Enzymatic Synthesis of Glucose Monodecanoate in a Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvent
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
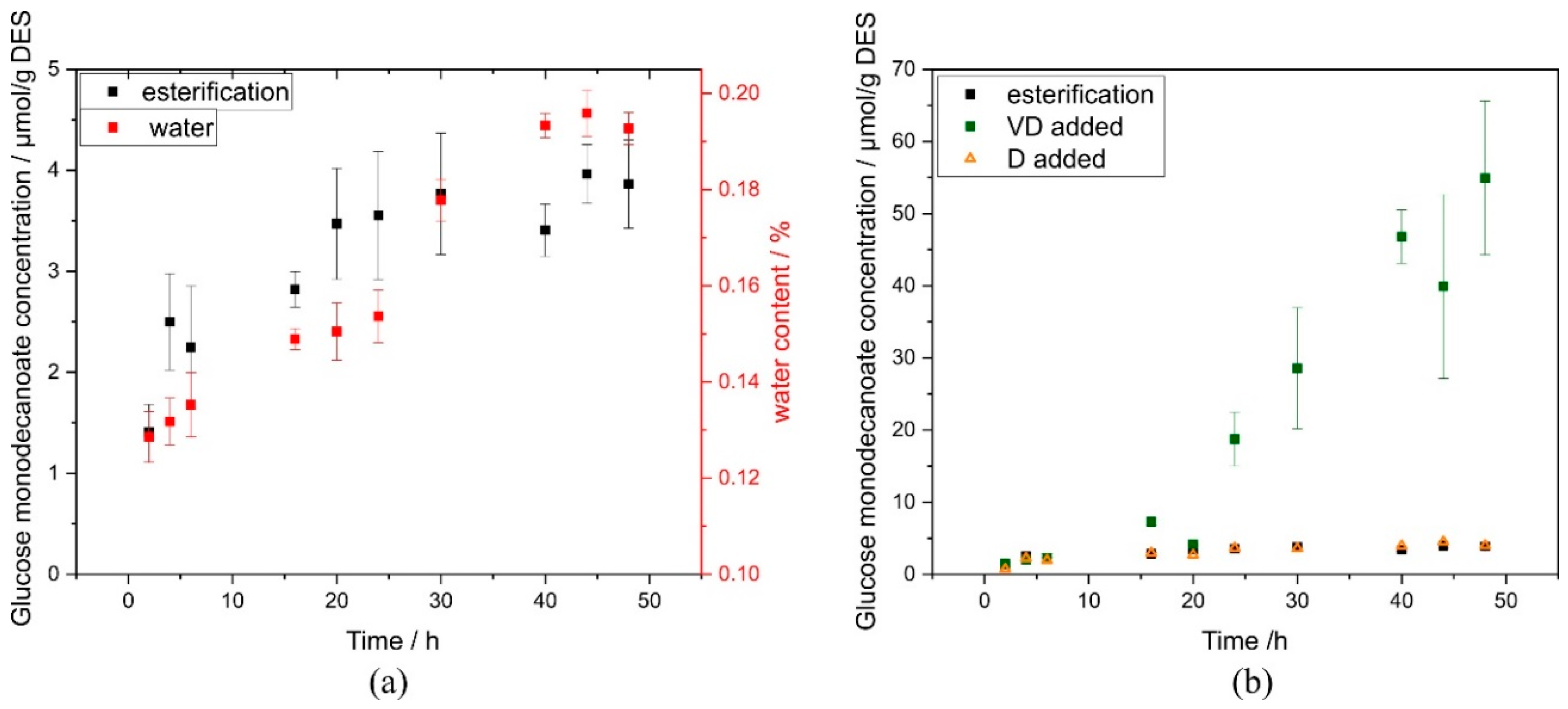
2.1. Reaction Time Course
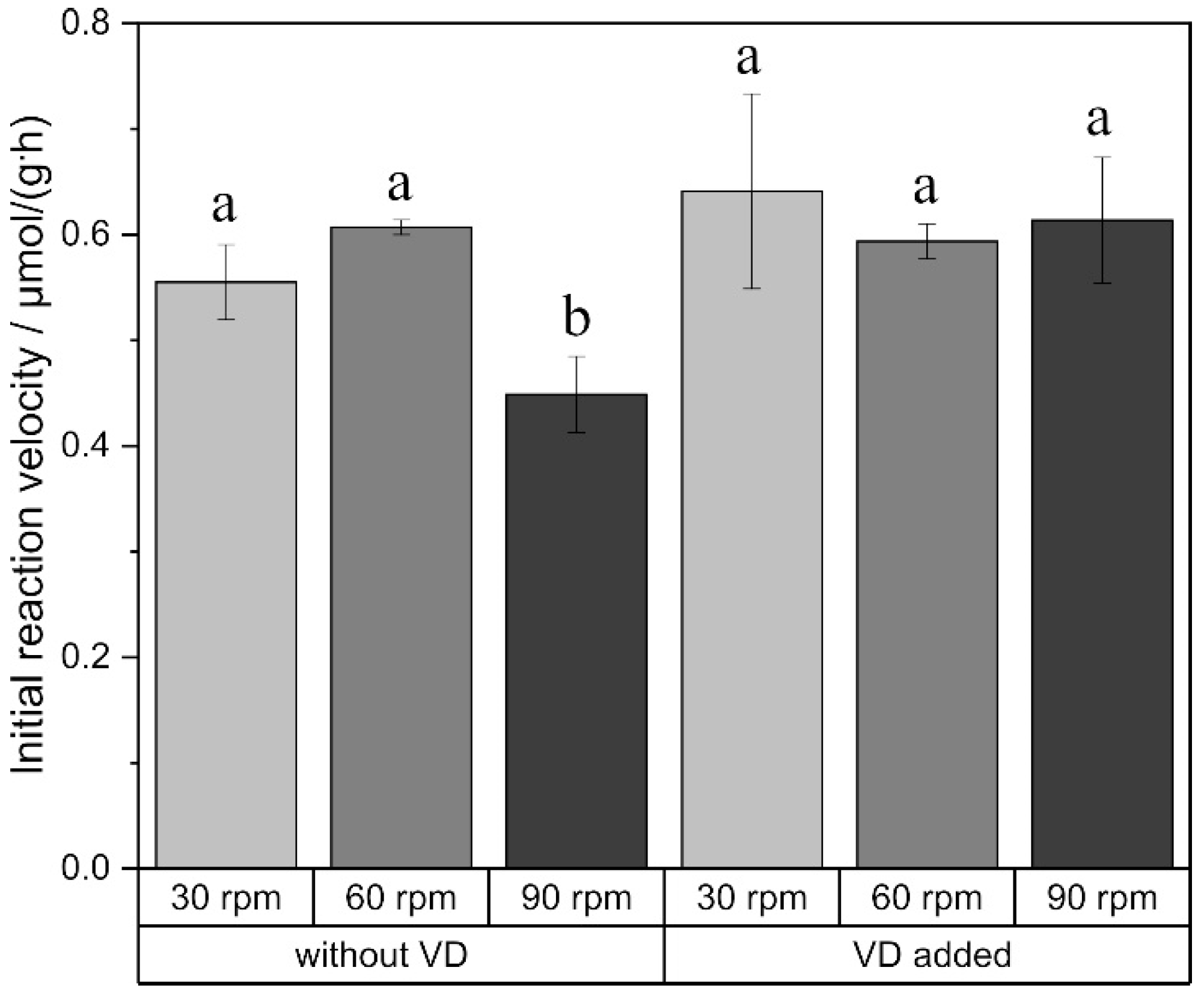
2.2. External Mass Transfer
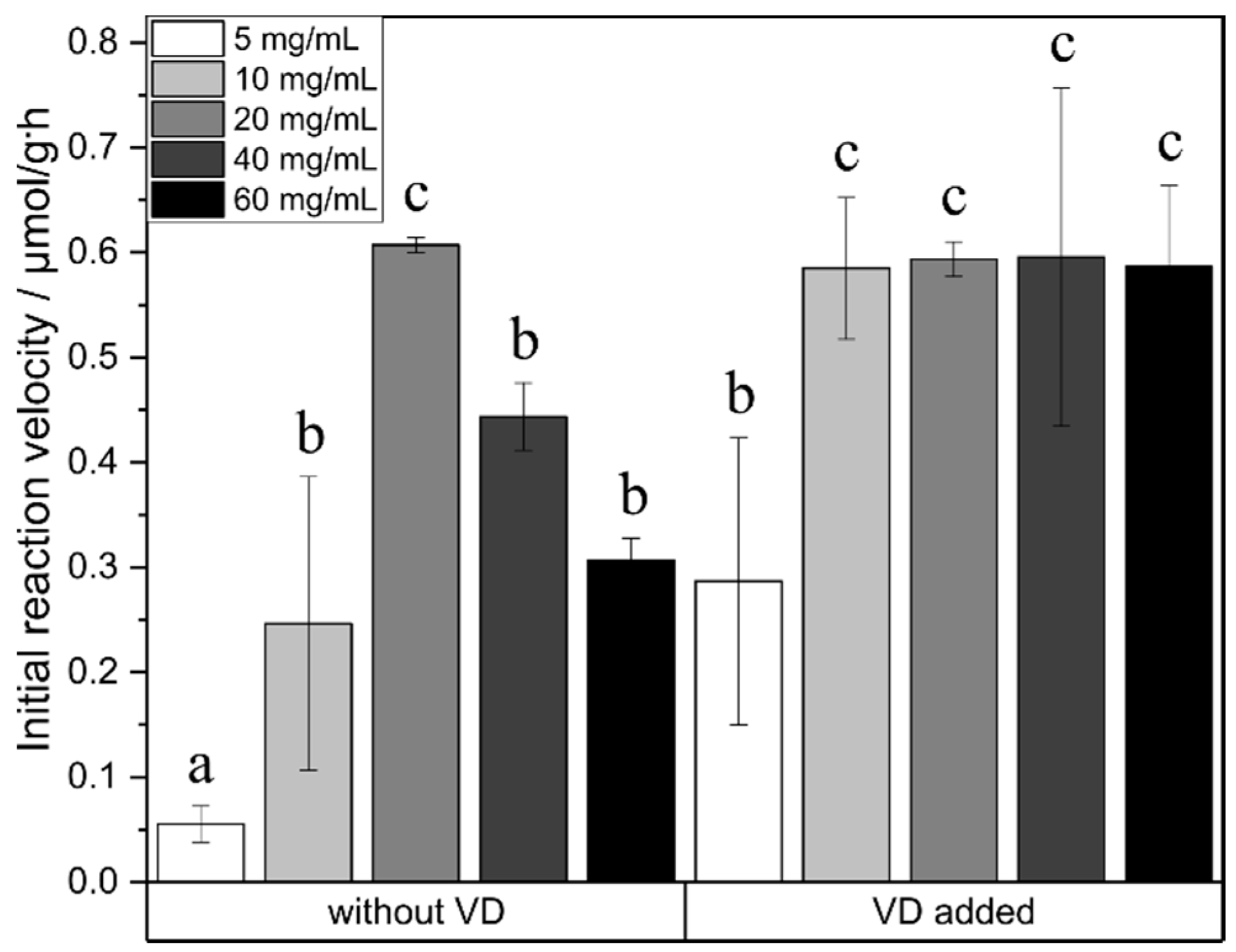
2.3. Effect of Enzyme Concentration
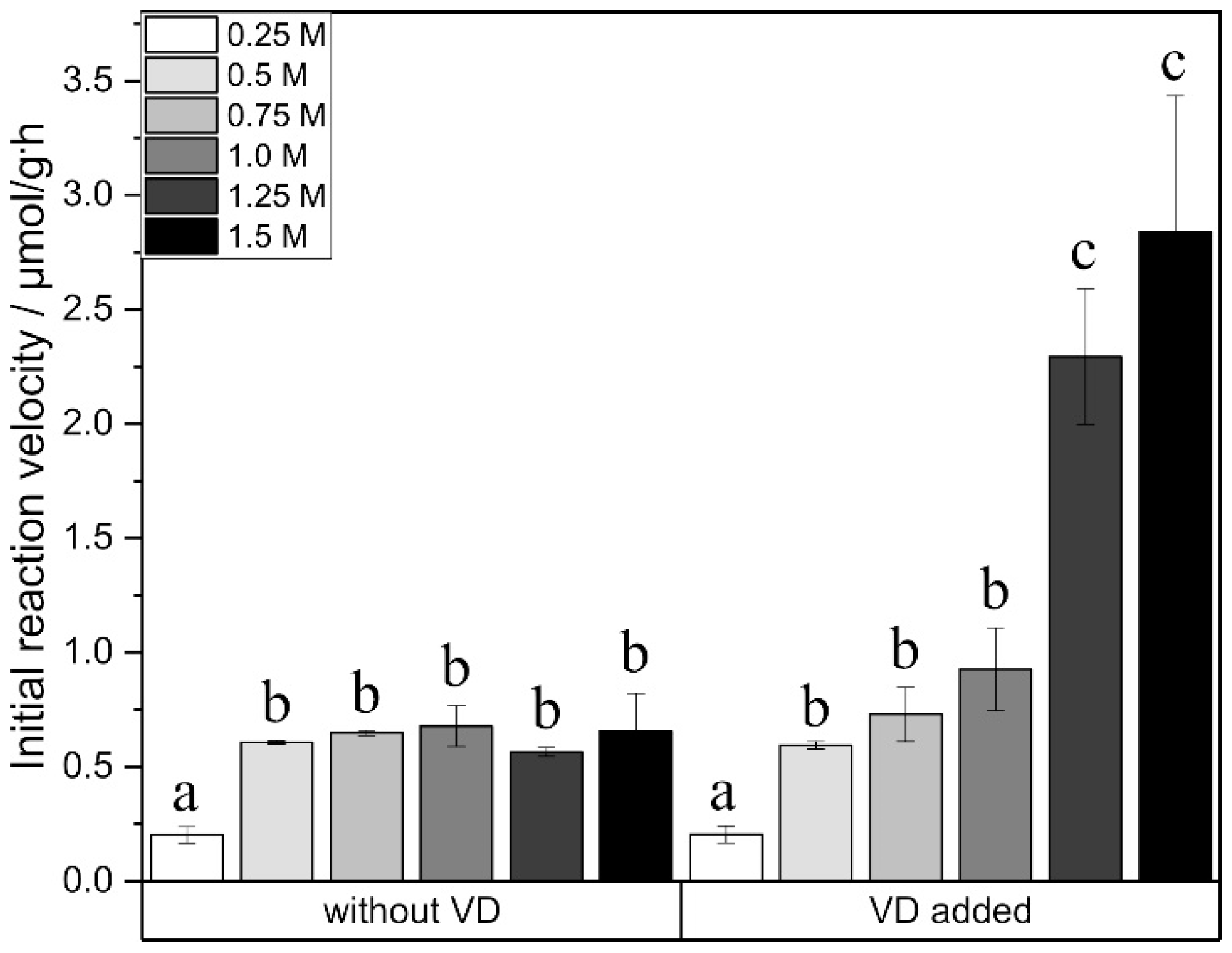
2.4. Effect of Initial Glucose Amount
2.5. Reusability of Enzyme
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Viscosity Measurements
4.3. Water Content Analysis
4.4. Glycolipid Synthesis
4.5. Initial Reaction Velocity
4.6. Influence of Enzyme Concentration
4.7. Optimization of Glucose Amount
4.8. Reusability of Enzyme
4.9. HPLC-ELSD-Analysis
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DES | Deep eutectic solvent |
| D | Decanoic |
| VD | Vinyl decanoate |
References
- Santos, D.K.F.; Rufino, R.D.; Luna, J.M.; Santos, V.A.; Sarubbo, L.A. Biosurfactants: Multifunctional biomolecules of the 21st century. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shete, A.M.; Wadhawa, G.; Banat, I.M.; Chopade, B.A. Mapping of patents on bioemulsifier and biosurfactant: A review. J. Sci. Ind. Res. 2006, 65, 91–115. [Google Scholar]
- Perinelli, D.R.; Lucarini, S.; Fagioli, L.; Campana, R.; Vllasaliu, D.; Duranti, A.; Casettari, L. Lactose oleate as new biocompatible surfactant for pharmaceutical applications. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 124, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younes, M.; Aggett, P.; Aguilar, F.; Crebelli, R.; Dusemund, B.; Gundert-Remy, U. Refined exposure assessment of sucrose esters of fatty acids (E 473) from its use as a food additive. EFSA J. 2018, 16, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Dörjes, J. Experimentelle Untersuchungen zur Wirkung von Rohöl und Rohöl/Tensid-Gemischen im Ökosystem Wattenmeer. XVI. Zusammenfassung und Schlußfolgerungen. Senckenbergiana maritima. Int. J. Mar. Sci. 1984, 16, 267–271. [Google Scholar]
- Poremba, K.; Gunkel, W.; Lang, S.; Wagner, F. Toxicity testing of synthetic and biogenic surfactants on marine microorganisms. Environ. Toxicol Water Qual. 1991, 6, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, I.J.; Matthews, B.; Suares, H.; Krodkiewska, I.; Furlong, D.N.; Grieser, F.; Drummond, C.I. Sugar fatty acid ester surfactants: Structure and ultimate aerobic biodegradability. J. Surfactants Deterg. 2000, 3, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, P.S.; Vaidya, A.N.; Bal, A.S.; Kapur, R.; Juwarkar, A.; Khannan, P. Kinetics of biosurfactant production by Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain BS2 from industrial wastes. Biotechnol. Lett. 1996, 18, 263–268. [Google Scholar]
- Siebenhaller, S.; Muhle-Goll, C.; Luy, B.; Kirschhöfer, F.; Brenner-Weiss, G.; Hiller, E.; Syldatk, C. Sustainable enzymatic synthesis of glycolipids in a deep eutectic solvent system. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2016, 133, S281–S287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaks, A.; Klibanov, A.M. Substrate Specificity of Enzymes in Organic Solvents vs. Water Is Reversed. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1986, 108, 2767–2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroyo, M.; Sánchez-Montero, J.M.; Sinisterra, J.V. Thermal stabilization of immobilized lipase B from Candida antarctica on different supports: Effect of water activity on enzymatic activity in organic media. Enzyme Microb Technol. 1999, 24, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamouleau, F.; Coulon, D.; Girardin, M.; Ghoul, M. Influence of water activity and water content on sugar esters lipase-catalyzed synthesis in organic media. J. Mol. Catal A Chem. 2001, 11, 949–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; Rasheed, R.K.; Tambyrajah, V. Novel solvent properties of choline chloride/urea mixtures. Chem Commun. 2003, 9, 70–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pätzold, M.; Siebenhaller, S.; Kara, S.; Liese, A.; Syldatk, C.; Holtmann, D. Deep Eutectic Solvents as Efficient Solvents in Biocatalysis. Trends Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 943–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radošević, K.; Cvjetko Bubalo, M.; Gaurina Srček, V.; Grgas, D.; Landeka Dragičević, T.; Redovniković, R.I. Evaluation of toxicity and biodegradability of choline chloride based deep eutectic solvents. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 112, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Q.; Chen, J.X.; Tang, Y.L.; Wang, J.; Yang, Z. Assessing the toxicity and biodegradability of deep eutectic solvents. Chemosphere 2015, 132, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbous, Y.P.; Hayyan, M.; Wong, W.F.; Looi, C.Y.; Hashim, M.A. Unraveling the cytotoxicity and metabolic pathways of binary natural deep eutectic solvent systems. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durand, E.; Lecomte, J.; Villeneuve, P. Deep eutectic solvents: Synthesis, application, and focus on lipase-catalyzed reactions. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2013, 115, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Hao, J.W.; Mo, L.P.; Zhang, Z.H. Recent advances in the application of deep eutectic solvents as sustainable media as well as catalysts in organic reactions. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 48675–48704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, Y.H.; Shang, Z.R.; Hu, H.C.; Zhang, Z.H. Supported molybdenum on graphene oxide/Fe3O4: An efficient, magnetically separable catalyst for one-pot construction of spiro-oxindole dihydropyridines in deep eutectic solvent under microwave irradiation. Catal. Commun. 2017, 88, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Gioia, M.L.; Cassano, R.; Costanzo, P.; Herrera Cano, N.; Maiuolo, L.; Nardi, M.; Procopio, A. Green synthesis of privileged benzimidazole scaffolds using active deep eutectic solvent. Molecules 2019, 24, 2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durand, E.; Lecomte, J.; Baréa, B.; Dubreucq, E.; Lortie, R.; Villeneuve, P. Evaluation of deep eutectic solvent-water binary mixtures for lipase-catalyzed lipophilization of phenolic acids. Green Chem. 2013, 15, 2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pöhnlein, M.; Ulrich, J.; Kirschhöfer, F.; Nusser, M.; Muhle-Goll, C.; Kannengiesser, B.; Hausmann, R. Lipase-catalyzed synthesis of glucose-6-O-hexanoate in deep eutectic solvents. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2015, 117, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollenbach, R.; Bindereif, B.; van der Schaaf, U.S.; Ochsenreither, K.; Syldatk, C. Optimization of glycolipid synthesis in hydrophilic deep eutectic solvetns. Front. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2020, 8, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Dordick, J.S.; Garde, S. Hydration of enzyme in nonaqueous media is consistent with solvent dependence of its activity. Biophys J. 2004, 87, 812–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouzaouit, N.; Bidjou-haiour, C. Response Surface Methodological Study of Glucose Laurate Synthesis Catalyzed by Immobilized Lipase from Candida cylindracea. Biol. Forum. 2016, 8, 420–427. [Google Scholar]
- Šabeder, S.; Habulin, M.; Knez, Ž. Lipase-catalyzed synthesis of fatty acid fructose esters. J. Food Eng. 2006, 77, 880–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.S.; Wen, Q.; Huang, Z.L.; Cai, Y.Z.; Halling, P.J.; Yang, Z. Impacts of ionic liquids on enzymatic synthesis of glucose laurate and optimization with superior productivity by response surface methodology. Process. Biochem. 2015, 50, 1852–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florindo, C.; Branco, L.C.; Marrucho, I.M. Quest for Green-Solvent Design: From Hydrophilic to Hydrophobic (Deep) Eutectic Solvents. ChemSusChem 2019, 12, 1549–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florindo, C.; Branco, L.C.; Marrucho, I.M. Development of hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents for extraction of pesticides from aqueous environments. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2017, 448, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, M.A.; Crespo, E.A.; Pontes, P.V.; Silva, L.P.; Bülow, M.; Maximo, G.J.; Coutinho, J.A. Tunable Hydrophobic Eutectic Solvents Based on Terpenes and Monocarboxylic Acids. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 8836–8846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hümmer, M.; Kara, S.; Liese, A.; Huth, I.; Schrader, J.; Holtmann, D. Synthesis of (-)-menthol fatty acid esters in and from (-)-menthol and fatty acids—Novel concept for lipase catalyzed esterification based on eutectic solvents. Mol. Catal. 2018, 458, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, Y.; Park, S.; Yoo, E.; Jo, S.; Hong, J.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, S.H. Dihydrogen-bonding deep eutectic solvents as reaction media for lipase-catalyzed transesterification. Biochem. Eng. J. 2019, 142, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cauglia, F.; Canepa, P. The enzymatic synthesis of glucosylmyristate as a reaction model for general considerations on “sugar esters” production. Biores. Technol. 2008, 99, 4065–4072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillo, E.; Pezzotti, F.; Navarro, A.; López-Munguía, A. Lipase-catalyzed synthesis of xylitol monoesters: Solvent engineering approach. J. Biotechnol. 2003, 102, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Bornscheuer, U.T.; Schmid, R.D. Lipase-catalyzed solid-phase synthesis of sugar esters. Influence of immobilization on productivity and stability of the enzyme. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 1999, 6, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bornscheuer, U.; Herar, A.; Kreye, L.; Wendel, V.; Capewell, A.; Meyer, H.H.; Kolisis, F.N. Factors affecting the lipase catalyzed transesterification reactions of 3-hydroxy esters in organic solvents. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 1993, 4, 1007–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducret, A.; Giroux, A.; Trani, M.; Lortie, R. Characterization of enzymatically prepared biosurfactants. J. Am. Oil. Chem. Soc. 1996, 73, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, J.; Deng, L.; Wang, F.; Tan, T. Optimization of Candida sp. 99–125 lipase catalyzed esterification for synthesis of monoglyceride and diglyceride in solvent-free system. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2011, 72, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcos, J.A.; Hill, C.G.; Otero, C. Kinetics of the lipase-catalyzed synthesis of glucose esters in acetone. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2001, 73, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durand, E.; Lecomte, J.; Baréa, B.; Piombo, G.; Dubreucq, E.; Villeneuve, P. Evaluation of deep eutectic solvents as new media for Candida antarctica B lipase catalyzed reactions. Process. Biochem. 2012, 47, 2081–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idris, A.; Bukhari, A. Immobilized Candida antarctica lipase B: Hydration, stripping off and application in ring opening polyester synthesis. Biotechnol. Adv. 2012, 30, 550–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Different DES | Glucose Monodecanoate Yield (24 h) |
|---|---|
| Choline chloride: urea DES with VD | 0.15 μmol/g DES (0.03%) [24] |
| (-)-menthol: decanoic acid DES | 3.55 μmol/g DES (0.71%) |
| (-)-menthol: decanoic acid DES with VD (0.5 M glucose) | 18.73 μmol/g DES (3.75%) |
| (-)-menthol: decanoic acid DES with VD (1.5 M glucose) | 164.27 μmol/g DES (10.95%) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hollenbach, R.; Ochsenreither, K.; Syldatk, C. Enzymatic Synthesis of Glucose Monodecanoate in a Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvent. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4342. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21124342
Hollenbach R, Ochsenreither K, Syldatk C. Enzymatic Synthesis of Glucose Monodecanoate in a Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvent. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(12):4342. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21124342
Chicago/Turabian StyleHollenbach, Rebecca, Katrin Ochsenreither, and Christoph Syldatk. 2020. "Enzymatic Synthesis of Glucose Monodecanoate in a Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvent" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 12: 4342. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21124342
APA StyleHollenbach, R., Ochsenreither, K., & Syldatk, C. (2020). Enzymatic Synthesis of Glucose Monodecanoate in a Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvent. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(12), 4342. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21124342






