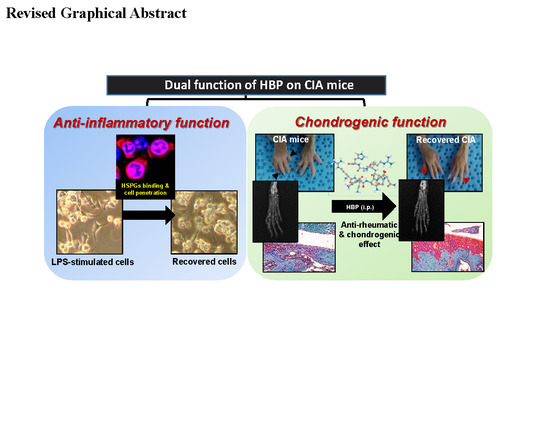
A Synthetic Cell-Penetrating Heparin-Binding Peptide Derived from BMP4 with Anti-Inflammatory and Chondrogenic Functions for the Treatment of Arthritis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Characterization of HBP
2.2. Cellular Uptake Activity of HBP
2.3. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of HBP on LPS-Treated RAW264.7 Cells
2.4. Effects of HBP on Proteins Related to the Inflammation Pathway
2.5. Chondrocyte Recovery Effect of HBP in Human Articular Chondrocytes
2.6. Antiarthritic Effects of HBP on CIA Mice
2.6.1. Hind Paw Swelling, Arthritis Score, and Histological Recovery of CIA Mice Injected with HBP
2.6.2. HBP Induces Suppression of Serum Inflammatory Cytokine Levels
2.6.3. Safranin O-Fast Green Staining and Immunohistochemical Analysis of IL6 in Cartilage of CIA Mice
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Peptide Preparation
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. MTT Assay
4.4. RNA Isolation and Quantitative RT-PCR
4.5. In Vitro Cellular Internalization
4.6. Western Blot Analysis
4.7. Induction of CIA in Mice and Peptide Treatment
4.8. Assessment of Clinical Signs of Inflammation
4.9. Histological Examinations
4.10. Serum Cytokine Levels
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BSA | bovine serum albumin |
| CD | circular dichroism |
| CIA | collagen-induced arthritis |
| COLII | Type II collagen |
| COX2 | cyclooxygenase |
| DMARD | disease-modifying anti rheumatic drug |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium |
| EDAC | N-ethyl-N0-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-carbodiimide hydrochloride |
| EDTA | fetal bovine serum |
| FBS | ethylenediaminetetracetate |
| HBP | 10-mer synthetic anti-inflammatory heparin binding peptides |
| HE | hematoxylin and eosin |
| HBSS | Hank’s balanced salt solution |
| HRP | horse radish peroxidase |
| IFN | interferon |
| IL | interleukin |
| LPS | lipopolysaccharide |
| NHAC | Normal Human Articular Chondrocyte |
| NHS | N-hydroxysuccinimide |
| PBS | phosphate-buffered saline |
| RA | rheumatoid arthritis |
| SAHA | suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid |
| SDS-PAGE | sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis |
| TFA | trifluoroacetic acid |
| TFE | trifluoroethanol |
| TNF-α | tumor necrosis factor-alpha |
| T-TBS | Tween-Tris-buffered saline |
References
- Kim, H.K.; Cho, S.K.; Kim, J.W.; Jung, S.Y.; Jang, E.J.; Bae, S.C.; Yoo, D.H.; Sung, Y.K. An Increased Disease Burden of Autoimmune Inflammatory Rheumatic Diseases in Korea. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korean Statistical Information Service (KOSIS). Available online: http://kosis.kr/eng/statisticsList/statisticsListIndex.do?menuId=M0101vwcd=MTETITLE&parmTabId=M_01_01&statId=1962001&themaId=#SelectStatsBoxDiv (accessed on 13 March 2020).
- Furst, D.E.; Emery, P. Rheumatoid Arthritis Pathophysiology: Update on Emerging Cytokine and Cytokine-Associated Cell Targets. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2014, 9, 1560–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, D.H.; Hrycaj, P.; Miranda, P.; Ramiterre, E.; Piotrowski, M.; Shevchuk, S.; Kovalenko, V.; Prodanovic, N.; Abello-Banfi, M.; Gutierrez-Urena, S.; et al. A Randomised, Double-Blind, Parallel-Group Study to Demonstrate Equivalence in Efficacy and Safety of Ct-P13 Compared with Innovator Infliximab When Coadministered with Methotrexate in Patients with Active Rheumatoid Arthritis: The Planetra Study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 10, 1613–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.K.; Lee, E.Y.; Chung, S.M.; Mun, S.H.; Yoo, B.; Moon, H.B. Effects of Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs and Antiinflammatory Cytokines on Human Osteoclastogenesis through Interaction with Receptor Activator of Nuclear Factor Kappab, Osteoprotegerin, and Receptor Activator of Nuclear Factor Kappab Ligand. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2004, 12, 3831–3843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choy, E.H.; Panayi, G.S. Cytokine Pathways and Joint Inflammation in Rheumatoid Arthritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 12, 907–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, S.K. Biologic Agents in Rheumatoid Arthritis: An Update for Managed Care Professionals. J. Manag. Care Pharm. 2011, 9, S14–S18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burmester, G.R.; Pope, J.E. Novel Treatment Strategies in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Lancet 2017, 10086, 2338–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepriano, A.; Kerschbaumer, A.; Smolen, J.S.; van der Heijde, D.; Dougados, M.; van Vollenhoven, R.; McInnes, I.B.; Bijlsma, J.W.; Burmester, G.R.; de Wit, M.; et al. Safety of Synthetic and Biological Dmards: A Systematic Literature Review Informing the 2019 Update of the Eular Recommendations for the Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silvagni, E.; Di Battista, M.; Bonifacio, A.F.; Zucchi, D.; Governato, G.; Scire, C.A. One Year in Review 2019: Novelties in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2019, 4, 519–534. [Google Scholar]
- Blanchard, F.; Chipoy, C. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors: New Drugs for the Treatment of Inflammatory Diseases? Drug Discov. Today 2005, 3, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minucci, S.; Pelicci, P.G. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors and the Promise of Epigenetic (and More) Treatments for Cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 1, 38–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.H.; Park, S.H.; Lee, H.Y.; Lee, J.W.; Lee, B.K.; Lee, B.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, M.S. An Injectable, Electrostatically Interacting Drug Depot for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Biomaterials 2018, 154, 86–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, J.; Park, S.H.; Kim, M.J.; Ju, H.J.; Yin, X.Y.; Min, B.H.; Kim, M.S. Injectable Click-Crosslinked Hyaluronic Acid Depot to Prolong Therapeutic Activity in Articular Joints Affected by Rheumatoid Arthritis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 28, 24984–24998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ain, Q.; Zeeshan, M.; Khan, S.; Ali, H. Biomimetic Hydroxyapatite as Potential Polymeric Nanocarrier for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2019, 12, 2595–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; McCrate, J.M.; Lee, J.C.; Li, H. The Role of Surface Charge on the Uptake and Biocompatibility of Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles with Osteoblast Cells. Nanotechnology 2011, 10, 105708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Huang, X.; Cai, Y.; Tang, R.; Yang, D. Size Effect of Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles on Proliferation and Apoptosis of Osteoblast-Like Cells. Acta Biomater. 2009, 1, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaspar, A.A.; Reichert, J.M. Future Directions for Peptide Therapeutics Development. Drug Discov. Today 2013, 18, 807–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craik, D.J.; Fairlie, D.P.; Liras, S.; Price, D. The Future of Peptide-Based Drugs. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2013, 1, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malemud, C.J. Recent Advances in Neutralizing the Il-6 Pathway in Arthritis. Open Access Rheumatol. 2009, 1, 133–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Cho, M.L.; Kim, J.I.; Moon, Y.M.; Oh, H.J.; Kim, G.T.; Ryu, S.; Baek, S.H.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, H.Y.; et al. Interleukin 17 (Il-17) Increases the Expression of Toll-Like Receptor-2, 4, and 9 by Increasing Il-1beta and Il-6 Production in Autoimmune Arthritis. J. Rheumatol. 2009, 36, 684–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ospelt, C.; Brentano, F.; Rengel, Y.; Stanczyk, J.; Kolling, C.; Tak, P.P.; Gay, R.E.; Gay, S.; Kyburz, D. Overexpression of Toll-Like Receptors 3 and 4 in Synovial Tissue from Patients with Early Rheumatoid Arthritis: Toll-Like Receptor Expression in Early and Longstanding Arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2008, 58, 3684–3692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, C.D.; Mutch, B.E.; Workman, S.; McDaid, J.P.; Horwood, N.J.; Foxwell, B.M. Bmx Tyrosine Kinase Regulates Tlr4-Induced Il-6 Production in Human Macrophages Independently of P38 Mapk and NF kappa B Activity. Blood 2008, 111, 1781–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smolen, J.S.; Schoels, M.M.; Nishimoto, N.; Breedveld, F.C.; Burmester, G.R.; Dougados, M.; Emery, P.; Ferraccioli, G.; Gabay, C.; Gibofsky, A.; et al. Consensus Statement on Blocking the Effects of Interleukin-6 and in Particular by Interleukin-6 Receptor Inhibition in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Other Inflammatory Conditions. Ann. Rheum. Dis 2013, 72, 482–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremer, J.M.; Bloom, B.J.; Breedveld, F.C.; Coombs, J.H.; Fletcher, M.P.; Gruben, D.; Krishnaswami, S.; Burgos-Vargas, R.; Wilkinson, B.A.; Zerbini, C.A.; et al. The Safety and Efficacy of a Jak Inhibitor in Patients with Active Rheumatoid Arthritis: Results of a Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Phase Iia Trial of Three Dosage Levels of Cp-690,550 Versus Placebo. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2009, 60, 1895–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winthrop, K.L. The Emerging Safety Profile of Jak Inhibitors in Rheumatic Disease. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2017, 13, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atzeni, F.; Gianturco, L.; Talotta, R.; Varisco, V.; Ditto, M.C.; Turiel, M.; Sarzi-Puttini, P. Investigating the Potential Side Effects of Anti-Tnf Therapy for Rheumatoid Arthritis: Cause for Concern? Immunotherapy 2015, 7, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keiserman, M.; Codreanu, C.; Handa, R.; Xibille-Friedmann, D.; Mysler, E.; Briceno, F.; Akar, S. The Effect of Antidrug Antibodies on the Sustainable Efficacy of Biologic Therapies in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Practical Consequences. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2014, 10, 1049–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fosgerau, K.; Hoffmann, T. Peptide Therapeutics: Current Status and Future Directions. Drug Discov. Today 2015, 20, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaman, O.; Kelebek, S.; Demirci, E.A.; Ibis, F.; Ulu, M.; Ercan, U.K. Synergistic Effect of Cold Plasma Treatment and Rgd Peptide Coating on Cell Proliferation over Titanium Surfaces. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2018, 15, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Park, J.H.; Park, J.B.; Suh, J.S.; Choi, Y.S.; Lee, S.J.; Chung, C.P.; Park, Y.J. The Identification of a Heparin Binding Domain Peptide from Bone Morphogenetic Protein-4 and Its Role on Osteogenesis. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 7226–7238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Suh, J.S.; Park, Y.S.; Chung, C.P.; Park, Y.J. Dual-Function Synthetic Peptide Derived from Bmp4 for Highly Efficient Tumor Targeting and Antiangiogenesis. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 4643–4656. [Google Scholar]
- Ganz, T. Defensins: Antimicrobial Peptides of Innate Immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 3, 710–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schibli, D.J.; Hunter, H.N.; Aseyev, V.; Starner, T.D.; Wiencek, J.M.; Mc, P.B.; Tack, B.F.; Vogel, H.J. The Solution Structures of the Human β Defensins Lead to a Better Understanding of the Potent Bactericidal Activity of Hbd3 against Staphylococcus Aureus. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 8279–8289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joosten, L.A.; Helsen, M.M.; Loo, F.A.; Berg, W.B. Anticytokine Treatment of Established Type Ii Collagen-Induced Arthritis in Dba/1 Mice. A Comparative Study Using Anti-Tnfα, Anti-Il-1α/Beta, and Il-1ra. Arthritis Rheumatol. 1996, 39, 797–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Zhao, M.; Mundy, G.R. Bone Morphogenetic Proteins. Growth Factors 2004, 22, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.Y.; Suh, J.S.; Kim, J.M.; Kim, J.H.; Park, H.J.; Park, Y.J.; Chung, C.P. Identification of a Cell-Penetrating Peptide Domain from Human Beta-Defensin 3 and Characterization of Its Anti-Inflammatory Activity. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 5423–5434. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, S.G.; Sayers, E.J.; He, L.; Narayan, R.; Williams, T.L.; Mills, E.M.; Allemann, R.K.; Luk, L.Y.P.; Jones, A.T.; Tsai, Y.H. Cell-Penetrating Peptide Sequence and Modification Dependent Uptake and Subcellular Distribution of Green Florescent Protein in Different Cell Lines. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrugia, B.L.; Lord, M.S.; Melrose, J.; Whitelock, J.M. The Role of Heparan Sulfate in Inflammation, and the Development of Biomimetics as Anti-Inflammatory Strategies. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2018, 66, 321–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alunno, A.; Carubbi, F.; Giacomelli, R.; Gerli, R. Cytokines in the Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis: New Players and Therapeutic Targets. BMC Rheumatol. 2017, 13, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Dey, P.; Panga, V.; Raghunathan, S. A Cytokine Signalling Network for the Regulation of Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase Expression in Rheumatoid Arthritis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, S.; Zhang, C.; Liu, J. Platelet-Rich Plasma Exhibits Beneficial Effects for Rheumatoid Arthritis Mice by Suppressing Inflammatory Factors. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 4082–4088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietrosimone, K.M.; Jin, M.; Poston, B.; Liu, P. Collagen-Induced Arthritis: A Model for Murine Autoimmune Arthritis. Bio-Protocol 2015, 20, e1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haraoui, B.; Bykerk, V. Etanercept in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2007, 3, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, H.; Kim, J.; Jung, H.; Rim, Y.A.; Kim, Y.; Jung, S.M.; Park, S.-H.; Ju, J.H. Induced Production of Anti-Etanercept Antibody in Collagen-Induced Arthritis. Mol. Med. Rep. 2014, 9, 2301–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldring, S.R. Pathogenesis of Bone Erosions in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2002, 14, 406–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Kraan, P.M. The Interaction between Joint Inflammation and Cartilage Repair. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2019, 16, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irawan, V.; Sung, T.C.; Higuchi, A.; Ikoma, T. Collagen Scaffolds in Cartilage Tissue Engineering and Relevant Approaches for Future Development. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2018, 15, 673–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Seo, Y.N.; Park, H.J.; Park, Y.J.; Chung, C.P. The Cell-Penetrating Peptide Domain from Human Heparin-Binding Epidermal Growth Factor-Like Growth Factor (Hb-Egf) Has Anti-Inflammatory Activity In Vitro and In Vivo. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 419, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xia, M.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X. Cell-Penetrating Peptide-Modified Quantum Dots as a Ratiometric Nanobiosensor for the Simultaneous Sensing and Imaging of Lysosomes and Extracellular Ph. Chem. Commun. (Cambridge) 2019, 56, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, J.Y.; Kim, D.W.; Ahn, J.H.; Choi, E.J.; Kim, Y.H.; Jeun, M.; Kim, E.J. Propofol Suppresses Lps-Induced Inflammation in Amnion Cells Via Inhibition of Nf-Kappab Activation. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2019, 16, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishikawa, M.; Myoui, A.; Tomita, T.; Takahi, K.; Nampei, A.; Yoshikawa, H. Prevention of the Onset and Progression of Collagen-Induced Arthritis in Rats by the Potent P38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Inhibitor Fr167653. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2003, 48, 2670–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mossiat, C.; Laroche, D.; Prati, C.; Pozzo, T.; Demougeot, C.; Marie, C. Association between Arthritis Score at the Onset of the Disease and Long-Term Locomotor Outcome in Adjuvant-Induced Arthritis in Rats. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2015, 17, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, D.H.; Lee, D.; Jo, B.S.; Park, K.-S.; Lee, K.E.; Choi, J.K.; Park, Y.J.; Lee, J.-Y.; Park, Y.S. A Synthetic Cell-Penetrating Heparin-Binding Peptide Derived from BMP4 with Anti-Inflammatory and Chondrogenic Functions for the Treatment of Arthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4251. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21124251
Choi DH, Lee D, Jo BS, Park K-S, Lee KE, Choi JK, Park YJ, Lee J-Y, Park YS. A Synthetic Cell-Penetrating Heparin-Binding Peptide Derived from BMP4 with Anti-Inflammatory and Chondrogenic Functions for the Treatment of Arthritis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(12):4251. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21124251
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Da Hyeon, Dongwoo Lee, Beom Soo Jo, Kwang-Sook Park, Kyeong Eun Lee, Ju Kwang Choi, Yoon Jeong Park, Jue-Yeon Lee, and Yoon Shin Park. 2020. "A Synthetic Cell-Penetrating Heparin-Binding Peptide Derived from BMP4 with Anti-Inflammatory and Chondrogenic Functions for the Treatment of Arthritis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 12: 4251. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21124251
APA StyleChoi, D. H., Lee, D., Jo, B. S., Park, K.-S., Lee, K. E., Choi, J. K., Park, Y. J., Lee, J.-Y., & Park, Y. S. (2020). A Synthetic Cell-Penetrating Heparin-Binding Peptide Derived from BMP4 with Anti-Inflammatory and Chondrogenic Functions for the Treatment of Arthritis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(12), 4251. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21124251