HLA-B*44 and C*01 Prevalence Correlates with Covid19 Spreading across Italy
Abstract
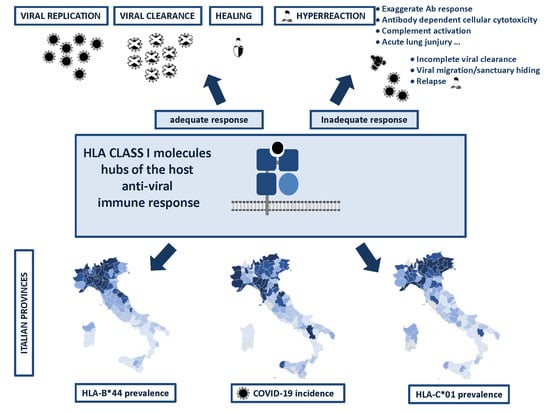
:1. Introduction
2. Results
Correlation between HLA-A, B, and C Allele Frequency and COVID-19 Incidence in Italian Provinces
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Data source and Population Sample
4.2. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO Virtual press conference on COVID-19. Available online: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/transcripts/who-audio-emergencies-coronavirus-press-conference-full-and-final-11mar2020.pdf?sfvrsn=cb432bb3_2. (accessed on 14 July 2020).
- Mutti, L.; Pentimalli, F.; Baglio, G.; Maiorano, P.; Saladino, R.E.; Correale, P.; Giordano, A. Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19): What Are We Learning in a Country With High Mortality Rate? Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livingston, E.; Bucher, K. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Italy. JAMA 2020, 323, 1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leaked Coronavirus Plan to Quarantine 16 m Sparks Chaos in Italy. World News|The Guardian. Available online: https://www.theguardian.com/world/2020/mar/08/leaked-coronavirus-plan-to-quarantine-16m-sparks-chaos-in-italy. (accessed on 14 July 2020).
- Li, X.; Geng, M.; Peng, Y.; Meng, L.; Lu, S. Molecular immune pathogenesis and diagnosis of COVID-19. J. Pharm. Anal. 2020, 10, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Luo, R.; Wang, K.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Z.; Dong, L.; Li, J.; Yao, Y.; Ge, S.; Xu, G. Kidney disease is associated with in-hospital death of patients with COVID-19. Kidney Int. 2020, 95, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriguchi, T.; Harii, N.; Goto, J.; Harada, D.; Sugawara, H.; Takamino, J.; Ueno, M.; Sakata, H.; Kondo, K.; Myose, N.; et al. A first Case of Meningitis/Encephalitis associated with SARS-Coronavirus-2. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 95, 55–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.; Zhao, S.; Yu, B.; Chen, Y.-M.; Wang, W.; Song, Z.-G.; Hu, Y.; Tao, Z.-W.; Tian, J.-H.; Pei, Y.-Y.; et al. A new coronavirus associated with human respiratory disease in China. Nature 2020, 579, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, L.; Zhao, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fan, G.; Xu, J.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 2020, 395, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Z.; Shi, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Huang, L.; Zhang, C.; Liu, S.; Zhao, P.; Liu, H.; Zhu, L.; et al. Pathological findings of COVID-19 associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Lancet. Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 420–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, A.; David, J.K.; Maden, S.K.; Wood, M.A.; Weeder, B.R.; Nellore, A.; Thompson, R.F. Human leukocyte antigen susceptibility map for SARS-CoV-2. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e00510-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hyun-Jung Lee, C.; Koohy, H. In silico identification of vaccine targets for 2019-nCoV. F1000Research 2020, 9, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lurie, N.; Saville, M.; Hatchett, R.; Halton, J. Developing COVID-19 Vaccines at Pandemic Speed. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1969–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Wei, Z.; Zhang, J.; He, J.; Zhu, F. Distribution of HLA allele frequencies in 82 Chinese individuals with coronavirus disease-2019. HLA 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amoroso, A.; Ferrero, N.; Rendine, S.; Sacchi, N. Le caratteristiche HLA della popolazione Italiana: Analisi di 370.000 volontari iscritti all’IBMDR. Analysis 2010, 23, 23–104. [Google Scholar]
- Sacchi, N.; Castagnetta, M.; Miotti, V.; Garbarino, L.; Gallina, A. High-resolution analysis of the HLA-A, -B, -C and -DRB1 alleles and national and regional haplotype frequencies based on 120 926 volunteers from the Italian Bone Marrow Donor Registry. HLA 2019, 94, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wölfel, T.; Klehmann, E.; Müller, C.; Schütt, K.H.; Meyer zum Büschenfelde, K.H.; Knuth, A. Lysis of human melanoma cells by autologous cytolytic T cell clones. Identification of human histocompatibility leukocyte antigen A2 as a restriction element for three different antigens. J. Exp. Med. 1989, 170, 797–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowley, N.J.; Darrow, T.L.; Quinn-Allen, M.A.; Seigler, H.F. MHC-restricted recognition of autologous melanoma by tumor-specific cytotoxic T cells. Evidence for restriction by a dominant HLA-A allele. J. Immunol. 1991, 146, 1692–1699. [Google Scholar]
- Hunt, D.F.; Henderson, R.A.; Shabanowitz, J.; Sakaguchi, K.; Michel, H.; Sevilir, N.; Cox, A.L.; Appella, E.; Engelhard, V.H. Characterization of peptides bound to the class I MHC molecule HLA-A2.1 by mass spectrometry. Science (80-) 1992, 255, 1261–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McDonnell, A.M.; Robinson, B.W.S.; Currie, A.J. Tumor antigen cross-presentation and the dendritic cell: Where it all begins? Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2010, 2010, 539519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falk, K.; Rötzschke, O.; Stevanovié, S.; Jung, G.; Rammensee, H.G. Allele-specific motifs revealed by sequencing of self-peptides eluted from MHC molecules. Nature 1991, 351, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, G.; Margalit, A. Targeting tumor-associated antigens to the MHC class I presentation pathway. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets 2007, 7, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmonds, M.J.; Gough, S.C.L. Genetic insights into disease mechanisms of autoimmunity. Br. Med. Bull. 2004, 71, 93–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, S.; Jiao, H.; Yu, X.; Strong, A.J.; Shao, Y.; Sun, Y.; Altfeld, M.; Lu, Y. Human leukocyte antigen class I and class II allele frequencies and HIV-1 infection associations in a Chinese cohort. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2007, 44, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vejbaesya, S.; Thongpradit, R.; Kalayanarooj, S.; Luangtrakool, K.; Luangtrakool, P.; Gibbons, R.V.; Srinak, D.; Ngammthaworn, S.; Apisawes, K.; Yoon, I.-K.; et al. HLA Class I Supertype Associations With Clinical Outcome of Secondary Dengue Virus Infections in Ethnic Thais. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 212, 939–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, L.E.; Allen, R.L. Leukocyte Ig-like receptors—A Model for MHC class i disease associations. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rallón, N.; Restrepo, C.; Vicario, J.L.; Del Romero, J.; Rodríguez, C.; García-Samaniego, J.; García, M.; Cabello, A.; Górgolas, M.; Benito, J.M. Human leucocyte antigen (HLA)-DQB1*03:02 and HLA-A*02:01 have opposite patterns in their effects on susceptibility to HIV infection. Hiv Med. 2017, 18, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falfán-Valencia, R.; Narayanankutty, A.; Reséndiz-Hernández, J.M.; Pérez-Rubio, G.; Ramírez-Venegas, A.; Nava-Quiroz, K.J.; Bautista-Félix, N.E.; Vargas-Alarcón, G.; Castillejos-López, M.D.J.; Hernández, A. An Increased Frequency in HLA Class I Alleles and Haplotypes Suggests Genetic Susceptibility to Influenza A (H1N1) 2009 Pandemic: A Case-Control Study. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 2018, 3174868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correale, P.; Saladino, R.E.; Nardone, V.; Giannicola, R.; Agostino, R.; Pirtoli, L.; Caraglia, M.; Botta, C.; Tagliaferri, P. Could PD-1/PDL1 immune checkpoints be linked to HLA signature? Immunotherapy 2019, 11, 1523–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, P.A.; Thomson, W.; Dyer, P.A.; Grennan, D.M. Haplotypes bearing HLA-A, -B, and -DR: Bf and C4 genes in rheumatoid arthritis families. Tissue Antigens 1989, 33, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orchard, T.R.; Thiyagaraja, S.; Welsh, K.I.; Wordsworth, B.P.; Gaston, J.S.H.; Jewell, D.P. Clinical phenotype is related to HLA genotype in the peripheral arthropathies of inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology 2000, 118, 274–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grams, S.E.; Moonsamy, P.V.; Mano, C.; Oksenberg, J.R.; Begovich, A.B. Two new HLA-B alleles, B*4422 and B*4704, identified in a study of families with autoimmunity. Tissue Antigens 2002, 59, 338–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueta, M.; Kannabiran, C.; Wakamatsu, T.H.; Kim, M.K.; Yoon, K.-C.; Seo, K.Y.; Joo, C.-K.; Sangwan, V.; Rathi, V.; Basu, S.; et al. Trans-ethnic study confirmed independent associations of HLA-A*02:06 and HLA-B*44:03 with cold medicine-related Stevens-Johnson syndrome with severe ocular surface complications. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jung, E.S.; Cheon, J.H.; Lee, J.H.; Park, S.J.; Jang, H.W.; Chung, S.H.; Park, M.H.; Kim, T.-G.; Oh, H.-B.; Yang, S.-K.; et al. HLA-C*01 is a Risk Factor for Crohn’s Disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2016, 22, 796–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, D.T.; Mehaffey, G.; Thomas, J.; Young, K.R.; Wiener, H.; Li, J.; Go, R.C.P.; Schroeder, H.W. Increased frequency of HLA-B44 in recurrent sinopulmonary infections (RESPI). Clin. Immunol. 2006, 119, 346–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fadda, L.; Körner, C.; Kumar, S.; van Teijlingen, N.H.; Piechocka-Trocha, A.; Carrington, M.; Altfeld, M. HLA-Cw*0102-restricted HIV-1 p24 epitope variants can modulate the binding of the inhibitory KIR2DL2 receptor and primary NK cell function. Plos Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mori, M.; Wichukchinda, N.; Miyahara, R.; Rojanawiwat, A.; Pathipvanich, P.; Miura, T.; Yasunami, M.; Ariyoshi, K.; Sawanpanyalert, P. Impact of HLA allele-KIR pairs on disease outcome in HIV-infected Thai population. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2018, 78, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pende, D.; Falco, M.; Vitale, M.; Cantoni, C.; Vitale, C.; Munari, E.; Bertaina, A.; Moretta, F.; Del Zotto, G.; Pietra, G.; et al. Killer Ig-Like Receptors (KIRs): Their Role in NK Cell Modulation and Developments Leading to Their Clinical Exploitation. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vitale, M.; Cantoni, C.; Della Chiesa, M.; Ferlazzo, G.; Carlomagno, S.; Pende, D.; Falco, M.; Pessino, A.; Muccio, L.; De Maria, A.; et al. An Historical Overview: The Discovery of How NK Cells Can Kill Enemies, Recruit Defense Troops, and More. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grant, W.B. The role of geographical ecological studies in identifying diseases linked to UVB exposure and/or vitamin D. Dermatoendocrinol. 2016, 8, e1137400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




| COVID-19 | A*25 | B*08 | B*14 | B*18 | B*44 | B*49 | B*51 | B*15:01 | C*01 | C*03 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| COVID-19 † | 1.0000 | ||||||||||
| A*25 | 0.6446 | 1.0000 | |||||||||
| p < 0.0001 | |||||||||||
| B*08 | 0.6969 | 0.7196 | 1.0000 | ||||||||
| p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | ||||||||||
| B*14 | −0.5133 | −0.4193 | −0.5617 | 1.0000 | |||||||
| p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | |||||||||
| B*18 | −0.4704 | −0.4573 | −0.6161 | 0.6053 | 1.0000 | ||||||
| p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | ||||||||
| B*44 | 0.6438 | 0.5555 | 0.6865 | −0.5512 | −0.7056 | 1.0000 | |||||
| p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | |||||||
| B*49 | −0.5920 | −0.6280 | −0.7144 | 0.5331 | 0.3019 | −0.5715 | 1.0000 | ||||
| p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | p = 0.0033 | p < 0.0001 | ||||||
| B*51 | 0.5036 | 0.5478 | 0.6196 | −0.4405 | −0.4851 | 0.4296 | −0.5702 | 1.0000 | |||
| p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | |||||
| B*15:01 | 0.6060 | 0.5780 | 0.6826 | −0.6238 | −0.5760 | 0.6092 | −0.6247 | 0.5695 | 1.0000 | ||
| p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | ||||
| C*01 | 0.6316 | 0.6367 | 0.6196 | −0.3433 | −0.2754 | 0.3501 | −0.6037 | 0.6752 | 0.4997 | 1.0000 | |
| p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | p = 0.0008 | p = 0.0075 | p = 0.0006 | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | |||
| C*03 | 0.5011 | 0.4817 | 0.5527 | −0.5509 | −0.5378 | 0.4638 | −0.5607 | 0.4817 | 0.7834 | 0.4396 | 1.0000 |
| p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 |
| COVID-19 | Regression Coefficient | Adjusted Growth Rate † | (95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A*25 | 0.2908 | 1.34 | (0.86–2.08) | n.s |
| B*08 | 0.0804 | 1.08 | (0.90–1.30) | n.s |
| B*14 | 0.0805 | 1.08 | (0.88–1.33) | n.s |
| B*18 | 0.0492 | 1.05 | (0.94–1.17) | n.s |
| B*44 | 0.1484 | 1.16 | (1.00–1.35) | 0.050 |
| B*49 | 0.1431 | 1.15 | (0.93–1.43) | n.s |
| B*51 | −0.0174 | 0.98 | (0.89–1.08) | n.s |
| B*15:01 | −0.0305 | 0.97 | (0.73–1.29) | n.s |
| C*01 | 0.1747 | 1.19 | (1.01–1.41) | 0.042 |
| C*03 | −0.0530 | 0.95 | (0.78–1.15) | n.s |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Correale, P.; Mutti, L.; Pentimalli, F.; Baglio, G.; Saladino, R.E.; Sileri, P.; Giordano, A. HLA-B*44 and C*01 Prevalence Correlates with Covid19 Spreading across Italy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5205. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21155205
Correale P, Mutti L, Pentimalli F, Baglio G, Saladino RE, Sileri P, Giordano A. HLA-B*44 and C*01 Prevalence Correlates with Covid19 Spreading across Italy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(15):5205. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21155205
Chicago/Turabian StyleCorreale, Pierpaolo, Luciano Mutti, Francesca Pentimalli, Giovanni Baglio, Rita Emilena Saladino, Pierpaolo Sileri, and Antonio Giordano. 2020. "HLA-B*44 and C*01 Prevalence Correlates with Covid19 Spreading across Italy" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 15: 5205. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21155205
APA StyleCorreale, P., Mutti, L., Pentimalli, F., Baglio, G., Saladino, R. E., Sileri, P., & Giordano, A. (2020). HLA-B*44 and C*01 Prevalence Correlates with Covid19 Spreading across Italy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(15), 5205. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21155205