Ipragliflozin Ameliorates Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Apoptosis through Preventing Ectopic Lipid Deposition in Renal Tubules
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effects of Ipragliflozin on Fatty Liver Shionogi ob/ob (FLS-ob/ob) Mice
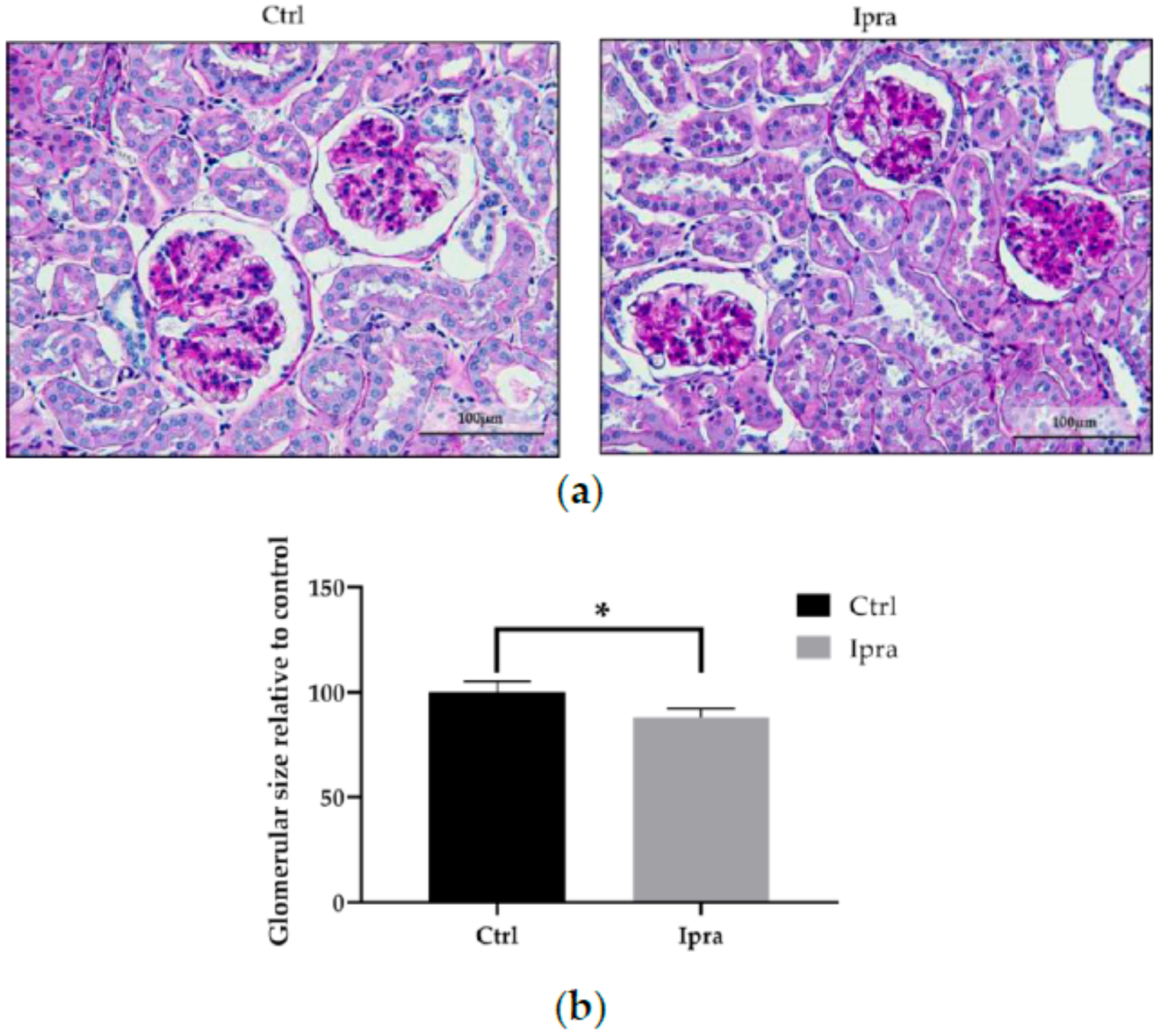
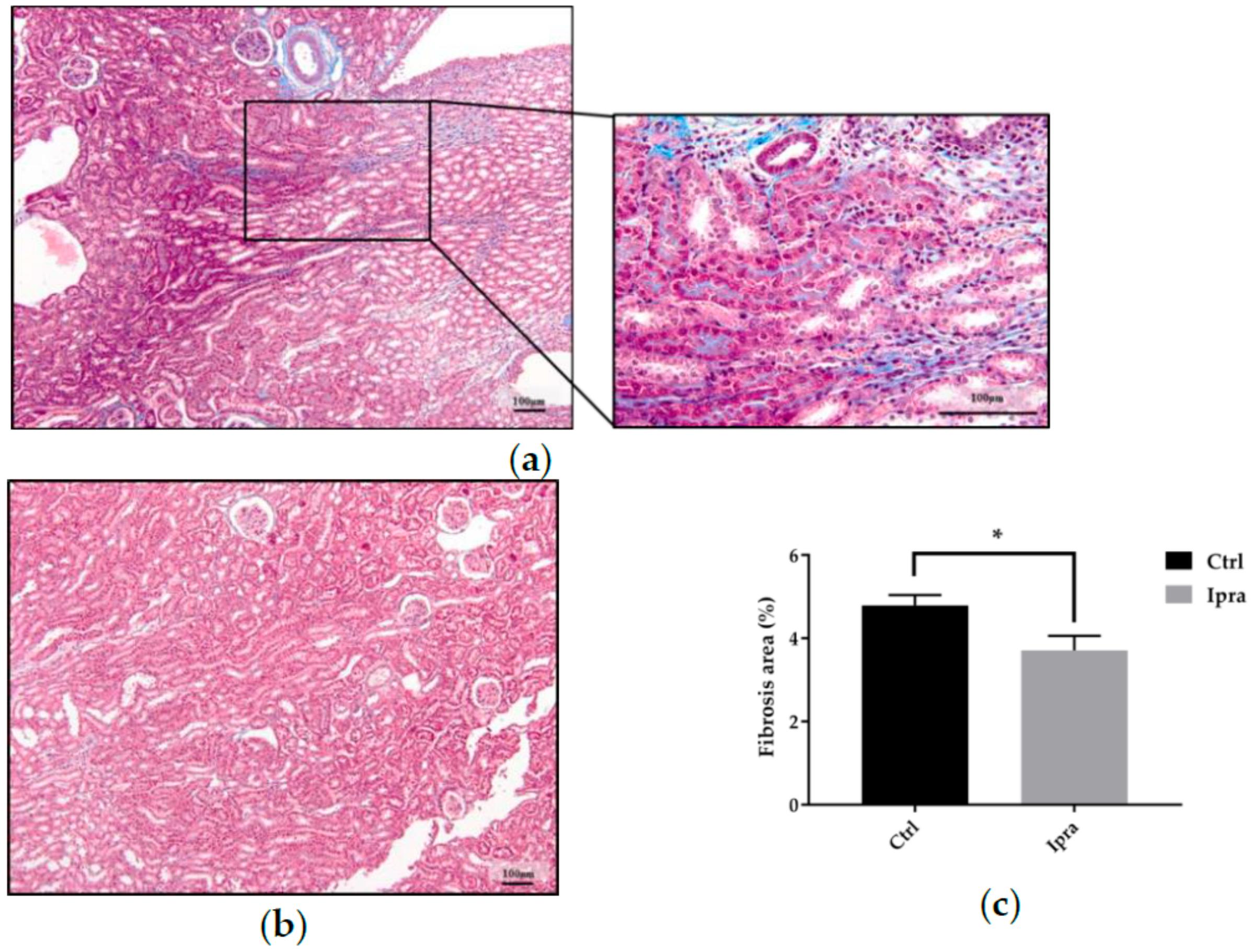
2.2. Impact of Ipragliflozin on the Histological Changes in FLS-ob/ob Mice
2.3. Advanced Glycation End Product in Plasma and Kidney
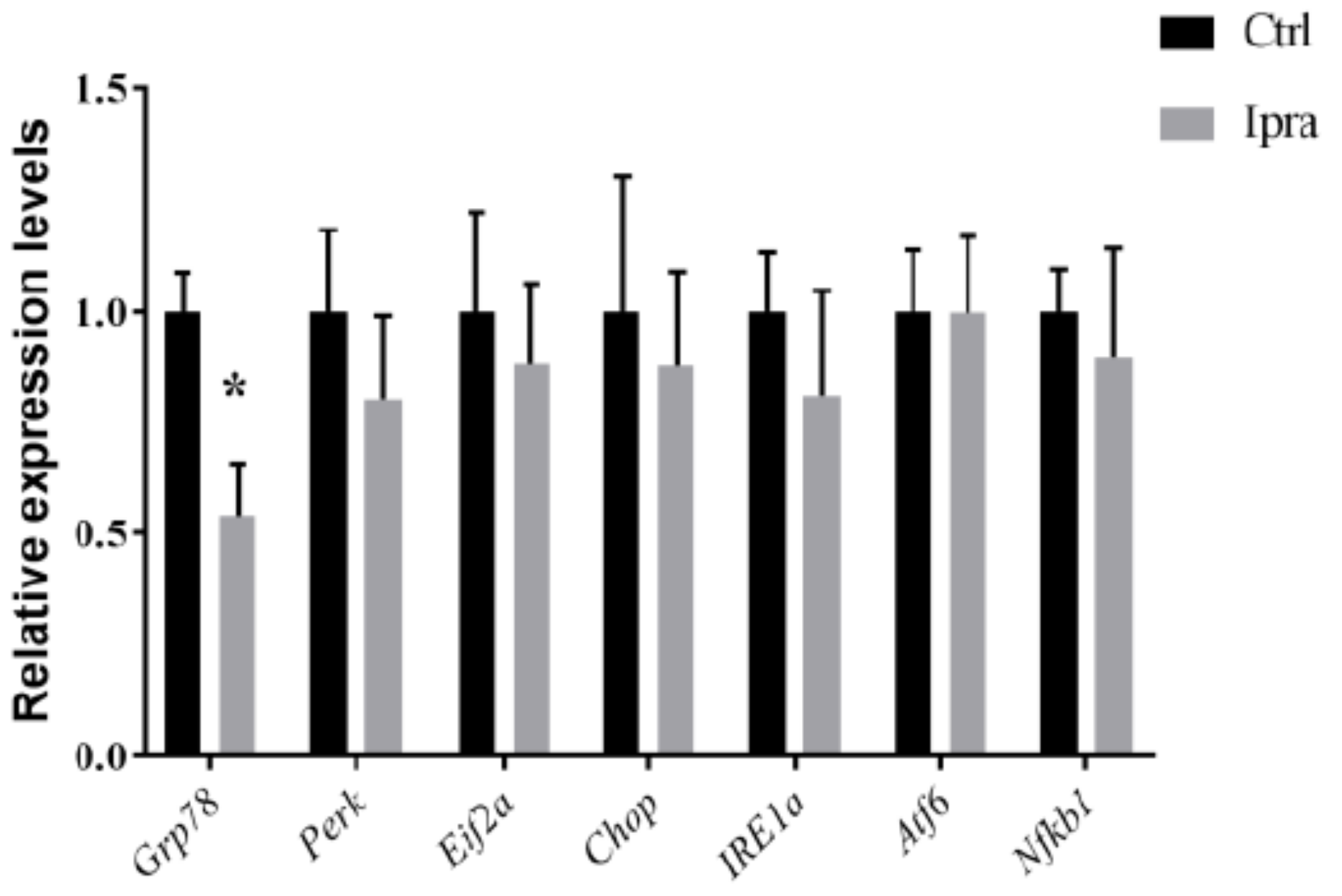
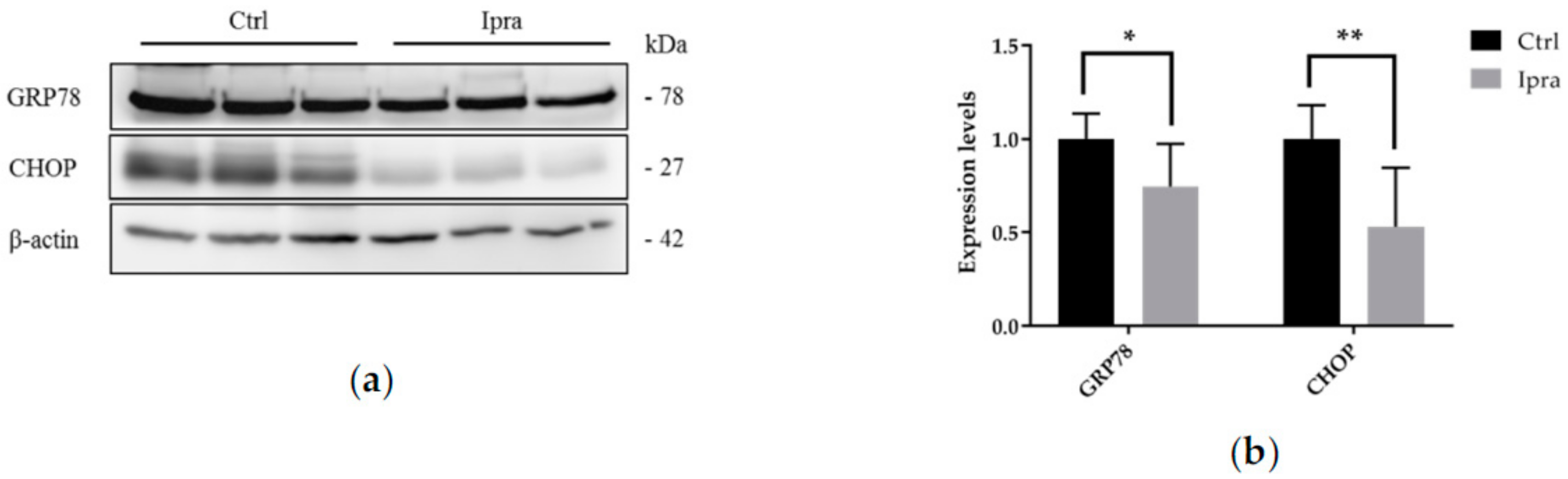
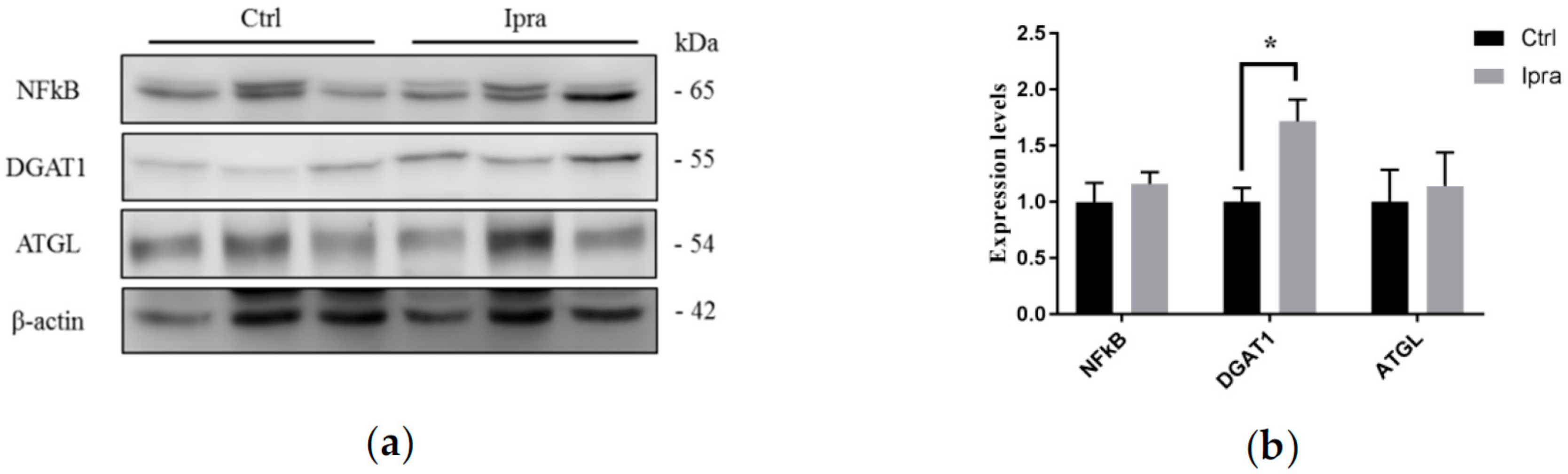
2.4. Reduced Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in FLS-ob/ob Mice Treated with Ipraglifilozin
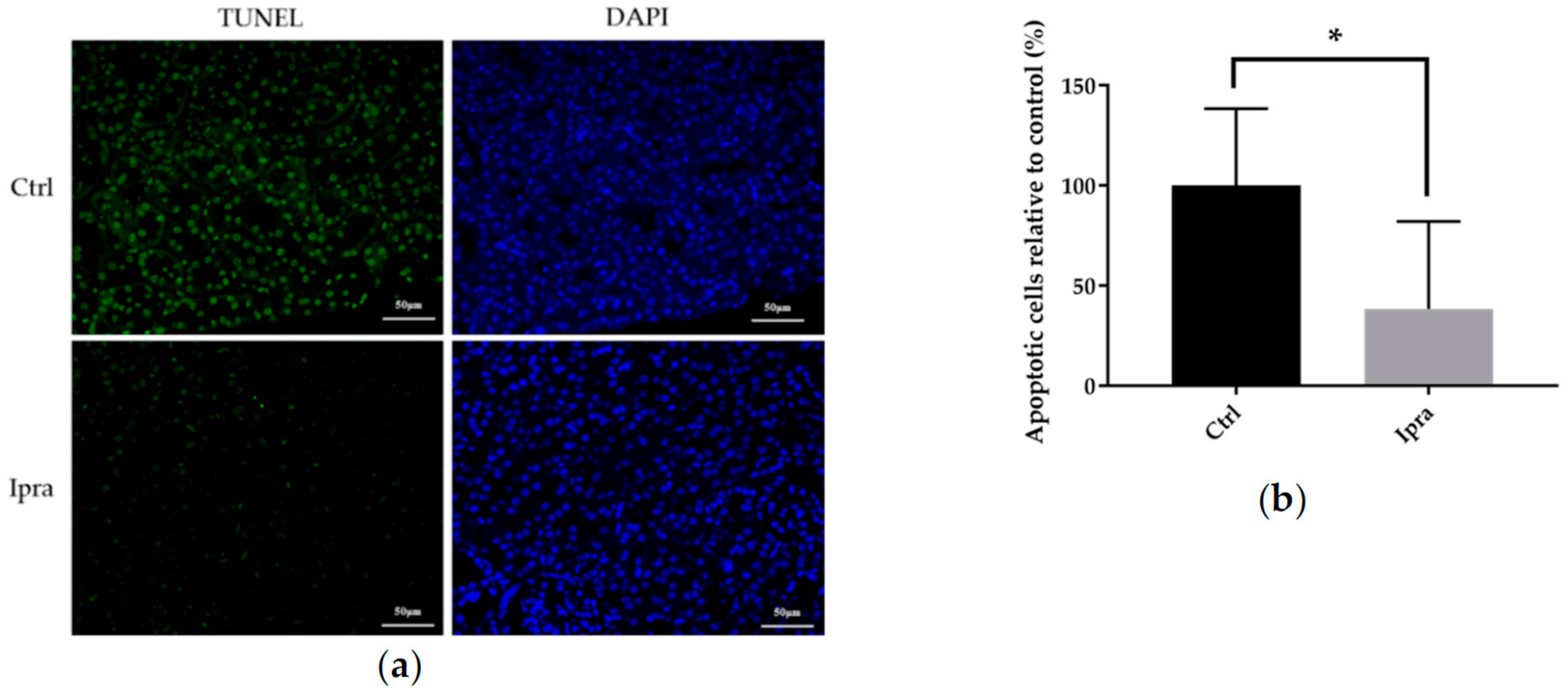
2.5. Ipragliflozin Reduced Cellular Apoptosis in FLS-ob/ob Mice
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals and Experimental Designs
4.2. Histological Analysis
4.3. Quantification of AGE in the Plasma and Kidney
4.4. Apoptosis Assay in Tissues
4.5. Gene Expression Analysis
4.6. Western Blot Analysis
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CKD | Chronic kidney disease |
| NASH | Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis |
| ELD | Ectopic lipid deposition |
| ER | Endoplasmic reticulum |
| SGLT2 | Sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 |
| FLS-ob/ob | Fatty liver Shionogi ob/ob |
| BW | Body weight |
| AGE | Advanced glycation end product |
| GRP78 | Glucose-regulated protein-78 |
| PERK | Protein kinase RNA-activated-like ER kinase |
| eIF2α | Eukaryotic initiation factor 2α |
| IRE1α | Inositol requiring enzyme 1α |
| ATF6 | Activating transcription factor 6 |
| CHOP | C/EBP homologous protein |
| NFkB | Nuclear factor kappa B |
| DGAT | Diacylglycerol O-acyltransferase |
| ATGL | Adipose triglyceride lipase |
| TUNEL | Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor-alfa |
| PAS | Periodic acid-Schiff |
| DAPI | 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole |
References
- Go, A.S.; Chertow, G.M.; Fan, N.; McCulloch, C.E.; Hsu, C.-Y. Chronic Kidney Disease and the Risks of Death, Cardiovascular Events, and Hospitalization. New Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 1296–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceranowicz, P.; Warzecha, Z.; Dembinski, A. Peptidyl hormones of endocrine cells origin in the gut—Their discovery and physiological relevance. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2015, 66, 11–27. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moellmann, J.; Klinkhammer, B.M.; Onstein, J.; Stöhr, R.; Jankowski, V.; Jankowski, J.; Lebherz, C.; Tacke, F.; Marx, N.; Boor, P.; et al. Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 and Its Cleavage Products Are Renoprotective in Murine Diabetic Nephropathy. Diabetes 2018, 67, 2410–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guebre-Egziabher, F.; Alix, P.M.; Koppe, L.; Pelletier, C.C.; Kalbacher, E.; Fouque, D.; Soulage, C.O. Ectopic lipid accumulation: A potential cause for metabolic disturbances and a contributor to the alteration of kidney function. Biochimie 2013, 95, 1971–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuboi, N.; Okabayashi, Y.; Shimizu, A.; Yokoo, T. The Renal Pathology of Obesity. Kidney Int. Rep. 2017, 2, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanyal, A.J. NASH: A global health problem. Hepatol. Res. 2011, 41, 670–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Targher, G.; Bertolini, L.; Rodella, S.; Zoppini, G.; Lippi, G.; Day, C.; Muggeo, M. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is independently associated with an increased prevalence of chronic kidney disease and proliferative/laser-treated retinopathy in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetologia 2008, 51, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jang, H.R.; Kang, D.; Sinn, D.H.; Gu, S.; Cho, S.J.; Lee, J.E.; Huh, W.; Paik, S.W.; Ryu, S.; Chang, Y.; et al. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease accelerates kidney function decline in patients with chronic kidney disease: A cohort study. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Medina, J.; Fernández-Salazar, L.I.; García-Buey, L.; Moreno-Otero, R. Approach to the pathogenesis and treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Diabetes Care 2004, 27, 2057–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, L.; Ota, T. Emerging roles of SGLT2 inhibitors in obesity and insulin resistance: Focus on fat browning and macrophage polarization. Adipocyte 2018, 7, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, W.; Luo, Y.; Yang, S.; Zeng, M.; Zhang, S.; Liu, J.; Han, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, X.; Wu, H.; et al. Ectopic lipid accumulation: Potential role in tubular injury and inflammation in diabetic kidney disease. Clin. Sci. 2018, 132, 2407–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akazawa, Y.; Nakao, K. To die or not to die: Death signaling in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 53, 893–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nagahara, R.; Matono, T.; Sugihara, T.; Matsuki, Y.; Yamane, M.; Okamoto, T.; Miyoshi, K.; Nagahara, T.; Okano, J.-I.; Koda, M.; et al. Gene Expression Analysis of the Activating Factor 3/Nuclear Protein 1 Axis in a Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis Mouse Model. Yonago Acta Med. 2019, 62, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, L.; Nagata, N.; Nagashimada, M.; Zhuge, F.; Ni, Y.; Chen, G.; Mayoux, E.; Kaneko, S.; Ota, T. SGLT2 Inhibition by Empagliflozin Promotes Fat Utilization and Browning and Attenuates Inflammation and Insulin Resistance by Polarizing M2 Macrophages in Diet-induced Obese Mice. EBioMedicine 2017, 20, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamane, M.; Matono, T.; Okano, J.-I.; Nagahara, R.; Matsuki, Y.; Okamoto, T.; Miyoshi, K.-I.; Sugihara, T.; Nagahara, T.; Koda, M.; et al. Protective Effects of Ipragliflozin, a Sodium-glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitor, on a Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis Mouse Model. Yonago Acta Med. 2019, 62, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gilbert, R.E. Sodium–glucose linked transporter-2 inhibitors: Potential for renoprotection beyond blood glucose lowering? Kidney Int. 2014, 86, 693–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heerspink, H.J.; Kosiborod, M.; Inzucchi, S.E.; Cherney, D.Z. Renoprotective effects of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors. Kidney Int. 2018, 94, 26–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matono, T.; Koda, M.; Tokunaga, S.; Kato, J.; Sugihara, T.; Ueki, M.; Murawaki, Y. Therapeutic effects of ezetimibe for non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in fatty liver shionogi-ob/ob mice. Hepatol. Res. 2011, 41, 1240–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugihara, T.; Koda, M.; Kishina, M.; Kato, J.; Tokunaga, S.; Matono, T.; Ueki, M.; Murawaki, Y. Fatty liver Shionogi-ob/ob mouse: A new candidate for a non-alcoholic steatohepatitis model. Hepatol. Res. 2013, 43, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, T.; Bouchi, R.; Terashima, M.; Sasahara, Y.; Asakawa, M.; Takeuchi, T.; Nakano, Y.; Murakami, M.; Minami, I.; Izumiyama, H.; et al. Ipragliflozin Reduces Epicardial Fat Accumulation in Non-Obese Type 2 Diabetic Patients with Visceral Obesity: A Pilot Study. Diabetes Ther. 2017, 8, 851–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitraju, C.; Mejhert, N.; Haas, J.T.; Diaz-Ramirez, L.G.; Grueter, C.A.; Imbriglio, J.E.; Pinto, S.; Koliwad, S.K.; Walther, T.C.; Farese, R.V. Triglyceride Synthesis by DGAT1 Protects Adipocytes from Lipid-Induced ER Stress during Lipolysis. Cell Metab. 2017, 26, 407–418.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, A.; Lee, M.Y.; Sessa, W.C. Lipid Droplet Biogenesis and Function in the Endothelium. Circ. Res. 2017, 120, 1289–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avril, T.; Vauléon, E.; Chevet, E. Endoplasmic reticulum stress signaling and chemotherapy resistance in solid cancers. Oncogenenis 2017, 6, e373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thethi, T.K.; Batuman, V. Challenging the conventional wisdom on diabetic nephropathy: Is microalbuminuria the earliest event? J. Diabetes its Complicat. 2019, 33, 191–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Żyłka, A.; Dumnicka, P.; Kuśnierz-Cabala, B.; Gala-Błądzińska, A.; Ceranowicz, P.; Kucharz, J.; Ząbek-Adamska, A.; Maziarz, B.; Drożdż, R.; Kuźniewski, M. Markers of Glomerular and Tubular Damage in the Early Stage of Kidney Disease in Type 2 Diabetic Patients. Mediat. Inflamm. 2018, 2018, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Allegretti, A.S.; Parada, X.V.; Ortiz, G.A.; Long, J.; Krinsky, S.; Zhao, S.; Fuchs, B.C.; Sojoodi, M.; Zhang, N.; Karumanchi, S.A.; et al. Serum Angiopoietin-2 Predicts Mortality and Kidney Outcomes in Decompensated Cirrhosis. Hepatology 2019, 69, 729–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sporek, M.; Dumnicka, P.; Gala-Bladzinska, A.; Ceranowicz, P.; Warzecha, Z.; Dembiński, A.; Stępień, E.; Walocha, J.; Drozdz, R.; Kuzniewski, M.; et al. Angiopoietin-2 Is an Early Indicator of Acute Pancreatic-Renal Syndrome in Patients with Acute Pancreatitis. Mediat. Inflamm. 2016, 2016, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jelenik, T.; Flögel, U.; Álvarez-Hernández, E.; Scheiber, D.; Zweck, E.; Ding, Z.; Rothe, M.; Mastrototaro, L.; Kohlhaas, V.; Kotzka, J.; et al. Insulin Resistance and Vulnerability to Cardiac Ischemia. Diabetes 2018, 67, 2695–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Parameter | Control | Ipragliflozin | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| BW (g) | 51.6 ± 2.6 | 53.4 ± 1.6 | 0.573 |
| Kidney weight/BW | 1.3 ± 0.2 | 1.3 ± 0.1 | 0.816 |
| Urine volume (mL/day) | 7.6 ± 1.9 | 3.3 ± 1.2 | 0.086 |
| Blood glucose (mg/dL) | 295.7 ± 64.4 | 183.3 ± 32.2 | 0.150 |
| Serum triglyceride (mg/dL) | 255.6 ± 39.2 | 154.0 ± 14.0 | 0.041 * |
| Creatinine clearance (mL/min/kg) | 7.3 ± 1.6 | 5.7 ± 2.2 | 0.568 |
| Urinary protein (g/g/Cr) | 13.2 ± 1.3 | 10.2 ± 2.2 | 0.256 |
| Gene Product | Forward Primer (5′-3′) | Reverse Primer (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| Grp78 | GAG GCG TAT TTG GGA AAG AAG G | GCT GCT GTA GGC TCA TTG ATG |
| Perk | TAT GCT ACG CAC ACG GGA CAA | ACT CGT TCC ATC TGG GTG CTG |
| Eif2a | GCA CTA CAT TGC AAC AAA TGG | CAA ACA CAG GAT CAC ACT TCA G |
| Chop | AGC TGG AAG CCT GGT ATG AG | AGC TAG GGA TGC AGG GTC AA |
| Ire1a | AAG GCT GGA TGG CAC CAG AG | ATG TTG GCC TGT CGG TAG AGA |
| Atf6 | TCG CCT TTT AGT CCG GTT CTT | GGC TCC ATA GGT CTG ACT CC |
| Nfkb1 | ATTCCGCTATGTGTGTGAAGG | GTGACCAACTGAACGATAACC |
| Actb | GCA TCC TCA CCC TGA AGT A | TGT GGT GCC AGA TTT TCT CC |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hosokawa, K.; Takata, T.; Sugihara, T.; Matono, T.; Koda, M.; Kanda, T.; Taniguchi, S.; Ida, A.; Mae, Y.; Yamamoto, M.; et al. Ipragliflozin Ameliorates Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Apoptosis through Preventing Ectopic Lipid Deposition in Renal Tubules. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 190. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21010190
Hosokawa K, Takata T, Sugihara T, Matono T, Koda M, Kanda T, Taniguchi S, Ida A, Mae Y, Yamamoto M, et al. Ipragliflozin Ameliorates Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Apoptosis through Preventing Ectopic Lipid Deposition in Renal Tubules. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(1):190. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21010190
Chicago/Turabian StyleHosokawa, Kohshiro, Tomoaki Takata, Takaaki Sugihara, Tomomitsu Matono, Masahiko Koda, Tsutomu Kanda, Sosuke Taniguchi, Ayami Ida, Yukari Mae, Marie Yamamoto, and et al. 2020. "Ipragliflozin Ameliorates Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Apoptosis through Preventing Ectopic Lipid Deposition in Renal Tubules" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 1: 190. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21010190
APA StyleHosokawa, K., Takata, T., Sugihara, T., Matono, T., Koda, M., Kanda, T., Taniguchi, S., Ida, A., Mae, Y., Yamamoto, M., Iyama, T., Fukuda, S., & Isomoto, H. (2020). Ipragliflozin Ameliorates Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Apoptosis through Preventing Ectopic Lipid Deposition in Renal Tubules. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(1), 190. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21010190






