The Connexin 43 Regulator Rotigaptide Reduces Cytokine-Induced Cell Death in Human Islets
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
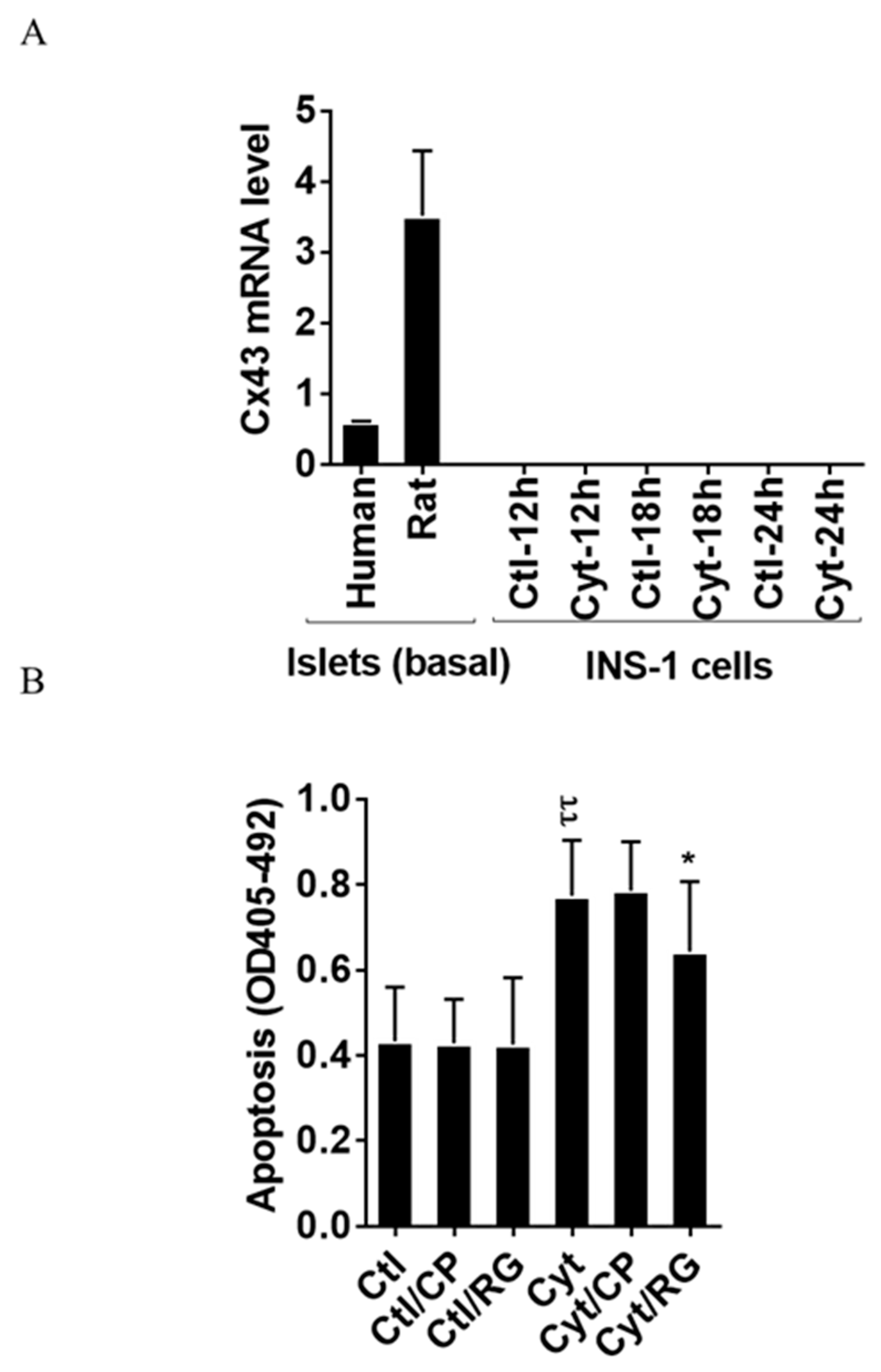
2.1. Rotigaptide Reduces Cytokine-Induced Apoptosis in Cx43-Expressing Human Islets
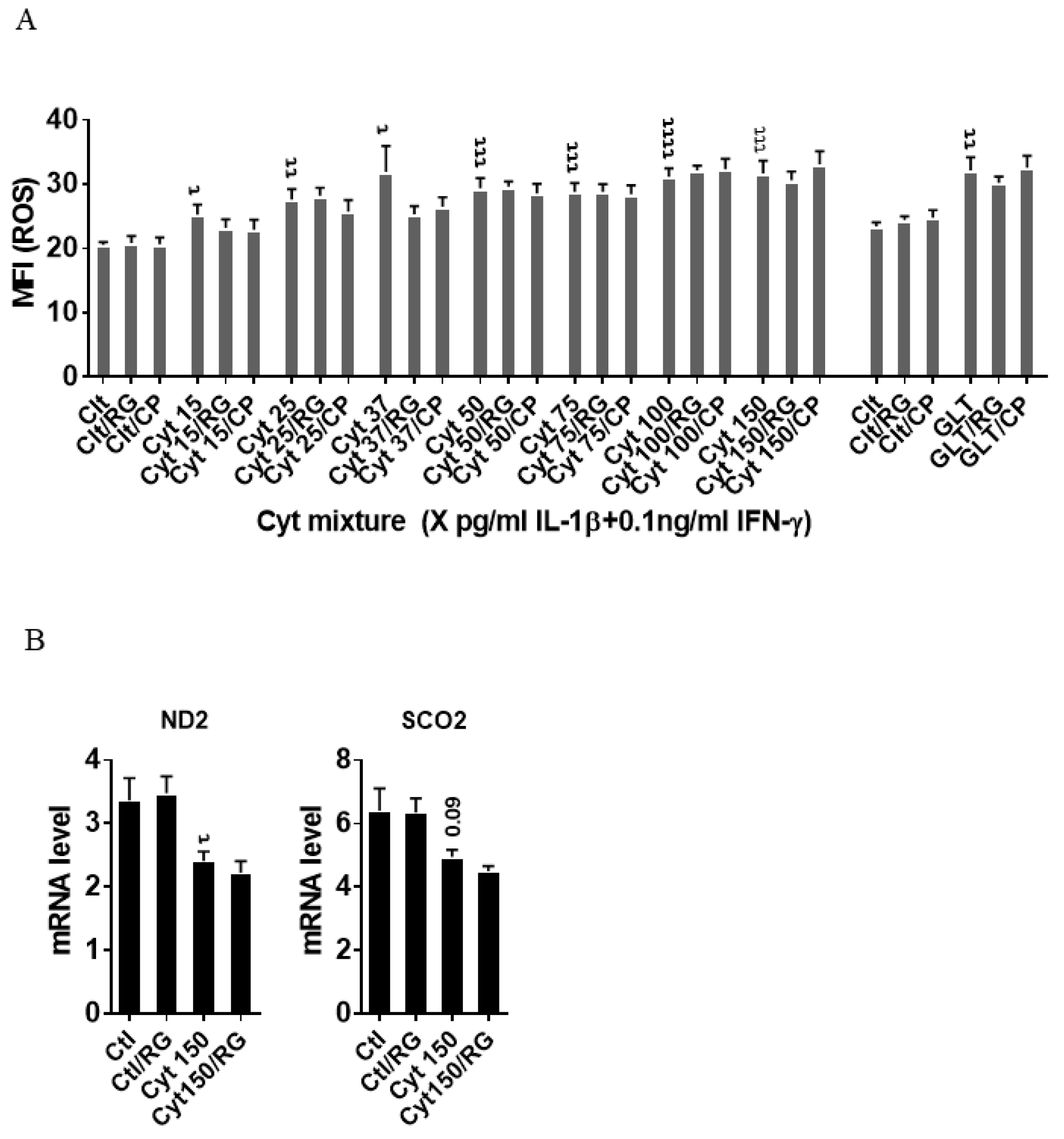
2.2. Rotigaptide Ameliorates Cytokine-Induced Apoptosis Associated with Improved Mitochondrial Function in Cx43-Deficient INS-1 Cells
2.3. Rotigaptide Reduces Neither Cytokine nor Glucolipotoxicity-Induced ROS Production in INS-1 Cells
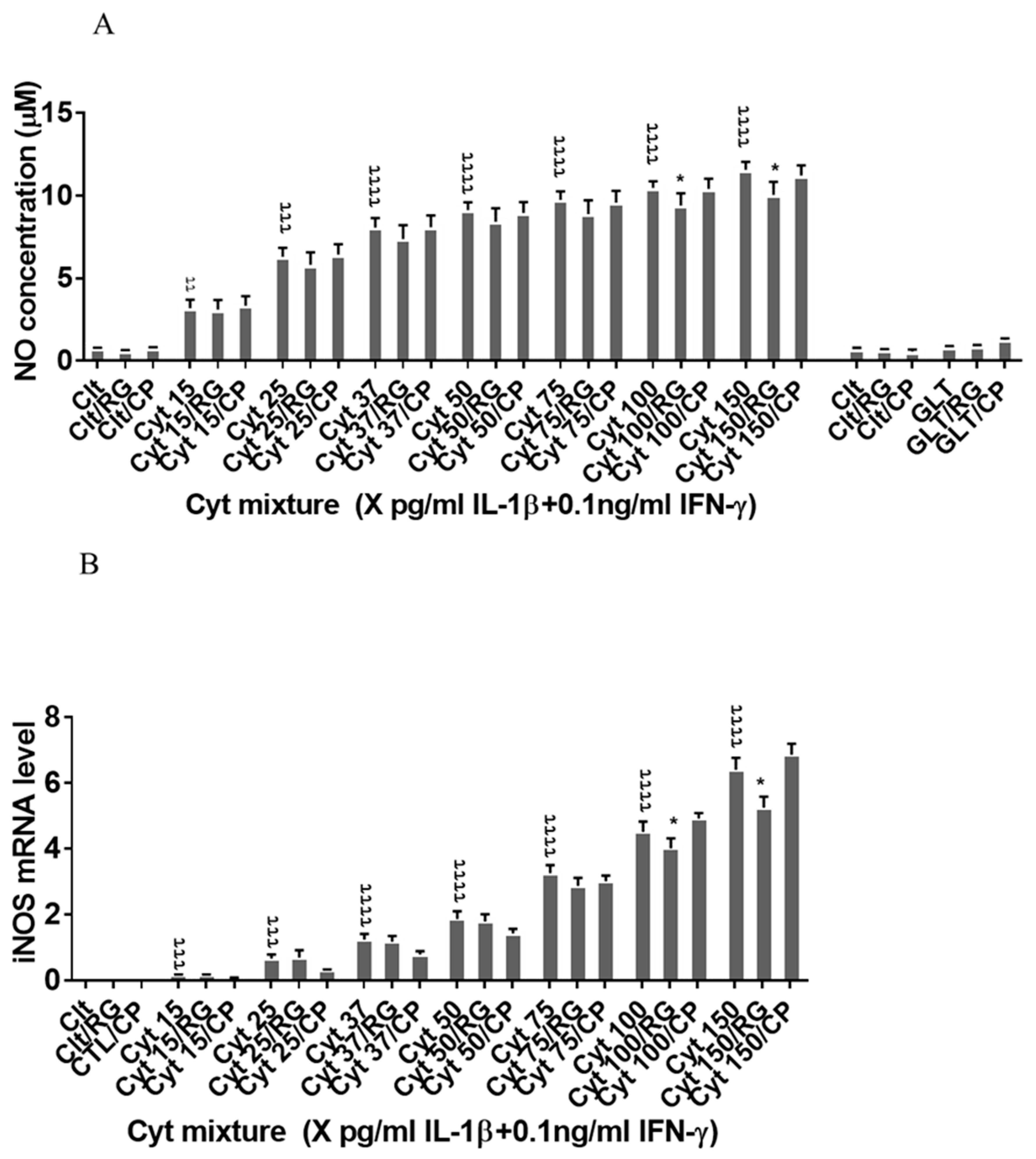
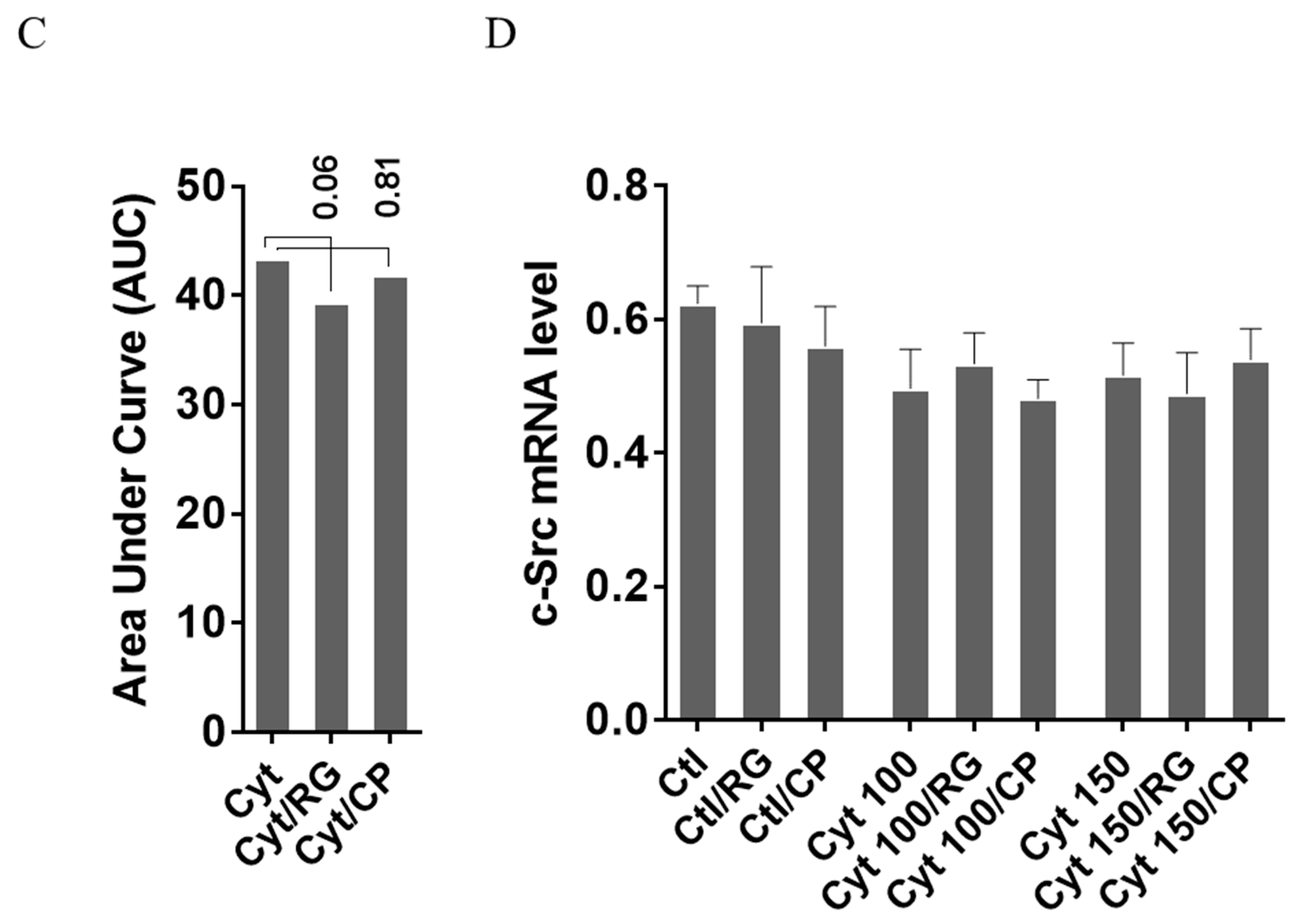
2.4. Rotigaptide Reduces Nitroxidative Stress Independently of Cx43
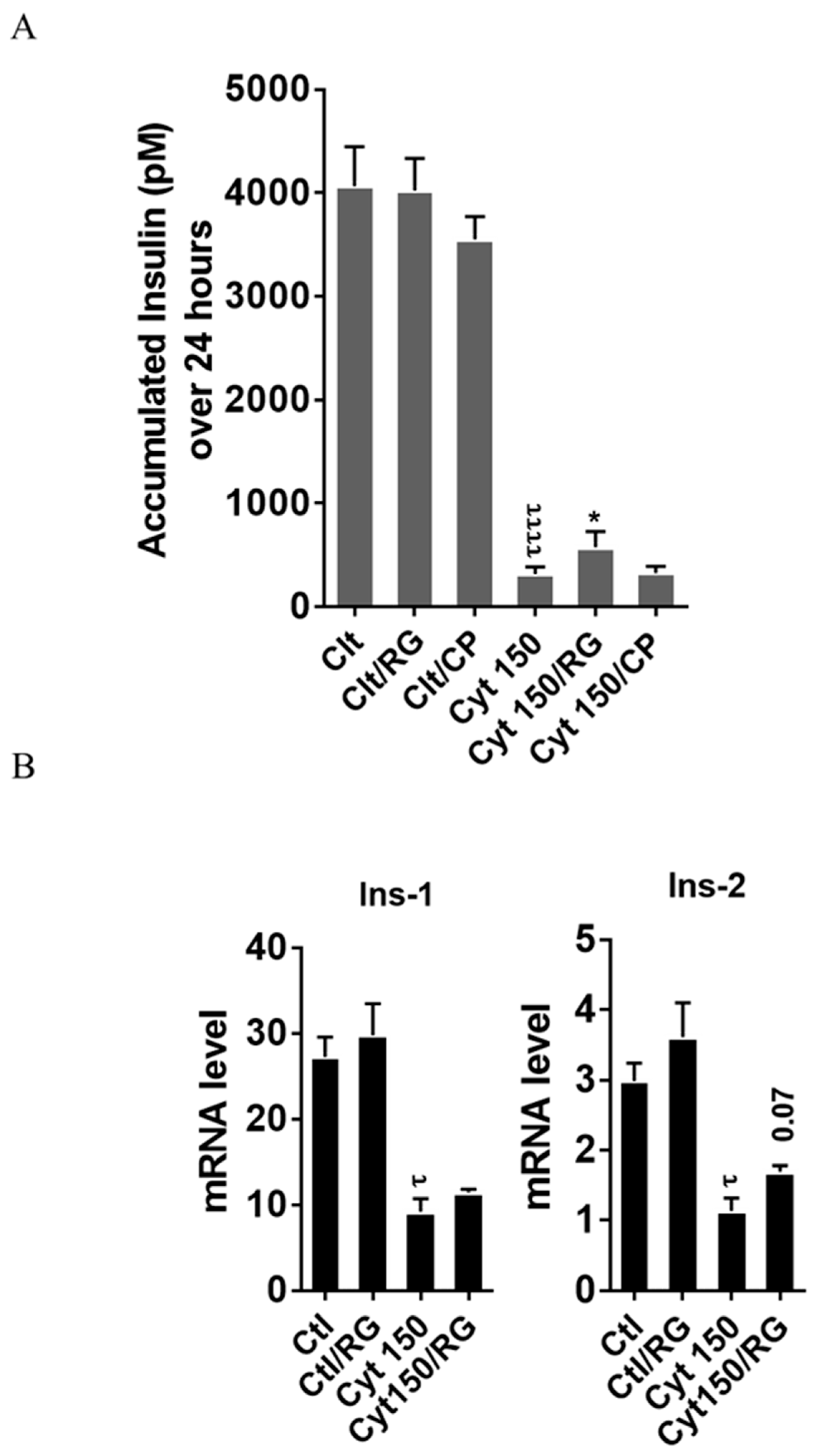
2.5. Rotigaptide Ameliorates High-Concentration Cytokine-Induced Inhibition of Insulin Secretion and Reduction of Insulin mRNA in INS-1 Cells
3. Discussion
4. Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Cell Culture and Exposures
4.3. Human Islet Culture and Exposures
4.4. Apoptosis and Cell Viability Assays
4.5. Nitric Oxide (NO) Assay
4.6. Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Assay
4.7. Real-Time Quantitative RT-PCR
4.8. Western Blot Analysis
4.9. Insulin Assay
4.10. Single-Cell RNA-Seq of Human Pancreatic Islets
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Berchtold, L.A.; Prause, M.; Storling, J.; Mandrup-Poulsen, T. Cytokines and Pancreatic beta-Cell Apoptosis. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2016, 75, 99–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, C.M.; Faulenbach, M.; Vaag, A.; Volund, A.; Ehses, J.A.; Seifert, B.; Mandrup-Poulsen, T.; Donath, M.Y. Interleukin-1-receptor antagonist in type 2 diabetes mellitus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 356, 1517–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, C.M.; Faulenbach, M.; Vaag, A.; Ehses, J.A.; Donath, M.Y.; Mandrup-Poulsen, T. Sustained Effects of Interleukin-1 Receptor Antagonist Treatment in Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2009, 32, 1663–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandrup-Poulsen, T.; Pickersgill, L.; Donath, M.Y. Blockade of interleukin 1 in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2010, 6, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran, A.; Bundy, B.; Becker, D.J.; DiMeglio, L.A.; Gitelman, S.E.; Goland, R.; Greenbaum, C.J.; Herold, K.C.; Marks, J.B.; Raskin, P.; et al. Interleukin-1 antagonism in type 1 diabetes of recent onset: Two multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials. Lancet 2013, 381, 1905–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera, S.M.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.G.; Jia, S.; Kaldunski, M.L.; Greenbaum, C.J.; Type 1 Diabetes TrialNet Canakinumab Study Group; Mandrup-Poulsen, T.; The AIDA Study Group; Hessner, M.J. Interleukin-1 antagonism moderates the inflammatory state associated with Type 1 diabetes during clinical trials conducted at disease onset. Eur. J. Immunol. 2016, 46, 1030–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastrandrea, L.; Yu, J.; Behrens, T.; Buchlis, J.; Albini, C.; Fourtner, S.; Quattrin, T. Etanercept treatment in children with new-onset type 1 diabetes: Pilot randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study. Diabetes Care 2009, 32, 1244–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ablamunits, V.; Henegariu, O.; Hansen, J.B.; Opare-Addo, L.; Preston-Hurlburt, P.; Santamaria, P.; Mandrup-Poulsen, T.; Herold, K.C. Synergistic reversal of type 1 diabetes in NOD mice with anti-CD3 and interleukin-1 blockade: Evidence of improved immune regulation. Diabetes 2012, 61, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cigliola, V.; Chellakudam, V.; Arabieter, W.; Meda, P. Connexins and beta-cell functions. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2013, 99, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klee, P.; Allagnat, F.; Pontes, H.; Cederroth, M.; Charollais, A.; Caille, D.; Britan, A.; Haefliger, J.A.; Meda, P. Connexins protect mouse pancreatic beta cells against apoptosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 4870–4879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farnsworth, N.L.; Benninger, R.K. New insights into the role of connexins in pancreatic islet function and diabetes. FEBS Lett. 2014, 588, 1278–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravier, M.A.; Guldenagel, M.; Charollais, A.; Gjinovci, A.; Caille, D.; Sohl, G.; Wollheim, C.B.; Willecke, K.; Henquin, J.C.; Meda, P. Loss of connexin36 channels alters β-cell coupling, islet synchronization of glucose-induced Ca2+ and insulin oscillations, and basal insulin release. Diabetes 2005, 54, 1798–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potolicchio, I.; Cigliola, V.; Velazquez-Garcia, S.; Klee, P.; Valjevac, A.; Kapic, D.; Cosovic, E.; Lepara, O.; Hadzovic-Dzuvo, A.; Mornjacovic, Z.; et al. Connexin-dependent signaling in neuro-hormonal systems. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1818, 1919–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meda, P.; Pepper, M.S.; Traub, O.; Willecke, K.; Gros, D.; Beyer, E.; Nicholson, B.; Paul, D.; Orci, L. Differential expression of gap junction connexins in endocrine and exocrine glands. Endocrinology 1993, 133, 2371–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serre-Beinier, V.; Mas, C.; Calabrese, A.; Caton, D.; Bauquis, J.; Caille, D.; Charollais, A.; Cirulli, V.; Meda, P. Connexins and secretion. Biol. Cell 2002, 94, 477–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moller, S.; Jacobsen, J.C.B.; Braunstein, T.H.; Holstein-Rathlou, N.H.; Sorensen, C.M. Influence of connexin45 on renal autoregulation. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2020, 318, F732–F740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Lampe, P.D.; Kensel-Hammes, P.; Hesson, J.; Ware, C.B.; Crisa, L.; Cirulli, V. Connexin 43 Functions as a Positive Regulator of Stem Cell Differentiation into Definitive Endoderm and Pancreatic Progenitors. iScience 2019, 19, 450–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, C.P.; Barbosa, H.C.; Britan, A.; Santos-Silva, J.C.; Boschero, A.C.; Meda, P.; Collares-Buzato, C.B. Beta cell coupling and connexin expression change during the functional maturation of rat pancreatic islets. Diabetologia 2010, 53, 1428–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klee, P.; Lamprianou, S.; Charollais, A.; Caille, D.; Sarro, R.; Cederroth, M.; Haefliger, J.A.; Meda, P. Connexin implication in the control of the murine beta-cell mass. Pediatr. Res. 2011, 70, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vozzi, C.; Bosco, D.; Dupont, E.; Charollais, A.; Meda, P. Hyperinsulinemia-induced hypoglycemia is enhanced by overexpression of connexin 43. Endocrinology 1997, 138, 2879–2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Vozzi, C.; Ullrich, S.; Charollais, A.; Philippe, J.; Orci, L.; Meda, P. Adequate connexin-mediated coupling is required for proper insulin production. J. Cell Biol. 1995, 131, 1561–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collares-Buzato, C.B.; Leite, A.R.; Boschero, A.C. Modulation of gap and adherens junctional proteins in cultured neonatal pancreatic islets. Pancreas 2001, 23, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serre-Beinier, V.; Le Gurun, S.; Belluardo, N.; Trovato-Salinaro, A.; Charollais, A.; Haefliger, J.A.; Condorelli, D.F.; Meda, P. Cx36 preferentially connects beta-cells within pancreatic islets. Diabetes 2000, 49, 727–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theis, M.; Mas, C.; Doring, B.; Degen, J.; Brink, C.; Caille, D.; Charollais, A.; Kruger, O.; Plum, A.; Nepote, V.; et al. Replacement by a lacZ reporter gene assigns mouse connexin36, 45 and 43 to distinct cell types in pancreatic islets. Exp. Cell Res. 2004, 294, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Short, K.W.; Head, W.S.; Piston, D.W. Connexin 36 mediates blood cell flow in mouse pancreatic islets. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 306, E324–E331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haugan, K.; Olsen, K.B.; Hartvig, L.; Petersen, J.S.; Holstein-Rathlou, N.H.; Hennan, J.K.; Nielsen, M.S. The antiarrhythmic peptide analog ZP123 prevents atrial conduction slowing during metabolic stress. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2005, 16, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhein, S.; Larsen, B.D.; Petersen, J.S.; Mohr, F.W. Effects of the new antiarrhythmic peptide ZP123 on epicardial activation and repolarization pattern. Cell Commun. Adhes. 2003, 10, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axelsen, L.N.; Stahlhut, M.; Mohammed, S.; Larsen, B.D.; Nielsen, M.S.; Holstein-Rathlou, N.H.; Andersen, S.; Jensen, O.N.; Hennan, J.K.; Kjolbye, A.L. Identification of ischemia-regulated phosphorylation sites in connexin43: A possible target for the antiarrhythmic peptide analogue rotigaptide (ZP123). J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2006, 40, 790–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahlhut, M.; Petersen, J.S.; Hennan, J.K.; Ramirez, M.T. The antiarrhythmic peptide rotigaptide (ZP123) increases connexin 43 protein expression in neonatal rat ventricular cardiomyocytes. Cell Commun. Adhes. 2006, 13, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.L.; Suzuki, K.; Lu, Y.; Hirano, S.; Fukuda, K.; Kumagai, N.; Kimura, K.; Nishida, T. Inhibition of gap junction-mediated intercellular communication by TNF-alpha in cultured human corneal fibroblasts. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2005, 46, 1195–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Retamal, M.A.; Froger, N.; Palacios-Prado, N.; Ezan, P.; Saez, P.J.; Saez, J.C.; Giaume, C. Cx43 hemichannels and gap junction channels in astrocytes are regulated oppositely by proinflammatory cytokines released from activated microglia. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 13781–13792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segerstolpe, A.; Palasantza, A.; Eliasson, P.; Andersson, E.M.; Andreasson, A.C.; Sun, X.; Picelli, S.; Sabirsh, A.; Clausen, M.; Bjursell, M.K.; et al. Single-Cell Transcriptome Profiling of Human Pancreatic Islets in Health and Type 2 Diabetes. Cell Metab. 2016, 24, 593–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, W.S.; Kuzmicic, J.; Burrill, J.S.; Donoghue, M.A.; Foncea, R.; Jensen, M.D.; Lavandero, S.; Arriaga, E.A.; Bernlohr, D.A. Proinflammatory cytokines differentially regulate adipocyte mitochondrial metabolism, oxidative stress, and dynamics. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 306, E1033–E1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funakoshi-Tago, M.; Tago, K.; Andoh, K.; Sonoda, Y.; Tominaga, S.; Kasahara, T. Functional role of c-Src in IL-1-induced NF-kappa B activation: c-Src is a component of the IKK complex. J. Biochem. 2005, 137, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; Lan, T.; Chang, X.; Huang, K.; Huang, J.; Wang, S.; Chen, C.; Shen, X.; Liu, P.; Huang, H. Connexin43 mediates NF-kappaB signalling activation induced by high glucose in GMCs: Involvement of c-Src. Cell Commun. Signal. 2013, 11, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthoud, V.M.; Minogue, P.J.; Laing, J.G.; Beyer, E.C. Pathways for degradation of connexins and gap junctions. Cardiovasc. Res. 2004, 62, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musil, L.S.; Le, A.C.; VanSlyke, J.K.; Roberts, L.M. Regulation of connexin degradation as a mechanism to increase gap junction assembly and function. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 25207–25215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storling, J.; Zaitsev, S.V.; Kapelioukh, I.L.; Karlsen, A.E.; Billestrup, N.; Berggren, P.O.; Mandrup-Poulsen, T. Calcium has a permissive role in interleukin-1beta-induced c-jun N-terminal kinase activation in insulin-secreting cells. Endocrinology 2005, 146, 3026–3036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sekine, N.; Fasolato, C.; Pralong, W.F.; Theler, J.M.; Wollheim, C.B. Glucose-induced insulin secretion in INS-1 cells depends on factors present in fetal calf serum and rat islet-conditioned medium. Diabetes 1997, 46, 1424–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poitout, V.; Amyot, J.; Semache, M.; Zarrouki, B.; Hagman, D.; Fontes, G. Glucolipotoxicity of the pancreatic beta cell. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1801, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugliani, M.; Syed, F.; Masini, M.; Marselli, L.; Suleiman, M.; Novelli, M.; Filipponi, F.; Boggi, U.; Masiello, P.; De Tata, V.; et al. Direct effects of rosuvastatin on pancreatic human beta cells. Acta Diabetol. 2013, 50, 983–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Storling, J.; Binzer, J.; Andersson, A.K.; Zullig, R.A.; Tonnesen, M.; Lehmann, R.; Spinas, G.A.; Sandler, S.; Billestrup, N.; Mandrup-Poulsen, T. Nitric oxide contributes to cytokine-induced apoptosis in pancreatic beta cells via potentiation of JNK activity and inhibition of Akt. Diabetologia 2005, 48, 2039–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, J.B.; Tonnesen, M.F.; Madsen, A.N.; Hagedorn, P.H.; Friberg, J.; Grunnet, L.G.; Heller, R.S.; Nielsen, A.O.; Storling, J.; Baeyens, L.; et al. Divalent metal transporter 1 regulates iron-mediated ROS and pancreatic beta cell fate in response to cytokines. Cell Metab. 2012, 16, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghiasi, S.M.; Krogh, N.; Tyrberg, B.; Mandrup-Poulsen, T. The No-Go and Nonsense-Mediated RNA Decay Pathways Are Regulated by Inflammatory Cytokines in Insulin-Producing Cells and Human Islets and Determine beta-Cell Insulin Biosynthesis and Survival. Diabetes 2018, 67, 2019–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundh, M.; Christensen, D.P.; Rasmussen, D.N.; Mascagni, P.; Dinarello, C.A.; Billestrup, N.; Grunnet, L.G.; Mandrup-Poulsen, T. Lysine deacetylases are produced in pancreatic beta cells and are differentially regulated by proinflammatory cytokines. Diabetologia 2010, 53, 2569–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kekow, J.; Ulrichs, K.; Muller-Ruchholtz, W.; Gross, W.L. Measurement of rat insulin. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay with increased sensitivity, high accuracy, and greater practicability than established radioimmunoassay. Diabetes 1988, 37, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghiasi, S.M.; Dahllof, M.S.; Osmai, Y.; Osmai, M.; Jakobsen, K.K.; Aivazidis, A.; Tyrberg, B.; Perruzza, L.; Prause, M.C.B.; Christensen, D.P.; et al. Regulation of the beta-cell inflammasome and contribution to stress-induced cellular dysfunction and apoptosis. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2018, 478, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| No. | Lab Code | Gender | Age | BMI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | HE-5-15 | F | 22 | 22.8 |
| 2 | HE-10-16 | F | 60 | 23.6 |
| 3 | HE-15-16 | M | 34 | 23.1 |
| 4 | HE-17-16 | M | 50 | 24.8 |
| 5 | HE-2-17 | M | 52 | 25.1 |
| Rat Primers | ||
| Target | Forward | Reverse |
| iNOS | CACCACCCTCCTTGTTCAACA | CAATCCACAACTCGCTCCAA |
| Ins-1 | TCTGCTCCCTCTACCAACTG | TGCTCATTCAAAGGCTTTATTCAT |
| Ins-2 | CCCTAAGTGACCAGCTACAG | GAAGCGGATCCACAGGGC |
| HPRT1 | GCAGACTTTGCTTTCCTT | CCGCTGTCTTTTAGGCTT |
| Sco2 | TGGCTTACCCATTTCAACTTGG | GATGAGGAATACAATTATTAGGGTGTG |
| ND2 | AAACCCAATCACCCTAATCATTA | CAATCCTACTCATATTAGGAGTAAGT |
| c-Src | GGCCCAAGTCATGAAGAAAC | CATGCCTGAAGCAATCTGAG |
| Cx43 | CGCAATTACAACAAGCAAGC | TCATGTCCAGCAGCAACTTT |
| Human Primers | ||
| Target | Forward | Reverse |
| Cx43 | ATGAGCAGTCTGCCTTTCGT | TCTGCTTCAAGTGCATGTCC |
| HPRT1 | ATG CTG AGG ATT TGG AAA GG | TAA TCC AGC AGG TCA GCA AA |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ghiasi, S.M.; Hansen, J.B.; Christensen, D.P.; Tyrberg, B.; Mandrup-Poulsen, T. The Connexin 43 Regulator Rotigaptide Reduces Cytokine-Induced Cell Death in Human Islets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4311. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21124311
Ghiasi SM, Hansen JB, Christensen DP, Tyrberg B, Mandrup-Poulsen T. The Connexin 43 Regulator Rotigaptide Reduces Cytokine-Induced Cell Death in Human Islets. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(12):4311. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21124311
Chicago/Turabian StyleGhiasi, Seyed Mojtaba, Jakob Bondo Hansen, Dan Ploug Christensen, Björn Tyrberg, and Thomas Mandrup-Poulsen. 2020. "The Connexin 43 Regulator Rotigaptide Reduces Cytokine-Induced Cell Death in Human Islets" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 12: 4311. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21124311
APA StyleGhiasi, S. M., Hansen, J. B., Christensen, D. P., Tyrberg, B., & Mandrup-Poulsen, T. (2020). The Connexin 43 Regulator Rotigaptide Reduces Cytokine-Induced Cell Death in Human Islets. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(12), 4311. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21124311






