TAGCGAATTCGAGCTCAGGAGGAATTAACCATGCTGCTGGCTGACGTCGGTA |
| SPI12298 | AGCCAAGCTTTTAAGCCTGCACGACCGGG |
| SPI12299 | TAGCGAATTCGAGCTCAGGA |
| SPI12303 | GCGAGCTGCTTCTCGAATTGATGCTGCTGGCTGACG |
| SPI12304 | AGCAGCATCAATTCGAGAAGCAGCTCGCGCTTATCG |
| SPI12307 | CGTCGGTATGTTGGTGATGCCAAACGCGG |
| SPI12308 | CCGCGTTTGGCATCACCAACATACCGACG |
| SPI12309 | GAAATATACATCCAGGATCTG |
| SPI12310 | ATCCTGGATGTATATTTCCAG |
| SPI12311 | TTAGTGTTCATCAAGATCGATCTG |
| SPI12312 | ATCGATCTTGATGAACACTAACC |
| SPI12313 | AAGATCTATCTGCTGGATAAGGT |
| SPI12314 | CAGCAGATAGATCTTGTTGAACA |
| SPI12315 | TATCTGAACTCTGCGGCGAG |
| SPI12316 | CGCCGCAGAGTTCAGATAATATTT |
| SPI12659 | TTATCAGCAAGCTGGAAAAATACAG |
| SPI12660 | TTTTCCAGCTTGCTGATAATAATACG |
| SPI12663 | CGAGCTGATGCTGCTGGCTGAC |
| SPI12664 | GCAGCATCAGCTCGCGCTTATCG |
| SPI12764 | CTTCCTGAAGCGCCTGGAACGTTGCCGCGTCCTGT |
| SPI12765 | CGTTCCAGGCGCTTCAGGAAGCGAATGCCCAGACC |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dewachter, L.; Deckers, B.; Martin, E.; Herpels, P.; Gkekas, S.; Versées, W.; Verstraeten, N.; Fauvart, M.; Michiels, J. GTP Binding Is Necessary for the Activation of a Toxic Mutant Isoform of the Essential GTPase ObgE. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21010016
Dewachter L, Deckers B, Martin E, Herpels P, Gkekas S, Versées W, Verstraeten N, Fauvart M, Michiels J. GTP Binding Is Necessary for the Activation of a Toxic Mutant Isoform of the Essential GTPase ObgE. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(1):16. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21010016
Chicago/Turabian StyleDewachter, Liselot, Babette Deckers, Ella Martin, Pauline Herpels, Sotirios Gkekas, Wim Versées, Natalie Verstraeten, Maarten Fauvart, and Jan Michiels. 2020. "GTP Binding Is Necessary for the Activation of a Toxic Mutant Isoform of the Essential GTPase ObgE" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 1: 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21010016
APA StyleDewachter, L., Deckers, B., Martin, E., Herpels, P., Gkekas, S., Versées, W., Verstraeten, N., Fauvart, M., & Michiels, J. (2020). GTP Binding Is Necessary for the Activation of a Toxic Mutant Isoform of the Essential GTPase ObgE. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(1), 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21010016